IELTS2B consumerism
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
unprecedented (adj) /ˌʌnˈpresɪdentɪd/
never having happened or existed before.

surge (n) /sɜːdʒ/
a sudden and significant increase.

consumerism (n) /kənˈsjuːmərɪzəm/
the belief that buying goods and services is very important for a society.

acquisition (n) /ˌækwɪˈzɪʃən/
the act of gaining or obtaining something, especially knowledge, skills, or assets.

exact a toll on (phrase) /ɪɡˈzækt ə təʊl ɒn/
to cause harm, damage, or suffering to someone or something.

ecosystem (n) /ˈiːkəʊˌsɪstəm/
a community of living organisms and the environment they interact with.

repercussion (n) /ˌriːpəˈkʌʃən/
an indirect or unexpected negative consequence of an action.

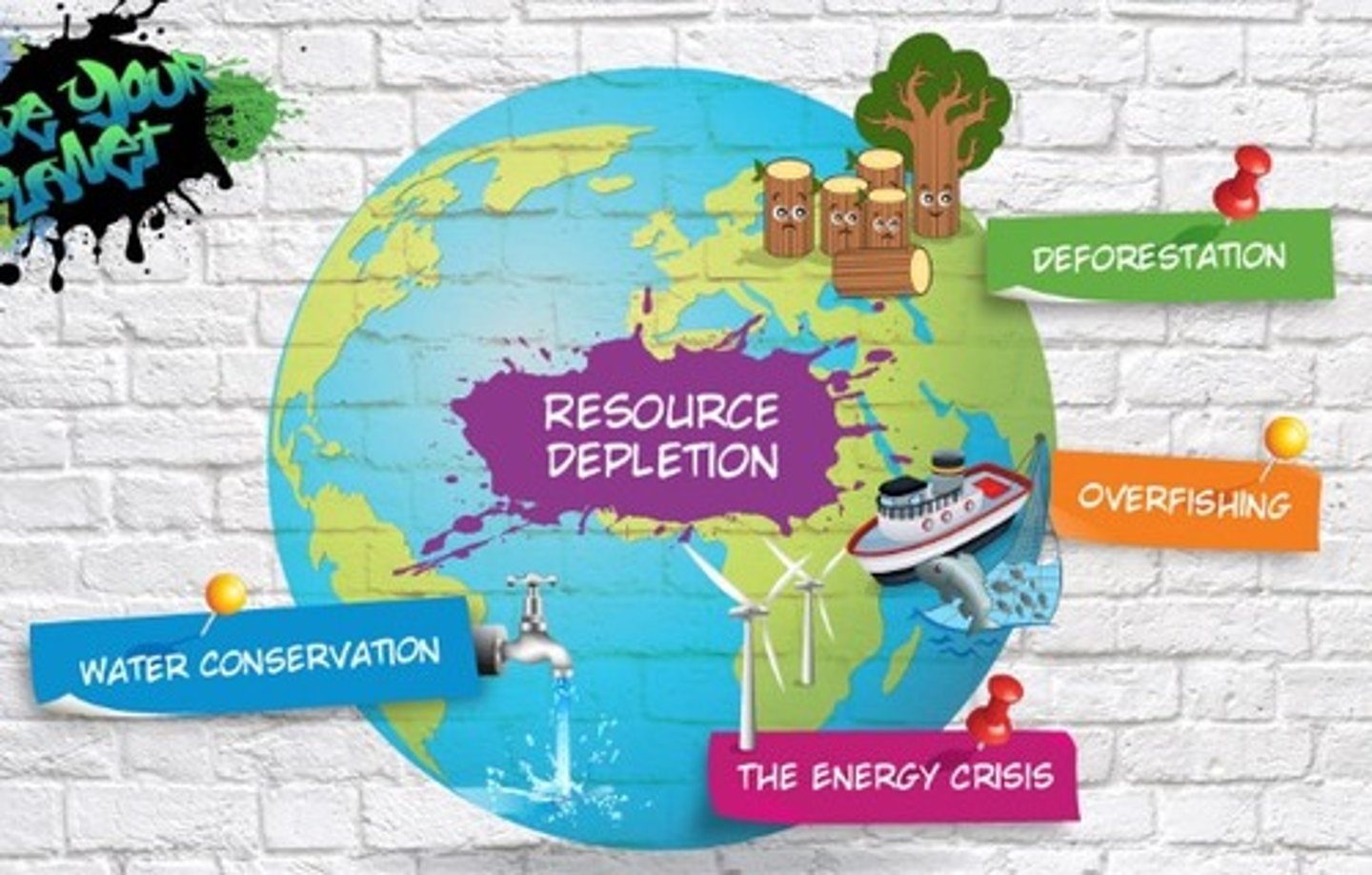
resource depletion (n) /rɪˈzɔːs dɪˈpliːʃən/
the reduction or exhaustion of natural resources.
extraction (n) /ɪkˈstrækʃən/
the process of removing or obtaining something from the environment, especially minerals or fossil fuels.

