Ocular Block 2
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
76 Terms
Orbit
Eye socket
Globe
Eyeball
Adnexa
Everything except the globe
Includes: orbit, extracellular muscles, eyelids, conjunctiva, third eyelid/nictitating membrane, and lacrimal system
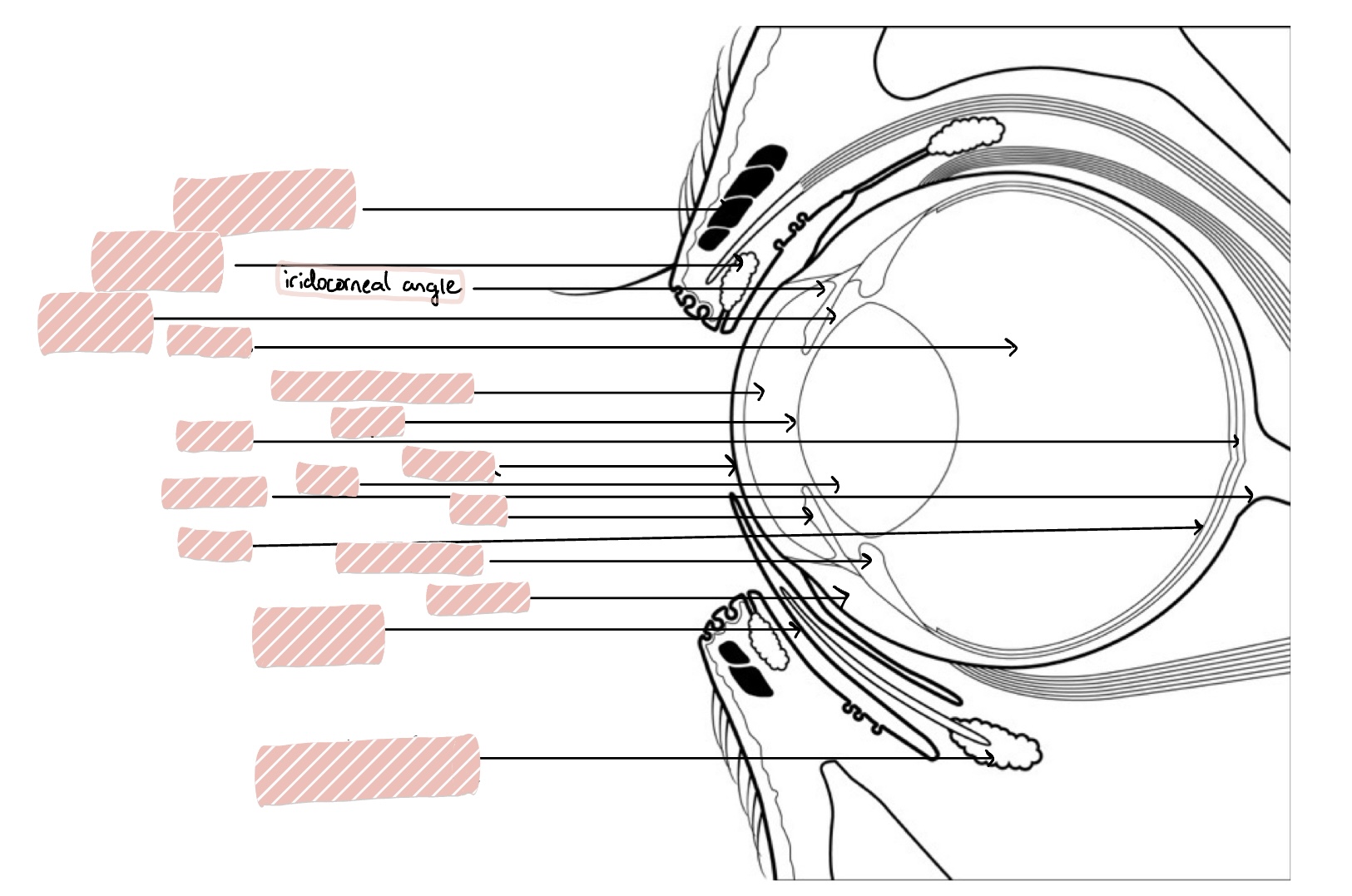
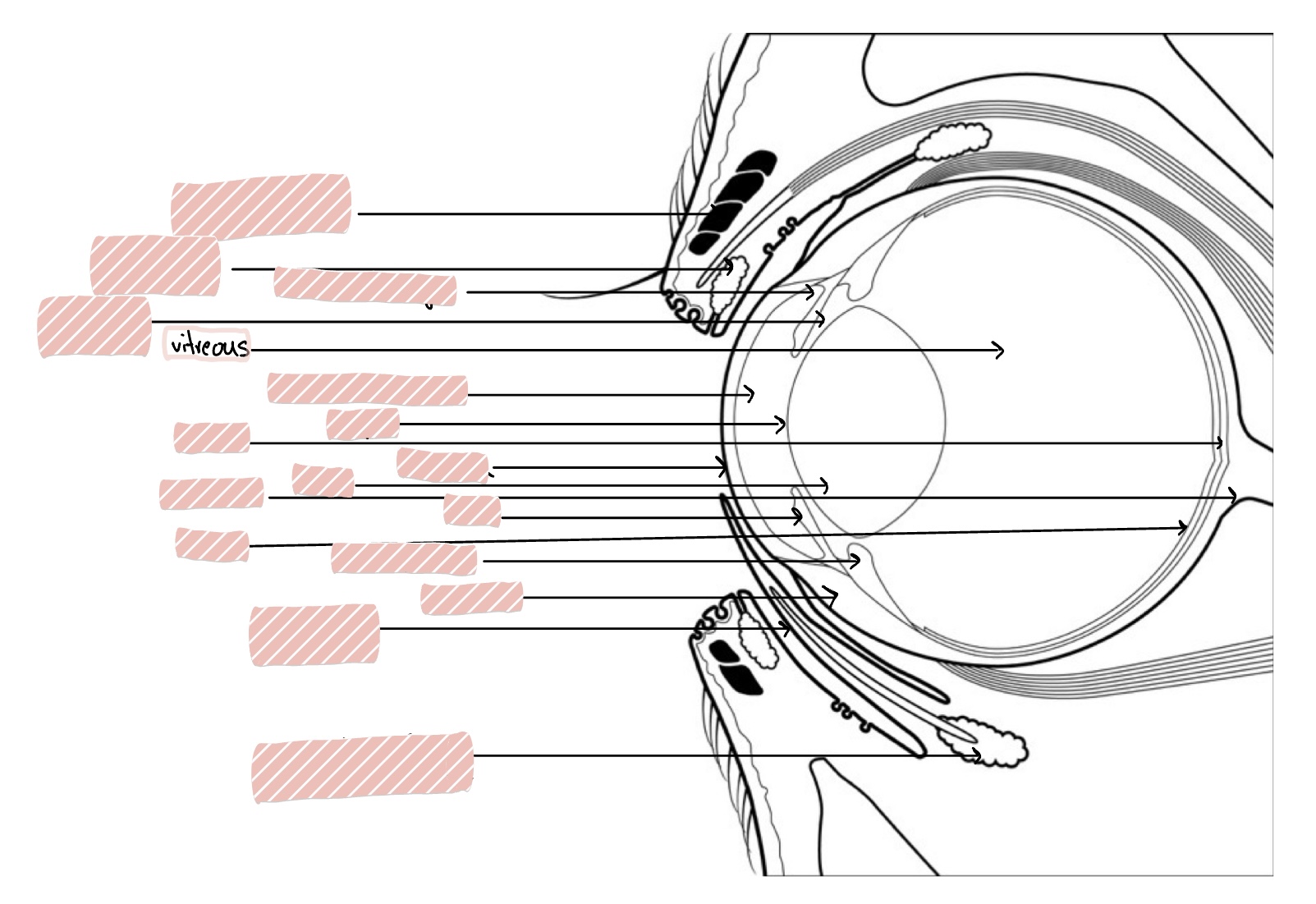
Anterior segment of eye includes…
