OPT 311 Midterm 1 part 3 (Small pupils: horners + syph)
1/114
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
115 Terms
How many neurons (and synapses) are involved in the sympathetic innervation of the iris?
3 neurons
3 synapses
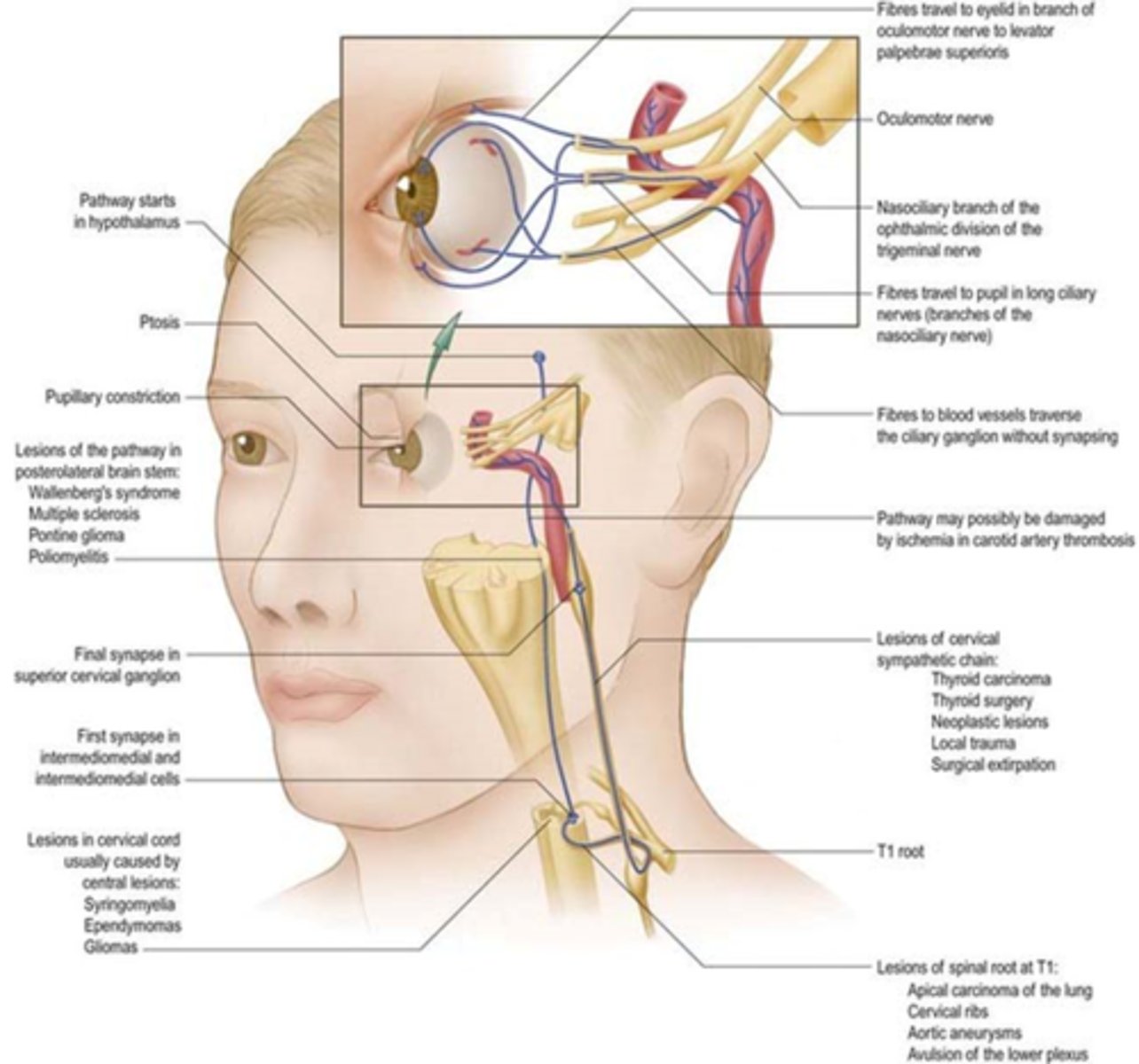
Explain the pathway of the sympathetic innervation of the iris.
