Lower Extremity Ligaments
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
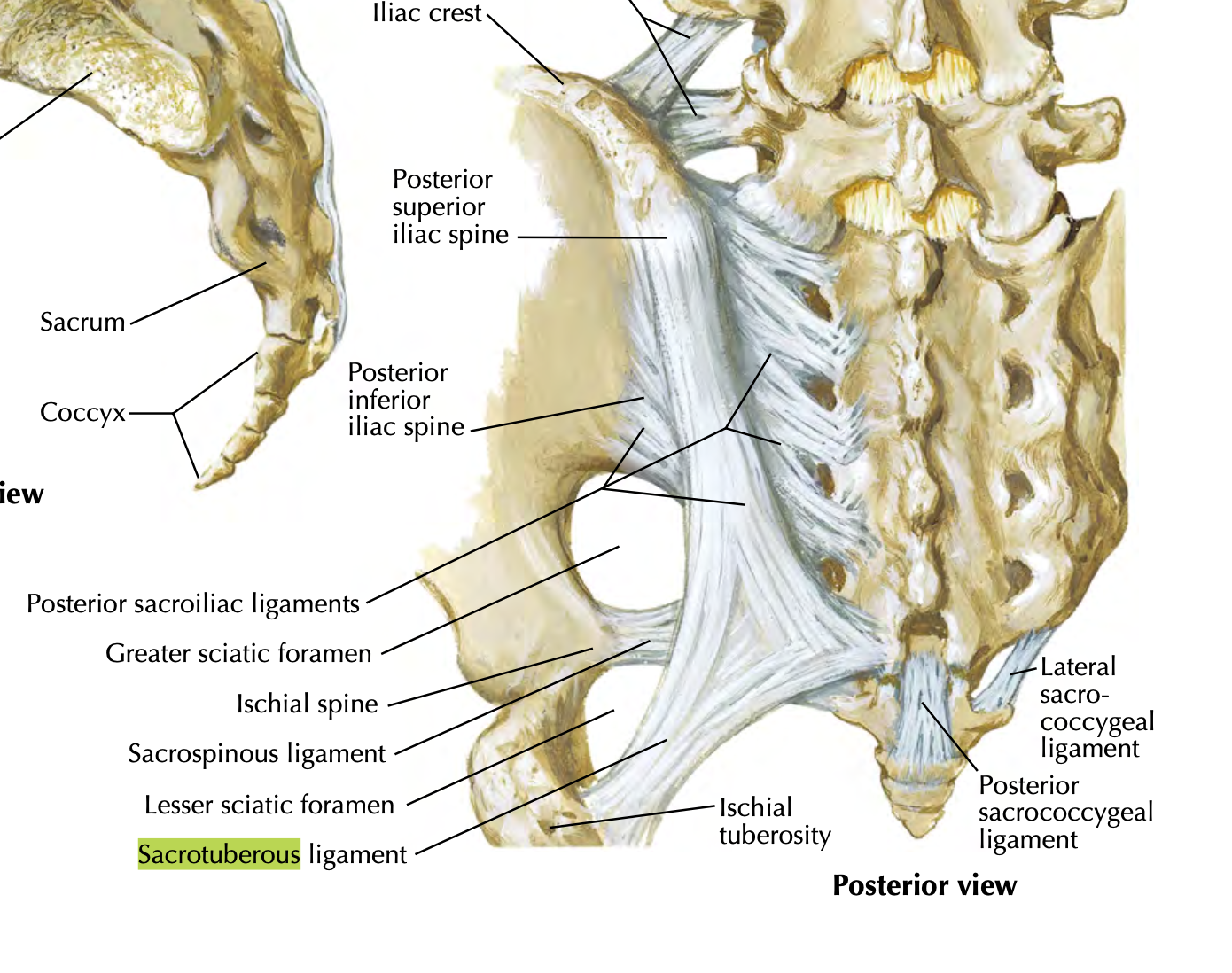
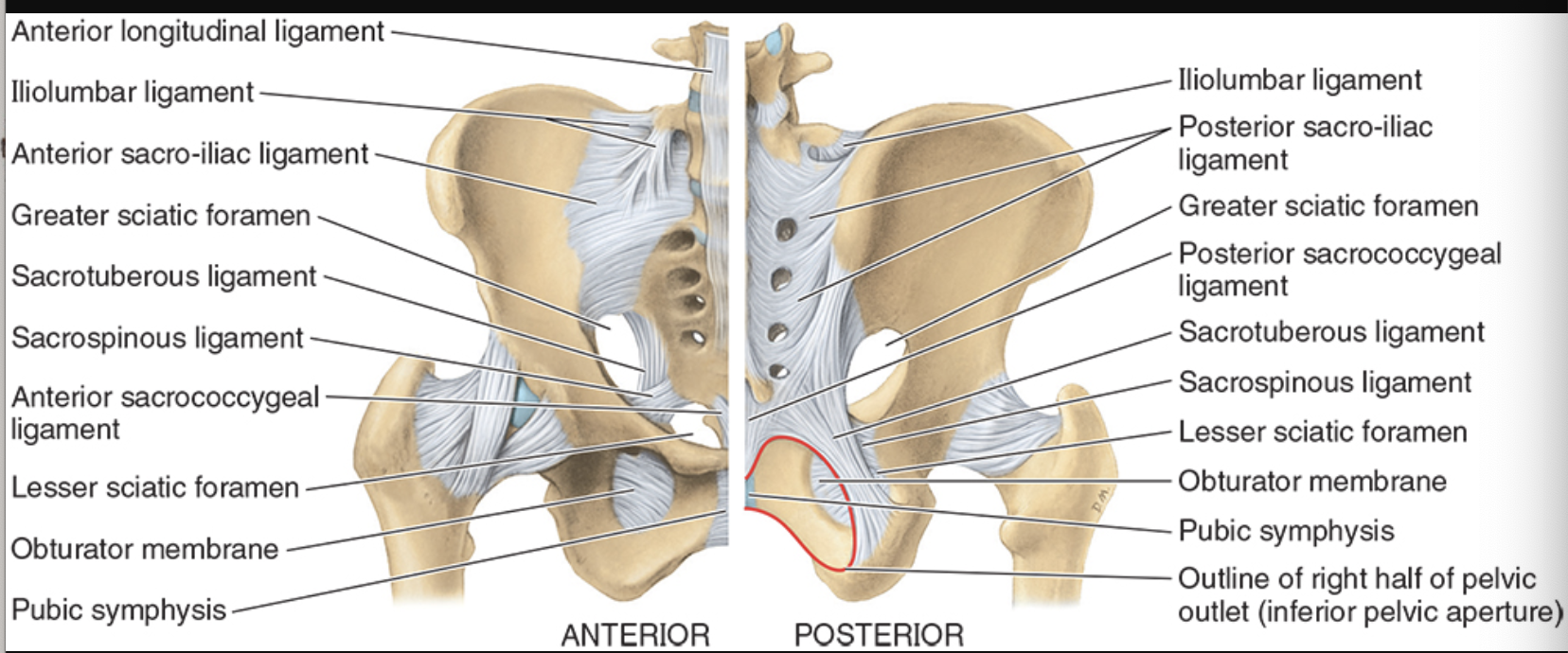
Sacrotuberous Ligament
extends from sacrum to ischial tuberosity
helps convert greater sciatic notch into greater sciatic foramen
forms greater sciatic foramen and less foramen with sacrospinous ligament
limits upward movement of the inferior end of the sacrum (anterior tilt)
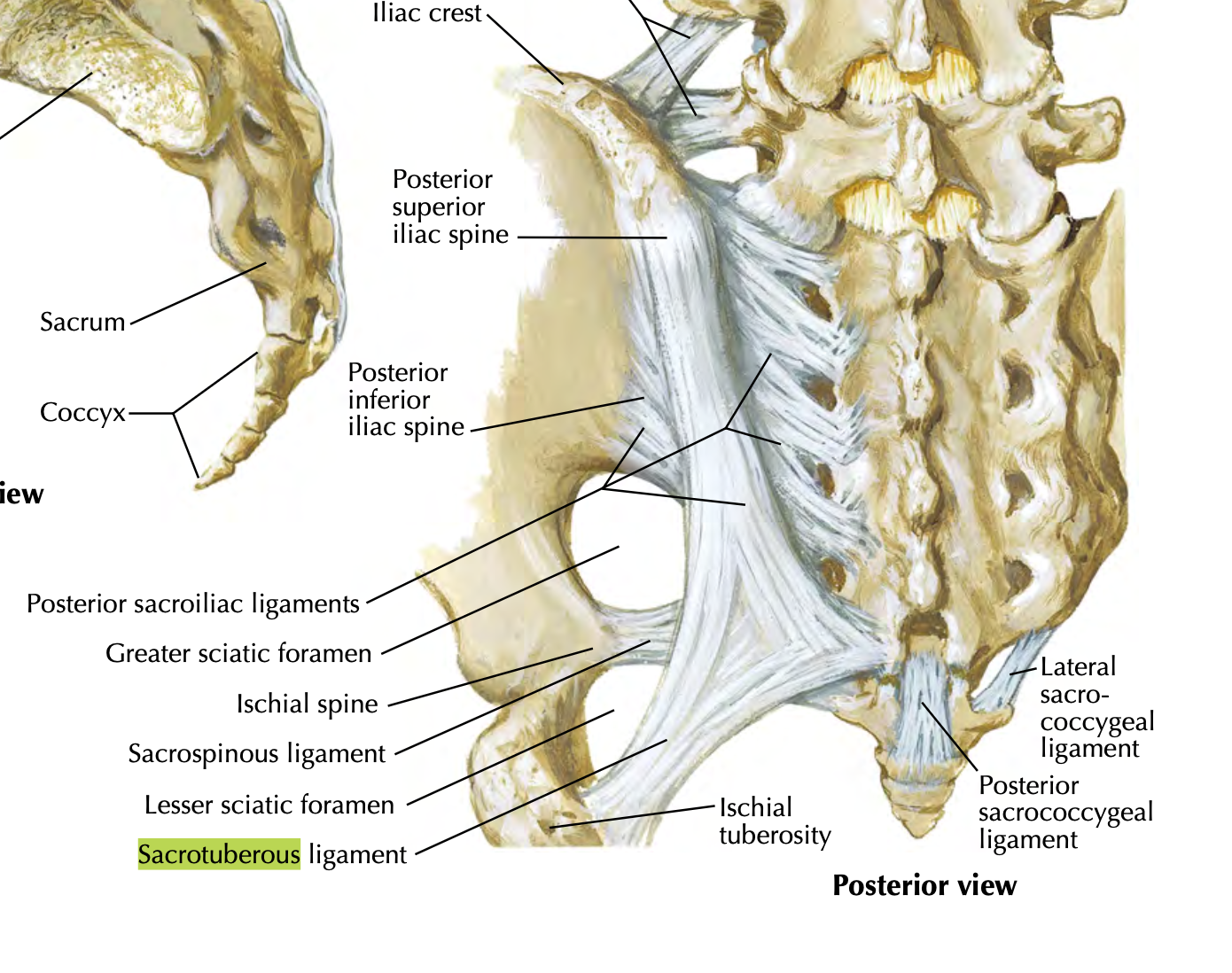
Sacrospinous Ligament
from sacrum to ischial spine
helps form lesser sciatic foramen
limits upward movement of the inferior end of sacrum
Anterior sacroiliac ligament
thin band that extends from anterior surface of the sacrum to the medial aspect of iliac fossa to ilium
strengthens joint anteriorly
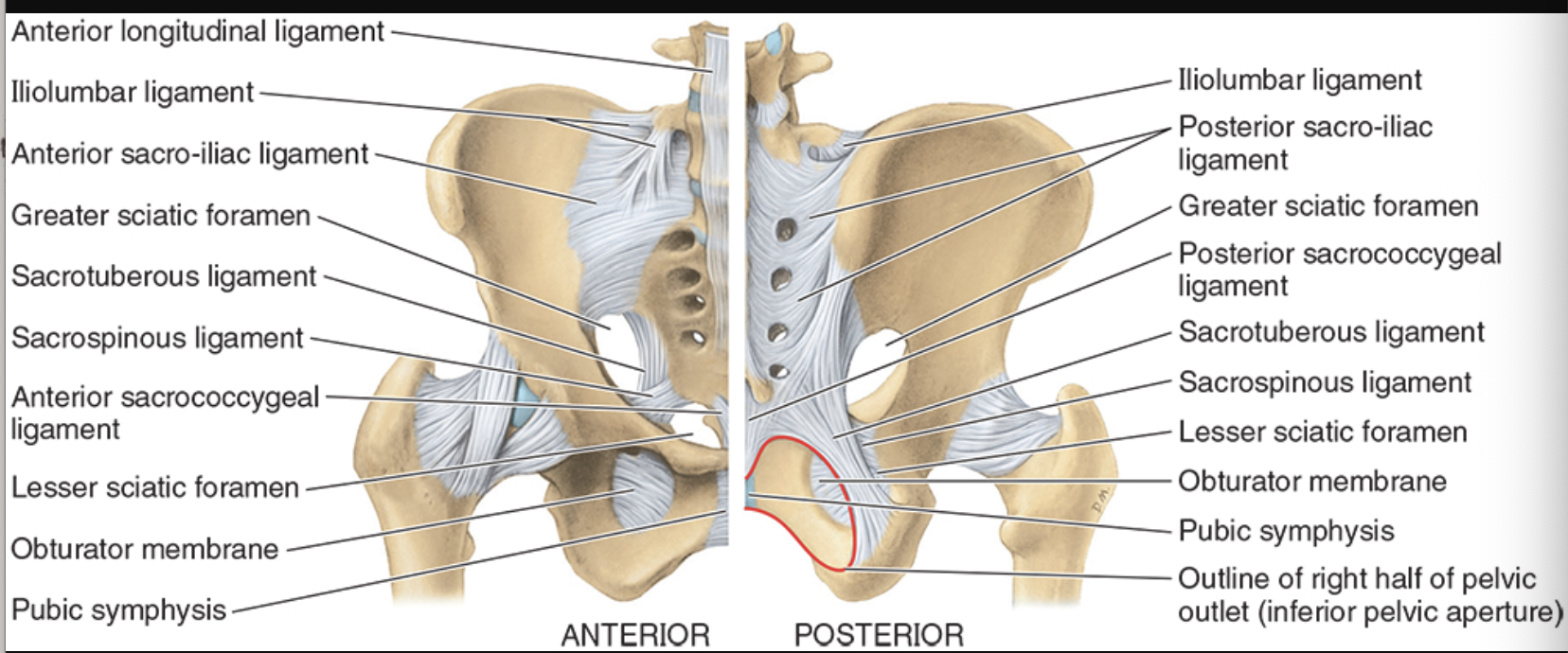
Interosseous sacroiliac ligament
very strong
primary structure for force transmission and in WB
