CPCT: Professionalism and Communication
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
Why is it important to weigh patients accurately
Weight can determine treatments and medication dosages
Which patients can gain many pounds very quickly due to fluid retention?
Congestive heart failure (remember that in heart failure fluid accumulates in either the lungs or the body)
Make sure a scale is set to ______ before use.
Zero
How to use a mechanical scale
Zero scale (move all weights to the left)
Have patient step on
Move bottom (larger) weight first
Move top (smaller) weight first
Adjust weights until balance bar is floating in the middle of the frame
Add the two weights together to determine the weight
If using a bed or wheelchair scale, what must do you to determine the actual weight of the patient?
Subtract the weight of the bed/sheets/equipment/wheelchair.
Empathy
sensitivity to and identification with another person's feelings
Most important communication skill
Listening
Signs of active listening
smile
eye contact
erect posture
attention to what the speaker is saying
nonverbal communication
communication using body movements rather than speech
gestures
mannerisms
facial expressions
body posture
stance
eye contact
movements
touch
personal space
therapeutic communication
Verbal and nonverbal communication techniques that encourage patients to express their feelings and to achieve a positive relationship
health literacy
knowledge of health information needed to make good choices about your health
patients need to know basic medical terminology for this, or medical words need to be explained to them
What should you do if your patient speaks a different language than you?
Get an interpreter
Patients with vision loss
Explain everything that is happening
Escort them if necessary to prevent injury
Patients with hearing loss
Face them when speaking
Speak at a normal volume and tone
Enunciate words without over-enunciating
If they cannot hear at all, provide written communication
Use a sign language interpreter if needed
Service animals
Do not speak to, touch, or talk about the animals
They are not "pets"
Patients with mental health issues
Do not act as a counselor
Patients with developmental delays
Allow them to do as much as they can
Rounding on patients
Routine checking on patients
It is an opportunity to observe for any changes in patient's condition and report them to the nurse
intake and output (I&O)
nursing procedure that documents the total amount of fluid intake and the total amount of fluid output
always document in mL (1 oz = 30 mL)
document anything that is liquid at room temperature
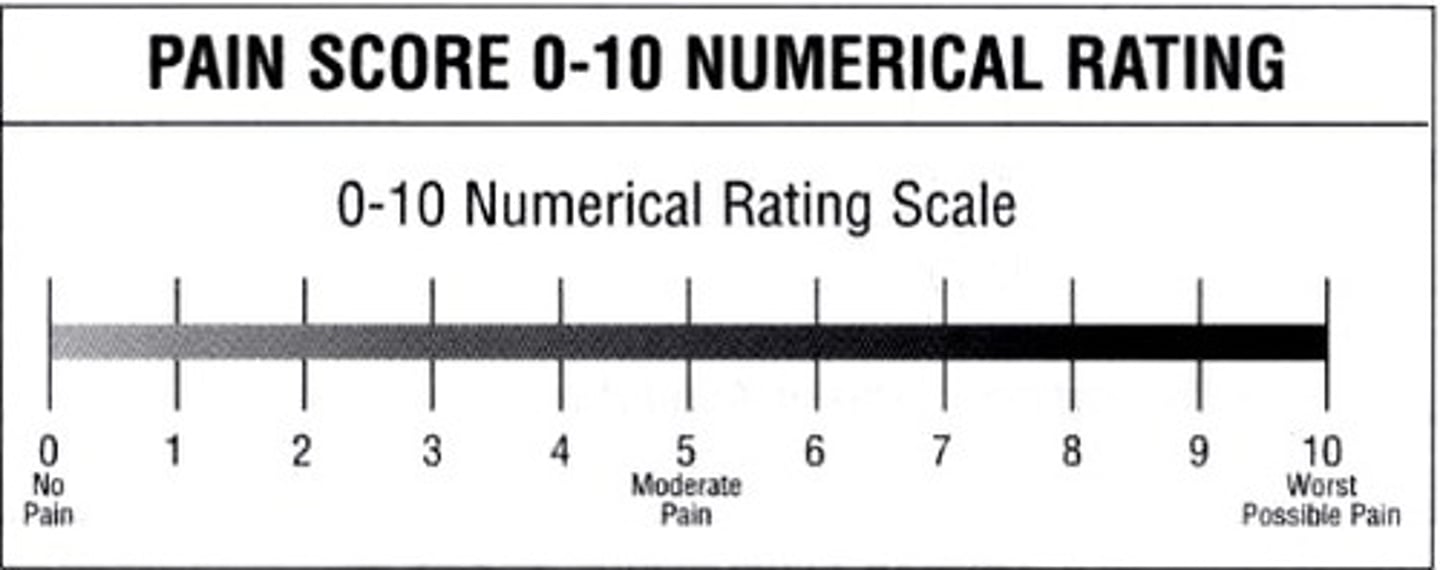
numerical pain scale
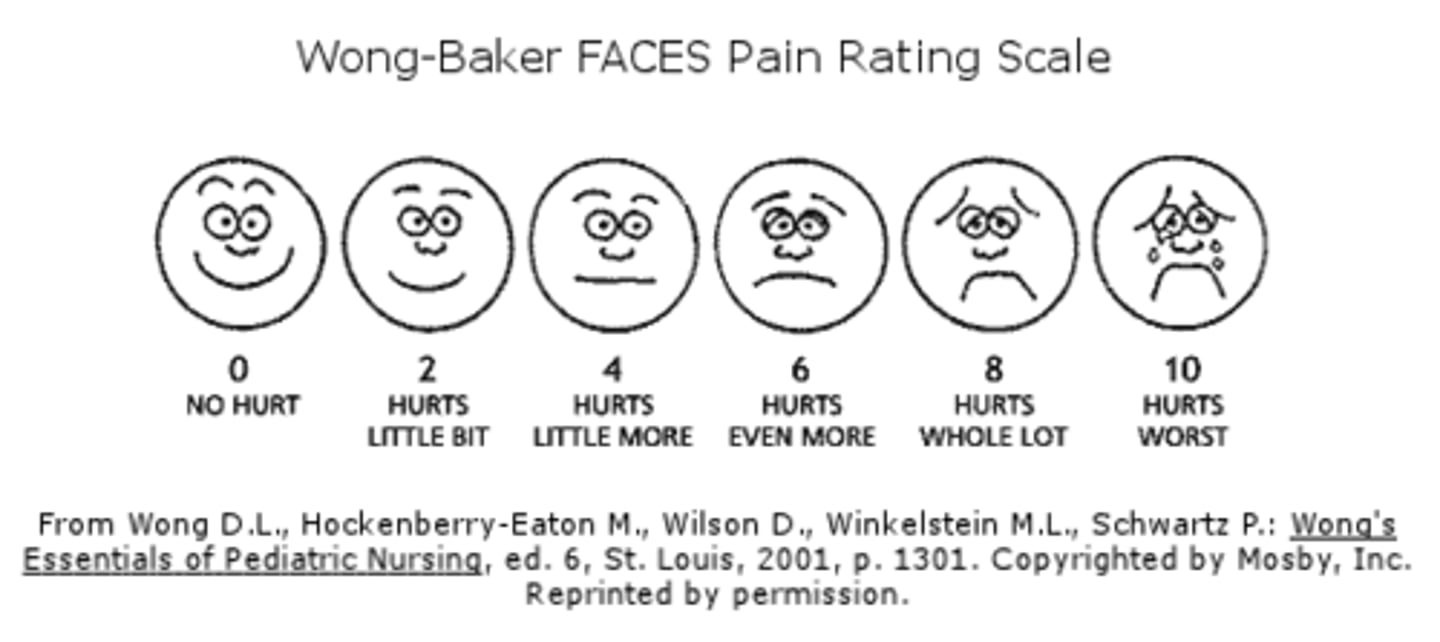
FACES pain scale
for children, mentally disabled, or language barrier
Who determines a patient's pain level?
