GCSE Chemistry- C6 Chemical changes
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
observations for a chemical reaction
colour change, change in temperature, effervescence, solid/precipitate formed
rate of reaction
how fast reactants are used up and how fast products are made
Methods to determine rate of reaction
mass loss- loss of mass in reactants over time (weighed before vs after with balance), gas collection- volume of gas formed over time (gas syringe), precipitation- formation of a precipitate over time
Mean rate of reaction
quantity of reactant used/time taken or quantity of product formed/time taken
uncertainty
range in which the true value should lie
uncertainty equation
±range/2
mole
1 mol is the amount of substance that contains the same number of particles as there are atoms in 12.0g of carbon12
Measuring moles
no direct way of measuring moles- calculated using mass or volume then divided over time
higher concentration of reacting solutions
increase ROR, as there are more particles in the same volume- meaning collisions are more frequent
higher pressure of reacting gases
increases ROR as there are the same number of particles in less volume, or there are more particles in the same volume
higher surface area of solid reactants
increases ROR as there is a greater surface area to volume ratio (SA:V)- meaning more collisions can occur more frequently
higher temperature
increases ROR as particles have more kinetic energy and move faster- meaning collisions are more frequent with enough energy to overcome the activation energy
Catalysts
increases ROR by providing an alternative reaction pathway with a lower activation energy
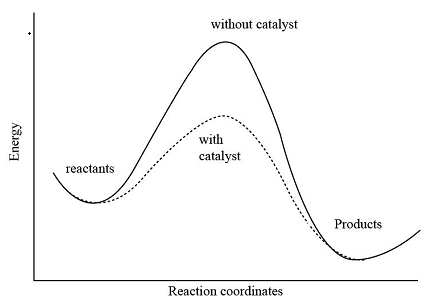
collision theory
chemical reactions can only occur when reacting particles collide with each other with sufficient energy
activation energy
the minimum amount of energy that particles must have to react
reaction to completion
the reactants are used up to form the product molecules and the reaction stops when all of the reactants are used up
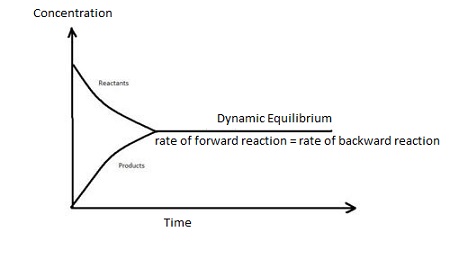
reversible reactions
product molecules can react themselves with each other or decompose and form the reactant molecules again
reversible reaction theory
Forward reaction (forms products): A+B→ C+D
Reverse reaction (forms reactants): C+D→ A+B
written as A+B⇌C+D
Dynamic equlibrium
rate of the forward reaction is the same as the rate of the reverse reaction
chemical reaction
when a new substance is made
effect of concentration on ROR RP reaction
sodium thiosulphate + hydrochloric acid → sodium chloride + sulfur dioxide + sulfur
Na2S2O3 (aq) + 2HCl (aq) → NaCl (aq) + H2O (l) + SO2 (aq) + S (s)
variables in effect of concentration on ROR RP
independent variable- sodium thiosulphate concentration
dependent variable- time taken for cross to disappear (ROR)
control: Volume of HCl, concentration of HCl
Le chatlier’s principle
if a system is at equilibrium and a change is made to any of the conditions, then the system responds to counteract the change
Sodium hydroxide used to identify some metal ions (cations)
solutions of Al, Ca and Mg ions form white precipitate when sodium hydroxide solution is added, but only the aluminium hydroxide solution precipitate dissolves in excess sodium hydroxide solution from displacement, Na is more reactive than Al
Solutions of Copper (II), Iron (II) and Iron (III) used for identification
Cu (II) forms blue precipitate when sodium hydroxide solution added
Fe (II) forms green precipitate when sodium hydroxide solution added
Fe (III) forms brown precipitate when sodium hydroxide solution added
Carbonate identification reaction
reacts with dilute acids to form carbon dioxide gas- CO2 can be identified with limewater-forms cloudy/milky solution through precipitates
Halide identification reaction
produces precipitates with silver nitrate solution in presence of dilute nitric acid- doesn’t displace
silver chloride- white precipitate formed
silver bromide- cream precipitate formed
silver iodide- yellow precipitate formed
sulphates identification
produces a white precipitate with barium chloride solution in presence of dilute HCl
Photon
particle of light with a set wave length
Wavelengths of metal compounds
Lithium- crimson colour
Sodium- yellow-orange colour
Copper- blue-green colour
potassium- lilac
instrumental methods
elements and compounds can be detected and identified using instrumental methods using a machine
advantages of instrumental methods
accurate, sensitive, rapid
Flame emission spectroscopy
an example of an instrumental method used to analyse metal ions in solution
Flame emission spectroscopy process
sample put in flame and light given out is passed through a spectroscope, output is aline spectrum that can be analysed to identify the metal ions in the solution and measure their concentrations