Regulation of Ca2+ and Phosphate (Sayner)
1/130
Earn XP
Description and Tags
(Sayner)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
131 Terms
Extracellular calcium is under tight ________ control
Endocrine
Calcium intake via the intestine is dependent upon _____
Vitamin D
Calcium exchange between the intestine, kidney, and bone is ______ regulated.
hormone

Whole body daily calcium turnover
175 mg/day net uptake and 175 mg/day urine excretion
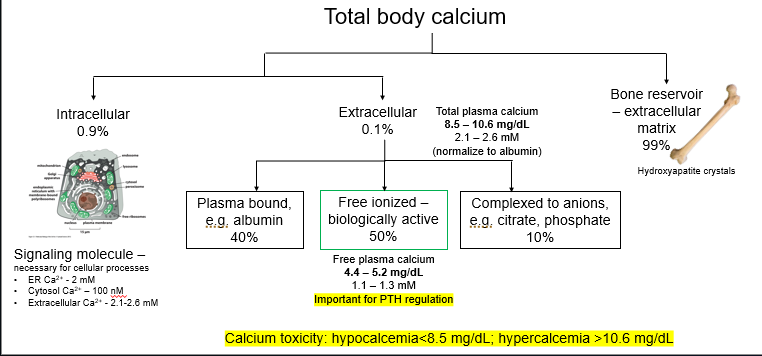
Distribution of total body calcium
Hypocalcemia <____ mg/dL
8.5
Hypercalcemia > __ mg/dL
10.6 symptomatic around 11.5
Which form of calcium is important for PTH regulation?
Free plasma calcium
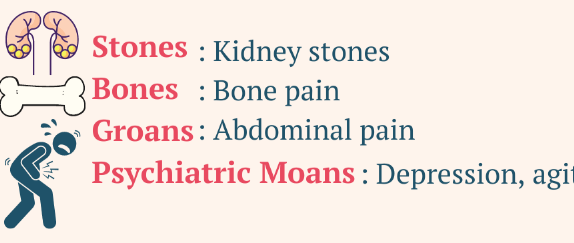
Hypercalcemia especially above 11.5
99 of calcium is stored in ____
Bone
hydroxyapatite crystals
Within cytoplasm, calcium concentration is
Low
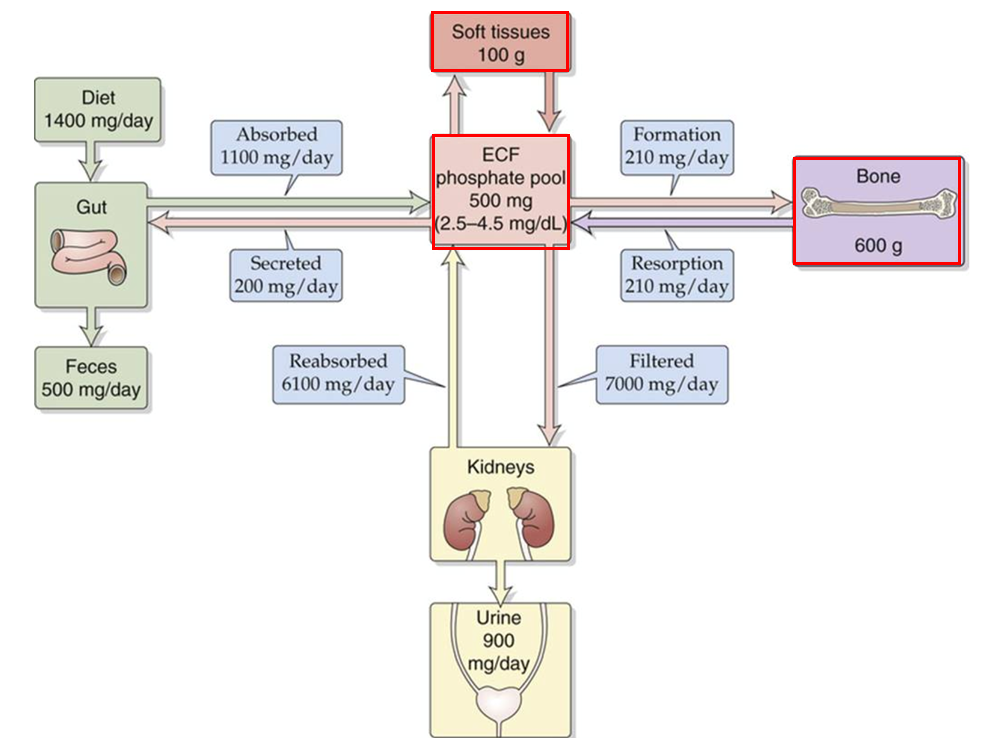
Whole body daily phosphate turnover
Net uptake 900 mg/day
Net loss from urine 900 mg/day
Phosphate uptake in the small intestines is dependent upon _____.