keeps the SI joint as close as they can be
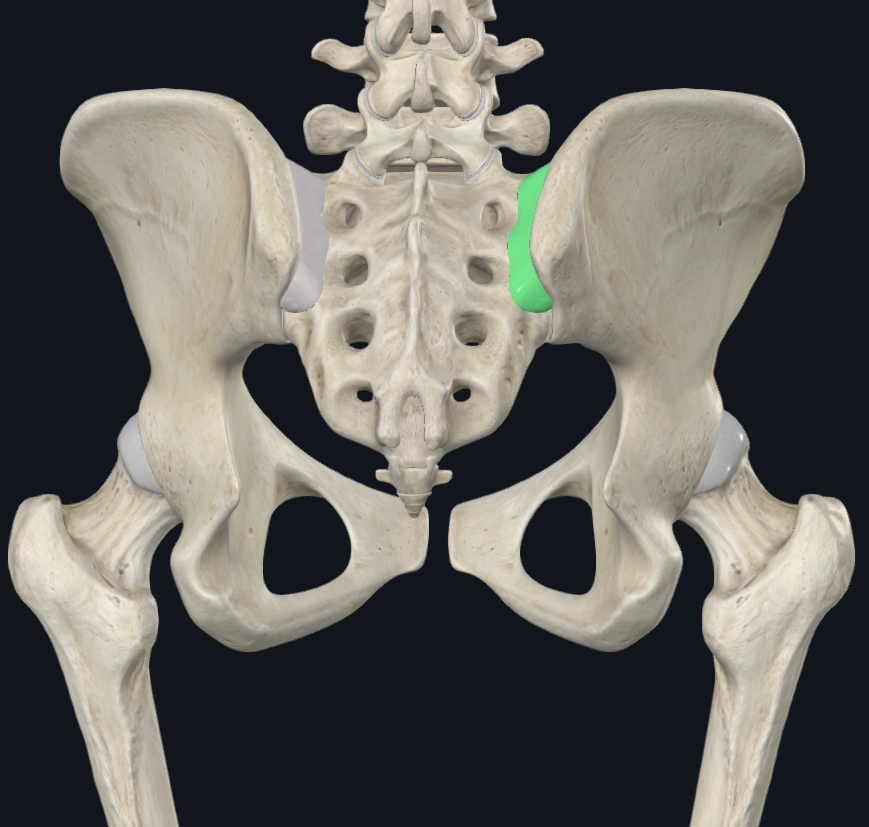
Posterior sacroiliac ligament
thick band from posterior surface of articulating bones
continuous with interosseous sacroiliac ligaments
strengthens joint posteriorly
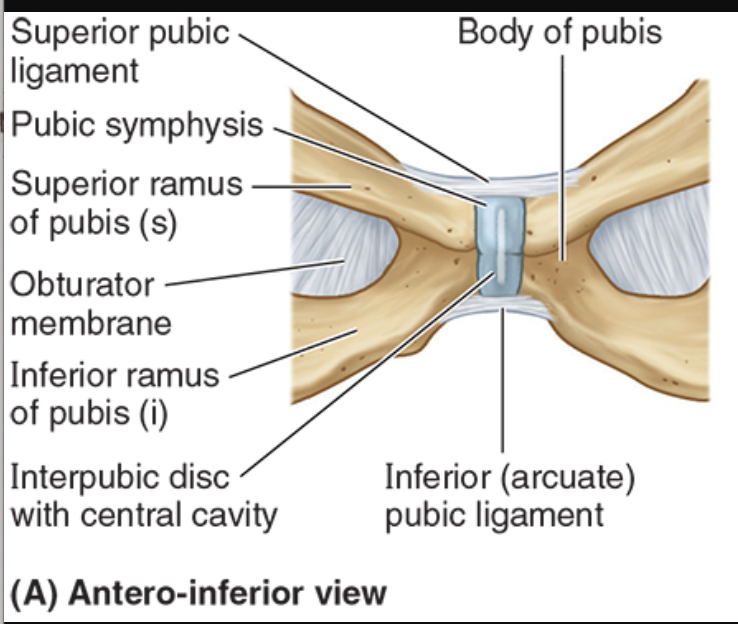
Superior pubic ligament
b/t the two pubic crests
strengthens superiorly
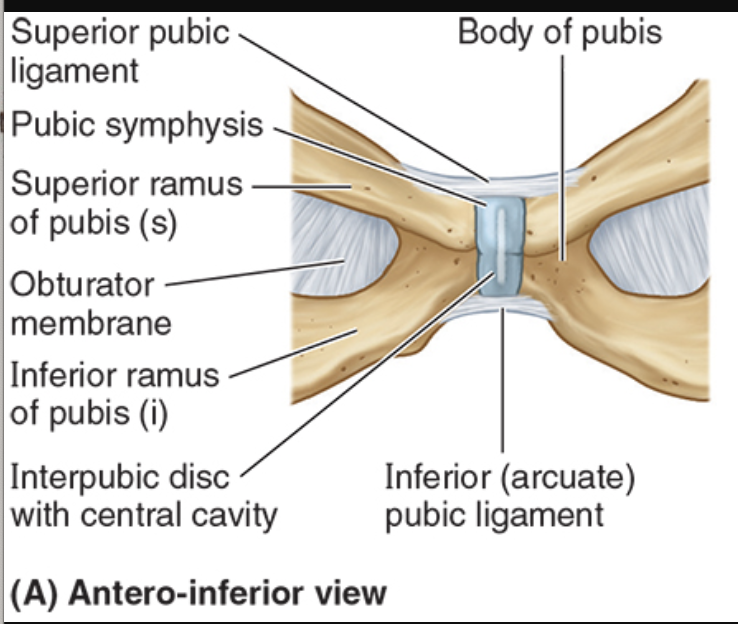
Arcuate (inferior) pubic ligament
b/t inferior pubic rami
strengthens inferiorly
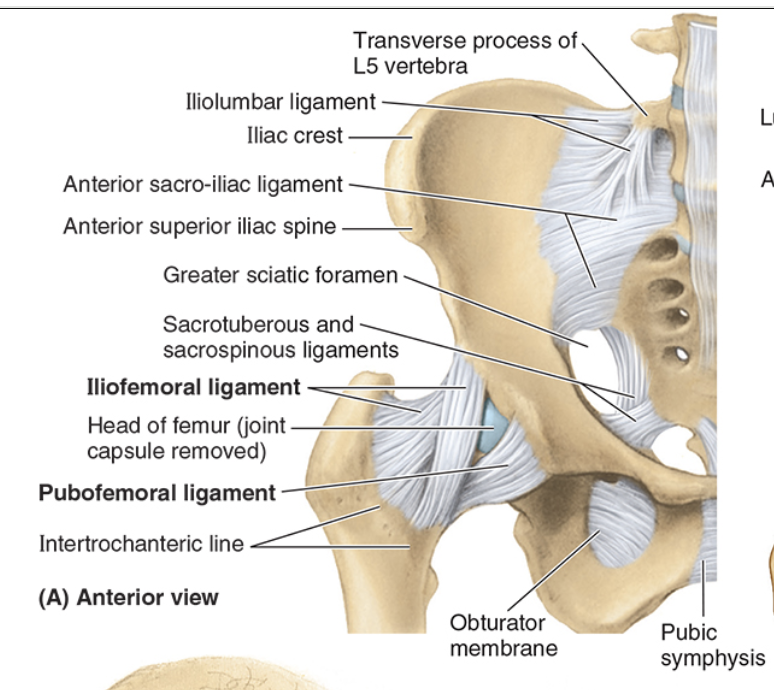
Iliofemoral (Y) ligament
strongest, limits hyperextension
ASIS to intertrochanteric line
provides static restraint to gravitational pull during standing
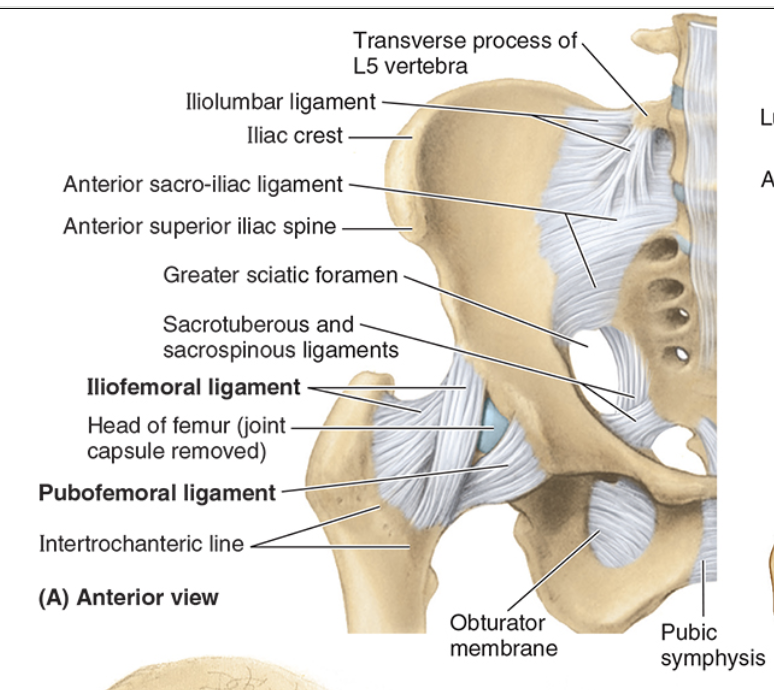
Pubofemoral ligament
limits abduction and extension
pubis to fibrous capsule
reinforces inferiorly and anteriorly
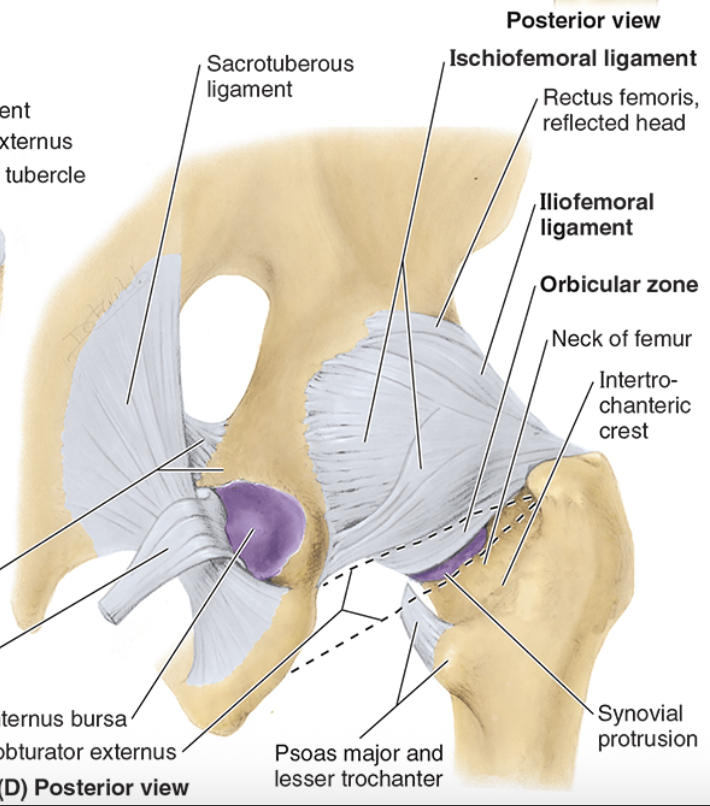
Ischiofemoral Ligament
posterior, limits internal rotation & extension