intensify (v) /ɪnˈtensɪfaɪ/
to increase in strength, degree, or seriousness.

habitat destruction (n) /ˈhæbɪtæt dɪˈstrʌkʃən/
the process of damaging or eliminating the natural home of plants or animals.

insatiable appetite (phrase) /ɪnˈseɪʃəbl ˈæpətaɪt/
a desire that cannot be satisfied, no matter how much is consumed.

throwaway culture (n) /ˈθrəʊəweɪ ˌkʌltʃə/
a society where people frequently discard items rather than reuse or repair them.
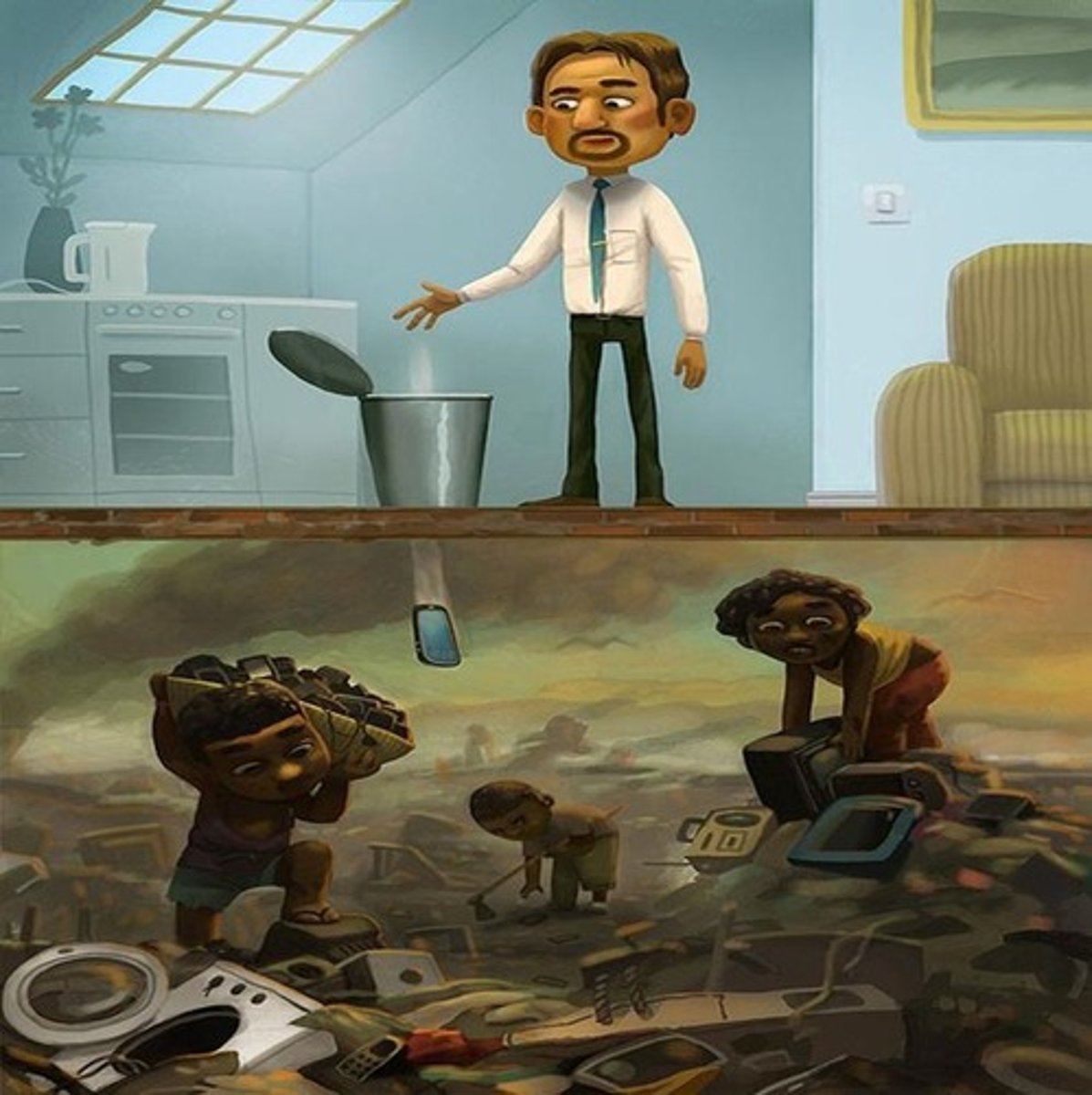

discarded (adj) /dɪˈskɑːdɪd/
thrown away because it is no longer wanted or needed.

