NEUROLOGIC EXAMINATION p1
1/102
Earn XP
Description and Tags
page 1-5
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
103 Terms
When checking mental status for cerebral examination, what are the global brain functions?
Level of alertness
Attention
Cooperation
Checking the following are necessary for cerebral examinations except:
General behaviour and appearance
Orientation
Motor Coordination
Calculation
Except Motor Coordination
Which hemisphere is responsible for language
Left hemisphere
Which lobe is responsible for neglect and constructions
Parietal
In the MMSE-P, when you ask the patient to repeat 3 words, what does this test?
Registration (only involves attention, no retention)
When you ask the patient to repeat the 3 words after a few minutes what does this test?
Recent/Short term memory
Cut off score for the MMSE-P
27/30
The Mini-Mental Status Examination - Philippines is usually used in what condition?
Dementia
What does MOCA-P stand for?
Montreal Cognitive Assessment - Philippines
True or False:
When calculating the total score for the MOCA-P sum up all subscores on right hand side then add one point for those with 15yrs or fewer of formal education, for a max score of 30
False:
+1 for 12yrs or fewer not 15yrs
Normal MOCA-P cut off score:
DSP MOCA-P cut off score:
26/30
21/30
When testing for level of Alertness, Attention and Cooperation, what is the normal digit span a person can repeat forwards and backwards?
6 or more forward
4 or more backward
When naming months forward and backward how long does it take to recite the months backwards compared to reciting it forwards?
Twice as long
Structure in the brain responsible for consciousness
A small lesion here can impair consciousness
Reticular formation
found in the tegmentum in all levels of the brainstem
Consciousness can be severely impaired when the lesion in the cerebral hemispheres or thalami is _______
Mildly impaired if the lesion is _______
Bilateral
Unilateral
dysfunction of cerebral functions
Encephalopathies
Hypoxic (no oxygen)
Hepatic ()
causes behaviour and mood disorders
You ask the patient to recall 3 items after a delay of 3-5 mins what does this test?
Recent memory
Another way to test this is to give the patient several words to remember and test for recall 4-5 min later
During the delay, distractions are provided to prevent what?
rehearsing
Memory for historical or verifiable personal information
Remote Memory
If the patient has no attention this signifies?
Impaired Registration or Immediate Recall
What structures are affected when the patient has an Impaired Delayed Recall
Medial temporal lobes and medial diencephalon
inappropriate substitutions of words or syllables
Paraphrasic errors
Creation of non-existent words
Neologisms
Fluency, abundance, content, tonal modulation (cerebellum), grammar are all elements of?
Spontaneous Speech
Thinking for language is important for?
Form and content
Grammar and structure
Understanding simple questions and commands requires?
Comprehension
Agnosia and apraxia implicate a lesion at the ____________ or its connections
Association Cortices
Cannot follow instructions but is able to do it alone/spontaneously
Apraxia
Inability to formulate the correct movement sequence or Inability to carry out an action in response to verbal command, in the absence of any comprehension deficit, motor weakness or incoordination.
Ideomotor Apraxia
Ideomotor Apraxia arises from a lesion in what area
dominant temporoparietooccipital area
Inability to recognize letters or numbers traced on the palm
Agraphesthesia/Agraphognosia
Inability to understand meaning, import, or symbolic significance of ordinary sensory stimuli even through the sensory pathways and sensorium are relatively intact
Agnosia
Inability to recognize faces but recognize the voice and can describe the parts
Prosopagnosia
Lack of awareness of body defect
Anosognosia
abnormality in attention to one side that is not due to a primary or secondary sensory or motor disturbance
Hemineglect
lesions on the right parietal lobe causes?
Left hemineglect
Tests for neglect
Neglect drawing tests
Visual extinction
Copy drawing
Tactile extinction
Manual alternating sequence test, written alternating sequence test, auditory go-no-go are examples of?
