CSC258: Introduction & Transistors
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
false
low voltage, 0
true
high voltage, 1
logic gates
are the hardware equivalent of propositional operators, gates determine whether the output of a circuit will be on or off as an expression of the input signals
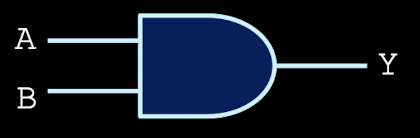
AND gates
high when both inputs are high
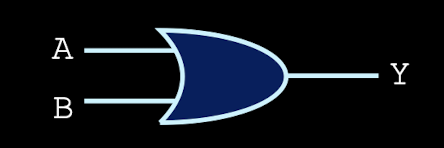
OR gates
high when either input is high
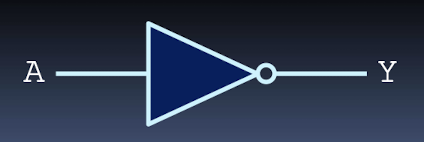
NOT gates
high when input is low
XOR gates
high when one input is high, but not both

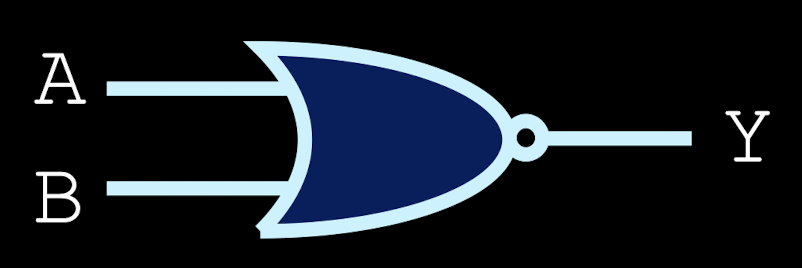
NAND gates
high when either input is low
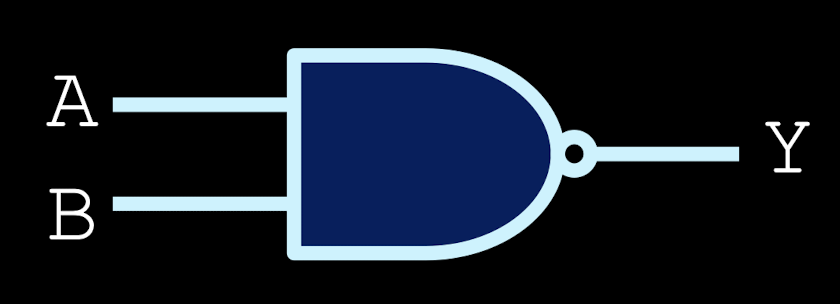
NOR gates
high when both inputs are low
transistors
form the basic building blocks of all computer hardware, used for applications such as switching and digital logic design
what do transistors do?
connect from point A to point B, based on the value at point C
eg. if the value at point C is high, A&B are connected, and if the value at point C is low, A&B are not
electrical faucets
if C=1, output is connected to 0V
if C=0, output is connected to 5V
what is electricity?
flow of charged particles (usually electrons) through a material, stems from electron movement
where do the charged particles come from?
atoms which are made up of protons (positive charge), neutrons (no charge) and electrons (negative charge)
What is electrical potential referred to as?
voltage
What is the rate of electron flow called?
current
What is electrical potential similar to?
gravitational potential
From which regions do electrical particles (like electrons) flow?
From regions of high electrical potential (many electrons) to regions of low electrical potential (fewer electrons).
water anology
electrons flow from high to low potential like water would flow from the reservoir to the ground, voltage = elevation of the water above the ground, current = rate at which the water flows
relationship between voltage (V) and current (I)
called resistance, R = V/I
how to measure current?
as the movement/flow of positive charges
do protons move?
no! when electrons move from point A to point B, the result is that B becomes more negative and A more positive
static electricity example
when you shuffle your feet back and forth on a carpet, you pick up extra electrons in ur body and develop an electrical imbalance, relative to the ground. when you touch an object or person who is electrically balanced, those extra electrons transfer over to that object or person
where does these electrons (and this electricity) come from?
two common sources include batteries or outlets
batteries
have a concentration of particles stored inside them, these will run out eventually (eg a water reservoir)
electrical outlets
where most of the electricity we use comes from, constantly being supplied with electric particles that never run out (eg waterfalls)
the path of electricity
current always flows toward the zero voltage point of a circuit (ground)
electricity always takes the path of least resistance from source to ground
remember: even though electrical current is the flow of electrons through a medium, its direction is typically expressed as the movement of the positive charges
How can the movement of electric particles be used?