Vit D
Stored in bone and soft tissue.
Phosphate
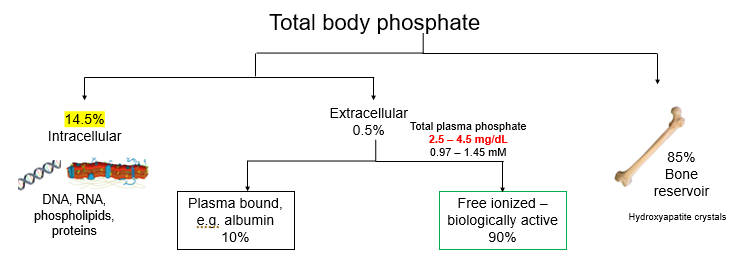
Distribution of total body phosphate
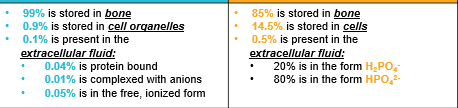
Calcium blue
Phosphate orange
distribution
2.5 – 4.5 mg/dL is total plasma ______
phosphate
4.4 – 5.2 mg/dL is _____ plasma calcium
Free
8.5 – 10.6 mg/dL is total plasma _____
calcium
(Stones, bones, moans and groans) nausea, vomiting, abdominal or flank pain, constipation, altered mental status, headache, confusion, depression, weakness, myalgias, arthralgias, polyuria, polydipsia, and nocturia.
Hypercalcemia
Severe hypercalcemia can cause ____
Coma
Physical exam findings include hypertension, bradycardia, hyperreflexia, and tongue fasciculations.
Hypercalcemia
increased intestinal calcium absorption in response to elevated PTH levels
PTH-mediated hypercalcemia
Acute _______– symptoms include: syncope, congestive heart failure, numbness and tingling, muscle spasms and tetany, bronchospasm and wheezing, laryngospasm and dysphagia, irritability, depression, fatigue, and seizures.
hypocalcemia
Chronic ________ can lead to coarse hair, brittle nails, psoriasis, dry skin, pruritus, poor dentition, and cataracts.
hypocalcemia
The most common physical exam findings include neural hyperexcitability, psychological disturbances, and cardiac arrhythmias.
Hypocalcemia
The Chvostek and Trousseau signs are indicative of ______ states.
Hypocalcemic
Regulation of extracellular calcium is under tight endocrine control:
PTH
Vitamin D
Fibroblast growth factor 23 (FGF-23)
Calcitonin
Estrogen and glucocorticoids
PTH affects on
Bone:
Kidney:
resorption - osteoblast-mediated regulation of osteoclast activity – ↑ serum calcium
↑calcium reabsorption, ↓phosphate reabsorption, ↑vitamin D
PTH → Bone →
resorption - osteoblast-mediated regulation of osteoclast activity – ↑ serum calcium
PTH to kidney → ______ calcium reabsorption, → _______ phosphate resorption → ______ vitamin D
Increased
Decreased
Increased
PTH secreted by ____ cells of the parathyroid gland
Chief

Parathyroid gland
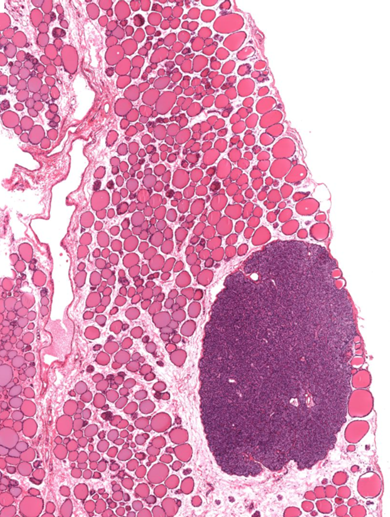
Thyroid gland with parathyroid gland
sensor for free Ca2+
Chief cells
Parathyroid gland often surrounded by _____ tissue.