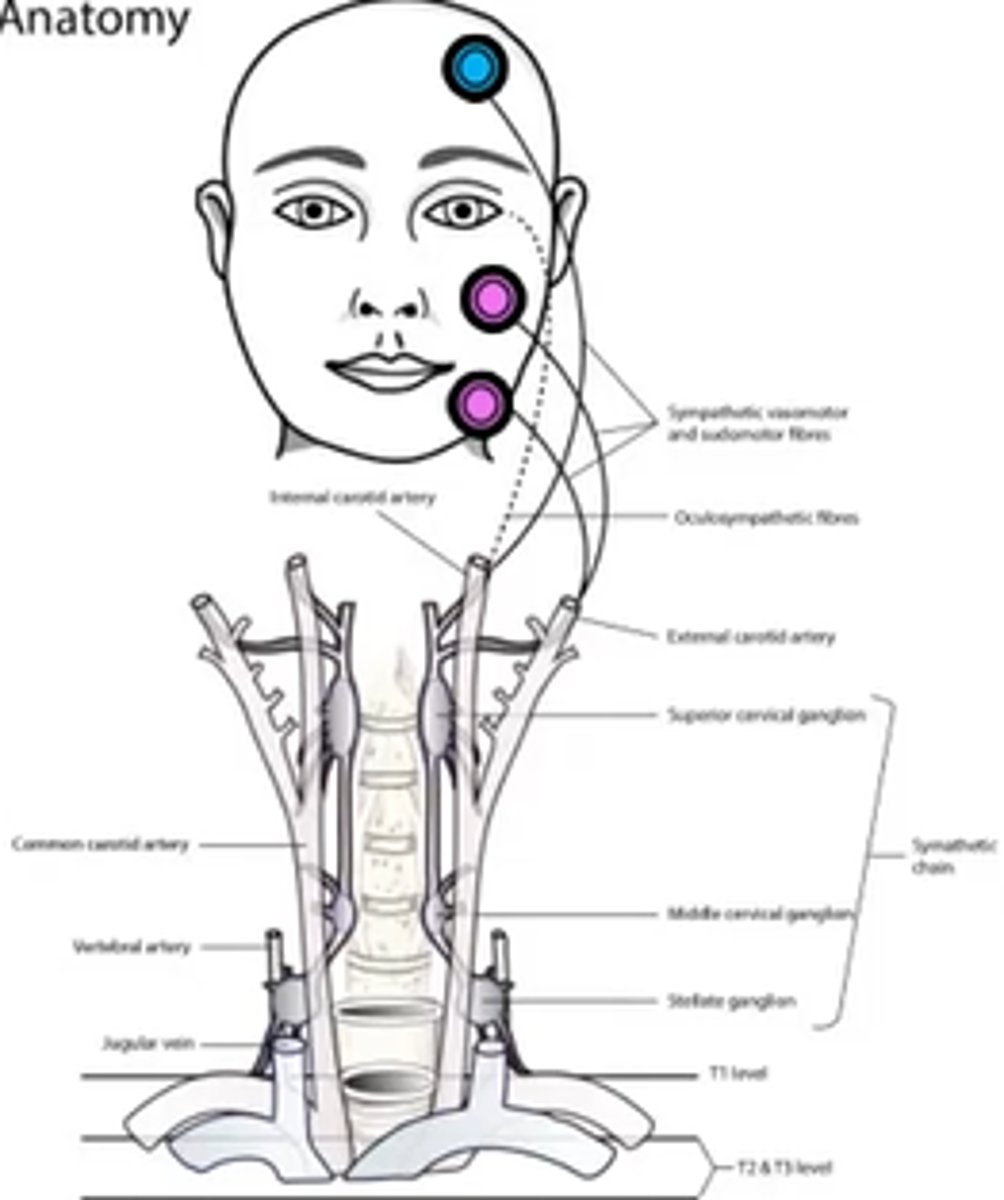
1st axon starts in hypothalamous (midbrain) = 1st synapse in ciliospinal center of budge at C8 = axon extends over apex of lung = 2nd synapse in sup cervical