Superpower
1/237
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
238 Terms
What is a superpower- key features of a superpower nation
global dominance
Economically stable
Influence and command other counties
Present a universal ideology
Other countries depend on them (aid,debt,resources)
Disproportionate degree of power (usually through having disproportionate amounts of resources) = they have the capacity to effect other countries
Definition of a hyperpower
An unchallenged superpower that is dominant in all aspects of power
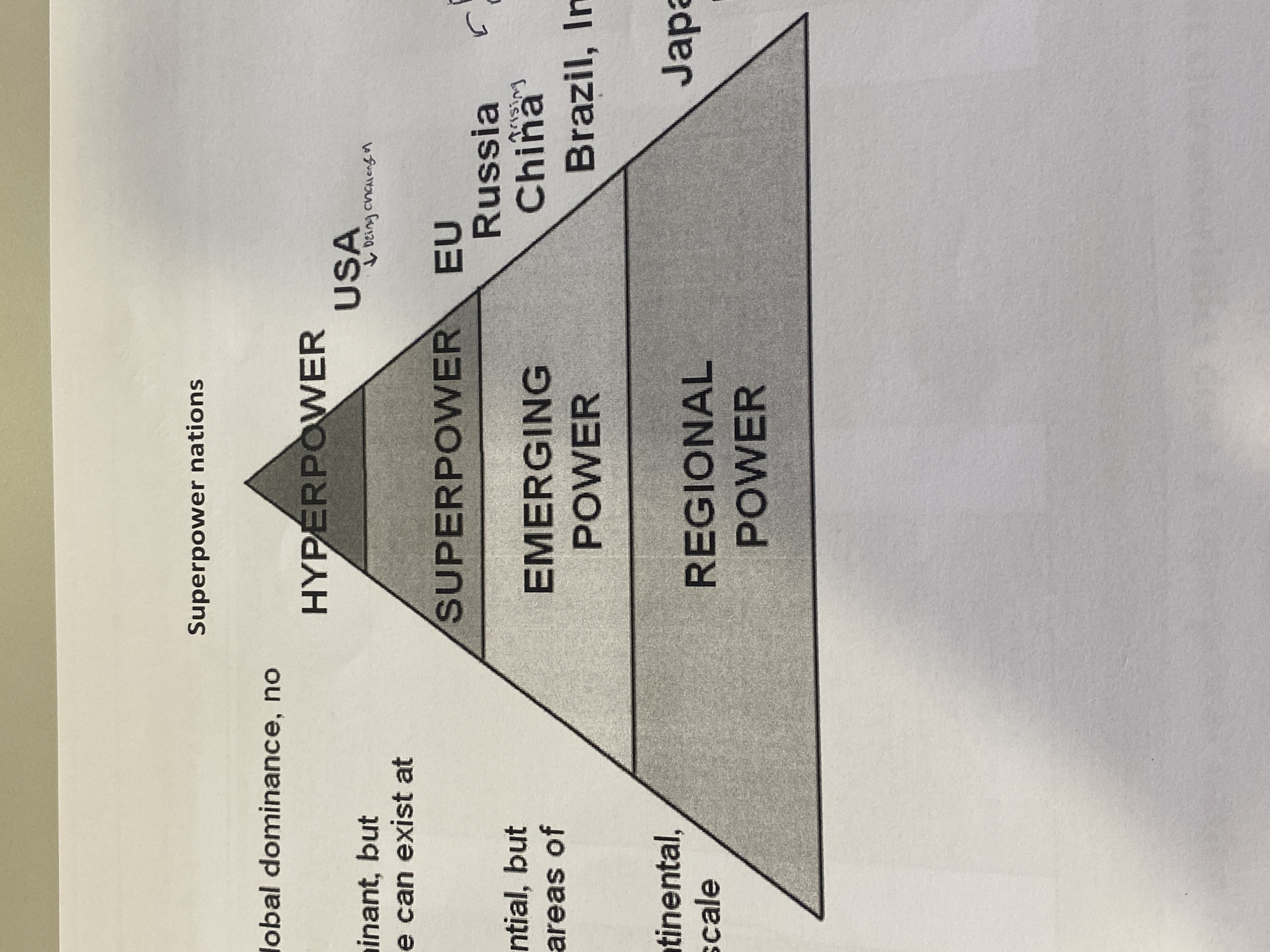
Hierarchy of power of a nation
Hyper power- complete global dominance, no rivals e.g. USA (this is changing)
Superpower- globally dominant, but more than one can exist at one time e.g. EU
Emerging power- Globally influential, but only in certain areas of influence e.g. Russia, China (rising), Brazil + India
Regional power- Leads on a continental but not global scale e.g. Japan, Mexico, Nigeria
What are the ‘pillars’ (and base) of superpower status
Military, geography, ideology, politics, economic base
How does Military make a country powerful
direct military power = threatens others + used to invade land as well as aid others during conflict e.g. UK large military
Indirect power- a tyrant of perceived power = army size and nuclear power acts as a deterrent and defeat from/ prevent conflict
Weaponry e.g. nuclear power= another deterrent e.g. China + Russia
NATO- hold a lot of power as they are a group with large military power to protect territory
How does geography make a country powerful
lots of natural resources means countries are less reliant on others and others are more reliant on then especially for fossil fuels = you have control over that country as they depend on you
Population gives a country the potential to have power but it relies on other factors e.g. literacy and health = potential for a strong economy.