adipose
Normal blood levels of ionized/free calcium inhibit PTH secretion via ______ on Chief cells.
calcium sensing receptor (CaSR)
As serum free calcium levels ____, inhibition of chief cells is lost and PTH secreted.
Drop
______ calcium binds to calcium sensing receptor (CaSR) on Chief cells. CaSR is coupled through ___ signaling and elevation of calcium to inhibit secretion of ___.
High
Gq
PTH
Gq – PLC- PIP2- DAG + IP3 – Calcium inhibits secretion of PTH vacuoles
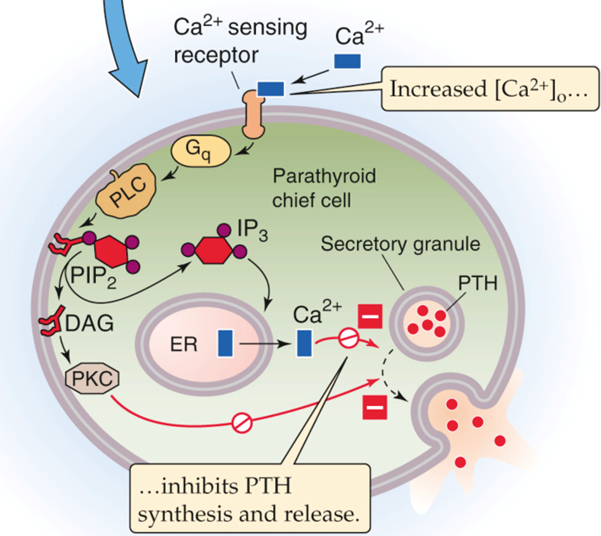
Calcium inhibition of PTH synthesis and release
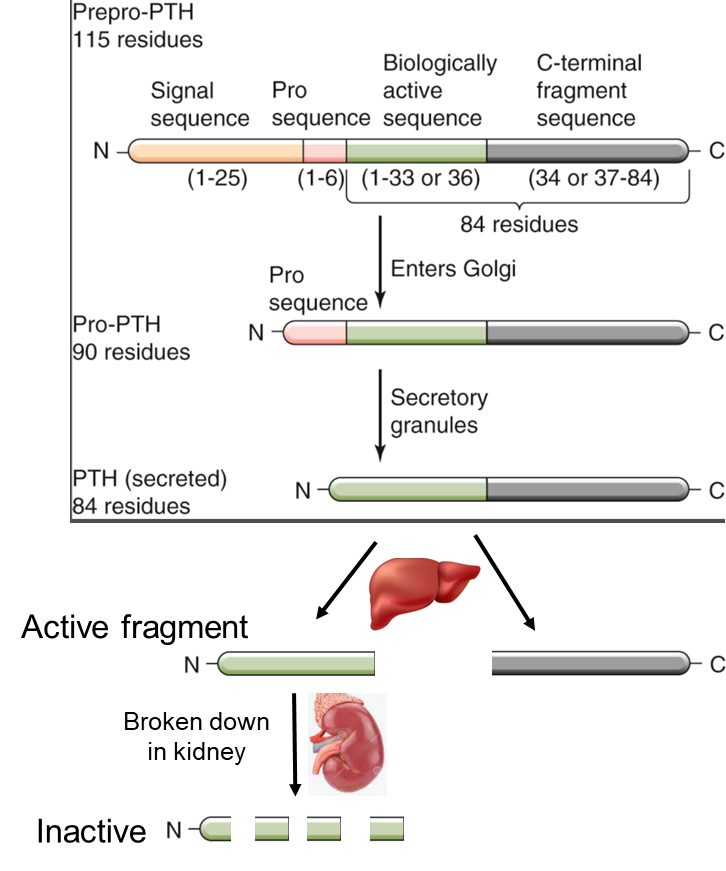
PTH processing
PTH Short __-terminal active fragment (half-life 4 minutes – breakdown in the kidney).