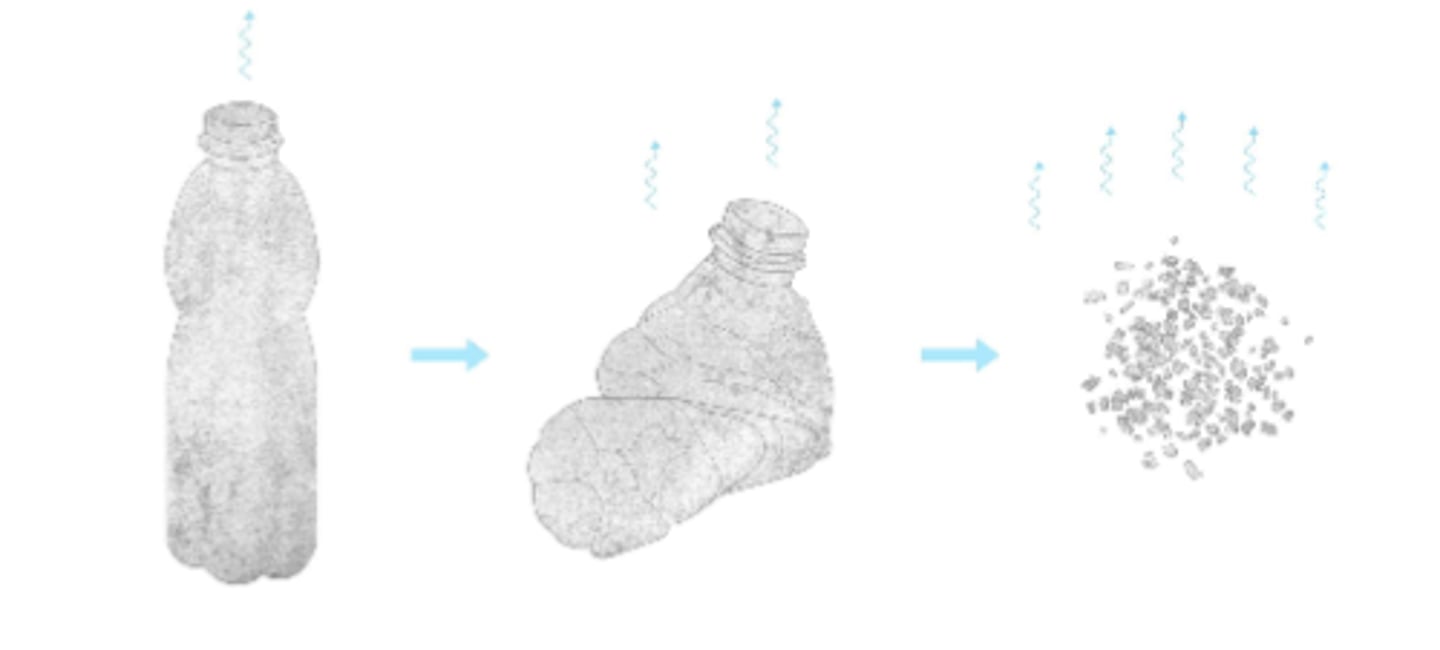
microplastics (n) /ˌmaɪkrəʊˈplæstɪks/
extremely small pieces of plastic that pollute the environment.
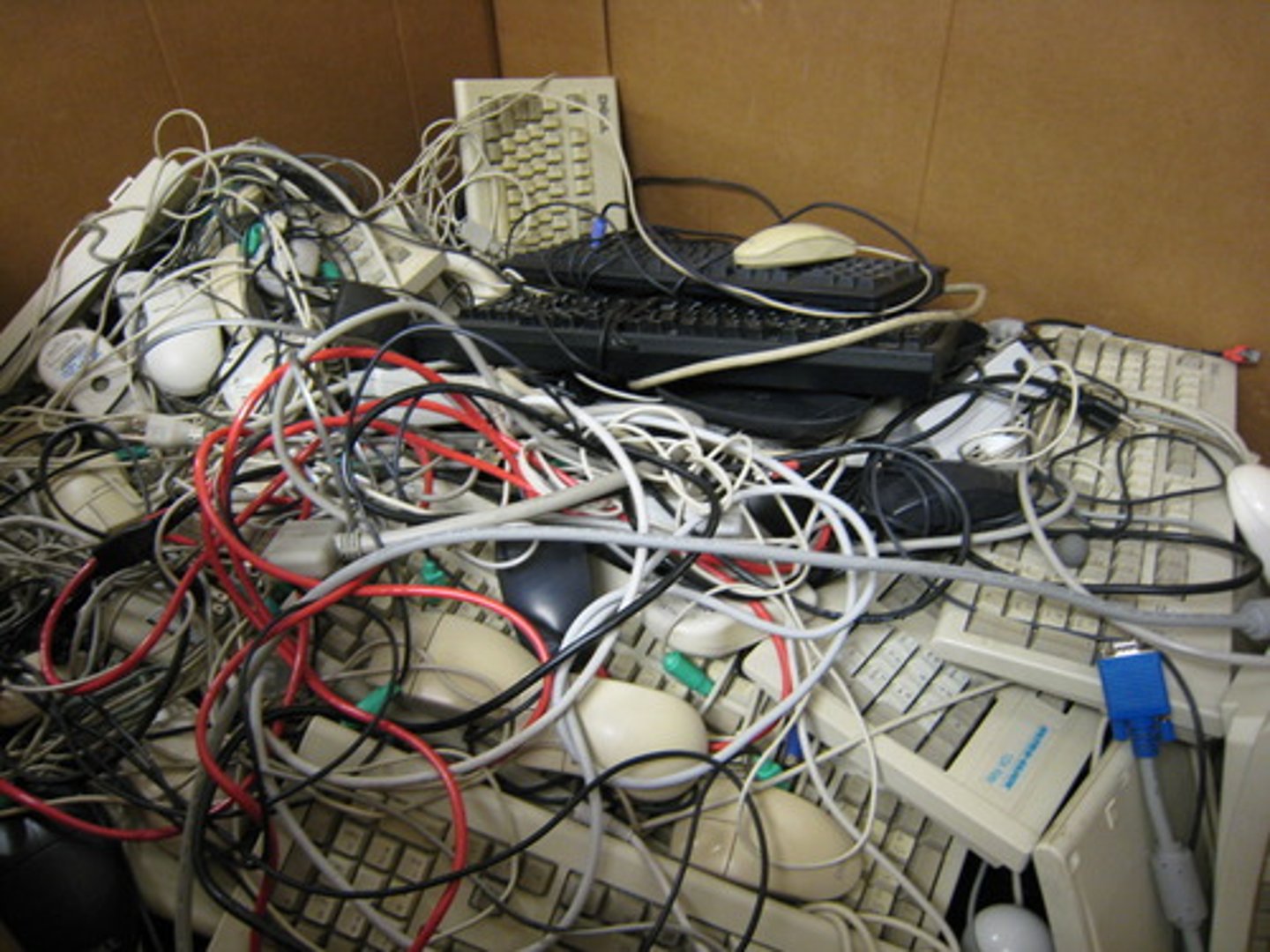
e-waste (n) /ˈiː ˌweɪst/
electronic waste, such as old phones, computers, and appliances.