ischial part of acetabulum to neck of femur
reinforces capsule posteriorly
prevents hyperextension- pulls femoral head into the acetabulum
Ligament of femoral head (ligamentum teres)
from acetabular notch to fovea on femoral head
small contribution to stability
houses a small artery in children
Patellar ligament
strong thick fibrous band
extends from patella to tibial tuberosity
restricts excessive knee flexion
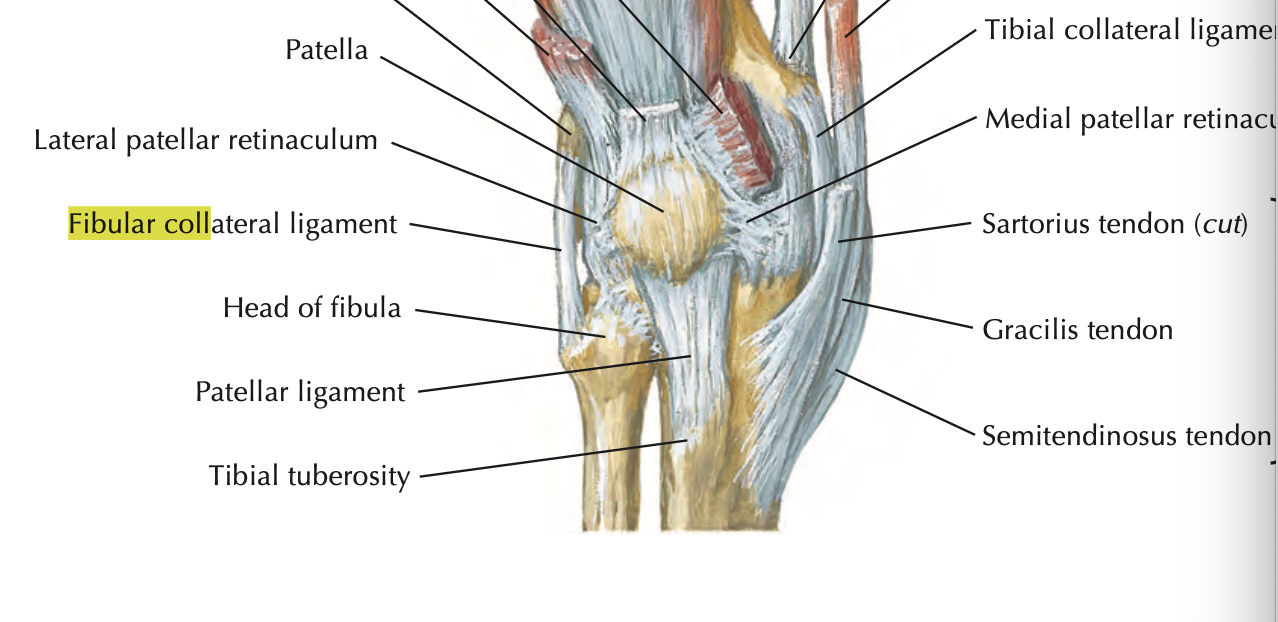
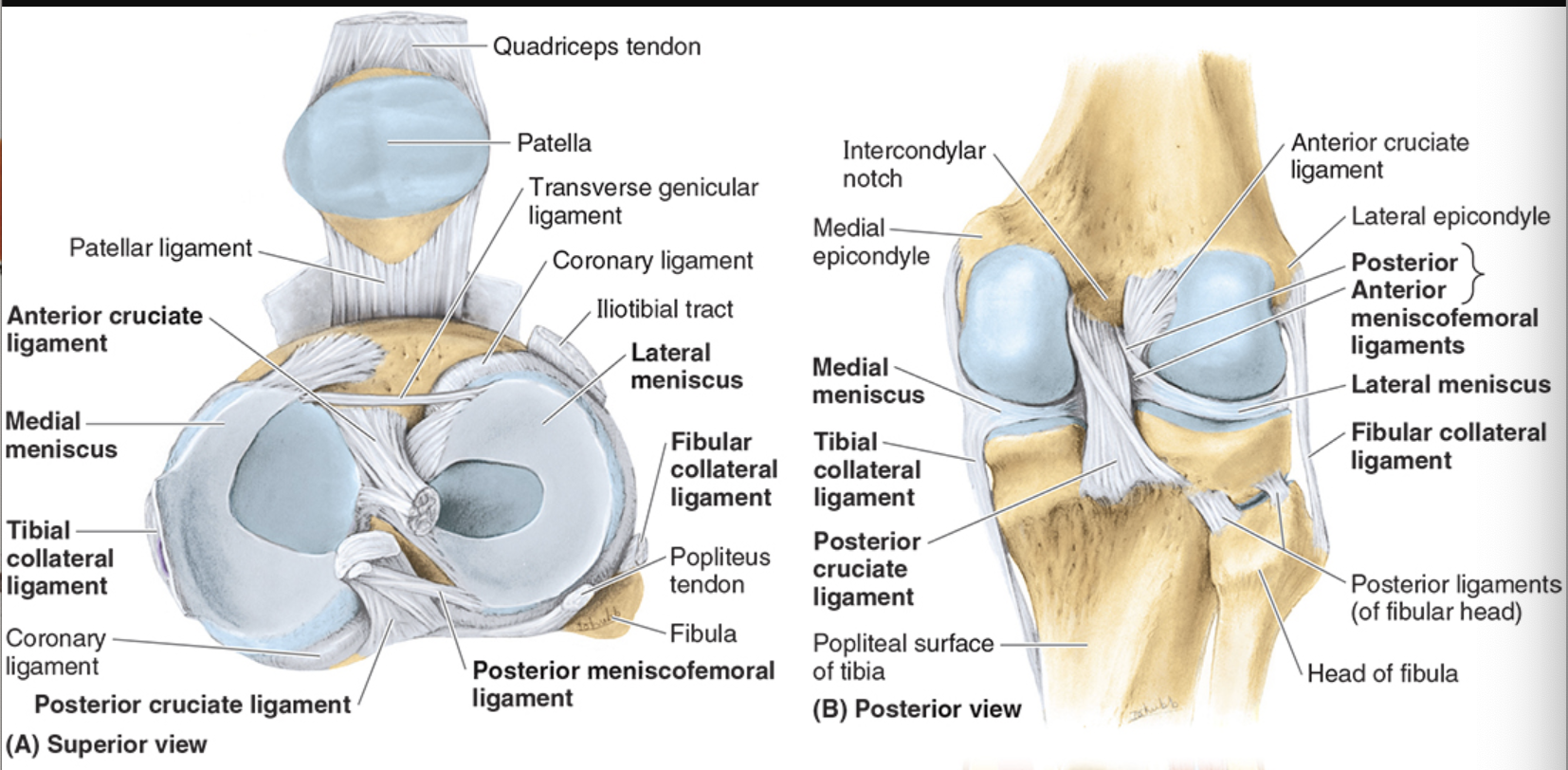
Fibular (collateral) ligament
restricts varus stress and lateral rotation of tibia
strong, cord-like
extends from lateral epicondyle of femur to lateral surface of fibular head
doesn’t attach to lateral meniscus
Tibial (medial) collateral
restricts valgus stress and lateral rotation of tibia
medial epicondyle of femur to medial condyle of tibia
deep fibers attach to medial meniscus
