Topic 5
1/151
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
152 Terms
Why is there a vast number of compounds containing carbon (i.e. organic compounds)
1. each carbon atom can form four covalent bonds with most other non-metal atoms e.g. H, Cl, O, Br, S, N
2. carbon atoms can form chains of virtually unlimited length containing a succession of carbon-carbon bonds
What are aliphatic hydrocarbons?
Straight-chain compounds: do not contain a benzene ring
What is a result of alkanes' structure?
These compounds are saturated because each carbon is bonded to the maximum number of atoms
What are Isomers?
Compounds with the same molecular formula, but different structures/arrangements of atoms.
What may isomers have?
Different physical and chemical properties
What are position structural isomers?
Isomers that differ in the point of attachment of the methyl group
What happens because alkane reacting with excess oxygen is an exothermic reaction?
This reaction is exothermic but not spontaneous (it has a reasonably high activation energy). Because they are exothermic, these reactions are widely used as fuels
What do alkanes contain?
Strong, single covalent bonds between the atoms and are therefore reasonably unreactive.
When are cycloalkanes formed?
When the carbon atoms are connected in a ring structure
What can some alkenes exhibit?
Geometrical isomerism
What are geometric isomers?
They have the same molecular formula as alkenes. but the groups, attached to carbon atoms joined by a double bond, are in different positions in space
Why does geometrical isomerism occur for alkenes?
Because the carbon atoms joined by the double bond are unable to rotate about the double bond. However, if there is only a single bond between two carbon atoms, then the carbon atoms can rotate about the bond. Therefore, geometrical isomerism does not exist for alkanes
When will an alkene exhibit geometrical isomerism?
If both of the carbons joined by the double bond have different groups attached to them. As the double bond is rigid, the arrangements of the different side chains are fixed around the bond. This leads to slightly different physical and chemical properties.
What are the most common additions in addition reactions?
Hydrogen, Hydrogen halides (e.g. HCl) and halogens
What is the addition of halogens called?
Halogenation (or bromination, chlorination etc)
What is the addition of hydrogen called and what does it require?
Hydrogenation and it requires the presence of a catalyst (e.g. Pt)
What do cycloalkenes behave chemically like?
Alkenes
What is benzene?
The simplest aromatic hydrocarbon
What is benzene composed on?
Composed on 6 carbon atoms joined in a ring, with one hydrogen atom singly bonded to each carbon. It is a planar (flat) molecule
Is the benzene ring a stable unit?
Due it's structure, the benzene ring is a reasonable stable unit (fairly unreactive compared to alkenes/alkynes)
What are aromatic compounds composed of?
A benzene ring with atoms/groups bonded to it
What does a benzene substitution reaction require?
A catalyst (e.g. FeCl3) and high temperature
What is the shape of a molecule determined by?
The positions of the nuclei that make up the molecule
What do the positions of the nuclei depend on?
The arrangement of the electron pairs surrounding the central atom of the molecule.
What is the Valence Shell Electron Repulsion theory (VSEPR)?
States that the electron pairs in the valence shell (outer energy level) of an atom, repel each other, and as a result, these electron pairs are arranged as far apart as possible.
What is a linear molecular shape (single)?
Single bonds only.
Any diatomic molecule must have a linear shape, regardless of whether the bond is a single, double or triple covalent bond
e.g. O2, F2, N2, HF, HCl and CO.
Occurs when there are only 2 bonding pairs of electrons around the central atom (non-octet). In this situation, the bond angles are 180 degrees.
