alpha carbon rxns
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
what is acid tautomerization mech
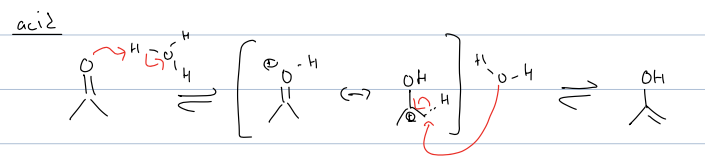
always want pos charge on a carbon bc acidic conditoins
what is base tatuo mech
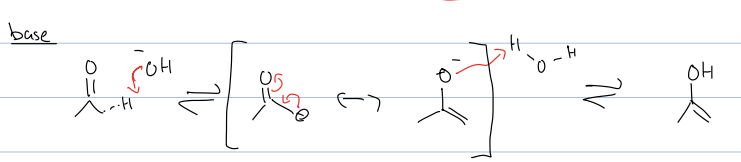
always want neg charge on carbon bc basic cond/
what are two ways to form enolate from ketone
use NaOH to get ketone and enolate
use LDA to get enolate
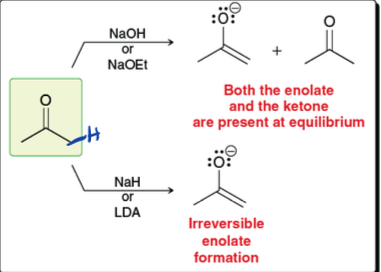
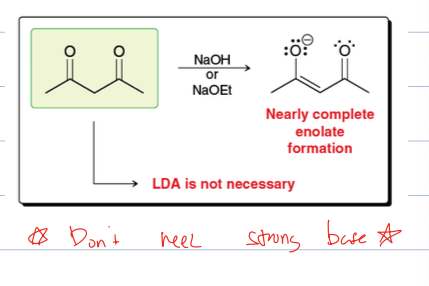
what are the two nucleophilic sties of an enolate

what is the difference between the reactants in aldol condensation and aldol addition rxn
