P11 , P12 AND P13
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
Magnetic poles
Unlike poles attract, like poles repel
Magnetic materials
Cobalt, steel, iron, nickel
Permanent magnet
Always produce their own magnetic field
Magnetic force vs. distance
Force decreases as distance increases
Magnetic field around a bar magnet is
Strongest at the poles
Direction of magnetic field lines
From North to South
Concentration of field lines
Closer lines indicate stronger magnetic field
Plotting compass
Used to show magnet field shape and direction
Using a plotting compass
Mark field direction, move compass, connect lines
Earth's magnetic field
Generated by the magnetic outer core
induced magnet
only produce a magnetic field in the presesence of another magnet
magnet
any material or object that produces a magnetic field
the force between permanent and induced magnet
always attractive
magnetically soft material
loses/gains magnetism slowly
magnetically hard material
loses/gains magnetism quickly
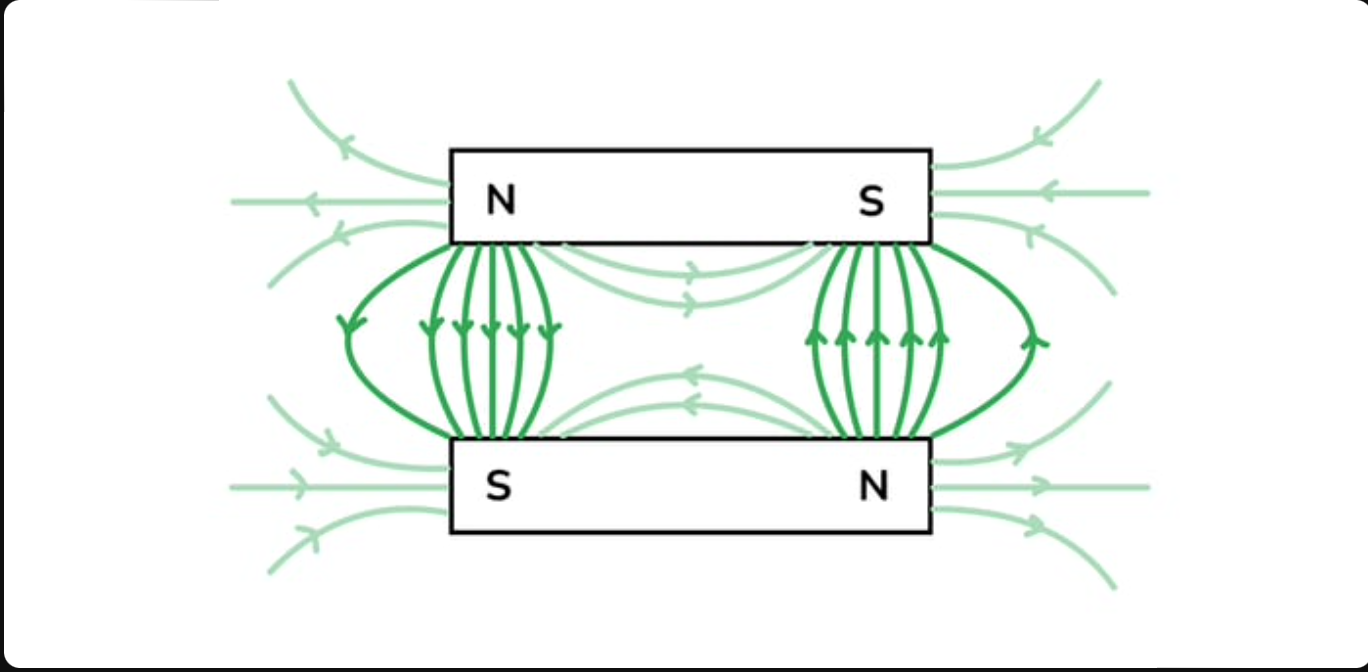
what diagram is this
2 sideways magnet attraction
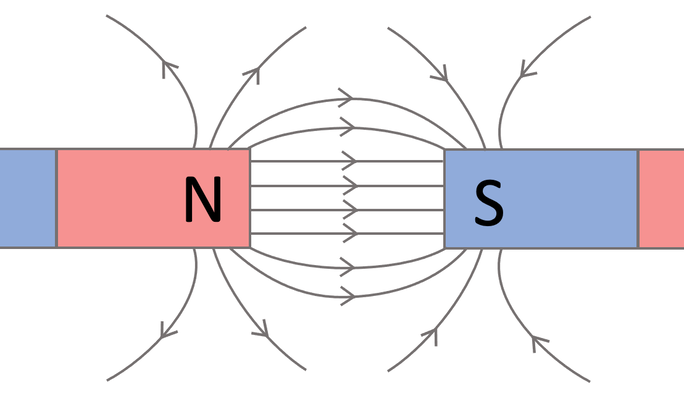
what diagram is this
poles attraction
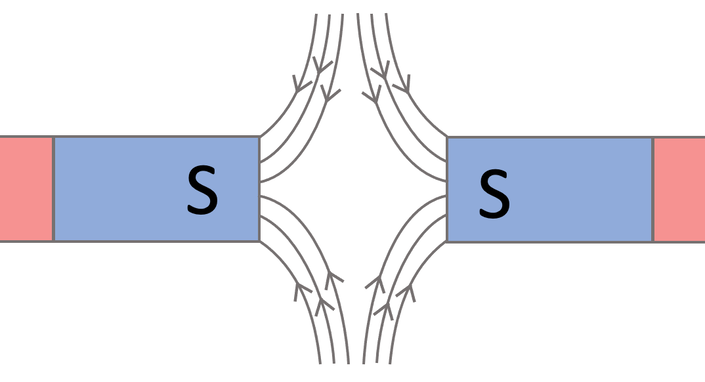
what diagram is this
poles repulsion
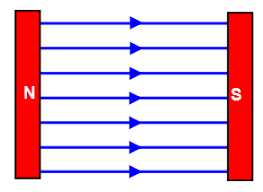
what diagram is this
uniform magnetic field
step up transformers
increase voltage, decrease current
step down transformers
decrease voltage, increase current
journey of electricity In national grid
power stations - step up transformer - pylons - step down transformer- homes
in a step up transformer what side has more coils
secondary coil
how do transformers work
when supplied with alternating current , it then induces an alternating magnetic field in the iron core which induces an alternating current in the secondary core
Fleming right hand rule
point your thumb to the direction of the current, the direction your fingers are curled in is the magnetic field direction .
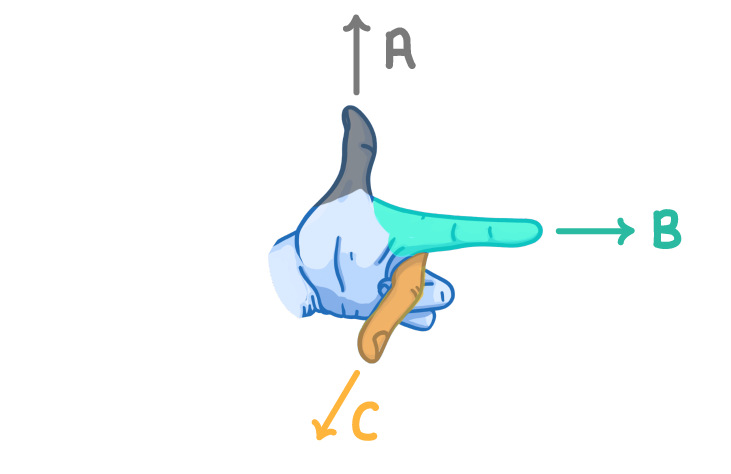
Fleming left hand rule
a : direction of force
b: direction of magnetic field
c: direction of current
what can flemings left hand rule tell us
the direction of the force experienced by a current carrying wire in a magnetic field.
motor effect
current carrying wire in a magnetic field will experience a force
how does an electric motor work
a coil of wire carrying current in placed in a magnetic field, it then turns due to the motor effect. Then a split-ring commutator is used to change the direction every half turn so it turns fully
