In-Class Quiz 2
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/109
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 7:46 PM on 2/27/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
110 Terms
1
New cards
How do aldoses and ketoses differ?
Aldoses are monosaccharides that contain aldehydes
Ketoses are monosaccharides that contain ketones
Ketoses are monosaccharides that contain ketones
2
New cards
Define: Triose
Monosaccharides with three carbons (the simplest monosaccharides are trioses)
3
New cards
Define: Epimer
Diastereomers that differ at only one carbon atom
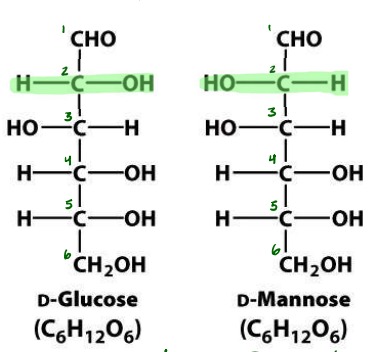
4
New cards
Define: Anomer
Differ at which asymmetric carbon is involved in ring closure
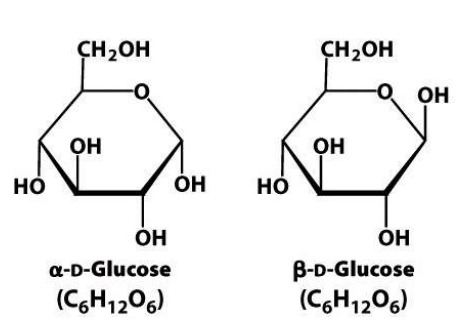
5
New cards
Define: Diastereoisomers
Isomers that are not mirror images
6
New cards
Define: Enantiomers
Isomers that are non-superimposable mirror images
7
New cards
Define: anomeric center
The location at which aldehyde/ketone groups react with alcohol groups to form a ring
8
New cards
What is the term for a 6 figured ring?
Pyran
9
New cards
What is the term for a 5 figured ring?
Furan
10
New cards
How do alpha-anomers and beta-anomers differ?
On anomeric carbon:
A - OH group below
B - OH group above (Or OH group on the same side as carbon 6 - large group)
A - OH group below
B - OH group above (Or OH group on the same side as carbon 6 - large group)
11
New cards
When does the pyranose form of fructose dominate?
When fructose is free in solution
12
New cards
When does the furanose form of fructose dominate?
In many fructose derivatives
13
New cards
Draw the open chain forms of glucose, galactose, mannose, ribose, and fructose
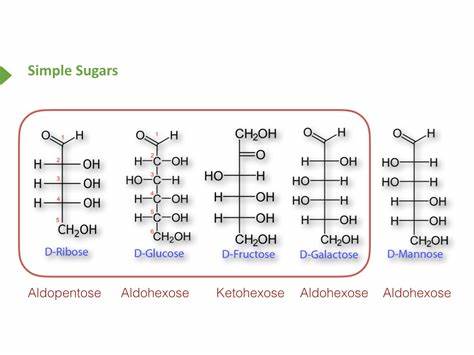
14
New cards
Define: Glycosidic bond
Bond formed between the anomeric carbon of one monosaccharide to the alcohol of a carbohydrate, protein, or lipid.
15
New cards
What is the chemical name of sucrose?
a-D-glucopyranosyl-B-D-fructofuranose
16
New cards
What is the chemical name of maltose?
a-D-glucopyranosyl-(1-4)-a-D-glucopyranose
17
New cards
What is the chemical name of Lactose?
B-D-galactopyranosyl-(1-4)-a-D-glucopyranose
18
New cards
Draw sucrose, maltose, and lactose
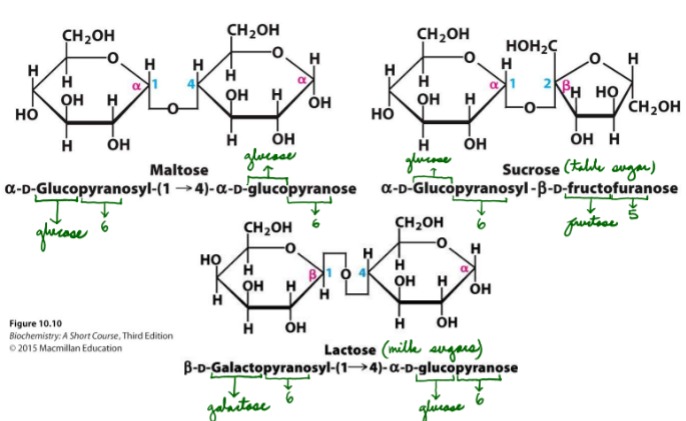
19
New cards
Define: Reducing sugar
Sugars with open forms that can react with oxidizing agents via interactions with their aldehyde group. (Ketoses can tautomerize to aldoses to react)
20
New cards
Both glucose and fructose are reducing sugars, why isn’t sucrose a reducing sugar?
