Inflammation and Wound Healing 8/13/25
1/54
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Vocabulary flashcards covering key terms and definitions from inflammation and wound healing.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms

Inflammation
A nonspecific but predictable response of living tissue to injury. Generally protective, can cause complications
Noxius
agents or stimuli causing harm, triggering inflammation or injury responses in tissues.
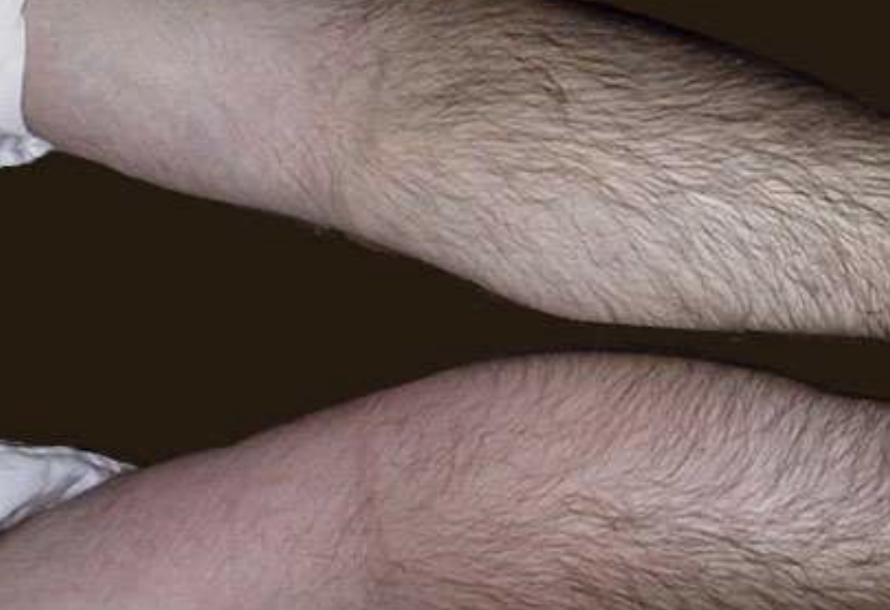
Calor
(Heat) One of the five cardinal signs of inflammation representing increased tissue temperature due to hyperemia.
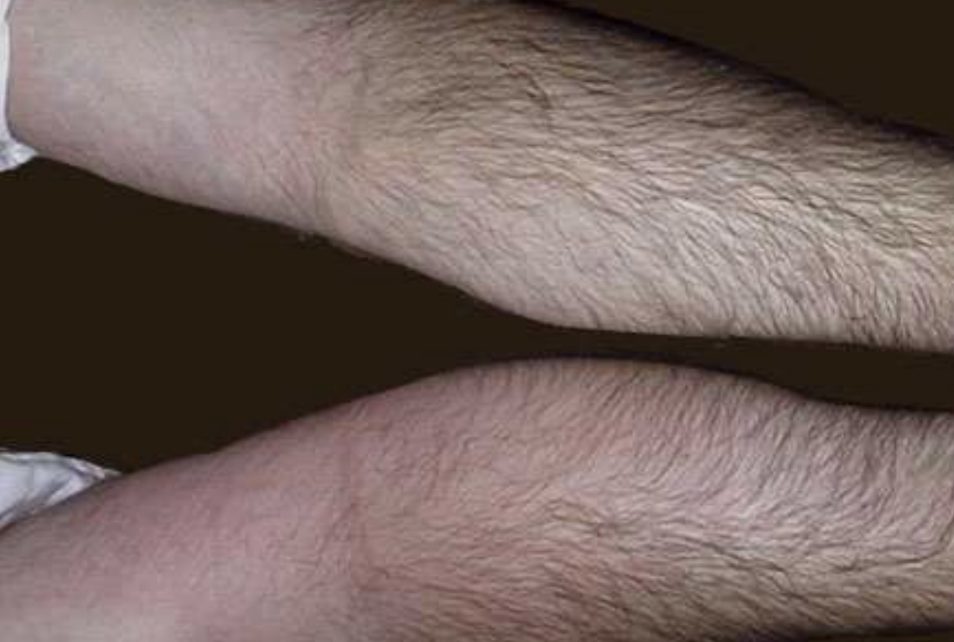
Rubor
(Redness) One of the five cardinal signs of inflammation caused by dilation of blood vessels and increased blood flow.
Tumor
(Swelling) One of the five cardinal signs of inflammation resulting from edema as plasma leaks into the interstitial spaces.
Dolor
(Pain) One of the five cardinal signs of inflammation caused by mediators and tissue swelling irritating nerves.
Functio laesa
(Loss of function) One of the five cardinal signs of inflammation indicating impaired tissue function.
Hyperemia
Increased blood flow to tissue causing redness and warmth.
Inflammatory circulatory changes
Vasoconstriction first that holds off pain, followed by vasodilation, leading to increased blood flow and the classic signs of inflammation. Increased pressure pushes fluid out of vessel and causes edema. This then causes hemoconcentration/congestion of RBCs
Vasodilation
Relaxation of smooth muscle in arterioles leading to increased blood flow into tissue.
Rouleaux
Stacking of red blood cells in small vessels that slows blood flow during inflammation.
Pavementing
Adherence of leukocytes to the endothelium, forming a 'pavement' along the vessel wall. Become sticky
Margination
WBCs move toward and line up along the endothelium before adhesion.