Large pop= bigger workforce= taxes= funding for other pillars e.g. China
How does ideology make a country powerful
If people in other countries idolize views from a country they can be influenced by your beliefs meaning you can manipulate them + influence their behaviours.
Examples= American dream (westernisation = power) + English speakers
How do politics make a country powerful
If they are members of large international organisations especially if they have a large weighting/ more voting power = more influential on international law= control over other countries laws.
EU= trade bloc= trading easier therefore strengthening relationships
Allies= intimidating
NATO= members have a military threat on global scale
USA- Brenton woods- nothing can be changed as US has over 50% of weighted vote
How does a stable economic base allow to build a superpower
It is a fundamental part of power but a country with only wealth doesn’t make it powerful. Money is needed for investment in all the pillars. Less reliant on other countries + can invest in other countries (aid, military, TNCs) means culture spreads + countries become reliant in debt.
How come having all these characteristics doesn’t always mean that a country will be powerful. Why?
If you have the geographical status- resources, pop size but not a stable economy it is hard to improve the other aspects of the pillar= no superpower status. Or e.g. Russia has geographical power + military power but aren’t idolised or strong politically = no superpower
Example: some countries may have significant valuable resources but not have the ability to extract them or process them into manufactured goods.
Which countries are the most powerful
It is very hard to tell as there isn’t a universal measurement but in our calculations it is the USA.
Which countries are the current superpowers
USA comes top + the Uk 2nd and China 3rd. This means that their pillars of power must be balanced and strong. USA is a long term superpower and China is an upcoming superpower. There are other factors that affect power like cultural aspects- westernisation that may push the US on top.
Who came up with the idea of hard and soft power and what did he argue
Joseph Nye 1990
He argued that counties use a range of mechanisms of power to influence other countries
What are the names of the spectrums od hard to soft power
Hardest
Military action or its threat
Economic sanctions and diplomatic actions
Coercive policy e.g. tied aid or trade agreements
Political influence, moral authority, economic influence
Cultural attractiveness
Softest
Examples of what Military action or its threat on power spectrum (hard)
Large air, naval and land forces
Military bases in foreign countries giving geographical reach
Nuclear weapons
Military alliances E.g.. NATO
Diplomatic threats to use force if negotiation fails
Use of force
Examples of economics nations and diplomatic actions on power spectrum (quite hard)
Using economic sanctions against countries e.g. trade tariffs trade restrictions
Western cut of Russian Olicgarchs + trade tariffs to hit their economy and large TNCs pulled out e.g. Maccies
Examples of Coercive policy e.g. tied aid or trade agreements (medium)
Providing allies with economic and technical assistance
Using aid to influence policy
Using aid in return for certain action, usually which benefit their own country
Examples of political influence ; moral authority, economic influence (quite soft)
Favouring certain trade partners by reducing import tarrifs
Trade blocs and alliance e.g. EU, North Atlantic free trade agreement
Membership of and say in intergovernmental organisations e.g. WTO
Being seen to do the right thing and made morally right decisions e.g. responding to human rights abuse, tackling climate change
Cultural attractiveness
Using the media to promote a particular image and message
Exporting culture in the form of film and TV
Gradually persuading other that a particular action or view is in their interest
Globally recongnised brands
Top 3 powerful counties in world by military strength ranking
US
Russia
China
Facts of military strength of countries
US- top = nearly 900B/yr
10x more than second (Russia)
3x more than 3rd (China)
US spend more than the next 9 highest spending countries combined
Russia + China are top for increase in spending recently
What is USA aim for power
Full spectrum dominance- USA wants to be too in all military power- air, land, sea, cyber power, nuclear, money, personnel, tech
Us military has global presence= ability to act quickly to aid, support + stop other countries e.g china from expanding to much and being to big
Who are the 8 states that have successfully detonated nuclear weapons
USA
Russia
UK
France
China
India
Pakistan
North Korea
Israel are believed to posses NW but this hasn’t be confirmed
Which countries who have successfully detonated nukes signed the NPT
USA
Russia
UK
France
China
These 5 are called nuclear-weapon states as they are allowed to have weapons as they were built and tested before treaty came into effect
Israel, Pakistan, India have never accepted the NPT and North Korea pulled out in 2003
What is the NPT + how many countries are part of it.
