Colligative properties
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
Colligative properties depend on
number of particles in a volume of solvent (the concentration)
Colligative properties do NOT depend on
the mass or identity of the solute particles
When you add a solute to a liquid, what happens to the freezing, boiling, and vapor pressure?
They change
Freezing-Point Depression
The magnitude of the freezing-point depression is proportional to the number of solute particles (as concentration increases, the freezing point will depress)
Why does freezing point depress when solute is added to a liquid?
When a substance freezes, the particles of the solid take on an orderly pattern. The presence of a solute in water disrupts the formation of this pattern because of the shells of water of solvation
Boiling point elevation
The magnitude of the boiling point elevation is proportional to the number of solute particles dissolved in the solvent (as concentration increases, the boiling point will elevate)
The more dissolved solute, the greater the changes.
Vapor pressure in a closed system
vapor is in dynamic equilibrium with its liquid stem.
Vapor pressure in a partially filled container
some of the particles at the surface of the liquid vaporize. These particles collide with the walls of the sealed container and produce a vapor pressure.
Vaporization vs Evaporation
Vaporization – conversion of a liquid to a gas or vapor
Evaporation – when such a conversion occurs at the surface of a liquid that is not boiling
During evaporation, only those molecules with a certain minimum kinetic energy can escape from the surface of the liquid.
Vapor Pressure in a system of constant pressure
dynamic equilibrium exists between the vapor and the liquid.
The system is in equilibrium because the rate of evaporation of liquid equal the rate of condensation of vapor.
Relationship between Vapor Pressure and Temp
An increase in the temperature of a contained liquid increases the vapor pressure
What is vapor pressure?
a measure of the force exerted by a gas above a liquid.
The vapor pressure indicates how volatile a liquid is, or how easily it evaporates.
Lowering Vapor Pressure in a solution
The solute particles occupy space at the surface.
The solute particles introduce a new set of attractive forces with the solvent molecules.
This hinders the liquid molecules from being able to be at the surface of the liquid and are unable to utilize their kinetic energy to break the surface of the liquid and escape as a gas
condensation
a gas becoming a liquid (]RELEASE of energy)
vaporization
a liquid becoming a gas (GAIN in energy)
sublimation
solid becoming a gas (GAIN of energy)
desposition
gas becoming a solid (LOSS of energy)
freezing
liquid becoming a solid (LOSS of energy)
melting
solid becoming a liquid (GAIN of energy)
What types of motions occur in solids?
Particles vibrate about the fixed positions.
What types of motions occur in liquids?
Particles move faster and are able to move around and remain attached to other particles.
What types of motions occur in gases?
Particles move freely and randomly with large spaces between them.
Does temperature change during melting or freezing processes? Where does the heat energy go if the temperature does not change?
Temperature does not change in either melting or freezing process. During melting, the heat energy absorbed is used to loosen the crystal lattice and weaken the hydrogen bonds between the molecules. In the freezing process, the energy is released into the surrounding environment
How is the melting point of a substance related to its freezing point?
The melting point and freezing point of a substance is the same. They are referring to the processes in opposite directions, with energy either being absorbed (melting) or released (freezing).
what happens in the substance in the vaporization or boiling process?
In the vaporization process, particles have sufficient kinetic energy to overcome the intermolecular forces between them, and the state of matter is transformed from the condensed liquid state to gaseous state.
How do the bubbles in a liquid form and what is inside the bubbles?
The bubbles form when the particles gain energy and the space between the particles increases between the particles in the vaporization process. Inside the bubbles is the vapor of the liquid.
What is the reason that different substances have different boiling points under the same conditions?
Substances have different boiling points because of the different types and strengths of the intermolecular forces among the particles.
What is the definition of evaporation?
Evaporation is the conversion of liquid to its vapor below the boiling point. Evaporation occurs only at the surface of the liquid.
How is evaporation different from boiling?
1) Boiling takes place at a definite temperature, while evaporation can take place at any temperature.
2) Temperature remains constant during the boiling process, while evaporation may or may not lead to decrease in temperature because the energy is “silently” supplied by the surroundings.
3) Boiling takes place throughout the mass of the liquid, while evaporation only occurs at the surface.
4) Boiling is a fast and vigorous process, while evaporation is a slow and silent process.
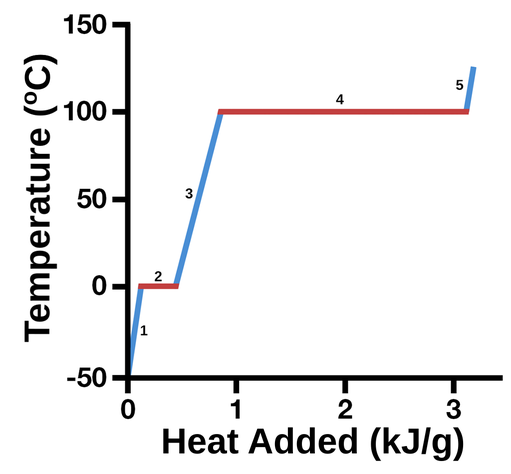
What do line segments represent on a heating curve like this one?
1) solid
2) melting/freezing solid and liquid
3) liquid
4) vaporization/condensation, liquid gas
5) gas
How can certain liquids boil under their estimated boiling points?
The external pressure or the surrounding pressure above the liquid is reduced.
What happens when a substance boils?
When a substance boils, the particles move faster and gain sufficient kinetic energy to break the intermolecular forces.