Adhesion (Leukocyte adhesion)
Leukocytes attach to activated endothelial cells via adhesion molecules during inflammation.
Chemotaxis
Active movement of neutrophils (PMNs) toward a chemical gradient from bacteria or damaged tissue.
2 structures that are part of adhesion
leukocyte/neutrophils and endothelial cells
Interleukins AKA
cytokines
Interleukins
concentrated at inflammation site
derived from platelets and leuks
Opsonins
Molecules (e.g., antibodies, C3b) that promote phagocytosis by coating the target. (make tasty)
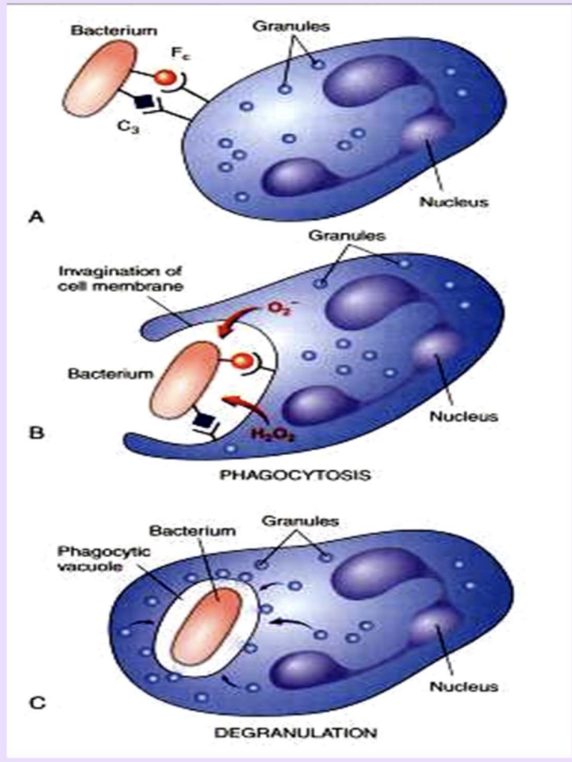
Phagocytosis
Engulfment and digestion of foreign material or bacteria by neutrophils or macrophages.
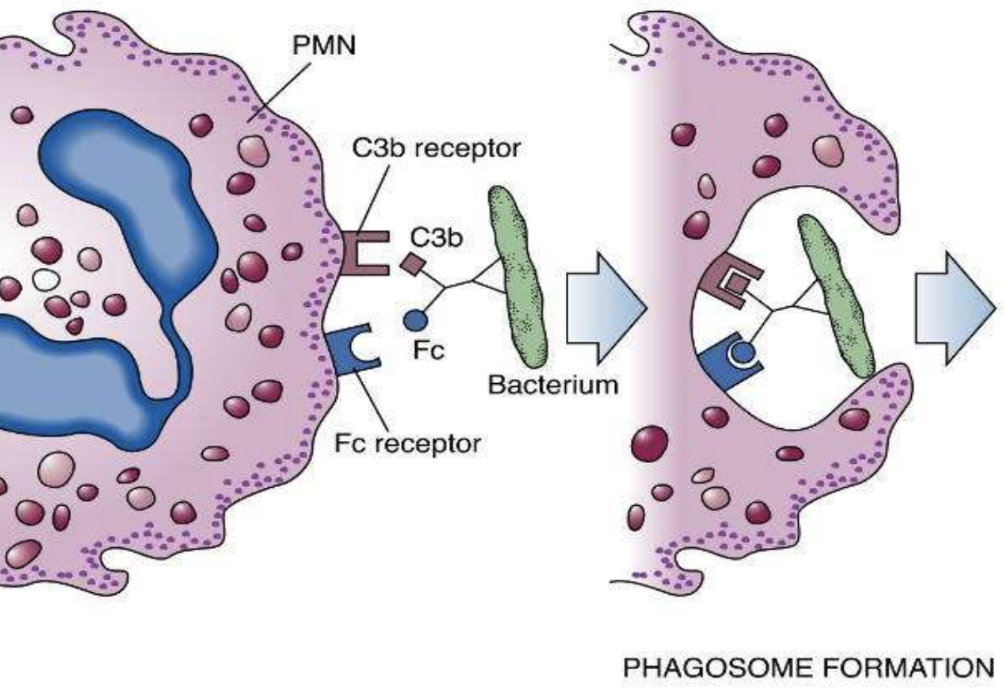
Phagosome
Intracellular vesicle formed after a particle is engulfed during phagocytosis.