ganglion = 3rd synapse in iris dilator mm
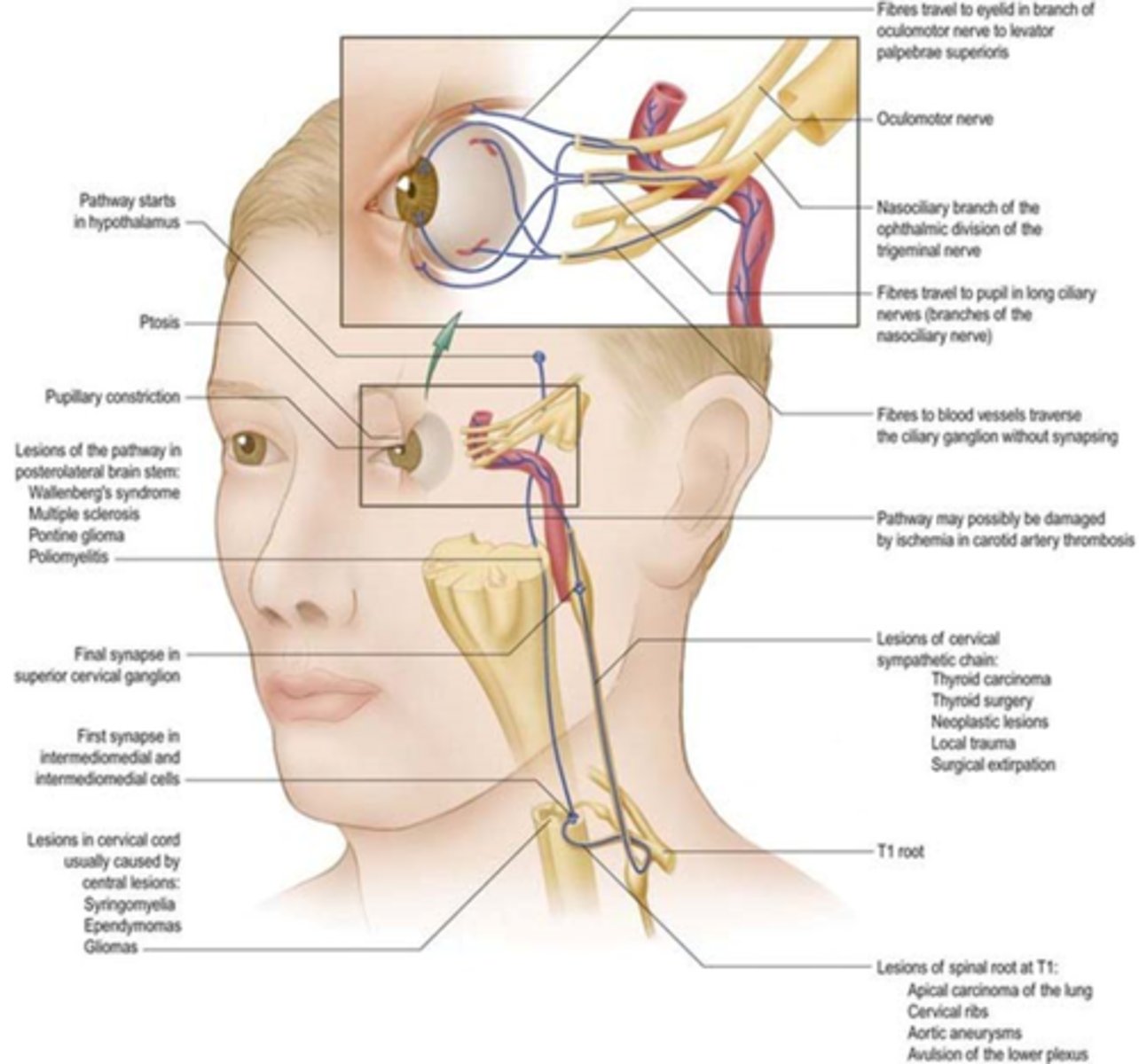
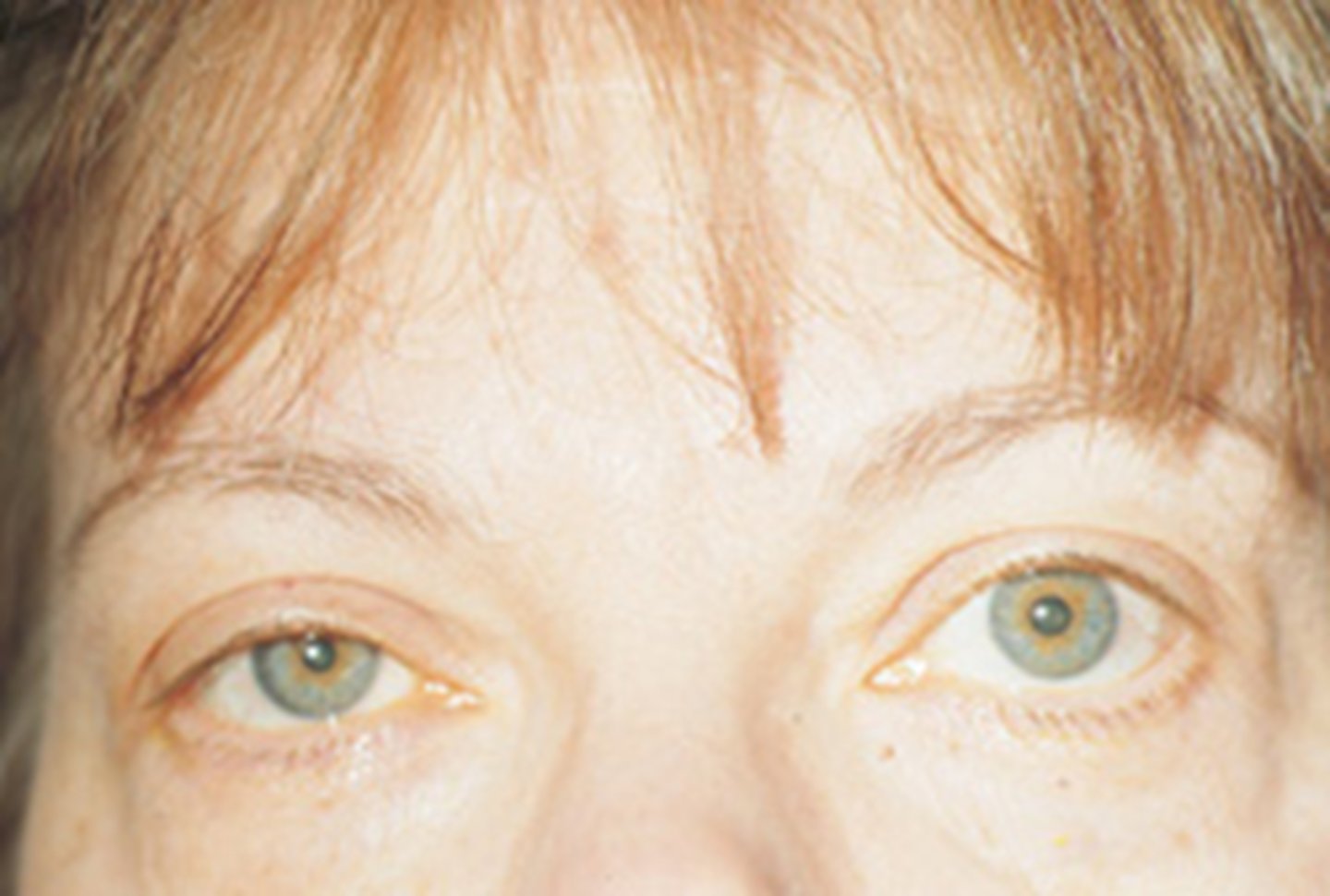
What are 5 findings that might indicate the Horner's syndrome is congenital?
