OCR GCSE Computing
1/134
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
135 Terms
act as the brain of the CPU → more allow instructions to be split up between the processors.
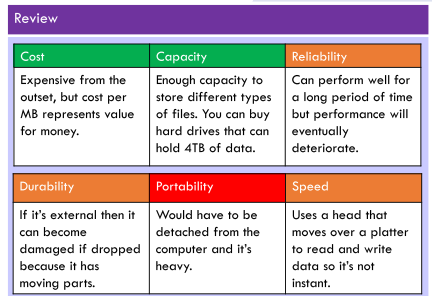
Eg. Hard Drive,
which contains a spinning platter with a thin magnetic coating, head moves writing 1’s and 0’s
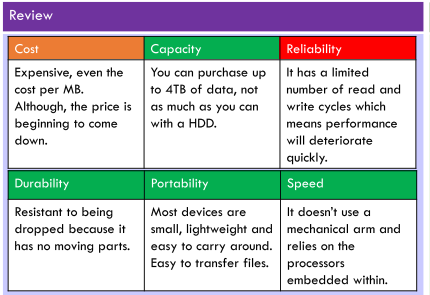
Eg. USB and SD card
Uses integrated circuits to store data persistently, typically using flash memory.
how well it can maintain the same level of performance over time.
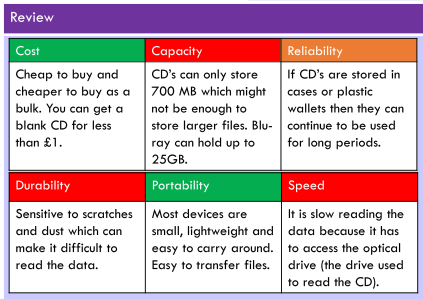
Eg. CD, DVD, Blu-ray
Any storage type in which data is written and read with a laser.
ASCII
consists of up to 256 characters.
data is permanently lost
impacts the quality
significantly reduces file size
eg. JPG
doesn’t remove data
reversible
overall quality is retained
large file size
Eg. PNG
This allows files to be stored centrally so workers can access files from any computer and all computers can update the central database. Backups can be implemented
Decentralized network where devices share resources equally. Each would have to perform backup and software updates
SQL Injection
used to interfere with queries that an application makes to its database in order to gain unauthorised access to users data
Packet Sniffers
used to intercept data packets on a network which are then analysed
Brute Force Attack
uses automated software to try millions of different password combinations
DDoS Attack
overloads the network by using bots to send useless requests to servers to a point in which is becomes flooded and unresponsive
Trojan
disguised as a normal file but once downloaded it performs malicious tasks
Worm
Malware that spreads across networks with the user’s action.
Ransomware
Malware that demands payment to decrypt personal data.
Spyware
used to track a user’s activity without their knowledge
Physical Security
Measures to protect physical access to networks like alarms