The anomeric centers of both glucose and fructose are in a glycosidic bond, making it so that they cannot convert to their open chain forms and act as reducing sugars
21
New cards
Describe: Glycogen
A glucose homopolymer, used for energy storage
* a-1,4 glycosidic bond backbone
* a-1,6 glycosidic bond branching every 10 glucose units
* a-1,4 glycosidic bond backbone
* a-1,6 glycosidic bond branching every 10 glucose units
22
New cards
What are the two starches?
Amylose and Amylopectin, these are the nutritional reservoir in plants
23
New cards
Describe: Amylose
A glucose homopolymer
* a-1,4 glycosidic bond backbone
* Linear, no branching
* a-1,4 glycosidic bond backbone
* Linear, no branching
24
New cards
Describe: Amylopectin
A glucose homopolymer
* a-1,4 glycosidic bond backbone
* a-1,6 glycosidic bond branching every 30 glucose units
* a-1,4 glycosidic bond backbone
* a-1,6 glycosidic bond branching every 30 glucose units
25
New cards
Describe: Cellulose
A glucose homopolymer, structural role in plants
* B-1,4 glycosidic bond backbone
* Linear, no branching
* Hydrogen bonds join chains
* Rigid structure
\
No human enzymes can break the B-1,4 bond
* B-1,4 glycosidic bond backbone
* Linear, no branching
* Hydrogen bonds join chains
* Rigid structure
\
No human enzymes can break the B-1,4 bond
26
New cards
Describe: O-linked glycosylation
Carbohydrates attached to side chain hydroxyl oxygen of SERINE or THREONINE
27
New cards
Describe: N-linked glycosylation
Carbohydrates attached to side chain amide nitrogen of ASPARAGINE
28
New cards
How are carbohydrates attached to proteins?
Catalyzed by an enzyme called glycosyltransferase
29
New cards
Which features of carbohydrate chemistry make carbohydrates information rich molecules?
* Complex structure allows for a number of glycosidic bonds, and the adding of many monosaccharides
* Different anomers
* Attached to proteins in many ways
* Different anomers
* Attached to proteins in many ways
30
New cards
How does glycosylation change the properties of proteins?
Additional chemical information for a variety of functions
31
New cards
What are the three classes of glycoproteins?
Glycoproteins
Proteoglycans
Mucins
Proteoglycans
Mucins
32
New cards
Summarize: Glycoproteins
* More protein than carb by weight
* N or O linked glycosylation
\
Ex) EPO: glycosylation improves the stability of protein in blood
* N or O linked glycosylation
\
Ex) EPO: glycosylation improves the stability of protein in blood
33
New cards
Summarize: Proteoglycans
* More carb than protein by weight
* Attached to glycosaminoglycans
\
Ex) Aggrecan: glycosaminoglycans have a (-) charge that absorbs water
* Attached to glycosaminoglycans
\
Ex) Aggrecan: glycosaminoglycans have a (-) charge that absorbs water
34
New cards
Summarize: Mucins
* More carb than protein by weight
* O-linked glycosylation
\
Ex) MUC2: glycans bind water, form gel, lubricate/protect intestines
* O-linked glycosylation
\
Ex) MUC2: glycans bind water, form gel, lubricate/protect intestines
35
New cards
Define: Lectins
Proteins that specifically bind carbs by non-covalent interactions
\
(Hemagglutinin promotes interactions between cells)
\
(Hemagglutinin promotes interactions between cells)
36
New cards
Define: Selectins
A type of lectin that helps the immune system bind to sites of energy by recognizing and binding carbs
37
New cards
What does a - or + value of G mean?
(+) Non-spontaneous reaction
(-) Spontaneous reaction
(-) Spontaneous reaction
38
New cards
How do enzymes affect reactions?
They speed up the rate of reaction by decreasing activation energy (G) (this is done by stabilizing the transition state)
39
New cards
Do enzymes alter the equilibrium of a reaction?
No, enzymes only affect rate
40
New cards
What are some features of an enzyme active site?
1. Residues forming the active site come from different positions of the primary sequence
2. Make up a small volume of the total protein
3. Unique microenvironment
4. Forms many weak interactions with substrates
5. Specificity depends on the precise arrangement of active site residues
41
New cards
Define: Co-factor
Non-protein compounds that bind to proteins and are needed for biological activity.