Sequencing Tasks
difficulty in changing from one action to the next when asked to perform repeated sequence of action
Perseveration
What task asks the patient to tap table with fist, open palm, side of open hand then repeat
Luria Manual Sequencing Tasks
Frontal release signs are also known as?
Primitive reflexes
Proverbs and similarities are used to test what frontal lobe function?
Abstract Reasoning
Judgement and Logic are also tested
These impairments are categorized as diffuse brain dysfunctions or psychiatric disorders
Delusions and Hallucinations
When examining mood for mental status watch out for the following:
Signs of depression, anxiety, mania
Congruence between external appearance and feelings
Psychiatric in origin
Biochemical neurotransmitter imbalances
Somatization and conversion disorders
Nasal obstruction, damage to olfactory nerves in the mucosa as they cross the cribriform plate, or intracranial lesions affecting the olfactory pathway can lead to what?
Anosmia
Parkinson’s disease can also cause anosmia
Tested using coffee grounds or beans
Cranial nerve 1 (olfactory)
Noxious odors may stimulate pain fibers of which CN
Trigeminal
Visualization of the retina, retinal vessels, optic nerve atrophic changes, papilledema
Ophthalmoscopy
swelling of optic disc; sign of increased intracranial pressure
Papilledema
a measure of the ability of the eye to distinguish shapes and the details of objects at a given distance, tested using a Snellen Chart
Visual acuity
What test is used to test for color vision
Ishihara test
The patient is instructed to fixate on examiner’s nose and report when a finger can be seen moving in each quadrant or how many fingers are held up, what is being tested?
Visual fields
double simultaneous stimulation is used to test for?
Visual extinction or hemineglect
Visual hemineglect is caused by a contralateral parietal lesion, more robust on which side?
Right
What are the afferent and efferent fibers of the direct and consensual pupillary light reflex?
Afferent: CNII
Efferent: CNIII
Characterized by convergence of the medial recti, pupillary constriction, and lens thickening
Accommodation (Near Response)
Observe for dysconjugate gaze, spontaneous nystagmus
Look in all directions without moving head
Ask for double vision (diplopia) → check if eye movement is not focused together
Can indicate problem in extraocular muscle
The following test which cranial nerves?
Cranial Nerves 3, 4, 6
patient can track full range of vertical and horizontal eye movement, this eye movement is known as?
Smooth pursuit
patient cannot track full range of vertical and horizontal eye movement and there is rapid fixation, this eye movement is known as?
Saccades
General Sensation of the face can be impaired in lesions of what structures?
CN V
trigeminal nuclear complex in brainstem
thalamus
somatosensory cortex
Tactile Extinction is caused by?
right parietal lesions
Corneal reflex afferent and efferent fibers:
Afferent: CNV
Efferent: CNVII
Impaired in UMN lesions that synapses with trigeminal motor nucleus to peripheral nerve, NMJ, and muscle
Masseter and Temporalis
Sign of hyperreflexia associated with UMN lesion to trigeminal motor nucleus
Jaw Jerk Reflex
Afferent and efferent → CN V
Observation
Asymmetry, depth of nasolabial fold (NLF), spontaneous facial expression, blinking
Compare with old photos
Smile, puff cheek, close eyes tightly, wrinkle eyebrows
Taste in anterior ⅔ of tongue
All of the above tests what nerve?
Cranial Nerve VII
Caused by lesions in the ear, cochlea, and CN VIII
Unilateral hearing loss
Screening for CN VIII tests
Finger rubbing
Whispered words
Ticking of watch
Weber’s Test
Location of tuning fork
Normal:
Conductive hearing loss:
Sensorineural hearing loss:
Weber’s Test:
Vertex of skull
Normal: pitch heard equally on both ears
Conductive hearing loss: louder on affected side
Sensorineural hearing loss: softer on affected side
Rinne’s Test
Location of tuning fork
Normal:
Conductive hearing loss:
Sensorineural hearing loss:
Rinne’s Test
EAM
Normal: AC > BC
Conductive hearing loss: BC>AC
Sensorineural hearing loss: AC>BC but decreased in affected ear
Exercise for CN VIII (???)
