The Hatchery
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
When do broiler breeders come to production?
~20-25 weeks old.
When do female breeders come into production?
~20 weeks old.
Summarise the process of an egg being released from the ovary to being layed out the cloaca
1) Largest ova is released into infundibulum where fertilisation occurs within 15 minutes (stay duration = 15-30 minutes)
2) Embryo travel to the magnum where synthesis and deposition of albumen occurs (stay duration = 2-3 hrs)
3)Embryo travels to the isthmus where synthesis of the shell membrane occurs (stay duration = 2-3 hrs)
4) Embryo travels to the uterus where the shell is synthesised (stay duration = 18-26 hrs)
5) Egg is released out of the cloaca
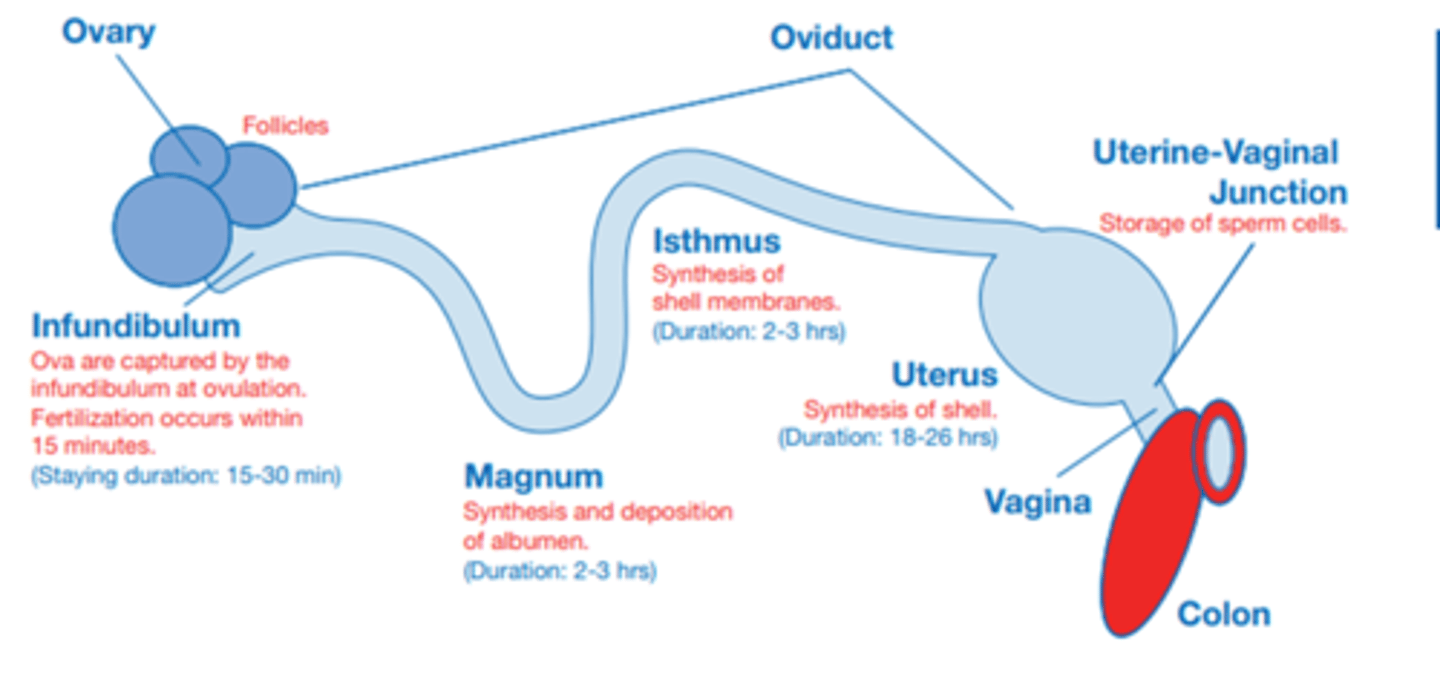
Where are sperm cells stored in the hen uterine system?
Uterine-vaginal junction.
Where does the developing embryo spend the longest in the hen?
Uterus.
How are eggs at risk of pathogen entry?
The shell contains many pores that are a route for pathogen entry.