electromagnetic induction
a potential difference is generated in a wire due to a change in magnetic field
how can I increase voltage by electromagnetic induction
increase magnetic field strength, more coils, move magnet faster
what’s the difference between an alternator and dynamo
dynamo has a split ring commutator by an alternator has slip rings and brushes
what does the dynamo produce
direct current as it changes direction every half-spin
what does an alternator produce
alternating current
static electricity
when two objects are rubbed together, the friction causes electrons to move building up charge
does static electricity work for conducting materials?
no as the electrons will flow back again
what does an electric field cause
a charge to feel a force
what direction do the field lines go in a positive point charge
outwards
what direction do the field lines go in a negative point charge
inwards
what does the distance between field lines tell you in an electric field
strength of the field
what is true about the electrical field between two parallel plates
it is uniform
what can be used to prevent electrostatic charge building up
earthing
how does earthing prevent electrostatic charge building up
charged object is connected to ground using a conductor, it provides a low resistance route for charges
how does the charge affect travel of electrons in earthing
electrons flow up to the conductor if its positive charge, and flow down to earth if its negative charge
what are 2 uses of static electricity
photocopiers , insecticide sprayers
how do photocopiers use static electricity
copies images onto a charged plate before printing them
how do insecticide sprays use static electricity
insecticide has an electrostatic charge so they all repel each other and cover a larger surface area
danger of static electricity
build up of static charge could mean that fuel gains charge when vehicle is being fuelled so if the charge causes a spark - it can ignite and explode
what is a spark
when electrons jump across the gap between a charged object and the earth
transformer equation for power across the 2 coils
Vp Ip = Vs Is
equation linked with turns of primary and secondary coil with voltage
Vp/Vs = Np/Ns
why are step up transformers used
increases voltage to reduce heat loss and increase efficiency
why are step down transformers used
decreases voltage to make it suitable for homes