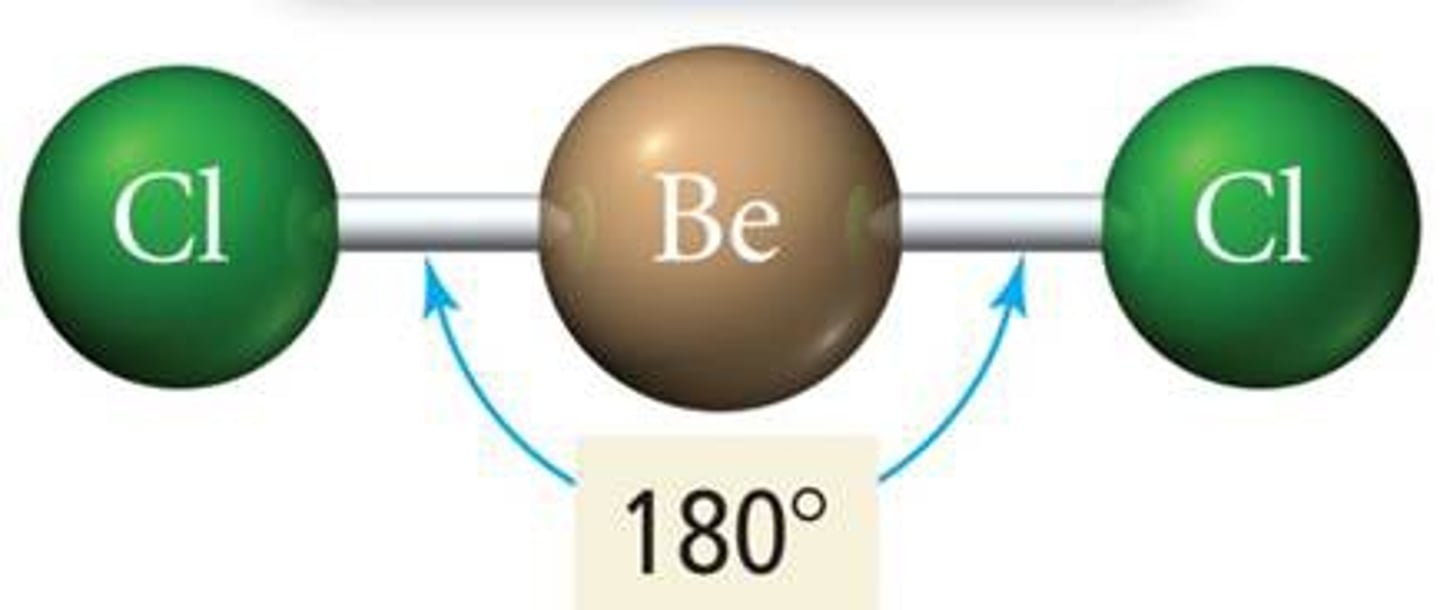
What is a trigonal planar molecular shape (single)?
Single bonds only.
This shape occurs when there are three bonding pairs of electrons around the central atom (non-octet).
The bond angles are 120 degrees.
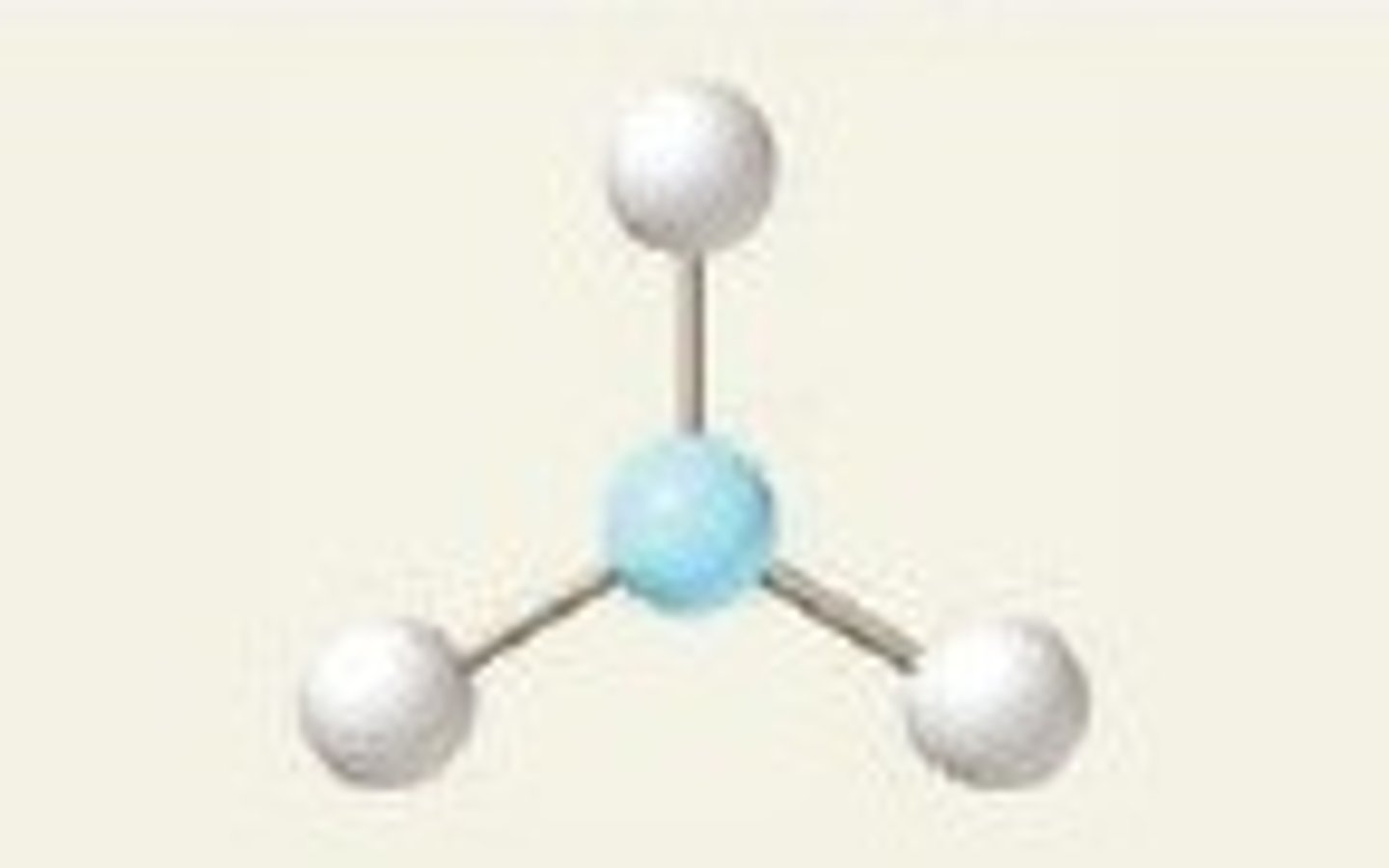
What is a V-shaped (bent) molecular shape (single)?
This shape occurs when there are four pairs of electrons around the central atoms, and two of these pairs are non-bonding pairs.
E.g. H2O, Cl2O, H2S
What is a linear molecular shape (double/triple)?
Any molecule with just 2 atoms is linear or 2 bonding areas around central atom. The bond angles around each carbon atom are 180 degrees.
Eg. C2H2
How does electronegativity relate to polarity?
All covalent bonds between different non-metal elements are polar to some extent. The bigger the difference in electronegativity is, the more polar the bond. (Where the difference in electronegativity is large e.g. metal/non-metal the electrons are so unevenly shared that they are transferred to the more electronegative element and ionic bonding occurs.
How to explain if the molecule is polar?
The molecule is not completely symmetrical due to .... (non bonding pair on central atom/atoms of different elements around central atom) and therefore bond dipoles do not cancel out.
What are intramolecular bonds?
Strong covalent bonds between atoms.
These bonds are not broken when a covalent molecular substance melts or boils.
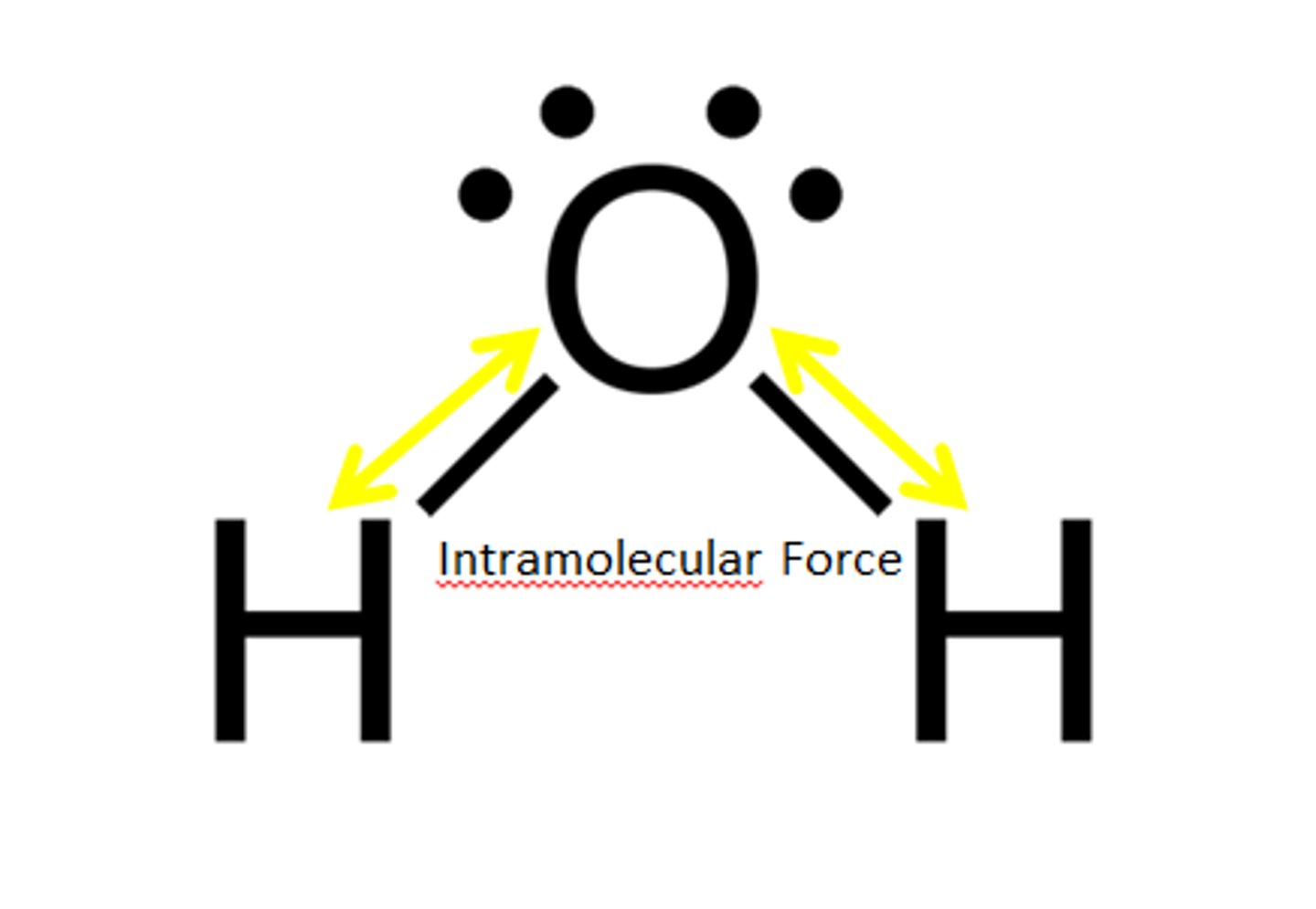
What does an understanding of intermolecular forces help us explain?