younger pt
heterochromic iris = lighter iris in the Horner's eye due to reduced tyrosinase activity = reduced melanin
straighter hair on Horner's side
anyhydrosis on Horner's side
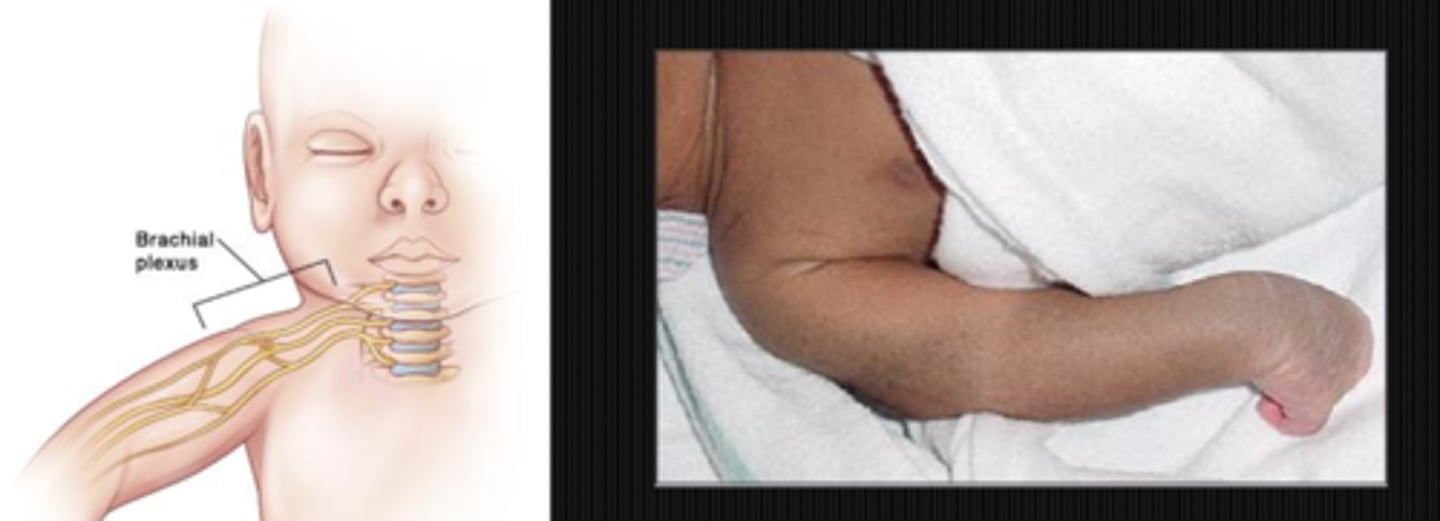
Klumpke's paralysis (spinal birth injury below C7-C8) = underdeveloped hand, paralysis, atrophy, absent triceps reflex
If your pt has congenital Horner's syndrome due to a birth injury, the lesion is likely located in which of the neurons?
2nd order
What are some other potential causes of Horner's syndrome in a pediatric pt?
spinal birth injury = most common
neuroblastoma
mediastinal mass
benign neck mass
infectious mass
What is the triad definition of Horner's syndrome?
ptosis, miosis, and anhydrosis with some other signs
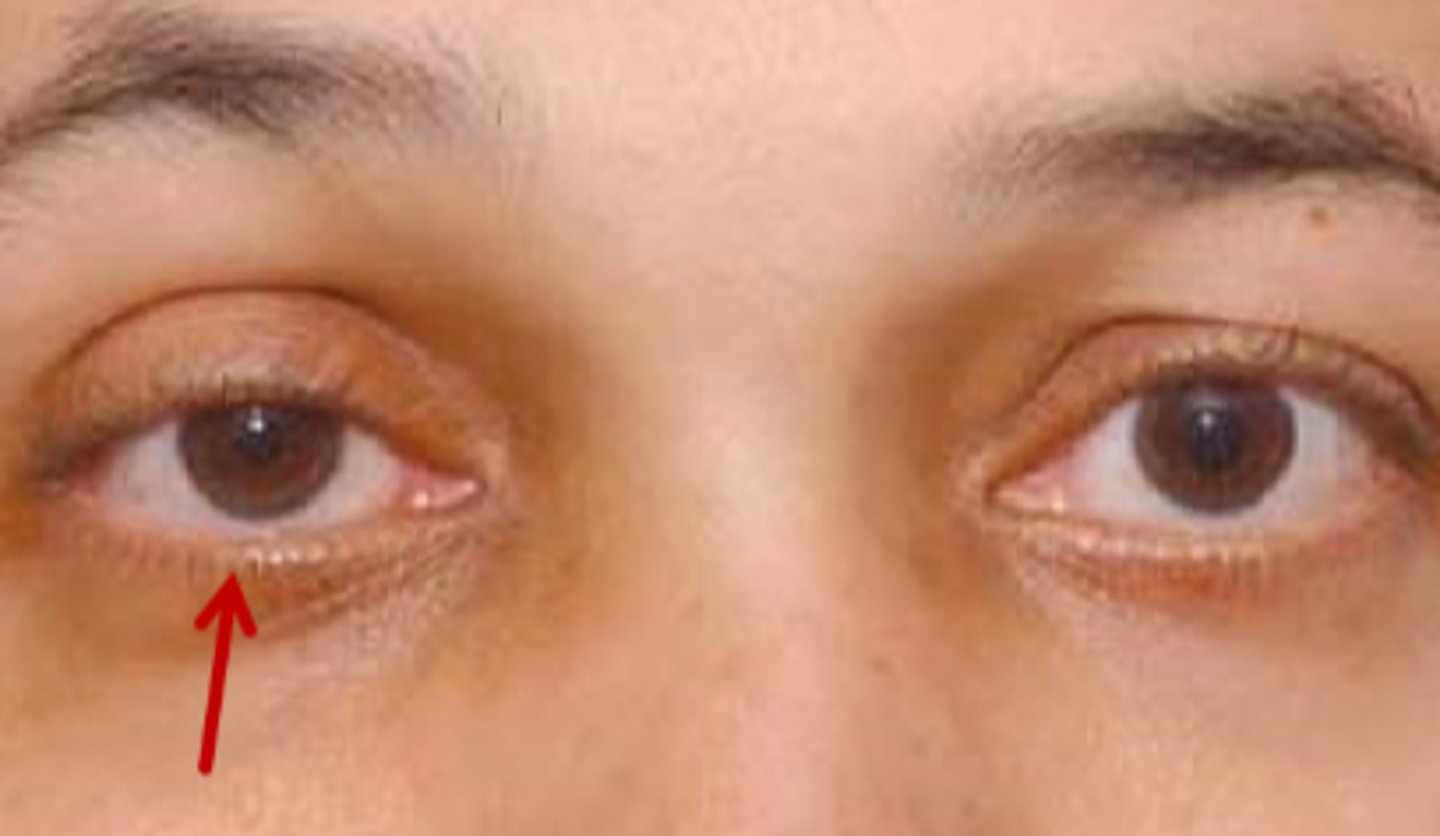
What are 3 ways in which a Horner's syndrome ptosis is different from a CN III palsy ptosis?
