Genetics - Grade 8
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
allele
Different forms of a gene for a trait
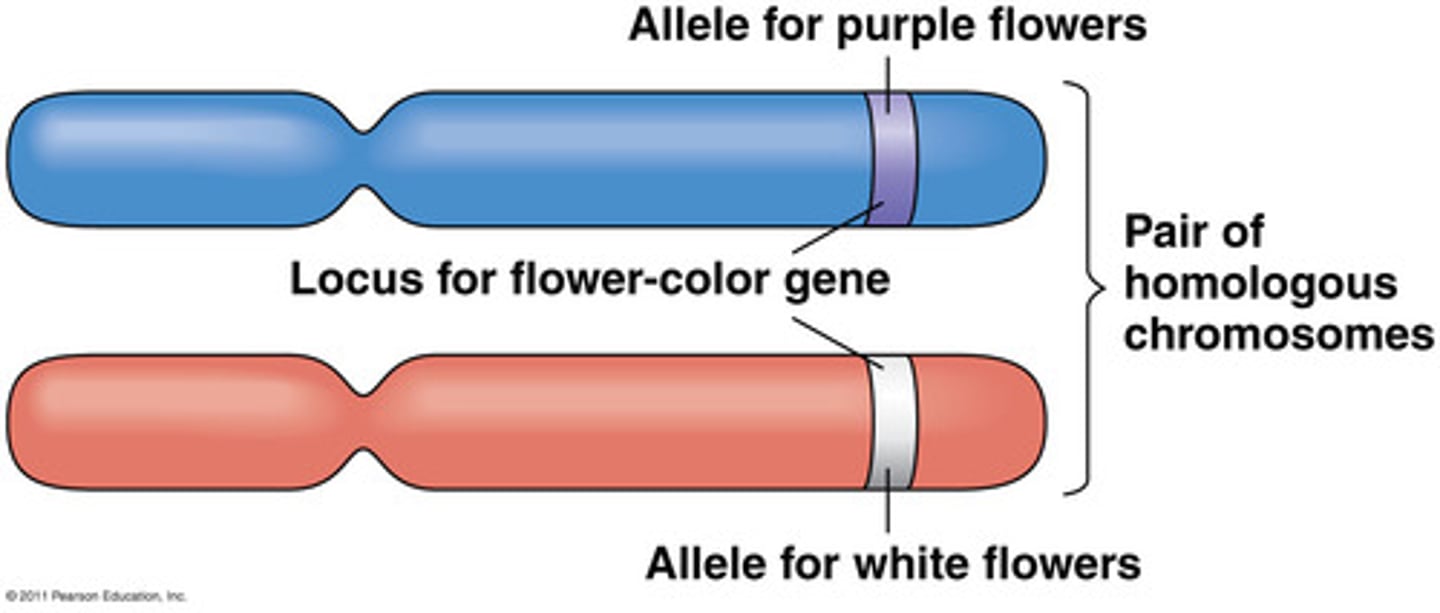
homozygous
when two alleles of a gene are the same

heterozygous
when the two alleles of a gene are different

dominant
An allele that is always expressed; "the bossy one"

recessive
a trait that can be hidden by the dominant trait; "the shy one"
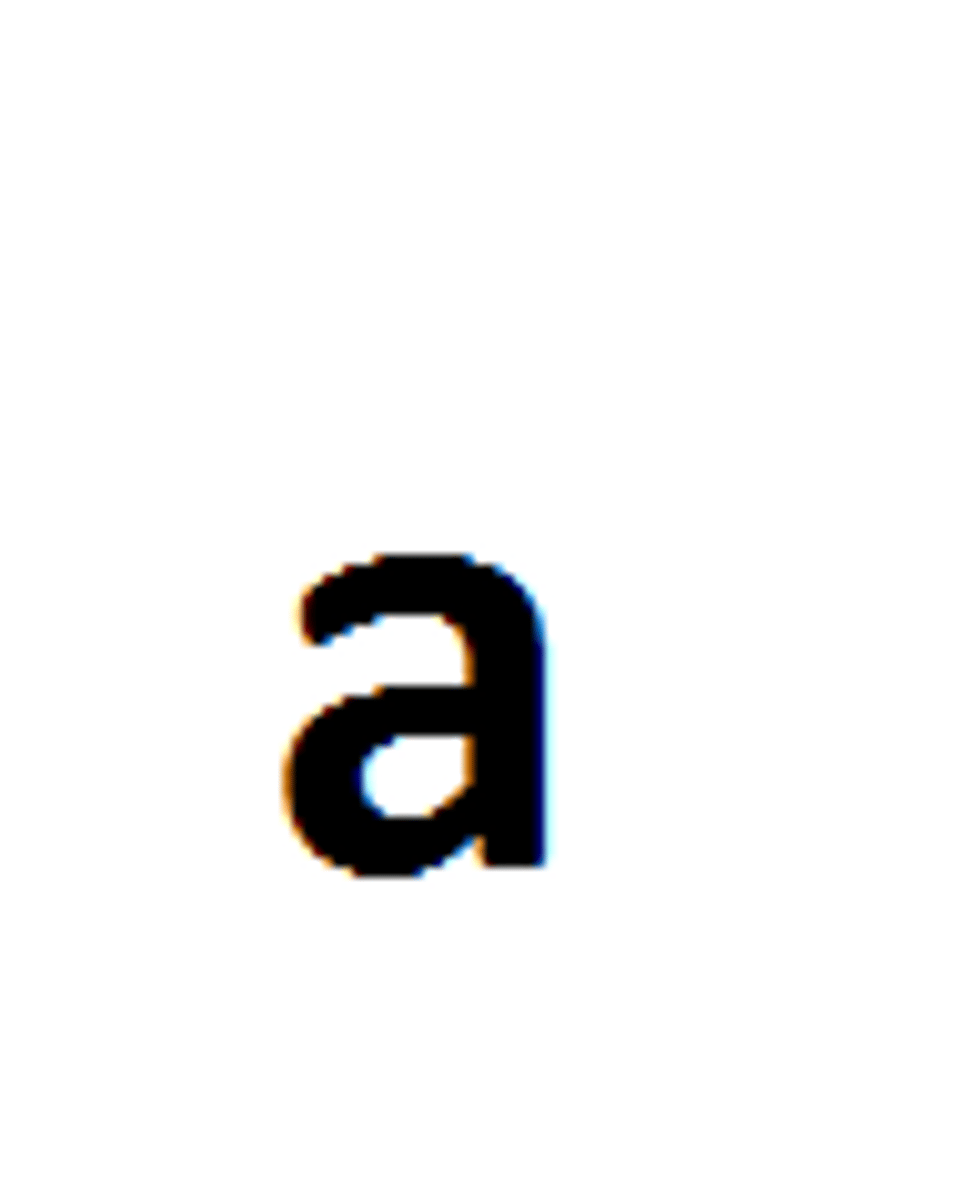
genotype
two letters that represent a gene's allele pair