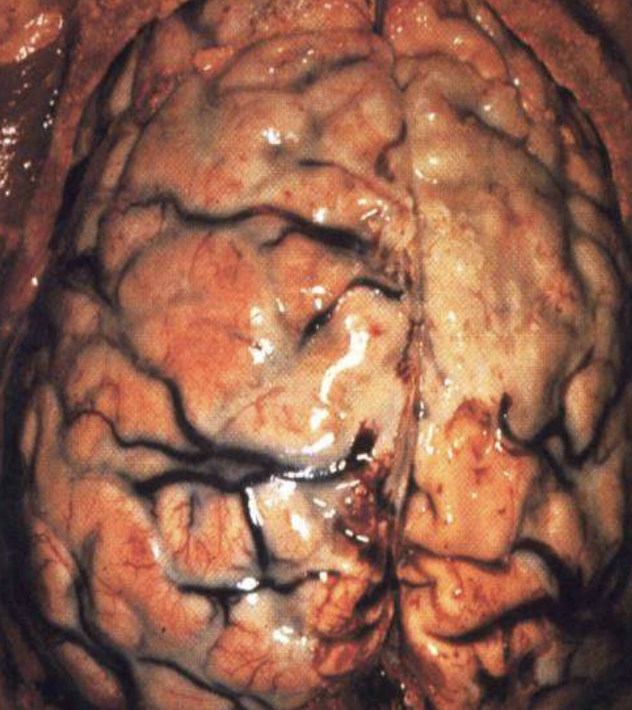
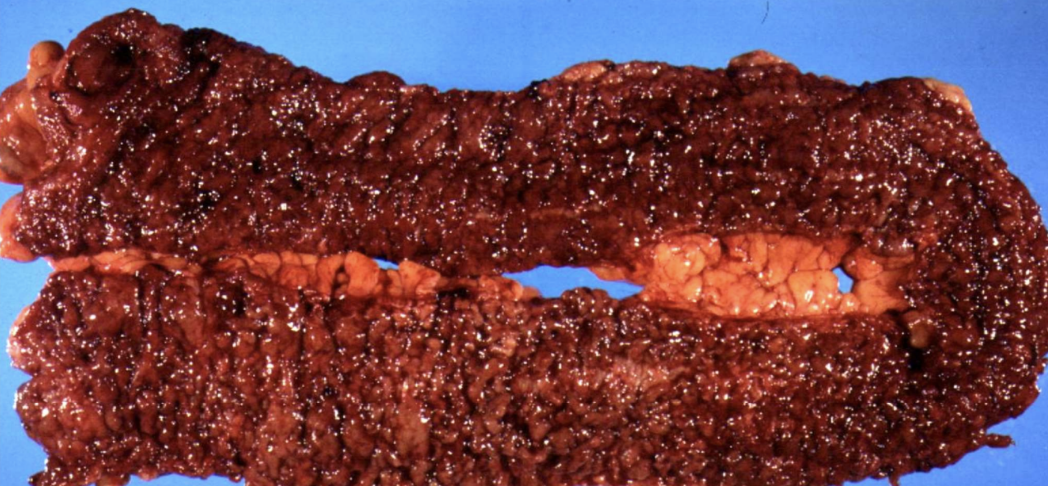
Purulent (Suppurative) inflammation
Inflammation with pus, dominated by dead neutrophils and debris; can form abscesses.
Typically caused by staph and strep
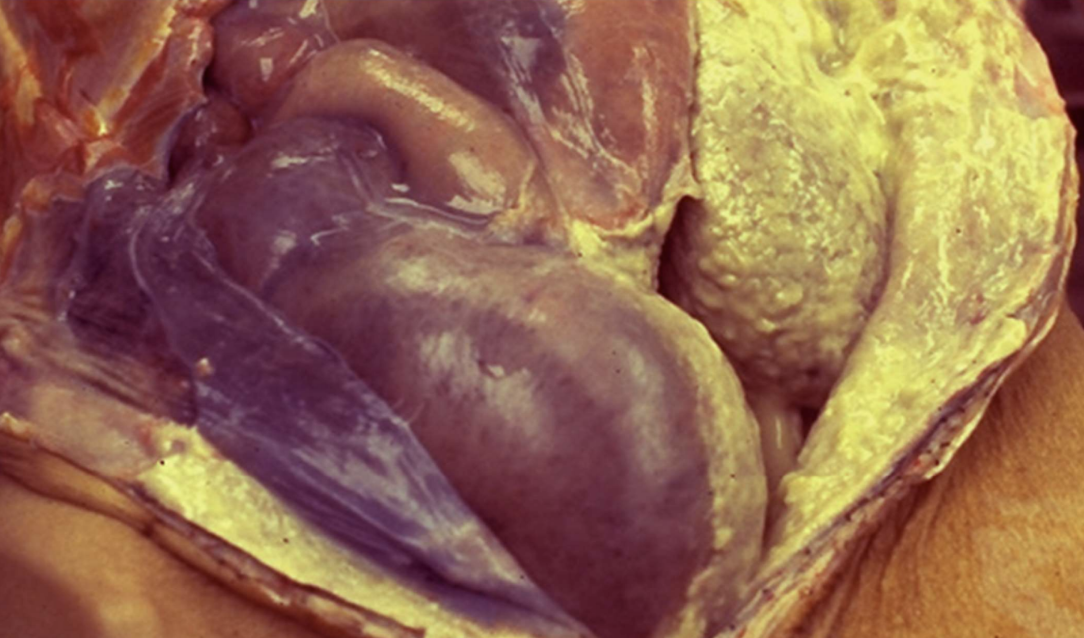
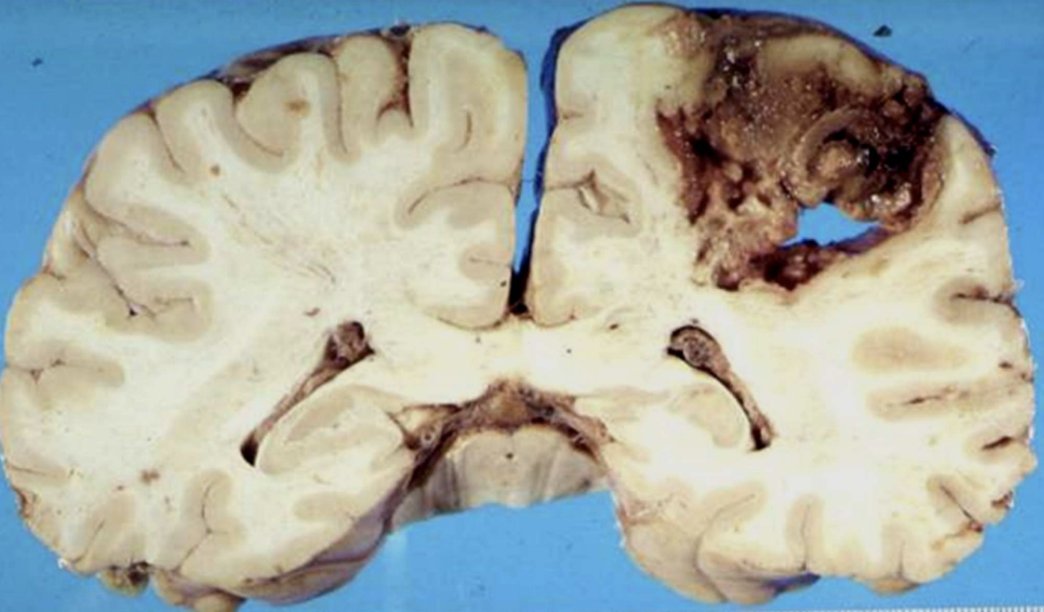
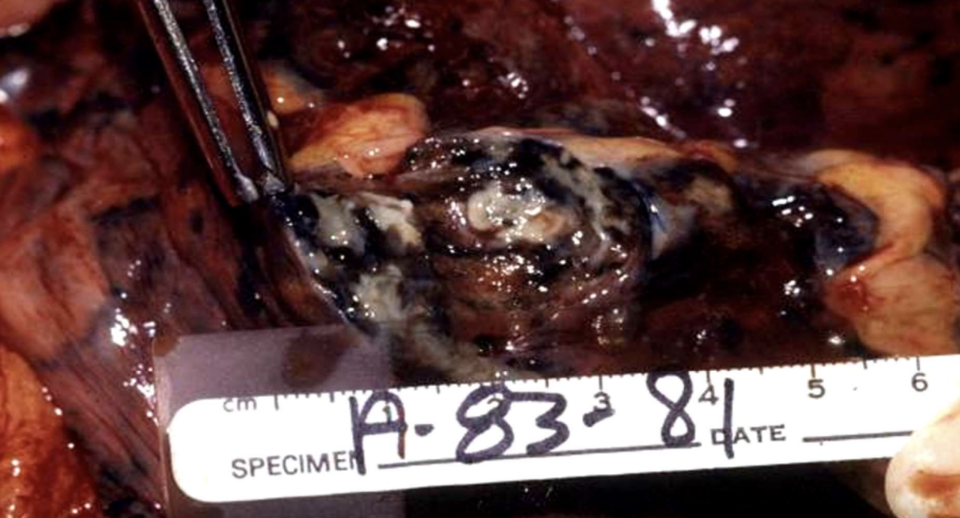
Abscess
capsule of granulation tissue