The movement of electric particles from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration can be used to drive circuits.
What are the key components of an electric circuit?
source of electrical particles, some path between the source and ground, and some resistance along this path that dissipates these electrons
electrical resistance
indicates how well a material allows electricity to flow through it
insulators
high resistance, dont conduct electricity at all (or only under special circumstances), eg wood & plastic
conductors
low resistance, conduct electricity well, generally used for wires, eg metal
semi conductors
somewhere in between conductors and insulators
how is electrical resistance determined?
largely by the position of the element on the periodic table
what is a transistor?
devices made of semiconductor material which can act as a conductor in some cases and an insulator in others
how can transistors be implemented?
multiple ways, most commonly the MOSFET (Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor)
what do MOSFETs contain?
three wires that define their behaviour: the source, the drain, and the gate
two main types of MOSFETs
nMOS transistors and pMOS transistors
nMOS transistor
allow electricity to conduct between the source and the drain when a positive voltage is applied to the gate
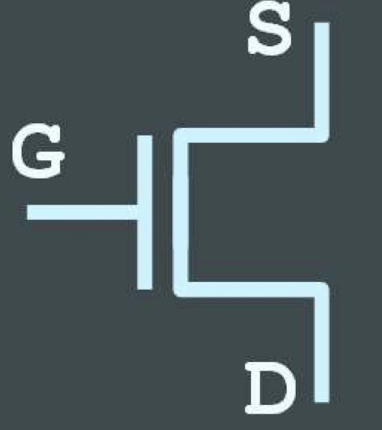
pMOS transistors
allow electricity to conduct between the source and the drain when a negative voltage is applied to the gate
what does the gate voltage determine?
whether the source and drain are connected, no current flows between them unless the source voltage is high
how to combine MOSFETS to create high & low voltage outputs, based on high and low voltage inputs?
create transistor circuits that make current flow to outputs from high or low voltage, based on transistor input values
making gates
since these transistors arent simply on/off switches, digital logic gates are created by a combo of transistors
what do you need to remember to make a gate from transistors?
every gate has one output and one or more inputs
every combo of input values MUST connect the output to either high voltage or low voltage (ground)
not connecting the output to high voltage isnt the same as connecting the output to low voltage
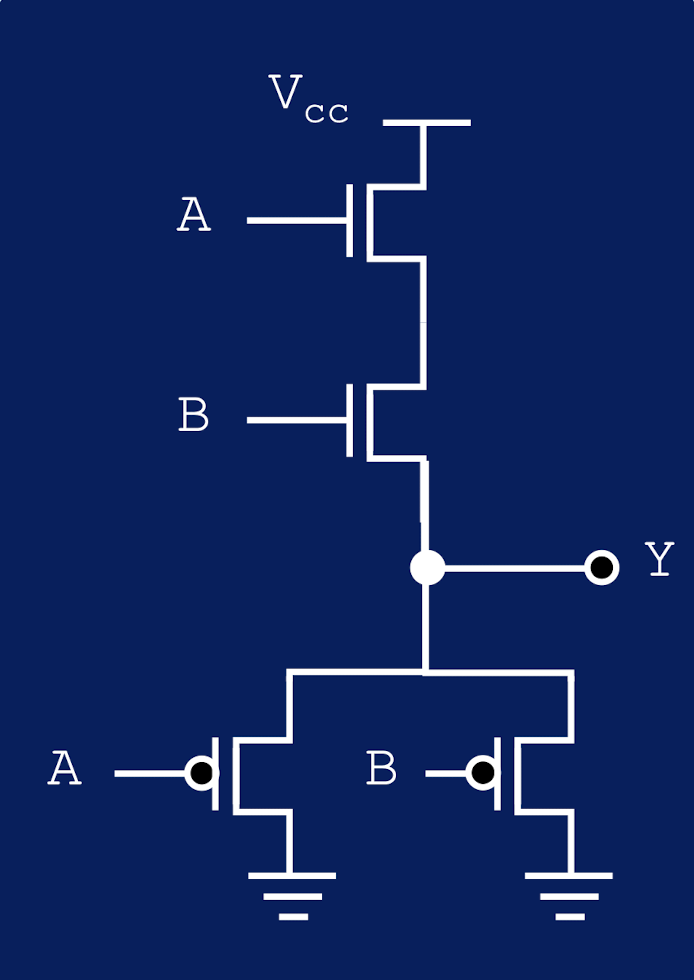
two input AND gates
if A or B is low, output is connected to the ground, output is high when both A and B are high