NTDT401 Exam #1
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/134
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 12:24 AM on 2/27/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
135 Terms
1
New cards
Essential nutrients
an element or organic compound required for normal body function
2
New cards
T/F: Essential nutrients can be synthesized by the body
False - Essential nutrients CANNOT be synthesized by the body
3
New cards
The 2 classfications of Vitamins:
1) Fat-soluble & Water-soluble
4
New cards
What was the first Vitamin discovered in history?
Thiamin (B1)
5
New cards
Vitamers
Multiple forms of 1 Vitamin
6
New cards
DRI comes from _______ individuals
Healthy
7
New cards
EAR covers ____% of individuals’ requirements
50%
8
New cards
_____ is needed to set RDA
EAR
9
New cards
T/F: All nutrients have UL
False
10
New cards
T/F: A nutrient cannot have both RDA and AI
True
11
New cards
Is recommendation or requirement larger?
Recommendation
12
New cards
T/F: If one takes vitamin C less than 40% of RDA for 2 days, he definitely will develop vitamin C deficiency
False, just 2 days will not lead to a deficiency
13
New cards
Vitamin name = form our body ______
absorbs
14
New cards
2 active coenzyme forms of Thiamin:
TDP & TPP
15
New cards
Thiamin food sources:
Pork, whole grains, enriched grains, watermelon
16
New cards
Thiamin exists in free form in ____ products, and TDP in ______ products
plant; animal
17
New cards
_______ are removed prior to absorption of Thiamin due to polarity and lack of absorption
Phosphates
18
New cards
Free Thiamin is absorbed from ______
intestines
19
New cards
_______ interferes with Thiamin absorption into the blood
Ethanol
20
New cards
Enzymes in Pyruvate Dehydrogenase:
E1, E2, E3
21
New cards
NADH competes with NAD+ for binding to which enzyme?
E3
22
New cards
Acetyl CoA competes with CoA for binding to which enzyme?
