05 Cerebral Cortex
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
▪ Connections between homologous areas of the two hemispheres
▪ The direction of the fibers is going from side-to-side, right to left, and left to right
A. Commissural fibers
B. Association fibers
C. Projection fibers
Commissural fibers
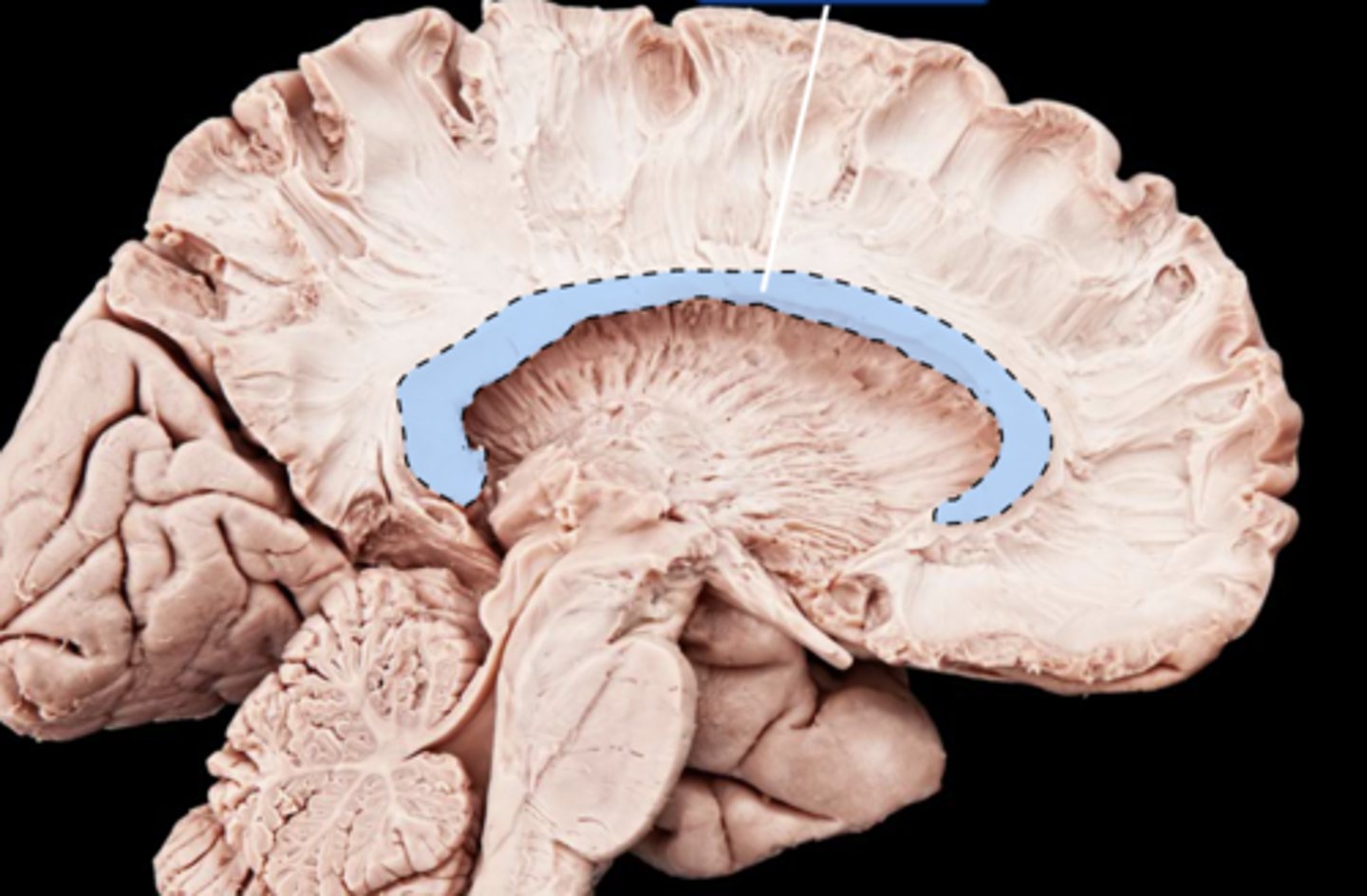
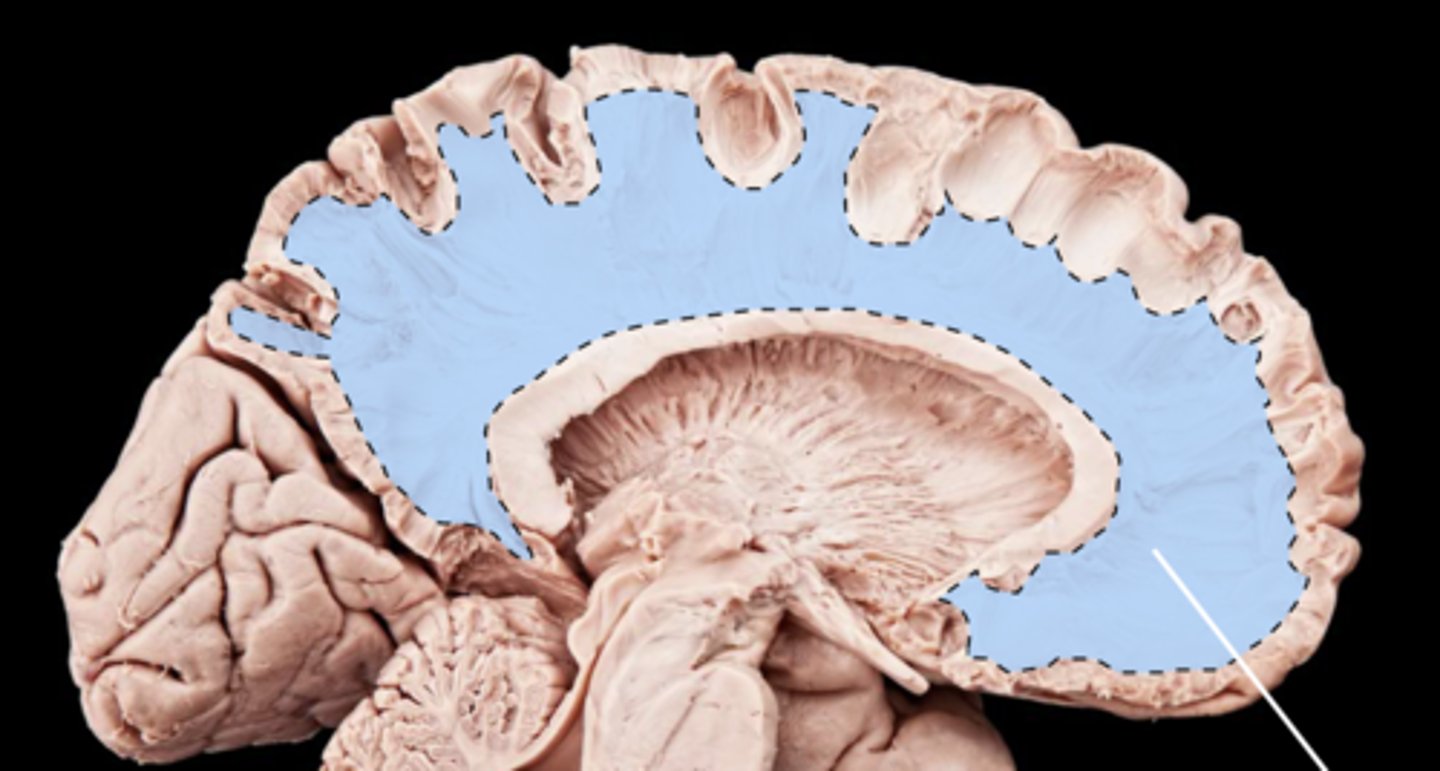
▪ Connections within the same hemisphere
▪ Going back and forth or front-to-back-back-to-front
A. Commissural fibers
B. Association fibers
C. Projection fibers
Association fibers