An international treaty trying to prevent the spread if nuclear weapons + tech + promote peaceful use of nuclear energy + further goal of achieving nuclear disarmament + complete disarmament.
191 countries are part of this treaty.
Examples of soft power
Businesses + innovations, Culture, Gov, Diplomacy, Education, TNCs, Media, NGOs…
Joseph Nye definition of soft power
The soft power of a country rests primarily on 3 resources: its culture (in places where it is attractive to others ), it political values ( when it lives up to them at home and abroad) and its foreign policies (when they are seen as legitimate and having moral authority)
Factors that positively effect the soft power of a country
stable economy in a time of global instability
Global products + brands
Leaders in science + tech
Aid
Trade
Education- Harvard, Oxford
Sustainable future
Gov
Hosting major events- Paris Olympics, Qatar FIFA
Factors that negatively effect the soft power of a country
gun violence + police brutality (USA)
Involvement in international conflict
Confrontational politics (Trump)
Hard power harms soft power (Russia, Ukraine, Israel)
Lack of free + fair media communication- Ukraine, Palestine
Politics (election of trump, England leaving EU)
Explain why soft power changes over time
Changes in gov- trump
Leaving EU
International conflict- Russia, Israel
Holding major events- Olympics, Football
Advantages + disadvantages of hard power
Advantages
Direct, immediate way to show power
Often immediate action
Disadvantages
Can be short lived outcome
Depends on scale of Country’s power- small= less likely to command hard power
Forces one to act different= can lead to dissent e.g. Russia is hated + hit by withdrawal from other countries funds as they forced Ukraine to war
Advantages + disadvantages of soft power
Advantages
Longer lasting + more sustained as perception are changed, lasts as ones attitude is voluntarily changed so beliefs are altered.
Disadvantages
Takes a wile to build soft power
Historical legacy + societal systems can prevent soft power developing
Intangible + harder to build up
Why type of power do you think is more effective
Overall appears that soft power is more effective in contemporary international systems than hard power strategies. Demise of hard power caused by change in world order, whereas strength of soft power is based one endurance + sustainability. Soft power has weakened recently + hard power in more needed due to conflicts so need smart power
Smart power= draws on both. An approach that understand the necessity of strong military but also investing in alliances, partnerships + institutions. The capacity to combine elements if hard + soft in ways that are mutually reinforcing.
What is Mackinder’s Heartland theory
Who rules East Europe commands the Heartland: who rules the heartland commands the World Island: who rules the world island commands the world.
1904 Mackinder produced a geo-strategic location theory
This continental land area, protected from invasion by sea, stretches from Russia to China + Himalayas to Artic. Mackinder argued it the key geo-strategic location because it commands a huge portion of the world’s physical and human resources.
What is geo-strategic
Policies in terms of securing needed resources, both within the country and globally
Heartland theory= influential because it contributed to policies of containment:
Attempts, after WW1 to limit ability of Germany to expand land area it controlled
Post-WW2 NATO allies attempt so contain Soviet Union from expanding into Western and Southern Europe.
