1.2.6 Government intervention
1/31
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
Negative externality of production
When third parties are negatively impacted by the production of a good/service, e.g. pollution
Negative externality of consumption
The third party spillover effects due to the consumption of a good/service (demerit goods). E.g. sugar, alcohol.
Types government intervention to stop negative externalities
Taxation
Subsidies
Fines
Government regulation
Polution permits
Tax
Financial charge made by a government on individuals, consumers and businesses.
Indirect tax
A type of tax applied to a good or service at the point of sale.
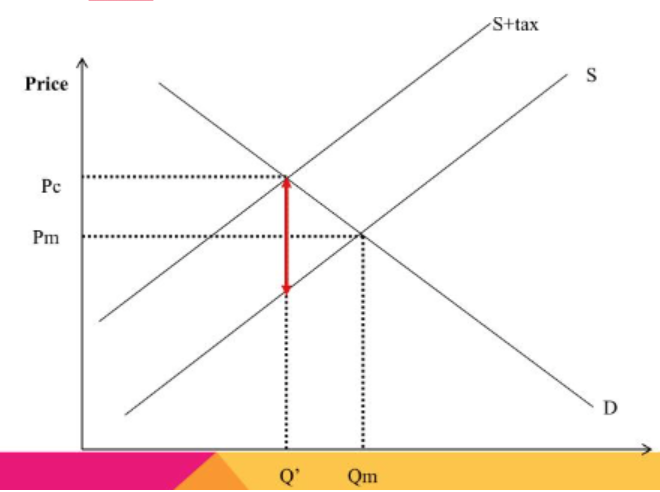
How will tax affect the supply curve
Causes its supply curve to shift to the left, because it causes the costs of the producer to rise
Advantages of tax
Reduces negative externalities
Provides revenue for the government
Disadvantages of tax
Difficult for the government to use the correct level of tax.
If demand is inelastic, the tax will not decrease demand much
Taxes can cause inequality
Cost of administration – the cost of collecting taxes. E.g. employing people to contact firms to ensure they are paying the correct level of tax.
Possibility of evasion – firms may avoid of evade paying tax
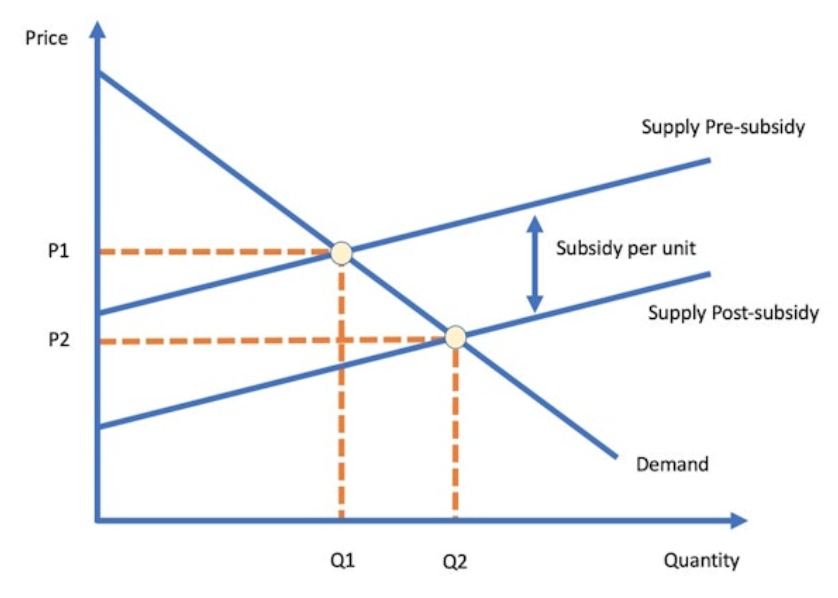
Subsidies
Government payments to firms to increase production and/or reduce cost of production for firms. They can also increase consumption of a good or service
How do subsidies affect the supply curve
Advantages of subsidies
Can result in increased production/consumption of goods with positive externalities, benefiting society.
If you subsidise public transport, it will encourage people to drive less, and reduce their negative externalities. In the long term, subsidies for a good will help change preferences. It will encourage firms to develop more products with positive externalities.
Disadvantages of subsidies
The cost will have to be met through taxation
Difficult to estimate the extent of the positive externality.
There is a danger that government subsidies may encourage firms to be inefficient and they come to rely on subsidy rather than improve efficiency.
The effect depends on the elasticity of demand. If demand is price elastic, a subsidy leads to large increase in demand. If demand is price inelastic, a subsidy is relatively ineffective in increasing demand.
Fine
Firms will need to make a payment to the government for doing something against regulation
What can firms be fined for
Firms can be fined if they pollute too much or if they do not act in the consumer interest
Advantages of fines
Can reduce negative externalities
Can increase government revenue
Disadvantages of fines
Depends on the level of the fine. Some firms may continue the behaviour and pay the fine if the fine is not big enough. If the fine is too much some firms may have to leave the market. Governments may not have enough information to set the fine at the correct level
If demand is inelastic, firms will simply pass the fine onto consumers in the form of higher prices.