▪ Connects cortex to subcortical nuclei
▪ Superior and inferior / up and down
A. Commissural fibers
B. Association fibers
C. Projection fibers
Projection fibers
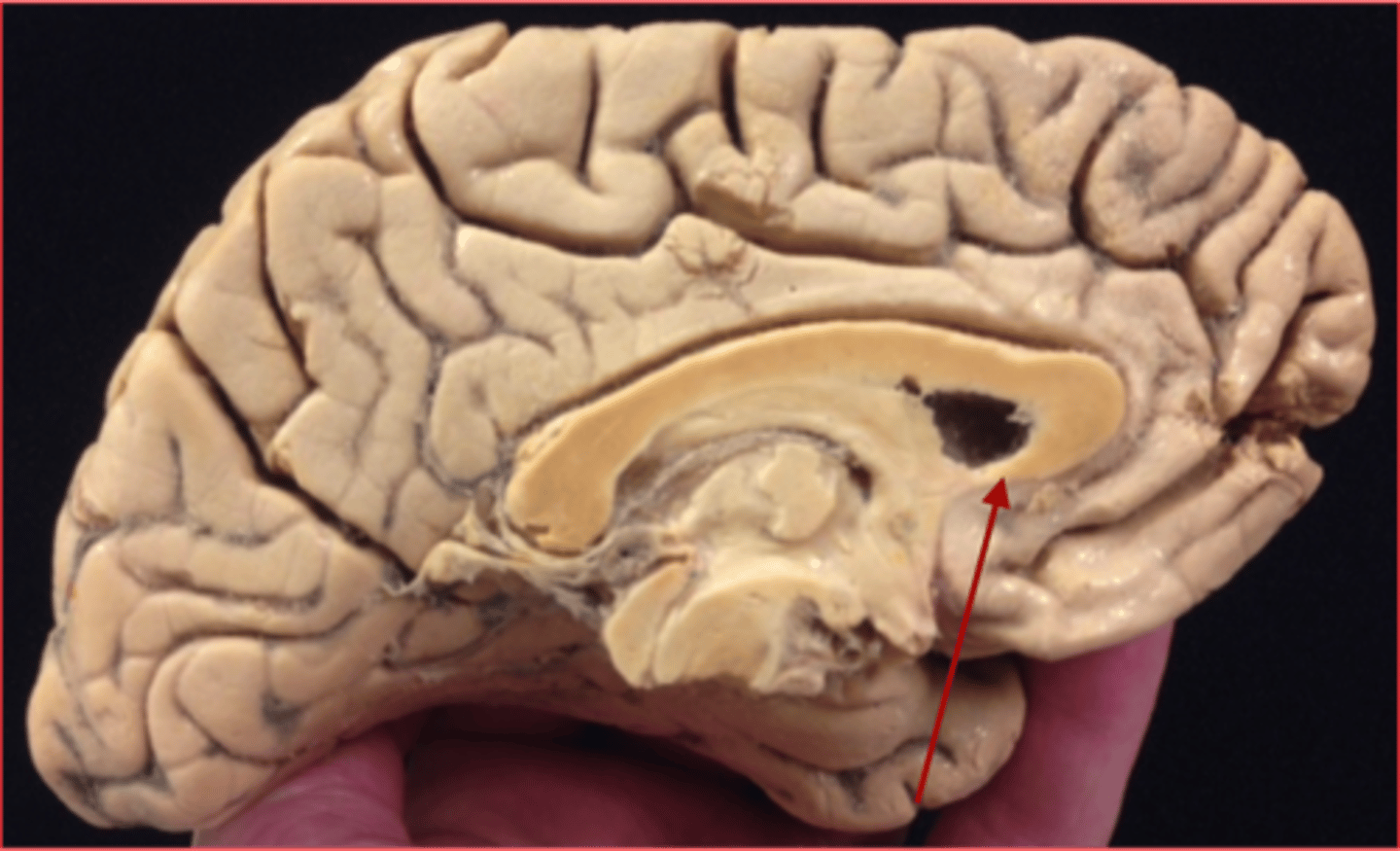
Interconnects the anterior part of the frontal lobe
A. Genu of corpus callosum
B. Rostrum of corpus callosum
Rostrum of corpus callosum
Connects the anterior part of the temporal lobe
A. Genu of corpus callosum
B. Rostrum of corpus callosum
Genu of corpus callosum
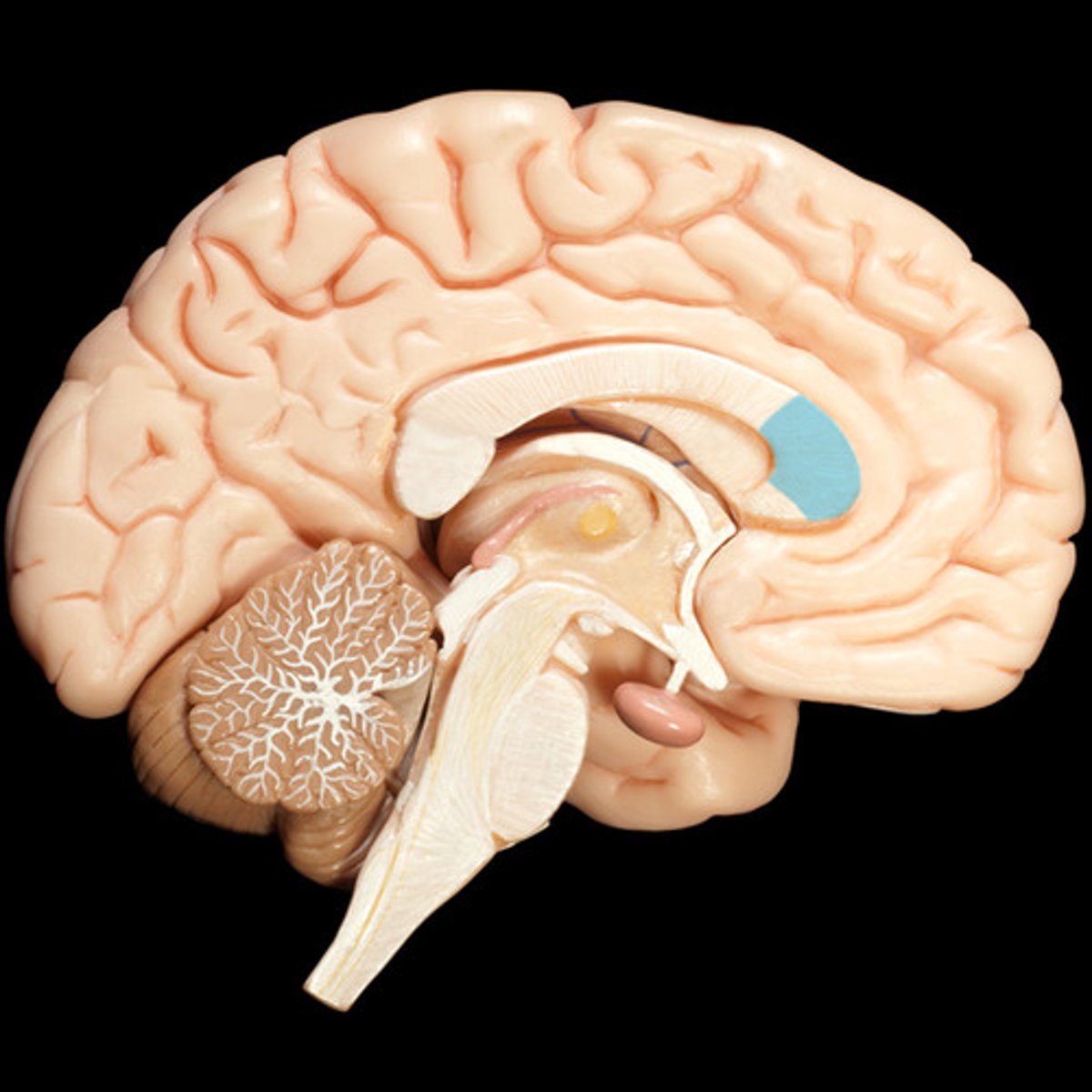
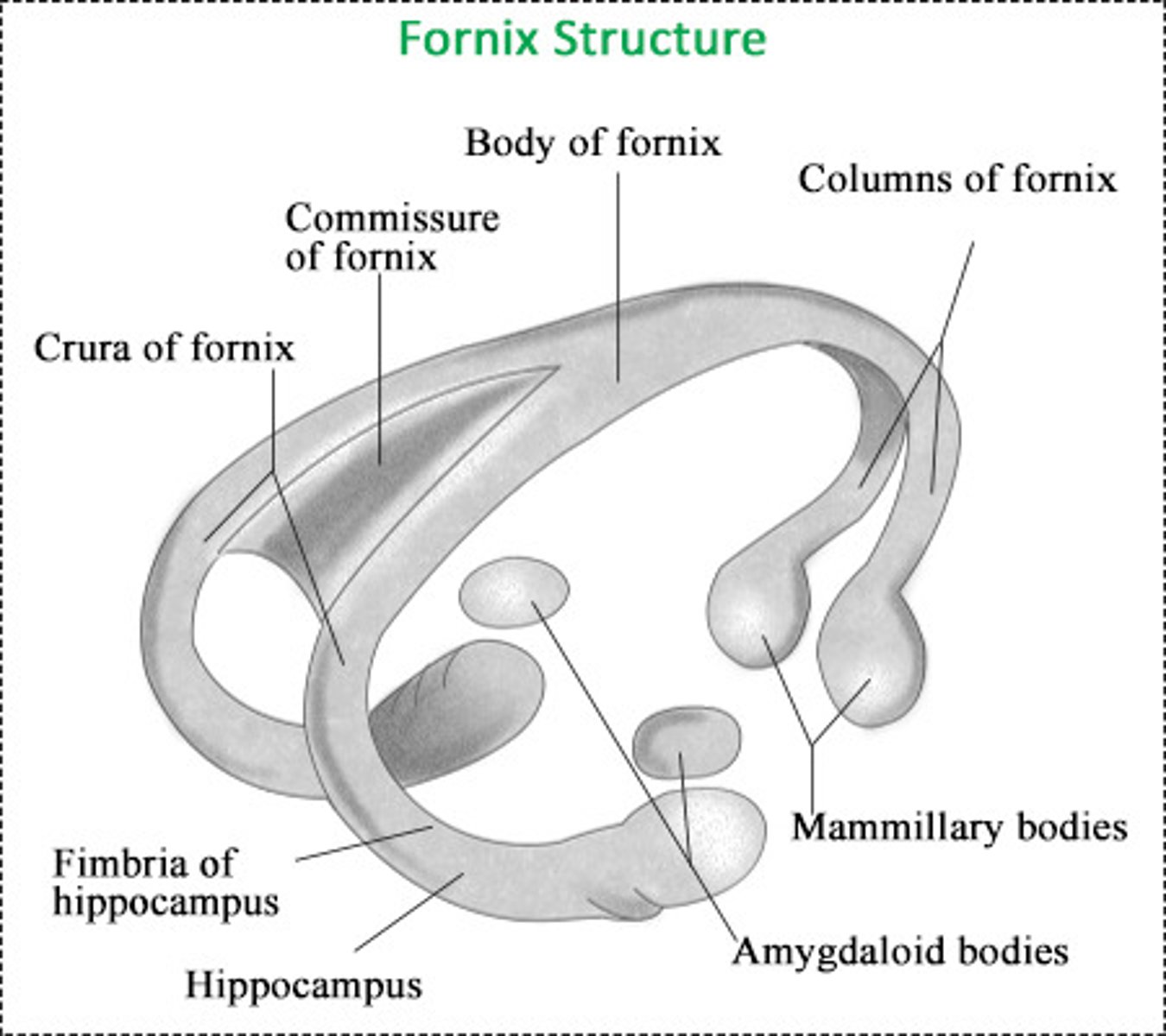
Function is to connect the hippocampal formations of the 2 sides