American ‘Truman Doctrine’ policy of 1940s + 1950s to contain the spread of communism from Soviet Union + China
Criticisms of the mckinders theory
in 21st century ideas seemed old:
modern military tech can hit dee inside another countries territory- size is no longer a protection
Physical resources are traded internationally: much less need to have them domestically
Period of time post WW2 war + conflict seemed abnormal whereas in past this was way of gaining power. The recent Russia/ Ukraine + Middle east conflicts has highlighted the renewable of importance of hard power as way of gaining power
How has the importance of hard + soft power changed over time
Hard power has always been important- Colonial expansion E.g. British empire depend on large miliary power, WW1 + 2= hard
Examples of hard- Russia- 2008- invaded Georgia + Ukraine/ Crimea in 2014 + 2022- war with Ukraine (still ongoing)
Soft power has become for common as a way of gaining + maintaining power
Example- UK- 6th largest economy- attractive for TNCs, FDI, BBC world service- more neutral + reliable than many gov broadcasts, Culture- Pride+ Prejudice, Downton Abbey, Harry potter, City of London dominates international finance, banking, law with NY
Americanisation has played a huge part in USA’s status as a superpower (TNCS, Hollywood, IGOs power..)
Hard power is necessary but to maintain power, soft power may be more significant in the long term.
Unipolar definition
A world dominated by one superpower (British empire, US)
Bipolar definition
A world in which 2 superpowers with opposing ideologies vie for power (USA + USSR Cold War)
Multi polar definition
A more complex works where many superpowers and emerging powers compete for power in different regions
Who was the superpower(s) in 1800-1919
Britain- Unipolar
How Britain maintained power (direct/indirect) and reason for growth or decline in 1800-1919
Direct political control- ran countries
Colonialism- owned 23% of worlds land + 23% of pop, Royal Navy dominated oceans, soft power came with (tea culture, English speakers..)
Reason- able to protect trade routes . Allowed trade + interests of private companies
Who was the superpower(s) in 1919-1945
US, Japan, Uk, Germany- multi-polar
How US,Japan,Uk, Germany maintained power (direct/indirect) and reason for growth or decline in 1919-1945
Cultural diffusion in colonised countries + investment in infrastructure + military investments
Reasons- Growth in trade links, Growth in military as countries prepare for war (hard power), Decline in British economy- facing comp from industrialising Germany
Who was the superpower(s) in 1945-90
USA + USSR- Bipolar
cold war period + 89’= berlin wall fell
How US,USSR maintained power (direct/indirect) and reason for growth or decline in 1945-90
Military power (cold war), Both had strong allies, USA cultural spread (democracy), both self sufficient, Neo-colonialism- post independence of developing countries, cap vs com
Reasons- UK= decline in power (post war bankruptcy + reconstruction= can’t keep empire + anti colonialism), UK dependant of US as support
Who was the superpower(s) in 1990-2030
USA- unipolar
How US maintained power (direct/indirect) and reason for growth or decline in 1990-2030
USA- created NATO + beat USSR for superpower status but kept building military + expanded bases for control + quick aid
Reasons- USA containment policy= contain Communism after WW2 end + contain USSR= collapse + USA rose as superpower
Soft- economic, TNCs, culture put USA top ut there is now more challange
Who will be superpower in future?
USA, China, Europe??
Multi
How USA, Europe, China maintained power (direct/indirect) and reason for growth or decline in future
Smart power- need threat of direct but subtle indirect power e.g. cultural, westernisation will carry on, providing aid (IMF,WB), countries follow pro-western democracies, cultural diffusion, TNCs
Reasons- China’s investment + trade with countries in Africa. 1 mill estimated Chinese living if Africa + China has build relation with their leaders, China’s rate of spend on military= fastest but their issue= aging pop- economy rates of growth falling
What does colonialism =
Direct political power
Main may superpowers impose direct control over vulnerable territories is?