toxic (adj) /ˈtɒksɪk/
poisonous or harmful to living organisms or the environment.
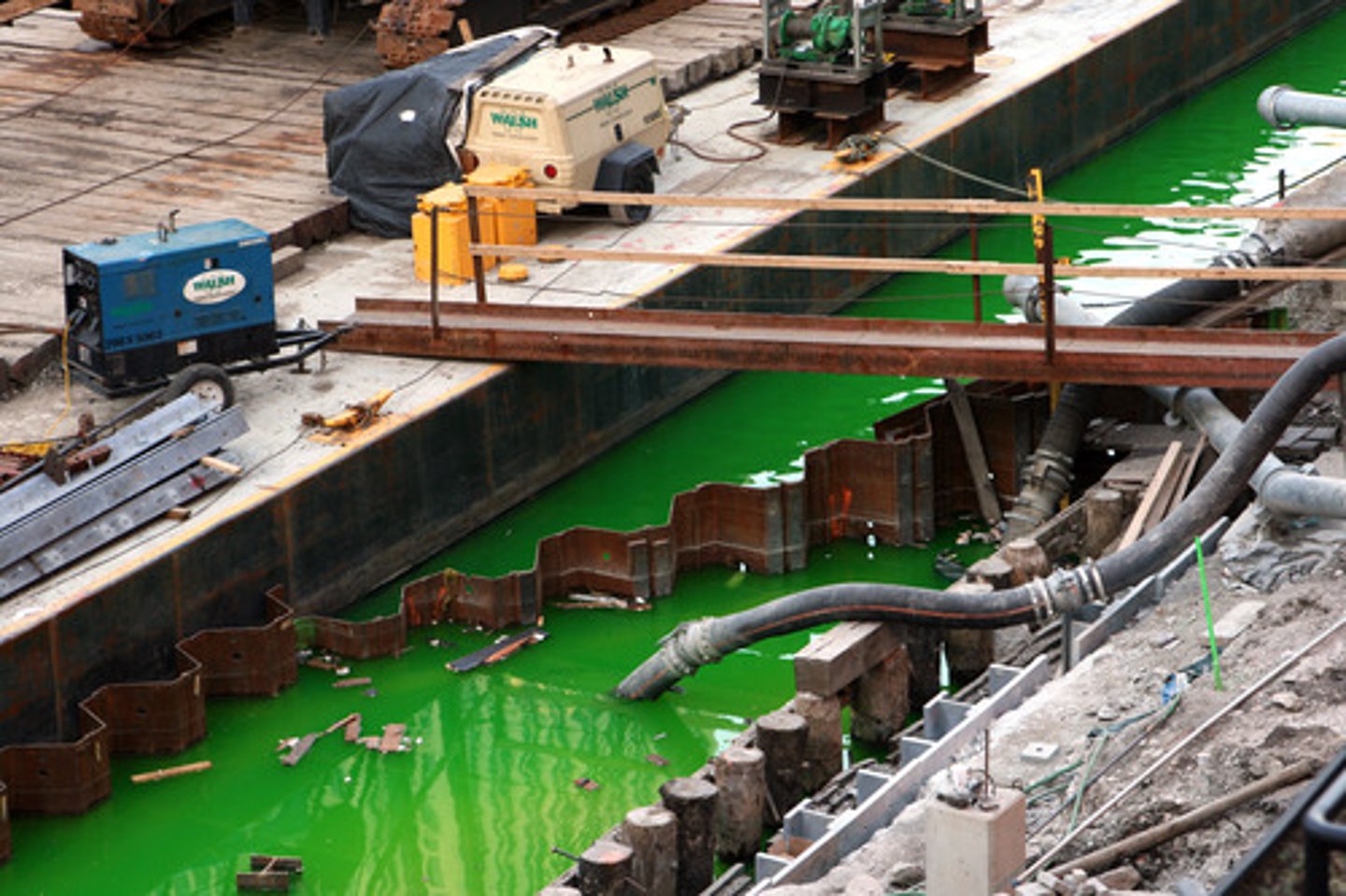

