Anatomy and Physiology - Tissues
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
91 Terms
Nervous Tissue
sensing stimuli and sending electrical impulses throughout the body
Muscle Tissue
provides movement
epithelial tissue
cover and protect the body
connective tissue
provide support
nervous tissue is made up of
neurons and glial cells
Neurons
a nerve cell; the basic building block of the nervous system
Glial Cells
cells in the nervous system that support, nourish, and protect neurons
Cell body (soma)
contains the nucleus and other parts of the cell needed to sustain its life
Dendrites
Branchlike parts of a neuron that are specialized to receive information.
Axon
the extension of a neuron, ending in branching terminal fibers, through which messages pass to other neurons or to muscles or glands
Types of muscle tissue
skeletal, cardiac, smooth
Skeletal muscle
A muscle that is attached to the bones of the skeleton and provides the force that moves the bones.

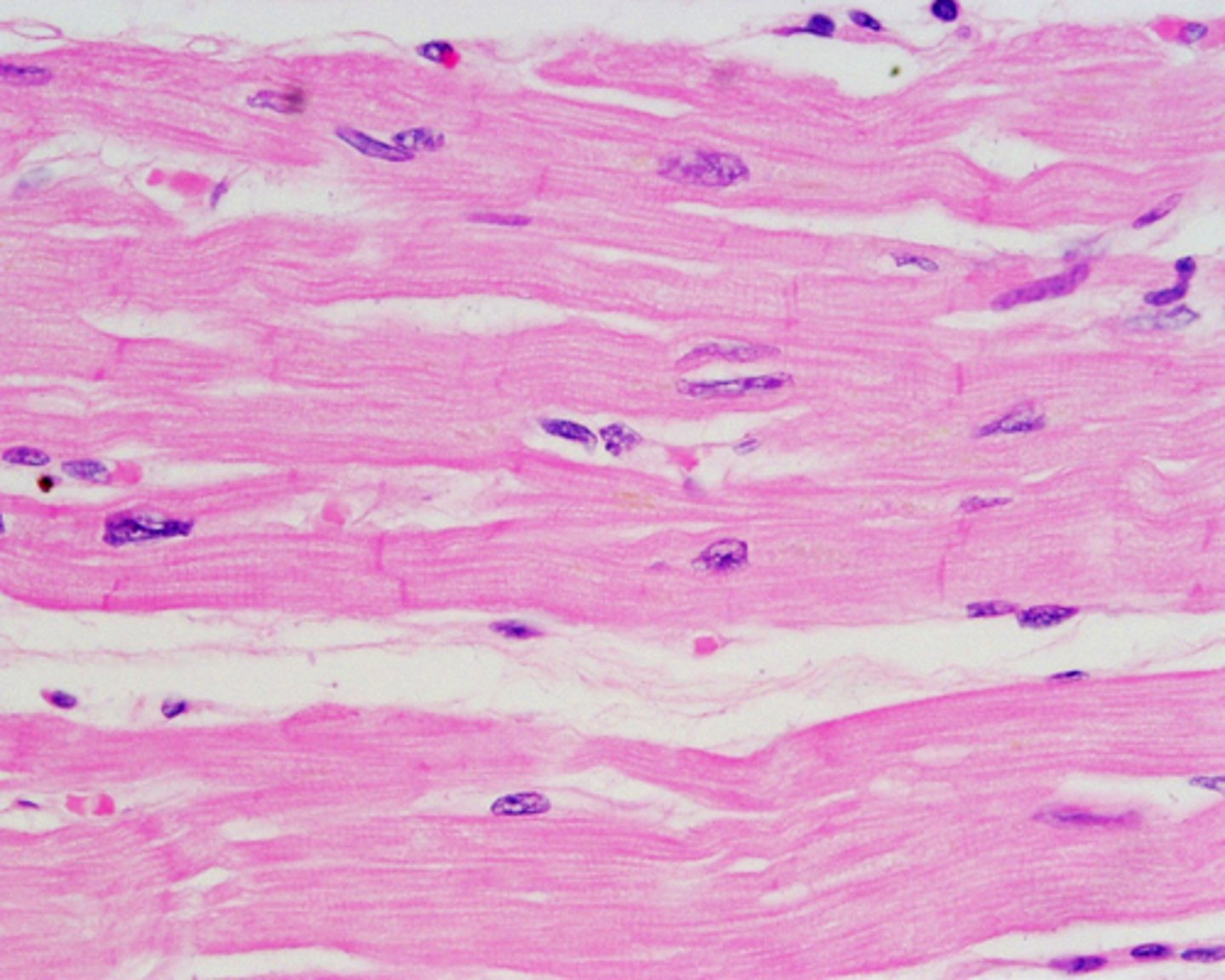
Cardiac muscle
Involuntary muscle tissue found only in the heart.
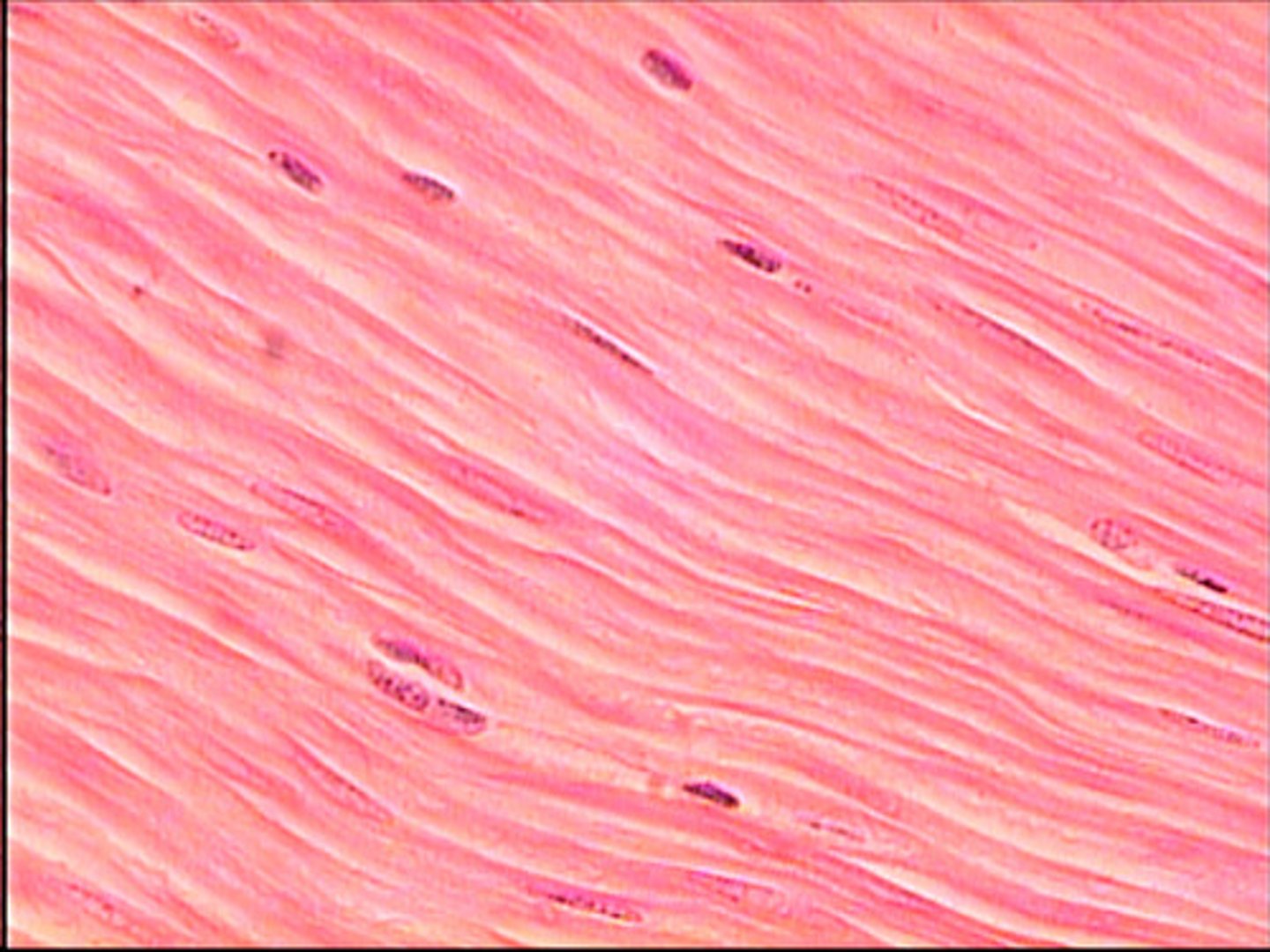
Smooth muscle
Involuntary muscle found inside many internal organs of the body
Proper Epithelium
covers and lines your outer and inner body
Glandular Epithelium
forms your glands and secretes hormones and other substances
primary epithelium
protects whole body inside and out
epithelial tissue function