more injuries here bc weaker than LCL
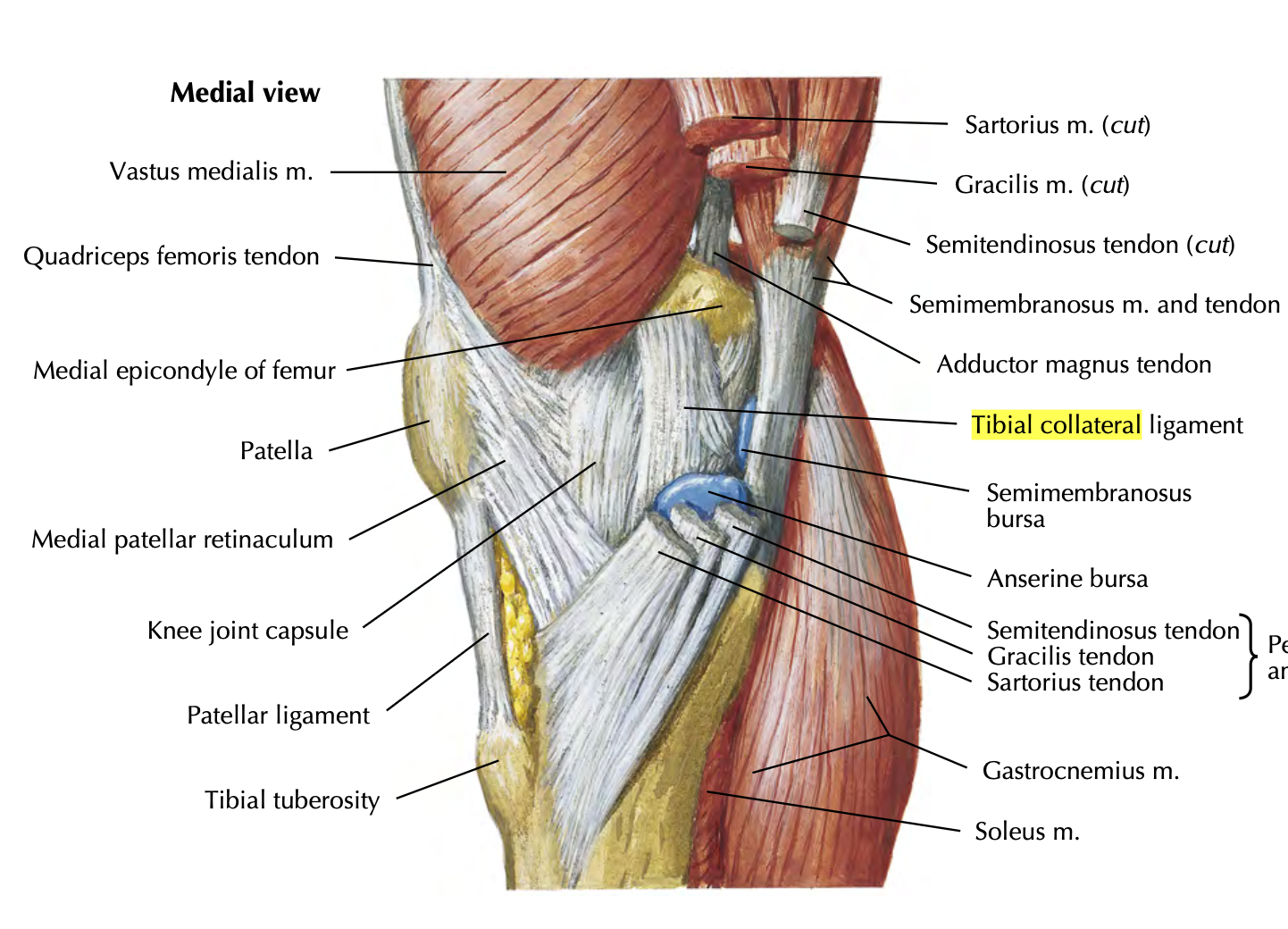
Oblique popliteal ligament
supports posterolateral knee
blends with fibrous capsule
restricts hyperextension
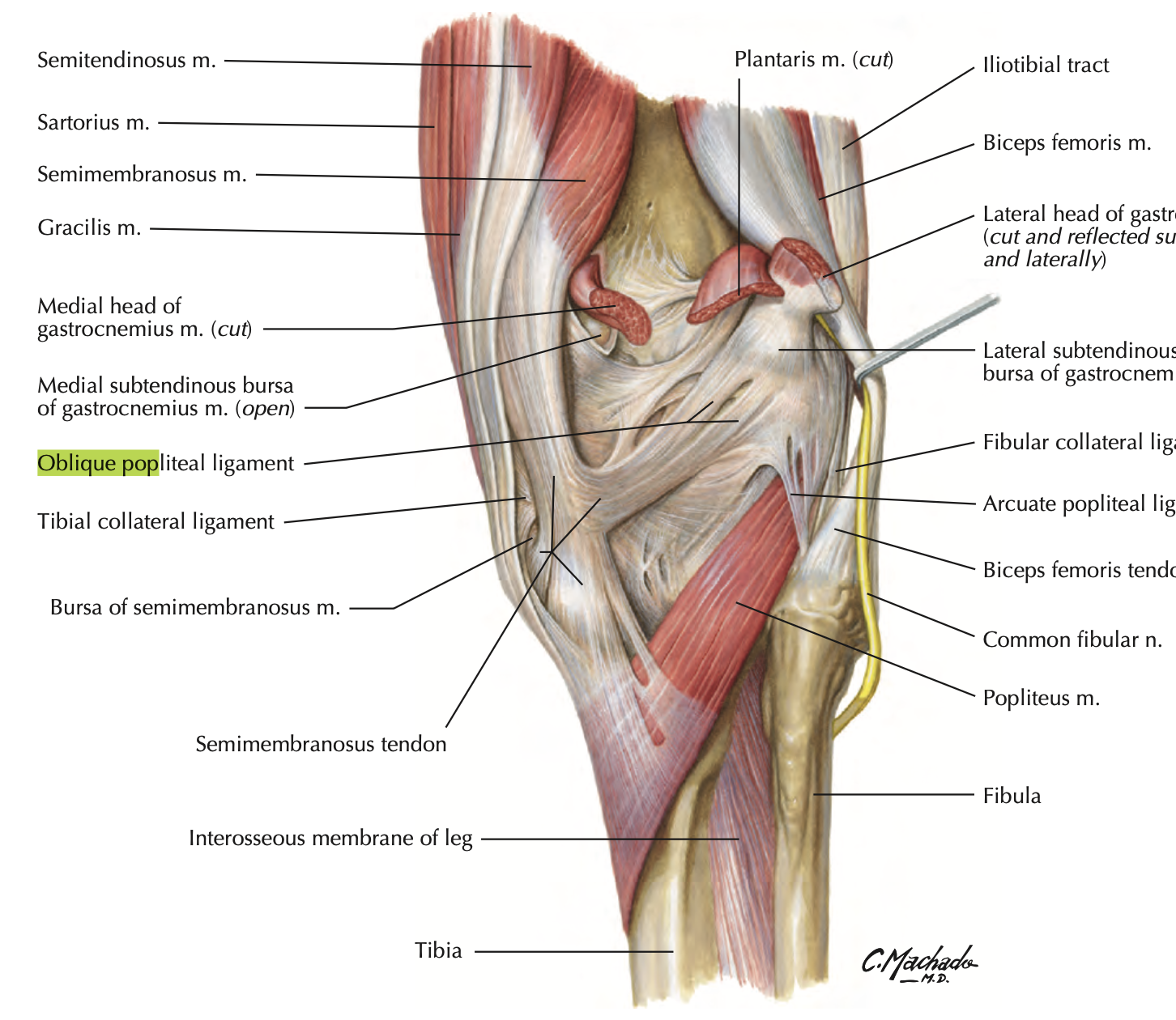
Arcuate popliteal ligament
supports posterolateral knee
passes over the popliteus tendon
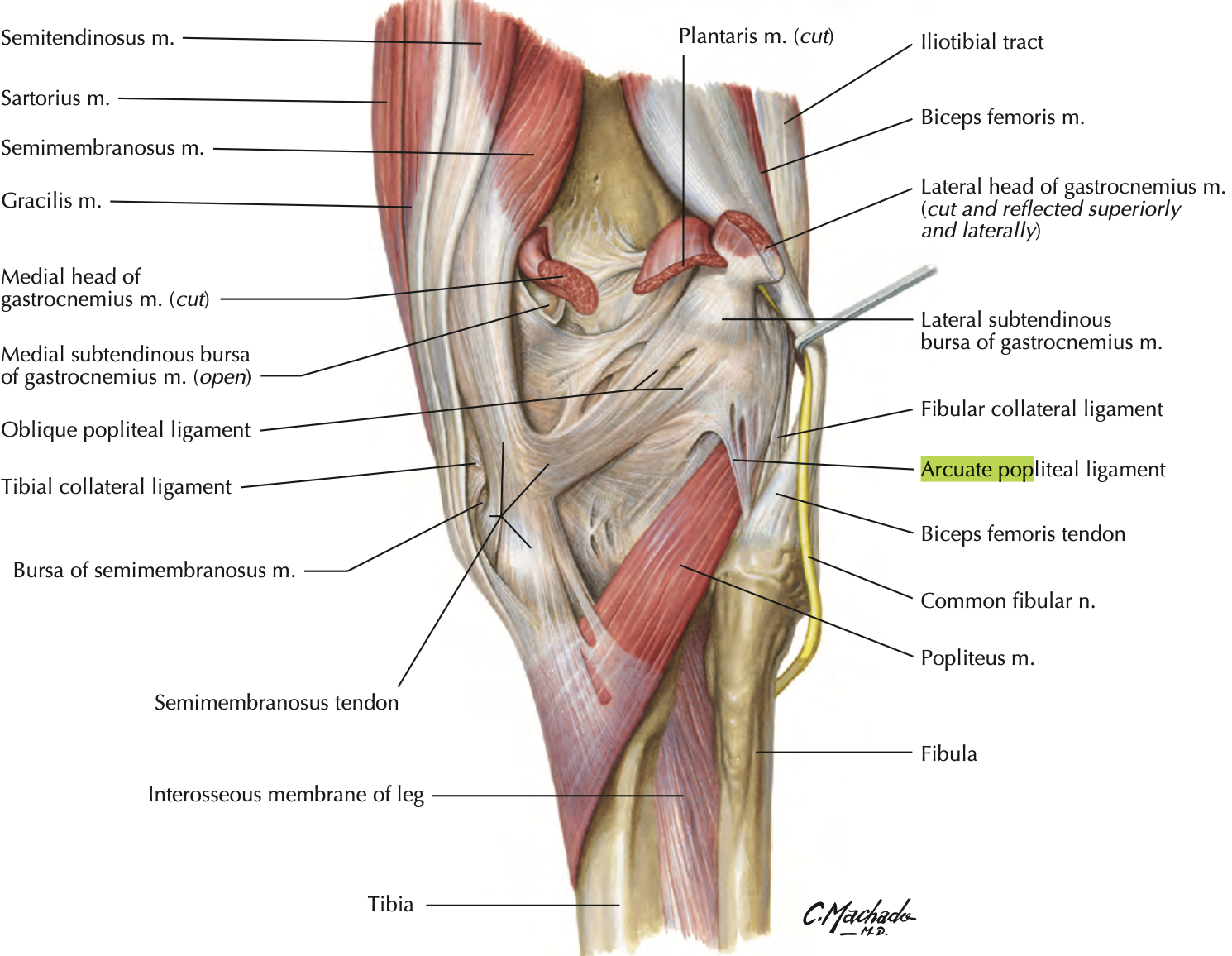
Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL)
most taut when knee in full extension
prevents posterior glide into hyperextension when femur is moving on fixed tibia (also anterior glide if tibia moving)
weaker than PCL
poor blood supply
Posterior Cruciate Ligament (PCL)
fibers taut in flexion
prevents anterior glide of femur on fixed tibia (prevents posterior glide if tibia moving)
stronger than ACL
injured w/ hyperflexion
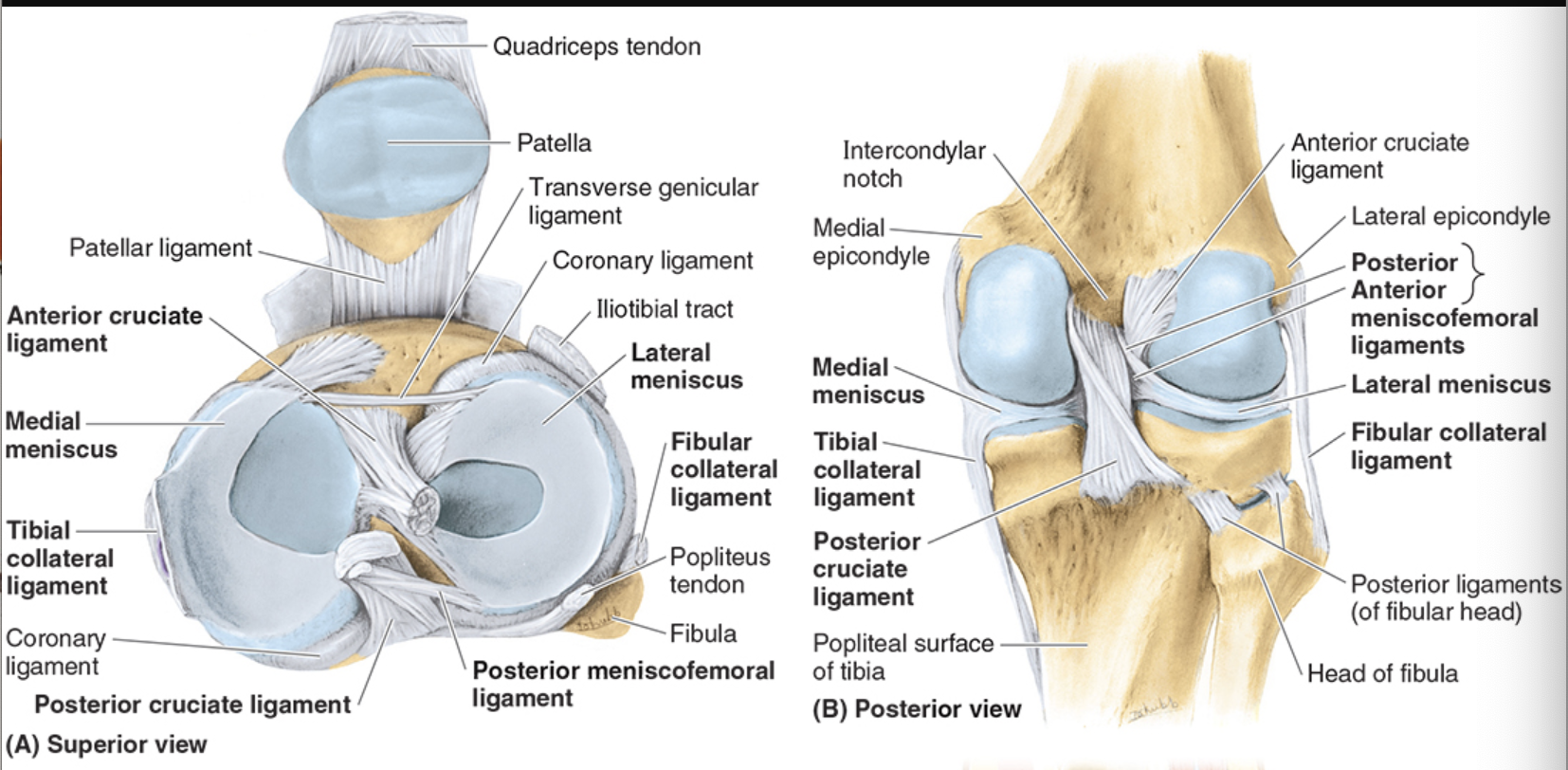
Medial Menisci
C-shaped
broader posteriorly
outer regions blend with MCL