* Co-enzymes are organic molecules derived from vitamins
* Metals (Zinc/Iron)
* Co-enzymes are organic molecules derived from vitamins
* Metals (Zinc/Iron)
42
New cards
Define: Apo-enzyme
An enzyme without the cofactor
43
New cards
Define: Halo-enzyme
An enzyme with the cofactor
44
New cards
Define: Prosthetic group
A cofactor that is very tightly bound to the enzyme
45
New cards
Define: Co-substrate
A cofactor that is loosely bound to the enzyme
46
New cards
Describe: The Lock and Key Model
A perfect fit exists between enzyme and substrate
47
New cards
Describe: The Induced Fit Model
Dynamic recognition of substrate causes a conformational change in the enzyme
48
New cards
Define: Initial velocity
The moles of product made per second when time = 0
49
New cards
What is Vmax dependent on?
Vmax is directly dependent on enzyme concentration.
50
New cards
When the concentration of substrate is much smaller than Km, what happens to velocity?
Velocity will be directly proportional to the concentration of substrate (Vmax = \[S\]/Km, V0 = Vmax X \[S\]/Km)
51
New cards
When the concentration of substrate is much larger than Km, what happens to velocity?
Velocity will be equal to Vmax, and the rate is zero order (V0 = Vmax)
52
New cards
When the concentration of substrate is equal to Km, what happens to velocity?
Km is equal to the \[S\] at which the reaction rate is half its maximal value (V0 = Vmax/2)
53
New cards
What is Km?
The concentration of substrate at which half of the enzyme molecules are bound to substrate
54
New cards
What does Km depend on?
Substrate, pH, temperature, and ionic strength
55
New cards
How can you determine Km from the X intercept?
Km = (-1)/Intercept
56
New cards
How can you determine Vmax from the Y intercept?
Vmax = (1)/Intercept
57
New cards
How can you determine slope?
Slope = Km/Vmax
58
New cards
What is Kcat?
The turnover number, or the number of substrate molecules that the enzyme can turn into product per unit time when fully saturated with substrate
\
Kcat=Vmax/\[E\]t
\
Kcat=Vmax/\[E\]t
59
New cards
A 10^-6 M solution of carbonic anhydrase catalyzes the \n formation of 0.6 M H 2CO3 per second when the \n enzyme is fully saturated with substrate. What is the \n kcat?
Kcat=Vmax/\[E\]
Kcat=(0.6M/s)/(10^-6 M)
Kcat=6x10^5 sec^-1
Kcat=(0.6M/s)/(10^-6 M)
Kcat=6x10^5 sec^-1
60
New cards
What is the specificity constant?
Kcat/Km
A measure of catalytic efficiency because it takes into account turnover number (Kcat) and the nature of the substrate-enzyme interaction (Km)
A measure of catalytic efficiency because it takes into account turnover number (Kcat) and the nature of the substrate-enzyme interaction (Km)
61
New cards
Define: Sequential reactions
Characterized by formation of a tertiary complex consisting of the two substrates and the enzyme.
\
May be ordered or random in terms of how substrates bind
\
May be ordered or random in terms of how substrates bind
62
New cards
Define: Double Displacement (Ping-Pong) reactions
Characterized by the formation of a substituted enzyme intermediate.
One or more products are released before all substrates bind the enzyme.
One or more products are released before all substrates bind the enzyme.
63
New cards
Allosteric Enzymes
Allosteric enzymes are enzymes that regulate the flux of biochemicals through metabolic pathways • They catalyze the “committed step” of metabolic pathways
64
New cards
Define: Feedback inhibition
Inhibitors bind the regulatory site on the enzyme, which inhibits activity
65
New cards
True or False: Allosteric Enzymes can recognize both inhibitory and stimulatory molecules
True, allosteric enzymes can be affected by feed forward (stimulatory) or feed backward (inhibitory) activation
66
New cards
How do the curves of Michaelis-Menten enzymes and allosteric enzymes differ?
Michaelis-Menten enzymes have a standard curve
Allosteric enzymes form sigmoidal curves
Allosteric enzymes form sigmoidal curves
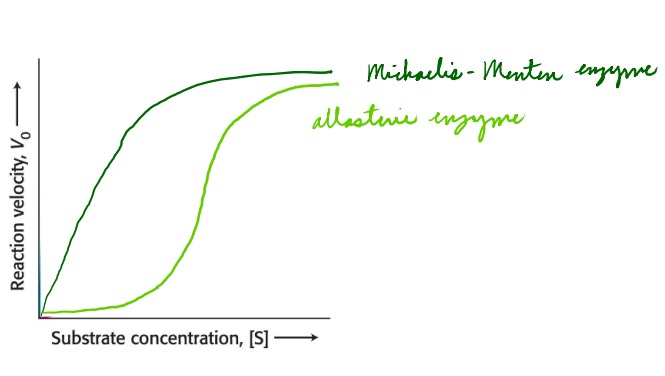
67
New cards
Which form of allosteric enzymes catalyzes reactions?