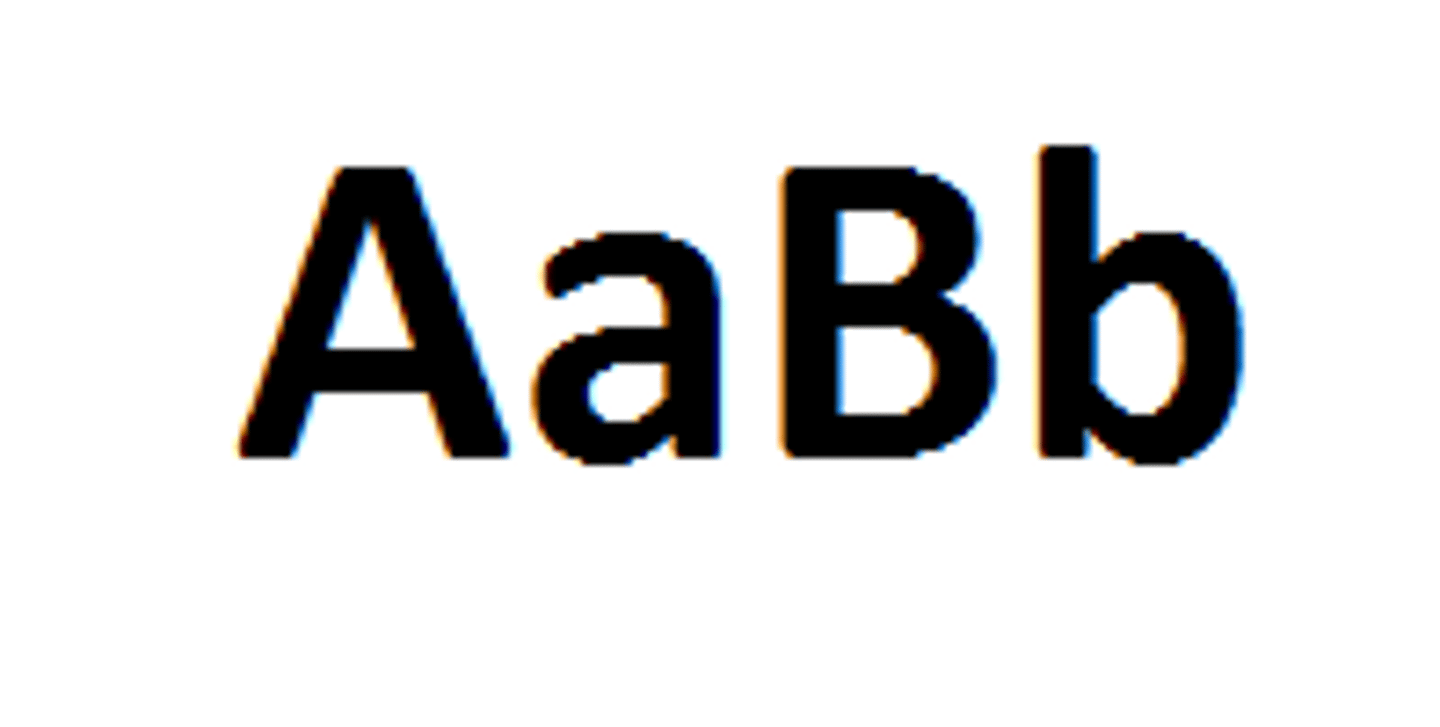
phenotype
An organism's physical appearance, or visible traits.
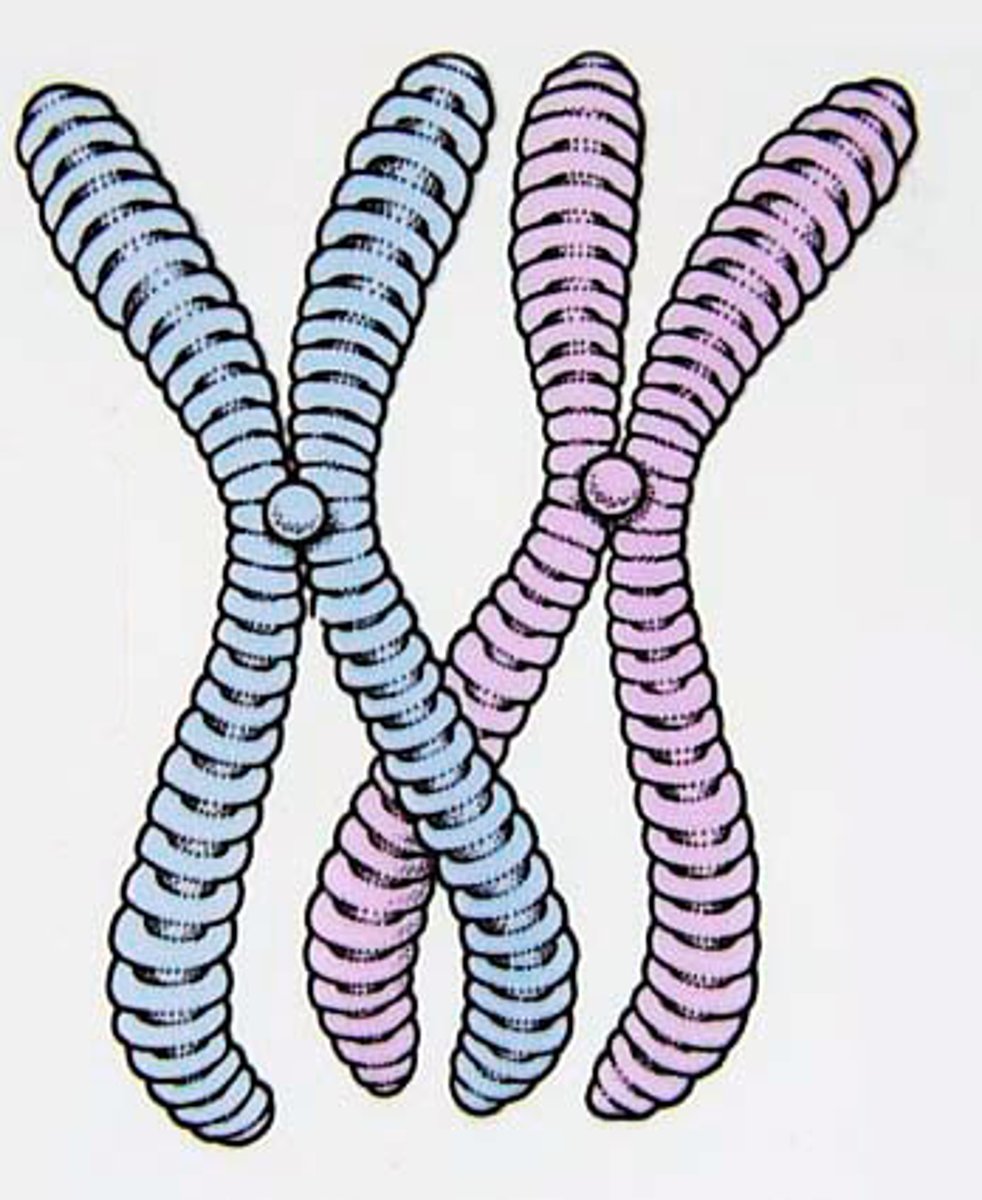
chromosome
Carries genes and found in the nucleus. Humans have 46 total chromosomes (23 pairs with 50% from each parent)
offspring
Product of reproduction, a new organism produced by one or more parents

genetics
The scientific study of heredity

Inheritance
The process in which genetic material is passed from parents to their offspring.