A. posterior commissure
B. commissure of the fornix
commissure of the fornix
(attach the two fornices)
- Fornix: is a bundle of nerve fibers that acts as the major efferent system of the hippocampus
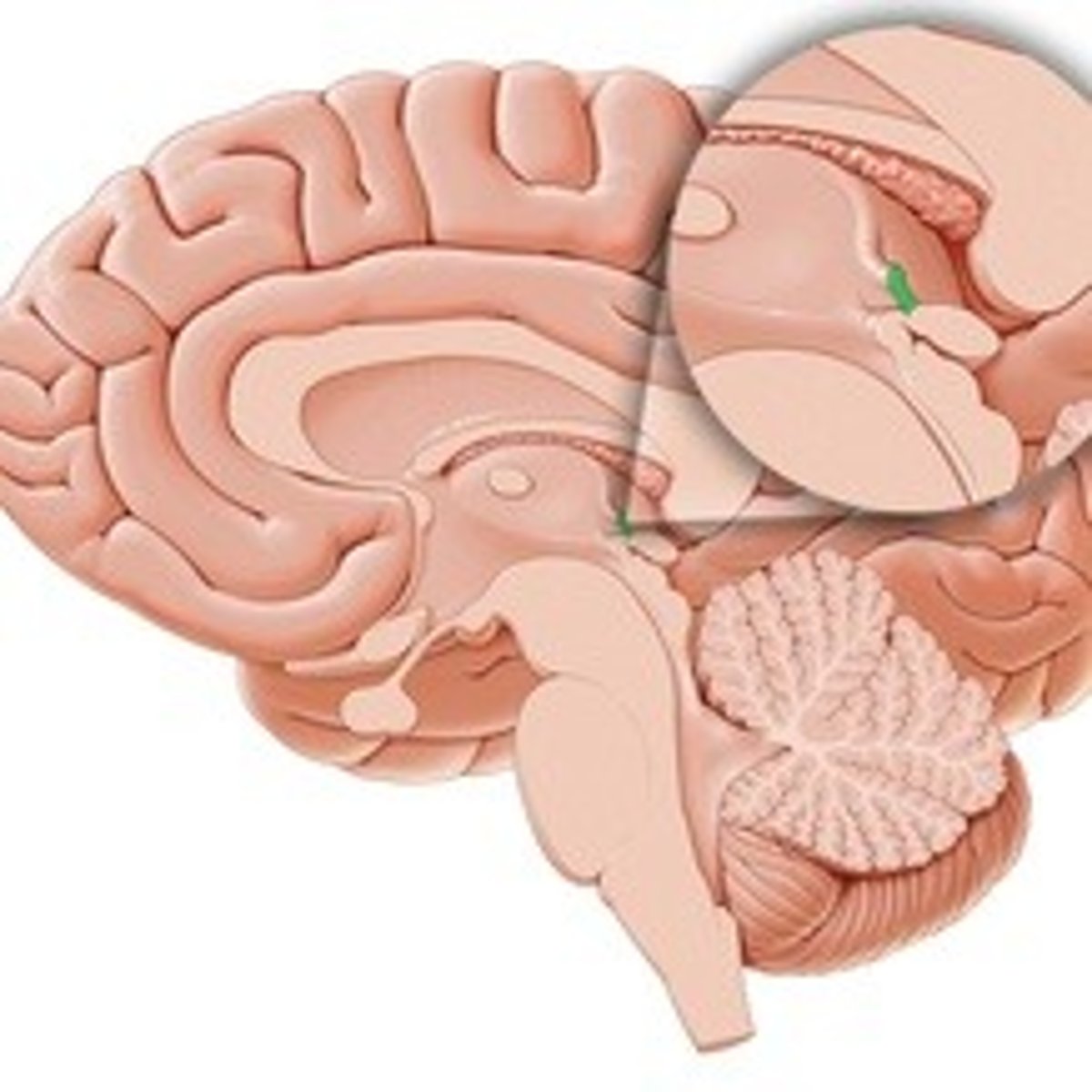
Consists of stria medullaris fibers crossing over to the contralateral habenular nuclei
A. habenular commissure
B. commissure of the fornix
habenular commissure
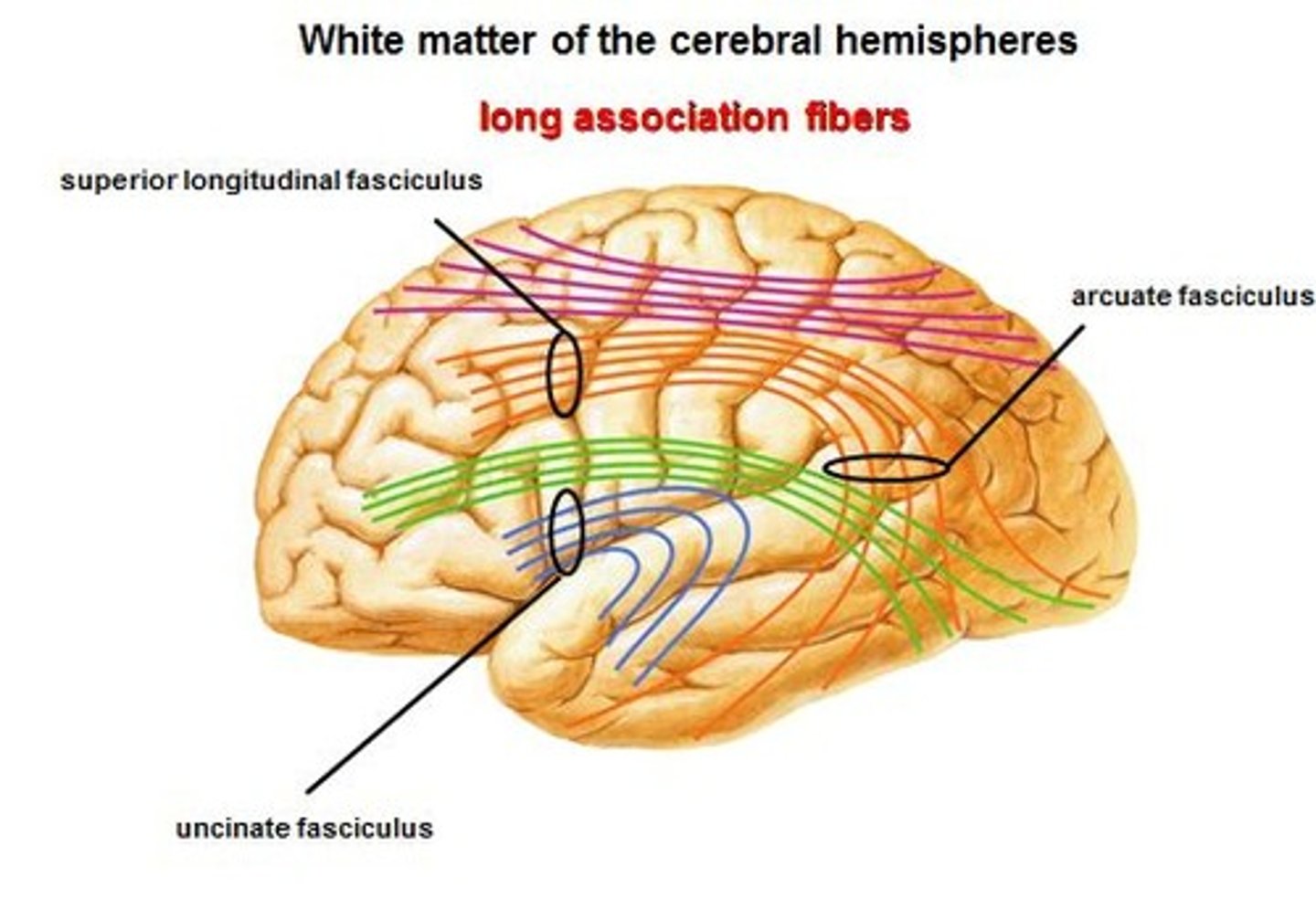
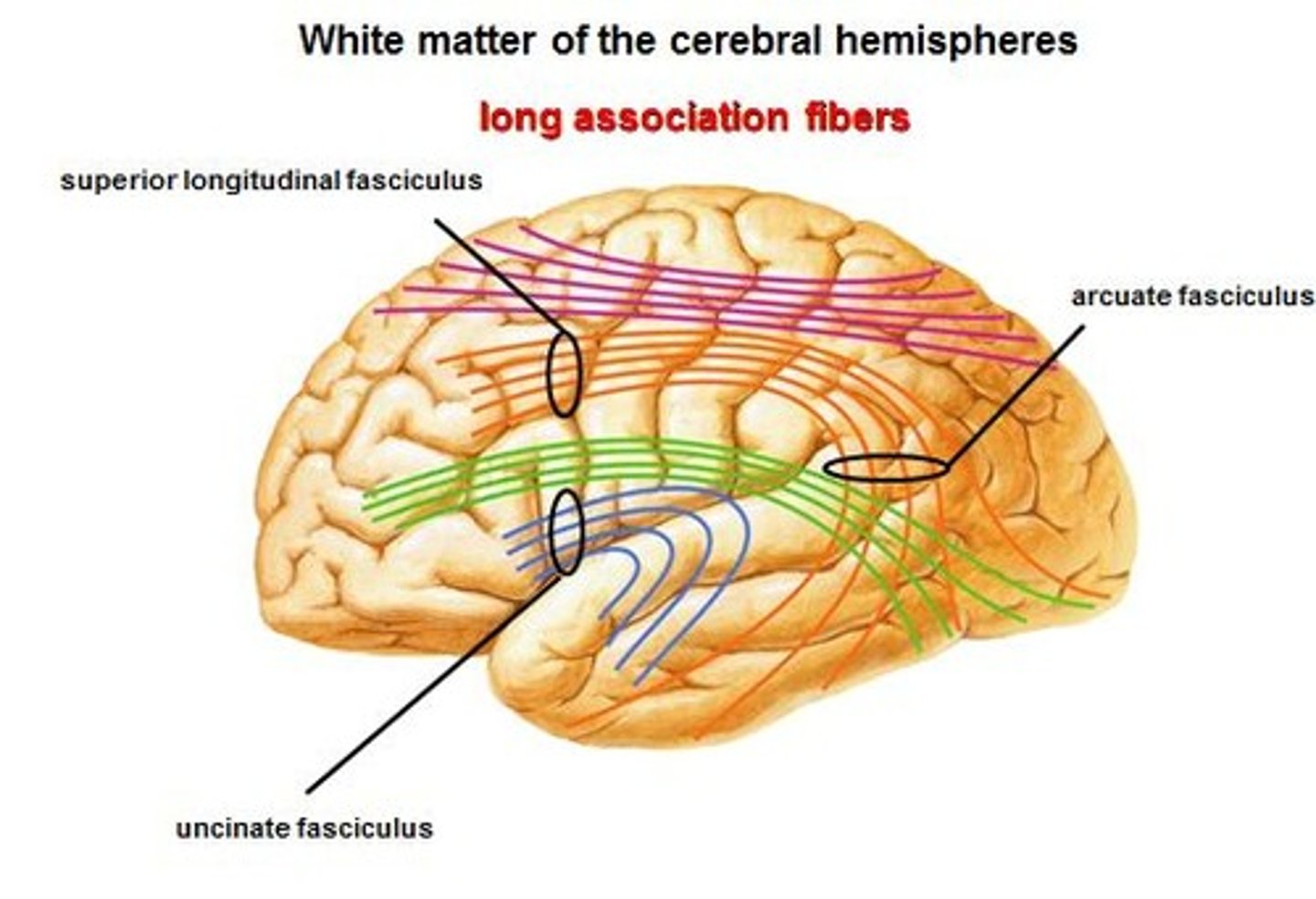
→ Connects the first motor speech area and the gyri on the inferior surface of the frontal lobe