full of pus, doesn’t heal on it’s own. can rupture or form fistula (ex. Crohns)
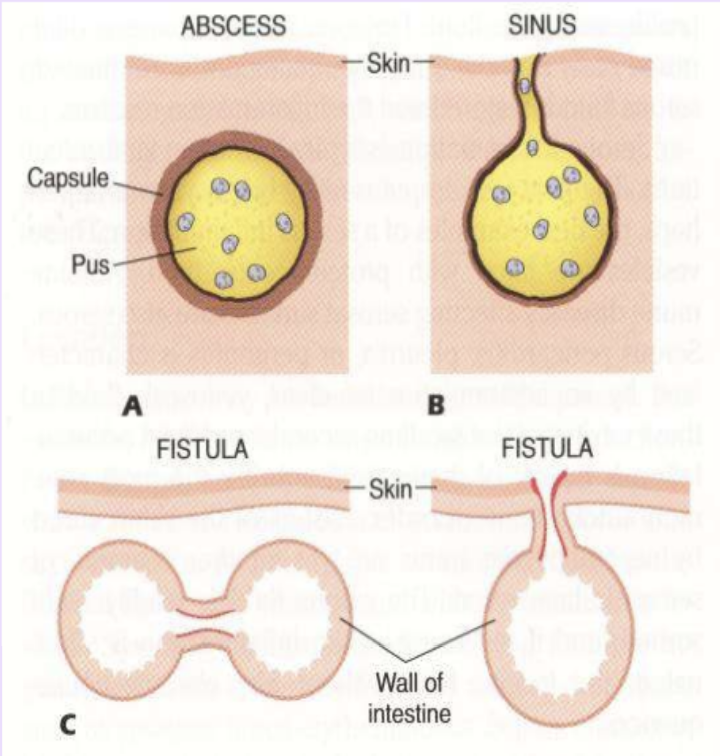
Fistula
channels formed between 2 preexisting cavities or hollow organs and the surface of the body.
Fever
Body temp over 37 C. Caused by endogenous pyrogens interleukin1 and Tumor Necrosis Factor that release cytokines that reset the hypothalamic thermostat, leading to increased body temperature.