N
PTH Long __-terminal inactive fragment (longer half life so continues to circulate).
C
Active PTH is proteolytically cleaved secretory vesicles (chief cells) and ____(circulation) into 2 fragments
liver
PTH is synthesized in the ___
ER
PTH is broken down in the
Kidney
Both the full length (84 peptide) and the short N-terminal fragment – bind PTH-R_
1
PTH-R1 is expressed on _____ and _____
Bone and Kidney
______ reside on the surface of bone and secrete the unmineralized matrix (osteoid) and regulate mineralization of bone.
Osteoblast
Mesenchymal stem cells -> ______ -> osteocytes
Osteoblasts
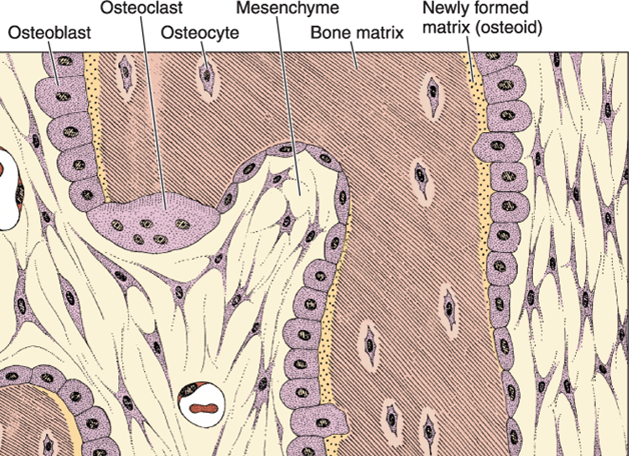
Cell types of bone
Bone is type __ collagen
1
Bone calcium phosphate ratio ___/___
1/0.7
Cancellous (trabecular) bone is turned over more _____ than compact bone
Rapidly
resorb bone tissue (removal of bone tissue and release of calcium and phosphate)
Osteoclast
Multinucleated for Howships lacuna where absorption takes place
Osteoclast
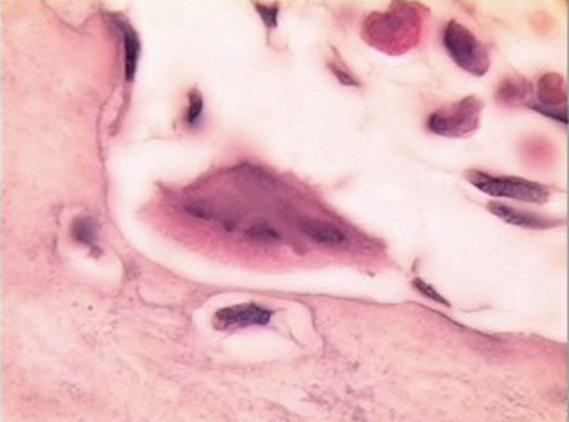
Osteoclasts
Acts via osteoblasts to increase RANK-RANKL and decrease OPG
PTH
PTH bind PTH-R1 expressed on ________– activates Gs signaling to increase cAMP
osteoblasts
Increases expression of ______ and decrease ___, thereby increasing osteoclastogenesis and bone resorption.
RANK-L
OPG
PTH inhibits ______ synthesis by osteoblasts and promotes release of proteases.
collagen
______ are derived from hematopoetic stem cells
Osteoclasts
When RANK is engaged by it’s receptor RANK-ligand this promotes the differentiation of the precursor into its mature form ________
Osteoclast
While engagement of RANK-L with the receptor activates differentiation, there is a decoy pathway whereby ____, released from ______, binds to RANK and inhibits its interaction with the ligand thereby preventing _______ differentiation.