→ Joins the orbital part of frontal lobe to temporal lobe
A. Inferior Occipitofrontal Fasciculus
B. Uncinate Fasciculus
Uncinate Fasciculus
While it is at the level of lentiform/lenticular nuclei, it is called the _____________.
A. internal capsule
B. corona radiata
internal capsule
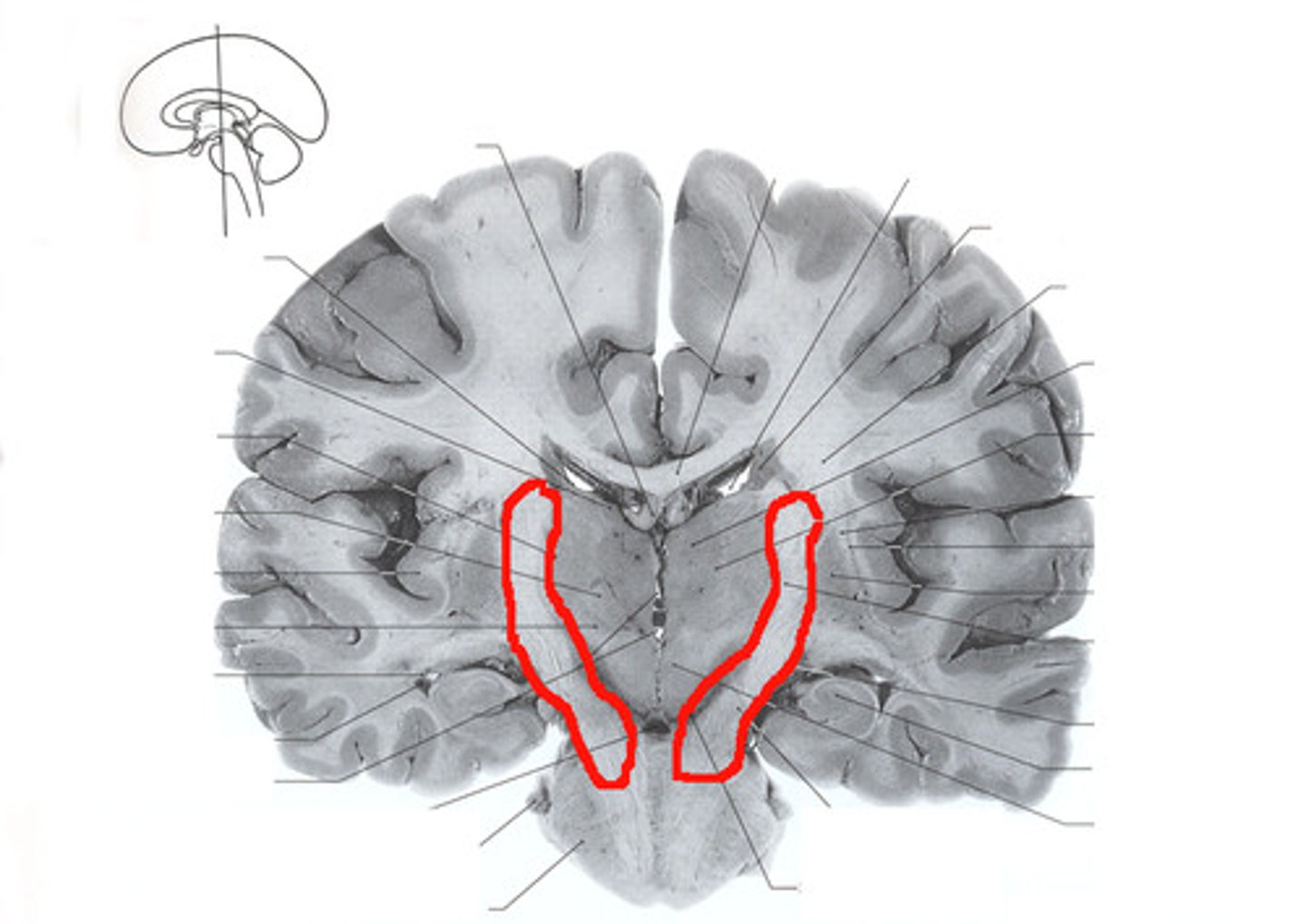
Once the fibers are located above lenticular nuclei, it is called __________________.
A. internal capsule
B. corona radiata
corona radiata
On the occipital part (posterior part), the corona radiata is called the optic radiations!