Serous inflammation
Mildest inflammation type with clear, watery exudate resembling serum. (blisters, herpes vesicles, autoimmune fluid)
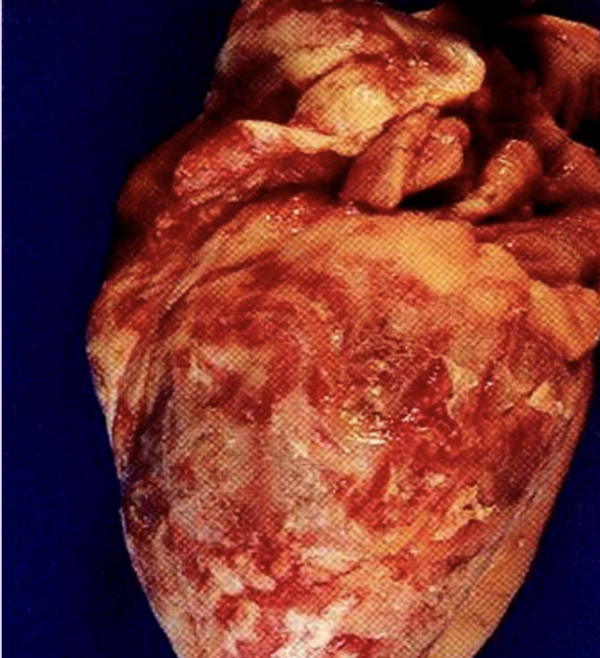
Fibrinous inflammation
Inflammation with fibrin-rich exudate that can form fibrous networks on surfaces made of fibrinogen (large plasma protein)
Seen in strep throat, pneumonia, fibrinous pericarditis
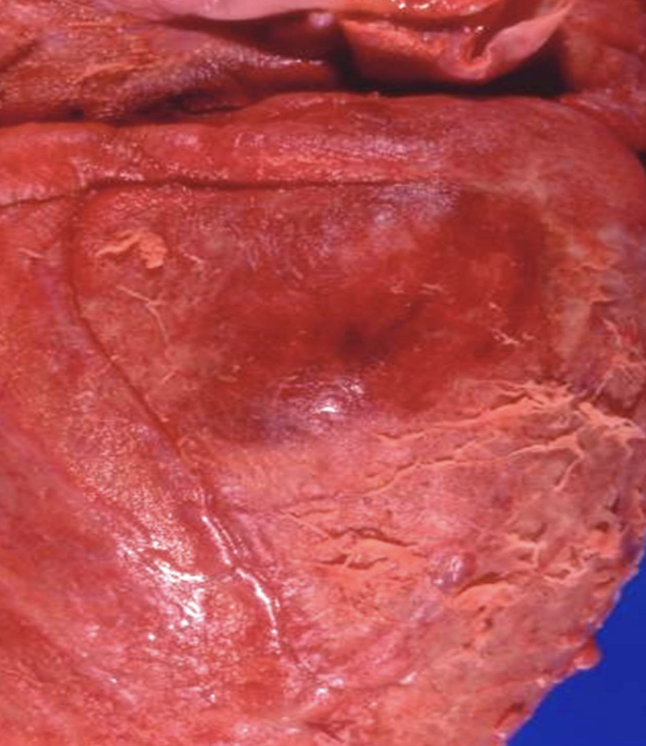
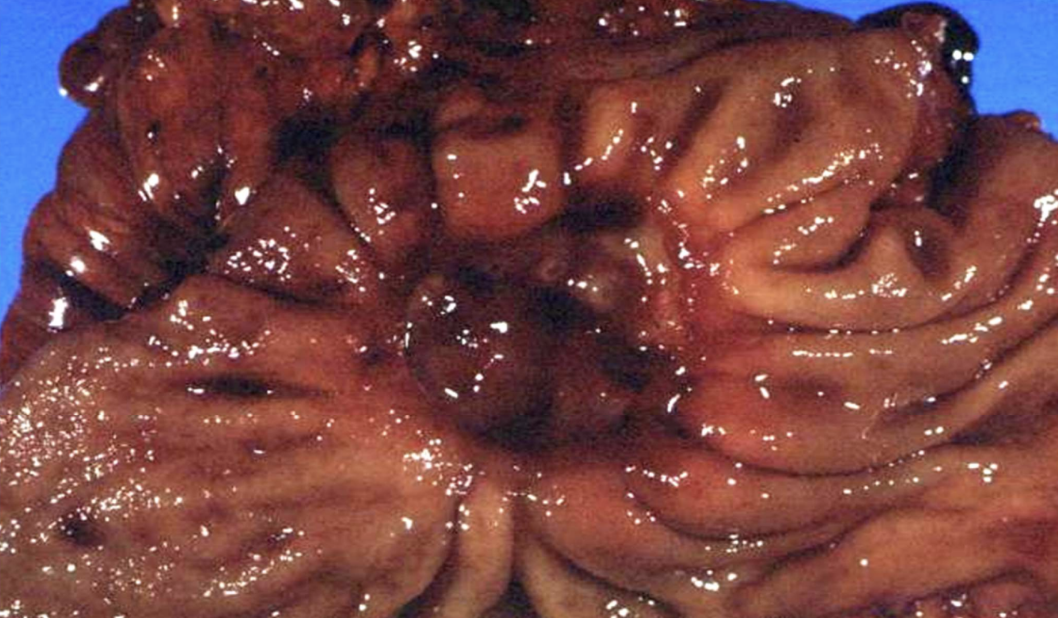
Ulcerative inflammation
Inflammation involving mucosal surfaces (stomach, intestine, etc) leading to epithelial loss and ulcer formation.