leach into (phr v) /liːtʃ ˈɪntuː/
to gradually pass into soil or water, usually causing contamination.
carbon footprint (n) /ˌkɑːbən ˈfʊtprɪnt/
the total amount of carbon dioxide produced by a person, activity, or product.

greenhouse gas emissions (n) /ˈɡriːnhaʊs ɡæs ɪˈmɪʃənz/
gases released into the atmosphere that trap heat and contribute to global warming.

fast fashion (n) /fɑːst ˈfæʃən/
inexpensive clothing produced rapidly to reflect current trends, often causing environmental harm.

supply chain (n) /səˈplaɪ tʃeɪn/
the system involved in producing and delivering a product to consumers.

water scarcity (n) /ˈwɔːtə ˈskɑːsɪti/
a situation where there is not enough clean water for people or ecosystems.

dead zones (n) /ˈded zəʊnz/
areas in oceans or lakes where oxygen levels are too low for marine life to survive.

ethical consumerism (n) /ˈeθɪkəl kənˈsjuːmərɪzəm/
buying products that are produced in ways that minimise harm to people, animals, and the environment.

sustainable practices (n) /səˈsteɪnəbl ˈpræktɪsɪz/
actions that protect the environment and ensure long-term resource availability.

circular economy (n) /ˈsɜːkjʊlə ɪˈkɒnəmi/
an economic system focused on reusing, repairing, and recycling materials to reduce waste.

curb (v) /kɜːb/
to control or limit something harmful.

carbon pricing (n) /ˈkɑːbən ˌpraɪsɪŋ/
a policy that sets a cost on carbon emissions to encourage reduction.

renewable energy (n) /rɪˈnjuːəbl ˈenədʒi/
energy from sources that naturally replenish, such as wind, solar, and hydro.

durability (n) /ˌdjʊərəˈbɪləti/
the ability of a product to last a long time without damage.

disposability (n) /dɪˌspəʊzəˈbɪləti/
the degree to which an item is designed to be used once and thrown away.