the cornea, sclera, anterior chamber, posterior chamber, iris, iridocorneal angle, ciliary body, and lens
Anterior Chamber
Space between the cornea and iris/lens
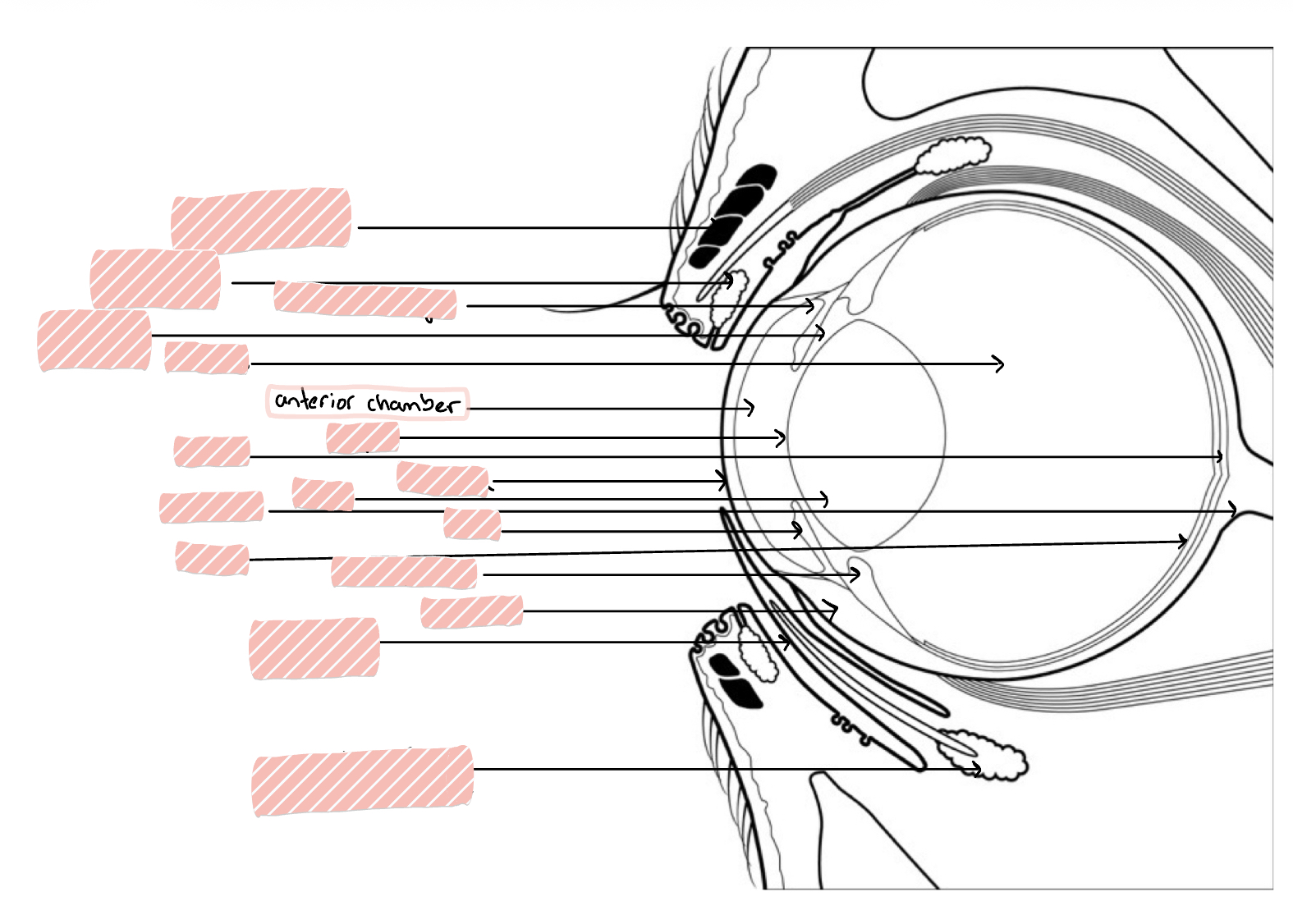
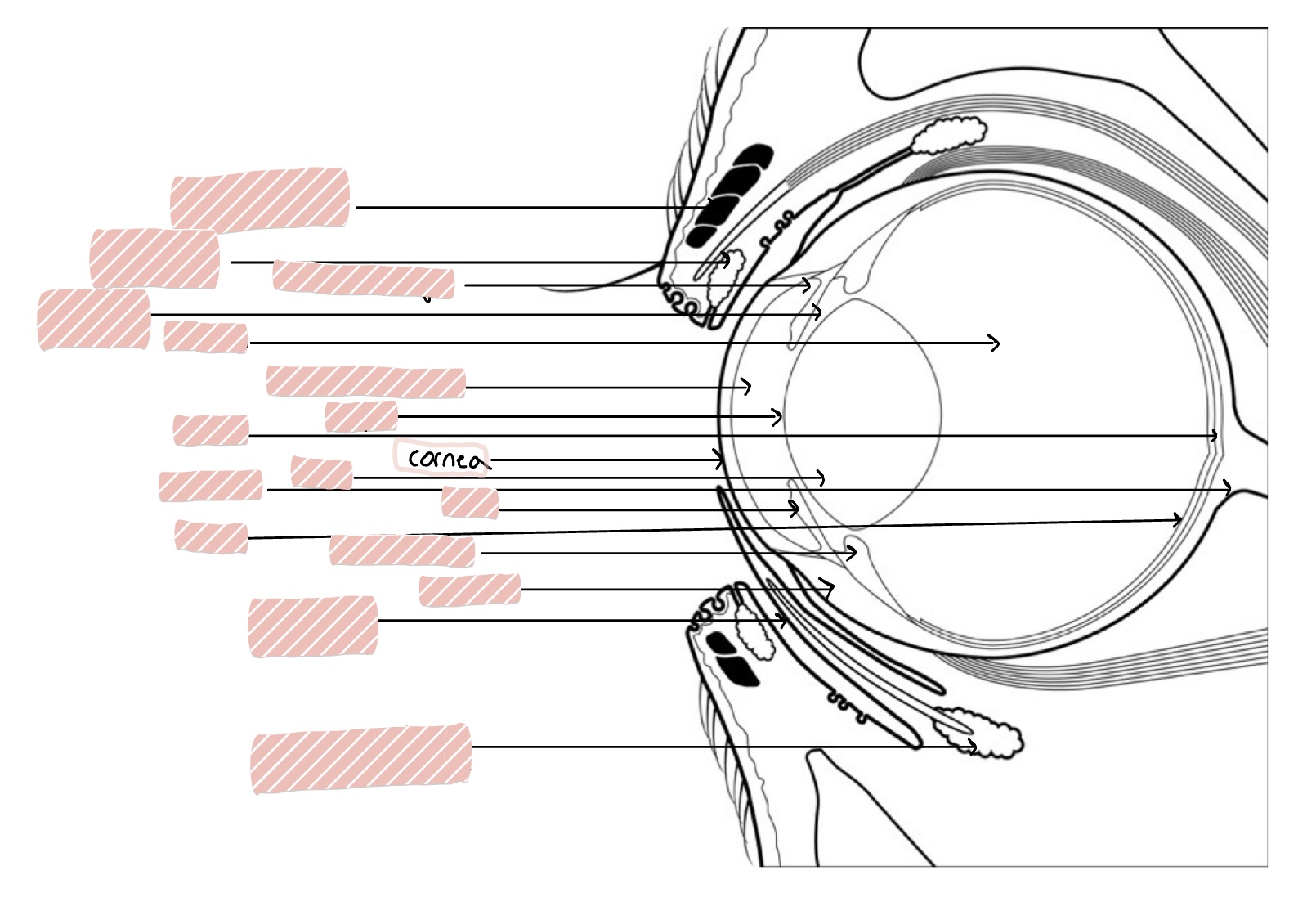