varies with time of day = typically worse later on
preserves the upper eyelid fold = less severe ptosis
Kearn's sign / inverse ptosis = due to Mueller's mm of the LL innervated by symp system
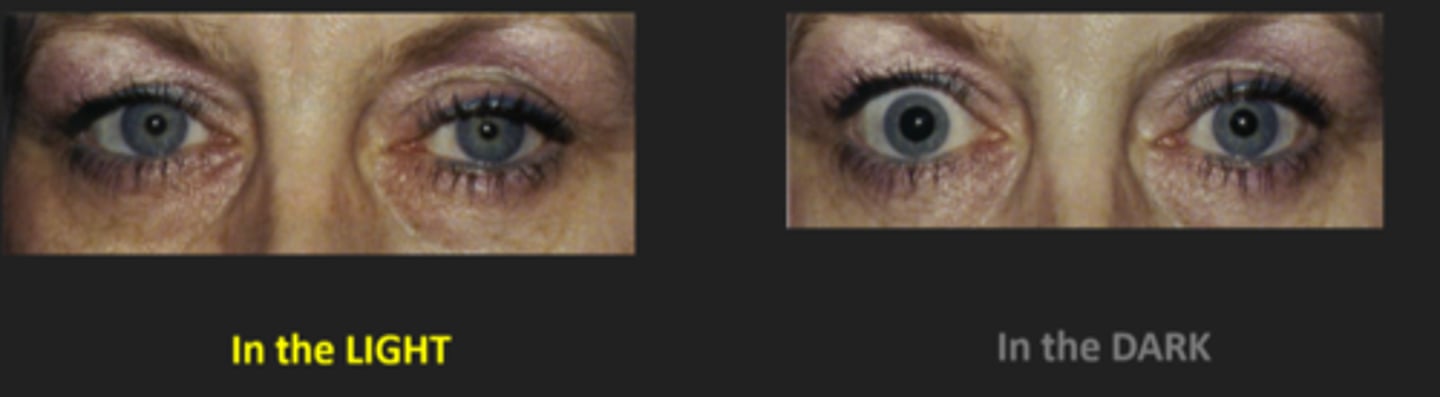
Explain what you will see with the Horner's syndrome miosis?
response to light and near are both intact
anisocoria is greater in dim illumination bc pupil cannot dilate = remains small
How might we determine is the pt has Horner's syndrome anyhydrosis?
exercise = one side of the face sweats while the other does not
skin temp = temp increases on the side that doesn't sweat
Quinizarin powder = purple colour indicates sweat is present (can be done colourless with corn starch)
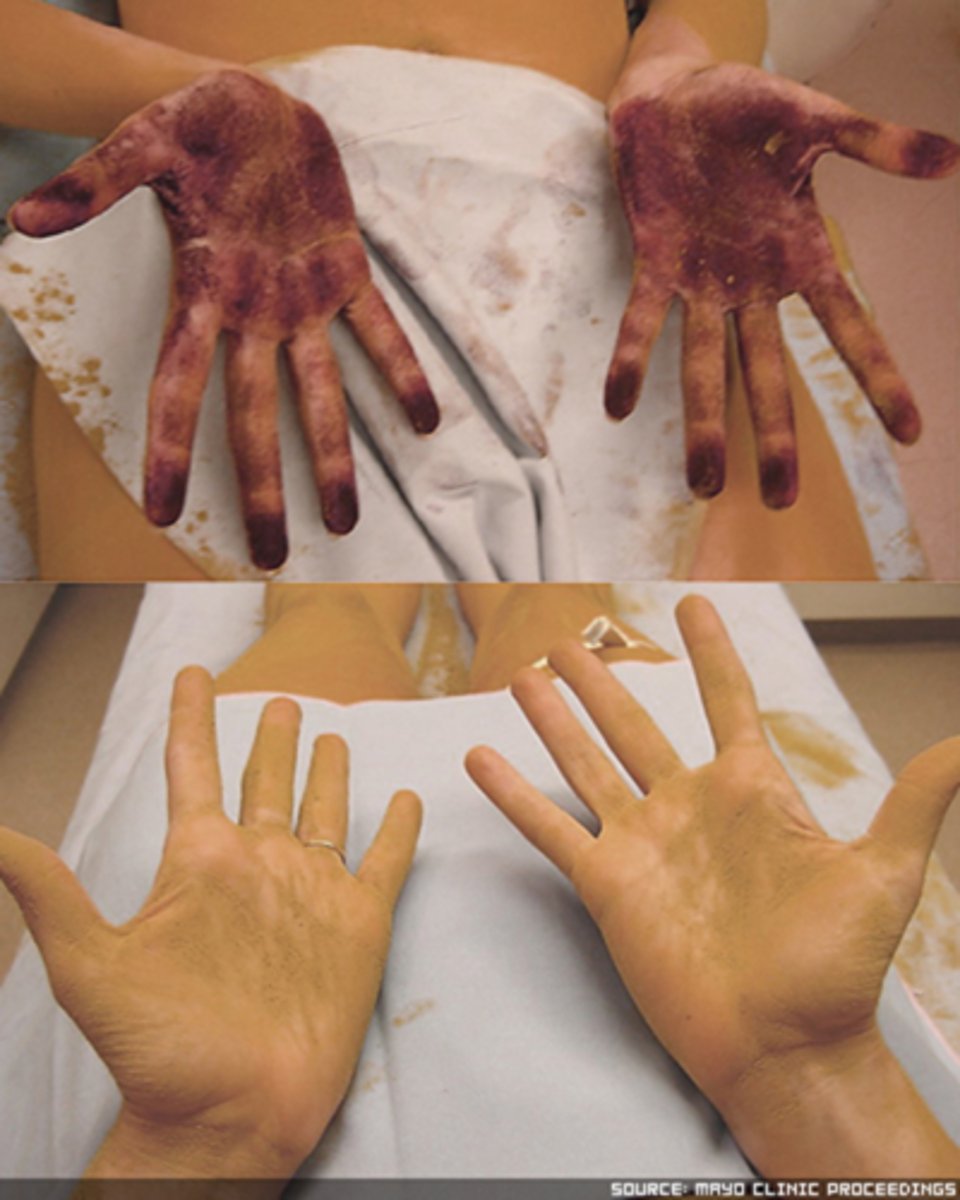
What are 4 other less helpful signs of Horner's syndrome?
