chapter 6 - electronegativity and polarity
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
how does electronegativity increase?
it increases across a period as the number of protons increases and the atomic radius decreases
this is because the electrons in the same shell are pulled in more
electronegativity meaning?
ability/tendency of an atom to attract electrons in a covalent bond
how does electronegativity decrease?
it decreases down a group because the distance between the nucleus and the outer electrons increases and the shielding of the inner electrons increases
what leads to a dipole (in electronegativity)?
what leads to a dipole (in electronegativity)?
factors affecting electronegativity?
atomic radius
nuclear charge
shielding
how does atomic radius affect electronegativity?
the closer bonding pair of electrons are to the nucleus, the stronger attraction there will be between the nucleus and bonding pair of electrons
how does nuclear charge affect electronegativity?
the greater the number of protons, the stronger the attraction between the nucleus and the outermost electrons
atomic radius decreases
how does shielding affect electronegativity?
as the number of full shells of electrons increases, the greater the repulsion between the electrons in inncer shells and those in the outermost shell
atomic radius increases
pauling scale?
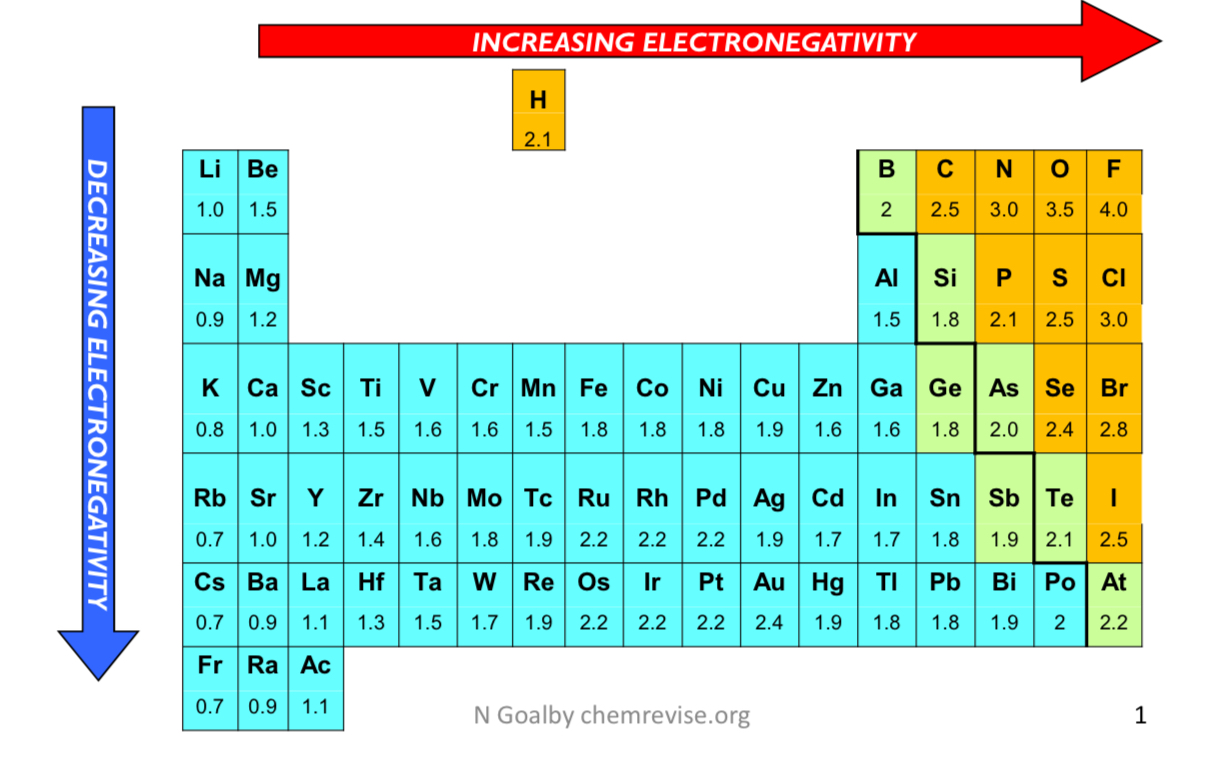
what type of bond is an electronegativity difference of more than 1.8?
an ionic bond
when will a bond be non-polar?
when the bonded atoms are the same
when the bonded atoms have the same or similar electronegativity
what happens in a polar bond?
the bonded electron pair is shared unequally between the bonded atoms
a bond will be polar when the bonding atoms are different and have different electronegativity values, resulting in a polar covalent bond
what is a dipole called in a polar covalent bond such as HCl?
a permanent dipole
to distinguish it from an induced dipole
polar molecule meaning?
molecule that requires polar bonds with dipoles that do not cancel out due to their direction
polar bond meaning?
when 2 atoms with different electronegativities share electrons unequally
this creates partial charges on the atoms
a molecule can contain polar bonds without being polar