State some ways farmers help limit the amount of floor eggs
-Have a good hen:nest box ratio
-Put more litter in the nest boxes than on the floor
-Provide toys in the nest boxes
-Limit the frequency of visits of staff to remove floor eggs
State the main ways of disinfecting the eggs
-Fumigation (formaldehyde; mainly used)
-Hydrogen peroxide
-Paracetic acid
-QAC
-Chlorine
What are the advantages and limitations to using fumigation for egg disinfection?
Advantages:
-Egg shell surface not wet
-No damage to egg cuticle
-No injury to developing embryo
Limitations:
-Health and safety issues
-Carcinogen
List the characteristics of a good egg disinfectant
-Lessens the egg shell bacterial count after treatment
-Has little to no impact on the cuticle cover
-Does not effect hatchability
How long can unincubated eggs be stored before hatchability drops?
7 days, after this, 1% drop in hatchability.
What factors must you consider when storing eggs?
-Temperature
-Humidity
-Ventilation
-Safety (from workers, rodents)
What is the function of a hatchery?
To provide a controlled environment for optimal incubation and hatching of healthy, viable and usable chicks.
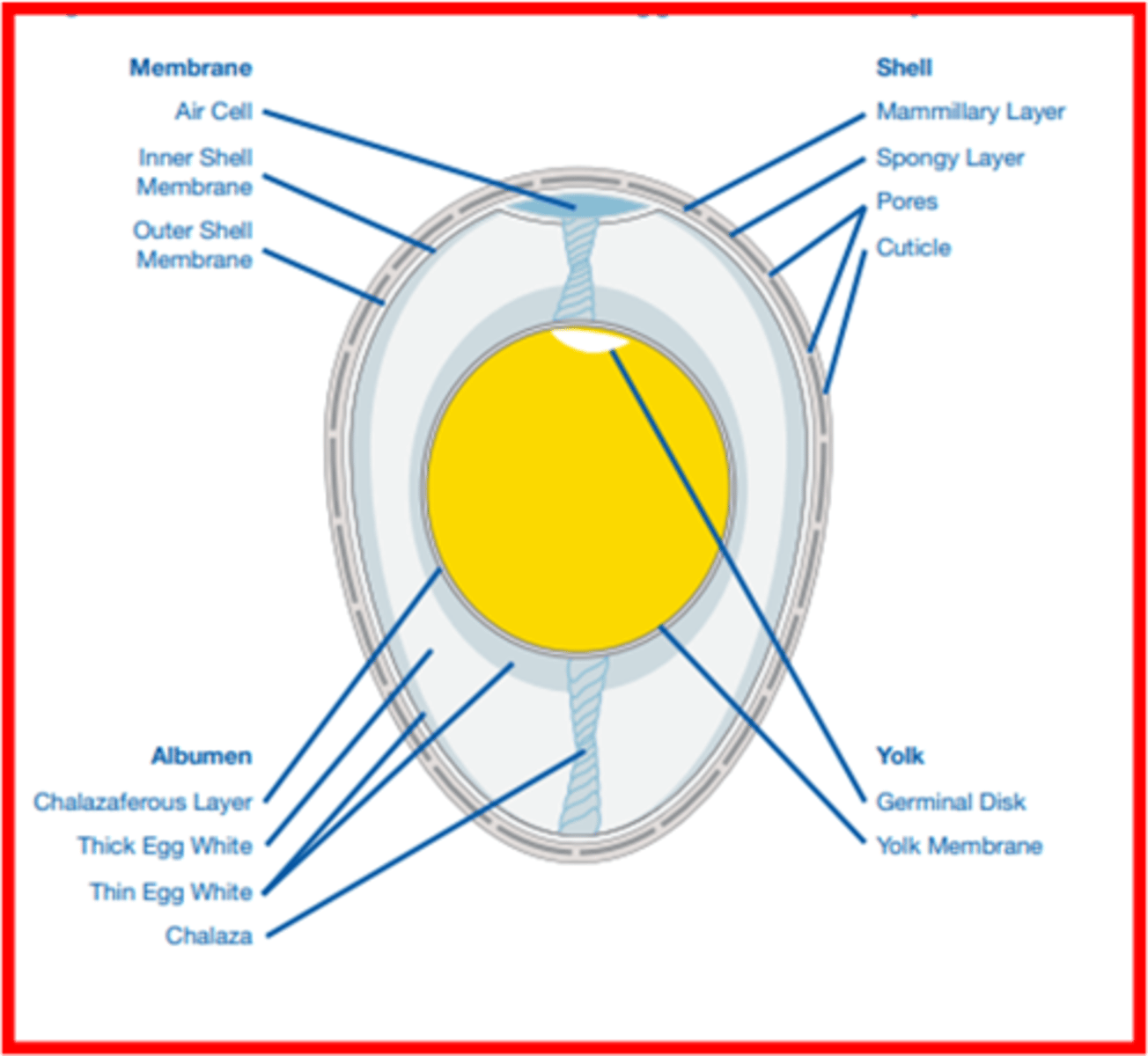
What aspects of the eggs are inspected prior to setting