resistance to galvanic current on dry skin that doesn't sweat
increased accom amp due to parasymp dominance
transient IOP decreased
change in tear viscosity
What are 3 potential brainstem lesion causes of Horner's syndrome?
Wallenberg's syndrome
Foville's syndrome
anterior medullary vellum lesion
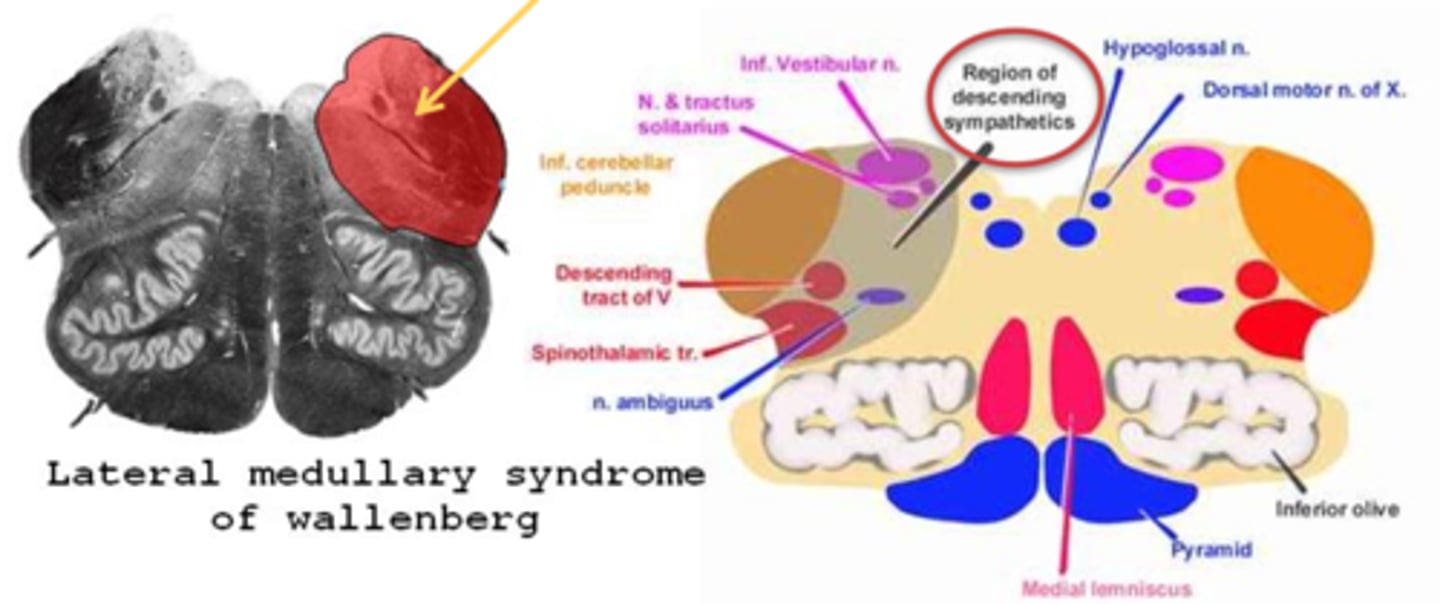
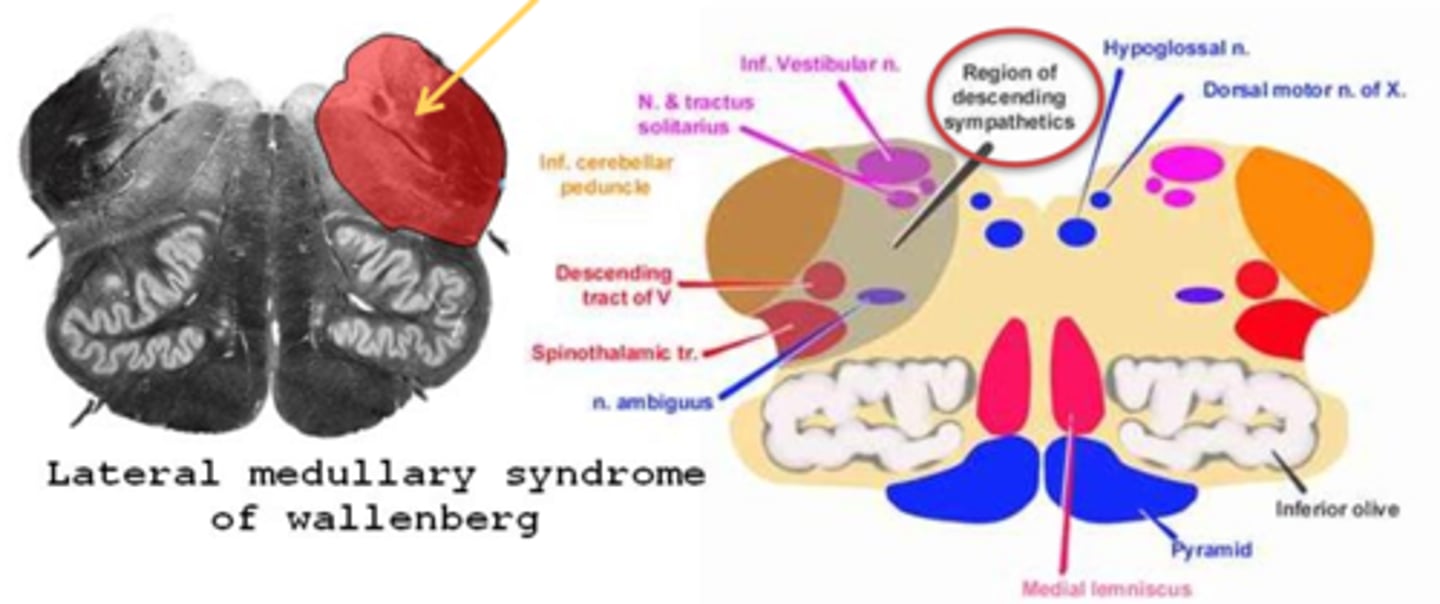
What is Wallenberg's syndrome?
aka lateral medullary syndrome = issue with the inferior cerebellar peduncle (medial and inf vestibular nuclei)
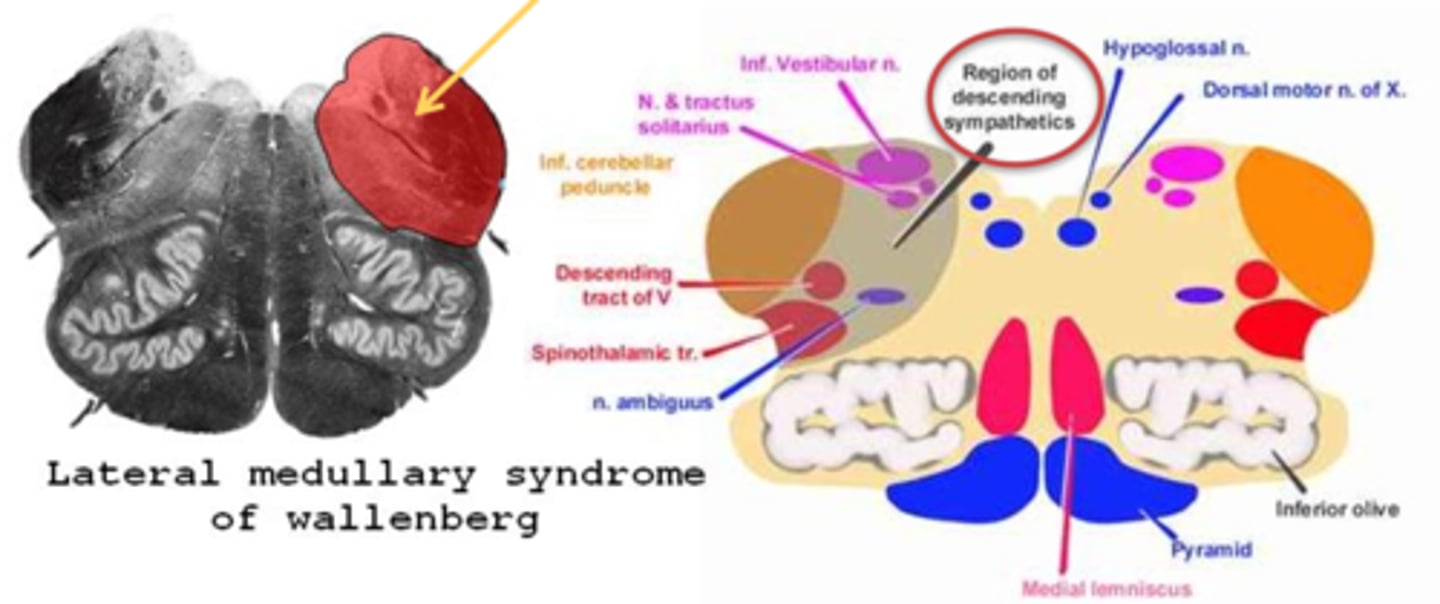
What typically causes Wallenberg's syndrome?