- physical properties such as vapour pressure, melting point, boiling point and the energy required to change phase
- the solubility of substances in various solvents
- the structure of biologically important molecules such as proteins and DNA
What is vapour pressure?
When a liquid is put into a closed container, evaporation and condensation occur at the liquid surface. Vapour pressure is the pressure that the gaseous particles exert on the closed container due to their collisions with the container wall when the rates of evaporation and condensation become equal.
How does vapour pressure relate to intermolecular forces?
In a liquid with strong intermolecular forces, the molecules are held together tightly, making it harder (needs more energy to overcome the forces) for them to evaporate from the surface of the liquid. Therefore vapour pressure is lower.
Because the stronger the forces, the more energy is required to overcome their forces.
What are dipole-dipole forces?
Weak attractive forces that occur between two polar molecules (between two dipoles).
The electrostatic attractions between oppositely charged ends of polar molecules.
Why do dipole-dipole forces occur?
These attractive forces occur because the part of the molecule which is slightly positively charged, can be attracted to the slightly negative part of another molecule.
Why are the dipole-dipole forces weak?
Because the charges involved are only very small, the dipole dipole forces are only weak.
How much stronger are hydrogen bonds than ionic or covalent bonds?
one tenth the strength
What are dispersion forces?
Dispersion forces are weak forces which exist between the particles in all substances.
Why do dispersion forces occur?
These forces are thought to arise because at any instant, an atom or a molecule will probably be an instantaneous dipole, due to the unsymmetrical arrangement of its electrons with respect to the nucleus.
This temporary dipolar atom/molecule will then induce a dipole in the neighbouring atom. These two atoms/molecules will then be attracted to one another. It is these attractive forces that are called dispersion forces or induced dipole interactions.
Dispersion forces are the only attractive forces between...
the neutral atoms or molecules that make up a non-polar substance
What are the weakest kind of intermolecular forces?
Dispersion forces. However, they increase with increasing molecular mass (because of the increasing number of electrons) and with the larger molecules, they become significant in determining trends in properties such as melting and boiling temperatures.
Do shapes of molecules influence the strength of dispersion forces?
Yes. The greater the surface contact that can occur between two molecules, the greater the strength of the dispersion forces will be.
What happens to forces between the particles when a substance melts or boils?
The forces between the particles that are partially or completely overcome. In these cases, it is the intermolecular (or interatomic for noble gases) that are overcome.
What are the physical properties that depend on intermolecular forces?
- vapour pressure
- melting/boiling point
- solubility
How does vapour pressure depend on intermolecular forces?