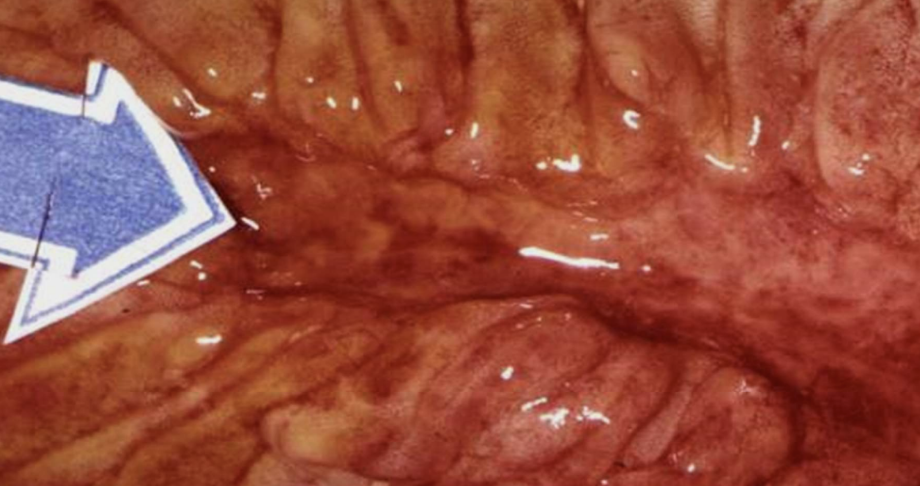
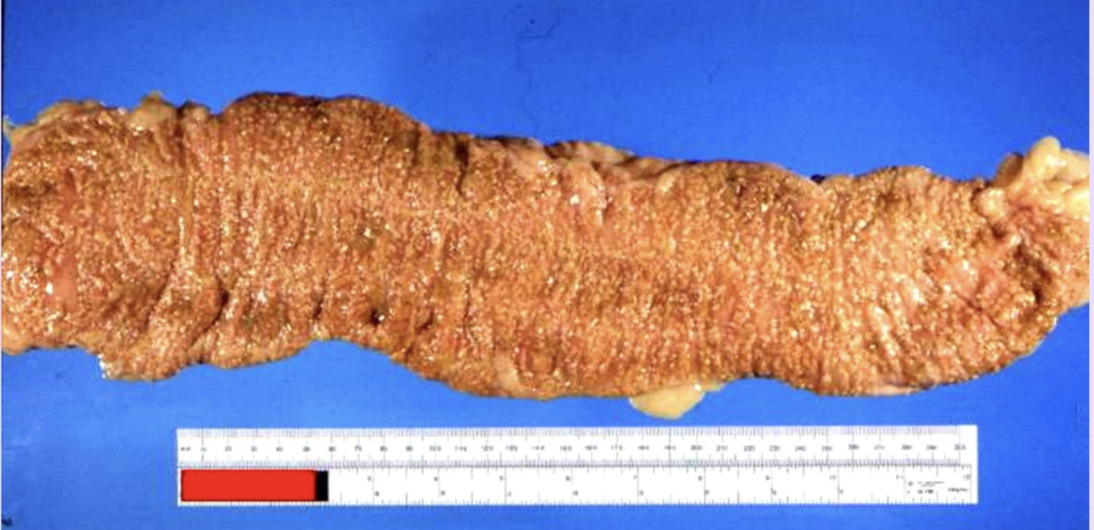
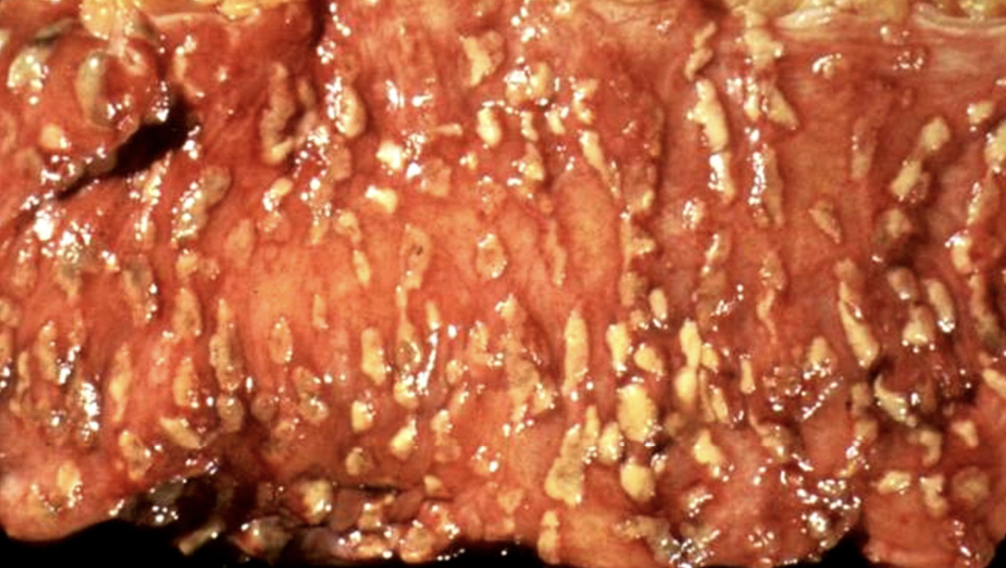
Pseudomembranous inflammation (colitis)
Inflammation with pseudomembrane formation, often due to fibrinopurulent exudate (e.g., C. difficile colitis). AKA antibiotic associated colitis
Granulomatous inflammation
A chronic form with granulomas; often cell-mediated; TB and certain fungi are examples.