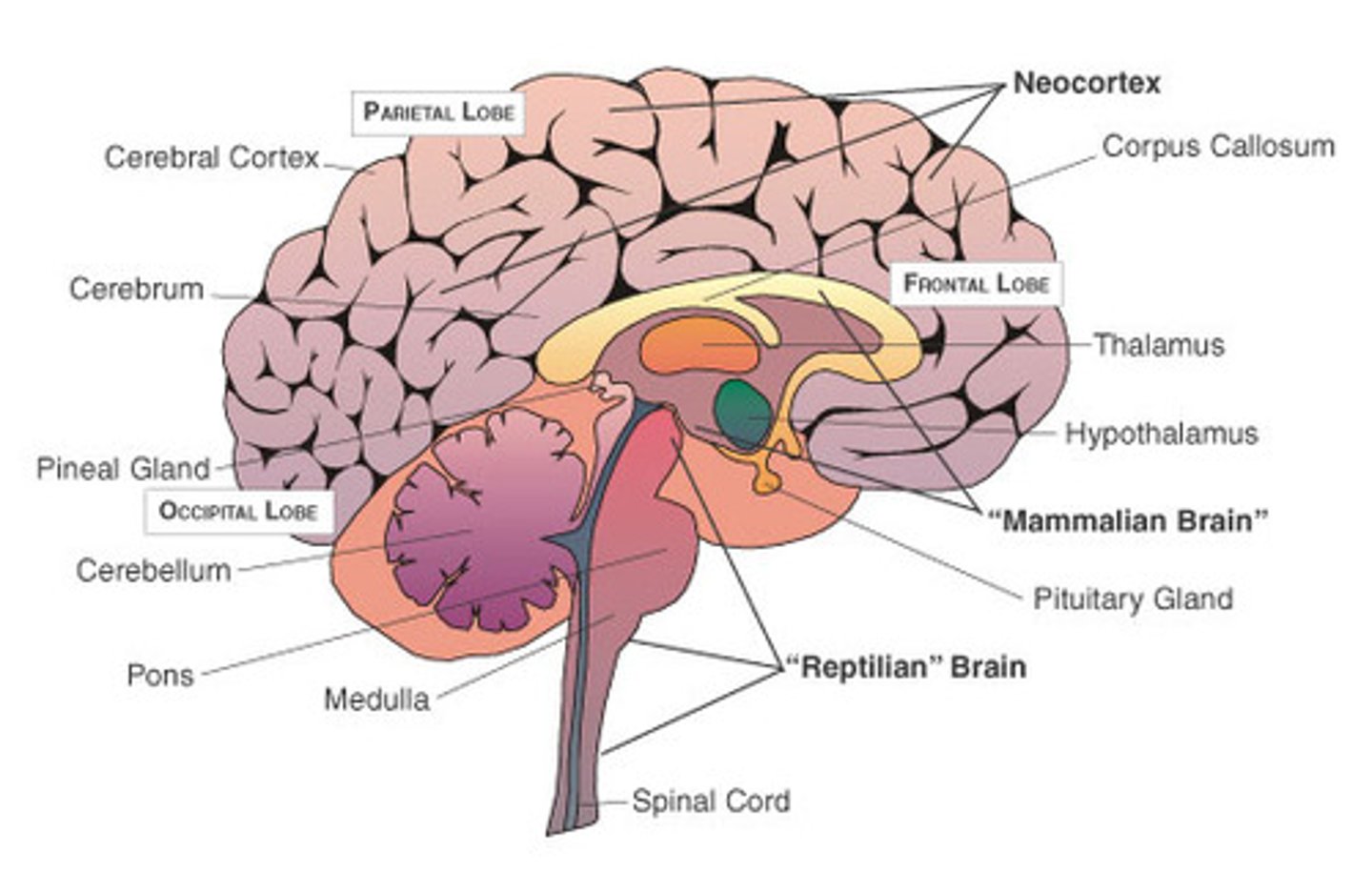
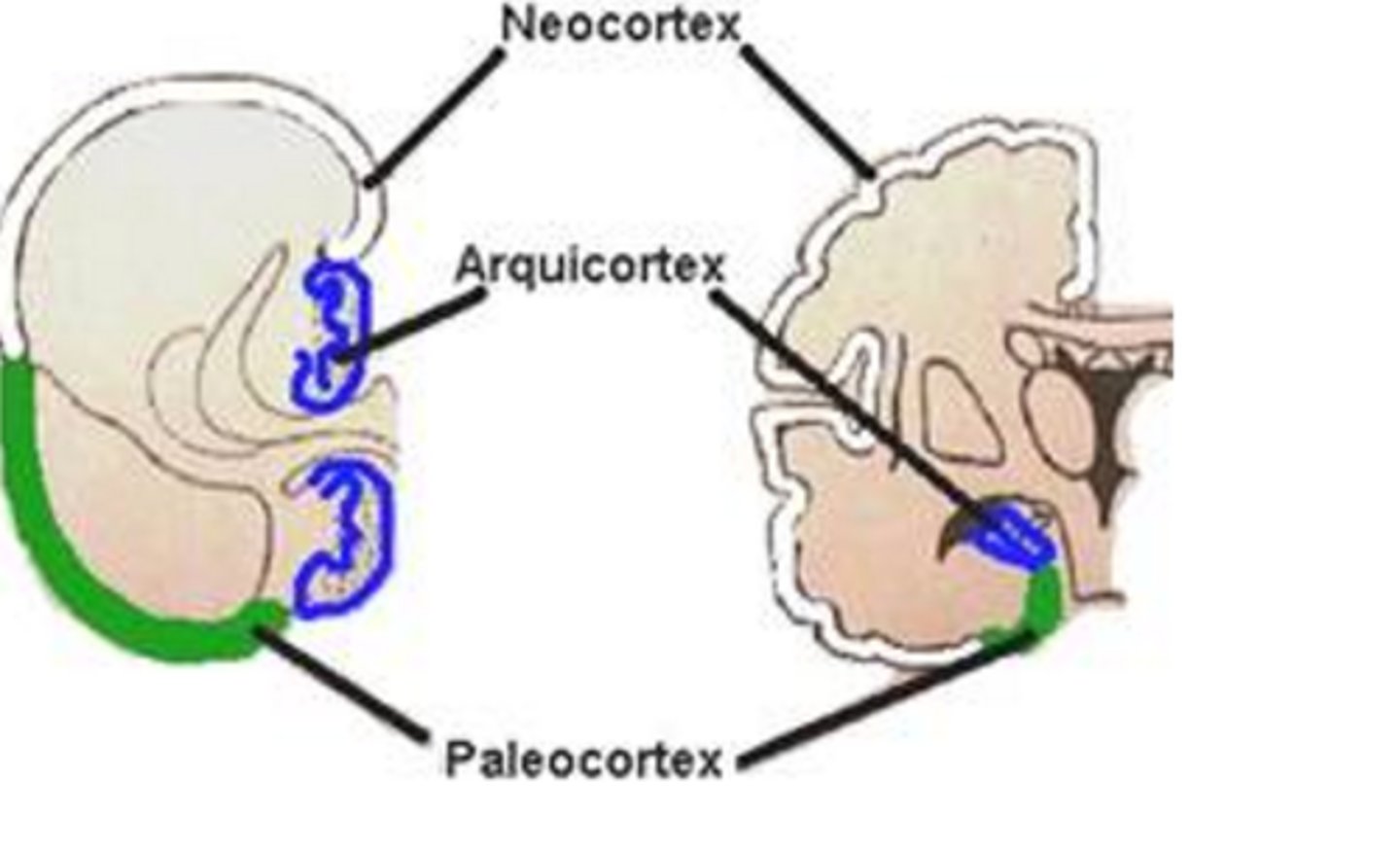
SUBDIVISIONS OF CORTEX
→ "New"
→ Last in evolution and it is 90% of the cortex
Neocortex
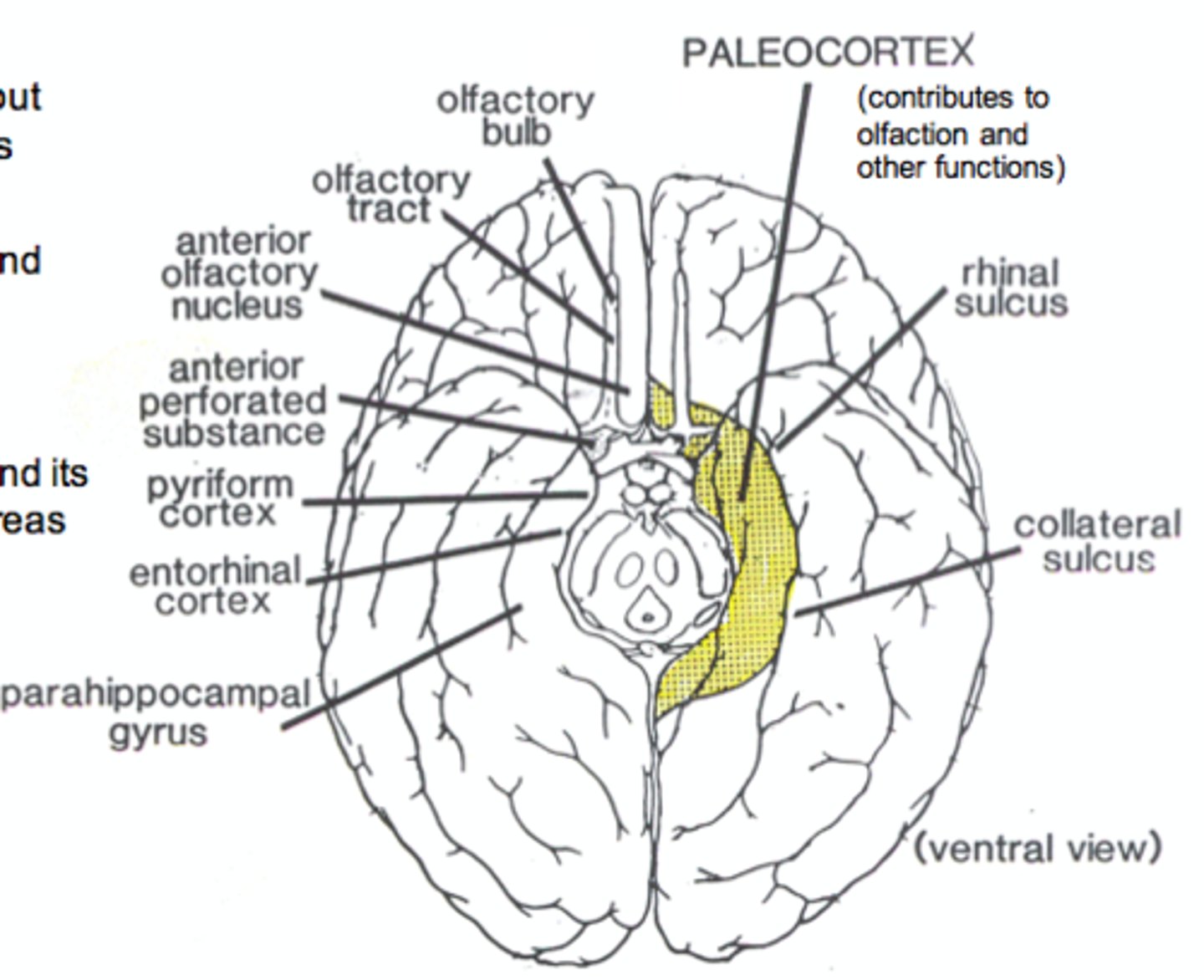
SUBDIVISIONS OF CORTEX
→ Restricted to the base of the hemisphere
→ Associated with the olfactory system
Paleocortex
The limbic system is composed of paleocortex and the archicortex.
SUBDIVISIONS OF CORTEX
→ Oldest/first to develop
→ Make up the hippocampal formation
Archicortex
The limbic system is composed of paleocortex and the archicortex.