-Egg size (too small or too large shouldn't be set)
-Egg morphology (abnormal shapes shouldn't be set)
-Egg integrity (cracked shouldn't be set)
-Egg hygiene (dirty eggs shouldn't be set)
-Shell quality
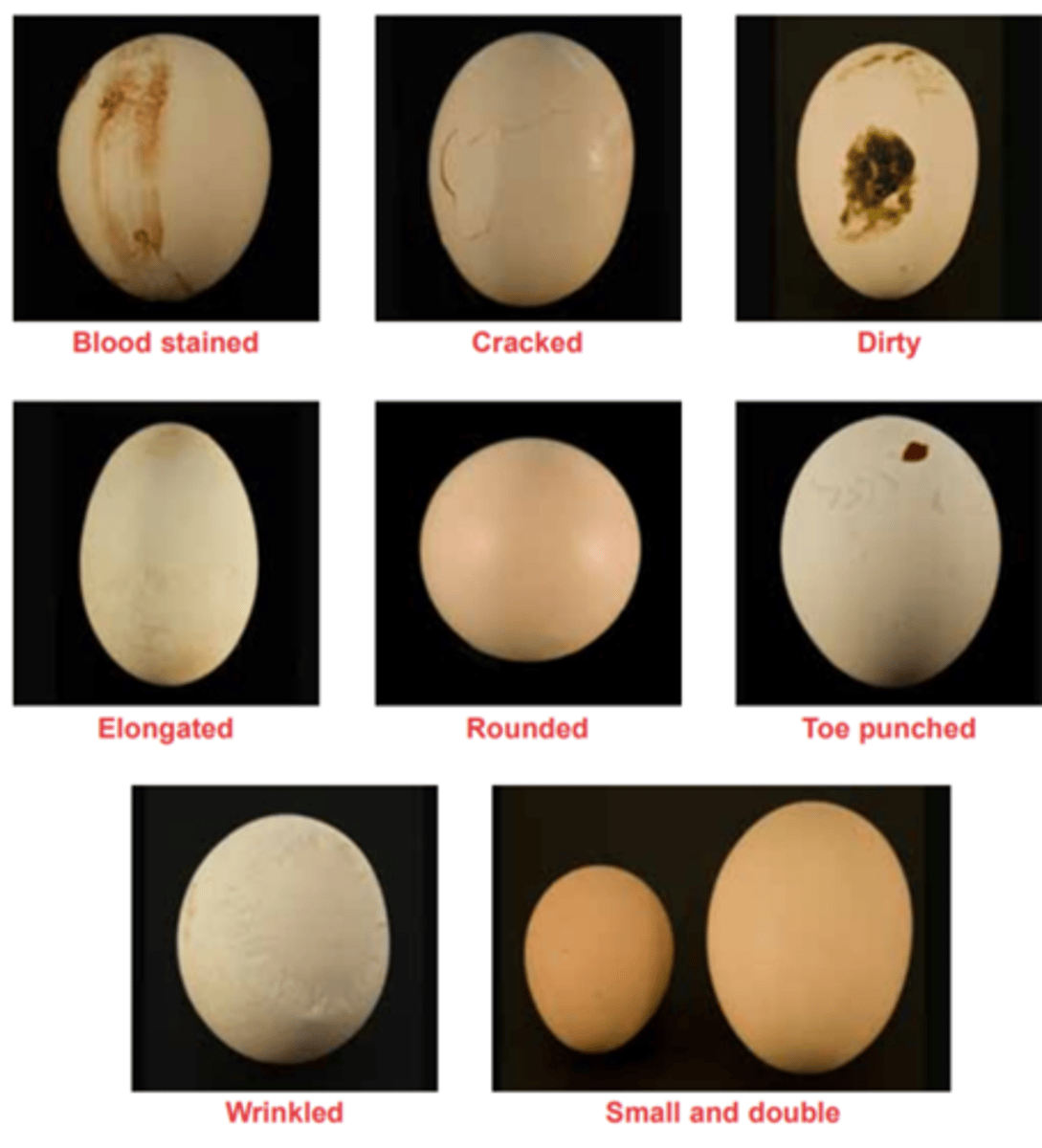
List typical eggs that are unsuitable for hatching
-Dirty
-Cracked
-Small
-Very large or double yolked
-Poor shell quality
-Grossly misshapen
Describe the heating/cooling of eggs from the bird to storage to the hatchery
From the bird to storage:
-Cool gradually
-Slow decrease in temperature to ~21 degrees
-Over 3-4 days
From storage to hatchery:
-Preheat eggs gradually to ~27 degrees
-Place in setter (~37.5 degrees)
Describe the effects of storage prior to setting
-Storage prolongs incubation time. 1 day in storage = 1 extra hour incubation time
-Hatchability decreases with storage greater than 7 days (1% decrease)
-Chick quality = Eggs stored for greater than 14 days causes reduced body weight in broilers
What is the incubation time for a chicken?
21 days.
What are the main factors that are considered during incubation of eggs?
-Temperature
-Humidity
-Ventilation
-Egg turning
-Microbial contamination
How many times should eggs in an incubator be turned?
5-6x/day.
Why is egg turning important?
-Avoids embryo adhering onto shell membranes
-Better yolk sac and allantoic vascular development
-Improves blood vessels under the shell to maximise oxygen absorption
-Improves embryo positioning before hatching
What does candling provide information about?
-Condition of the farm
-Percentage fertility
-Storage condition of the eggs
-Condition of embryos during the incubation process
What are the benefits of interval candling?
-Early detection of fertility problems in the farm
-Provides information about male condition and general health
-Highlight storage condition issues (if present)
-Gives an estimation for the percentage of hatched chicks
-Done in intervals (6d, 10d, 18d)
What can occur in the incubator if some eggs are contaminated?
Explosion.
What are the differences between a hatcher and an incubator?
-Hatcher for hatching the developed eggs, incubator for developing the fertilised eggs
-Humidity is higher in the hatcher
When are eggs likely to be in-ovo vaccinated?
During the transition from the incubator to the hatcher (day 18).
Is in-ovo vaccination common in the UK?
No. Mostly used in USA.
What percentage of eggs are expected to be hatched?
95-97%.
What happens to a chick after they have hatched?