OPG
Osteoblasts
Osteoclast
During maturation ____ is necessary for osteoclast differentiation and activation
RANK
___ decoy receptor can bind RANKL so it cannot bind RANK
OPG
Increase ___ decreased activation and differentiation of osteoclast- less bone breakdown
OPG
_____ is on the osteoblasts increases expression of rank L and decreased OPG promoting bone resorption
PTH-R1
RANK ligand ______ osteoclast differentiation
Increases
OPG ______ osteoclast differentiation
Decreases
PTH-R1 is on the osteo_last and stromal cells
B
OPG is produced by the ________
Osteoblasts
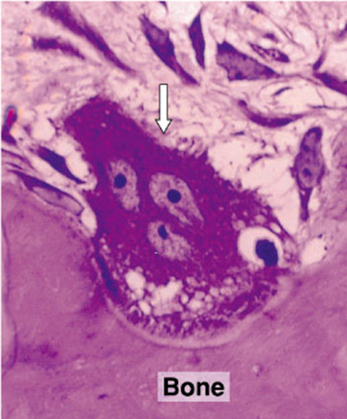
Howship’s lacuna
Osteoclasts
In a condition of low free calcium, _________ release of PTH acts on osteoblasts to promote osteoclast differentiation and activity
persistent/continuous
____________ PTH bone synthesis – anabolic effect - increases bone density
Intermittent/pulsatile
Why is teriparatide used for osteoporosis if it is a recombinant PTH?
Because PTH in intermittent or pulsatile releases actually increases bone density
PTH has _____ effects in the intestines.
Indirect
Since the effects of PTH in the kidney regulate vitamin D synthesis which in turn regulates calcium absorption in the intestines
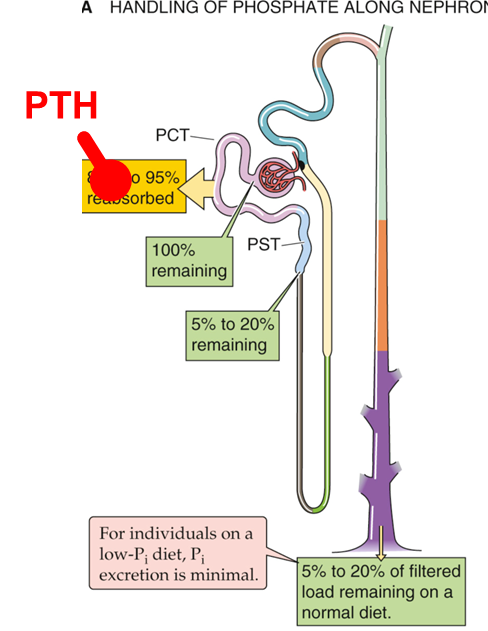
In kidney reabsorption of calcium from the lumen of the ____ back into the blood
distal convoluted tubule DCT
____ regulation of calcium primarily occurs in the thick ascending limb (TAL), distal convoluted tubule (DCT) and connecting tubule
PTH
In the kidney, PHT binding to the PTH-R1 - coupled to adenylyl cyclase via G⍺s to increase cAMP, activate PKA and the transcription factor ___
CREB
increases calcium channel gene expression in kidneys
CREB
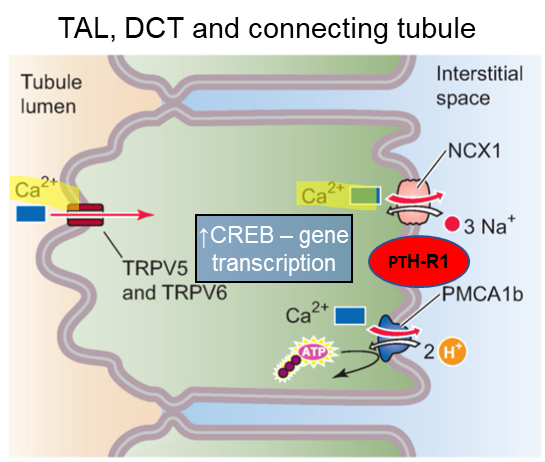
PTH regulation of calcium reabsorption
PTH acts on the proximal (PCT) to inhibit _______ reabsorption to prevent unwanted calcium phosphate crystal formation.