protect your deeper layers of tissue from injury or infection
Avascular
without a blood supply
Epithelial tissues are
avascular
Squamous Cells
flattened and scale-like
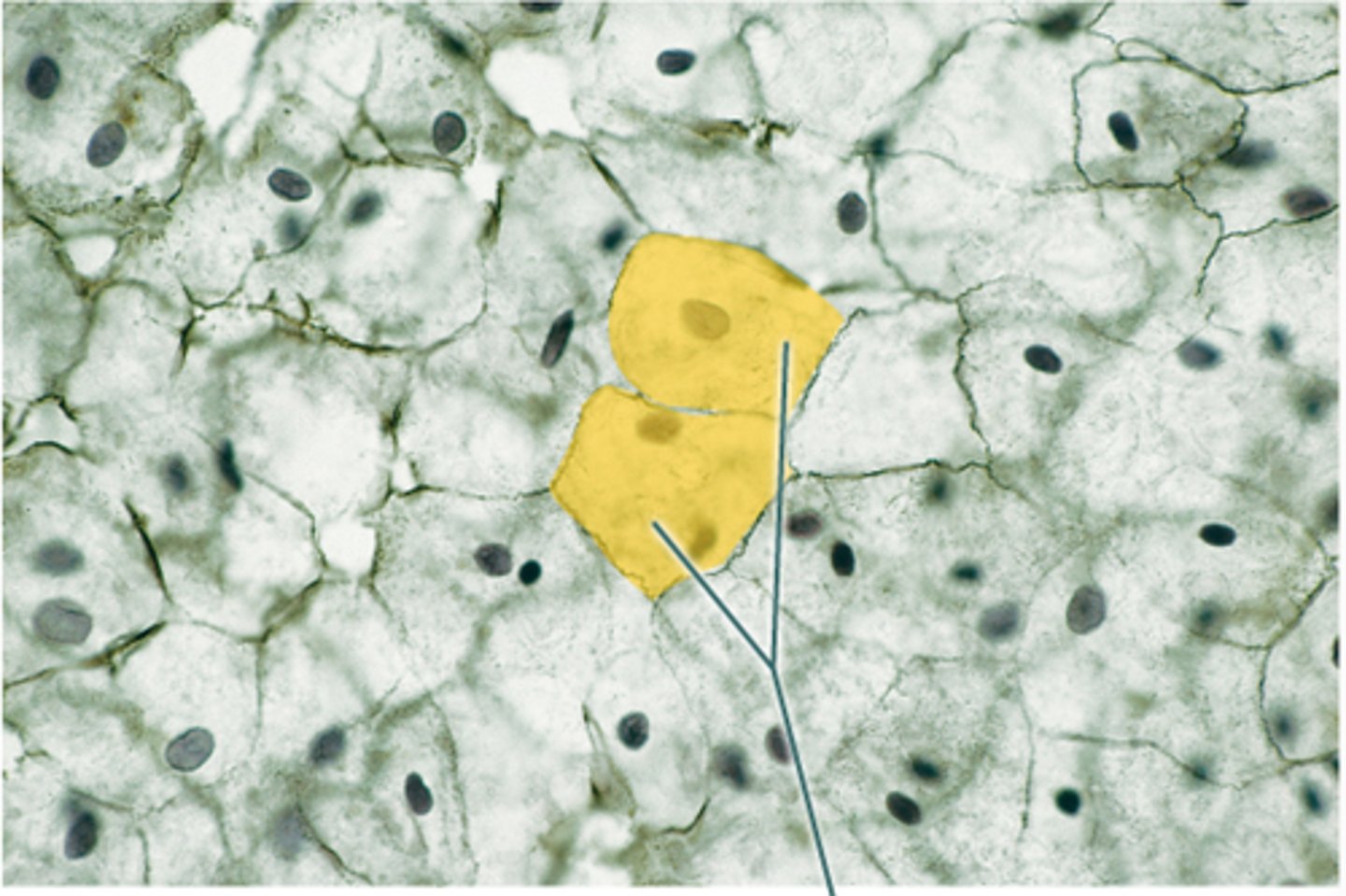
Squamous Cells function
fast absorption and diffusion, making thin membranes
Cuboidal Cells
cube shaped cells

Cuboidal Cells function
absorb nutrients and produce secretions
Columnar Cells
tall and column shaped
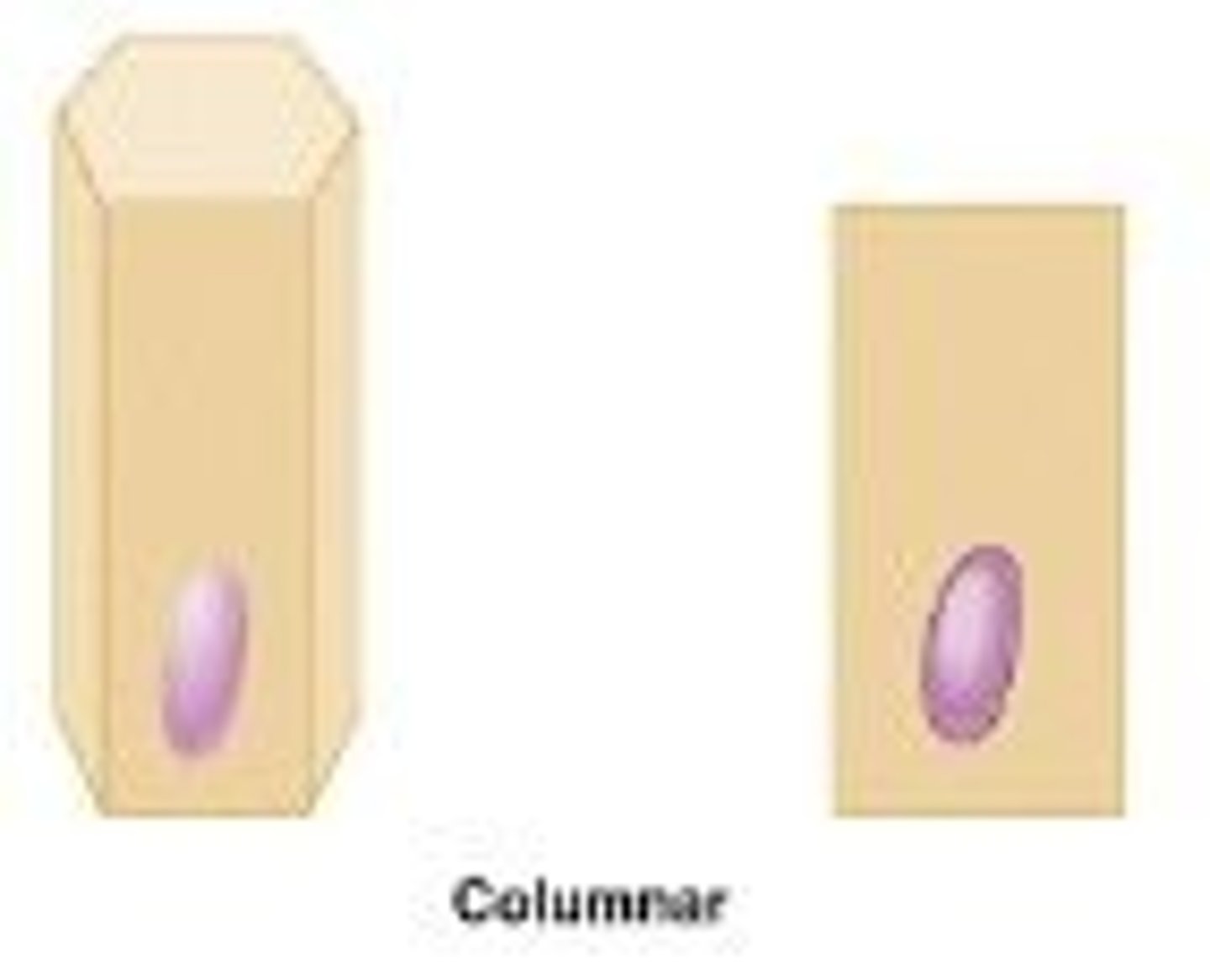
Columnar Cells function
secretion and absorption
Simple Epithelium
single layer of cells
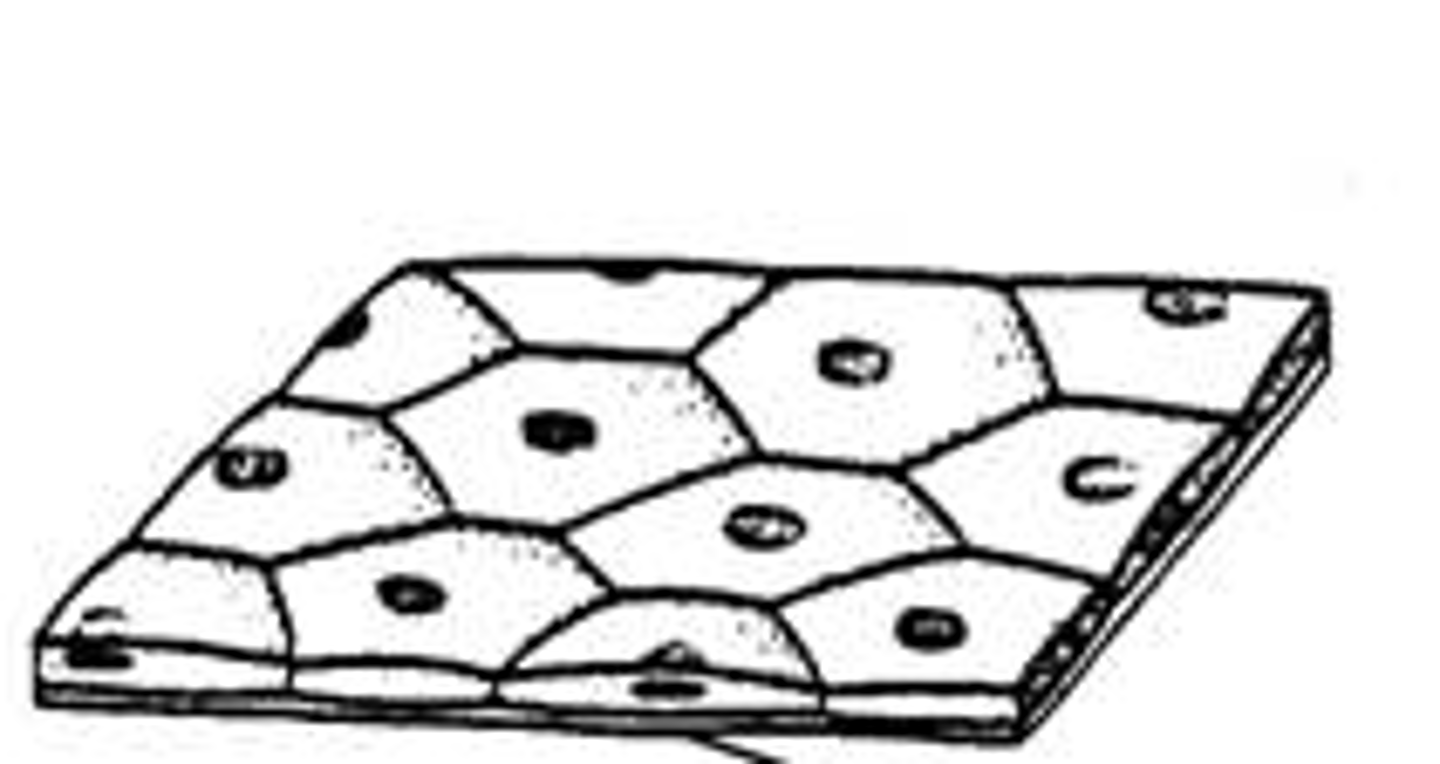
Stratified Epithelium
several layers of cells
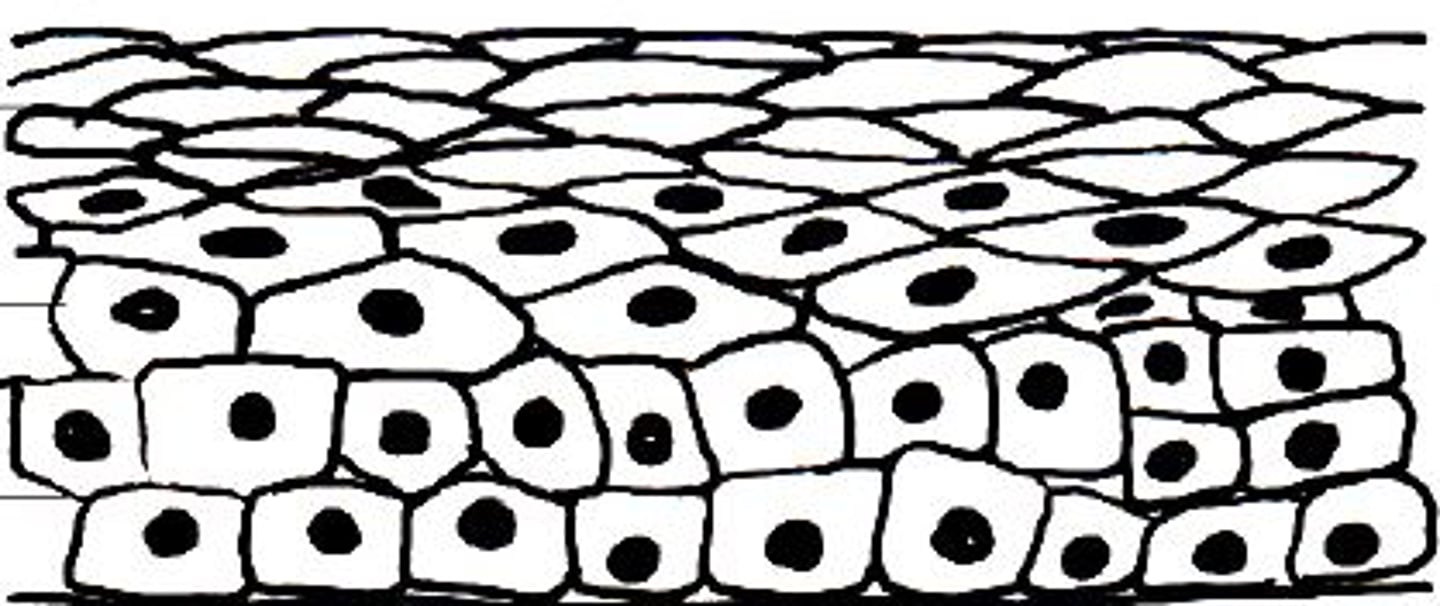
Pseudostratified Epithelium
Appears layered but is a single layer.