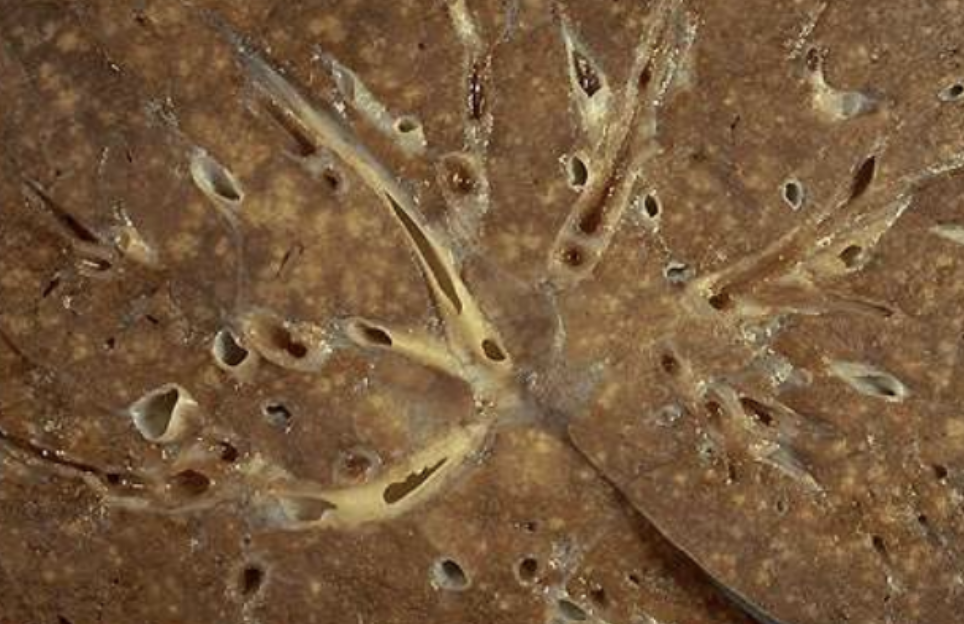
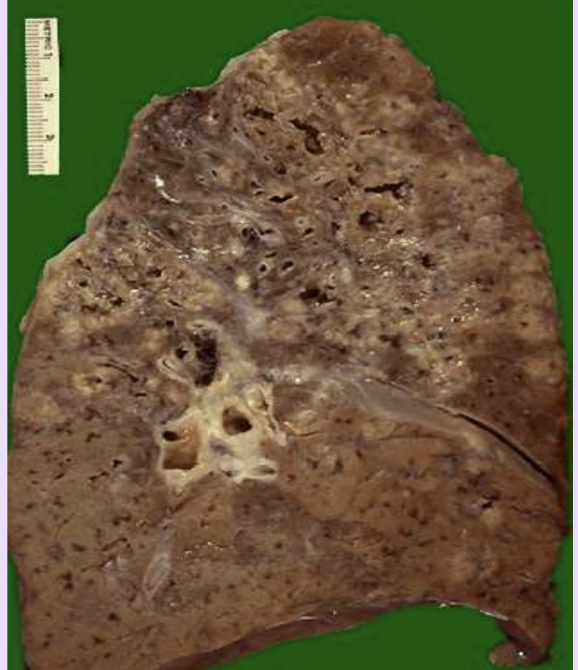
Tuberculosis
Prototype granulomatous disease with caseating granulomas. Miliary spread is baddd
Abscess
Localized collection of purulent material typically walled off by fibrous tissue.
Sinus (inflammation context)
A tract draining pus from an abscess to the surface of the body.
Fistula
An abnormal channel between two cavities or surfaces due to inflammation.
Pseudomembranous colitis
Inflammation of the colon with pseudomembrane formation, often from antibiotic-associated colitis.
Wound healing
Repair of tissue after injury, which may resolve or form scar tissue (fibrosis).
Labile cells
Continuously dividing cells (e.g., stem cells, bone marrow) capable of constant regeneration throughout lifespan. Chemo treatments mess with these
Stable (quiescent) cells
Cells that do not divide regularly but can re-enter the cell cycle to regenerate if needed (e.g., hepatocytes after partial hepatectomy).