there is heat in the condensation reaction
what is alpha halogenation in acidic conditions
have ketone to form enolate
reagent: H3O, Br2
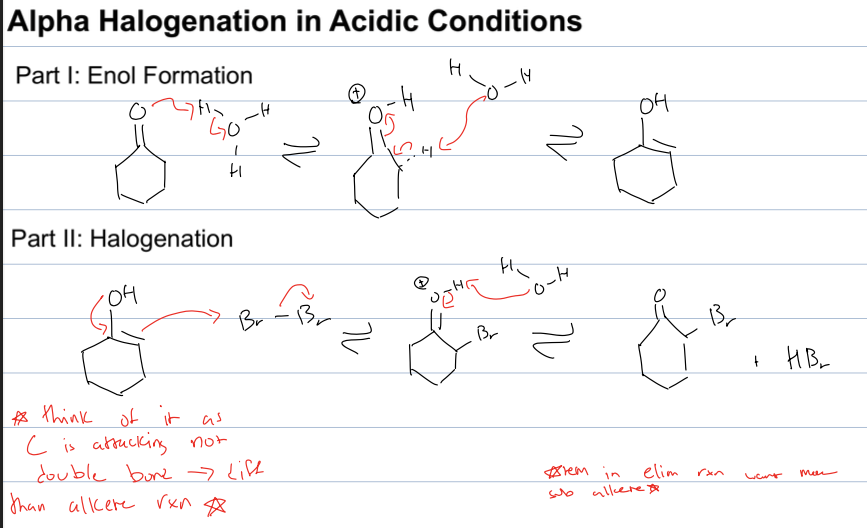
want more sub alkene
what is the Hell Volhard Zelinsky reaction (HVZ)
add BR at alpha pos of carbox acid
reagent: 1)PBR3,BR2 2)H2O
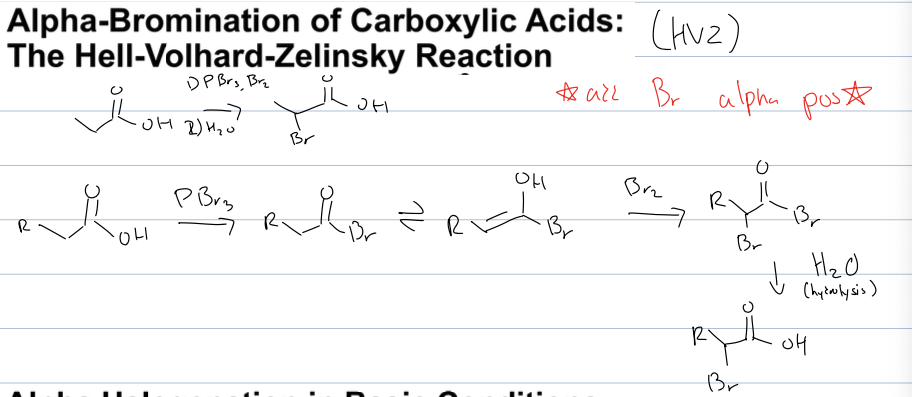
what is alpha halogenation rxn in basic conditions
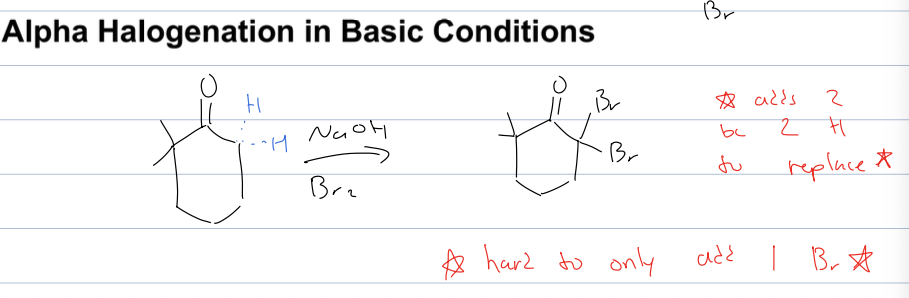
no need to form enolate
reagents: NaOH, Br2
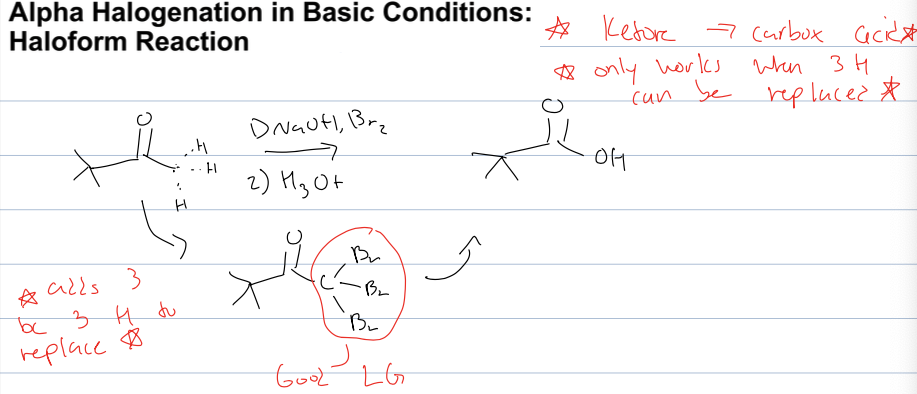
what is the haloform reaction for halogenation in basic cond.