The weaker the cumulative effect of the intermolecular forces the higher the vapour pressure
How does melting/boiling point depend on intermolecular forces?
The weaker the cumulative effect of the intermolecular forces the lower the boiling and melting points as less energy. is required to overcome these forces
How does solubility depend on intermolecular forces?
A solute will dissolve in a solvent if the energy released as solute-solvent intermolecular forces form compensates for the energy required to overcome the solute-solute and solvent-solvent intermolecular forces
How do similar sized molecules correlate to cumulative forces between molecules, when comparing substances?
When comparing substances with similar sized molecules (similar number of electrons in the electron cloud) the greater the cumulative forces between molecules the more energy required to break those forces and the higher the boiling point.
What is lowest cumulative forces?
- non-polar molecules with only dispersion forces
- polar molecules with dipole-dipole and dispersion forces
What is a tetrahedral arrangement?
Each bond angle i.e. the angle between two C - H bonds, is approximately 109 degrees
What are some simple bonding rules for organic compounds?
- carbon atoms form four bonds
- hydrogen atoms form single bonds
- oxygen atoms form two bonds (6 valence electrons, need 2 more)
- halogen atoms (F, Cl, Br, I) form one bond (7 valence electrons, need 1 more)
- nitrogen atoms form three bonds (5 valence electrons, need 3 more)
- a double bond "counts" as two bonds, and a triple bond "counts" as three bonds
What is a molecular formula?
Indicates the actual number and type of atoms present in a molecule e.g. C3H8
What is a structural formula?
Shows the bonding and the arrangement of the atoms in a molecule
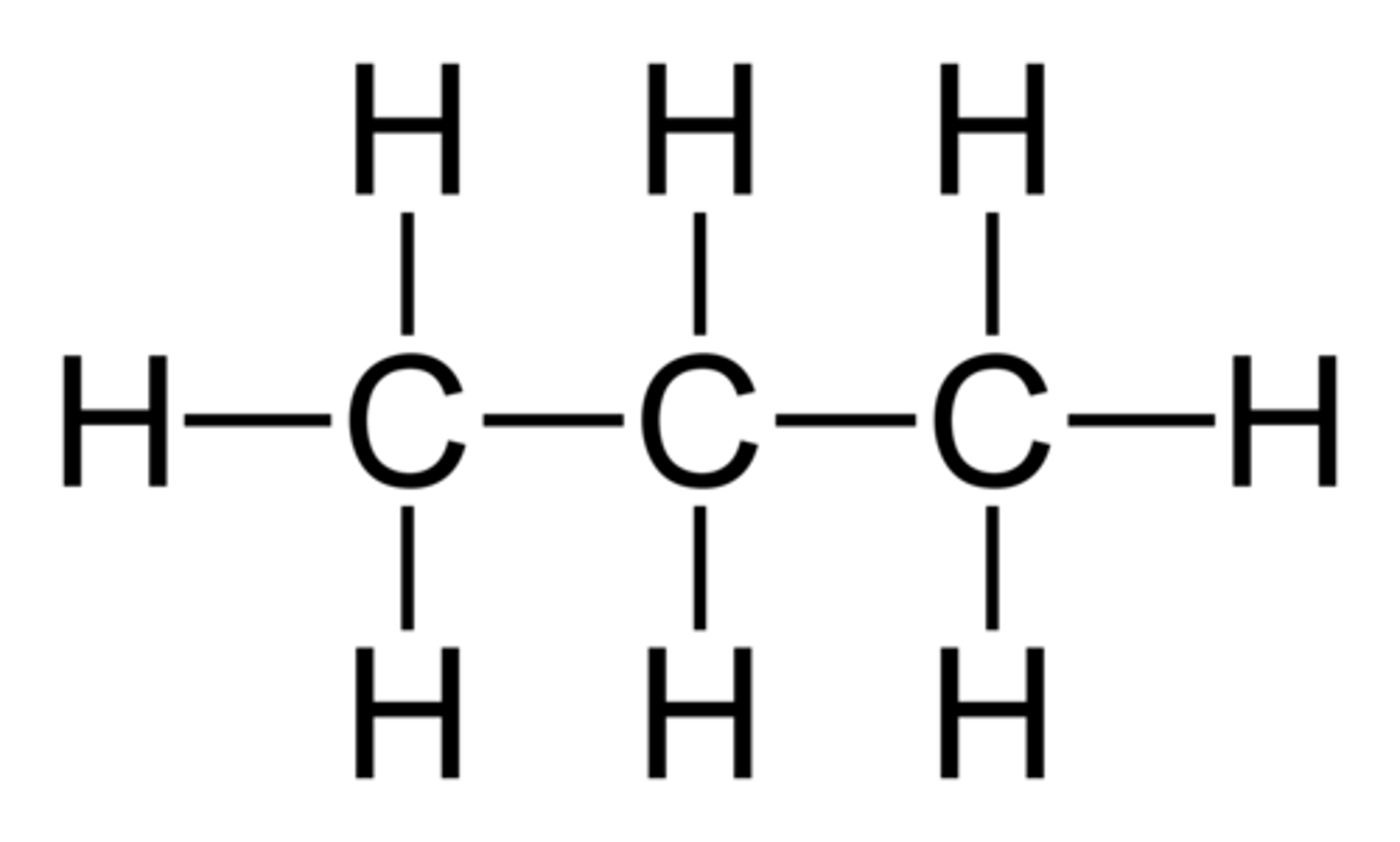
What are hydrocarbons?