E2
23
New cards
PDH is an enzyme found in _______
Mitochondria
24
New cards
T/F: PDH can be reversed
False, cannot be reversed
25
New cards
PDH cuts off how many Carbons from what?
1 Carbon from 3 Carbon pyruvate
26
New cards
Thiamin diphosphate (TDP) has ____ Carbons
5
27
New cards
Thiamin deficiency is called ______
Beri-beri
28
New cards
Wernicke’s Encephalopathy is mostly associated with _______,__ and can cause ___________
alcoholism; memory loss
29
New cards
_______ vitamin can treat Maple Syrup Urine Disease (MSUD)
Thiamin
30
New cards
Thiamin (PDH) reactants & products:
Pyruvate + CoA + NAD → CO2 + Acetyl CoA + NADH
31
New cards
Is PDH reversible or irreversible?
Irreversible
32
New cards
______ Beriberi occurs more frequently in adults
Dry
33
New cards
Describe Thiamin structure
Two rings, connected by Methylene bridge, Sulfur-containing
34
New cards
_______ vitamin is light sensitive
Riboflavin
35
New cards
B1 vitamin is _____
Thiamin
36
New cards
B2 vitamin is ________
Riboflavin
37
New cards
2 coenzymes for Riboflavin:
FMN, FAD
38
New cards
Riboflavin binds to ____, but can also bind to ____
proteins; metals
39
New cards
Food sources of Vitamin B2
Dairy products, eggs, liver, oysters, and mushroom
40
New cards
Food sources of Vitamin B1
pork, watermelon, whole grains, enriched grains
41
New cards
Riboflavin is converted to coenzymes in _______
the liver
42
New cards
FMN and FAD function as coenzymes for a wide variety of ______ enzyme systems
oxidative
43
New cards
Riboflavin is typically in ______ form
free
44
New cards
Name of Riboflavin deficiency:
Ariboflavinosis
45
New cards
FAD role in PDH:
FAD serves as __**intermediate electron carrier**__ in the PDH complex
46
New cards
FAD role in Succinate Dehydrogenase
converts succinate to from fumarate; forms FADH2 from FAD
47
New cards