War (direct military conquest) + then impose their own mechanisms such as legal systems, culture + economics
Colonialism in the past was done to fulfil superpowers agenda e.g. exploitation of raw materials or cheap labour but recently more of a shift towards more political agendas
Neo-colonialism definition
Indirect economic control
what are the 3 main examples of neo-colonialism
Trade, aid, debt
Aid in neo-colonialism
Aid is often given to allies who superpower wants to maintain relationship with
Lots of aid is supposed to be paid back to the country (tied aid)- often making the country in debt to the superpower
Superpowers often offer aid to countries who can’t decline + in future manipulate them because of their debt
Debt in neo-colonialism
Some aid is owed back to the superpower as debt
This cannels money from developing world to developed world, increasing polarisation (uneven political/ economics) between the 2
Power also becomes more polarised as when debt is owed the superpowers can become more powerful over the vulnerable territories
Debt relief schemes such as HIPC(heavily indebt poor countries) often still exert power over countries- must follow certain rules, certain policies of bankers in order to qualify for scheme
Trade + TNCs in Neo-colonialsim
The world trade system is essentially a western free trade
2 most dominant powers- the SA + EU (influence in WTO)
3 main stock markets (London, NY, Tokyo- all west)
TNCs= influence vulnerable territories- used by superpowers to assert dominance + maintain power + manipulate other countries into following certain trade rules
Low commodity export prices contrast with high prices for imported goods for developing countries= inhibits development
Military alliances in Neo- colonialism
Between developing nations + superpowers makes the developing nation dependant on miliary aid + equipment form the superpower
Break down of China’s Belt + Road initiative title
BELT- Overland silk road economic belt
ROAD- Maritime silk road
What is Chinas Belt + Road initiative
Originally devised to link East Asia + Europe through physical infrastructure + funding of SEZs
Has expanded to Africa, Oceania + Latin America
Aim- broaden China’s Economic + Political influence- expand international use of Chinese currency
Launched in 2013 by President Xi Jinping
US + Some of Asia fear it’s a Trojan horse for China-led regional development + military expansion#
Idea= Build series of railway, energy pipelines, highways etc
So fa 147 countries (2/3 world pop + 40% of global GDP have signed onto projects
China has already spent estimated $1 trillion + estimated to cost $8 trillion
Potential benefits of China’s Belt + Road initiative
Develop new trade links for China, cultivate export markets, boost Chinese incomes + export China’s excess productive capacity
Boost global economic links to China’s neglected Western region
Restructure China’s economy to avoid the middle income trap (wages up + qual life up as low skilled manufacturing ups but countries struggle to shift to producing higher value goods + services)
Potential costs of China’s Belt + Road initiative
Expensive (could cause countries to drop out)
Lots of low income BRI countries may struggle to repay loans= debt crisis
Connected with climate change: non- renewable energy investment has made up nearly ½ of BRI spending.
Stability of Uni-polar world
Dominant superpower has vested interest in stability, this leads to strenuous efforts to be dominant everywhere
In reality, this is impossible, leading to frequent, unpredictable, minor conflict + the dominant power being over stretched repeatedly
Stability of Bi-polar world
Both superpowers need to avoid all out conflict
This leads to Proxy-wars (wars fought between groups + smaller countries that represent interests of larger powers + may be supported by them)
The cold war suggests a ‘stable but scary’ situation where superpowers compete but avoid direct conflict
Stability of Multi-polar world
A mix of rising + declining powers
Complex alliances
Weaker powers will try to defend what they have + trying to expand
Figure on importance of hard power recently
NATO spending increased by 11% in 2024 compared to 3% in 2023
Assess the effectiveness of hard power in maintaining the status of superpowers (12) plan
P1- The effect of hard power ± (Russia)
P2- How power has changed over time- hard to soft back to hard?
P3- Effectiveness of soft power ± (USA,UK) + talk neo-colonialism
P4- Conc? Smart power
ASSESSMENT- smart power- hard is important but not alone as it can’t maintain status (USA)
MARK SCHEME
make sure to add definitions of Hard + Soft + Smart (Joseph Nye)
Historical evidence + Uni,bi,multi
Country examples + Stats
Add judgement statement to each para linking back to Qu- allows for coherent argument
How are the demographics and GDP of currents and emerging superpowers predicted to change in future?
By 2030, likely that USA + China will be more equal in power + India will have significantly more global power
EU could be a superpower (economy of 28 states + France + UKs nuclear threat) but has many weaknesses- rare all states politically agree= weakens global message + more ageing pop + still recovering from 2007-8 global financial crisis
EU + Japan= ageing pop
USA= future moderate economic + pop growth (compared to usual rapid)
China= Ageing pop but huge potential to shift into service based + consumerism economy= growth?
Future superpowers are likely to emerge from which 2 groups of countries?