Cover one EAM and hum
Cranial nerves responsible for Palatal Elevation and Gag Reflex
CN IX, X
Gag reflex makes you gag when the _______ pharynx is brushed
Posterior pharynx
When is gag reflex tested?
suspected brainstem pathology,
impaired consciousness
impaired swallowing
Cranial nerves responsible for the muscles of articulation:
CN V, VII, IX, X, XII
Lesions in these structures can cause impaired modulation of tone and sound, coordination
motor cortex, cerebellum, basal ganglia
abnormal pronunciation of speech (slurred speech)
Dysarthria
abnormality in language comprehension or production (cerebrum)
Aphasia
CN for traps and SCM
CN XI
What do we observe for when testing CN XII (tongue muscles)
muscle bulk, presence of fasciculations (spontaneous, quivering)
Fasciculations and atrophy are signs of _____ lesion
LMN lesion
Unilateral Tongue Weakness deviates towards the ____ side
weak side
LMN = ipsilateral to the lesion
UMN = contralateral to the lesion
Components of an UMN
Supraspinal neurons and their tracts
Components of a LMN
Anterior horn cell
Peripheral nerve
Neuromuscular junction
Muscle
Identify if UMN or LMN:
Weakness below the lesion
(+) Fasciculations
(-) Babinski reflex
Hyperreflexia
Areflexia
Hyporeflexia
Spastic muscle
Flaccid or hypotonic muscle
Identify if UMN or LMN:
UMN
LMN
LMN
UMN
LMN
LMN
UMN
LMN
Identify if UMN or LMN:
hemiplegic, quadriplegic, or paraplegic distribution
individual or sets of muscles in root or peripheral nerve distribution
severe atrophy
mild atrophy
Identify if UMN or LMN:
UMN
LMN
LMN
UMN
abnormal muscle twitching due to spontaneous activity in groups of muscle cells
Fasciculations
During inspection and palpation, there is need for special attention to intrinsic hand muscles, shoulder girdle, and thigh in patients with _____ disorders
LMN disorders
Amount of tension (or resistance to movement) in muscles or the partial state of contraction at rest
Muscle tone
Abnormalities in functional testing:
Pronator drift
Abnormalities in fine movements
Finger tapping, rapid foot tapping
MMT (Alam nyo na to)
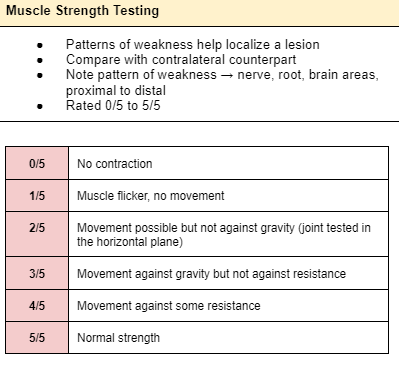
Spinal level of Ankle/Achilles reflex:
S1
Spinal level of the Brachioradialis reflex
C5-6
Spinal level of the Knee Reflex
L2-4 (predominantly 4)
Spinal level of the triceps reflex
C7-8 (predominantly 7)
Spinal level of the Jaw jerk / Masseter reflex
CN V3
Spinal level of the biceps reflex
C5-6
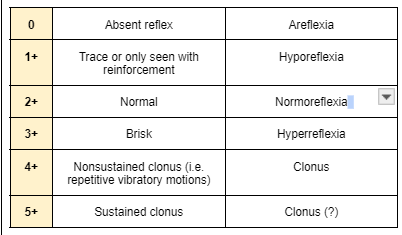
Grading for reflexes
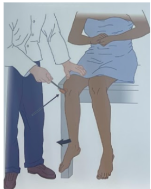
Name the reinforcement procedure
Pull method (of Jendrassik)
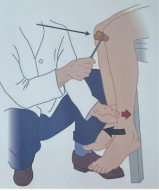
Name the reinforcement procedure
Counterpressure