BIOL 208: Lecture 5 - Aquatic Biomes
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
****How are Aquatic biomes Classified (2)
Salt
Fresh
****What are the further classifications of FRESH water?
Lotic = Moving (rivers + streams)
Lentic = Still (ponds, lakes + wetlands)
Define LIMNOLOGY?
The study of INLAND AQUATIC SYSTEMS
eg. rivers, lakes, ponds, wetlands etc.
******What are the 2 BROAD VERTICAL divisions of aquatic zones for ALL aquatic systems (oceans + others)?
Pelagic: Off bottom of aquatic environment in the water
Benthic: BOTTOM of aquatic environment
****What are the 5 OCEAN VERTICAL ZONES. Place them in order from top to bottom and indicate which are PELAGIC + which are BENTHIC
Pelagic (thus all have pelagic in name)
Epipelagic:
Mesopelagic
Bathypelagic
Benthic
Abyssal
Hadal
****What is the EPIPELAGIC ZONE also known as?
Photic zone
high light + temp
TRUE OR FALSE: Organisms in the EPIPELAGIC zone tend to be dull in color as they need to camouflage due to the high light that passes through the zone?
FALSE
tend to be BRIGHT COLOR
*****What type of Water movement is ALGAE BLOOMS related to and why?
COASTAL UPWELLING: replacing water moving away from shore due to Ekman transportation when the wind is blowing parallel to the coast with DEEPER waters
Deep waters = Nutrient rich
Are algae blooms good or bad?
Depends on:
species + density
What are the conditions in the BATHYPELAGIC ZONE?
LOW: Light + temp
HIGH Pressure
Organisms living in the Bathypelagic zone, adapt to their environment. How do they adapt their METABOLISM?
Slow it down
****What are the 2 water sources of RIVERS?
Rain runoff
Ground water
Finish the sentence: Rivers ___ most of the landscapes of this world
DRAIN
****What are the HORIZONTAL ZONES of RIVERS? Define each zone (3)
Furthest from shore
Wetted channel
Permanently has water
Active channel
Has water at certain times of the year
Riparian Zone
Transition between water + land
Closest to shore
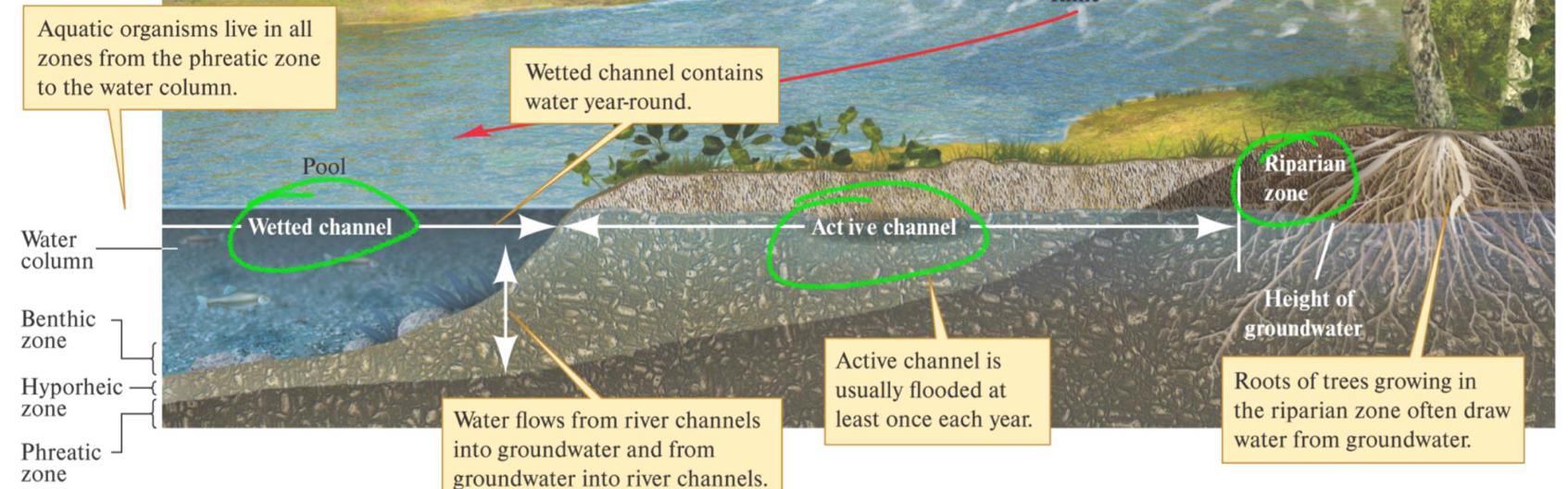
****What are the VERTICAL ZONES of a RIVER? List them in order. (4)
Water Zone
Benthic zone (Bottom)
