market failure-1.3 micro economics
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
What is market failure ?
When the price mechanism causes an inefficient allocation of resources leading to net welfare loss
What are externailities
these are either costs of benefits that affect third parties that are not included in the original transaction
What is an external costs ?
theses are negative consequences that affect third parties that are not part of the original transaction
what are private costs ?
costs internal to the market transaction which are therefore taken into account by the price mechanism
what the social costs ?
The sum of external cots and private costs from a market transaction
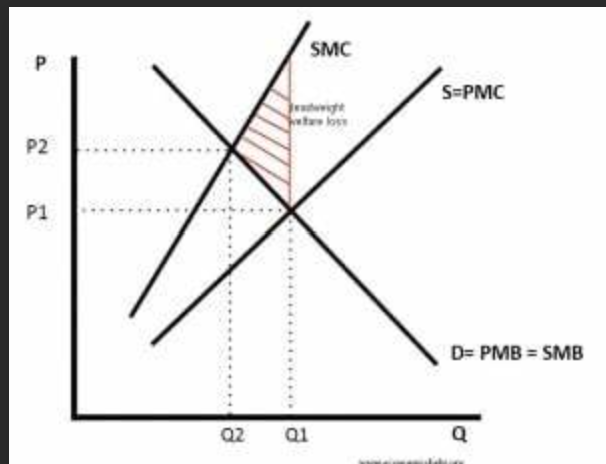
draw and external costs of production diagram ?
triangle = welfare loss
the gap between marginal social cost and marginal private cost is the external cost
the free market ignores the negative externalities mpc
however when the externalities are taken into account the curve deviates msc
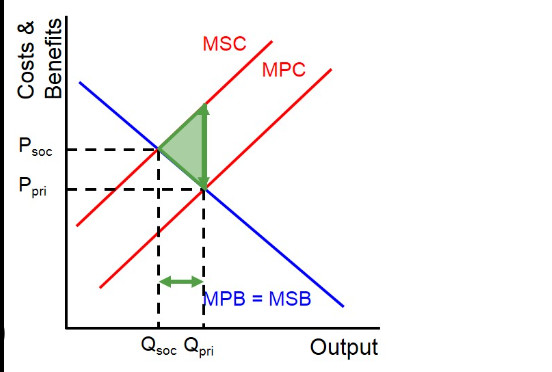
what is a private benefit ?
benefits internal to a transaction. which are therefore taken into account by the price mechanism
i.e. the revenue firms obtain from selling a good or service ?
what are social benefits
by adding private benefit to external benefit = social benefit
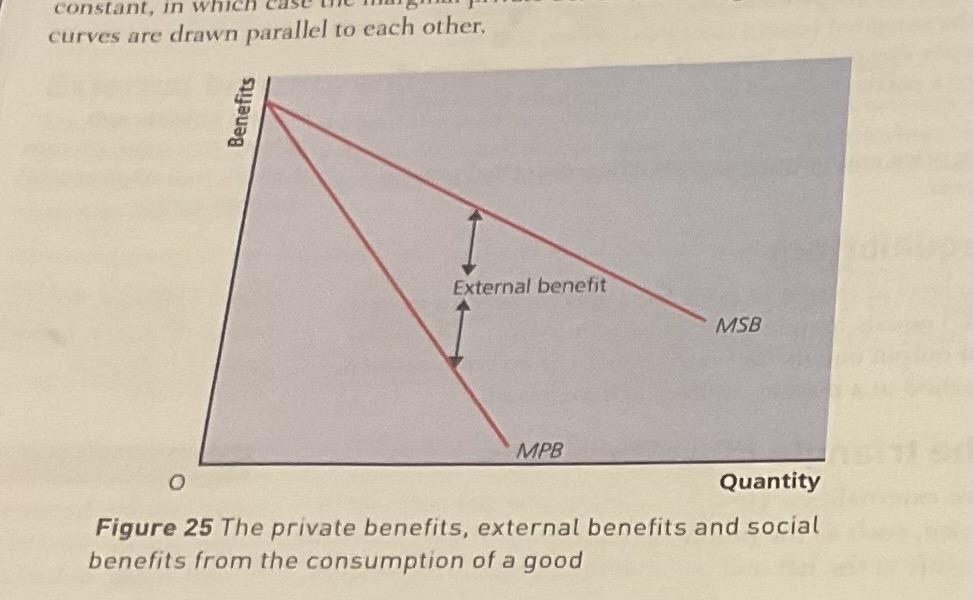
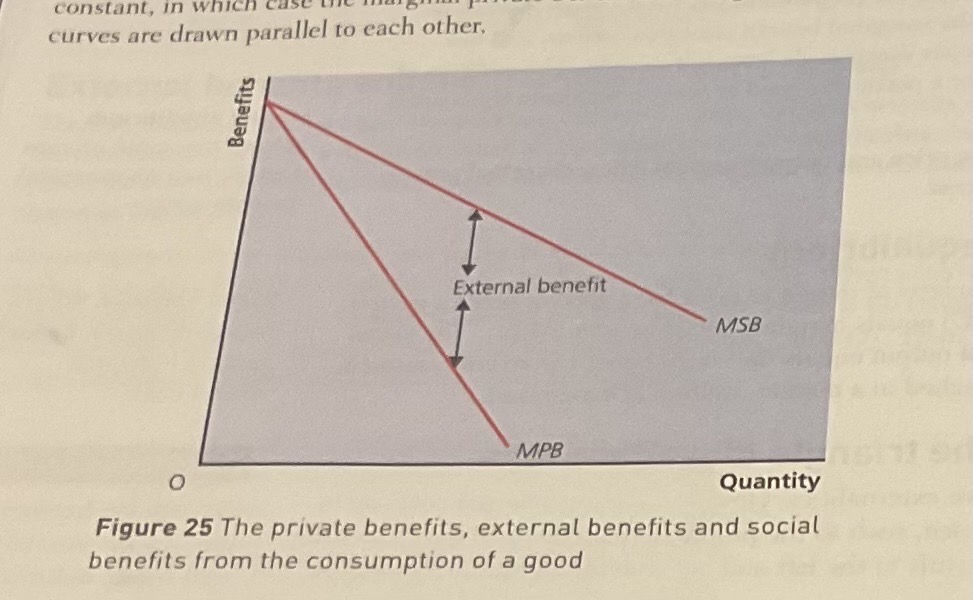
why do the marginal private benefit curve and the marginal social benefit curve often diverge
this is because it indicates that external benefits increases disproportionately with output consumed
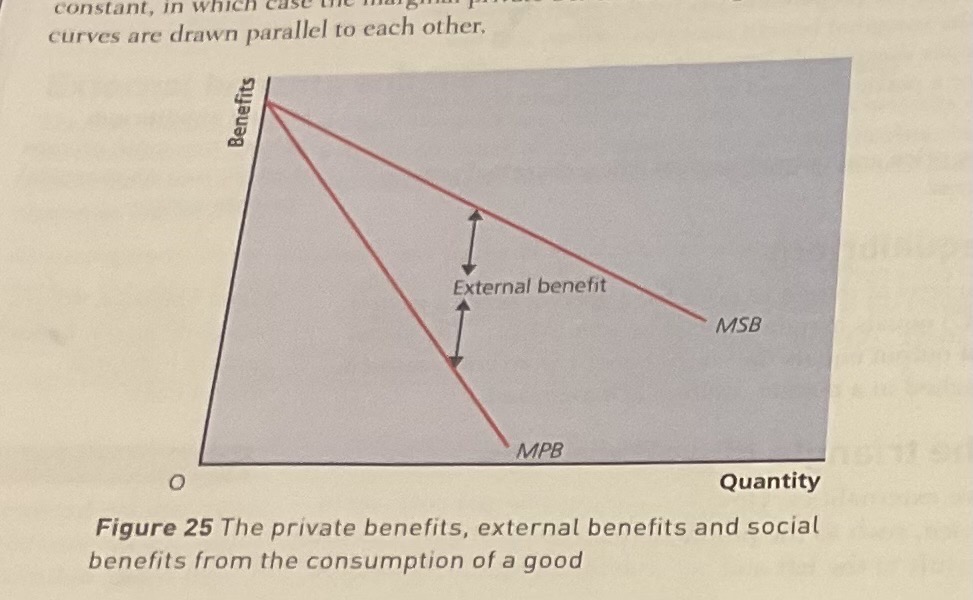
note :
diagrams of only
the external costs of production
external benefits of consumption
however u can use the external costs of consumption and external benefits of production in explanation
What is the supply curve for firm
this shows the cost on firms for producing a certain goods.
MPC curves of firms in a market for a particular good or service will form the market supply curve
what is market equilibrium ?
occurs at the price and output position where marginal private benefits equals marginal private cost
What is the demand curve for consumers ?
this is the marginal private benefit
economist assume that it is possible to measure benefit obtained from consuming a good by the price people are willing to pay for it
why do demand curves slope downwards i.e. demand curve for consumers - marginal private benefit ?
as an individual consumes more units of are marginal benefit utility will fall.
this is why the demand curve slopes downwards
what is the social optimum equilibrium?
this where the marginal social benefit equals marginal private benefit
the social cost of producing the last unit lf that good equal
s the social benefit of consuming it
when negative external costs aren’t realised how does it lead to market failure
it leads to market failure because there is an under pricing and overproduction of goods that cause harm i.e. tobacco
this results in excess social cost of social benefit
how does not realising external benefit in consumption lead to market failure
this causes market failure because their is an under pricing and underproduction of the good or service.
describe how the external cost diagram is produced
the free market does not take into account the negative externalities
however when the negative externalities are added it causes the supply curve of the firm to shift in and become marginal social costs