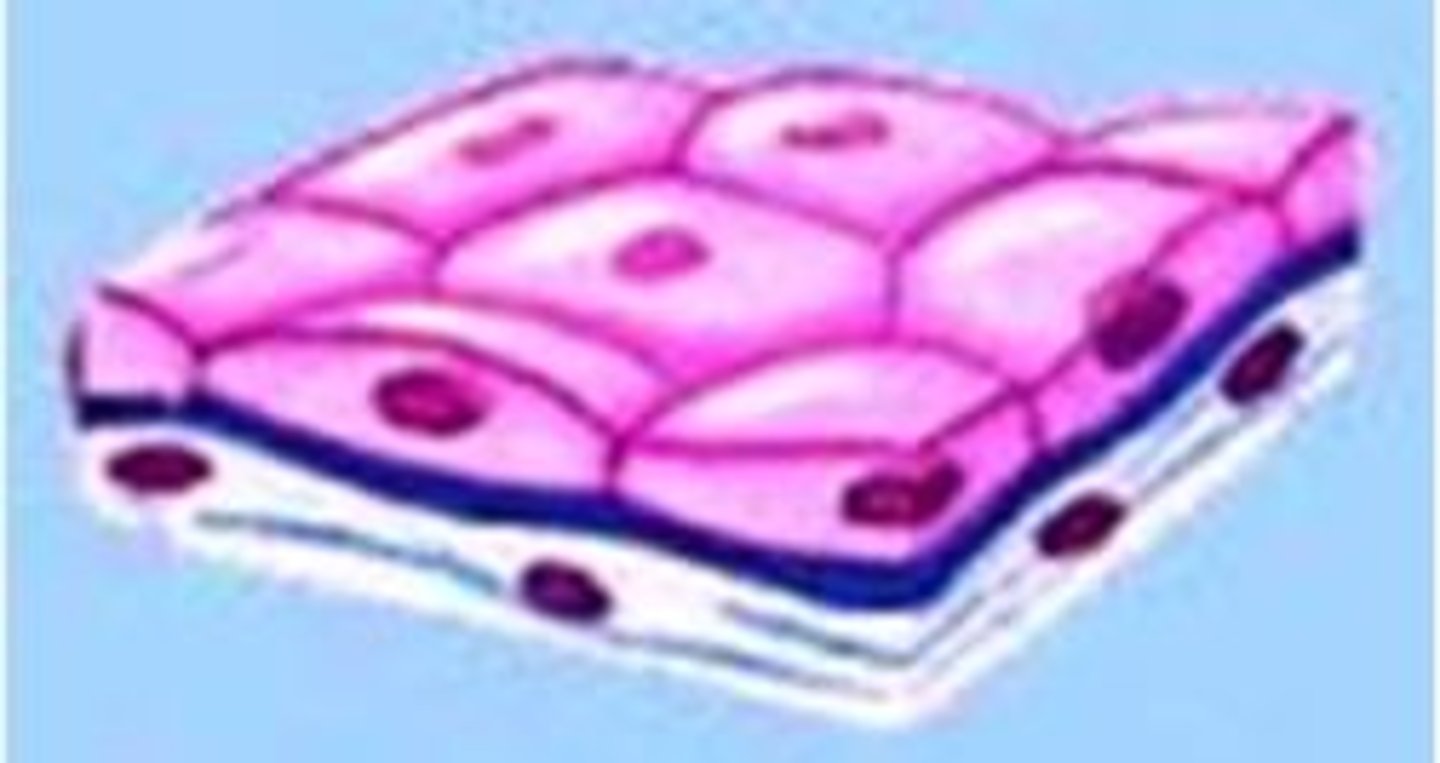
simple squamous epithelium
single layer of flattened cells
simple cuboidal epithelium
single layer of cube shaped cells
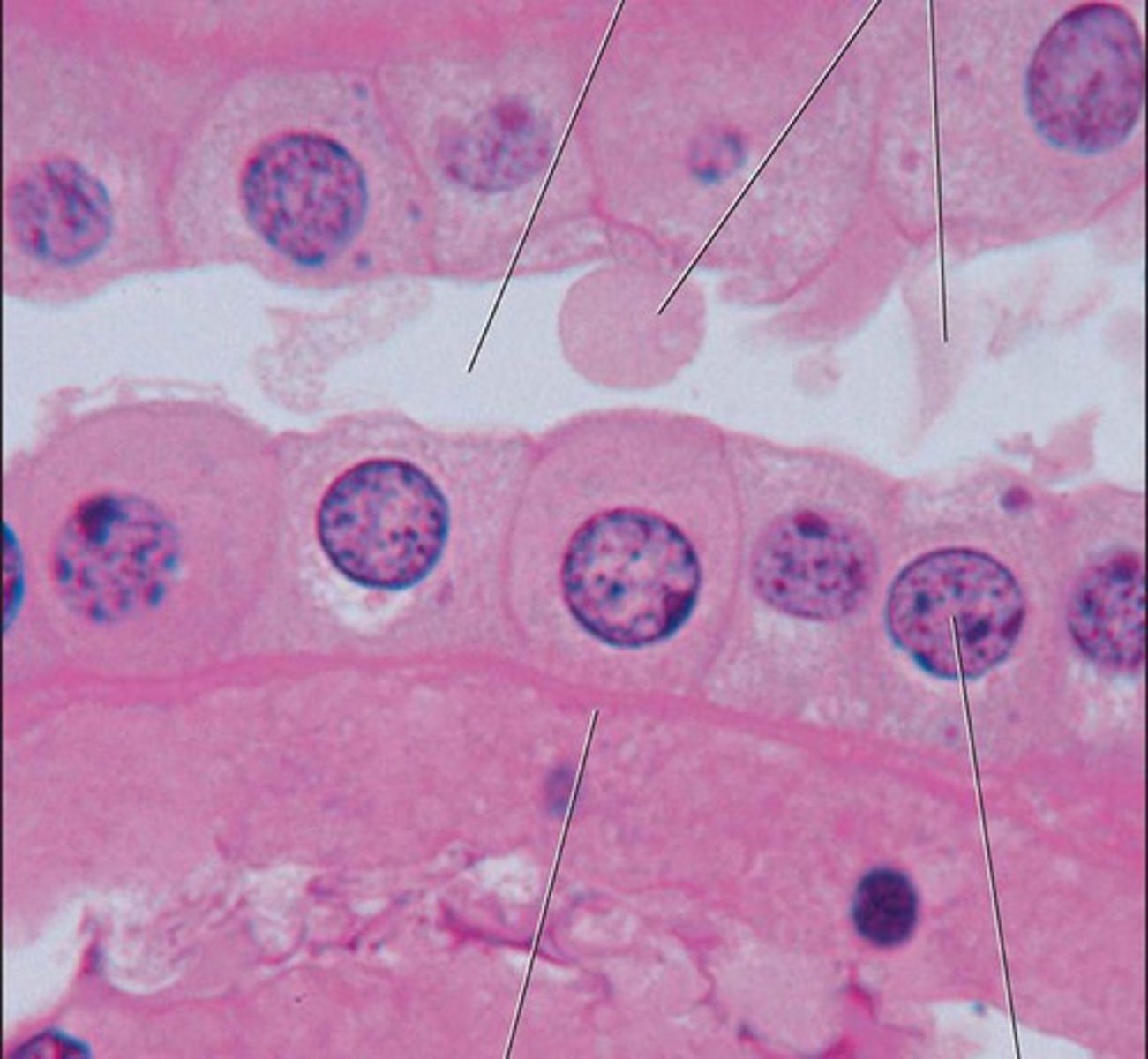
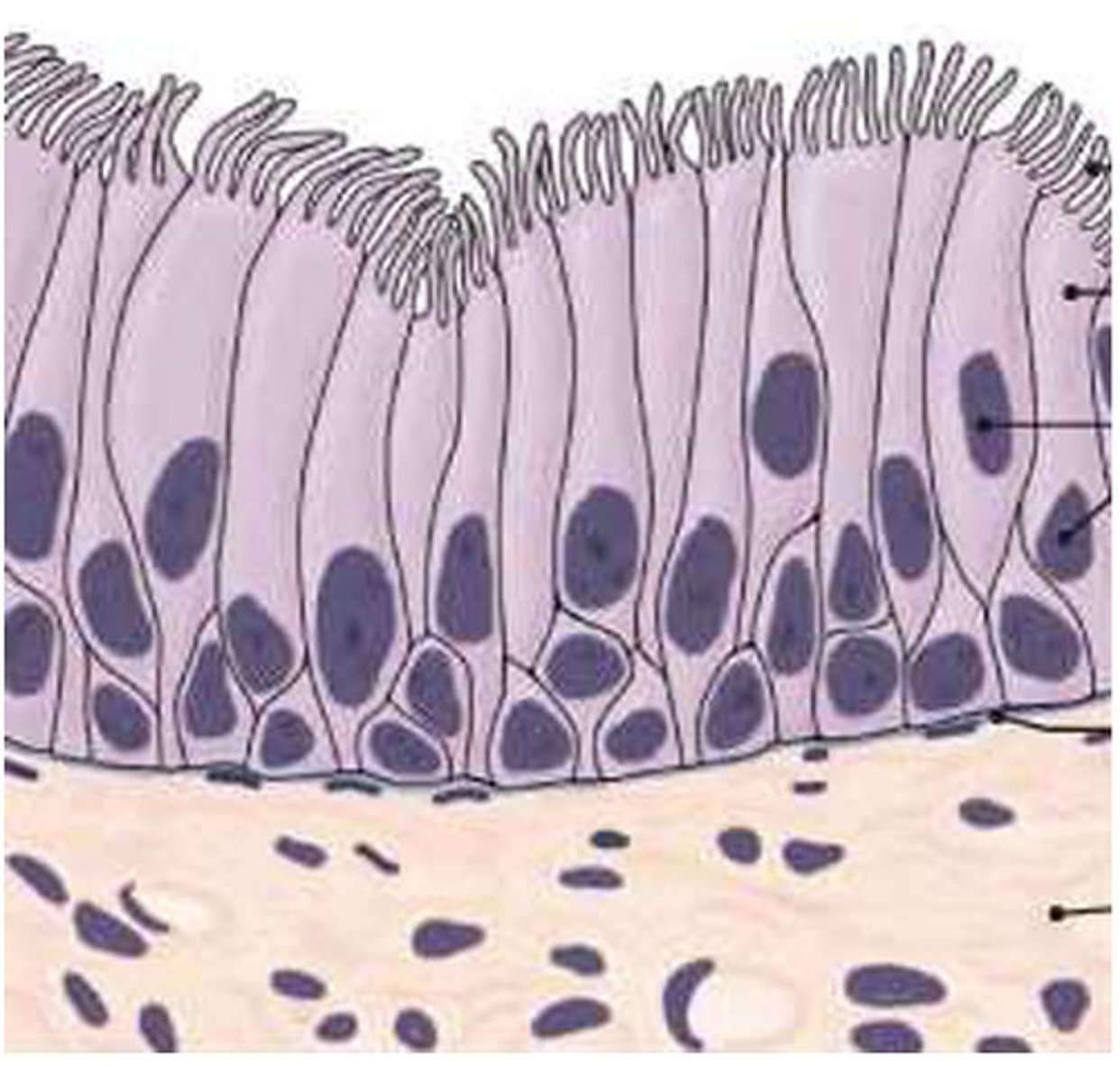
simple columnar epithelium
Made up of a single layer of tall cells that fit closely together
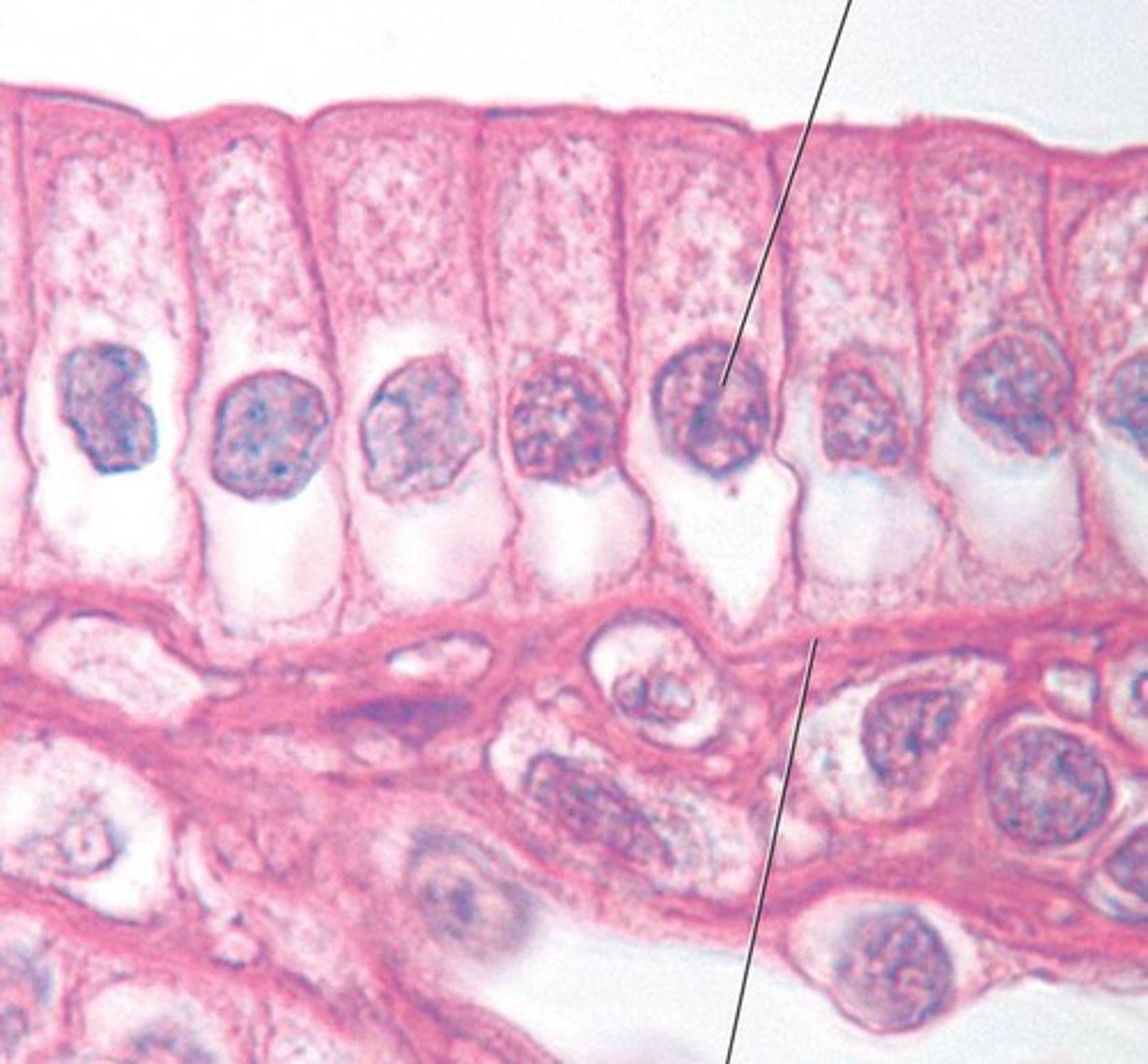
stratified squamous epithelium
multiple layers of flat cells
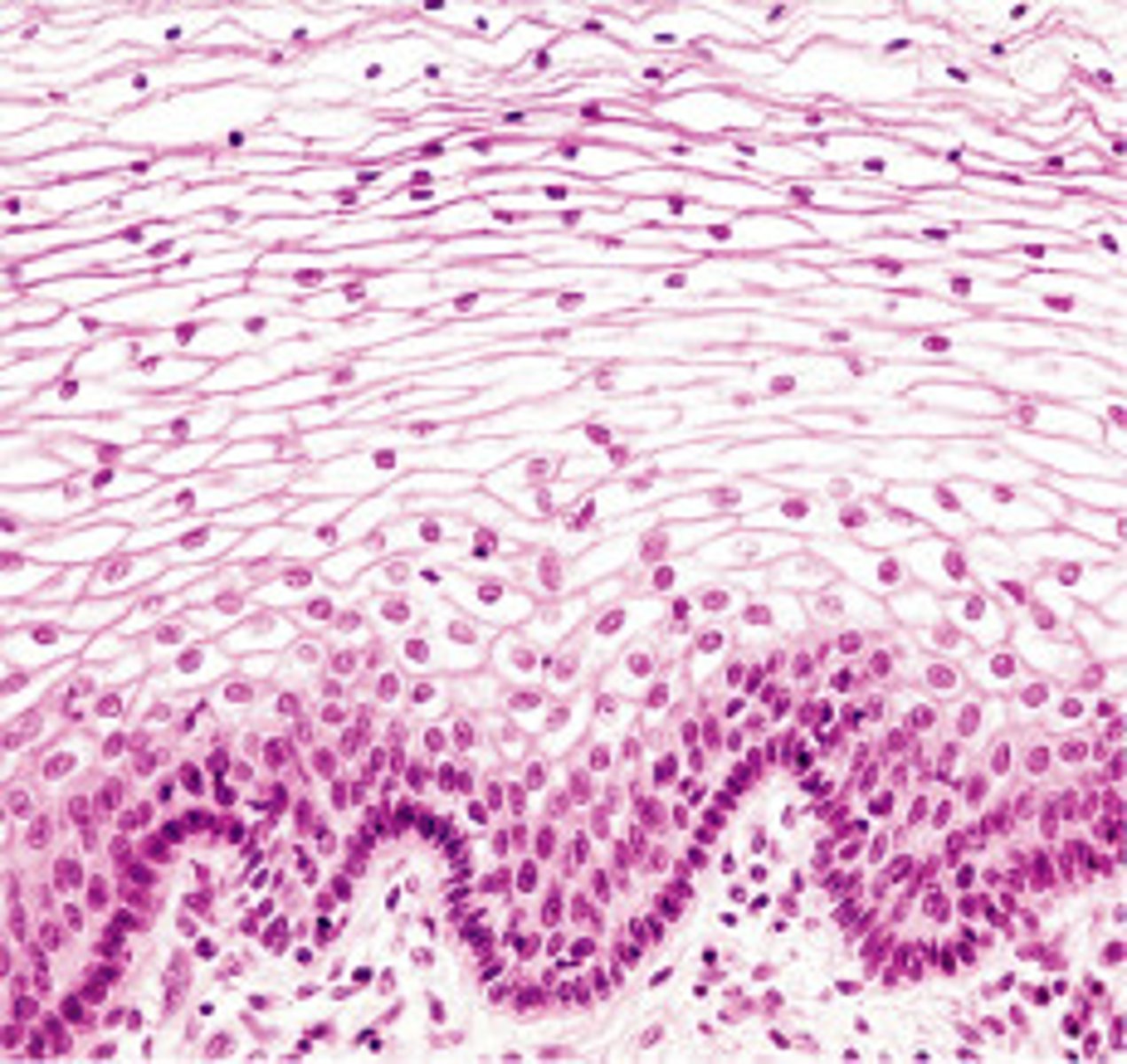
stratified cuboidal epithelium
multiple layers of cube shaped cells
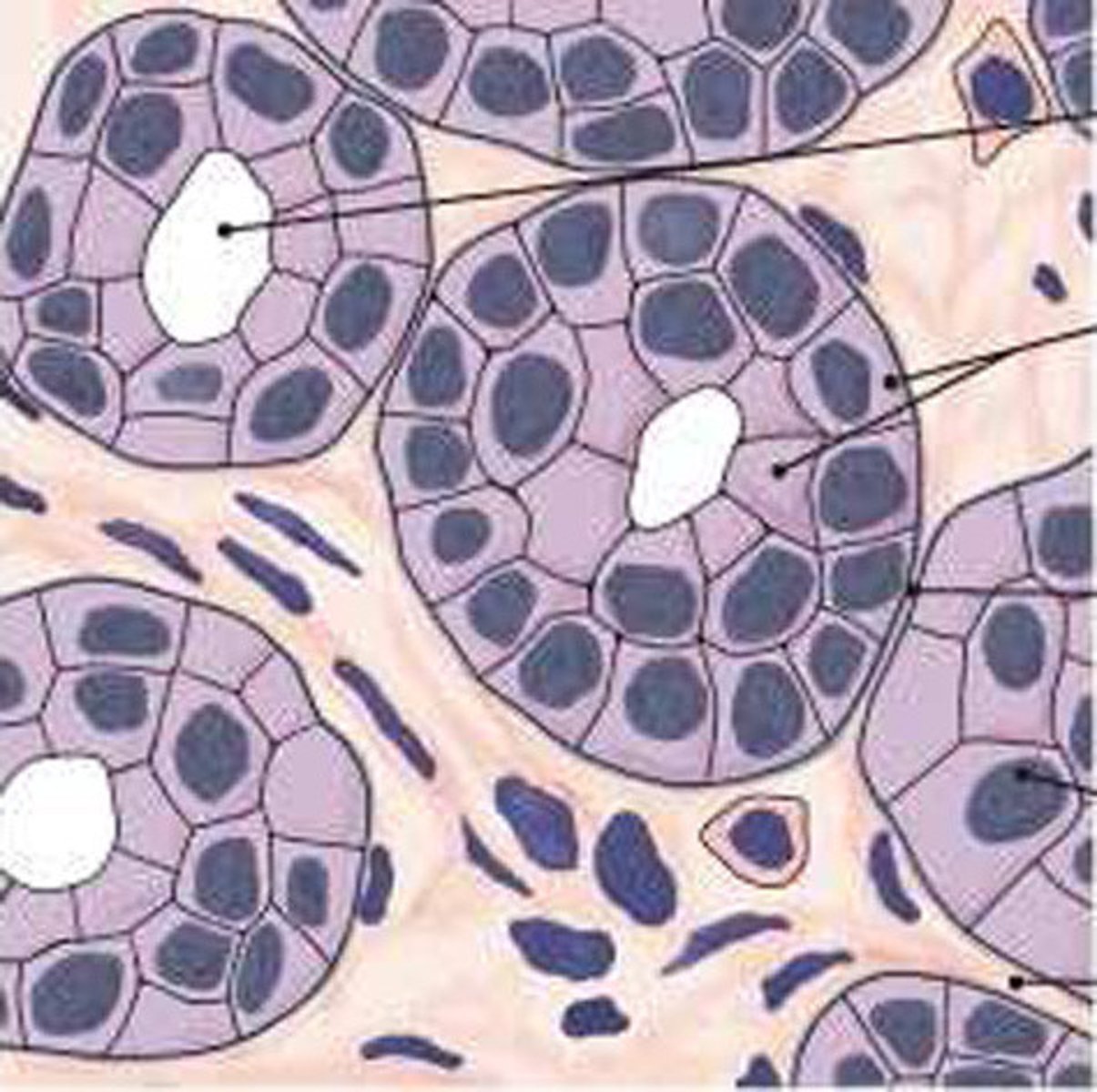
stratified columnar epithelium
tissue that consists of two or more layers of column-like cells