Hyporheic Zone
Phreatic zone
****Define Hyporheic + Phreatic Zone and What special organism live in each?
Hyporheic = Where Surface water meets ground water
Organism = HYPORHEOS
Phreatic zone = Ground water
Organism = Phreatobites
*****What are some Adaptations of HYPORHEOS + PHREATOBITES and How do they differ in LIFESPAN?
Hyporheos = adapted to HIGHER O2 + SHORTER LIFE SPAN
Phreatobites = no eyes b/c no light to see + LONGER LIFE SPANS = slower metabolism?
****What are the HORIZONTAL ZONES of STILL WATER? Define each zone (2)
Littoral = Along lake edge
Limnetic = open lake (further in)
*****What are the VERTICAL ZONES of STILL WATER? (3)
Epilimnion: warm
Metalimnion
Hypolimnion: Dark + cold
(Limnion Like LIMNETIC)
***Define Thermocline + identify which of the 3 vertical layers in still water = the Thermocline
Metalimnion
Thermocline = rapid decrease in temp
***What are some organisms are typically found in the Epilimnion?
Phytoplankton, fish + birds
****What is the O2 concentration at the HYPOLIMNION? Why?
LOW
Due to Organic matter settled + accumulated at bottom, decomposers= use up the O2 present
Also cannot dissolve more O2 from the atmosphere because it is separated from it
Define Thermal stratification
Water bodies, particularly lakes, develop separate layers due to temperature differences
Driven by solar heating
Is hot or cold water more dense?
Cold
Is ice less or more dense than water?
Less dense
*******At what temperature is Water the MOST DENSE?
4 degrees Celsius
****In temperate lakes specifically, during WHICH SEASONS is there THERMAL STRATIFICATION or is there ALWAYS Thermal stratification? If there is thermal strat. what are the temps?
Summer: Top = 28, middle = 8, Bottom = 4
Winter: Top = 0 (ice), middle = 3, Bottom = 4
****There is NO thermal stratification During spring + fall for Temperate Lakes; what does this allow to occur within the lake?
MIXING OF LAYERS as all layers are 4 degrees = TURN OVER
****How does the MIXING of Layers affect the Lake?
Increase productivity esp. of Phytoplankton (primary prod.)
evenly distribute Nutrients + O2 to all layers
****What are the 3 CLASSIFICATION of LAKES by Productivity
Oligotrophic
Eutrophic
Dystrophic
***Define OLIGOTROPHIC lakes by their: Color, Nutrients, Primary production, O2 lvls + Diversity/organisms
Color = Clear Blue
Nutrients = Low [N] + [P]
Primary Prod = Low (bc low nutrients)
O2 lvls = HIGH
Diversity = Animals adapted to conditions eg. trout (adapted to high o2)
Why is O2 lvls high in OLIGOTROPHIC lakes?