-They are graded
-They are vaccinated
-Beak is trimmed
-Cleaned and disinfected
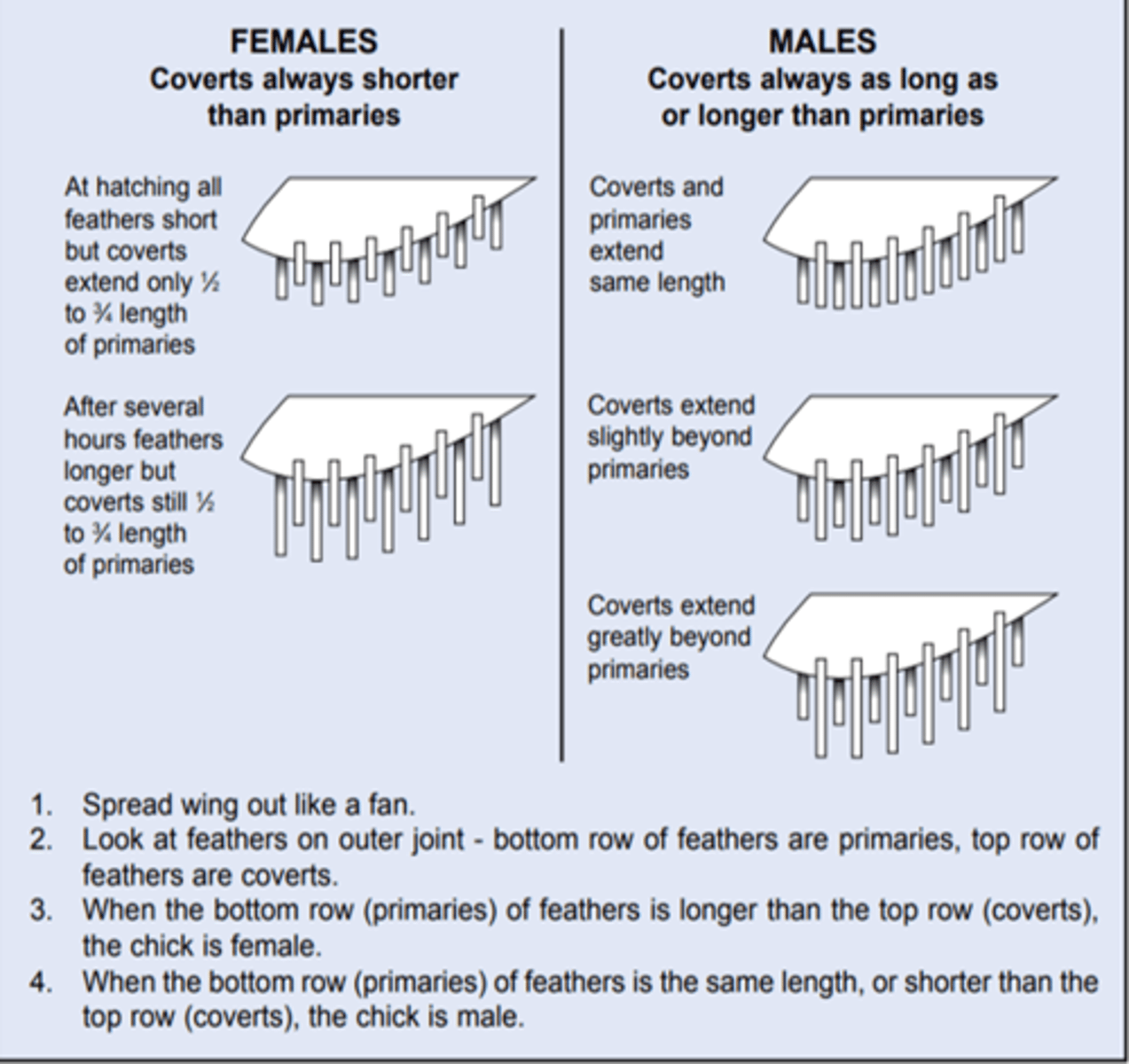
What is the main feature that distinguishes male chicks from female?
-Female coverts are always shorter than their primary feathers
-Male coverts are as long or longer than their primary feathers
What are the main vaccination methods for chicks giving the disease they protect against
Spray:
-Newcastle disease
-Infectious bronchitis
-Avian metapneumovirus
Subcutaneous injection:
-Marek's disease
-Infectious bursal disease
In-ovo:
-Marek's disease
-Infectious bursal disease
-Infectious laryngotracheitis
What are the vaccines typically given to long-term birds?
Any subcutaneous injection vaccines.
What are the key characteristics of good chicks?
-Normal looking
-Alert, active, standing well
-Uniformity
-Good yolk sac absorption with a soft belly
-Legs in perfect condition, not dehydrated or damaged, no red hooks
-Beak clean and not damaged or inflamed, caruncles perfect
-Fluff condition vaporised dry with a nice smell
-Yellow colour
What are the typical causes of abnormal chick colour?
-Formaldehyde pigmentation
-Poor mobilisation of yolk pigment (chick appears pale)
What are the typical factors considered when transporting chicks?
-Temperature of vehicle
-Humidity of vehicle
-Ventilation of vehicle
-Van is clean and hygienic
Summarise the hatchery process using a schematic diagram
Diagram.