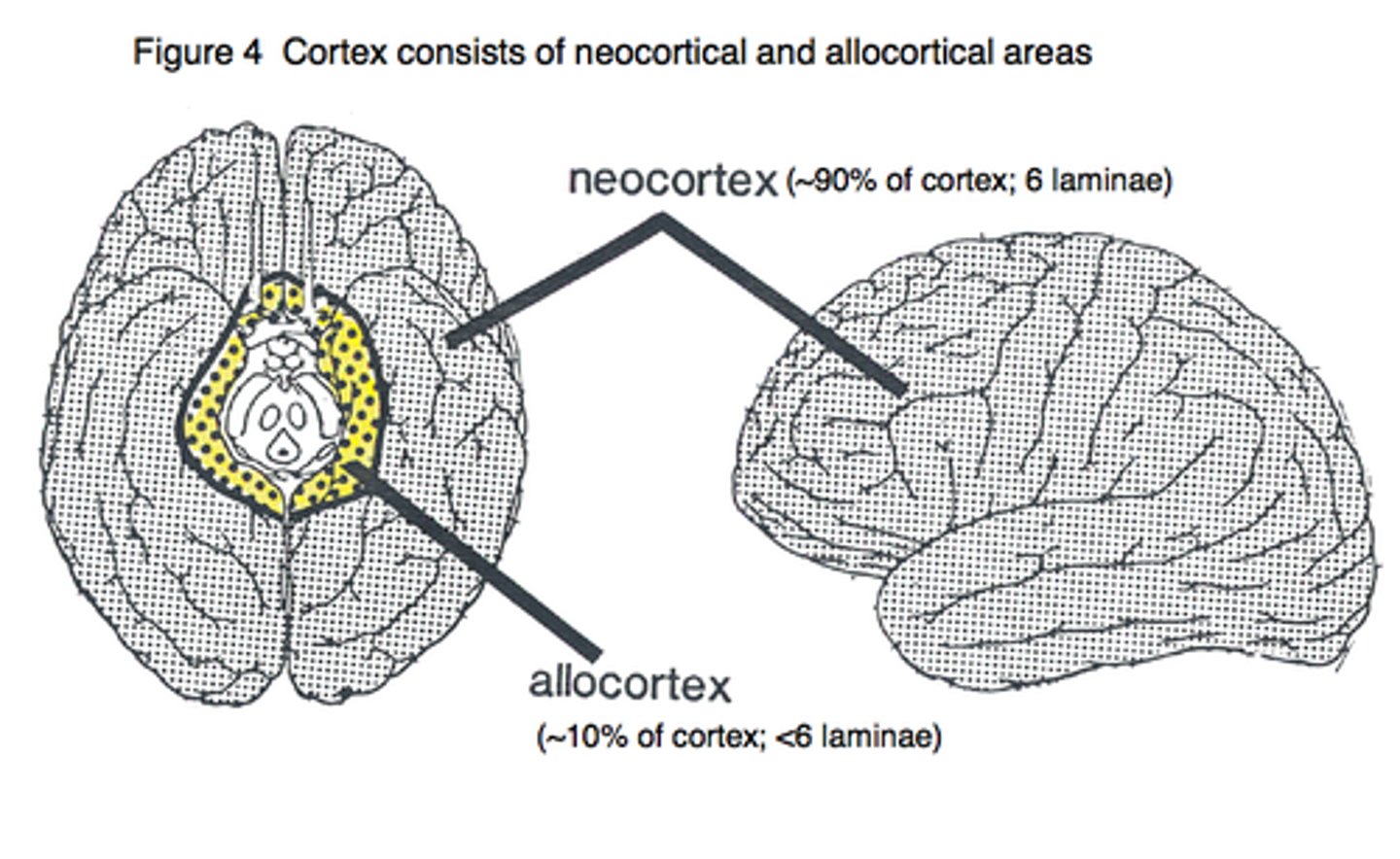
In REGIONS of cortex, the cortex is divided based on the _________________.
A. number of layers
B. order of development
number of layers
SUBDIVISIONS - order of development (neo, paleo, archi)
● Composed of 3 layers
● Found in the hippocampal formation and the piriform / primary olfactory cortex
A. ALLOCORTEX
B. MESOCORTEX
ALLOCORTEX (All = 3 letters)
all are HIPPOcrites and mabaho (olfactory),
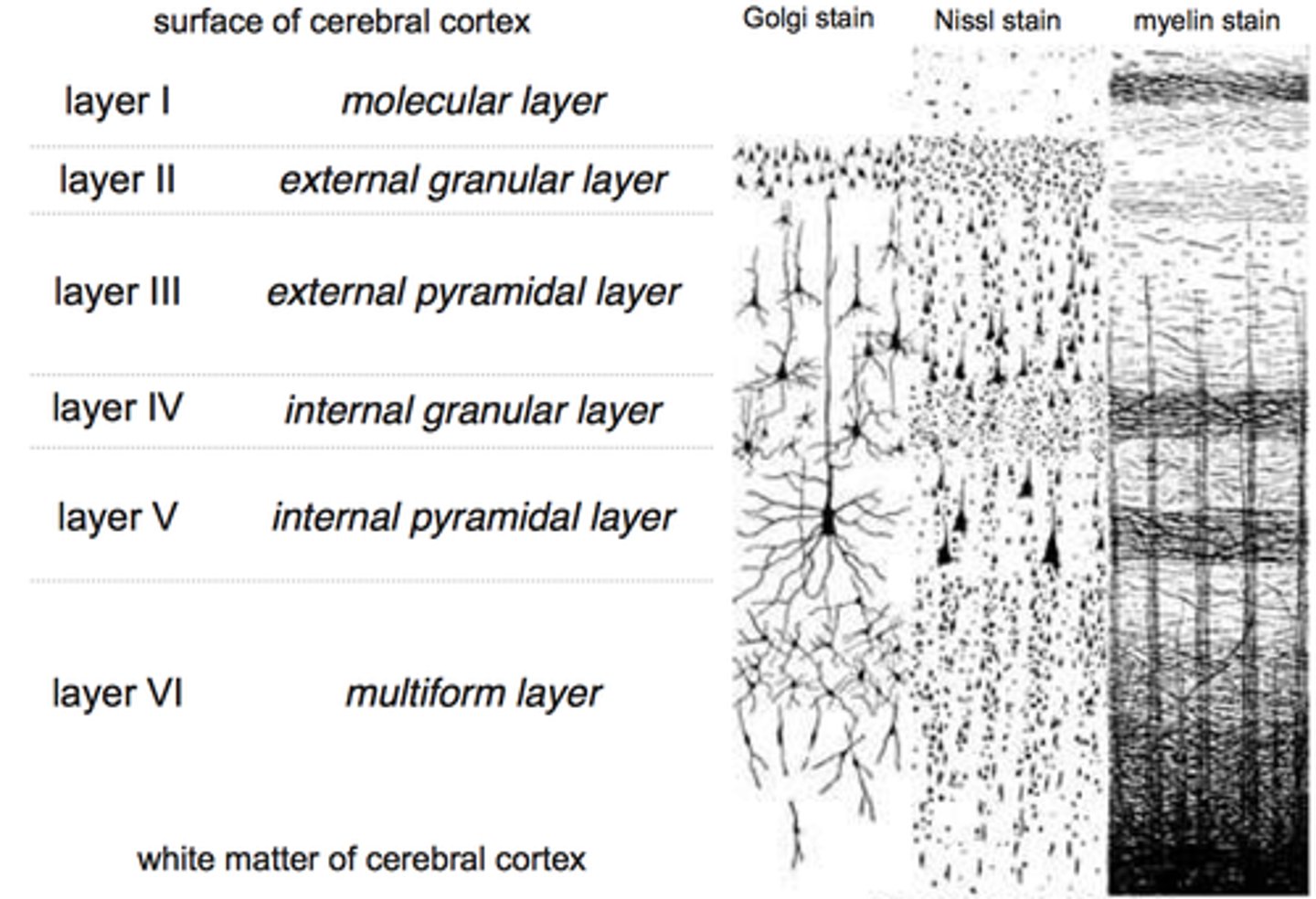
● The prototype cortex
● Composed of 6 layers
A. ISOCORTEX
B. MESOCORTEX
ISOCORTEX
Mesocortex is around 3-6 layers, depending on location
● Concentrated in the deepest layers of the cortex
● Inferior dendrites branches within the same cellular layer
● Superior dendrites ascends towards the surface and branch in the superficial layers
A. FUSIFORM CELLS
B. HORIZONTAL CELLS (OF CAJAL)
FUSIFORM CELLS
● Axon arises from the inferior pole as projection, association, and commissural fibers
Small neuron and its axon runs parallel to the surface and synapse with dendrites of pyramidal cells
A. FUSIFORM CELLS
B. HORIZONTAL CELLS (OF CAJAL)
HORIZONTAL CELLS (OF CAJAL)
The inferior dendrites of FUSIFORM CELLS branch within the same cellular layer while its superior branches goes to the surface.