more prone to injury than lateral menisci bc less mobile on tibial plateau
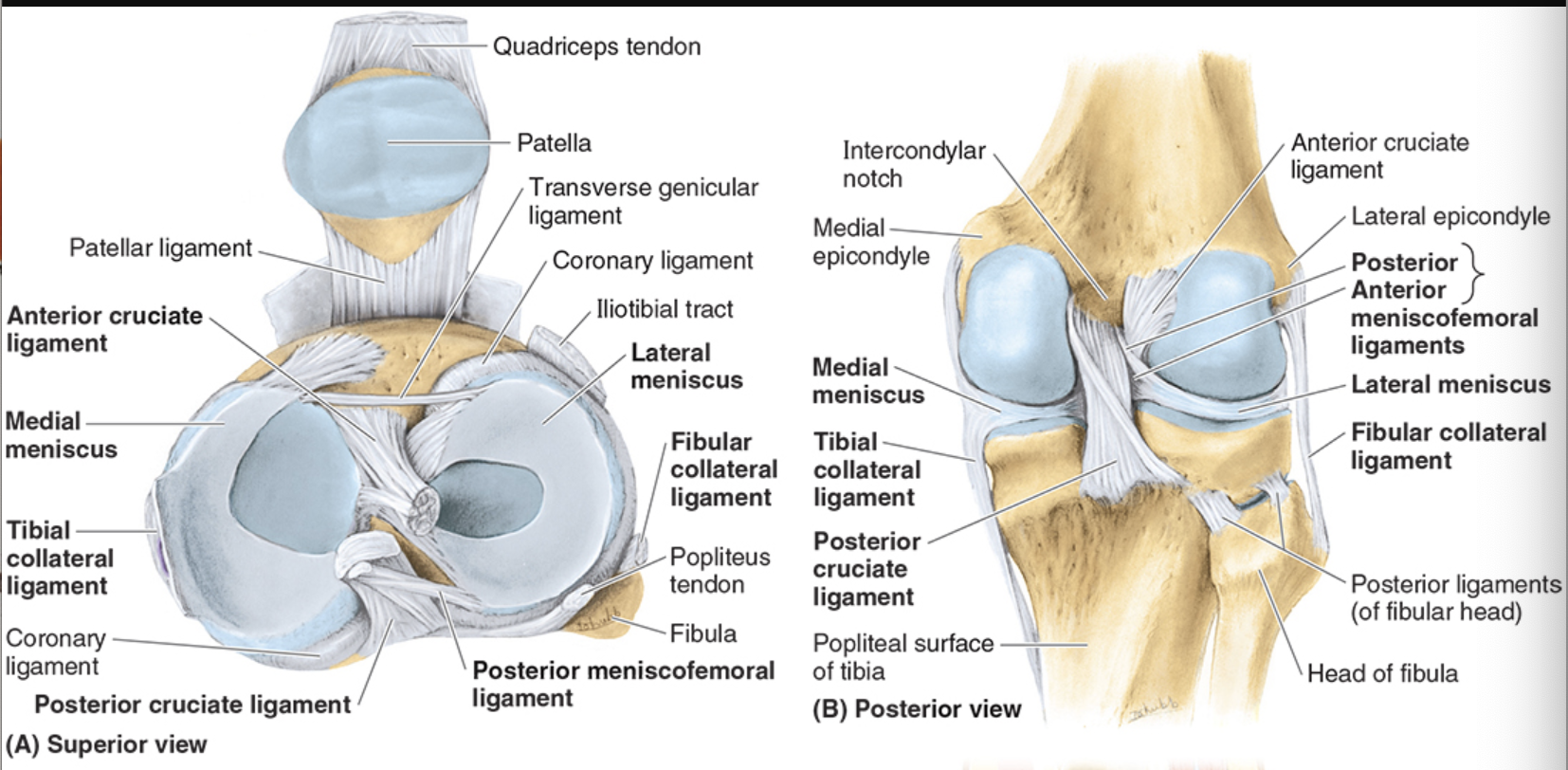
Lateral Menisci
separated from LCL to popliteus tendon
less prone to injury because more mobility
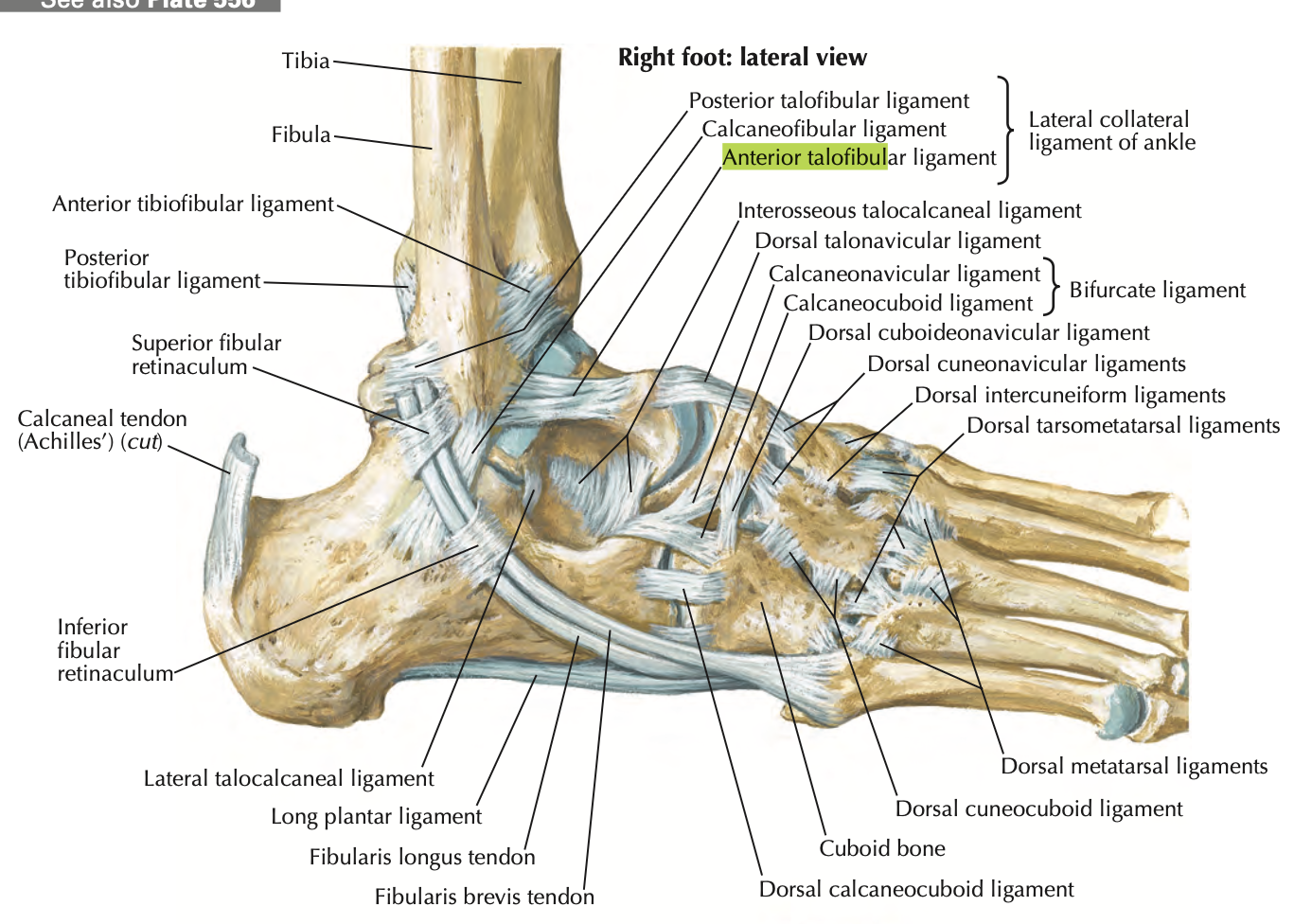
Lateral Collateral Ligament of ankle
Restricts foot inversion
Anterior talofibular- most commonly sprained
calcaneofibular
posterior talofibular
Medial Collateral Ligament/Deltoid Ligament
Restricts foot eversion
anterior tibiotalar
tibionavicular
tibiocalcaneal
posterior tibiotalar
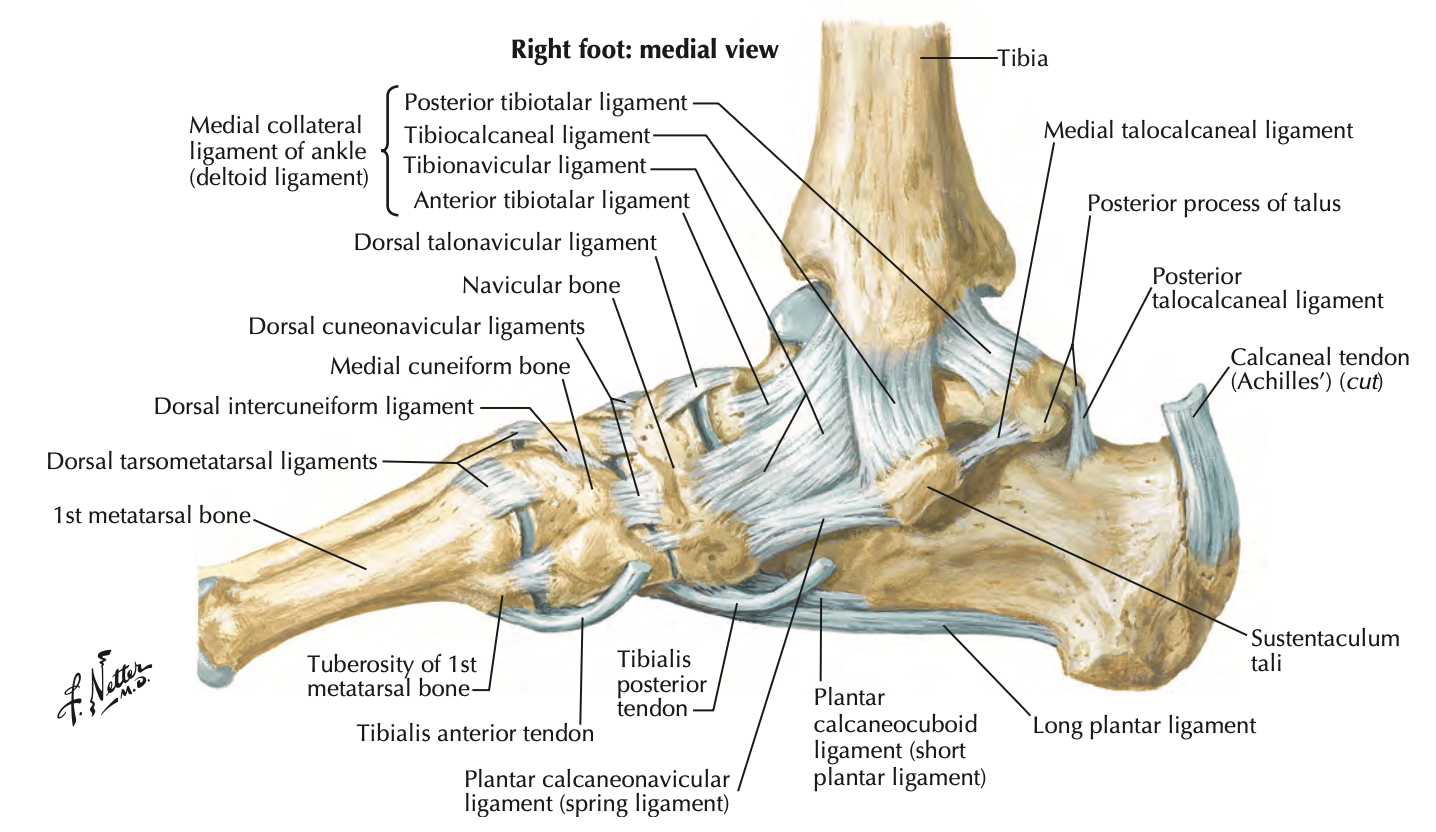
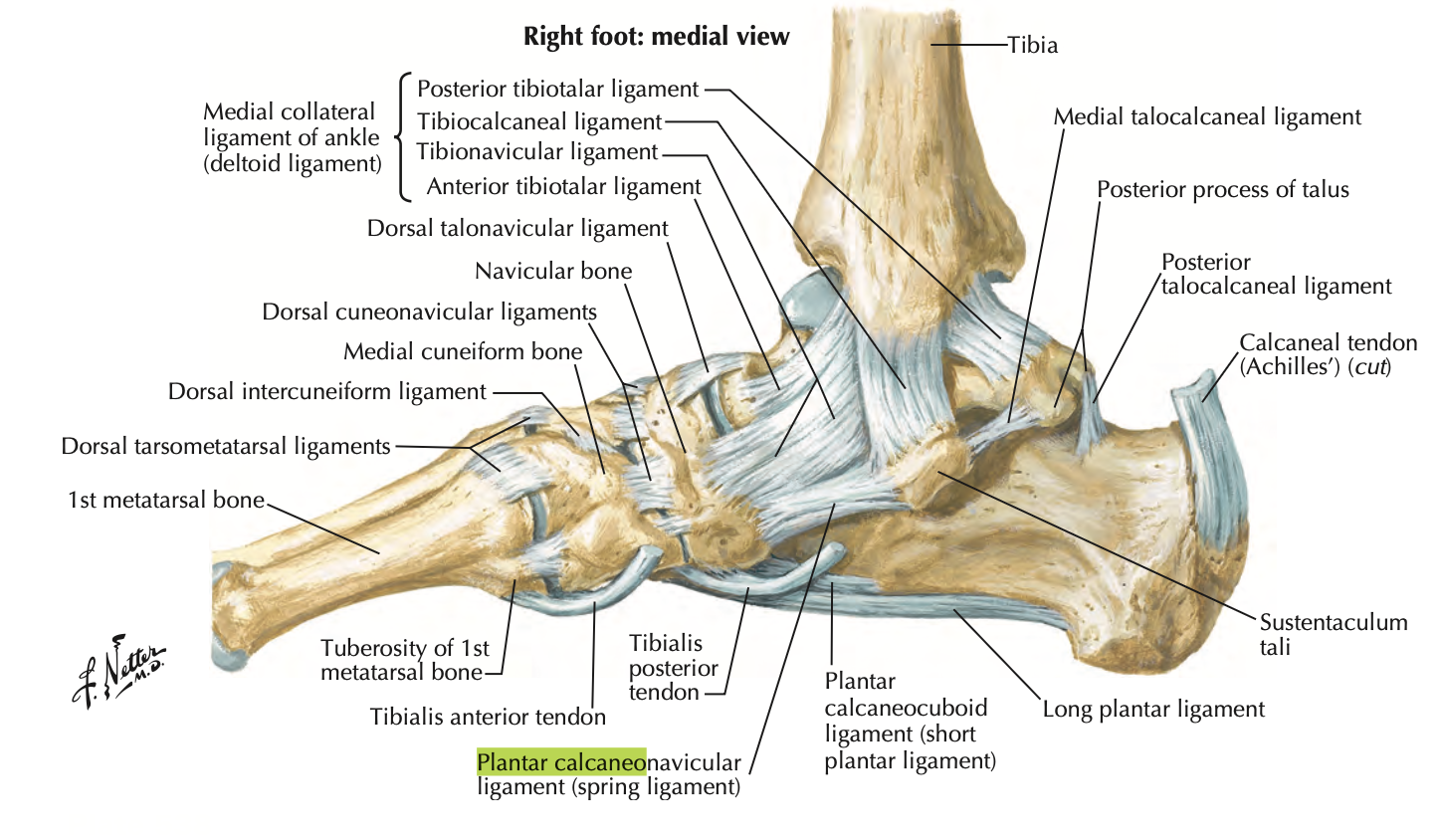
Spring Ligament (plantar calcaneonavicular)
extends from sustentaculum tali of calcaneus to the navicular
supports the head of the talus → prevents displacement of the talas b/t the navicular and calcaneus
Anterior Longitudinal Ligament
occiput to sacrum
supports anteriorly, restricts hyperextension (only one to do this!!)