Government intervention
It is difficult to get the tax/subsidy/fine level right. In some situations the government feels that their intervention needs to be a little more direct.
Examples of government intervention
Instead of taxing pollution, they may just ban it. Or at least legislate to control pollution levels. For example, cars now have to do an emissions test before they are allowed to be sold.
Another example of regulation is planning permission. In some countries, firms have to get permission from the government before they build on land, or they cannot build above the tree level etc.
Advantages of regulation
Can help reduce negative externalities
Can have a direct impact on firm behaviour
Disadvantages of regulation
Depends on how severe the regulation is
It may be difficult to control firm behaviour.
Pollution permits
Permits which only allow each country world-wide a certain amount of emissions of, say, greenhouse gases
Advantages of pollution permits
The total level of emissions allowed world-wide is fixed by the sum of the permits, so emissions should fall.
The countries that have to buy the spare permits because they struggle to keep their emissions down will probably also have lower costs.
Disadvantages of pollution
It is difficult to know how many permits to give out. The government may be too generous or too tight.
If firms buy more permits, they can just pass this extra cost onto consumers in the form of higher prices.
It can be difficult to measure pollution levels.
There are administration costs of implementing the scheme and measuring pollution levels.
For global pollution permits, countries who pollute more than their quotas can simply buy permits from other countries. Therefore rich developed countries can simply buy permits from less developed countries. This does not significantly reduce pollution but shifts it from the richer countries to poorer countries.
Types of government intervention to promote competition
Promoting competition
Controlling monopolies
Protecting consumer interests
Controlling mergers
Promoting competition
Encouraging the growth of small firms
Anti-competitive practices
Deregulation – can remove monopoly power and increase competition
Lowering barriers to entry – e.g. training and providing finance to firms
Privatisation
Controling monopolies
Price controls – Monopolies can be forced to set a maximum price.
Profit controls – The government set a level of profit a monopoly can earn and excess profit is taxed 100%.
Quality standards – A profit maximising monopolist focuses on profit and not quality. Governments can set quality standards.
Performance targets – Price, quality and other targets can be put in place to regulate monopolies. Targets include degrees of customer choice, costs of production etc.
Breaking-up the monopolist – The monopolist can be broken up into competing units by the government.
Lowering entry barriers
Deregulation – the process of removing government controls from markets.
Protect consumer interests
All legislation is aimed at protecting consumer interests. The government aim to control firms to lower prices and increase choice.
Controlling mergers
Mergers are investigated if they are too large. They can be prevented or fined.
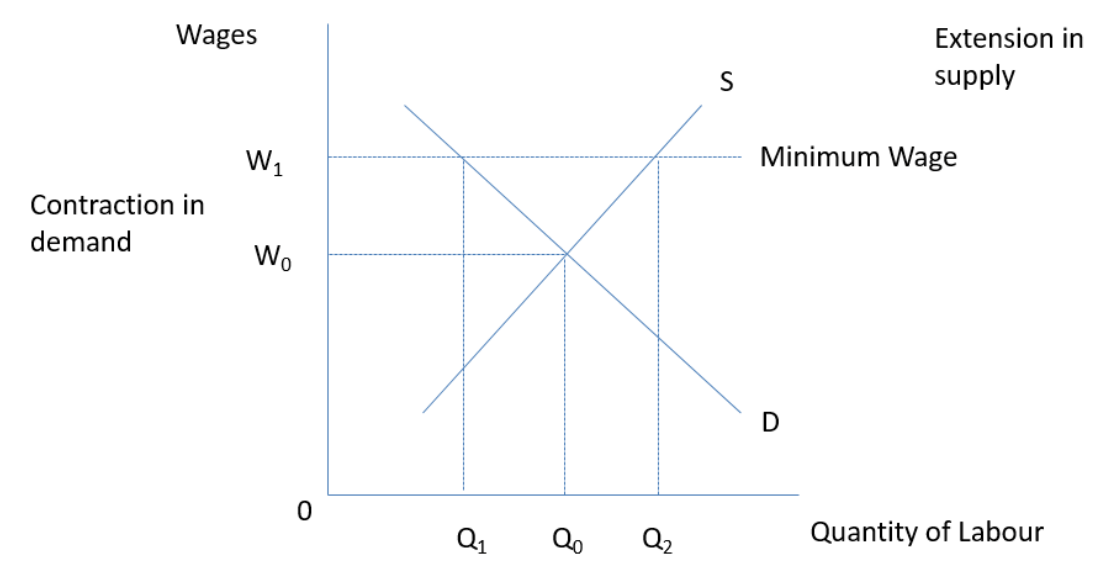
Minimum wage
legally enforced pay floor. Employers are not allowed to pay their employees a rate below the minimum wage
Minimum wage on a labour supply diagram
Advantages of having a minimum wage
Reducing poverty
Tax and benefits
The effect on productivity
Improved incentives
Disadvantages of minimum wage
Unemployment
High costs to employers