BRIC- Brazil, Russia, India, China
MINT- Mexico, Indonesia, Nigeria, Turkey
Future superpower potential
India= largest projected pop- 1,520m by 2023= potential to become much richer
USA= 3rd largest pop (360m by 2030) but mainly ageing pop= might not have the working pop to sustain its position as biggest GPD ($25 Trillion by 2030)
China has 2nd largest pop (1,390m by 2030)= potential to shift from an manufacturing based economy to a services + consumerism based economy= could increase GDP ($22 Trillion by 2030) to become more equal will USA + more equal in terms of superpower status
SWOT analysis for emerging superpowers- Turkey
Strengths Well-educated, youthful population that is capable of working in skilled secondary, tertiary + quaternary jobs can increase output. EU candidate nation= trade with EU if it joined the EU | Weaknesses Large scale armed conflict with 35,000 deaths in 1980-90s. Might reduce chance of trade with other countries or jeopardise Turkey joining EU |
Opportunities Member of NATO, so military support if required EU candidate nation= could exert greater economic + political influence on fellow member nations IF it joins | Threats Threat of war against Syria, Islamic state+ others on its borders. High cost is likely to slow economic growth Negotiations over joining EU have bee suspended due to ‘human rights concerns’ |
SWOT analysis for emerging superpowers- Indonesia
Strengths Low public debt- invest more money into making them more powerful Relatively functioning democracy= degree of stability Large pop= large pool of workers + large domestic market to support it’s economy | Weaknesses Doesn’t have strong military + not much economic power High urban + rural poverty Poor infrastructure throughout the country |
Opportunities Youthful, educated, potentially dynamic pop= potential for economic growth Large untapped natural resources= exploited for money + trade + leverage over other countries | Threats Deforestation= could lead to lower economic growth in tourism sector |
SWOT analysis for emerging superpowers- Mexico
Strengths 2nd largest pop in Latin America + 11th highest GDP 2014- produced 3.4% of worlds oil= dependence US dependant for exports Part of NAFTA trade block + has an advanced economy | Weaknesses High crime rates= poor soft power + global image= less influence Obesity= high healthcare costs Many well-educated, skilled workers migrate= brain drain, ageing pop + high dependency ratios Regional inequality Gov attempted to combat drug exporting issue + weakened their military= loss of hard power |
Opportunities Slowly becoming more democratic + open for business- more moral authority Increased trade= increased GDP + better relationships | Threats Pop= increasingly obese= higher healthcare costs could lead to debt + less spending on other services Cheaper Mexican produce exploited by USA |
SWOT analysis for emerging superpowers- Brazil
Strengths Large pop- 200m + 7th largest economy Strong agricultural economy + exports Energy independent in oil biofuels Young pop= potential for education, large consumer market + tax base for economy | Weaknesses Small military- only regional intervention capacity Economy suffers boom + bust phases Environmental pollution High crime rate Lacks trade agreements with other nations in the modern Western region |
Opportunities Independent in oil (one of few countries) 2014 World Cup + 2016 Olympics= opportunities for economy to become culturally influential | Threats Economy growing slow due to low productivity as result of lack of investment Corruption is among highest in the Americans |
SWOT analysis for emerging superpowers- Russia
Strengths Nuclear power + large military capacity = hard power Permanent seat on UN security council Huge oil + gas reserves= source of wealth | Weaknesses Extreme inequality Ageing, unhealthy, declining pop Economy is over dependant on oil + gas Difficult diplomatic = geo political relationships with US + EU War with Ukraine= economic sanctions= impact economy e.g. TNCs such as MacDonalds pulling out= geo political isolation |
Opportunities Nuclear + military threat= defence + attack threat Ability to trade oil + gas= other countries depend on Russia Current geo political tensions but remains major player due to involvement in international organisations e.g. UN security council Be more powerful (on world stage) if take over Ukraine- rests on this | Threats War with Ukraine may have weakened its military Strained relationships with West= economic struggle after war + economic sanctions could limit Russia’s access to international markets + tech Lack of soft power + reliance on hard power= bad public perceptions |