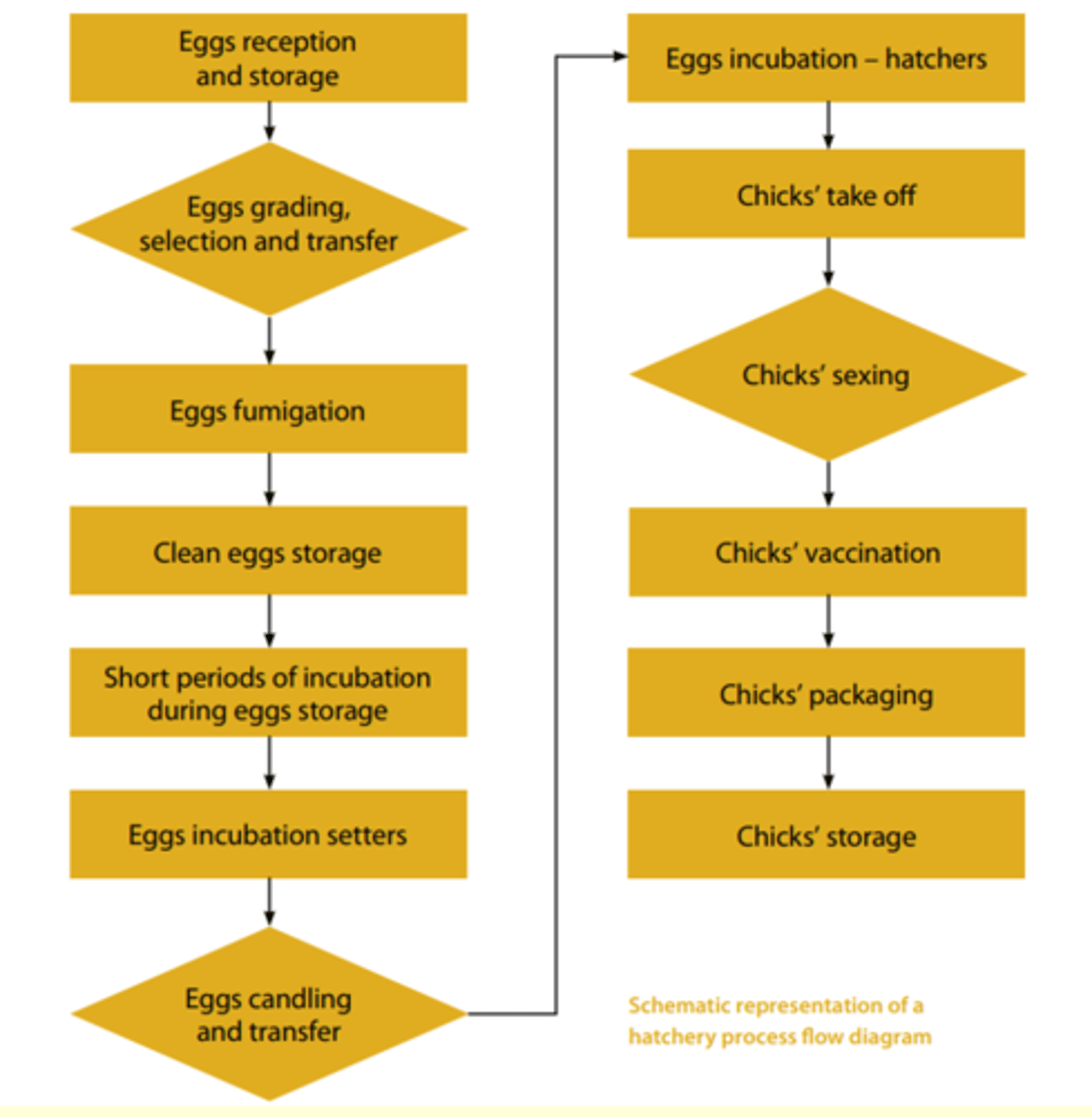
List the hatchery-related legislations for the UK
-The control of Salmonella in Poultry Order 2007 (hatcheries setting more than 1000 eggs)
-The Animal Welfare Act 2006
-THe Welfare of Animals at the Time of Killing Regulations 2013
-The Welfare of Animal Transport Order 2006