Cornea
transparent, avascular, 0.5-1mm thick rostral portion of eye; transmits light, refracts light, and protects internal contents
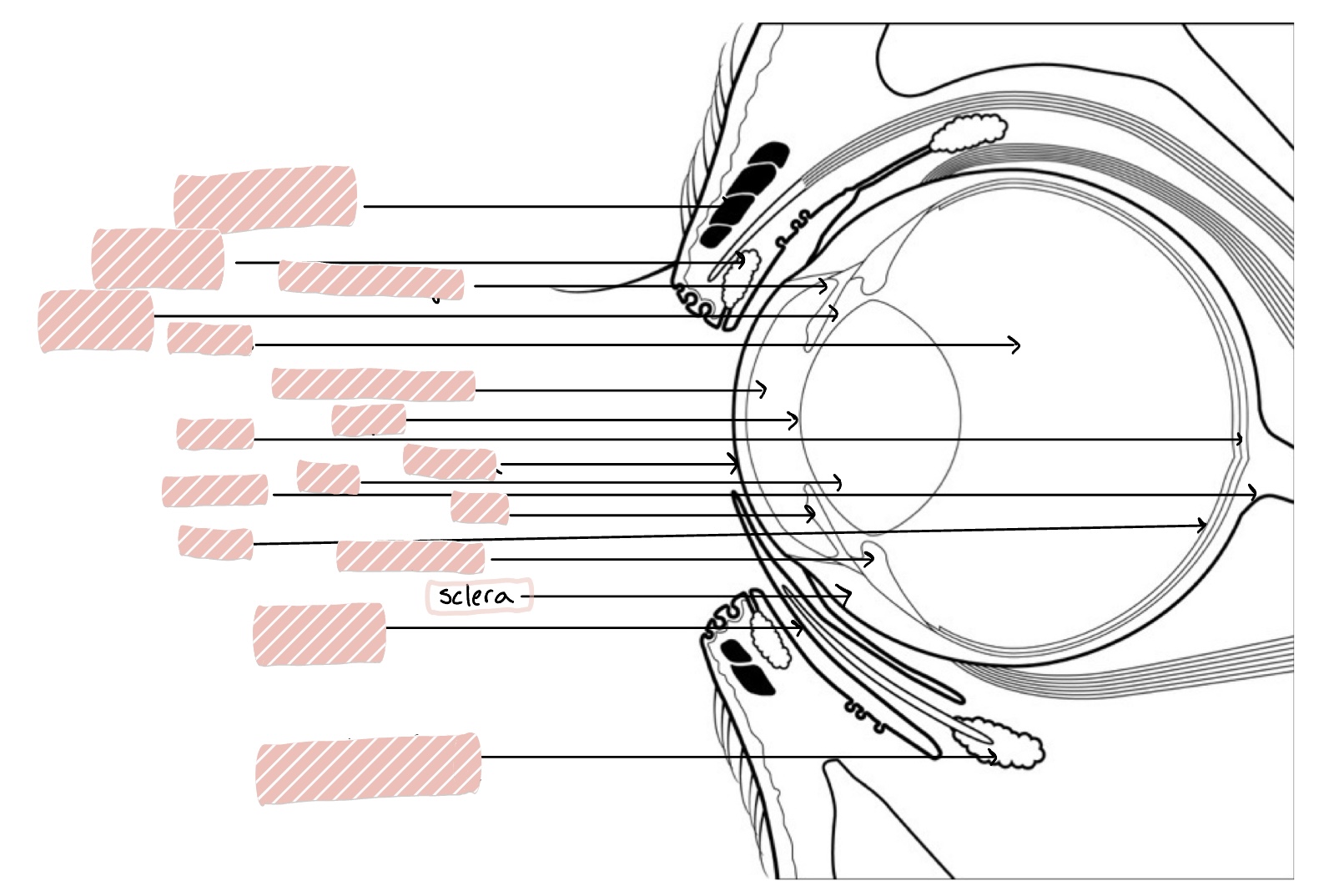
Sclera