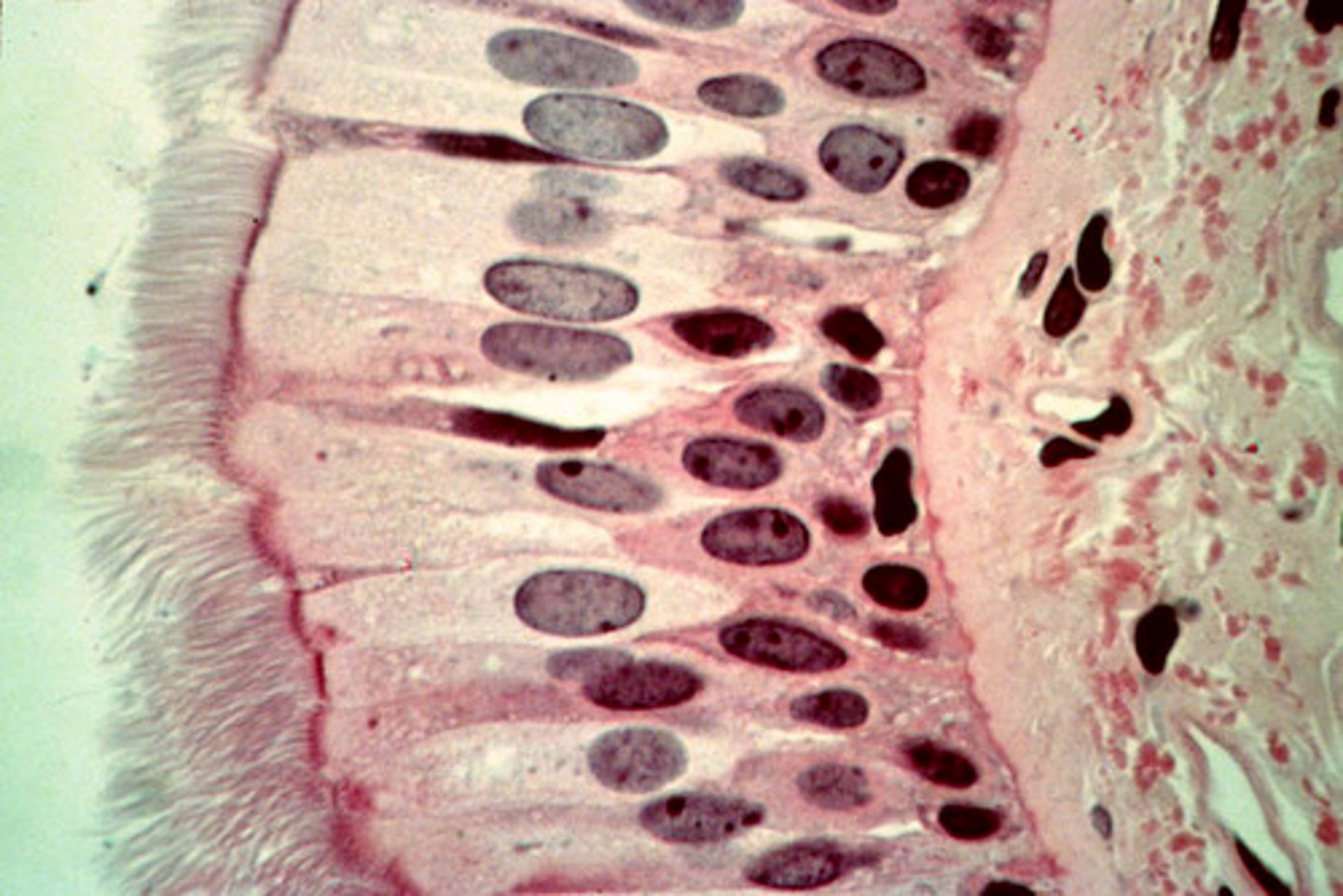
Epithelial cells are
polar
Apical side
faces either the outside of your body or whatever internal cavity its lining
Basal side
faces inside the body toward the blood
basement membrane
Cells at the base of an epithelial layer are attached to this.
glandular epithelium
Composed of cells that are specialized to produce and secrete substances.
endocrine glands
glands that secrete chemicals called hormones directly into the bloodstream
Exocrine glands
secrete chemical substances into ducts that lead either to other organs or out of the body
Proper connective tissue
loose and dense
fat
type of proper connective tissue which provides insulation and fuel storage
connective tissues originate from