Relaxed form
68
New cards
Which form of allosteric enzymes is stable and most common?
Tense form
69
New cards
What is the allosteric constant?
T/R = L0 (usually in the hundreds)
70
New cards
What is the symmetry rule?
\
All active sites must be in the same state (R or T)
All active sites must be in the same state (R or T)
71
New cards
Does substrate binds more readily to R or T enzymes?
R, this is why relaxed enzymes catalyze reactions
72
New cards
Describe the Concerted Model for Allosteric Enzymes
When \[S\] is low: More T than R, L0 is very large
As \[S\] increases it binds an active site on R, trapping all other active sites in R (symmetry rule)
More enzymes in R state makes it easier for substrate to bind and more active sites become R formed
As \[S\] increases it binds an active site on R, trapping all other active sites in R (symmetry rule)
More enzymes in R state makes it easier for substrate to bind and more active sites become R formed
73
New cards
How does the binding of substrate effect T-R equilibrium?
The binding of substrate disrupts the T-R equilibrium in favour of R, this is called COOPERATIVITY
74
New cards
Describe the threshold effect
Allosteric enzymes are more sensitive to \[S\] near KM than Michaelis-Menten enzymes with the same Vmax
* Acts as a lightswitch to dramatically change velocity as \[S\] changes
* Acts as a lightswitch to dramatically change velocity as \[S\] changes
![Allosteric enzymes are more sensitive to \[S\] near KM than Michaelis-Menten enzymes with the same Vmax
* Acts as a lightswitch to dramatically change velocity as \[S\] changes](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/2c4fc56d46144a628ed01cd9bcd8c920.jpeg)
75
New cards
Define: Heterotrophic effects
__Regulators__ shift sigmoidal curve left (activator) or right (inhibitor)
76
New cards
Describe: Homotrophic effects
Effects of __substrate__ on allosteric enzyme (sigmoidal curve)
77
New cards
Describe: Sequential Model for Allosteric Enzymes
Binding of substrate to one active site influences the binding of substrate to a neighbouring active site
78
New cards
What are the 4 catalytic strategies?
* Covalent catalysis
* General Acid-Base Equilibrium
* Metal Ion Catalysis
* Catalysis by approximation and orientation
* General Acid-Base Equilibrium
* Metal Ion Catalysis
* Catalysis by approximation and orientation
79
New cards
Describe: Covalent Catalysis
The active site contains a reactive group that becomes temporarily covalently modified
80
New cards
Describe: General Acid/Base Catalysis
A molecule other than water plays the role of a proton donor/acceptor
81
New cards
Describe: Metal Ion Catalysis
* Stabilize negative charge on intermediate
* Generate a nucleophile by increasing acidity of a nearby molecule (like water)
* Increase binding energy through interaction with substrate
* Generate a nucleophile by increasing acidity of a nearby molecule (like water)
* Increase binding energy through interaction with substrate
82
New cards
Describe: Approximation/Orientation Catalysis
Who substrates are brought into close proximity and correct orientation when bound to the enzyme
83
New cards
What are the types of reversible enzyme inhibitors?