heredity
passing of traits from one generation to the next
environmental factors
ecological or non-living factor that influences living organisms (weather, habitat, smoking)

genetic factors
Traits that are passed through the genes (for example, sickle cell anemia)

asexual reproduction
A reproductive process that involves only one parent and produces offspring that are identical to the parent. (pro: can produce a lot of offspring more quickly) (con: less genetic diversity so population more likely to be affected by disease)
sexual reproduction
A reproductive process that involves two parents that combine their genetic material to produce a new organism, which differs from both parents (pro: genetic diversity) (con: takes a lot of time and energy)
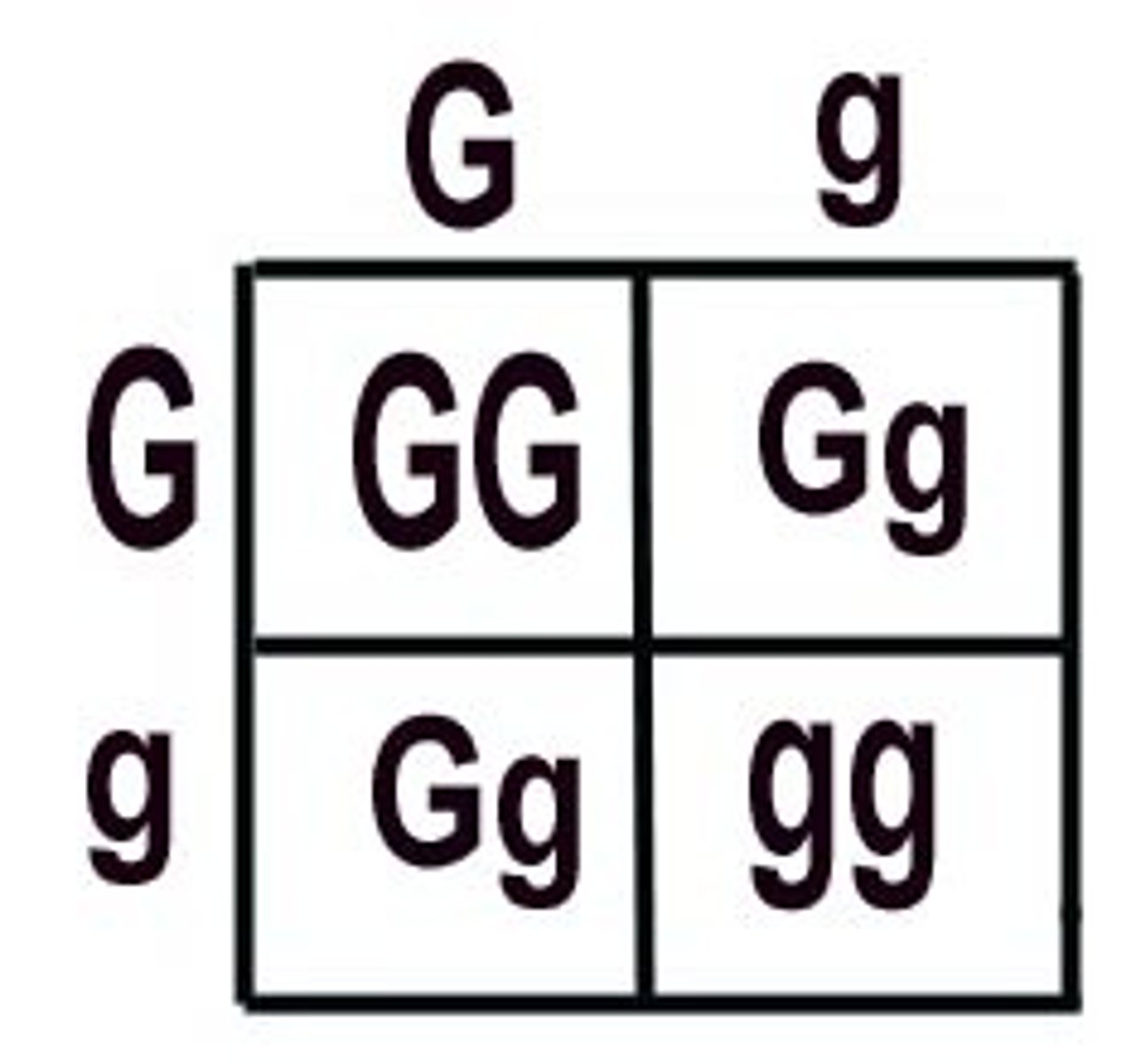
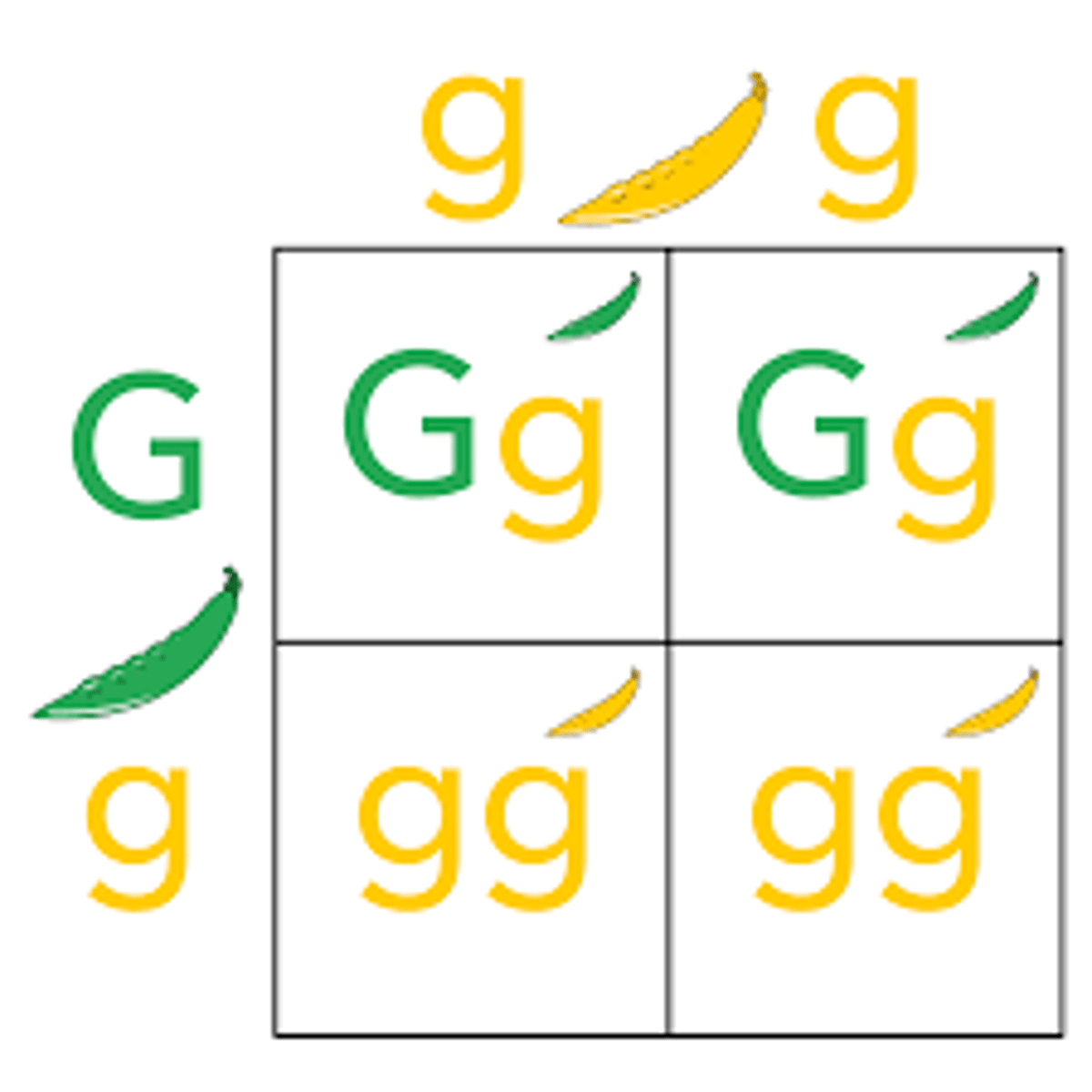
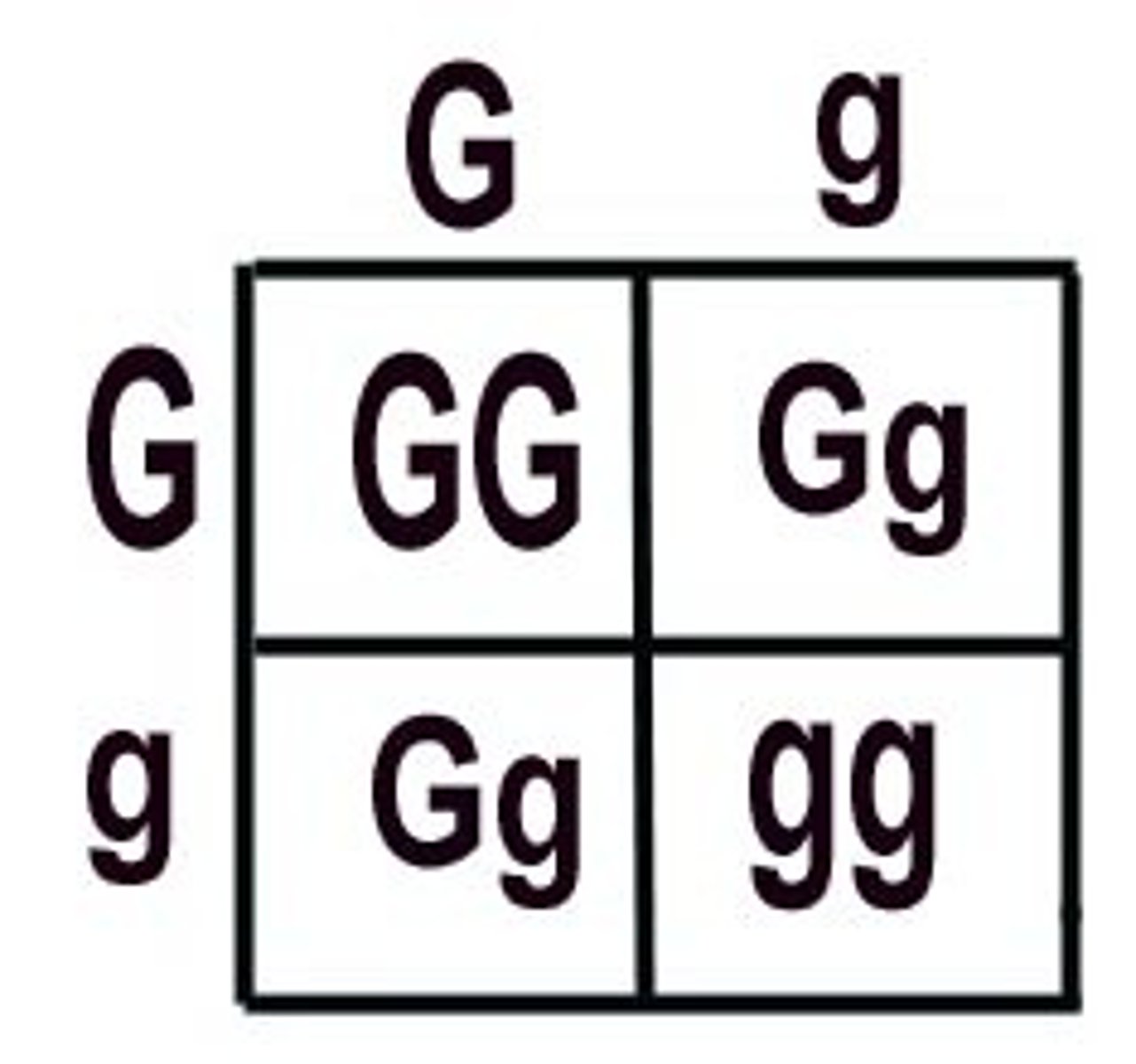
Punnett Square
A chart that shows all the possible combinations of alleles that can result from a genetic cross
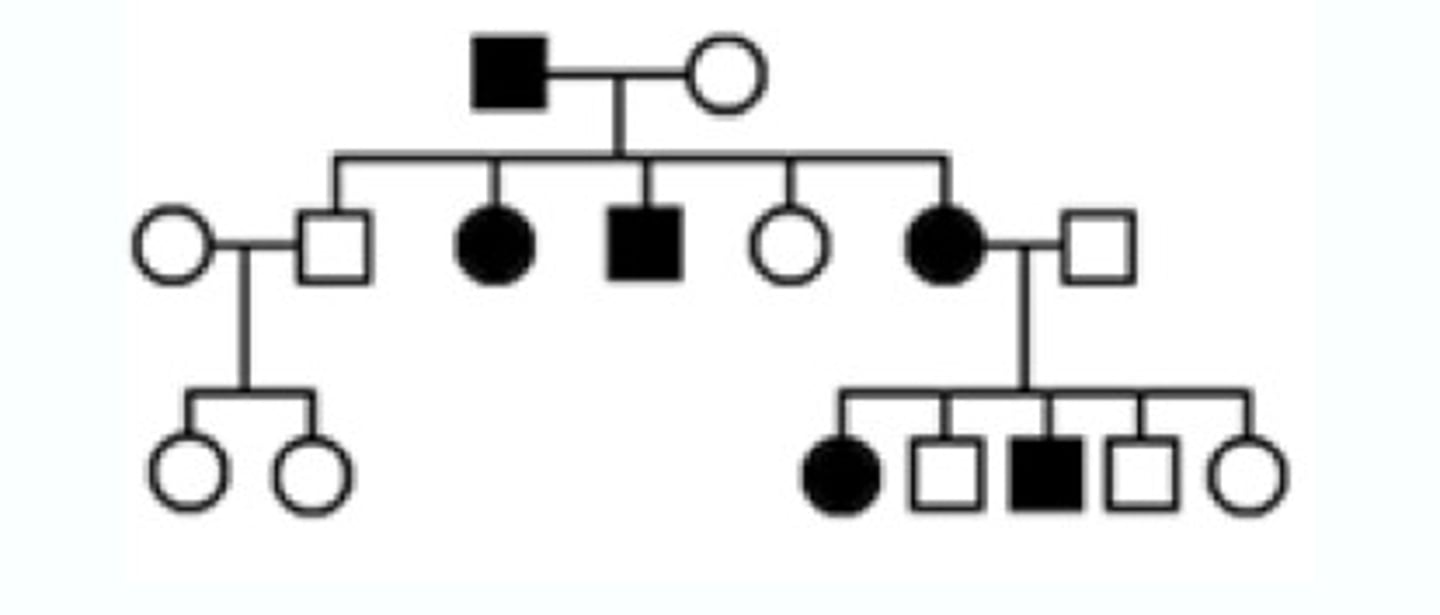
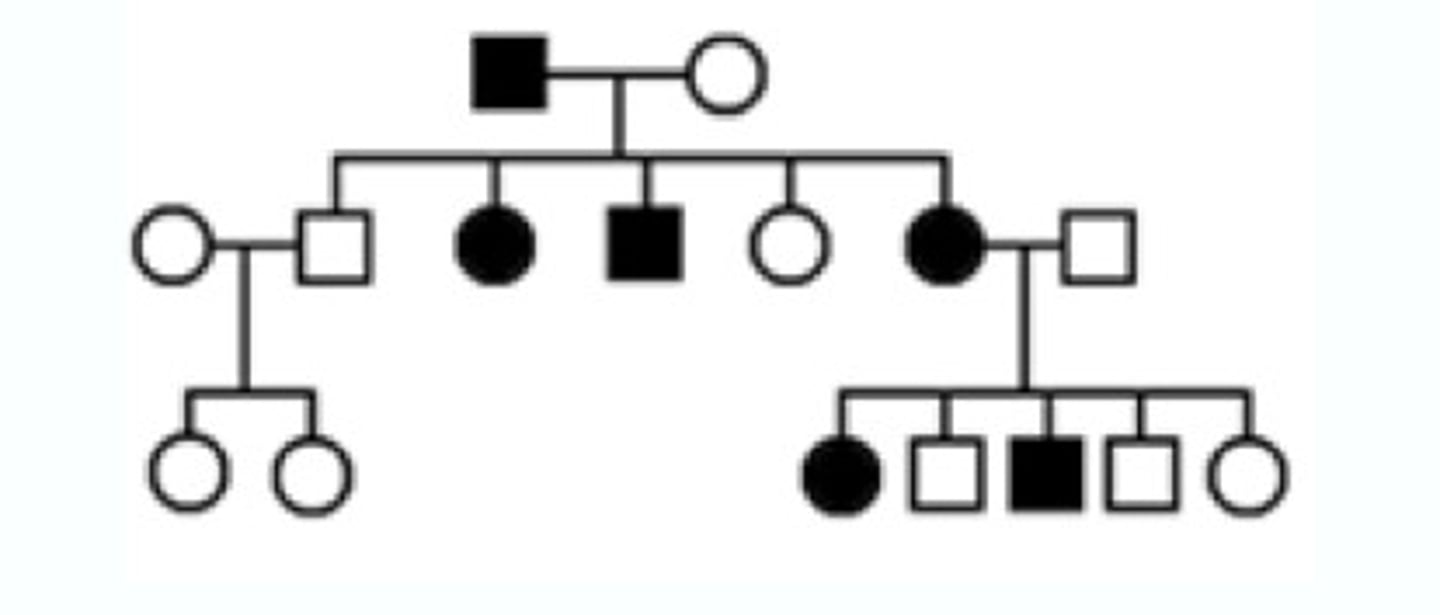
Pedigree
A chart or "family tree" that tracks which members of a family have a particular trait (squares=males). (circles=females) (generations I, II, III, IV, V) (shaded=exhibits the trait)
