Experiments in Political Science Research
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Experiments
Research methods increasingly used in political science.
Randomized Experiments
Address endogeneity by ensuring exogeneity.
Endogeneity Problem
Issue where cause and effect influence each other.
Exogeneity
Condition where variables are independent from each other.
Average Treatment Effect (ATE)
Effect of treatment calculated across the full sample.
OLS Model
Statistical model used for estimating relationships.
Treatment Variable (D)
Indicates whether a unit is treated or control.
Attrition
Dropout of units from an experiment.
Balance
Equal means of covariates across treatment groups.
Compliance
Whether subjects follow treatment assignment.
Intention-to-Treat Model
Analysis comparing groups by assignment, not treatment.
Covariates
Control variables that may affect outcomes.
Blocking
Designing groups to ensure balance in covariates.
Natural Experiments
Observational studies using naturally occurring events.
Social Norms
Shared beliefs influencing voter turnout behavior.
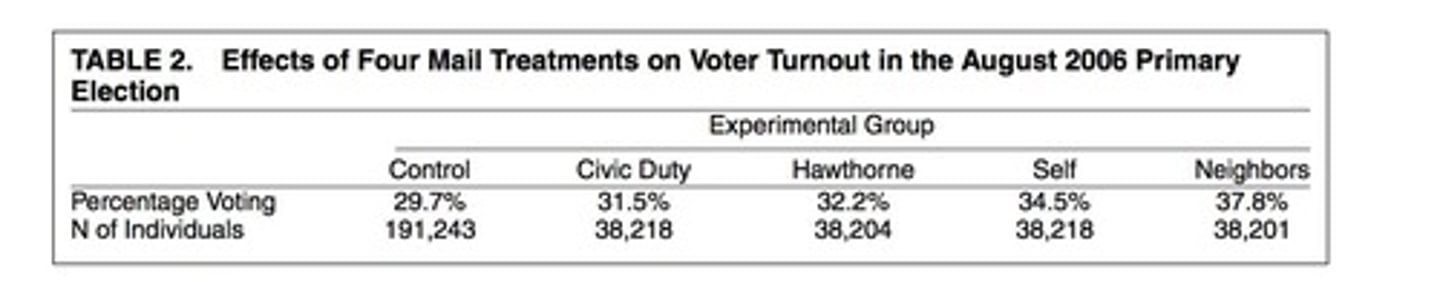
Electoral Turnout
Percentage of eligible voters who cast ballots.
Control Group
Group not receiving treatment for comparison.
H0 Hypothesis
Assumes no effect of social norms on turnout.
HA Hypothesis
Assumes social norms influence electoral turnout.
Treatment Conditions
Different experimental groups receiving varied interventions.
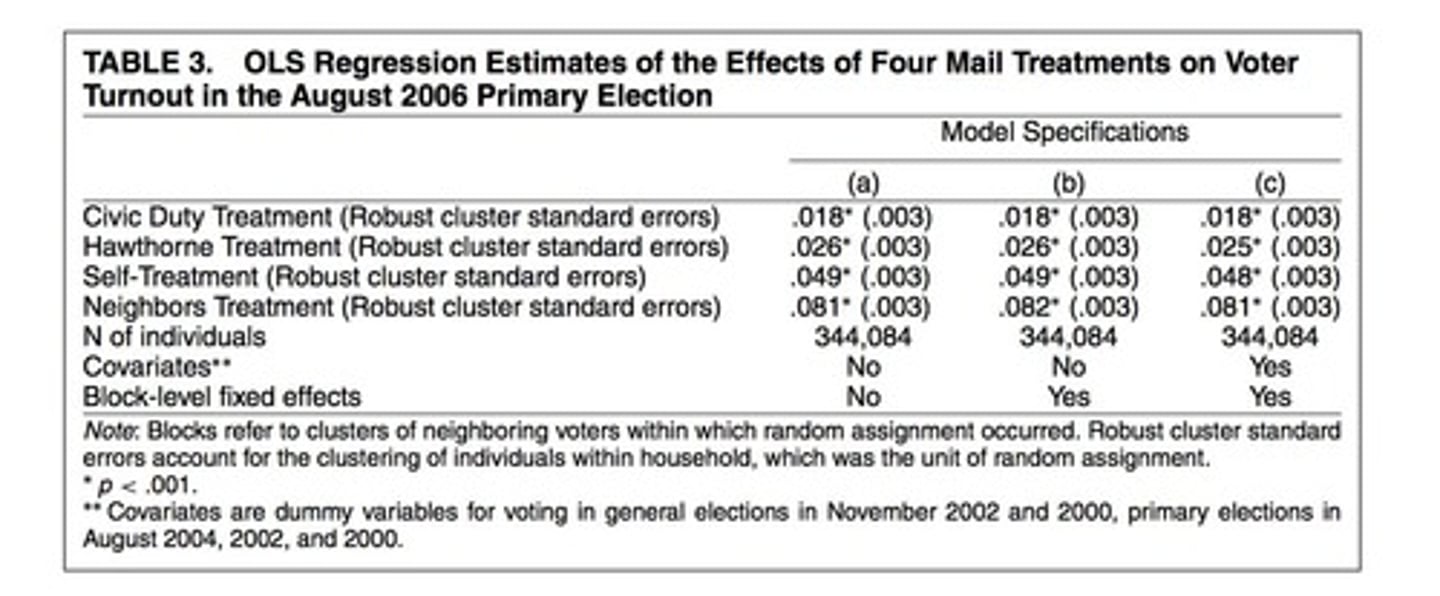
CIVIC DUTY Treatment
Baseline measure common to all treatment groups.
HAWTHORNE Treatment
Informs subjects they are being studied.
SELF Treatment
Includes individual voting records in communication.
NEIGHBORS Treatment
Informs subjects about neighbors' voting records.
Statistical Significance
Likelihood results are not due to chance.
Generalizability
Extent to which findings apply to other contexts.
External Validity
Degree results hold true in different settings.
Natural Experiment Example
Lottery winnings studied to assess political attitudes.