The patient
Pain is subjective
Nonverbal signs of pain
Moaning
Rocking
Pacing
Crying
Grimacing
Clenching jaw or teeth
Biting lips
Restlessness
Insomnia
Rigid or flaccid posturing
Holding, rubbing, guarding the area of the body
Inability to focus or concentrate
Avoidance of conversation
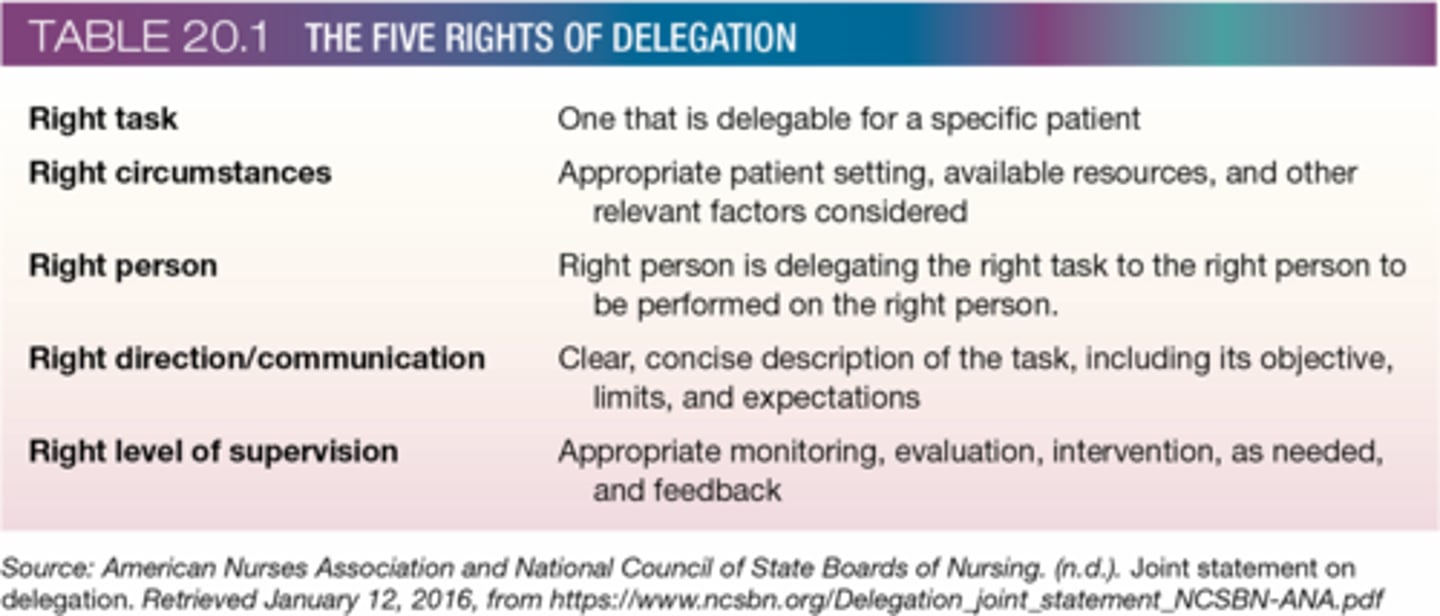
Five Rights of Delegation
a) Right Task
b) Right Circumstance
c) Right Person
d) Right Direction/Communication
e) Right Supervision
CPCT scope of practice
Things CPCT are trained and allowed to do
-measuring vital signs
-assisting with ADLs
-performing EKGs
-drawing blood
not in your scope of practice:
-administering medications
-performing sterile procedures (alone)
-invasive procedures (NG/Foley insertion)
-diagnosing
Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs
Patients need the lower levels to achieve the higher levels
(level 1) Physiological Needs
-food
-water
-shelter
-oxygen
-elimination
-temperature regulation
-sleep
(level 2) Safety and Security
-helping patient feel secure and well cared for
(level 3) Relationships, Love and Affection
-taking an interest in patients
-showing respect for their preferences
-speaking kindly to them
-friends and family
(level 4) Self Esteem
-confidence
-privacy
-hygiene
-allowing them to choose/assist
(level 5) Self Actualization
-set and achieve goals
-reaching your highest potential in life
Palliative care/Hospice
supportive medical and nursing care that keeps the patient comfortable but does not cure the disease
-oxygen
-fluids
-nutrition
-hygeine
-pain control
Can occur in the home, hospital, long term care facility, hospice facility
Usually patients enter hospice when they are terminally ill or decline life saving intervention and are expected to live < 6 months
Coping mechanisms
strategies to protect yourself from negative feelings
Kubler-Ross stages of grief
1. Denial
2. Anger
3. Bargaining
4. Depression
5. Acceptance
People can grieve using these stages in any order, they can skip stages. Everyone grieves differently and there is no correct way to grieve.