FAD plays a role in Vitamin __ metabolism, converting ______ to _______
A; retinal; retinoic acid
48
New cards
T/F: Riboflavin (B2) is abundant in our diet
True
49
New cards
T/F: FAD does not play a role in Fatty Acid Oxidation
False, acetyl CoA dehydrogenase requires FAD
50
New cards
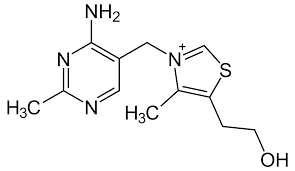
Thiamin (B1)
51
New cards
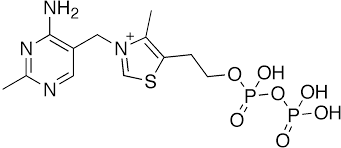
TPP
52
New cards
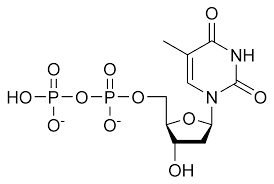
TDP
53
New cards
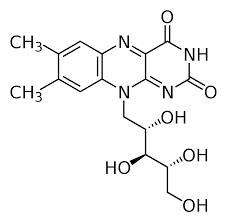
Riboflavin (B2)
54
New cards
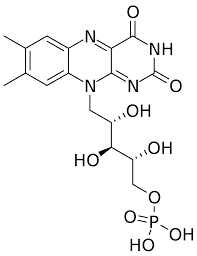
FMN
55
New cards
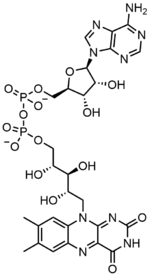
FAD
56
New cards
RDA Thiamin for adults
1\.1-1.2 mg/day
57
New cards
RDA Riboflavin for adults
1\.1 mg/day for women, 1.3 mg/day for men
58
New cards
What is Vitamin B3?
Niacin
59
New cards
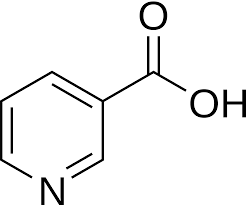
Niacin
60
New cards
Which vitamin is a vitamer?
Niacin (B3)
61
New cards
What are the 3 vitamers of Vitamin B3?
Nicotinic acid, Nicotinamide, & Nicotinamide riboside
62
New cards
Coenzymes for Niacin:
NAD, NADP
63
New cards
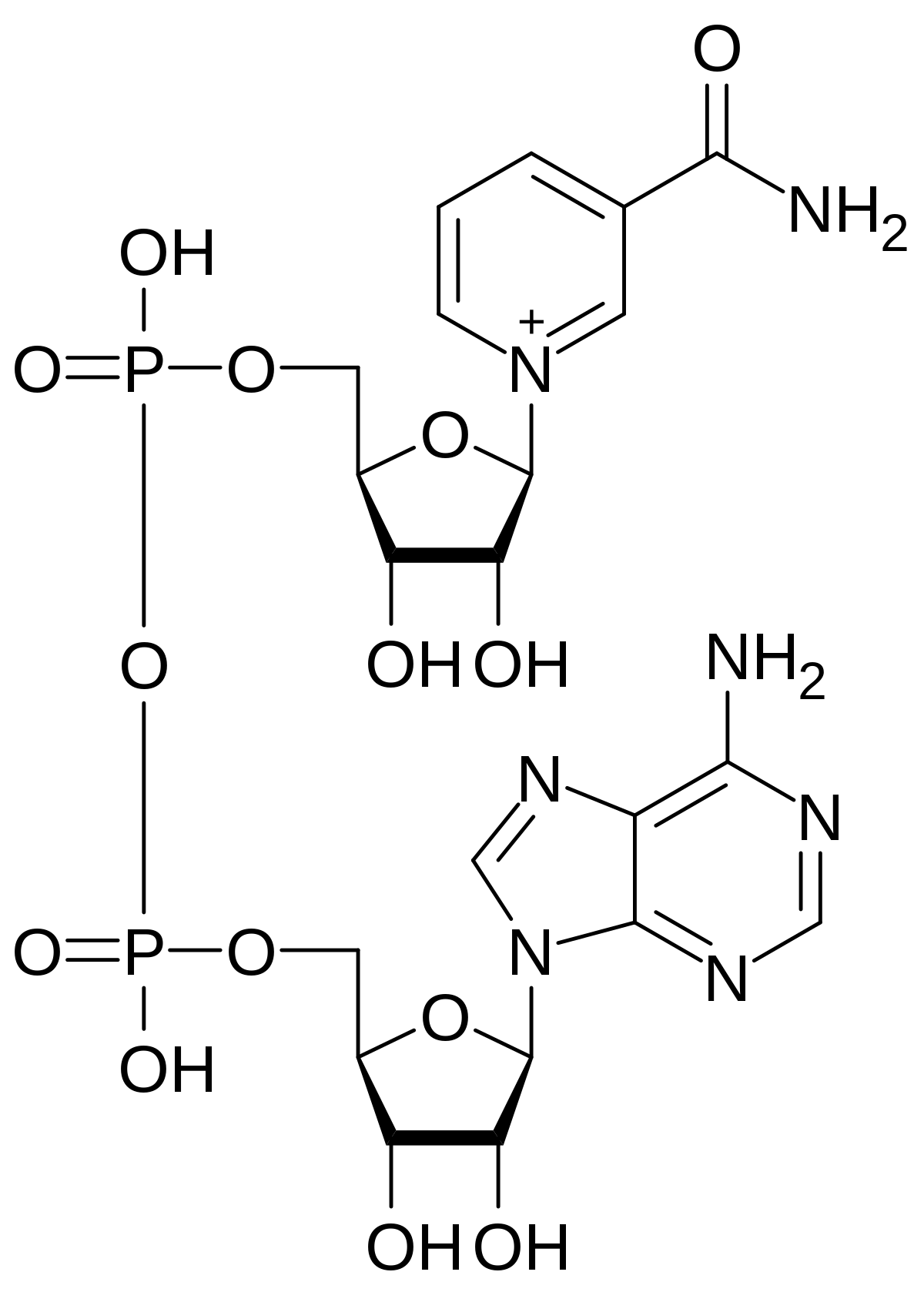
NAD
64
New cards
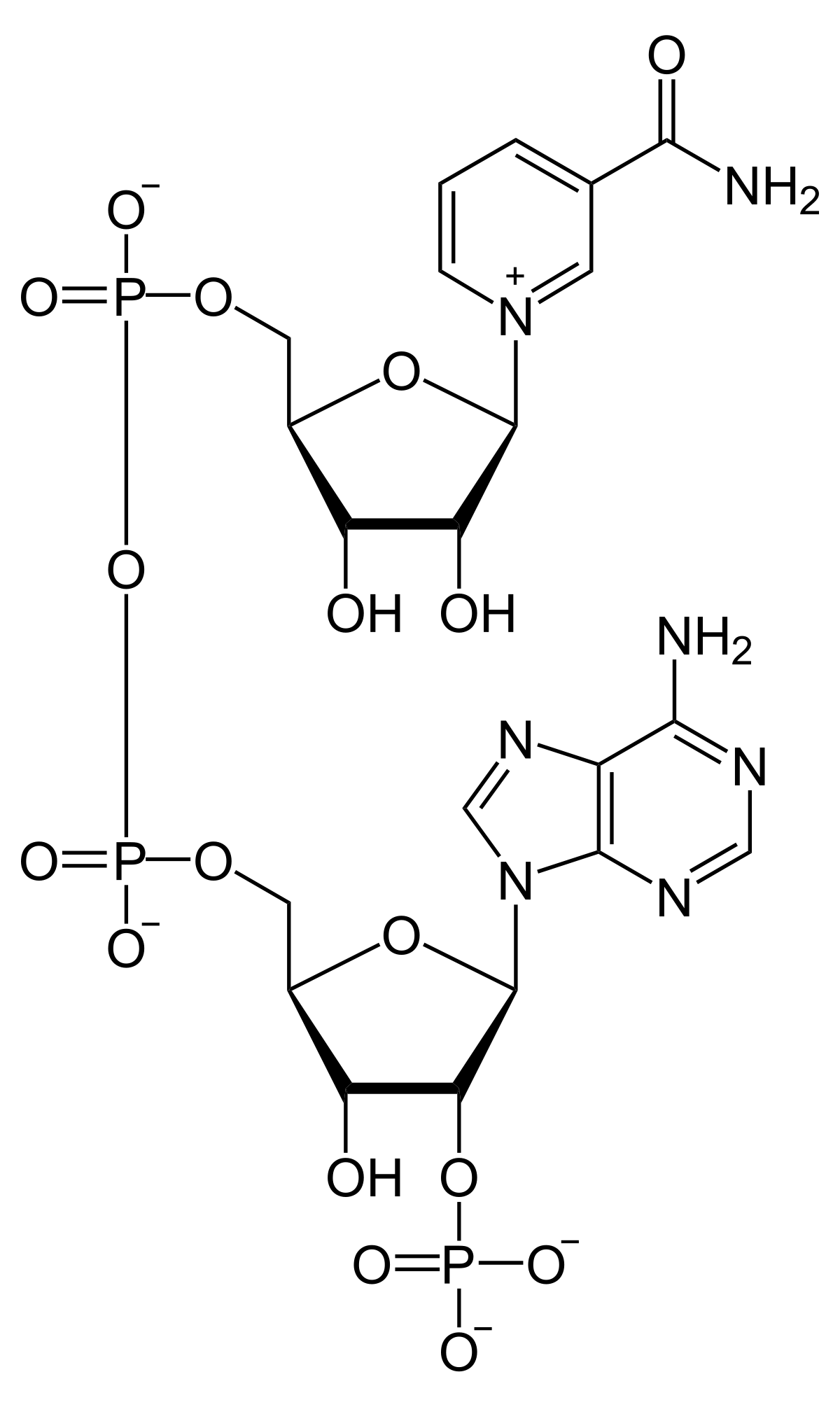
NADP
65
New cards
Food sources for Niacin come from ______
Tryptophan
66
New cards
Food sources Niacin:
Tuna, enriched breads, cereal grains, and meats
67
New cards
T/F: Niacin is stored in the liver
False, Niacin is not stored in the body
68
New cards
Tryptophan content of mixed proteins (%):
1%
69
New cards
Tryptophan content of animal proteins (%):
1\.4%
70
New cards
Tryptophan content of plant proteins (%):
0\.7%
71
New cards
*__ mg Tryptophan =* __ mg niacin = 1 Niacin \n Equivalent (NE)
60 mg Trp = 1mg niacin = 1 Niacin \n Equivalent (NE)
72
New cards
RDA covers ___% of the population
97\.5%
73
New cards
EAR covers ___% of the population
50%
74
New cards
Form of Niacin found in NAD:
Nicotinamide
75
New cards