ketone to carbox acid
only works when 3H can be replaced by BR
reagents: 1)NaOH, Br2 2) H3O+
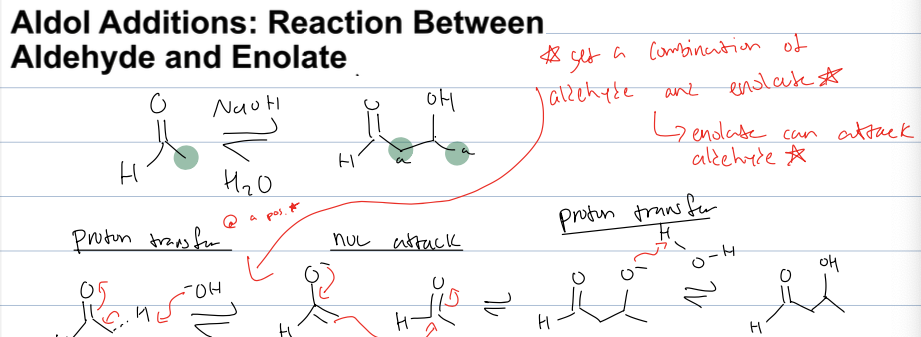
what is the aldol addition rxn between aldehyde and enolate
where an enolate can attacck aldehyde bc prod has both molecules
reagents: NaOH, H2O
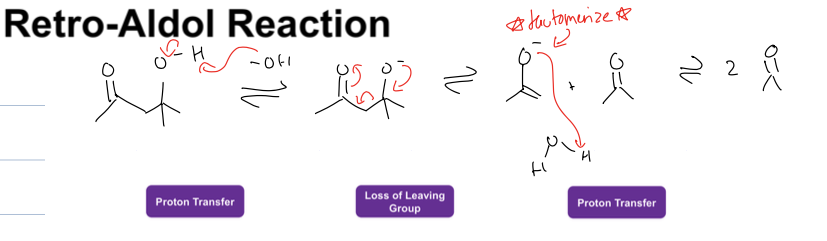
what is the retro aldol reaction
takes prodct from aldol addition to get two ketones
Reagent: NaOH
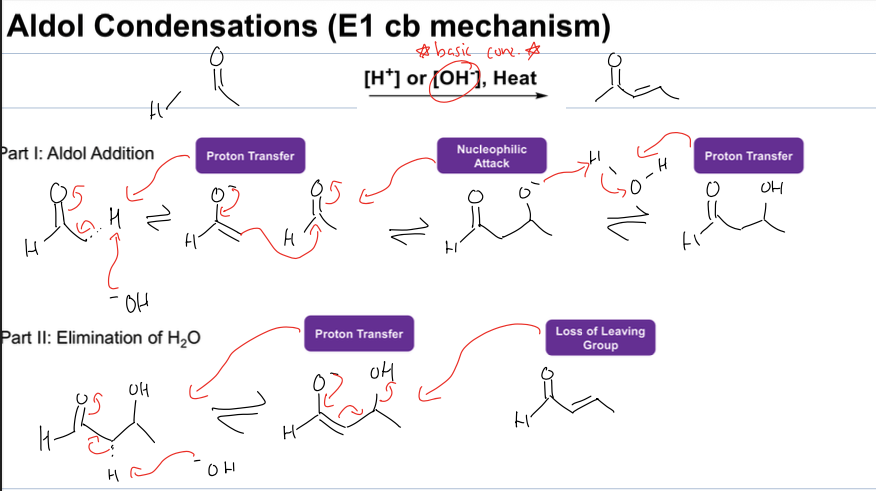
what is the aldol condensation rxn
add alkene to aldehyde
reagents:[OH-], heat
how do you control a crossed aldol reaction
By using one reactant that has no alpha hydrogens, which forces selectivity in the formation of the aldol product.