SWOT analysis for emerging superpowers- India
Strengths Youthful pop Nuclear + space + missile tech English is widely spoken + graduate education is widely spread | Weaknesses Possible future resource shortage especially water + energy Poor transport + infrastructure High levels of poverty + inequality Poor political relations with neighbours especially Pakistan Governing such large pop as democratic= hard for everyone to have say + prevents problems being solved |
Opportunities Youthful pop= large economic potential English widely spoken= access to English TNCs e.g. call centres Growth driven by investment into tech, energy + infrastructure puts India on track to becoming 3rd largest economy by 2030 | Threats Relationships with China + Pakistan= tense + pose risk of escalating into conflict= impact on region’s stability + economic growth Large portion of pop lives in poverty- addressing this inequality will be crucial for sustainable dev + social stability Environmental challenges- water pollution, deforestation = threat to health Digital + tech innovations= cyber security risk Rapid urbanisation= overcrowded cities= pressure on existing infrastructure + services |
SWOT analysis for emerging superpowers- China
Strengths Highly educated, technically innovative pop Soon to be world’s largest economy + leads in fields of science e.g. renewable energy Military tech is growing + challenging USA Modern transport infrastructure Have control- people have say in fixing problems= quicker | Weaknesses will soon have problem of aging pop Pollution- air + water= issue Tense relationship with neighbours in SE Asia except Paki Rising wages= higher costs for TNCs- future pull out Relies on imported raw materials Plays a limited geopolitical role |
Opportunities Heavy investment in tech= quaternary sector booms Belt + Road initiative= enhance geopolitical influence by investing in infrastructure projects across Asia, Africa + Europe= building strategic partnerships | Threats Rising wages= increased cost of products= other countries products may be cheaper + TNCs may move Shift from high growth, investment driven economy to hog qual, sustainable growth involves overcoming ageing pop, inequality + environmental issues Need s better relationships with West + SE Asia to become global influence US-China superpower rivalry |
Who are having an increase share of global GDP
emerging countries (the G20)
What have been set up as alternative to WB + IMF
NDB + AIIB- where US don’t have veto power + emerging countries have more of say
What is the NDB
Multilateral development bank established by BRICS states
Bank will support public + private projects through loans, guarantees + other financial instruments + work with International organisations + support projects via bank
Allowing BRICS to deepen co-operation
Examples of what NDB has provided loans for: 4 projects in China, Russia + India totalling more than 1.4b, water quality control projects, energy conservation, technology projects (2/3 projects towards sustainable infrastructure)
what is the AIIB
Multilateral development bank that aims to support the building of infrastructure in Asia- Pacific region. 56 current members + 24 prospective.
It will address need for infrastructure through Asia and interconnectivity + economic development though advancements in infrastructure to stimulate growth + access to basic services.
What is the G20
Group of 20= international forum brings together worlds 20 leading industrialised + emerging economies. Accounts for 85% of global GDP.
Combined GDP of BRICS
US$ 16.6 trillion
Predictions for economies for 2050
Emerging markets could grow 2x as fast as advanced economies
Largest economies : Chinas, India, US
UK= 10th, France out of top 10 + Italy out of top 20- overtaken by emerging economies e.g. Mexico, Turkey, Vietnam
Explain why emerging economies are becoming increasingly important in economic + political systems
As countries dev their influence increases. Economically- emerging countries have capacity to grow around 2x as fast as advanced countries.
Politically- as they grow economically they will have more global power= potential for UN security council + creation of alternative systems (IMF + WB taken over by NBD, AIIB
Environmental governance of BRICS facts
Their dev will have higher direct impact on global emissions but if they get sustainable dev right could pave way for other emerging countries + create economic opps without destroying planet
UN climate change conference
2015- countries accounting for 98% of global emissions agreed to global climate change strategy- each country submitted plan on how to move economy on with a lower carbon pathway.