phosphate
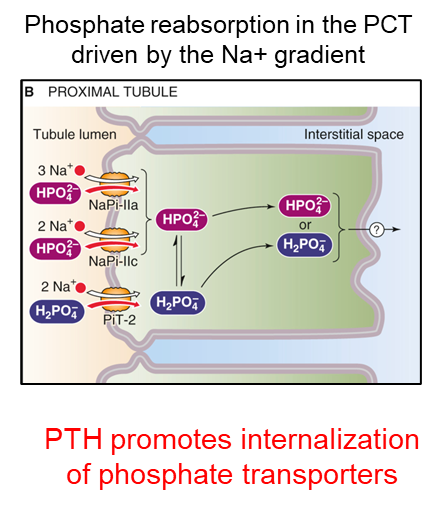
PTH increases renal phosphate excretion
____ promotes internalization of phosphate transporters
PTH
Binding of the PTH-R1 in kidney ___ leads to internalization of phosphate transporters.
PCT
Phosphate Thrashing Hormone
PTH
PTH in PCT of kidney stimulates vitamin D production by increasing ________ expression which hydroxylates inactive 25-hydroxycholecalciferol to the active form of vitamin D – 1,25 hydroxycholecalciferol (1,25 (OH)2D3, calcitriol)
1⍺-hydroxylase
Low phosphate also _______ 1⍺-hydroxylase to increase active vitamin D, while high phosphate and elevated levels of vitamin D _______ 1⍺-hydroxylase.
increase
inhibit
Since vitamin D regulates calcium and phosphate absorption in the intestines, PTH is considered to have ______ effects on the intestines.
Indirect
Where does vitamin D stimulation due to PTH happen in the kidney?
PCT
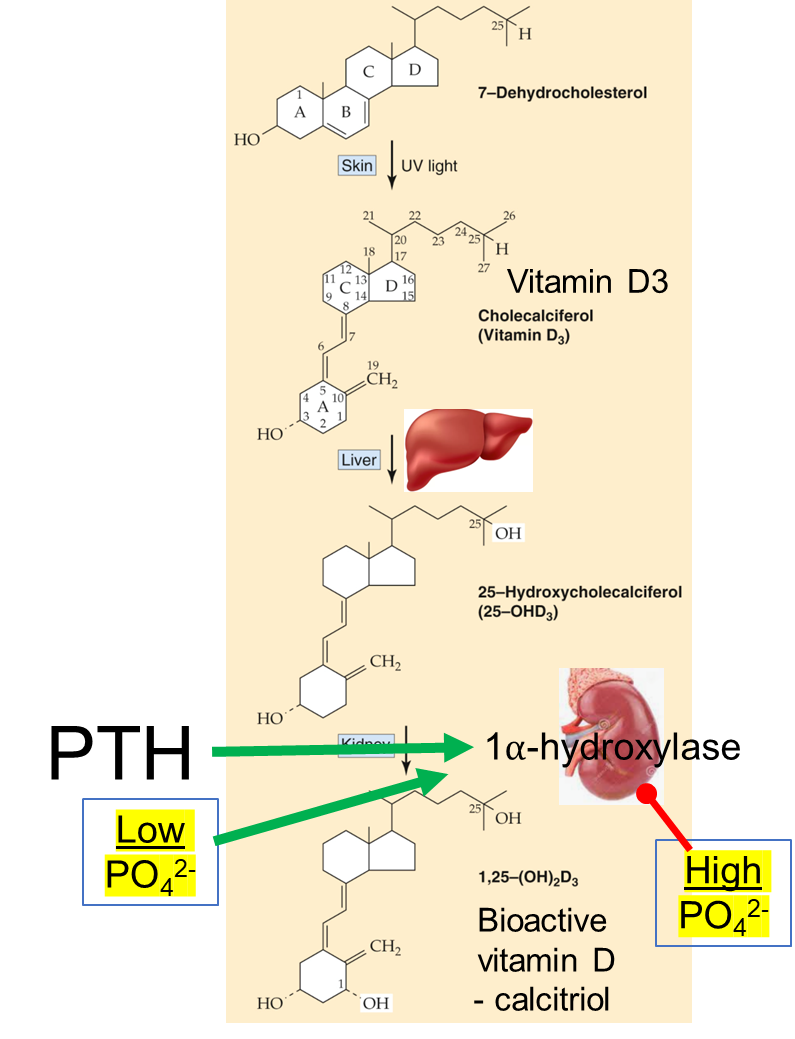
PTH increases vitamin D
Which is more active 25 hydroxycholecalciferol or calcitriol?