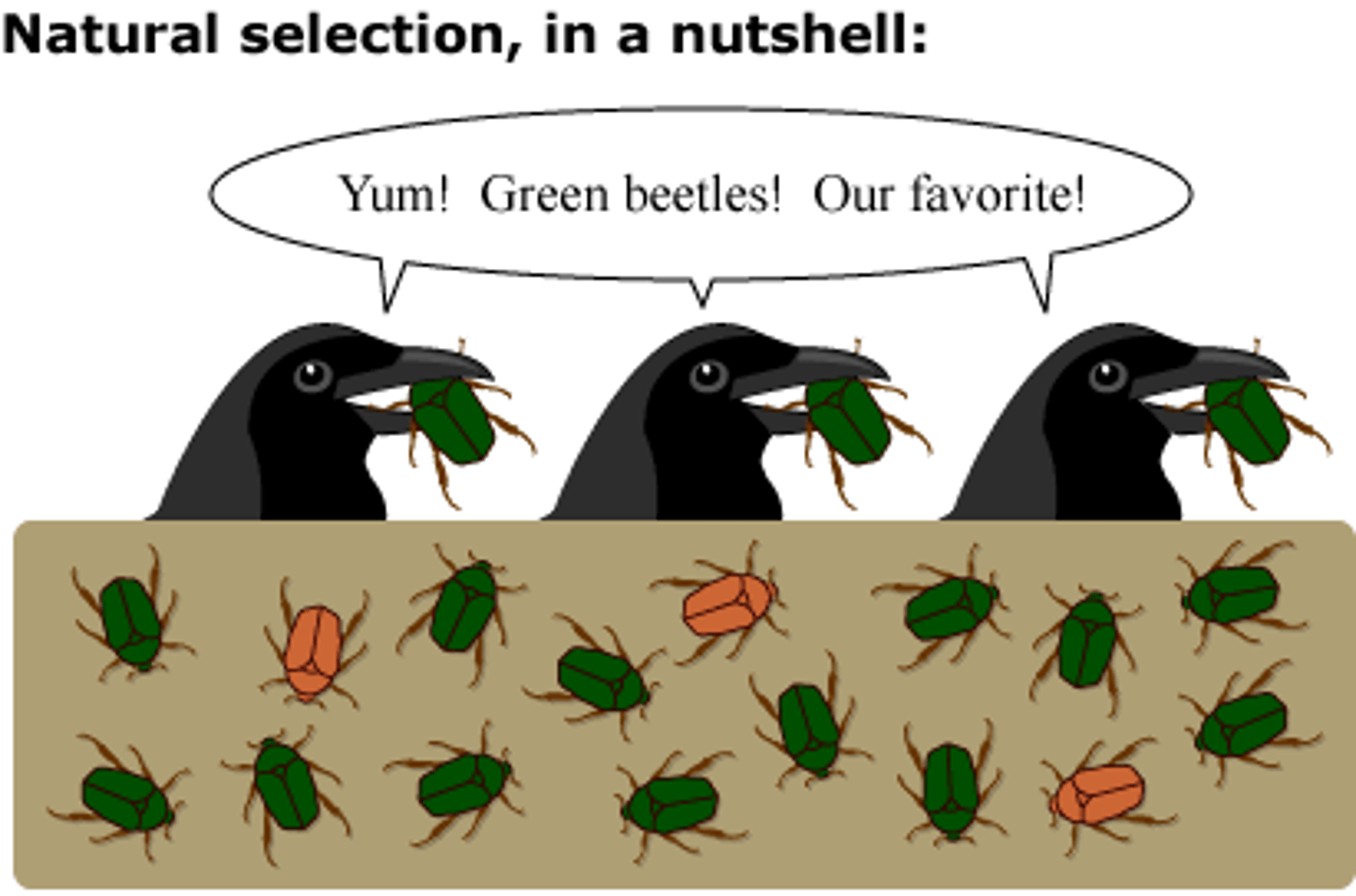
natural selection
organisms in a population develop traits that allow them to survive and reproduce (advantageous traits passed down to help survival); can lead to evolution
artificial selection
the selective breeding of organisms by humans for specific characteristics (for example, breeding hypoallergenic dogs) (pro: food that can grow in harsh conditions) (con:can decrease genetic diversity)

genetic probability
chance of getting certain gene (0%, 25%, 50%, 75%, or 100%)
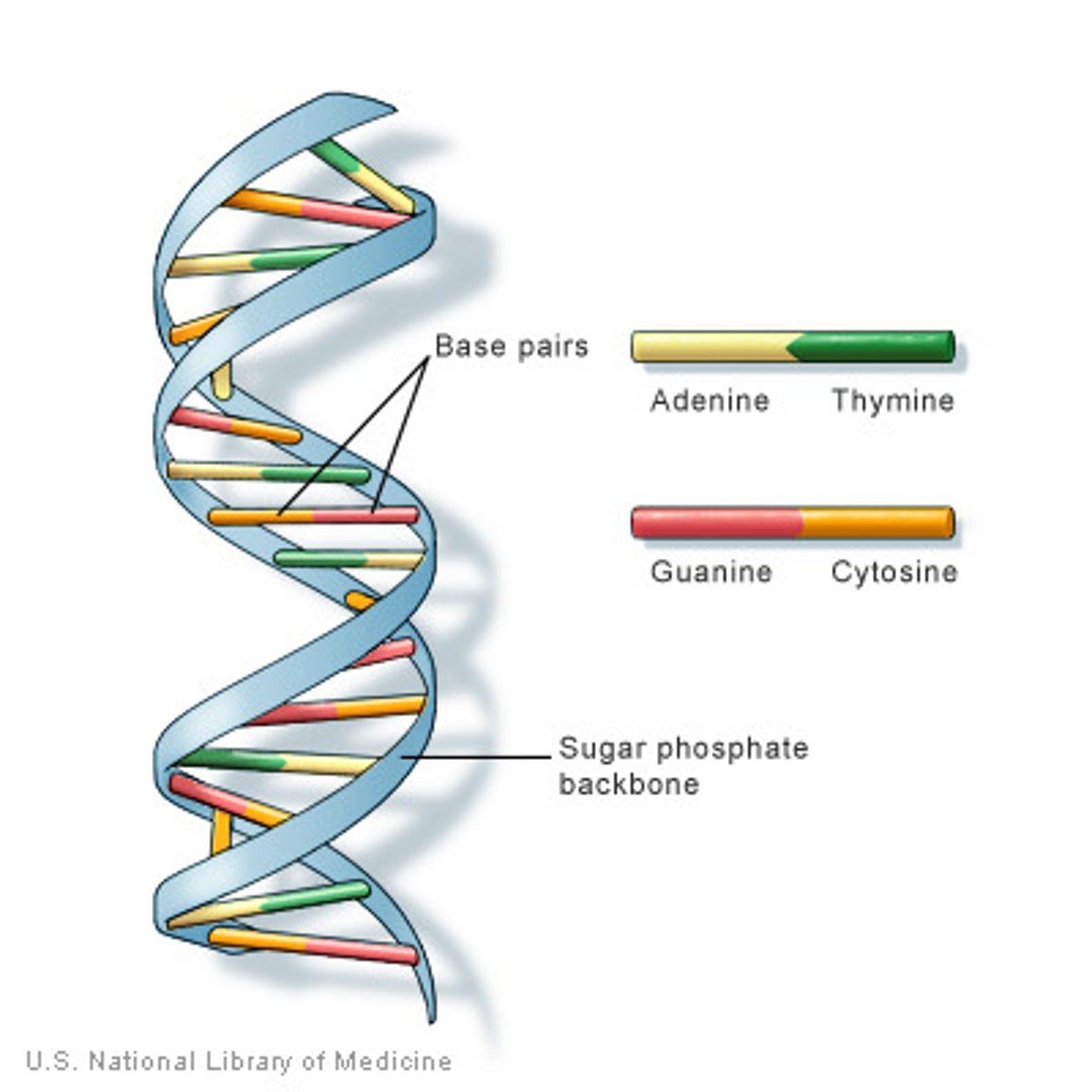
DNA
A complex molecule containing the genetic information that makes up the chromosomes. (deoxyribonucleic acid)
Pp, Purple
Purple is dominant in a flower (P). Pink is recessive (p). The flower is heterozygous. What is its genotype and phenotype?
pp, pink
Purple is dominant in a flower (P). Pink is recessive (p). The flower is homozygous recessive. What is its genotype and phenotype?
PP, Purple
Purple is dominant in a flower (P). Pink is recessive (p). The flower is homozygous dominant. What is its genotype and phenotype?
25%
Here is a cross between two heterozygous parents. What is probability an offspring will be homozygous recessive?