* Competitive
* Uncompetitive
* Noncompetitive
* Uncompetitive
* Noncompetitive
84
New cards
Describe: Competitive Inhibition
* Inhibitor resembles the substrate and binds to the active site
* As the concentration of inhibitor increases, higher concentrations of substrate are required to obtain a particular velocity
* The inhibitor has no effect on Vmax, but increases KM
* As the concentration of inhibitor increases, higher concentrations of substrate are required to obtain a particular velocity
* The inhibitor has no effect on Vmax, but increases KM
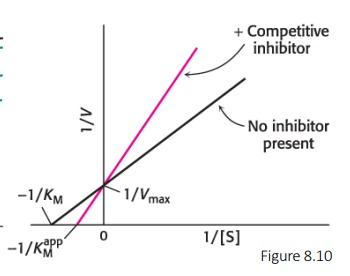
85
New cards
Describe: Uncompetitive Inhibition
* The inhibitor binds to the ES complex
* The enzyme-substrate-inhibitor (ESI) complex does not form any product
* With uncompetitive inhibitors both KM and Vmax decrease
* ESI complex decreases active enzyme (decreases Vmax)
* Inhibitor shifts E+S-ES equilibrium towards ES, which increases K and decreases Km
* The enzyme-substrate-inhibitor (ESI) complex does not form any product
* With uncompetitive inhibitors both KM and Vmax decrease
* ESI complex decreases active enzyme (decreases Vmax)
* Inhibitor shifts E+S-ES equilibrium towards ES, which increases K and decreases Km
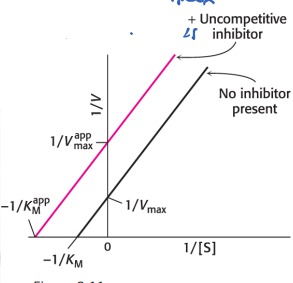
86
New cards
Describe: Noncompetitive Inhibition
* The substrate binds to the enzyme alone or the enzyme-inhibitor complex
* The enzyme-inhibitor (EI) and enzyme-substrate-inhibitor (ESI) complexes do not form any product
* With noncompetitive inhibitors Vmax decrease and KM is unchanged
* Decreases active enzyme (decreases Vmax)
* No effect on substrate binding to E, so Km is unchanged
* The enzyme-inhibitor (EI) and enzyme-substrate-inhibitor (ESI) complexes do not form any product
* With noncompetitive inhibitors Vmax decrease and KM is unchanged
* Decreases active enzyme (decreases Vmax)
* No effect on substrate binding to E, so Km is unchanged
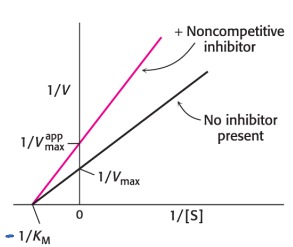
87
New cards
What are the types of irreversible inhibitors?
* Group specific
* Affinity label
* Transition state analog
* Suicide inhibitor (mechanism based)
* Affinity label
* Transition state analog
* Suicide inhibitor (mechanism based)
88
New cards
Describe: Group Specific Inhibitors
Modify specific R groups of amino acids and deactivate enzymes
89
New cards
Describe: Affinity Label Inhibitors
* Covalently modify active site residues
* Structurally similar to substrate
* Specific to enzymes
* Structurally similar to substrate
* Specific to enzymes
90
New cards
Describe: Transition-State Analog Inhibitors
Molecules that inhibit an enzyme by binding the active site and mimicking the transition state
91
New cards
Describe: Suicide Inhibitors
* Chemically modified substrate that binds and is initially processed by the enzyme
* Mechanism of catalysis results in chemically reactive intermediate that inactivate enzyme through covalent modification
* Mechanism of catalysis results in chemically reactive intermediate that inactivate enzyme through covalent modification
92
New cards
What are the seven classes of enzymes, what is the role of each?
* Oxidoreductases - transfer electrons, REDOX
* Transferases - transfer functional groups between molecules
* Hydrolases - cleave molecules by addition of H2O
* Lyases - add or remove atoms/functional groups to add/remove double bonds
* Isomerases - move function groups within a molecules
* Translocases - join molecules (ATP powered)
* Ligases - catalyze movement of ions/molecules accross membranes
* Transferases - transfer functional groups between molecules
* Hydrolases - cleave molecules by addition of H2O
* Lyases - add or remove atoms/functional groups to add/remove double bonds
* Isomerases - move function groups within a molecules
* Translocases - join molecules (ATP powered)
* Ligases - catalyze movement of ions/molecules accross membranes
93
New cards
Describe the mechanism of chymotrypsin
Cleaves on the carboxyl side of bulky hydrophobic amino acids (Phe, Met, Trp)
94
New cards
Define: Catalytic Triad (of Chemotrypsin)
His 57 acts as a general base and accepts a proton from Ser 195 → Creates a powerful nucleophile (alkoxide ion)
Asp 102 orients His 57 in the correct orientation to serve as a general base
Asp 102 orients His 57 in the correct orientation to serve as a general base
95
New cards
What class of enzyme is chymotrypsin?
Hydrolase
96
New cards
What is the function of the oxyanion hole?
The oxyanion hole stabilizes the negative charge on the tetrahedral intermediate. These interactions contribute to binding energy
97
New cards
What are the substrates of peptide hydrolysis by chymotrypsin?
Peptide (with C-terminal and N-terminal)
Water
Water
98
New cards
What are the products of peptide hydrolysis by chymotrypsin?
C-Terminal end of a peptide
N-terminal end of a peptide
N-terminal end of a peptide
99
New cards
What is the prosthetic group of hemoglobin?
Heme groups
100
New cards
What is the role of heme groups in myoglobin and hemoglobin
Myoglobin and Hemoglobin bind oxygen in heme groups