wider than posterior ligament
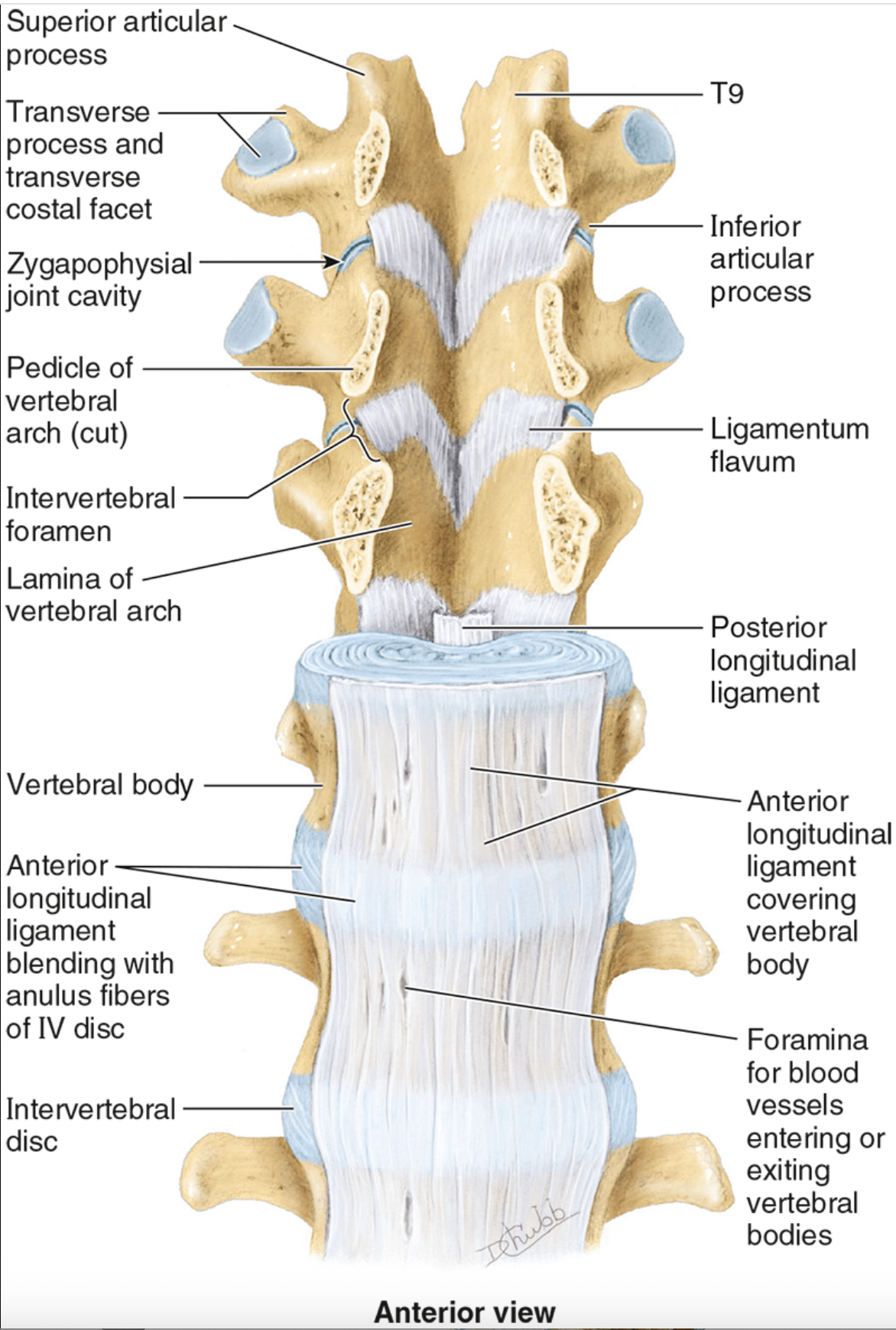
Posterior Longitudinal Ligament
occiput to sacrum
prevents hyperflexion of vertebral column and posterior protrusion of intervertebral disc
more narrow than anterior lig
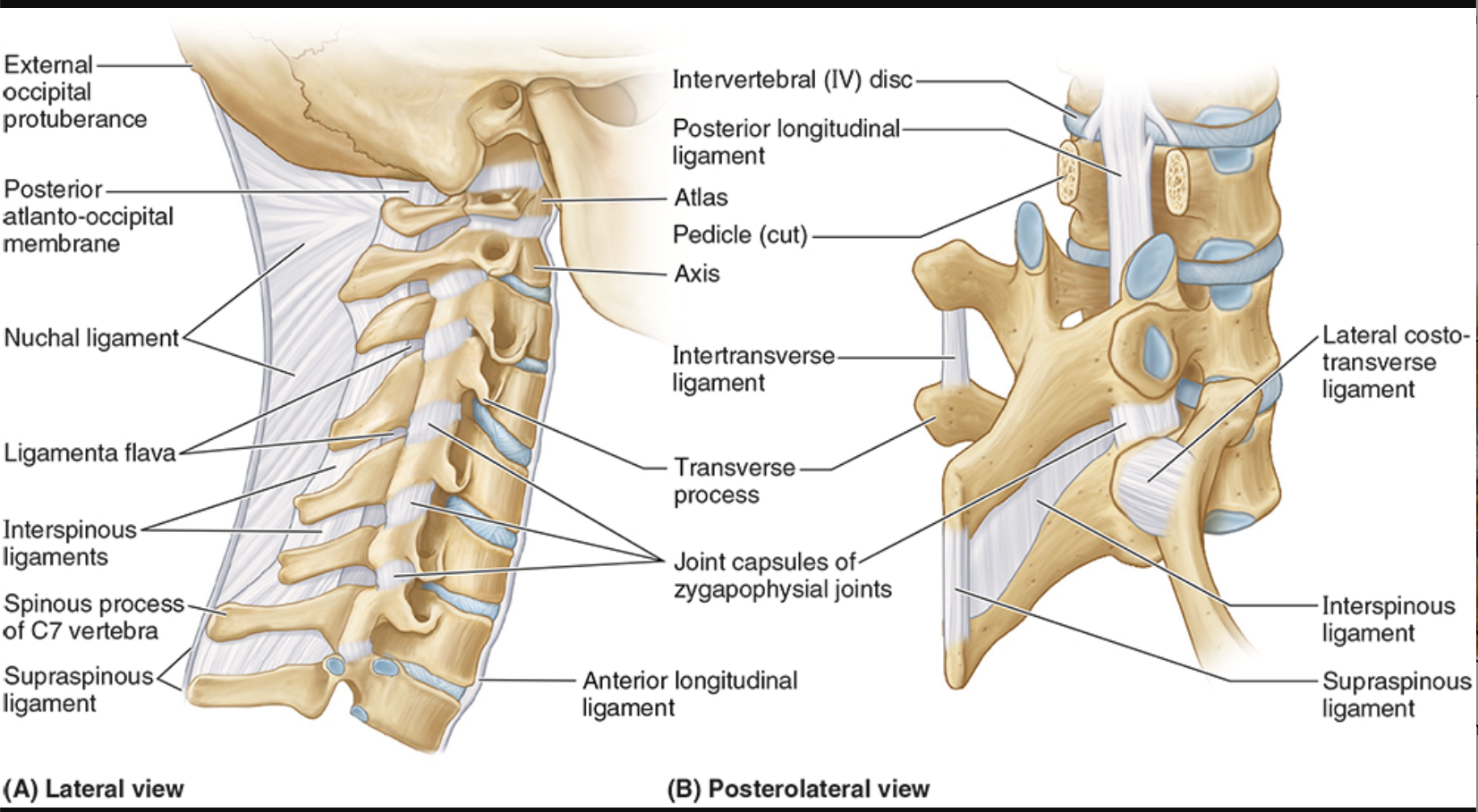
Ligamentum flavum
lamina to lamina, between each successive vertebrae
prevents separation of lamina, resists abrupt flexion
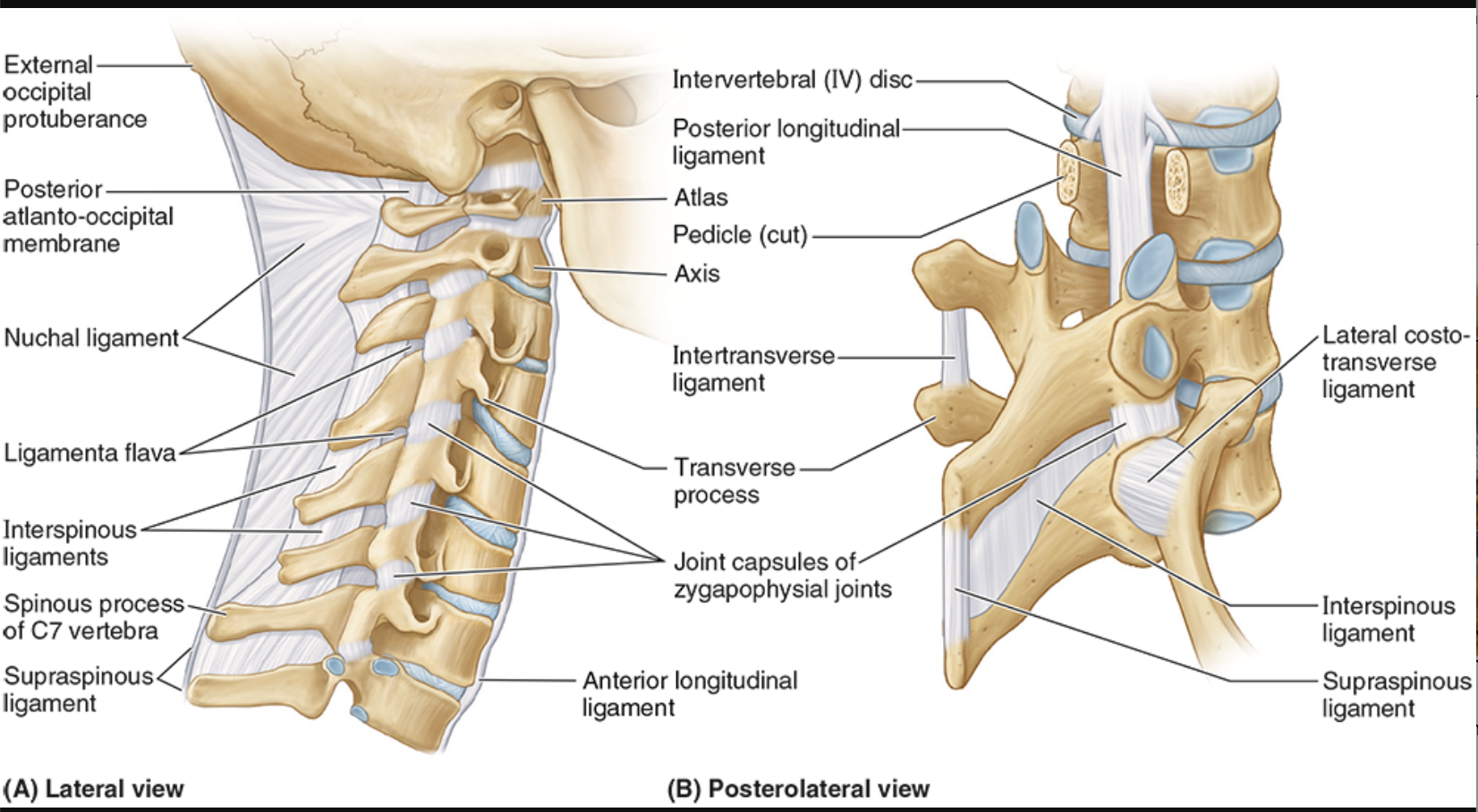