RDA for Niacin females and males:
Females 14 mg/day, Males 16 mg/day
76
New cards
Niacin deficiency
Pellagra
77
New cards
Describe Niacin toxicity:
Flushing of skin due to release of Histamine
78
New cards
What is Vitamin B5?
Pantothentic acid
79
New cards
Food sources for Pantothentic acid
All plant and animal foods (specifically egg yolks)
80
New cards
Vitamin B5 mostly occurs as a component of _______
CoA
81
New cards
CoA is hydrolyzed into Vitamin ___
B5 (Pantothenic acid)
82
New cards
Absorption of Pantothenic acid occurs in the _____ by _____ diffusion
jejunum; passive
83
New cards
T/F: Pantothenic acid contains Sulfur
False - it does NOT contain Sulfur
84
New cards
T/F: CoA contains Sulfur
True
85
New cards
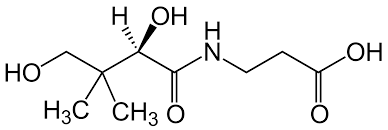
Pantothenic acid (B5)
86
New cards
Vitamin ___ is found in plasma
B5
87
New cards
Reactions involving Pantothenic acid:
PDH, Alpha KG complex, Beta oxidation of fatty acids, synthesis of fatty acids (starters)
88
New cards
Coenzymes for Vitamin B5:
CoA, ACP
89
New cards
How is Pantothenic acid excreted from the body?
CoA is converted to pantothenate
90
New cards
AI of Vitamin B5:
5 mg/day
91
New cards
Deficiency of Vitamin B5
Burning Feet Syndrome
92
New cards
Pantothenic acid deficiency is reported in people with ________
malnutrition
93
New cards
In 1881, ____ fed mice on a diet \n with pure _____, pure CHO, fats and \n mineral salts in the proportion similar to \n those in milk
Lunin; casein
94
New cards
Weak muscles occurs from ______ Beriberi
Dry
95
New cards
Edema occurs from ______ Beriberi
Wet
96
New cards
_______ Beriberi is observed in infants
Acute
97
New cards
Thiamin food inhibitors:
Tea & coffee
98
New cards
____ mg Thiamin in the human body
30
99
New cards
T/F: Thiamin has low bioavailability
False - Thiamin has high bioavailability
100
New cards
Active coenzyme form for Thiamin
TDP