USA withdrawal from Paris agreement
Sustainability for 1 BRICS- China
Problems faced- Top emitter- ¼ of worlds annual greenhouse gas emissions. Air pollution + carbon intensive industries caused water scarcity. Coal makes up 2/3 of China’s energy consumption
Moves to sustainability- Pledged to cut emissions under Paris agreement- reduce coal use + to be carbon neutral by 2060
President Xi Jinping= pledged carbon neutrality, renewable energy sources for 25% of consumption by 2030 + China= dominant for solar generation
Why is it important China is involved in global environment governance
Such a large producer of worlds annual greenhouse gases= if they aren’t onboard we wont see much change on global level
How can theories be used to help explain changing patterns of power?- Modernisation theory
Summary- Made by Rostow Transition from traditional to modern society in 5 stages | How explains changing patterns of power- All countries follow same path so countries need to seek correct preconditions for take off + they will rapidly industrialise + increase urbanisation | Limits- Only describes process of economic change + growth- doesn’t help with political + cultural aspects needed to be a superpower Outdated + some countries have pre-conditions but haven’t developed- Nigeria |
How can theories be used to help explain changing patterns of power?- Dependancy theory
Summary- Frank in Mid 1960s Developing countries export raw materials at low cost + dev countries export back for high prices + remain in control + Dev countries ‘buy’ loyalty through tied aid | How explains changing patterns of power- Superpowers exploit developing countries which limit their ability to dev. Periphery + core countries | Limits- Static theory- suggest countries are permanently stuck in undev state- rise of NIC suggests it’s more complex (Newly developed countries have freed and developed- Singapore, S Korea, Malaysia World economic structure =more complex than 2 tier world Frank suggests.
|
How can theories be used to help explain changing patterns of power?- World systems theory
Summary- Wallerstein- in 1970 Stressed dev should be viewed within global economic context rather than focus on individual country | How explains changing patterns of power- As global capitalist economy explained some periphery countries have become more important in world economy so now: Core reions- EU, USA, OECD Semi periphery- NIC Periphery- rest of developing world | Limits- Derived from observations of world affairs, doesn’t make predictions or offer solutions |
Since when has world be dominated by Free market capitalism economic system + why
Alternative economic systems have weakened:
Collapse of USSR (socialist)- End of cold war in 1990
China’s move away from socialist economy towards state capitalism
Reform in communist Cuba, allowing limited private business ownership
What does capitalism allow + example countries
Private ownership of property e.g. homes + possessions
Private ownership of businesses + wage based on supply vs demand + skill
Right to make profit + accumulate wealth
Buying + selling of goods in competitive free market
USA, Canada, Japan, Western Europe
What does socialism (centrally-planned) economic systems allow + example countries
Gov ownership of property + land
Profits taken by gov + used to provide public services
Price controlled by gov + control of supply of goods + services
Most business sate owned + wages determined centrally
USSR, China, Eastern Europe, Cuba
How do superpowers influence global economy through IGOs- World Bank + IMF
Description of how IGO encourages free market capitalism + free trade | Role of superpowers in IGO | Examples of how superpowers have influence the global economic systems + shown power over others |
Development loans within free market model that promotes trade, exports, industrialisation + private business= benefits TNCS | Share of votes determined by quota dependant on size of economy. USA= 16.5% + 85% needed to pass an issue USA= veto power+ all WB presidents = American | Structural adjustments programmes (SAP) in 1980s: IMF + WB have loans to LDCs in debt + involved them making cuts in public spending= neg impact on LDCs (neo-colonialism??) |
Promotes global security + stability + assist countries to reform economy. As result TNCS can enter easily | Similar to WB- USA= veto power | Above |
Issue with IMF recent example
In March 2024 Ecuador signed an agreement to borrow $4.2bn from IMF over 3yrs provided gov would adhere to a certain economic program. It was displayed by the IMF as a reform programme aimed at modernising the economy. But the programme included a enormous tightening of country’s national budget- about 6% of GDP over next 3yrs but cutting spending on public investments + raising taxes that fall disproportionately on poor people + firing tens of thousands of people from public sector
How do superpowers influence global economy through IGOs- World economic forum
Description of how IGO encourages free market capitalism + free trade | Role of superpowers in IGO | Examples of how superpowers have influence the global economic systems + shown power over others |
Swiss NGO- established 1995 Promotes globalisation + free trade with annual meetings bringing together global business + political elite | Discuss issues but no decisions made- just influence each other. Large TNCs, gives, key figures around world are invited Seen as’ rich club of global elites | Networking to influence other meeting were decisions are made Criticised of prioritising capitalism + globalisation at expense of tacking poverty |
How do superpowers influence global economy through IGOs- WTO
Description of how IGO encourages free market capitalism + free trade | Role of superpowers in IGO | Examples of how superpowers have influence the global economic systems + shown power over others |
IGO that regulates world trade, agreements aim to promote open trade + reduce protectionism | More dev countries have bigger say, can afford more delegates to go | Dominated by QUAD countries- USA, Canada, Eu, Japan, decisions often go in their favour- LDC voices= not heard |