mesenchyme
cartilage connective tissue
strong and flexible support material
bone connective tissue
mineralized and forms the skeleton
blood connective tissue
fluid extracellular matrix used to transport substances throughout the body.
Connective tissues have different degrees of
vascularity
all connective tissues are mostly composed of
non living material
extracellular matrix is made up of
ground substance and fibers
Ground substance
fluid or semi-fluid portion of the matrix
collagen fibers
strongest and most abundant
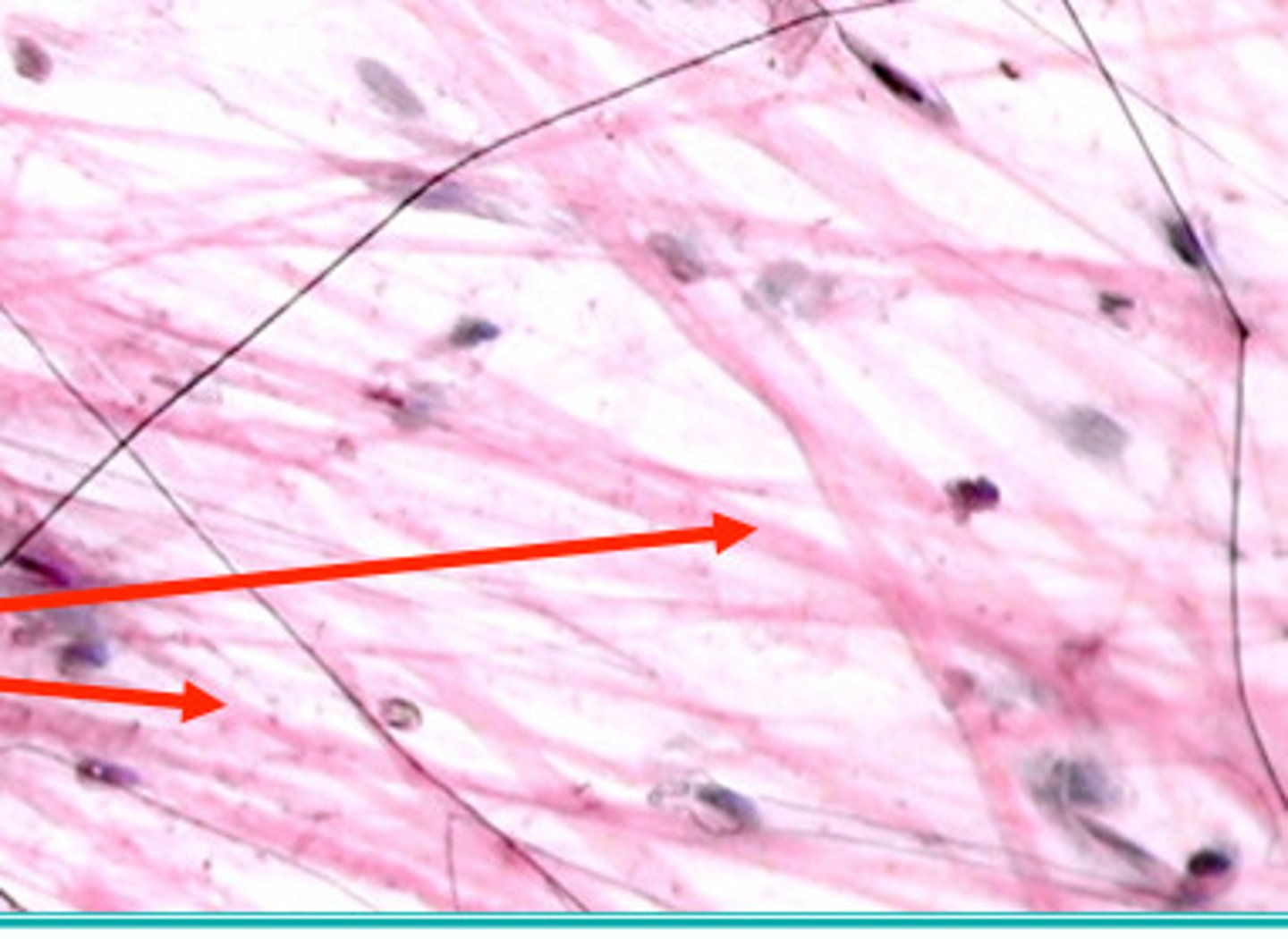
Elastic fibers
Flexible and "stretchy" fibers that add elasticity to tissue
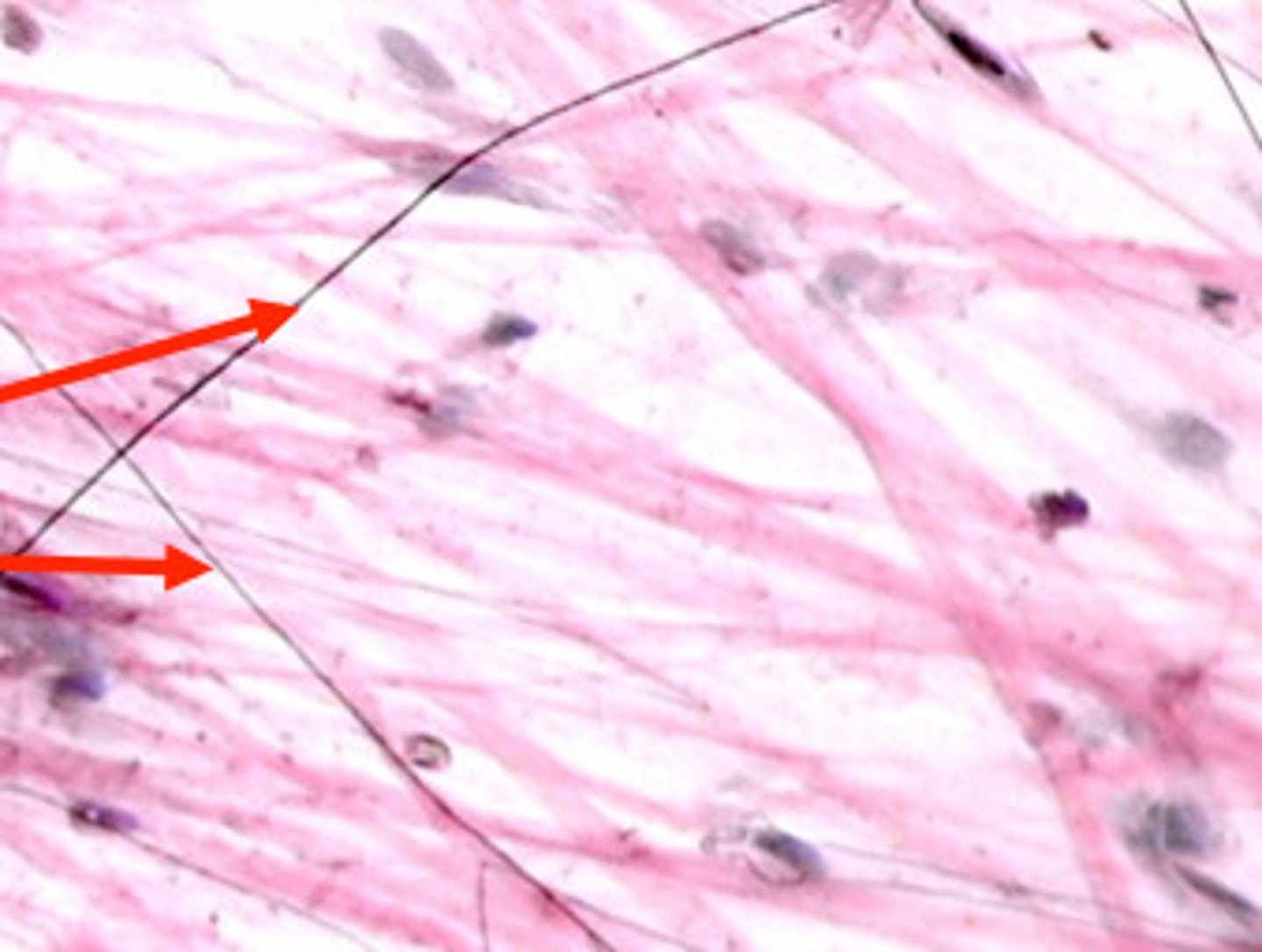
reticular fibers