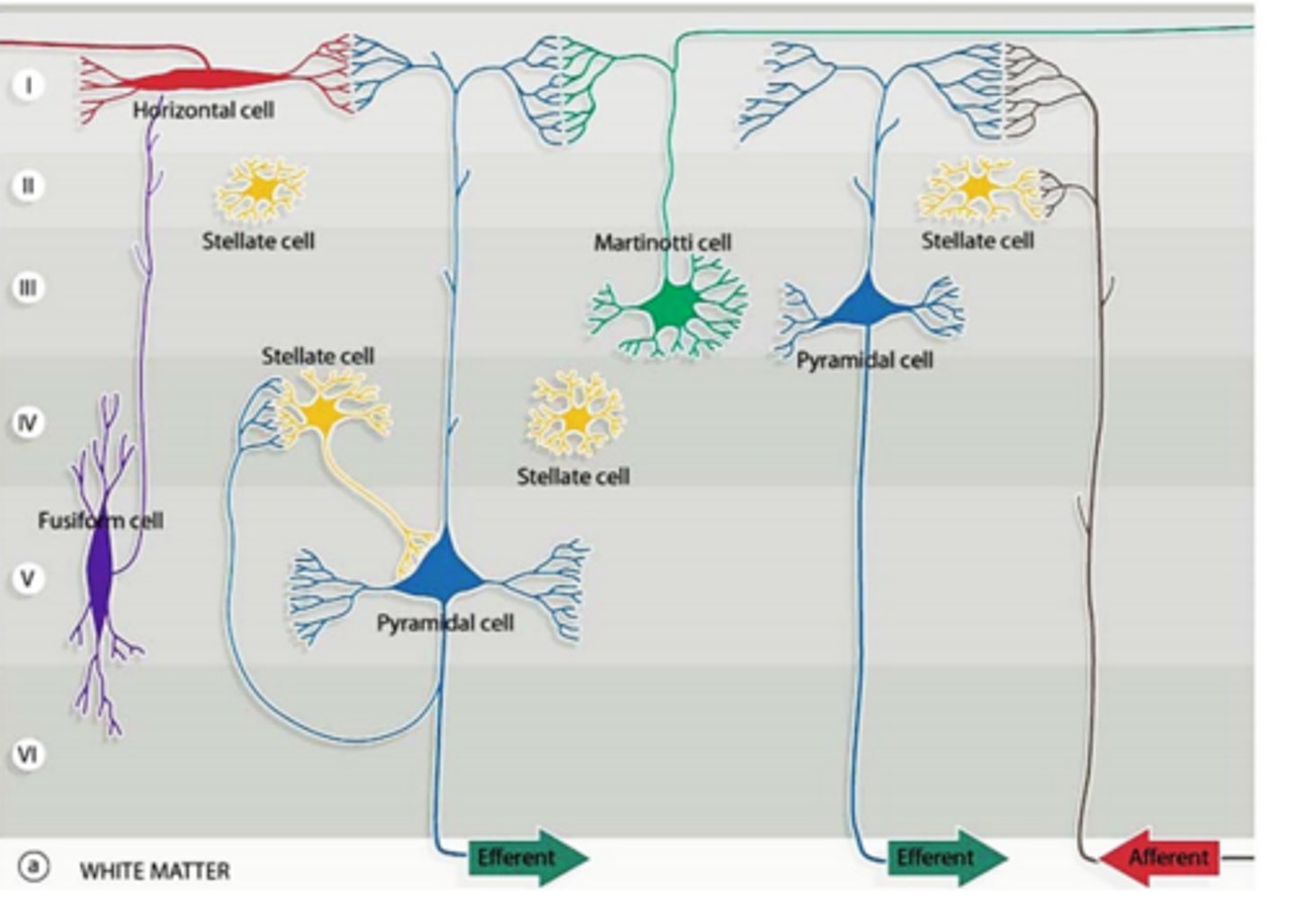
● Multipolar neurons present in all layers
● Short dendrites
● Axon is directed toward the surface and ends in the most superficial layer as origin of few short collateral branches
A. STELLATE CELLS
B. CELLS OF MARTINOTTI
CELLS OF MARTINOTTI
The axons of stellate cells do not go towards the most superficial layer. Its short axons that terminate on nearby neurons.
Seen in association areas of the brain
A. Homotypical
B. Heterotypical
Homotypical
→ All layers are equally developed
→ Well developed layers II & IV
→ Located in SENSORY areas (postcentral gyrus, superior temporal gyrus, parts of hippocampal gyrus)
A. Granular
B. Agranular
Granular
▪ Predominant cells are stellate cells
▪ Receive thalamocortical fibers (sensory functions)
▪ Well developed layers III & V
▪ Located in MOTOR areas of the brain (precentral gyrus, other areas of frontal lobe)
A. Granular
B. Agranular
Agranular
▪ Predominant cells are pyramidal cells (motor functions)
▪ These cells send efferent fibers
Association areas have 2 types: Unimodal and Heteromodal.
BA 9, 10, 11, 12: PREFRONTAL CORTEX is what type of association area?
Heteromodal
Association areas have 2 types: Unimodal and Heteromodal.
BA 5,7 (secondary sensory area) is what type of association area?
Unimodal
■ BA 5,7: secondary sensory area
■ BA 18,19: secondary visual area
■ BA 42: auditory association area
Association areas have 2 types: Unimodal and Heteromodal.
Wernicke's Area (temporoparietal association area) is what type of association area?
Heteromodal
What type of association area is BA 42?
Homotypical unimodal
BA 42 = Secondary Auditory association
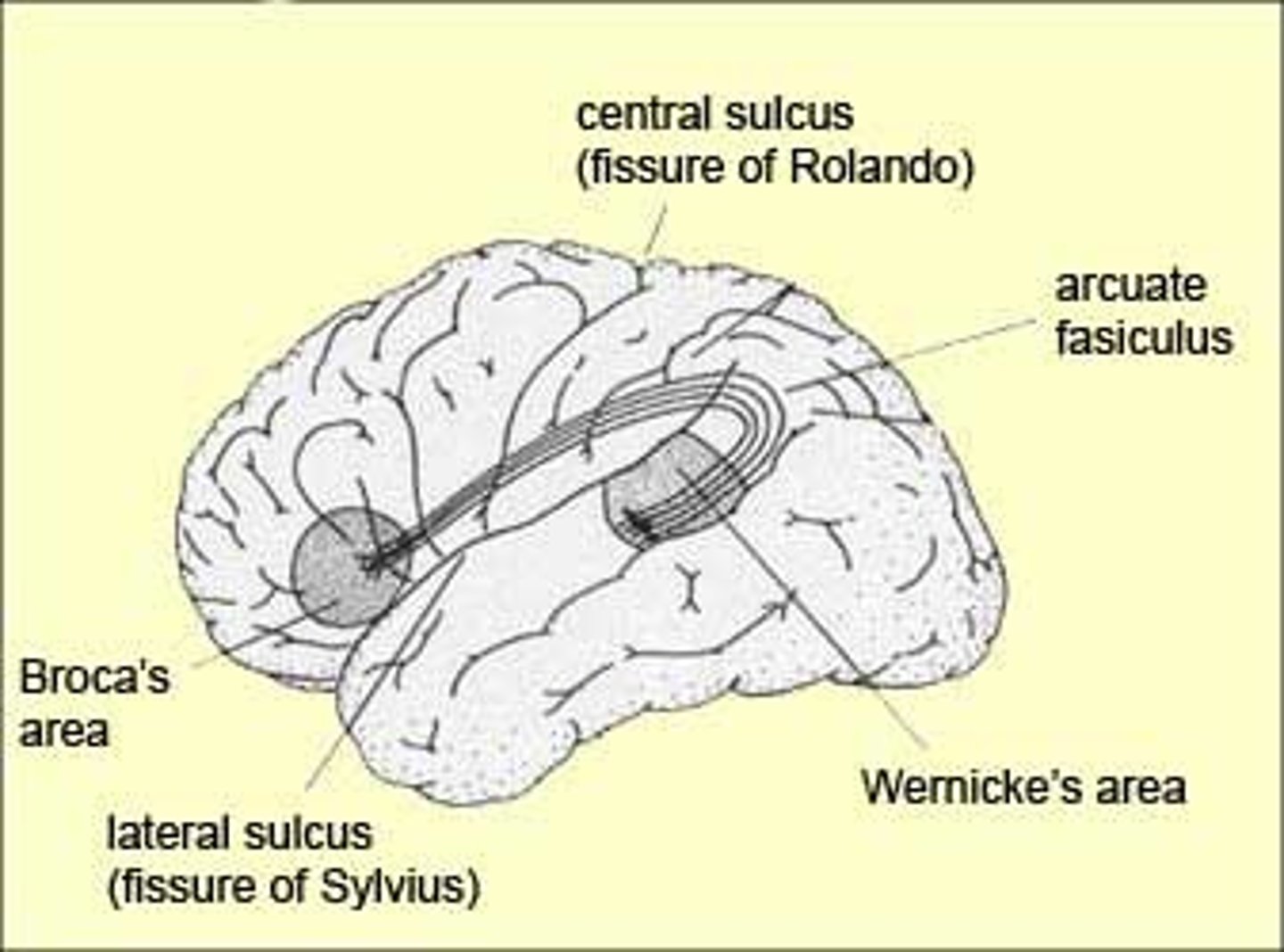
Wernicke's Area is connected to the Broca's area by what association fiber?
arcuate fasciculus
Failure to recognize visual stimuli when appropriate systems are intact
A. Alexia
B. Agnosia
Agnosia
Alexia: inability to read
Lesion in this BA will lead to alexia, dyslexia and agraphia.
