The integumentary system
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
What is the integumentary system made up of and what is it called?
• The integumentary system is made up of the skin and several accessory organs
• Also called the cutaneous membrane or the integument
What four tissue types comprise the integumentary system?
Connective, epithelial, muscle, and nervous
What is the largest organ of the body?
The integumentary
What are the functions of skin?
Protection
Temperature maintenance
Synthesis and storage of nutrients
Sensory reception
Excretion and secretion
How does the skin protect the body?
• Covers underlying tissues and organs from impacts, chemicals and infections
• Prevents loss of body fluids
How does the skin maintain temperature?
• Regulates heat exchange with the environment
How does the skin synthesize and store nutrients?
• Epidermis synthesizes vitamin D, a steroid building block for a hormone that aids in calcium uptake
• The dermis stores large reserves of lipids (fats) in adipose tissue
How does the skin receive sensations?
• Receptors in the skin detect touch, pressure, pain, and temperature stimuli and relay information to the nervous system
How does the skin excrete and secrete?
• Integument glands excrete water, salts and organic wastes
define homeostasis
tendency for physiological systems to stabilize internal conditions
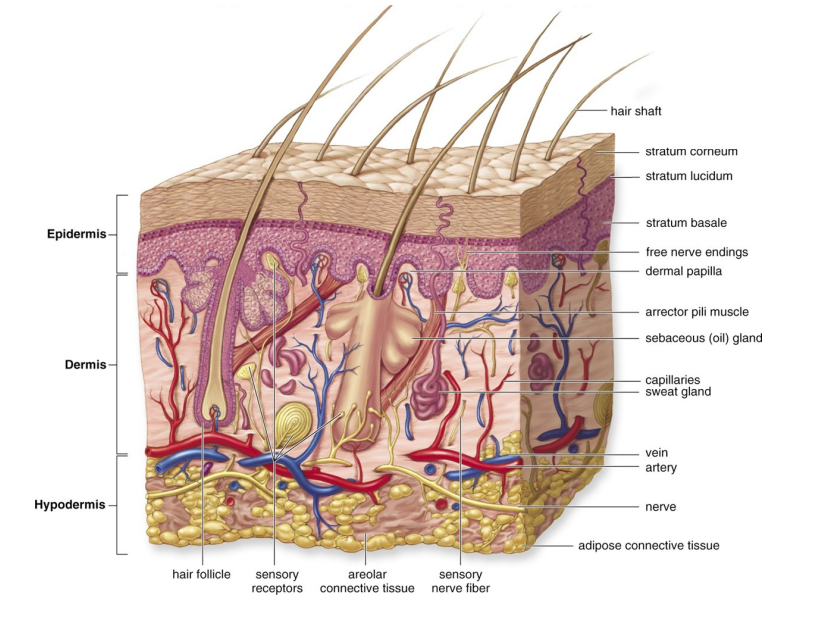
Describe the epidermis
• Outer, thinner region
• Composed of 5 layers, or strata
What are the 5 strata layers of the epidermis?
(listed from deepest to most superficial)
• Stratum Germinativum (or Stratum Basale) BALL
• Stratum Spinosum SOFT
• Stratum Granulosum GREY
• Stratum Lucidum LIKES
• Stratum Corneum CAT
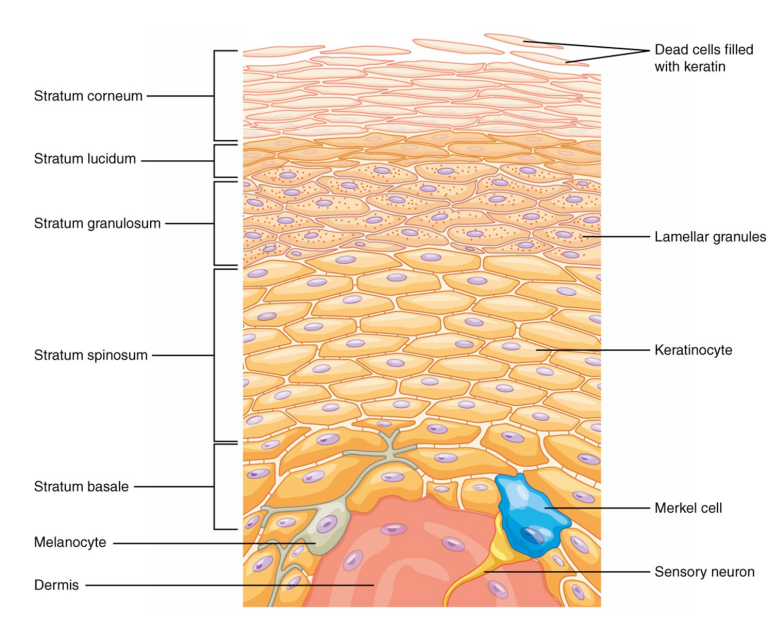
Describe the stratum germinativum (stratum Basale)
• Just superficial to the dermis
• Form epidermal ridges and dermal papillae where the epidermis and dermis meet
• Layer of new cell generation
• New cells replace old cells as they shed from the epithelial surface
• Contains melanocytes, which synthesize melanin.