White of eye
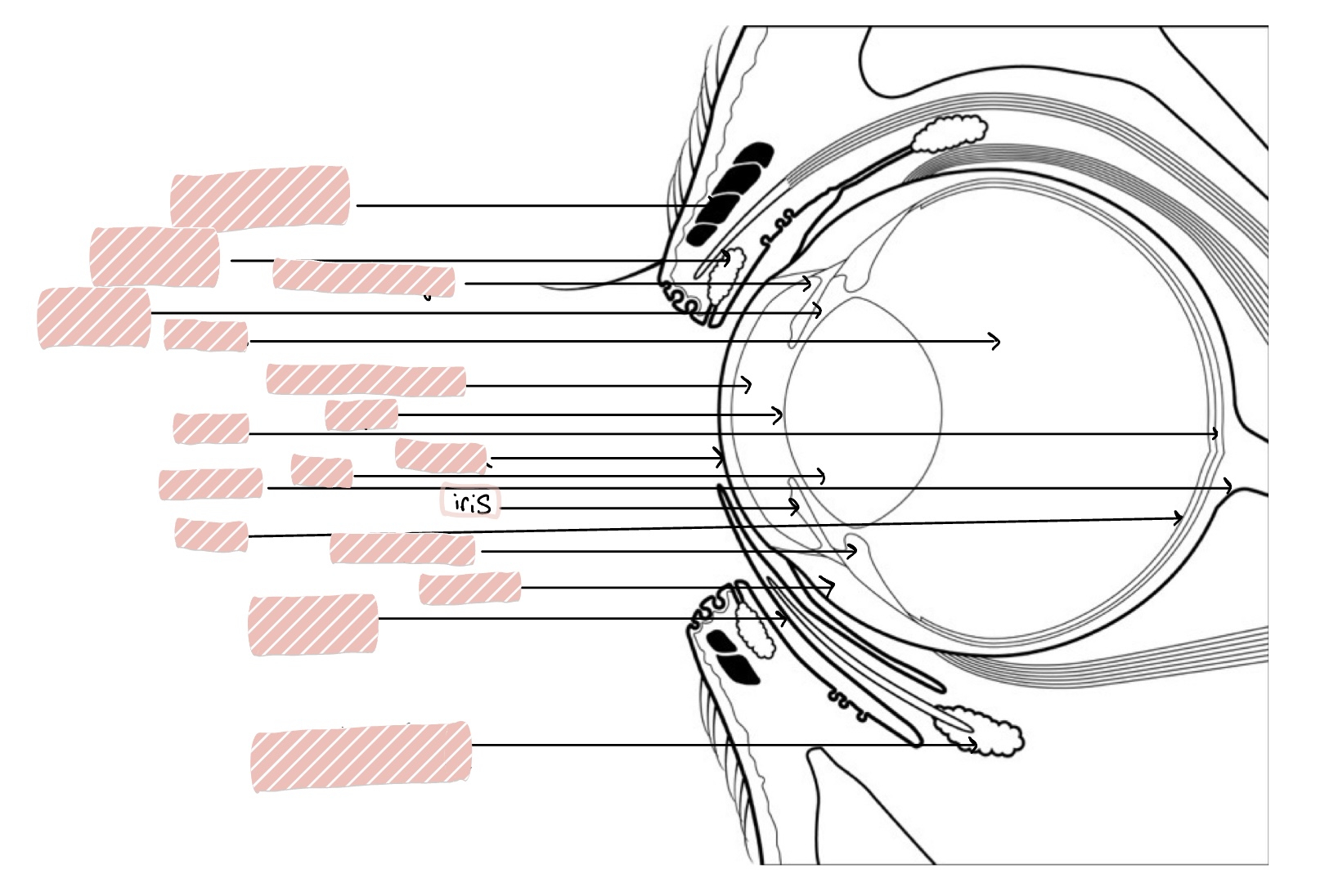
Iris
Constricts to control size of pupil
Iridocorneal Angle
Angle between iris and cornea
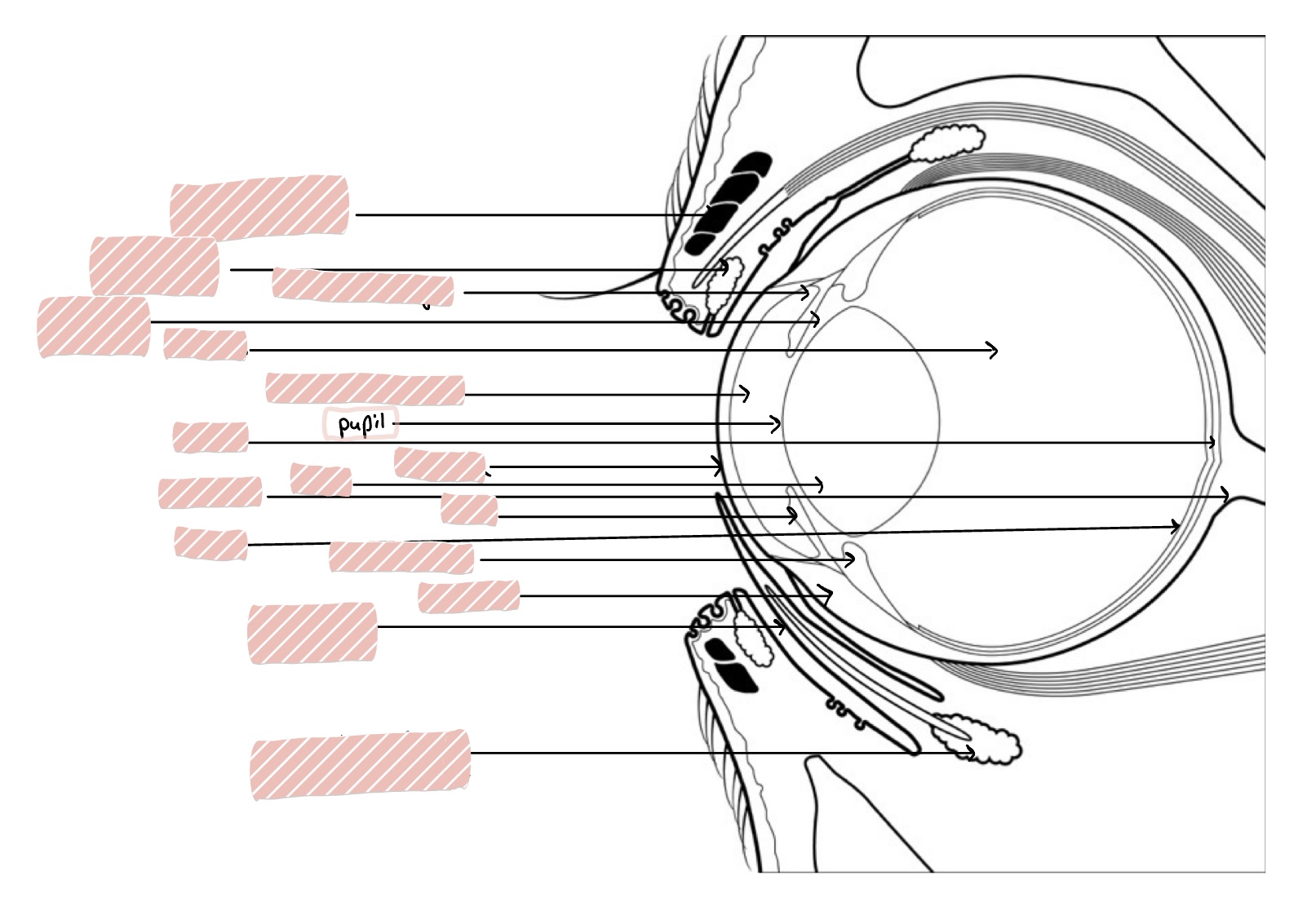
Pupil