Fibers made of collagen fibers that are very thin and branched. Form a tightly woven fabric that joins connective tissue to adjacent tissues.
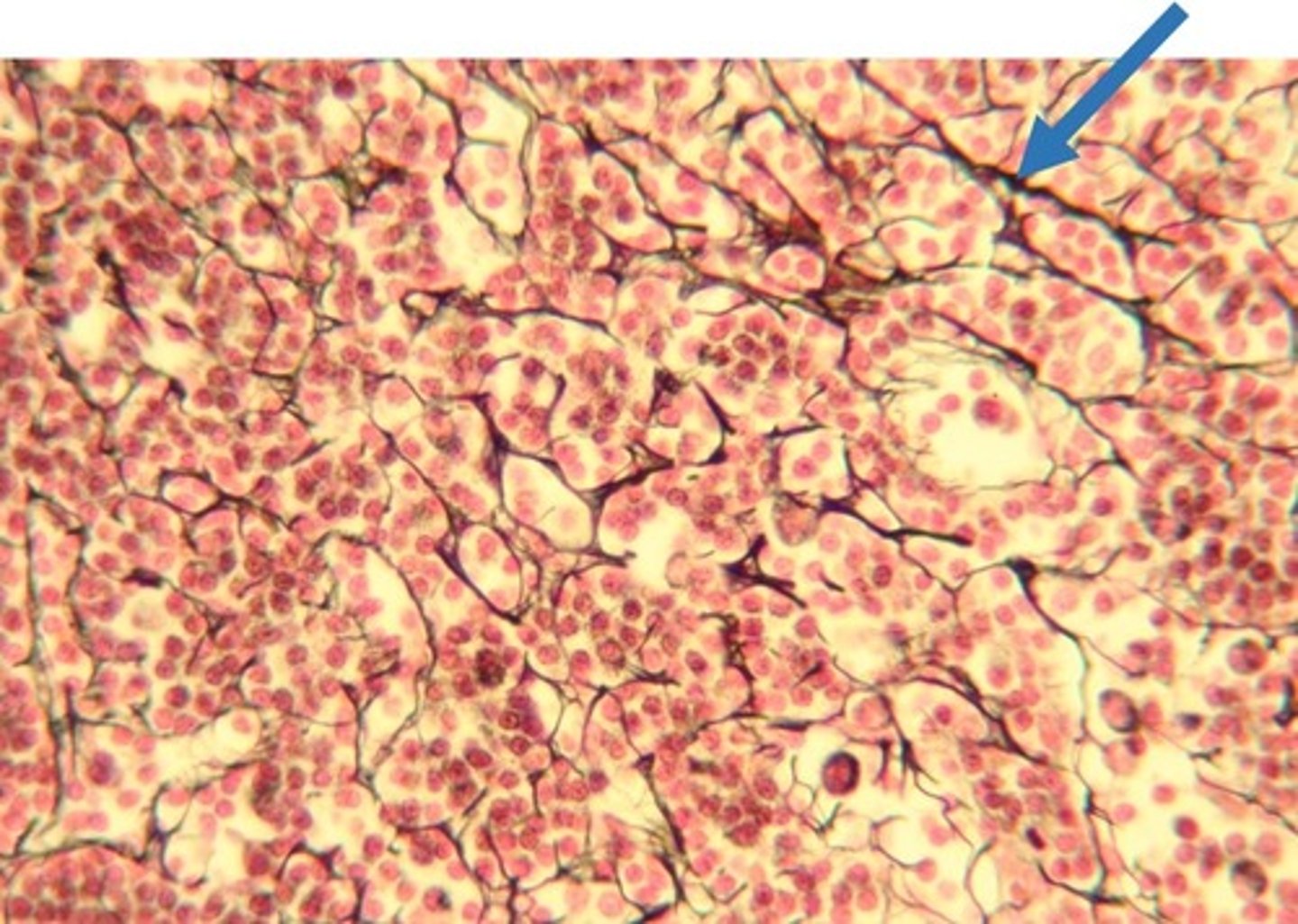
Immature
blast
stem cells are
blast cells
Blast cells function
to secrete the ground substance and fibers that form its unique matrix
Mature
cyte
cyte cells
maintain the health of the matrix but can revert to blast cells to regenerate matrix
Connective tissue proper types
loose and dense
Loose connective tissue
areolar, adipose, reticular
Dense connective tissue
Loose connective tissues have more
cells and ground substance
loose connective tissue have fewer
fibers
Areolar tissue
Binds skin to underlying organs
Adipose tissue
Tissue that stores fat.