ANGULAR GYRUS (BA 39)
- Gustatory/Taste Center
- : Inferior parietal lobule
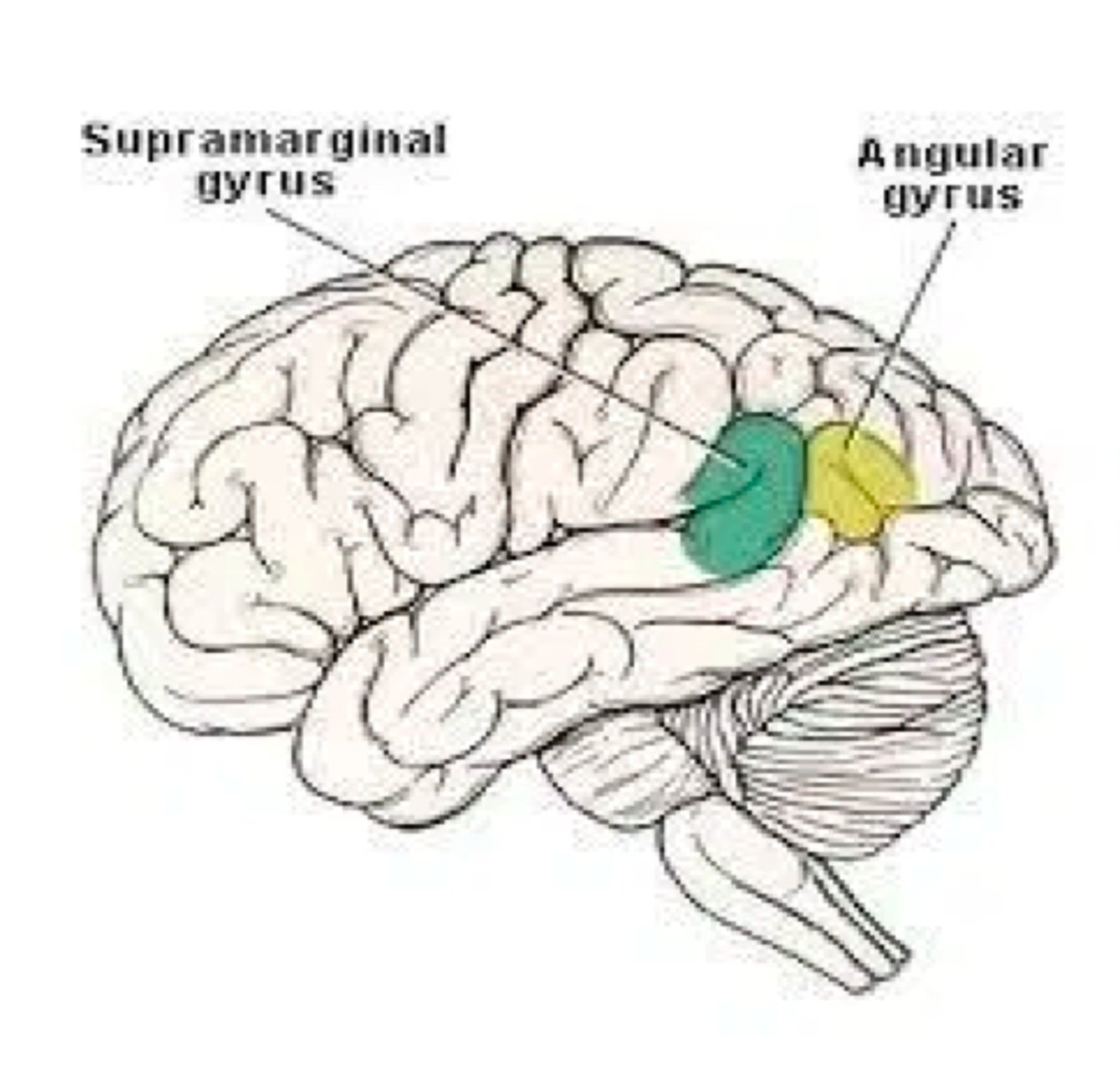
The lesion is located on the supramarginal gyrus (BA 40).
What type of agnosia will manifest?
A. Visual
B. Tactile
C. Auditory
TACTILE
Visual - Temporal aspect of visual unimodal association areas
Auditory - Posterior part of superior temporal gyrus (BA 22)
"Stand up, walk, and pick up the trash" - patient CANNOT follow ALL commands (multi-step), but CAN follow instructions given one at a time
A. IDEOMOTOR APRAXIA
B. IDEATIONAL APRAXIA
IDEATIONAL APRAXIA
Failure to carry out sequences of acts, although individual movements can be made correctly
Lesion: Dominant parietal lobe or corpus callosum
● Inability to execute fine acquired movements
● Lesion: Contralateral frontal lobe
A. IDEOMOTOR APRAXIA
B. MOTOR / KINETIC APRAXIA
MOTOR / KINETIC APRAXIA
● Lesion: Contralateral frontal lobe
Patients appears to have the feet "glued to the floor," where there is a series of incomplete walking movements, then patient may stride for one or two steps, only to develop another series of incomplete ambulatory movement.
A. MOTOR / KINETIC APRAXIA
B. GAIT APRAXIA
GAIT APRAXIA
Lesion: Bilateral frontal lobes
● Slow and effortful spoken language with poorly produced sounds
● Ungrammatical, telegraphic speech where the patient deletes many prepositions, nouns, and verbs
A. Lesion in BA 22
B. Lesion in BA 44,45
Lesion in BA 44,45 (Broca's Area)
AKA = Broca's, Expressive, Non-fluent, or Anterior aphasia, motor aphasia
Broca = Broken speech + with RIGHT HEMIPLEGIA
Rapid production of words with preserved grammatical construction, but cannot find the correct words to express thoughts
A. Lesion in BA 22
B. Lesion in BA 44,45
Lesion in BA 22 (Wernicke's Area)
Manifestation: a lot of verbal output but no meaning + NO HEMIPLEGIA
The patient understands and can have normal (not slow) output, causing frustration and repetition of response until correct.
A. Conduction aphasia
B. Global aphasia
Conduction aphasia
Lesion: Arcuate Fasciculus (Conduction pathway from Wernicke's area to the Broca's area)
Controls language, speech, behavior, analytical thinking, calculations and verbalizations
A. Non-Dominant Hemisphere
B. Dominant Hemisphere
Dominant Hemisphere
→ Non-Dominant Hemisphere: controls spatial perception, recognition of faces, and music
. A 2-year-old vehicular accident victim sustained damage to his dominant hemisphere specifically in the opercular area. Which of the following outcomes would MOST likely occur after several years?
A. He would not be able to speak.
B. He would likely develop normal speech
He would likely develop normal speech.
AGE 10 -establishment of cerebral dominance
The motor speech area is located in the _____ gyrus.
a. Superior temporal
b. Inferior frontal
c. Angular
Inferior frontal gyrus
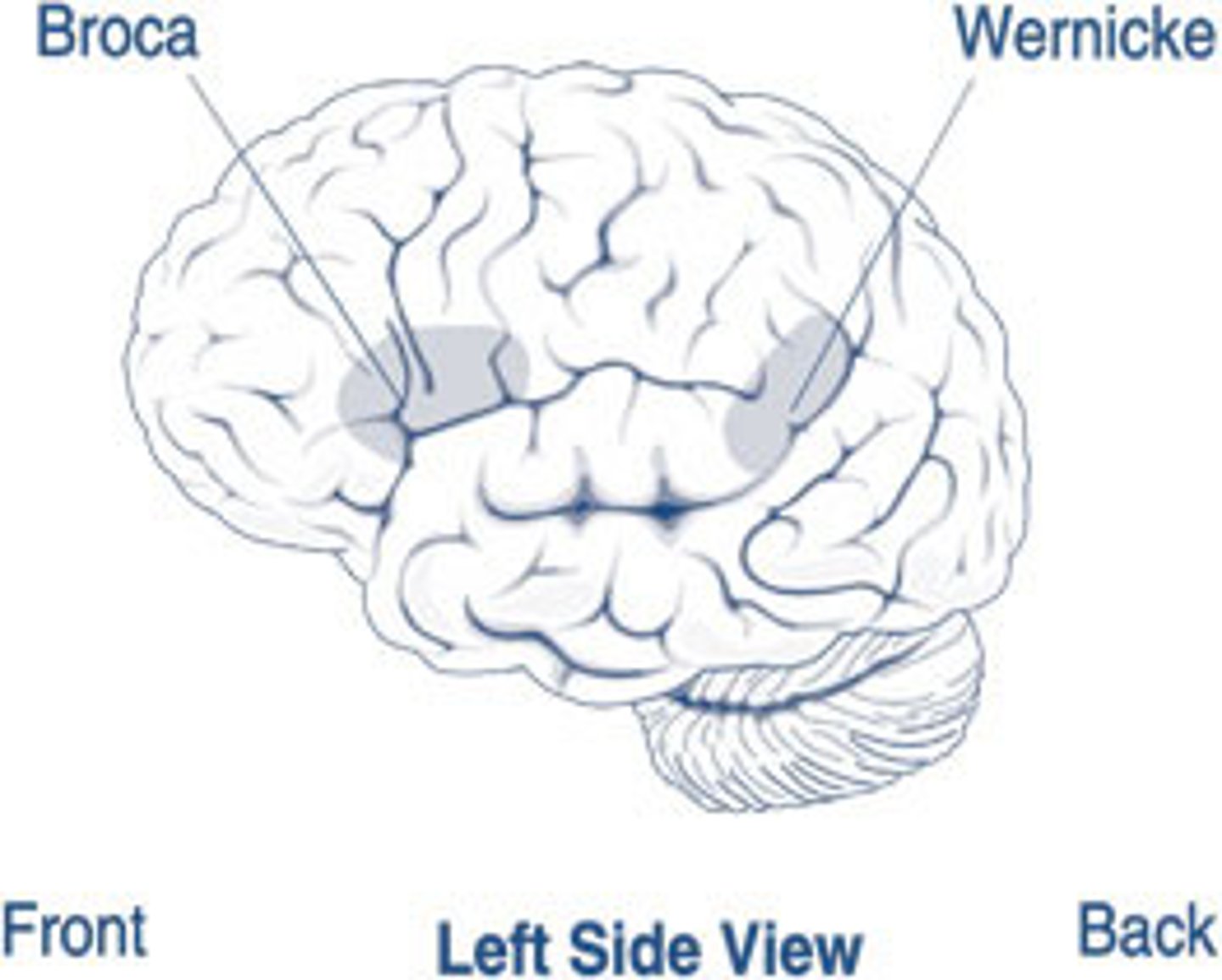
Majority of the left-handed individuals are which hemisphere dominant?
a. Right
b. Left
c. Equally dominant
Left