calcitriol
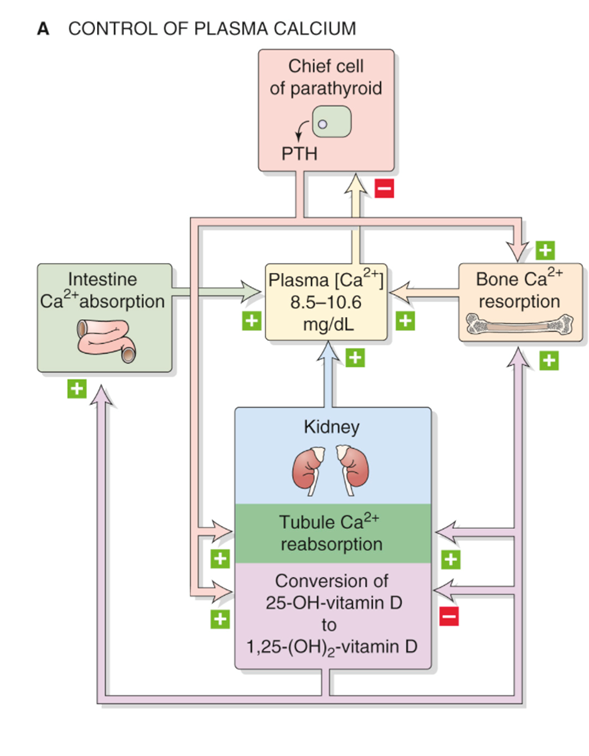
Control of plasma calcium PTH
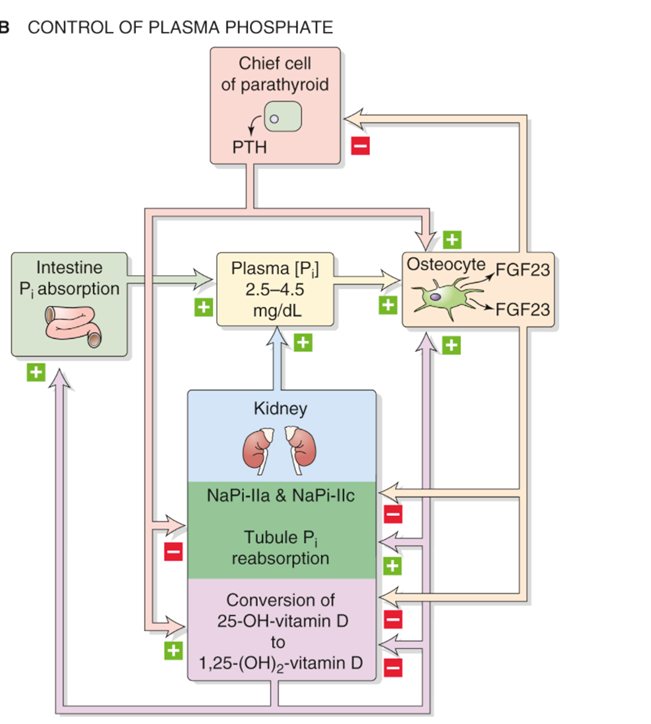
Control of plasma phosphate PTH
Vitamin D_ (ergocalciferol) – Dietary vegetables
Vitamin D_ (cholecalciferol):
Dietary intake (deep water fish, eggs, fortified milk)
Synthesis from 7-dehydrocholesterol – requires UV light.
2
3
Vitamin D2 and D3 → calcitriol
1 alpha hydroxylase
Both calcitriol and 25-hydroxycholecalciferol bind to the_____ receptor.
Vit D
Normal plasma calcitriol ____-__ pg/mL
20-60
Vitamin D _____ 1⍺-hydroxylase
inhibits