Form parenchymal organs (liver, kidneys, etc)
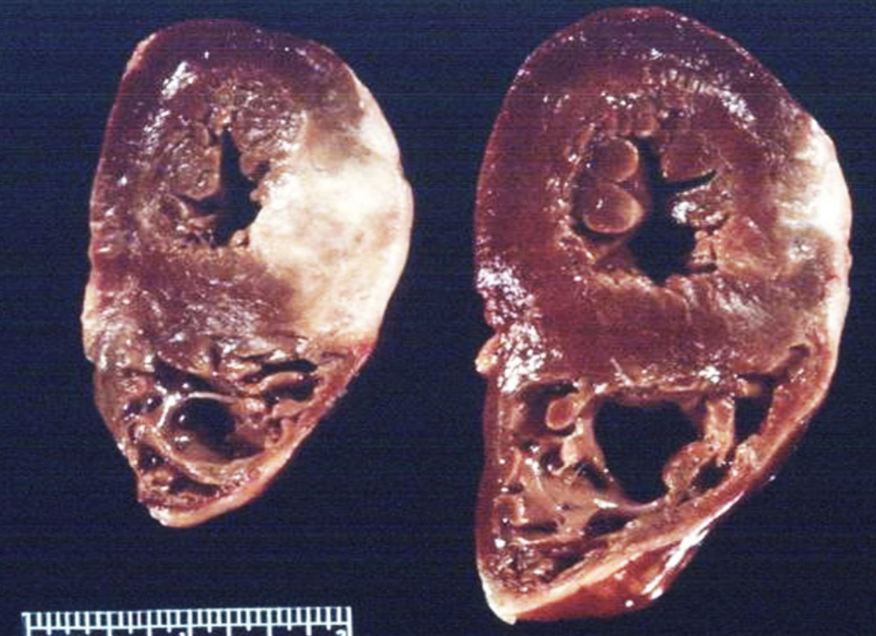
Permanent (nondividing) cells
Cells that do not proliferate ever (e.g., neurons, myocardial cells). Repairs damage with fibrous scarring, gliosis, etc but does not fully repair good as new. Never get the damaged cells back

Myofibroblasts
Hybrid cells with smooth muscle and fibroblast features; contract wound margins to aid healing. Reduces defect and helps new skin cells (epithelium, collagen, etc) cover the surface injury
Angioblasts
Precursors of blood vessels that form new vasculature sprouts in healing tissue. Allow blood with O2 and nutrients intothe healing area and support tissue regeneration.
Fibroblasts
Cells that produce extracellular matrix, including fibronectin (tensile strength, glue) and collagen.
Fibronectin
Glycoprotein that provides tensile strength and helps glue tissues together.
Collagen Type III
immature collagen laid down early in wound healing within granulation tissue, gets replaced by type 1
Collagen Type I
Mature collagen that provides tensile strength; increases during remodeling.
Granulation tissue
Vascularized connective tissue formed during healing, rich in macrophages, myofibroblasts, angioblasts, and fibroblasts.
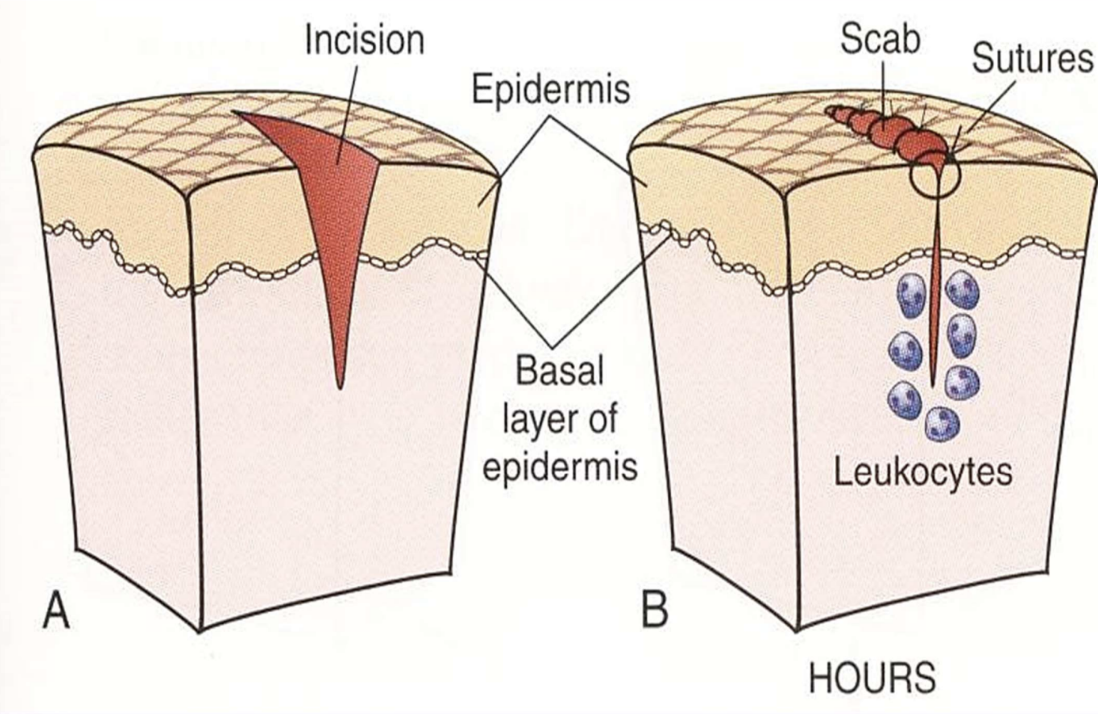
First (primary) intention healing
Wound healing with opposed, clean edges; rapid healing and minimal scar formation.
Secondary intention healing
Wound healing with separated edges and larger defects; slower healing with more scar. Lacks factors in primary healing that helps restore to normal
Delayed wound healing factors
Determinants include wound site, infection, mechanical factors, age, circulatory status, nutrition.
Dehiscence
Separation of wound margins due to weak scar or poor healing.
Keloid
Hypertrophic scar with excess Type III collagen from defective remodeling.
“proud flesh”
Leukocytosis
Elevated white blood cell count (often >12–15,000/µL) with neutrophil predominance in acute inflammation.
Fever (pyrexia)
Elevated body temperature driven by hypothalamic set point raised by pyrogens (IL-1, TNF) and prostaglandins.
Hypothalamus thermostat
Hypothalamic center that regulates body temperature in response to pyrogens.
Prostaglandins (PGs)
Mediators that raise the hypothalamic set point to cause fever during infection.