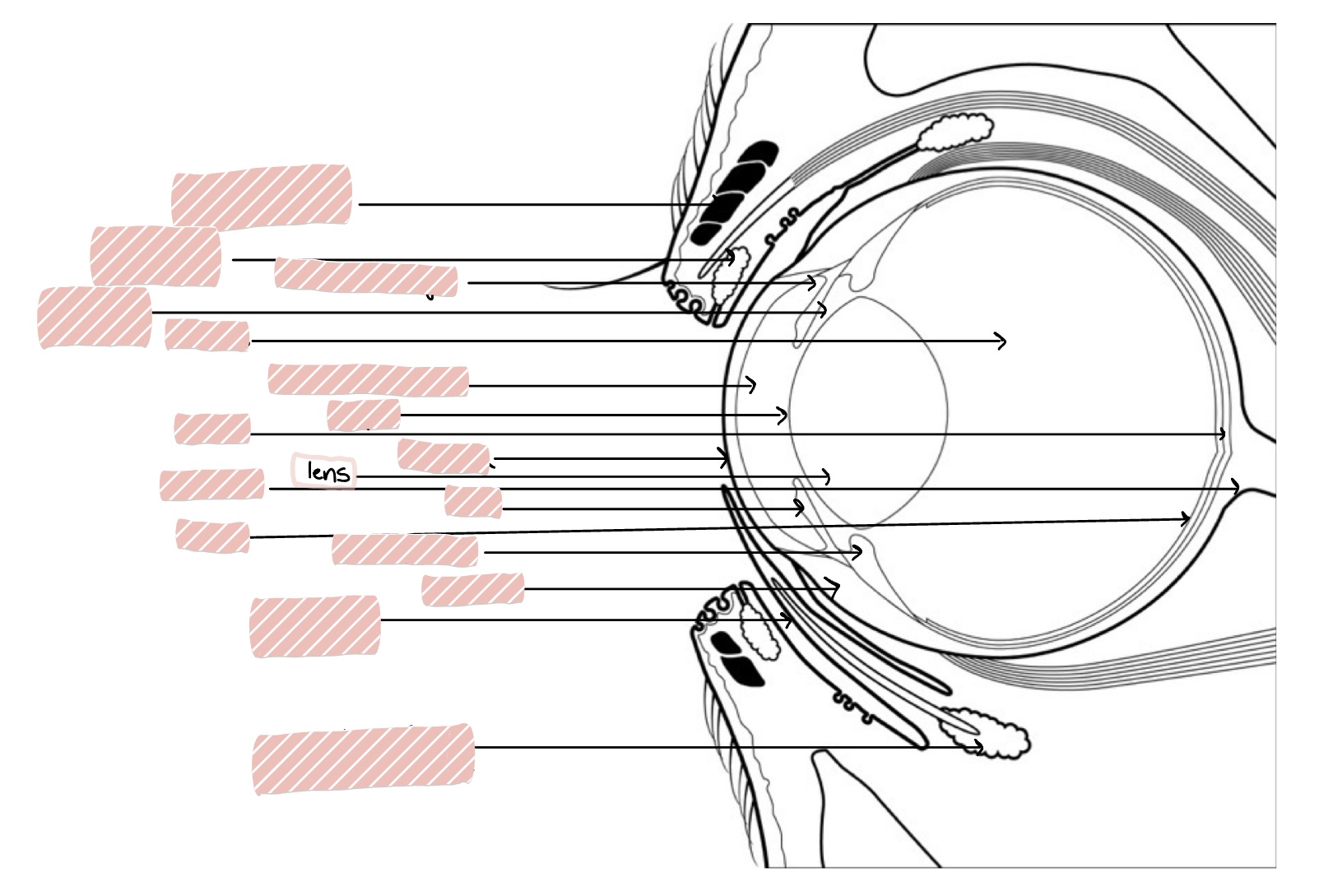
Lens
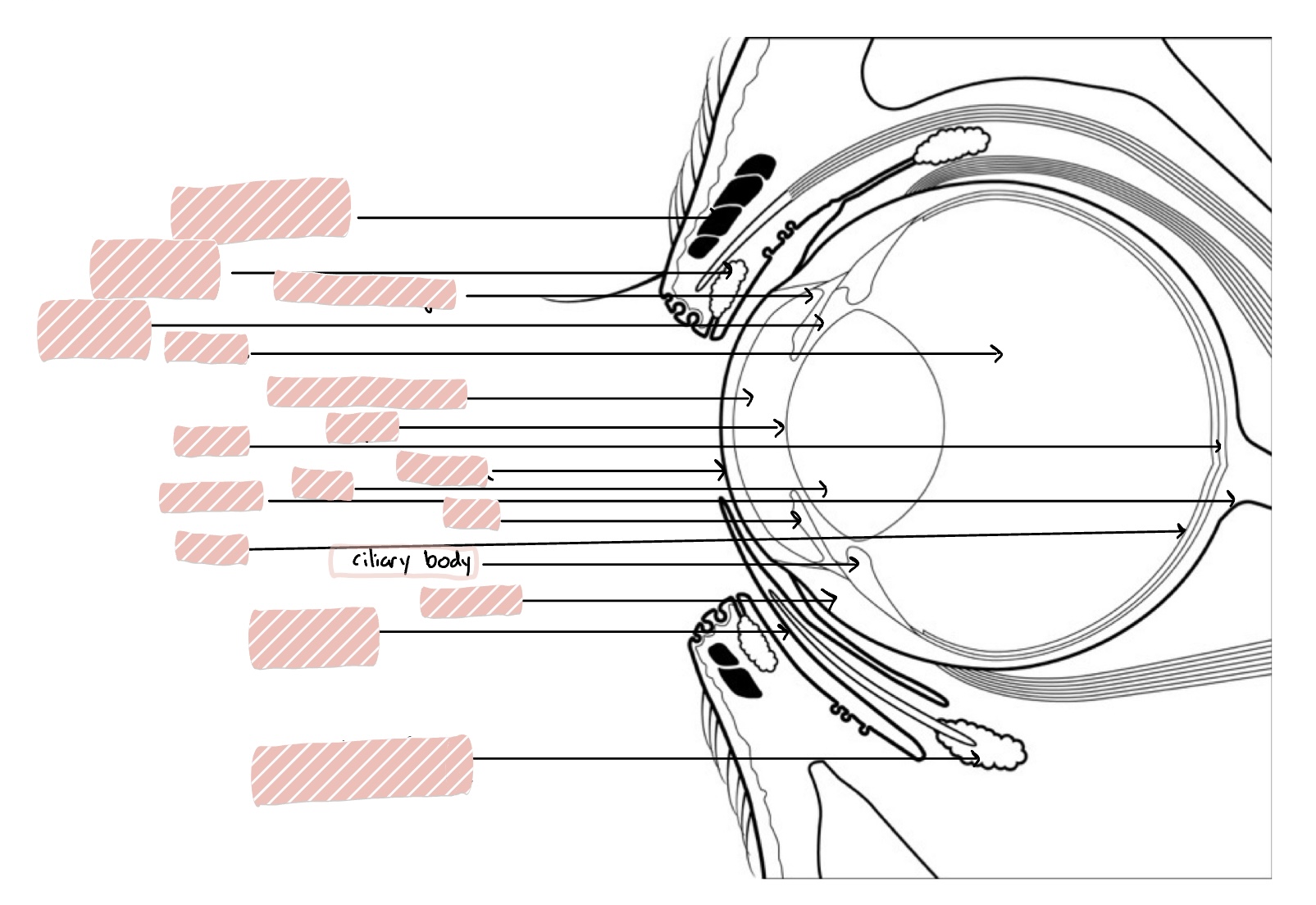
Ciliary Body
Vitreous
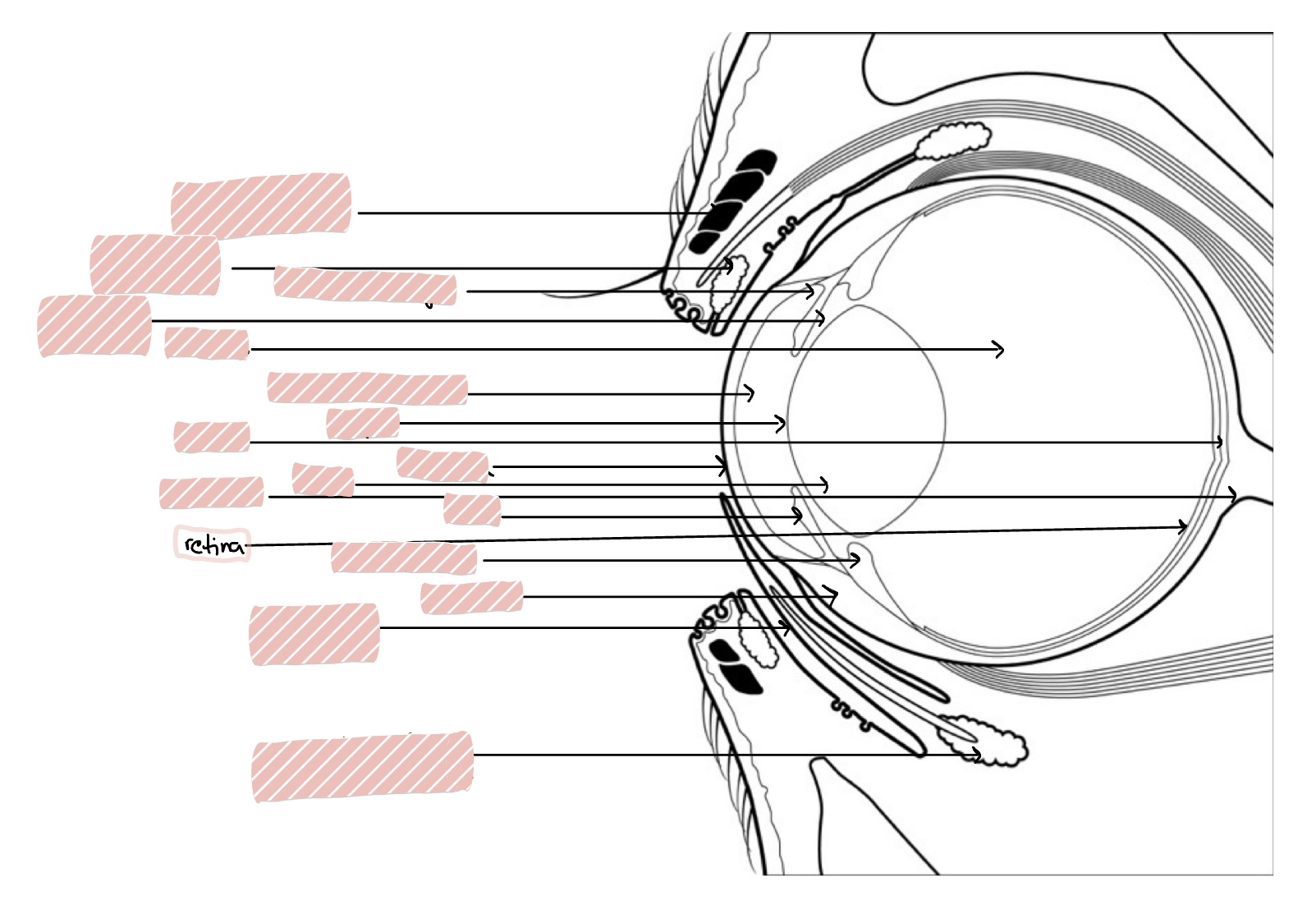
Retina
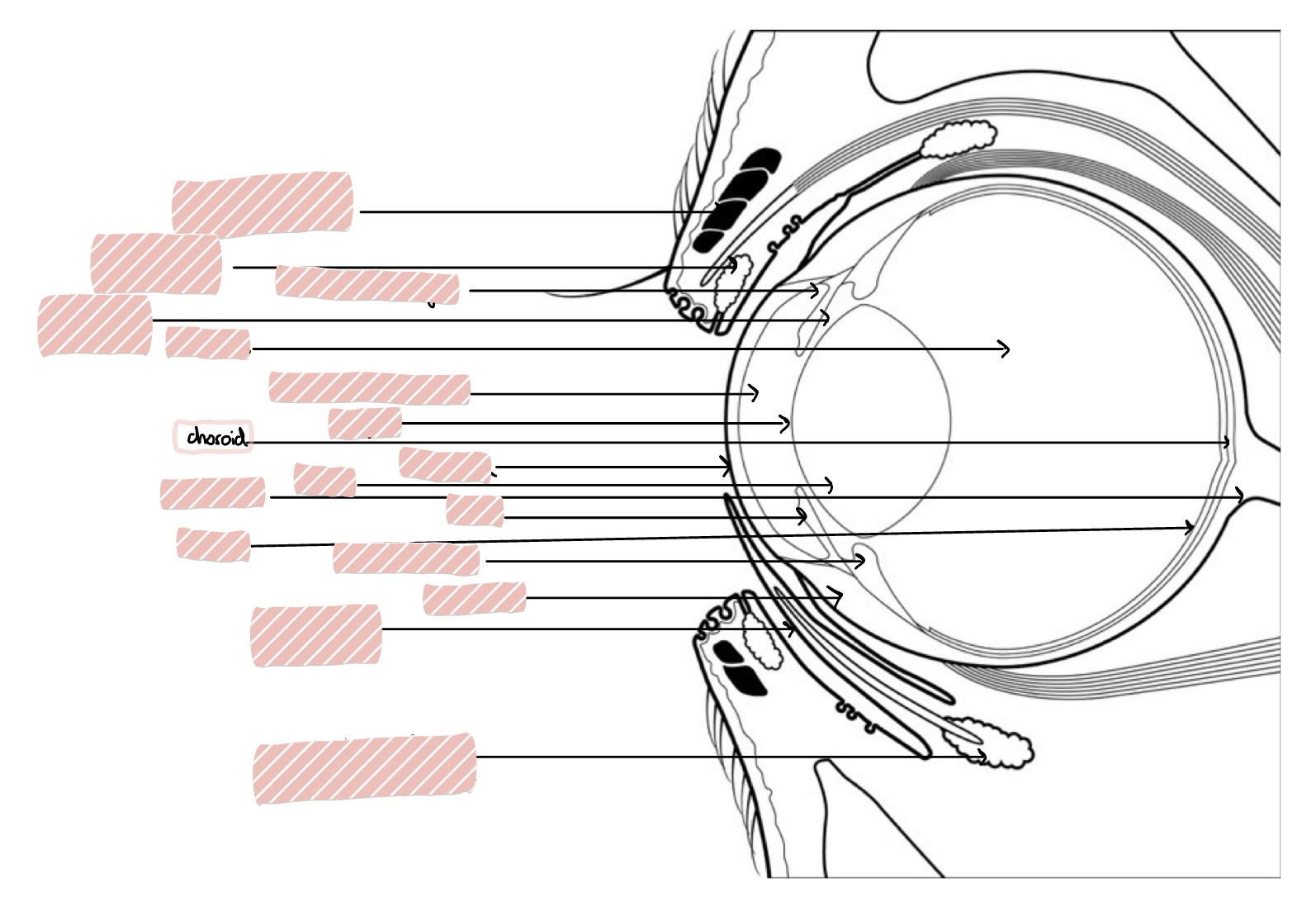
Choroid
Optic Nerve