-Melanin gives brown, yellow-brown, or black pigment to the epidermis
• Contains sensory nerves
-Free nerve endings – detect pain and temperature
-Tactile cells (Merkel cells) – touch sensations
Describe the stratum spinosum
Layer of continual divide of epithelial cells
Describe the stratum granulosum
• Cells stop dividing in this layer and begin producing the protein, keratin
• Keratin – Extremely durable and water-resistant protein; basic structure of hair, nails, and calluses
Describe the stratum lucidum
• Thick layers of flattened densely packed, keratin-filled cells
• Thick layers on palms and soles of feet
Describe stratum corneum
• Most superficial layer
• 15-30 layers of flattened and dead epithelial cells that are keratinized (hardened)
• Serves as a mechanical barrier against microbes
• Cells are so tightly connected, they shed in large groups or sheets
Describe the dermis
Lies beneath the epidermis
Has 2 layers
Contains vasculature, nerve fibers, and epidermal accessory organs (hair follicles and glands)
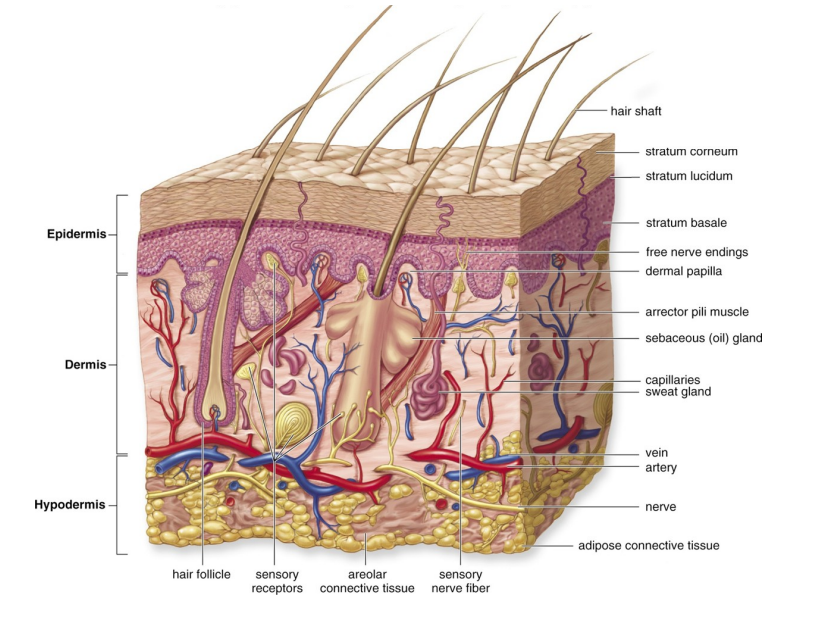
What are the two layers within the epidermis?
• Papillary layer – loose connective tissue that nourishes and supports the epidermis
• Reticular layer – mesh-like network of dense, irregular connective tissue
-Contains elastic fibers which allow for flexibility and collagen fibers which limit flexibility to prevent tissue damage
Describe the hypodermis
• Also called the subcutaneous layer, and lies beneath the dermis
• Important in stabilizing the position of the skin relative to the underlying tissues (bones, muscles, organs)
• Composed of loose connective tissue and many fat cells (adipose or subcutaneous fat)
• Energy reserves
• Insulation
• Shock absorber
Describe the accessory structure hair
• On all parts of the body except palms of the hands, soles of the feet, lips, and portions of external genital organs
• Nonliving structures produced by hair follicles in the dermis
Describe hair follicles and their components
• Formed from epidermal cells
• Cells become keratinized as they are pushed out
• Hair root – portion of hair within the follicle
• Hair shaft – portion of hair that extends beyond the surface of the skin
Describe sebaceous glands
• Also called oil glands which secrete oily lipids (called sebum) into hair follicles and onto the surrounding skin
• Lubricates the hair and skin and inhibits the growth of bacteria
Describe sweat glands
2 different types
• Merocrine – secrete directly onto the surface of the skin
• Apocrine – secrete through a hair follicle
Describe the arrector pili muscle
small smooth muscle that extends the hair and squeezes sebum out of the sebaceous glands
What are nails and their components?
• Formed from specialized, densely-compacted, keratinized epithelial cells
• Nail bed – area of epidermis covered by the nail
• Nail root – site of nail growth
• Cuticle (eponychium) – fold of stratum corneum that extends partially over the nail root
Define burn
To oxidize or be oxidized by fire or equivalent means, creating a tissue reaction or injury
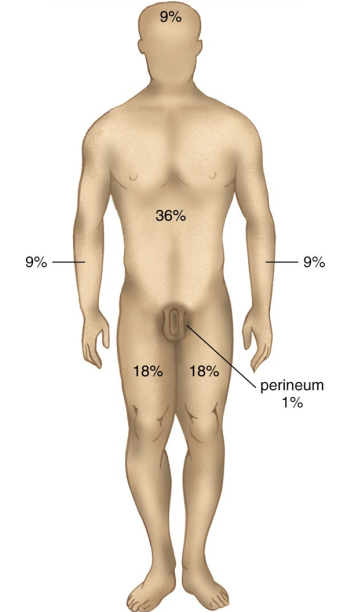
What is the rule oof nines used for?
to determine the extent of a burn to the human body
Describe a 1st degree burn
• Only epidermis is affected
• Pink or red skin
• No blisters or swelling
• No tissue destruction
Describe a 2nd degree burn
• Acute inflammation with blistering
• Extends into the dermis
• Red tissue discoloration
• No charring and no major tissue destruction
• Hair may be singed
Describe a 3rd degree burn
• Destruction of entire thickness of skin
• Usually expansion and splitting of tissue
Describe a 4th degree burn
• Charring
-Black, crumbling tissue
-Partially missing tissue
-Very discolored (black)
-Very dehydrated
• Complete incineration of skin and underlying tissue
• Muscle greatly affected
• Expansion and splitting of lesser charred areas