Interspinous ligaments
between spinous processes
resists flexion
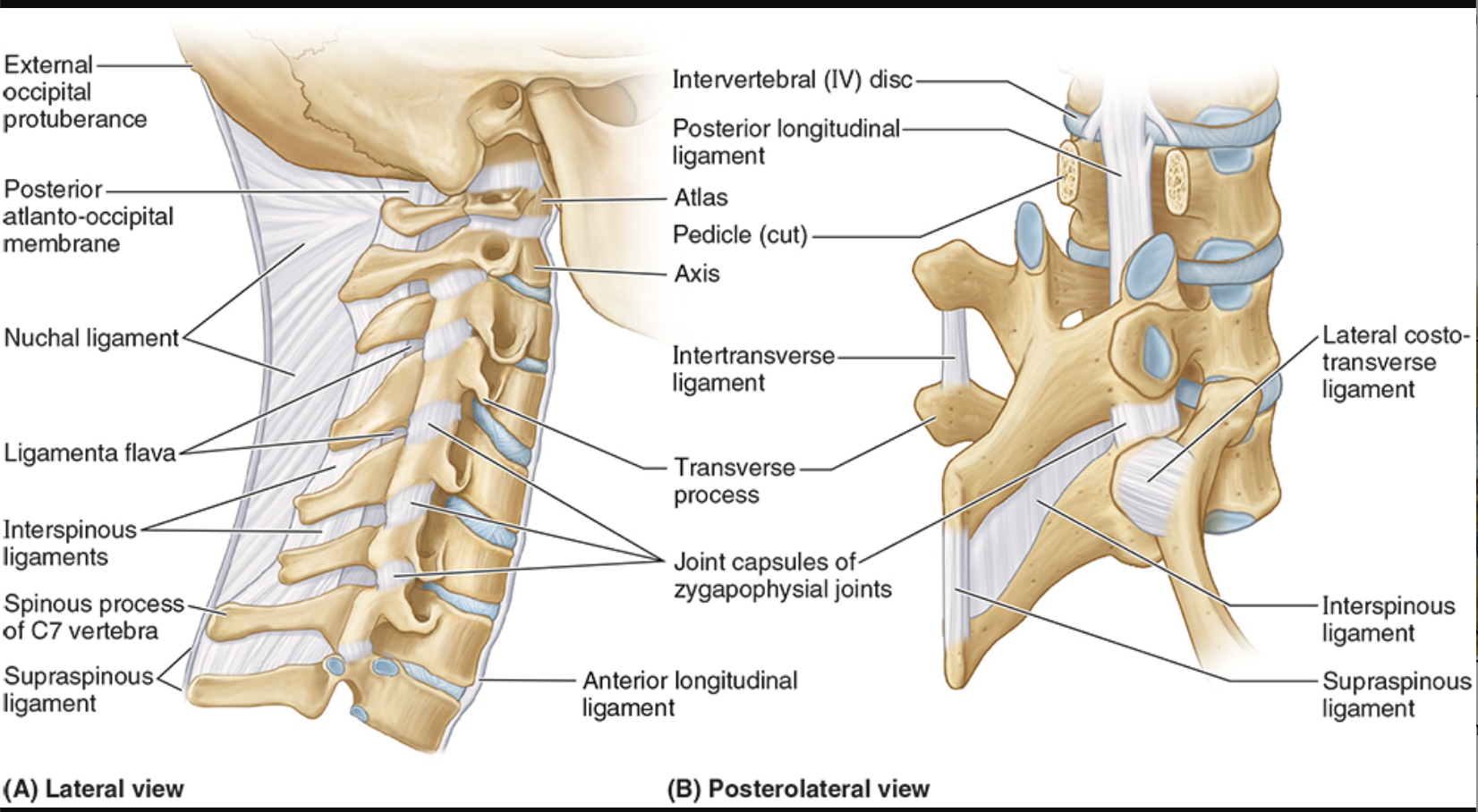
Supraspinous ligaments
connect adjoining spinous processes
resist flexion
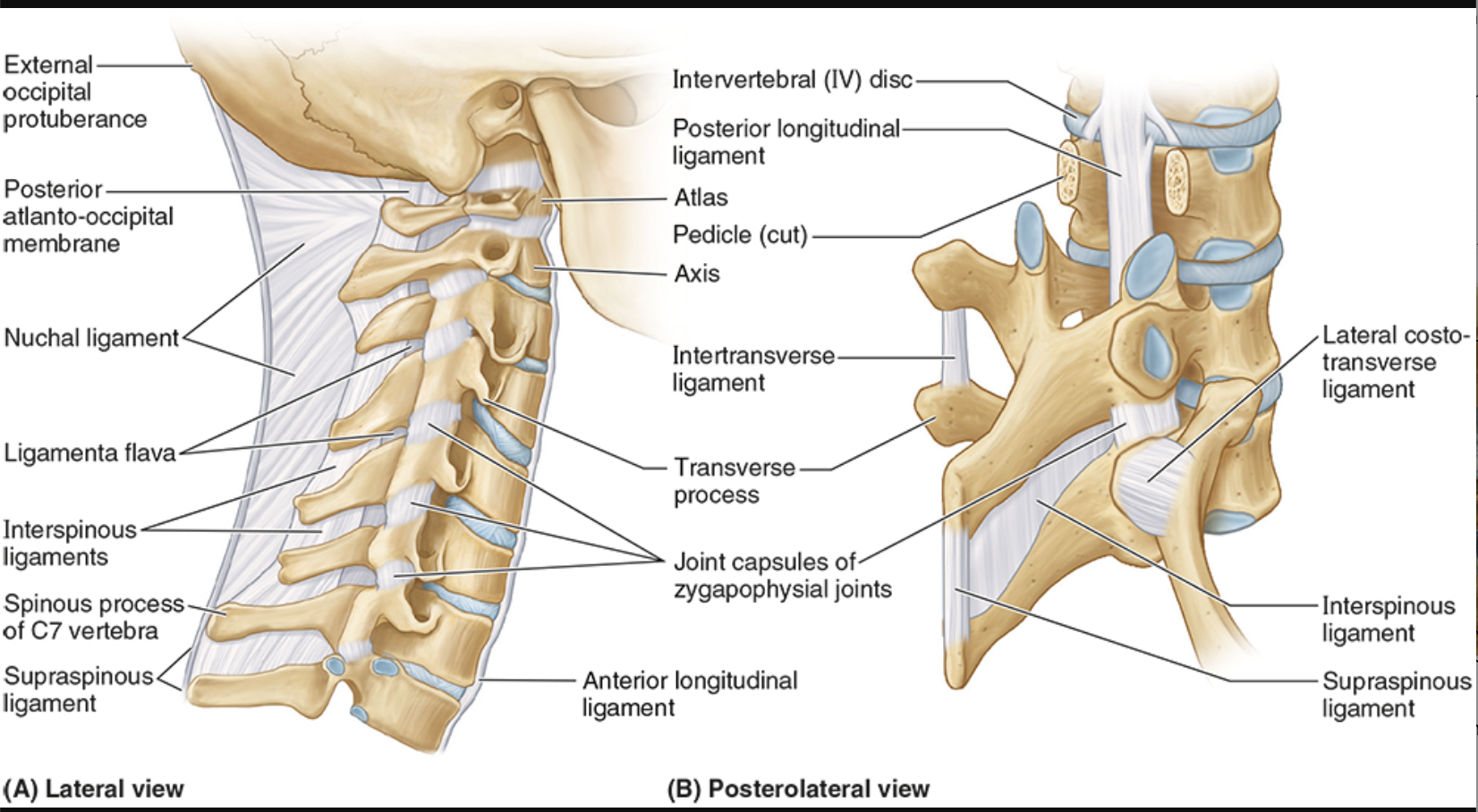
Intertransverse ligaments
connect adjacent transverse processes
prevent lateral flexion
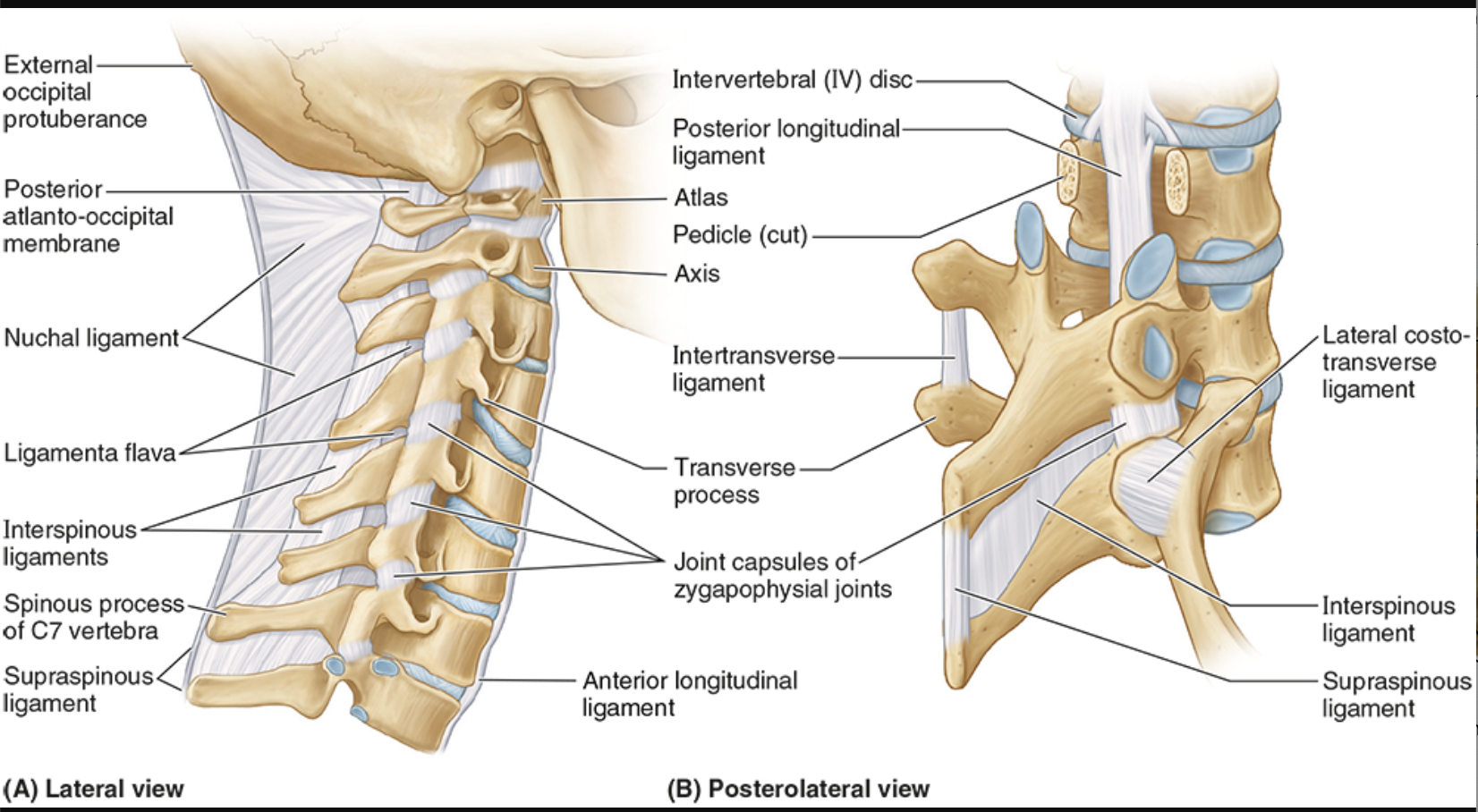
Nuchal ligament
occiput to cervical vertebrae
resists flexion
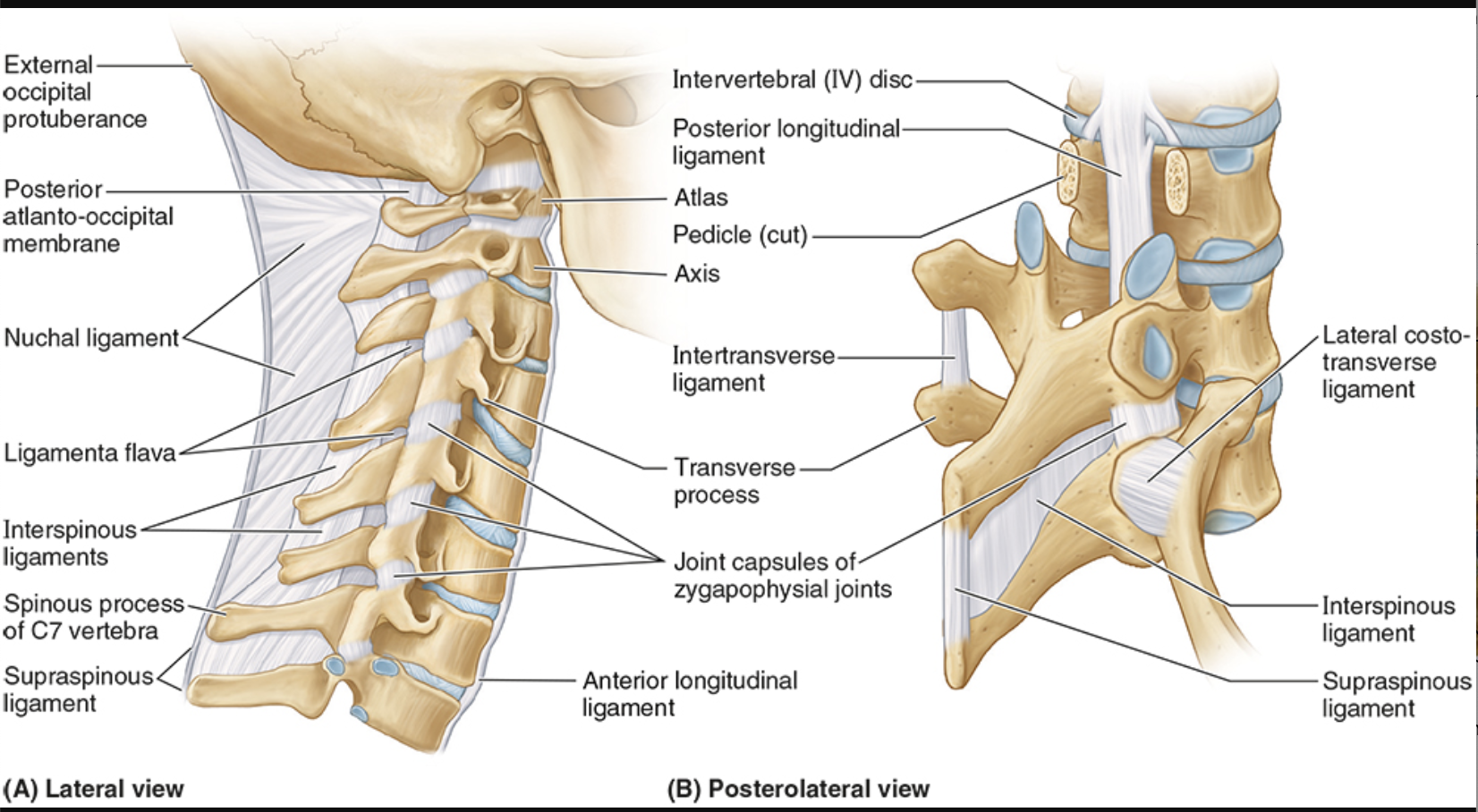