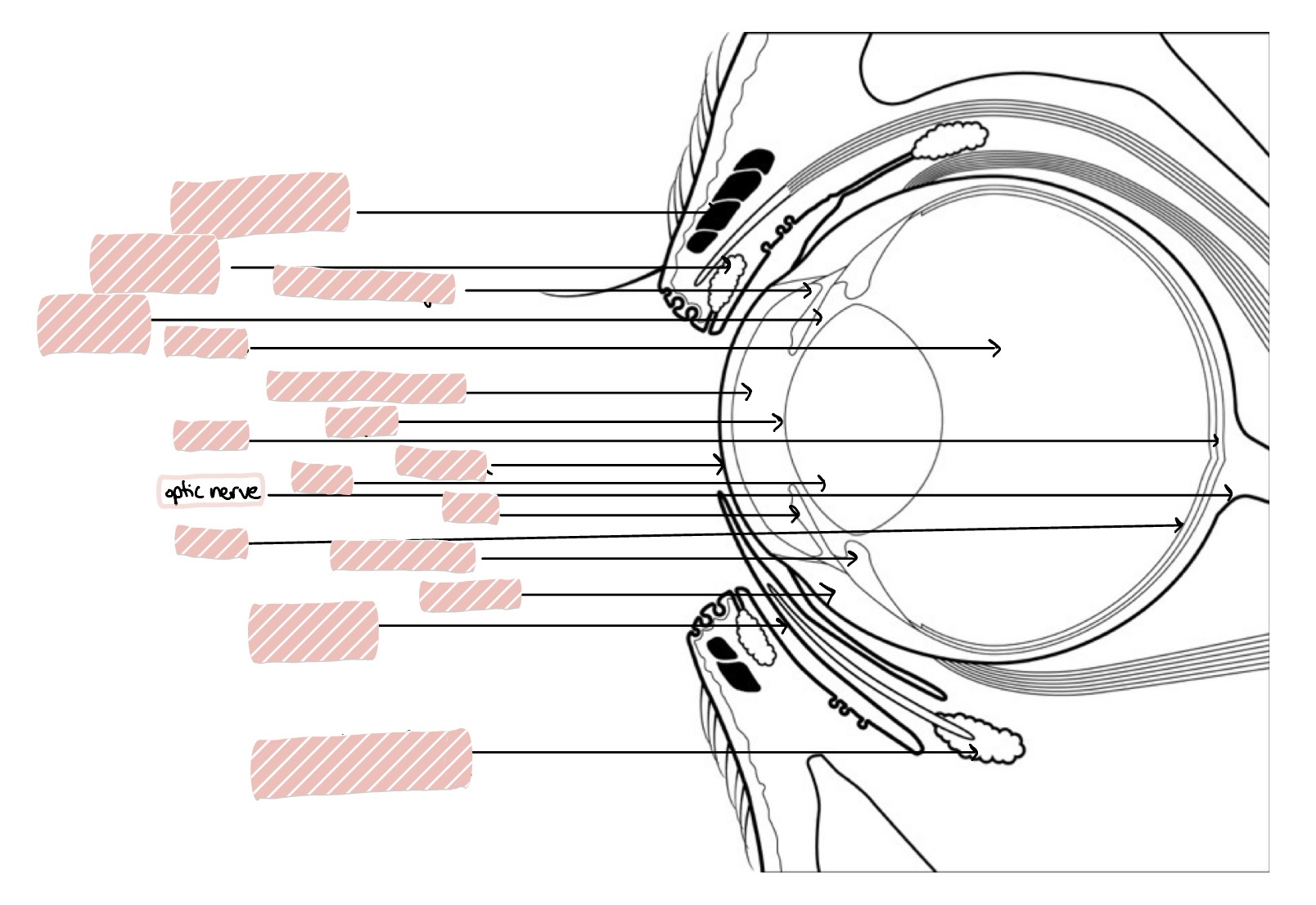
Posterior Segment of the eye includes…
Vitreous humor, retina, choroid, optic nerve, and posterior sclera
How is the orbit different in herbivores vs carnivores?