Adipose tissue is mostly
cells
reticular tissue
provides a supportive framework to soft organs
reticular connective tissue has what
reticular fibers instead of collagen and elastic fibers
reticular tissue examples
lymph nodes and spleen
reticular tissue is what holds your
blood in place in many of your organs
Loose connective tissue share
airy dispersal of fibers
dense regular tissue
Connective tissue made from collagen fibers that run in the same direction (makes tendons and ligaments)
dense regular tissue examples
tendons and ligaments
tendons
Connect muscle to bone
ligaments
Connect bone to bone
dense irregular tissue
irregularty arranged collaged fibers with few fibroblasts, withstands pulling in many directions
dense elastic tissue
allows stretching
Cartilage has no
blood or nerves
hyaline cartilage
The most abundant cartilage type in the body; provides firm support with some pliability
elastic cartilage
cartilage with abundant elastic fibers; more flexible than hyaline cartilage
3 types of cartilage
hyaline, elastic, fibrocartilage
Fibrocartilage
cartilage that contains fibrous bundles of collagen, such as that of the intervertebral disks in the spinal cord.
spongy bone tissue
hard, lightweight tissue of bone that has many spaces
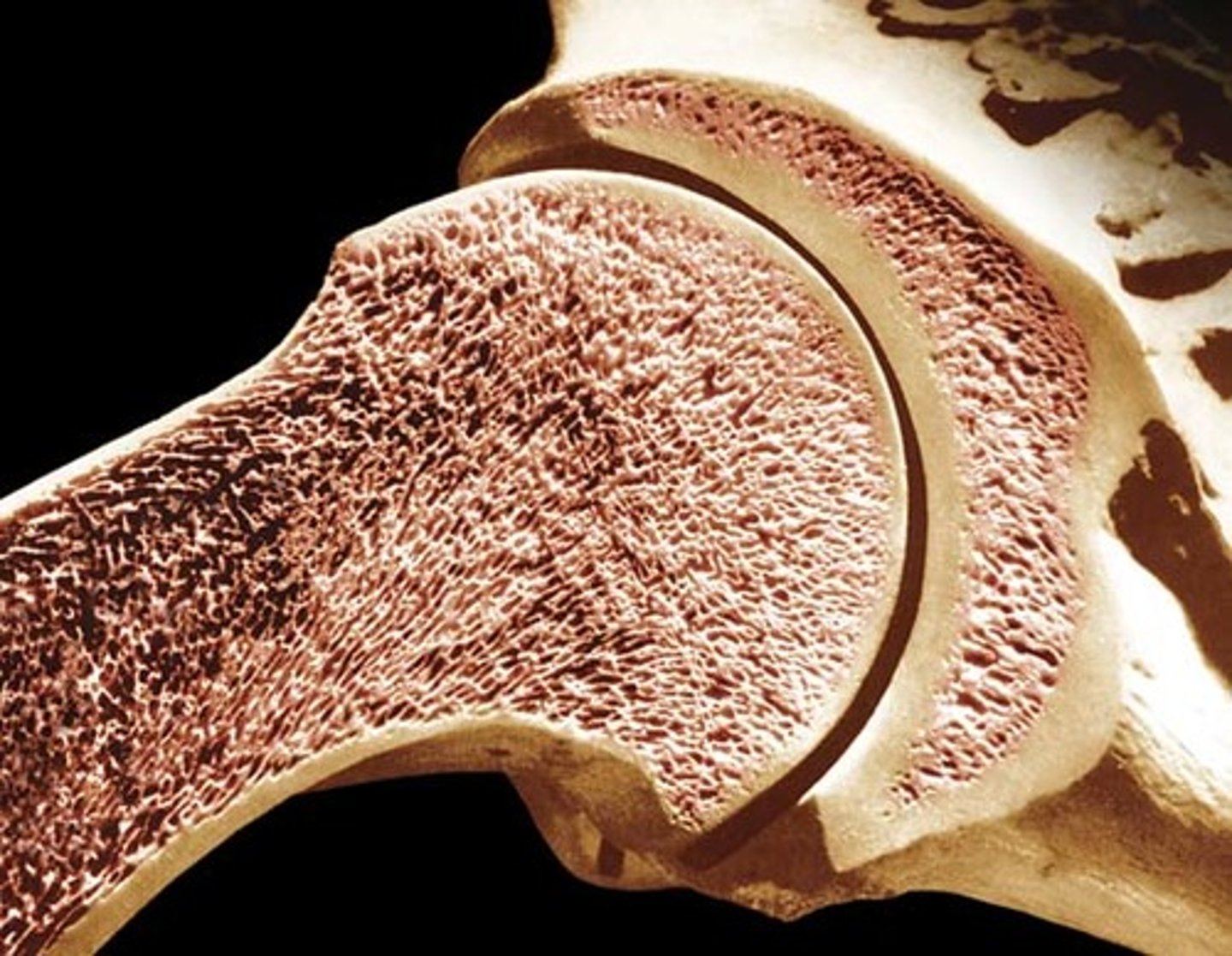
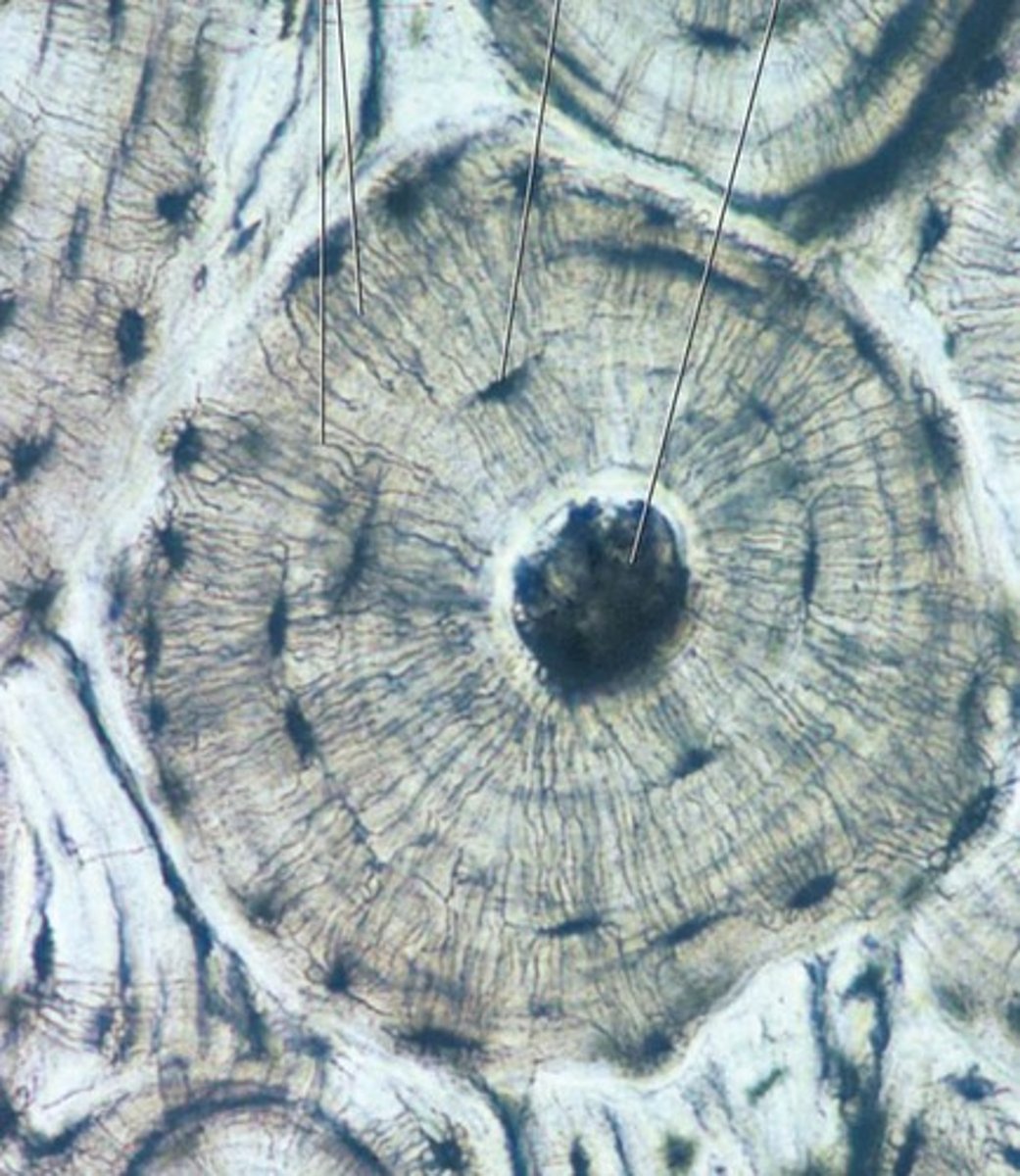
compact bone tissue
the strongest form of bone tissue that makes up the bulk of the diaphysis of a long bone
in blood connective the ground substance is your
blood plasma, which has protein fibers floating around it
Erythrocytes
red blood cells, carry oxygen
Leukocytes
white blood cells, fight infection
Platelets
blood clotting
In blood fibers are replaced by a bunch of
proteins