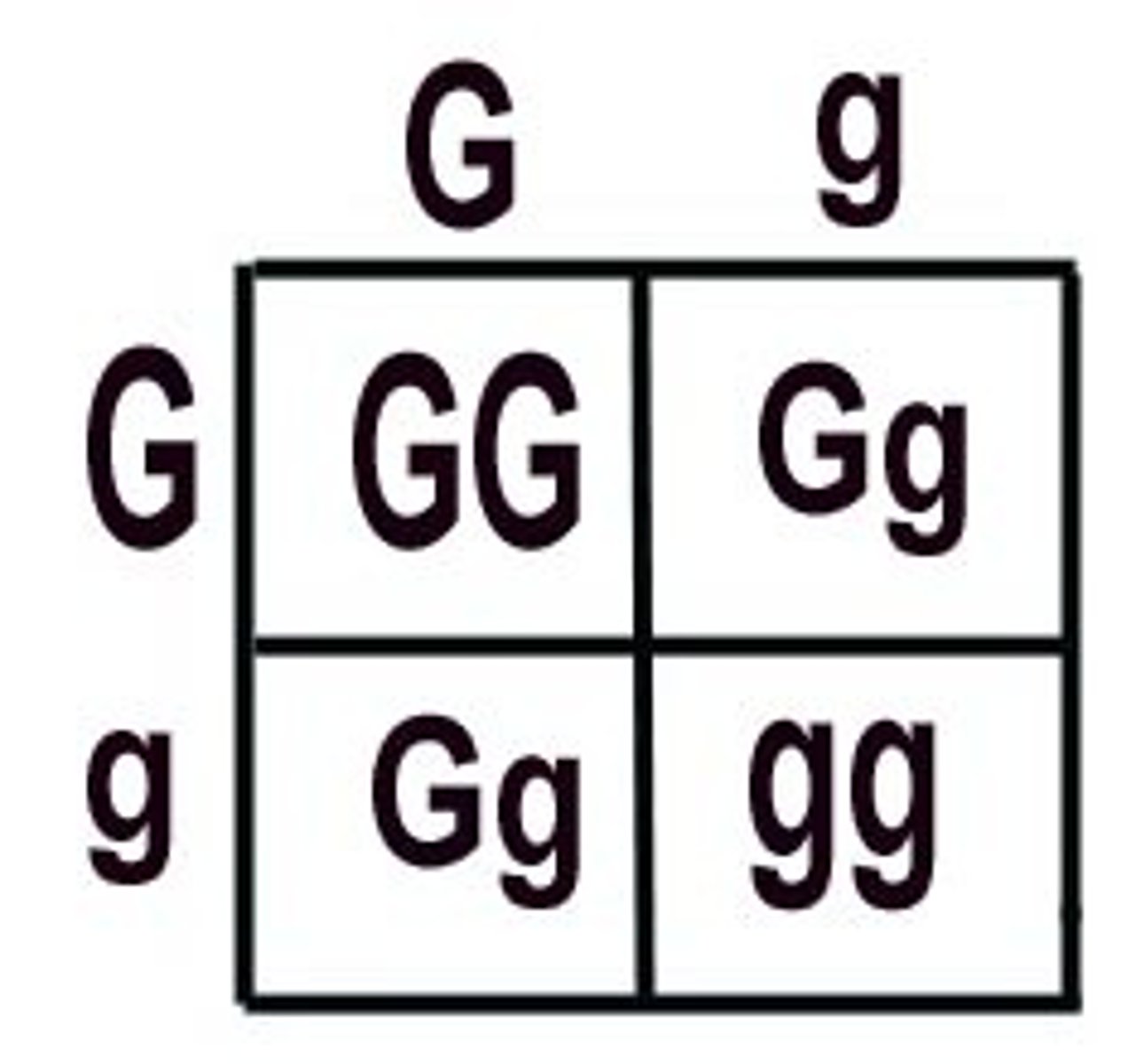
50%
Here is a cross between two heterozygous parents. What is probability an offspring will be heterozygous?
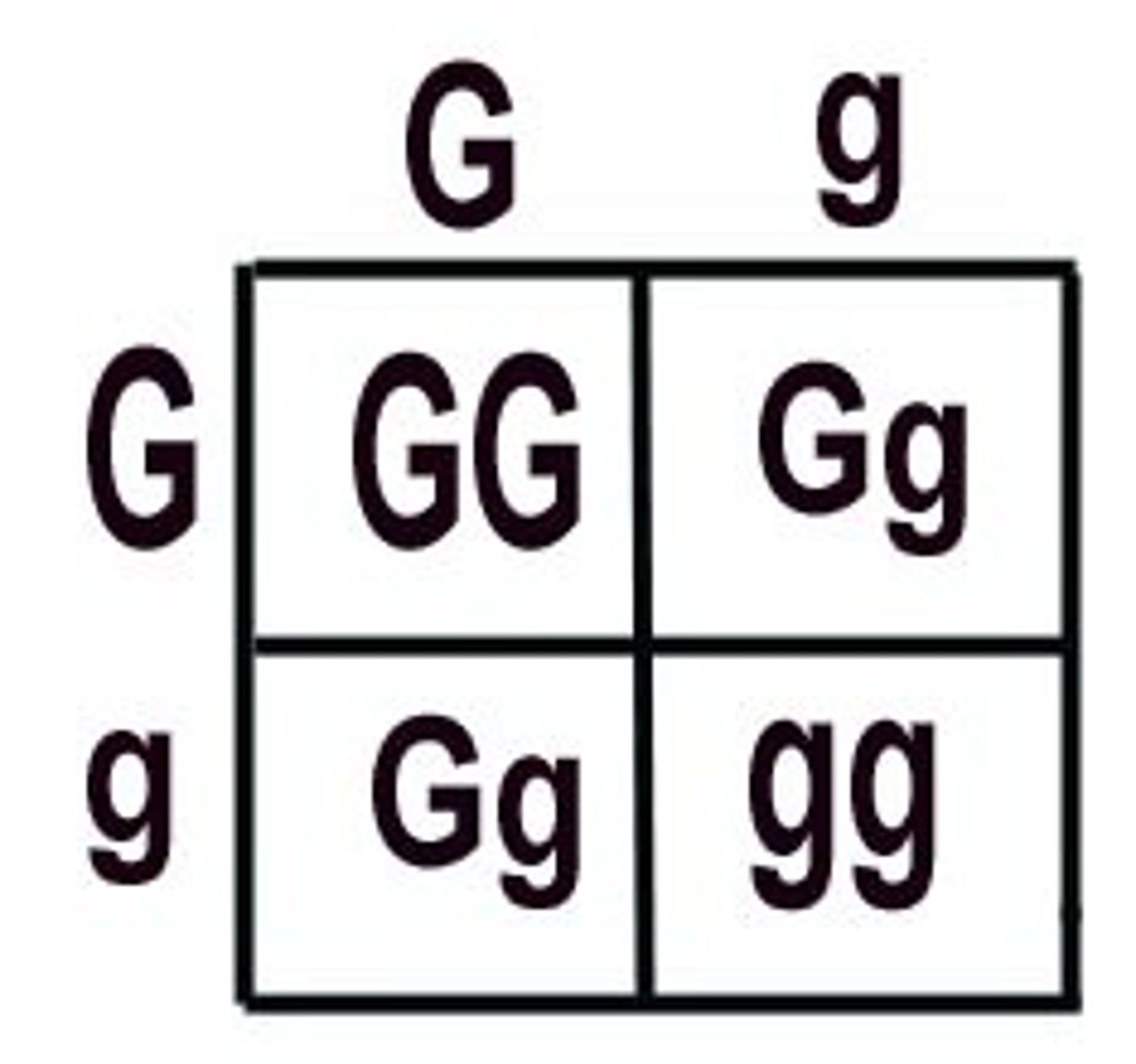
75%
Here is a cross between two heterozygous parents. What is probability an offspring will express the dominant trait?