Herbivores have a complete bony rim while carnivores have an incomplete bony rim with the orbital ligament.
What is in the orbit?
It is lined with fascia and contains the conjunctiva, nictitans, fat, extraocular muscles, muscles of mastication, blood vessels, glands, cranial nerves 2-8, and autonomic nerves.
What bone of the skull contacts the floor of the orbit?
Ramus
What structures can cause secondary orbital disease due to close nature?
Nose, sinuses, and teeth
What is the purpose of the extraocular muscles?
To move the globe in the orbit and the muscle cone anchors in the back of the orbit.
What do the dorsal/superior and ventral/inferior oblique muscles do?
Rotate the globe
What does the retractor bulbi muscle do?
Pulls globe back in orbit
What structures are on the eyelid?
Skin, hair, mucocutaneous junction, conjunctiva, glands, and muscles
Skin of the eyelid
Very thing to provide mobility and elasticity varies. Made up of epidermis and contains hair follicles
Cilia
Eyelashes! Varies among species and originate outside the meibomian gland openings
Meibomian glands definition
Row of sebacous glands on eyelid margin that open at the mucocutaneous junction and secrete lipid layer of the tear film
Tarsus
Collagen sheet that encompasses structures of eyelid margin (3-4mm) and gives rigidity and a surface for muscle attachment
Levator palpebrae superioris muscle
Elevates the upper eyelid, innervated by CN III
Orbicularis oculi muscle
Surrounds margins and closes upper and lower lids, innervated by CN VII
Malaris muscle
Lowers the inferior eyelid, innervated by CN VII
Mueller’s muscle
smooth muscle that provides tone to the tarsus (keeps eyes open), innervated by Sympathetic nerve
Medial and Lateral Canthal Ligaments
Ligamentous bands, anchor medial (wider and shorter) and lateral (longer and flexible) canthus to periosteum of orbital rim
Vascular supply of eyelids
Well vascularized by longitudinal vessels parallel to eyelid margins
Palpebral Conjunctiva
Lines eyelids
Bulbar Conjunctiva
Lines exposed surfaces of globe
Fornix Conjunctiva
cul-de-sac formed by reflections of conjunctiva at transition from lid to globe
Nictitans Conjunctiva
Convers palpebral and bulbar surfaces of the nictitating membrane
Conjunctiva appearance
Pale pink with some pigment is normal and a few lymphoid follicles
Histology of conjunctiva
Non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium with goblet cells between to secrete mucus
Conjunctiva functions
Allows smooth gliding of nictitans and eyelids over globe, secretes mucus layer of tear film, offers immune protection for ocular surface, and helps with corneal repair surgery
Nictitating membrane definition
Triangular piece of tissue in medial fornix/canthus, leading edge is pigmented
Nictitating membrane function
Moves dorsolaterlaly as globe is retracted, spreads tear film, protects globe, and removes particulate matter from surface
Structures of the nictitans
Stroma (fibrous connective tissue)
T-shaped cartilage for strucural support
Lacrimal gland at base (galnd of nictitans)
Covered in goblet cell rich conjunctiva
How do you exam the nictitans?
To expose nictitans during examination, retract the eyelids while applying digital pressure to the globe
What is a common name for a prolapsed gland of the nictitating membrane?
Cherry eye
Function of the lacrimal apparatus
Produce, distribute, and drain pre-corneal tear film to maintain lubrication and health of the ocular surface
Tear film layers
Lipid layer - produced by Meibomian gland
Aqueous layer - produced by lacrimal glands
Mucin layer - produced by goblet cells
Lacrimal Glands
Orbital lacrimal glands (dorsolateral orbit) and Gland of the nictitans (base oof nictitans)
Lacrimal Outflow Apparatus
Drains tears from eyelids to nose
Ocular puncta in eyelids
Canaliculi in eyelids
Lacrimal sac in medial canthus
Nasolacrimal duct
Nasal puncta
What are the 3 concentric tunics?
Fibrous
Vascular
Nervous
What structures make up the fibrous tunic?
sclera
cornea
What structures make up the vascular tunic?
ciliary body
iris
choroid
What structures make up the nervous tunic?
retina
optic nerve
Corneal Innervation
Sensory innervation from the opthalmic branch of the trigeminal nerve (CN V) in the anterior 1/3 of cornea
Corneal Anatomy
4 Layers:
epithelium
stroma
descemet’s membrane
endothelium
Corneal Epithelium
non-keratinized, non-pigmented squamous epithelium that is 8-15 cell layers thick
squamous cells
wing cells
basal cells
basement membrane
desmesomes
junctions between cells
hemidesmesomes
junctions between cells and basement membrane
What special structure are on the superficial cells on the corneal epithelium?
They have microvilli to help stabilize the tear film
What is the turnover rate of the cornea epithelium?
It takes 7 days from basal to superficial cells
How much of the epithelium makes up the stroma?
90% of the thickness
Composition of the cornea stroma?
collagen (regularly arranged), keratocytes, glycosaminoglycans, water (78%), and no blood vessels
Why is normal distance between fibrils important?
It is required for light to transmit well through the cornea, edema causes spreading of the fibrils from the normal arrangement
What is important about the corneal stroma?
It is hydrophilic and will imbibe water if there is a break in epithelial or endothelial barriers; needs to maintain deturgescence (dehyration) to be clear
Descemet’s membrane
basement membrane of the endothelium; modified basal lamina
What does descemet’s membrane do as a dog ages?
It gets thicker
Corneal endothelium
A single cell layer at the inner-most layer of the cornea made of hexagonal cells
Corneal endothelium function
actively pumps fluid out of cornea to maintain deturgescence and is mechanical barrier to stroma
How do cells heal in the corneal endothelium?
Cells do not undergo mitosis and heal by cellular enlargement and migration
polymegathism
cellular enlargement
pleomorphism
variable cell shape
Limbus
corneal-scleral junction; zone of transition from regularly arranged collagen and straight basement membrane of cornea
Sclera composition
Irregularly arranged densely packed collagen fibrils, vascularized, contains pigment and nerves, opaque, covered by bulbar conjunctiva, contains posterior opening for optic nerve
Lamina Cribosa
collagen sieve supporting axons of optic nerve, site of weakness