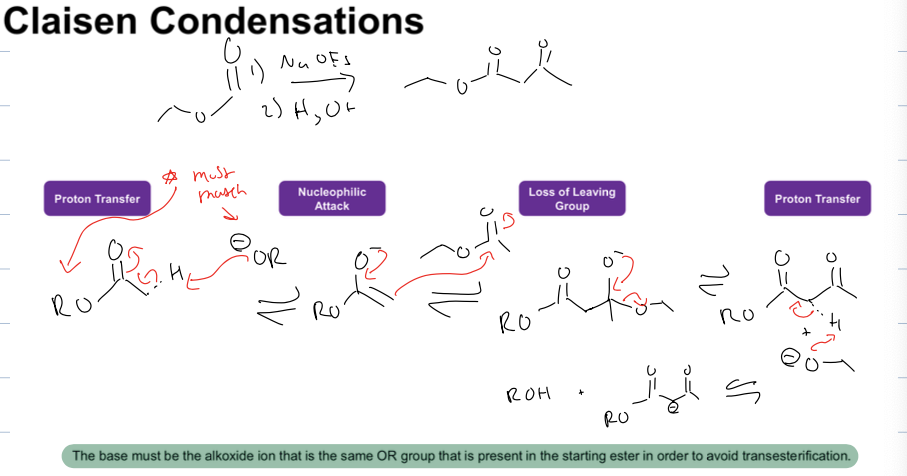
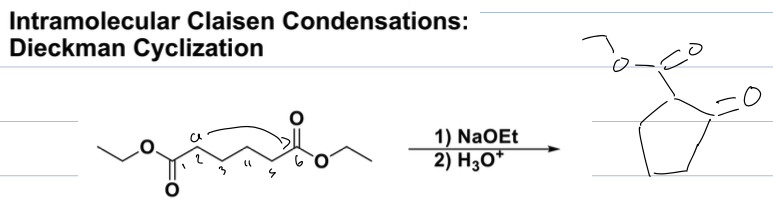
what is the claisen condensation rxn
reagents: 1)NaOEt 2) H3O
the alcoxide must match group on reagent
always an ester
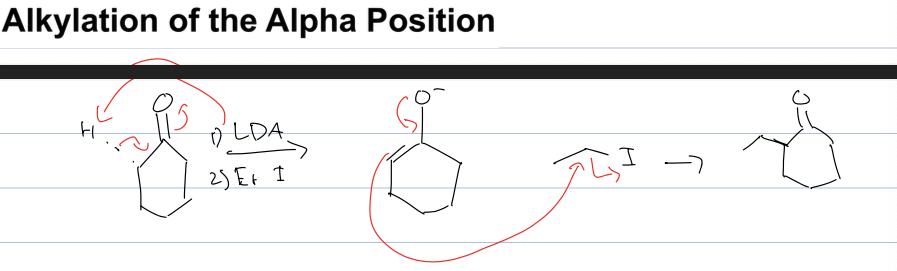
what is alklatoin of alpha position rxn
ketone to add alkyl group
reagent:1) LDA 2) alkyl halide that has R group you want
ADDS at less sub position bc of kinetic product being favored
what are the two products of the alklation of the alpha position when the ketone is unsymmetrical
kinetic enolate and thermodynamic enolate
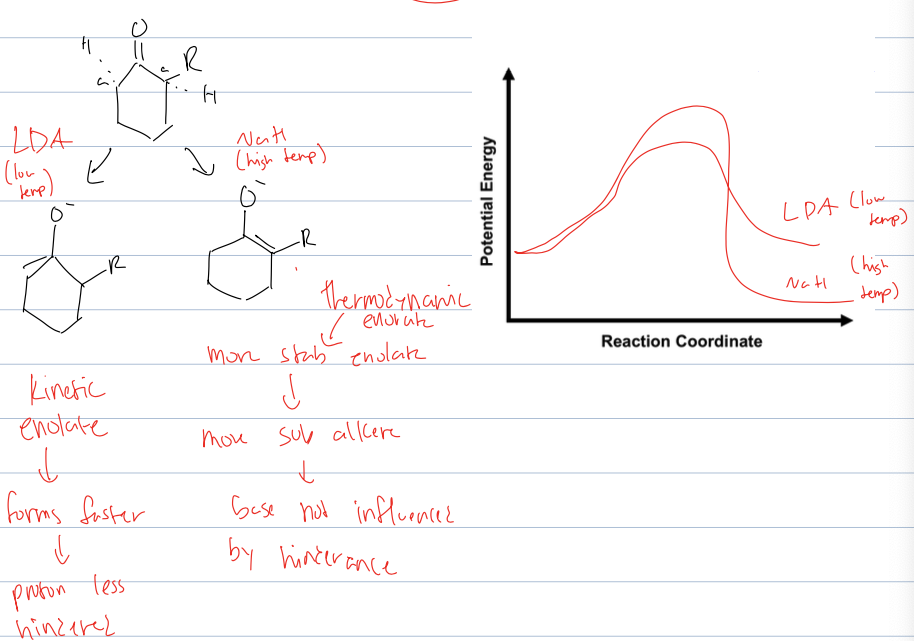
at low temp the kinetic one bc it cannot overcome Ea to be other product