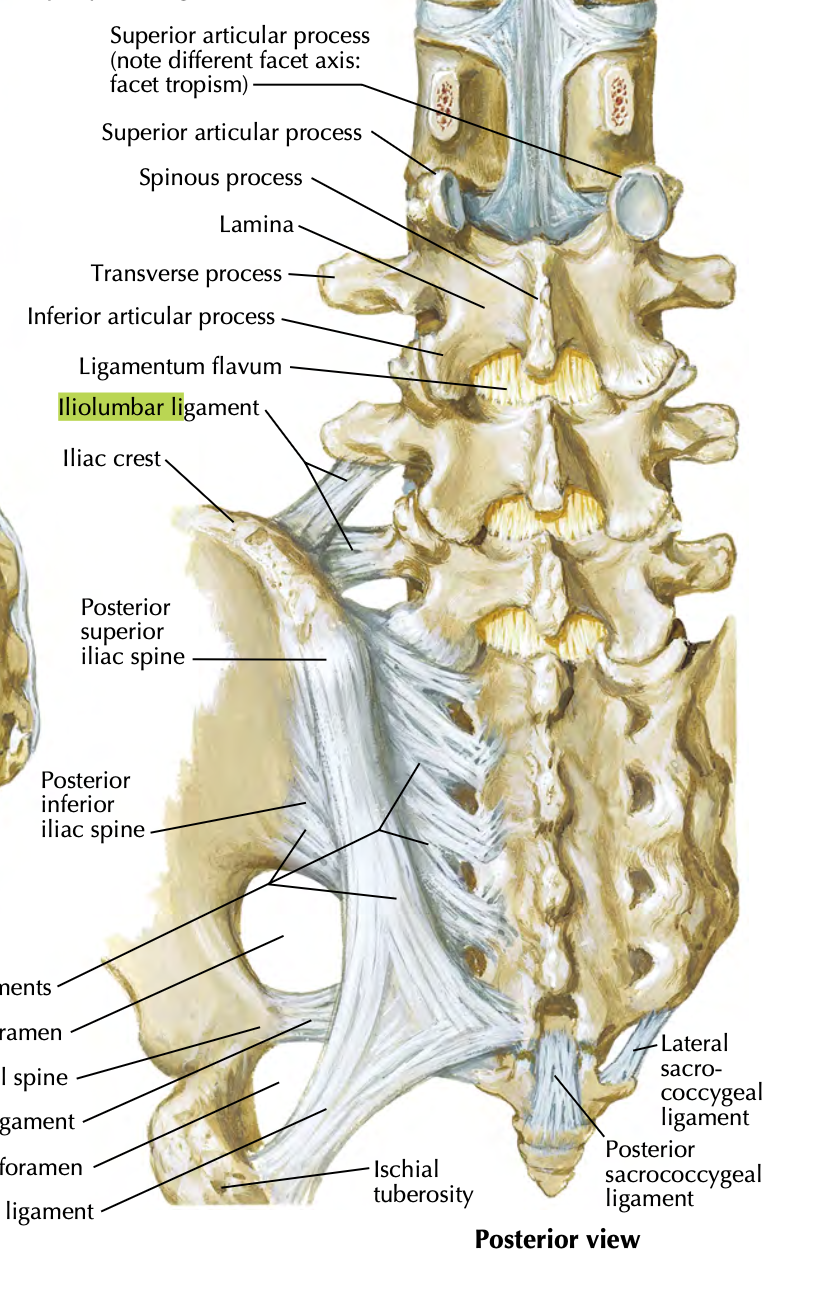
Iliolumbar ligament
LV 4-5
anchors lower vertebral column to iliac
stability to lumbosacral joint
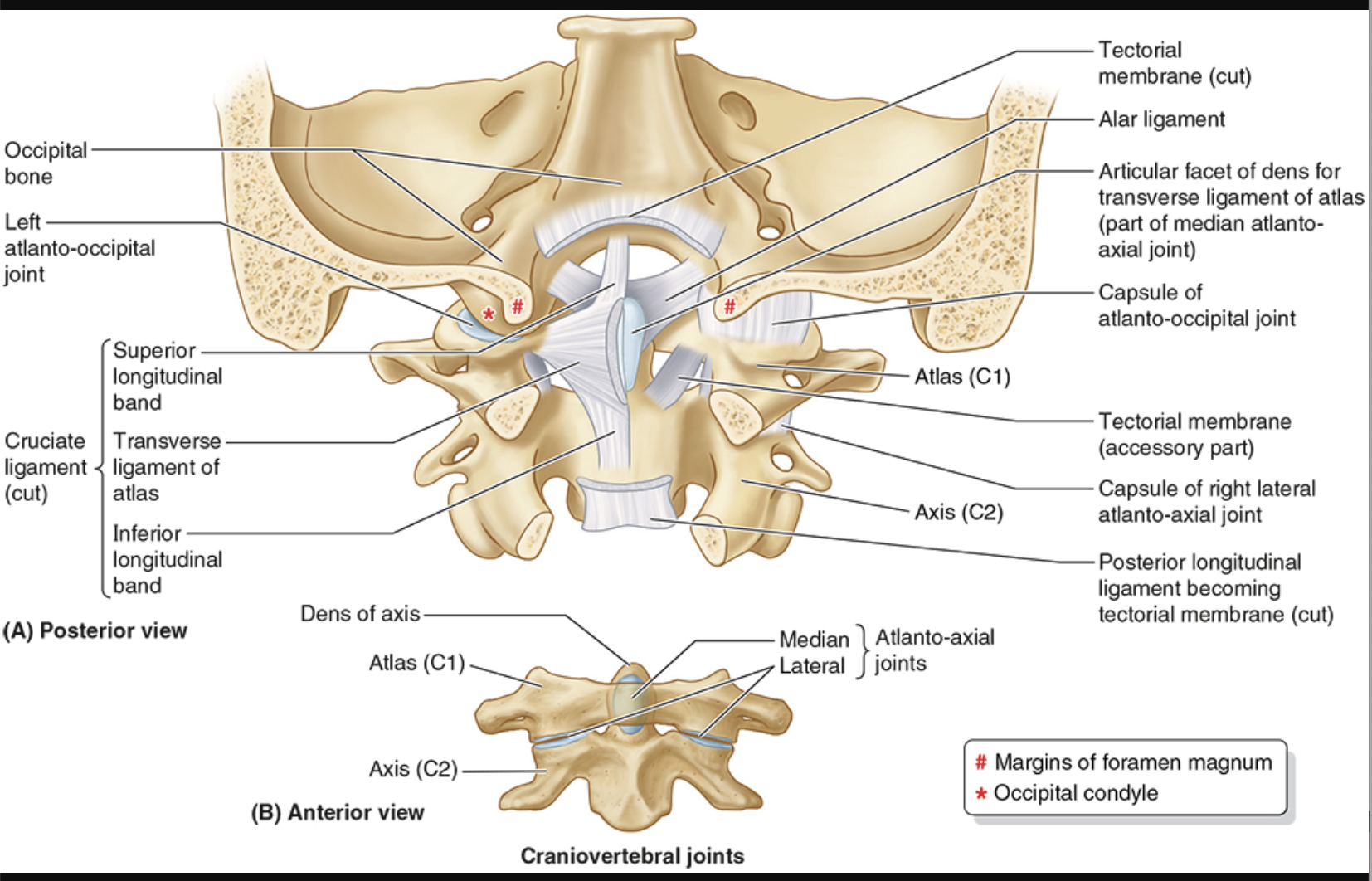
Cruciate ligament of atlas
looks like a cross
transverse ligament runs horizontal
vertical longitudinal bands (superior & inferior)
anchors dens to atlas
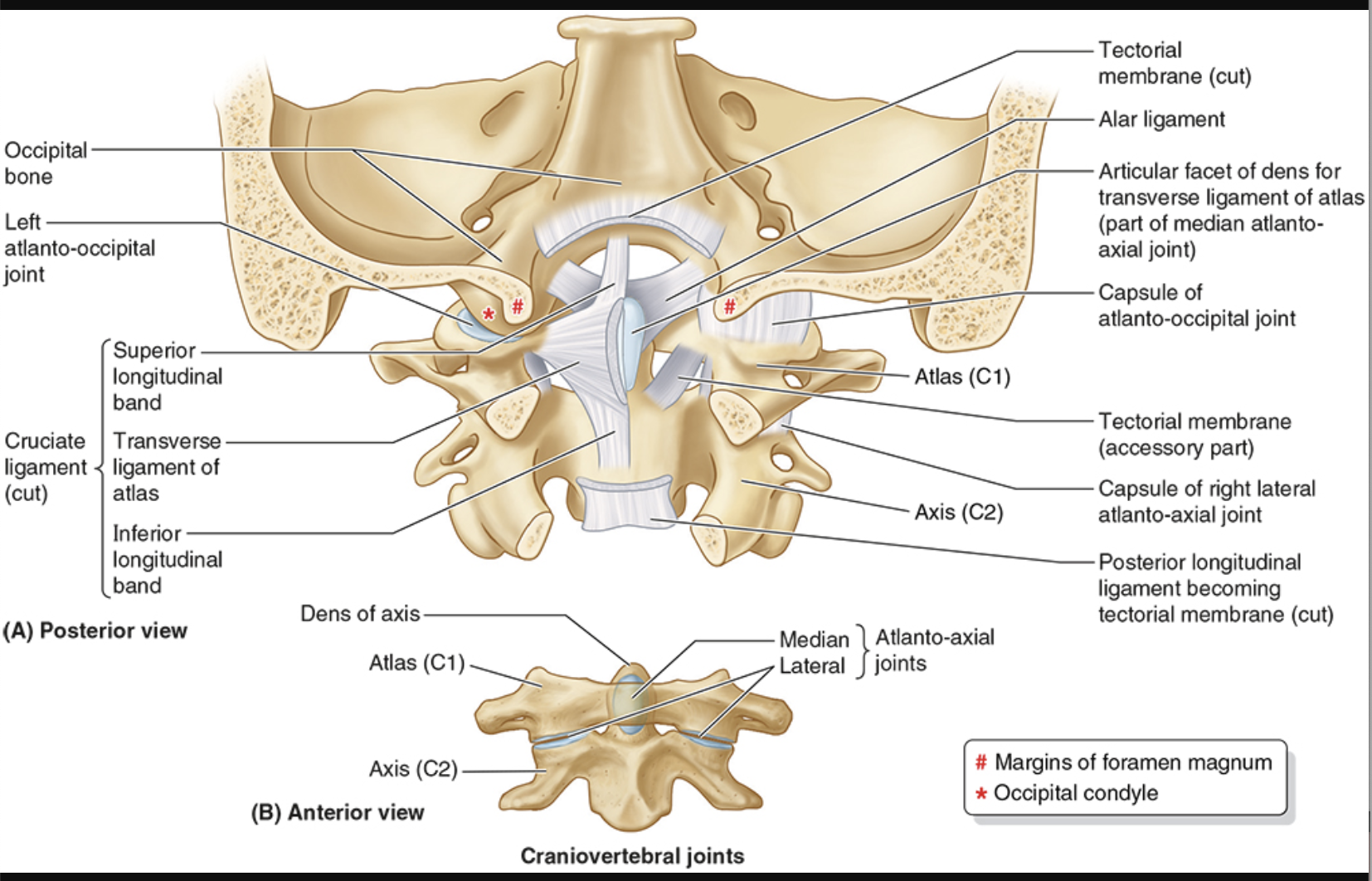
Alar Ligament
sides of dens to foramen magnus
prevents excessive rotation