[O2] is affected by: ALGAE growth + Rate of die-off + Decomposition of aquatic plants = related to high demand in O2
Low nutrients = Low algae growth = Less organic matter settled at bottom of lake = less decomposer activity
More light penetration b/c clear blue color = increase phytoplankton activity
***Define EUTROPHIC lakes by their: Color, Nutrients, Primary production, O2 lvls + Diversity/organisms
Color = Green
Nutrients = HIGH [N] + [P]
Primary Prod = HIGH (bc High nutrients)
O2 lvls = VARIES
In the summers = Low (LOTS OF ALGAE BLOOMS, block sun, use up o2 + create organic matter for decomposers)
Diversity = Animals adapted to conditions eg. cat fish
Define Eutrophication
Addition of EXCESS NUTRIENTS to a lake due to run off from farms etc. = cause algae blooms which reduce O2 concentrations
***Define DYSTROPHIC lakes by their: Color, Nutrients, Primary production, O2 lvls + Diversity/organisms
Color = Brown
Nutrients = HIGH HUMIC ACIDS
AKA Humic Lakes
Primary Prod = LOW (bc of Low pH)
O2 lvls = LOW
bacterial decomposition of the organic matter
Diversity = LOW
*What are the 2 Fresh water wetlands?
Fens
Bogs
*Compare + Contrast Fens + Bogs: Water source, pH, topography + Plant diversity
Water source:
Fens = Ground water
Bogs = Rainwater
PH
Fens = Varies (depends on minerals)
Bogs = ACIDIC (acid rain)
Topography
Fens = Flat
Bogs = Bumpy/lumpy
Plant diversity
Fens = Grasses, sedges, mosses + vascular plants
Bogs = Mosses, Carnivorous plants, shrubs + hardy tree species
****Define NICHE
Range of ABIOTIC conditions + BIOTIC interactions in which an organism can survive, grow + reproduce (required factors)
Abstract concept not a specific location
*****Fundamental vs. Realized niche?
Fundamental aka. Physiological conditions:
Physical conditions (ABIOTIC) under which a species might live in the absence of interactions w others
Realized:
Environmental conditions under which a species might live when restricted by interactions (BIOTIC) with other species
********What is the Competitive exclusion principle?
No 2 species that depend on the same limiting factors can occupy the same realized niche (coexist) indefinitely
Evolution of Niche: Joseph Grinnell
Focused on ABIOTIC CONDITIONS
Evolution of Niche: Charles Eton
Included BIOTIC to abiotic
****Evolution of Niche: HUTCHINSONIAN NICHE
MANY factors affect niche
****What is the n-Dimensional Hypervolume?
Hutchinsonian Niche
ALL the things that influence where something lives + allows it to live its best life GRAPHED in a HYPERVOLUME
Where ‘n’ = the # of environmental factors important to survival
More factors added = harder to graph
****Why do we Characterize the niche?
To predict where species are found + encountered
*What are 4 THINGS we can PREDICT/DO by characterizing the niche?
Actual + potential change in geographic range of a species
Bring back species from brink of extinction
Expansion of new invasive species
How far + fast will range of expansion occur with a change in environmental suitability
***What are 3 Ways we characterize the niche. And 1 specific way for Invasive species?
Historical data on species distribution
Geographic Information systems (GIS)
Climate modeling
Invasive
Habitat conditions found in regions of origin
***What are some Other factors used to characterize niche depending on species studies?
Soil type (eg. plants)
Presence of Predators + competitors (eg. Animals)
*******What did ROBERT MACARTHUR study
Competitive Exclusion Principle
Using Warblers
all insectivores that live in the same type of forest/trees
****What specific activity did ROBERT MACARTHUR Observe + what was his CONCLUSION?
Observed amount of time spent in each level of tree + how it differed between species of warblers
Conclusion: Each species had a distinct FEEDING ZONE
***What type of Strategy did the Warblers apply to decrease competition?
Avoidance strategy
*****How can species avoid being excluded from the niche?
NICHE PARTITIONING
*****Define NICHE PARTITIONING
Species in a community use the same limiting factors (resources) in Different ways
occupy different Realized niches + coexist
Decrease direct competition
****What are the types of Resource partitioning?
Where, Which, How or when Resources/factors are used
Spatial (warblers)
Dietary (food source change)
Temporal