Compounds that only contain carbon and hydrogen atoms
What are alicyclic hydrocarbons?
Compounds in which there are carbon atoms arranged in a closed ring (but not a benzene ring)
What are aromatic hydrocarbons?
compounds that contain at least 1 benzene ring
What are saturated compounds?
Have only single bonds between carbon atoms/each carbon atom is bonded to the maximum number of atoms
What are unsaturated compounds?
Have double or triple bonds between two or more carbon atoms
What are alkanes?
hydrocarbons with only single bonds between carbon atoms
What are alkenes?
hydrocarbons with at least one double bond between carbon atoms
What are alkynes?
hydrocarbons with at least one triple bond between carbon atoms
What is alkanes' general formula?
CnH2n+2
What is the stem name for 1 Carbon atom in chain
Meth-
What is the stem name for 2 Carbon atoms in chain
Eth-
What is the stem name for 3 Carbon atoms in chain
Prop-
What is the stem name for 4 Carbon atoms in chain
But-
What is the stem name for 5 Carbon atoms in chain
Pent-
What is the stem name for 6 Carbon atoms in chain
Hex-
What is the stem name for 7 Carbon atoms in chain
Hept-
What is the stem name for 8 Carbon atoms in chain
Oct-
What is the stem name for 9 Carbon atoms in chain
Non-
What is the stem name for 10 Carbon atoms in chain
Dec-
What are chain structural isomers?
Isomers that differ in the length of their longest chain
What is a combustion reaction?
The reaction of an alkane with oxygen
What is combustion?
Burning
What is produced when an alkane is reacted with excess oxygen?
When an alkane is reacted with excess oxygen (i.e. complete combustion), carbon dioxide and water are produced.
What type of energy (endo/exo) is alkane reacting with excess oxygen?
Exothermic
What type of substitution reaction will alkanes undergo?
A slow substitution reaction where the hydrogen atoms are replaced with halogens. These reactions require the presence of UV light to occur.
What is the products of substitution reactions?
Haloalkanes.
What is cycloalkanes' general formula?
CnH2n
What are cycloalkanes isomers with?
Alkenes
What do cycloalkanes behave chemically like?
Their straight-chain counterparts
What does each bend in a cycloalkane represent?
A carbon atom
What are hydrocarbons that contain double bonds called?
Alkenes
What are carbon compounds that contain double or triple bonds between the carbon atoms classed as?
Unsaturated
What is alkenes' general formula?
CnH2n
What are the physical properties of alkenes' similar to?
Alkanes
i.e. low melting and boiling points which increase with increasing molecular mass.
Are alkenes soluble in water?
No, they are insoluble in water
What is called the 'cis' isomer?
The isomer with the two groups on the same side of the double bond.
What is called the 'trans' isomer?
The isomer with the groups on the opposite side of the double bond
What are the products of combustion of alkenes?
Carbon dioxide and water
Is the double bond in alkenes reactive?
Reasonably reactive
What is an addition reaction?
Where the double bond in alkenes is broken and becomes a single bond, and two atoms are added into the compound where the double bond used to be.
How much faster are addition reactions than substitution reactions?
Normally much faster
What temperature does halogen addition readily occur?
Room temperature, and during this reaction the halogen is decolourised
What must be present in alkene substitution reactions?
UV light
Which reaction will occur first (addition or substitution)?
Addition reactions will always occur first, only consider substitution reactions as well if the question indicates an excess halogen and the presence of UV light
What happens if an alkene is mixed with excess halogen and allowed to react in the dark?
Then only an addition reaction will occur