Before an RN/CPCT begins postmortem procedures, what do they need to make sure has happened?
Doctor has certified the death and recorded the time and date of death
How to prepare a body for family to view
-Remove all equipment and supplies from room
-Prepare the body as soon as possible to prevent disfigurement or tissue damage
-Try to make the body look as natural and peaceful as possible
Postmortem care: eyes and mouth
Close the eyes and mouth
Keep dentures in place
Place small towel under chin if mouth will not close
Postmortem care: tubes and drains
Remove
If there is an autopsy scheduled: cut them to 1 inch and secure with tape
Postmortem care: body position
supine with small pillow under head to prevent pooling of blood in the face
Postmortem care: arms/hands
Arms at side of body, palms down
or
Arms across the abdomen without placing one hand on top of the other
Postmortem care: bandages/dressings
replaced soiled dressings/bandages with new ones
Postmortem care: hygeine
Bathe body
Comb hair
Place clean gown on body and cover with a clean sheet up to the shoulders, leaving face exposed
Postmortem care: Valuables
Place them in a bag/envelope with documentation
Offer to family
Postmortem care: Identification tags
One on the right big toe
One on the shroud (fabric wrapped around patient)
One on belongings
chain of command
the vertical line of authority that clarifies who reports to whom throughout the organization
CPCT reports directly to supervising nurse, then charge nurse, then nurse manager/supervisor, then chief of nursing
proceed up the chain of command if a problem is not being addressed appropriately
Abuse
the physical, mental, financial, emotional, or sexual mistreatment of one person by another
violation of basic rights (freedom, speech, privacy, expression worship)
neglect
failure to deliver care and maintain basic needs
exploitation
taking advantage of other people for selfish purposes
indications of abuse
lack of personal care
signs of malnourishment
signs of dehydration
pressure sores
signs of trauma
restraint trauma
inconsistent explanation of injuries
signs of anxiety
caregiver control
overmedication/oversedation
unusual repetitive behaviors
reports of abuse, neglect, exploitation
If a CPCT suspects abuse/neglect/exploitation, what should they do?
They are not obligated to investigate further or confirm suspicions
They should report it to the supervising nurse and then follow the chain of command if needed
Respite care
a type of care provided for caregivers of homebound ill, disabled, or elderly patients
designed to give caretakers of patients a break so that they don't feel stressed
caregivers who receive respite care are less likely to abuse/neglect/extort the patient
Patient's Bill of Rights/Patient Care Partership
outlines rights and responsibilities patients have in healthcare facilities
summarizes legal, ethical, and moral responsibilities of healthcare workers must adhere to when caring for patients
patients have the right to:
privacy
confidentiality of documentation of their care
information about their options
review and receive copies of their own medical records
prepare advance directives and have staff honor them
receive respectful care
make decisions about their care
refuse treatment
receive information about their diagnosis, treatment plan and prognosis
patients have the responsibility to:
provide correct and complete information about their health
offer insurance information or ensure payment for services
cooperate with health care staff
respect other patients and their privacy
try their best to understand and comply with instructions for treatment and self-care
ethics committee
committee made up of individuals who are involved in a patient's care, including health care practitioners, family members, clergy, and others, with the purpose of reviewing ethical issues in difficult cases
electronic health record (EHR)
AKA electronic medical record (EMR)
Systematic collection of a patient's health care and treatment in a digital format
how to protect patient information when using an electronic health record
use your own login and password to access the EHR
log off when leaving your computer
never share your login/password with anyone
shred anything you have printed
position the screen so that other people cannot see it
how to identify a patient
do not use room number/bed number
always ask the patient to state the information, do not say it for them (they may just agree or misunderstand you)
use at least two of the following identifiers:
-full name
-date of birth
-home address
-phone number
-social security number
-photo ID
how to document in an electronic health record
document something after you've done it, not before
document something as soon as you can after you've done it
without documentation there is no record that you have done something
only chart what you have done, not what you have observed someone else doing
chart specifics
never chart an assumption, only chart what you have done or seen
if documenting something someone says, use quotes