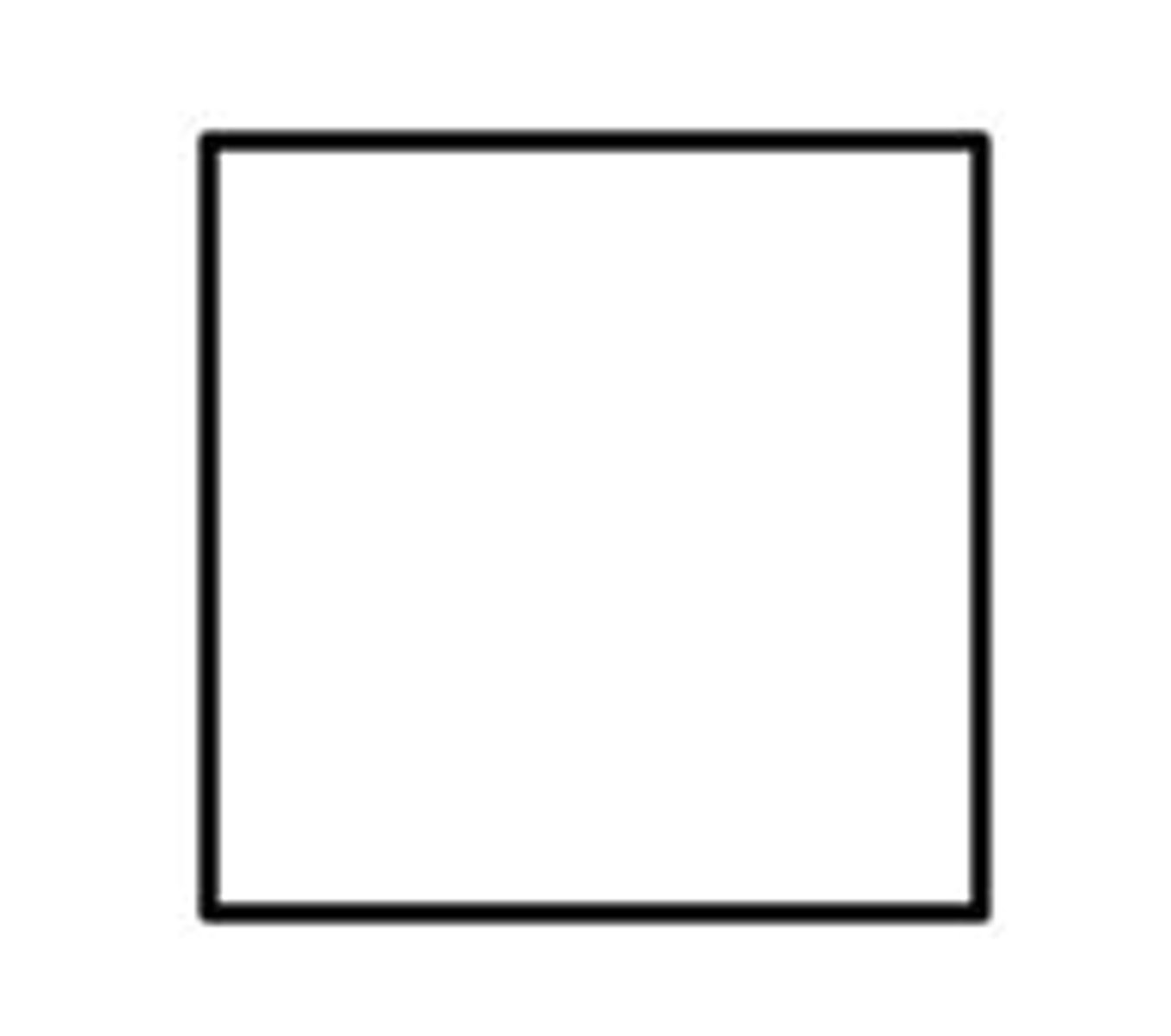
square
shape that represents a male in a Pedigree chart
3 (I, II, III)
number of generations in this Pedigree chart
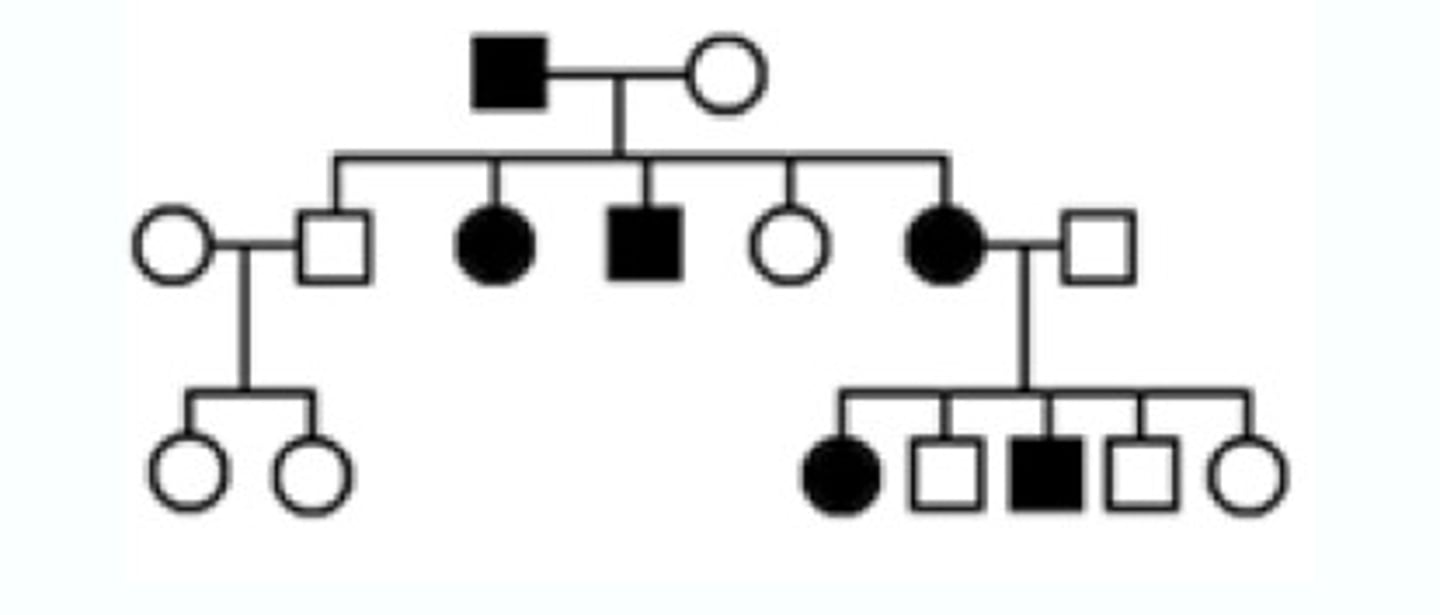
3 (3 circles are shaded)
number of females expressing the trait in this pedigree chart