caused most often by a brainstem stroke in the posterior inferior cerebral artery
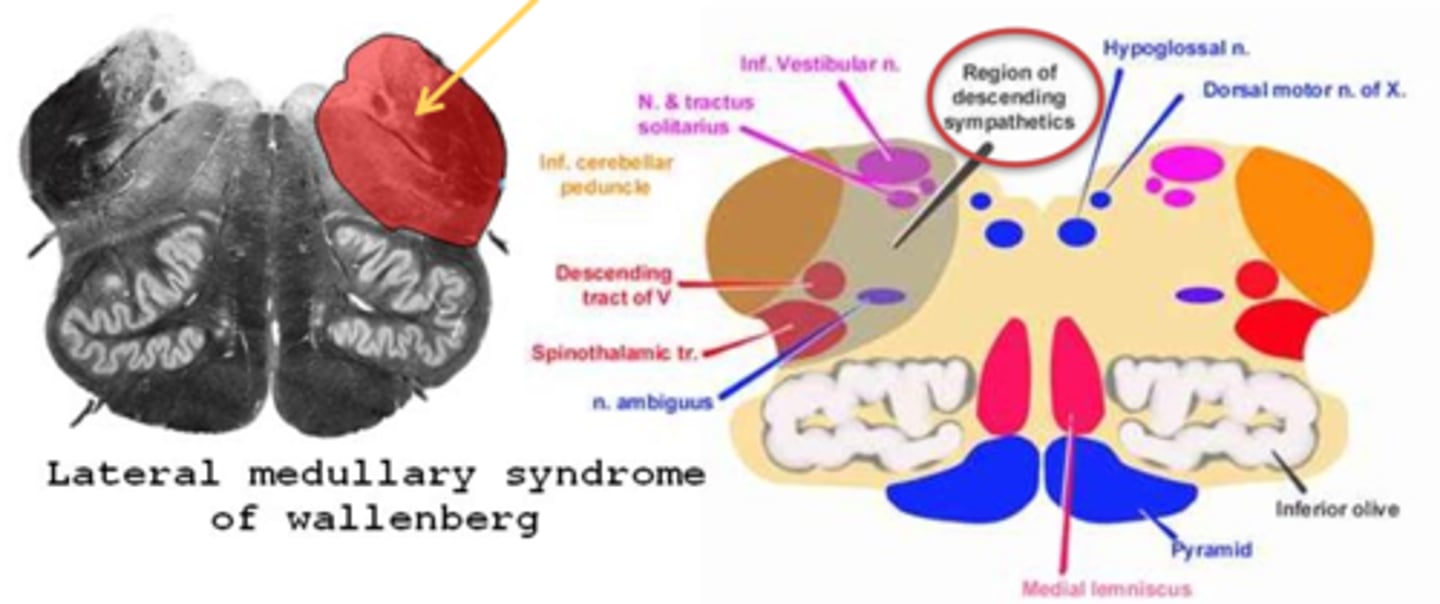
What are the 3 main pupil findings of Wallenberg's syndrome?
ipsilateral Horner's syndrome
reduced light response
intact near response
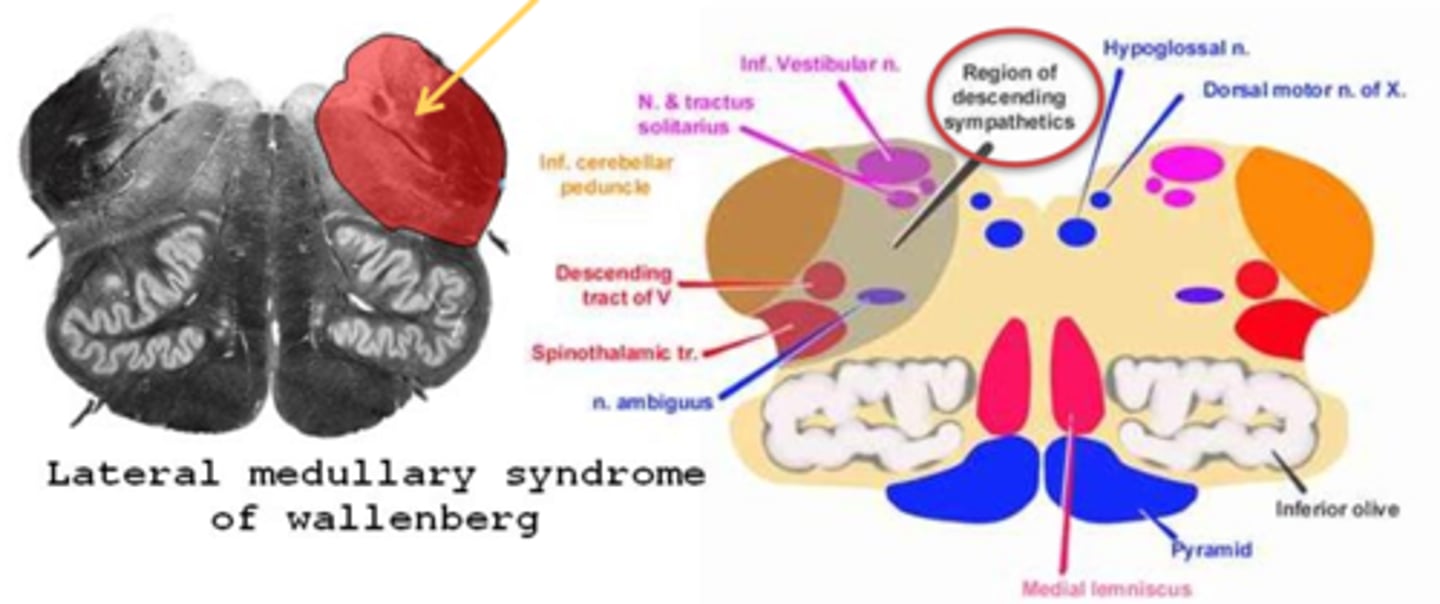
What are some other ocular findings of Wallenberg's syndrome?
nystagmus
Skew deviation = vestibular issues, head tilt/turn
saccadic dysmetria = overshoots towards the Horner's side, undershoots towards the other side
lateral pulsion and corrective movements with vertical saccades = when looking up, pt shows an oblique saccade and correction (like an "S")
Aside from the ocular findings, what are some other S/S of Wallenberg's syndrome?
vertigo
vomiting
contralateral loss of body pain/temp sense
ipsilateral loss of facial pain/temp sense
dysphagia
dysarthria
ipsilateral ataxia & hypotonia
+/- CN VII palsy
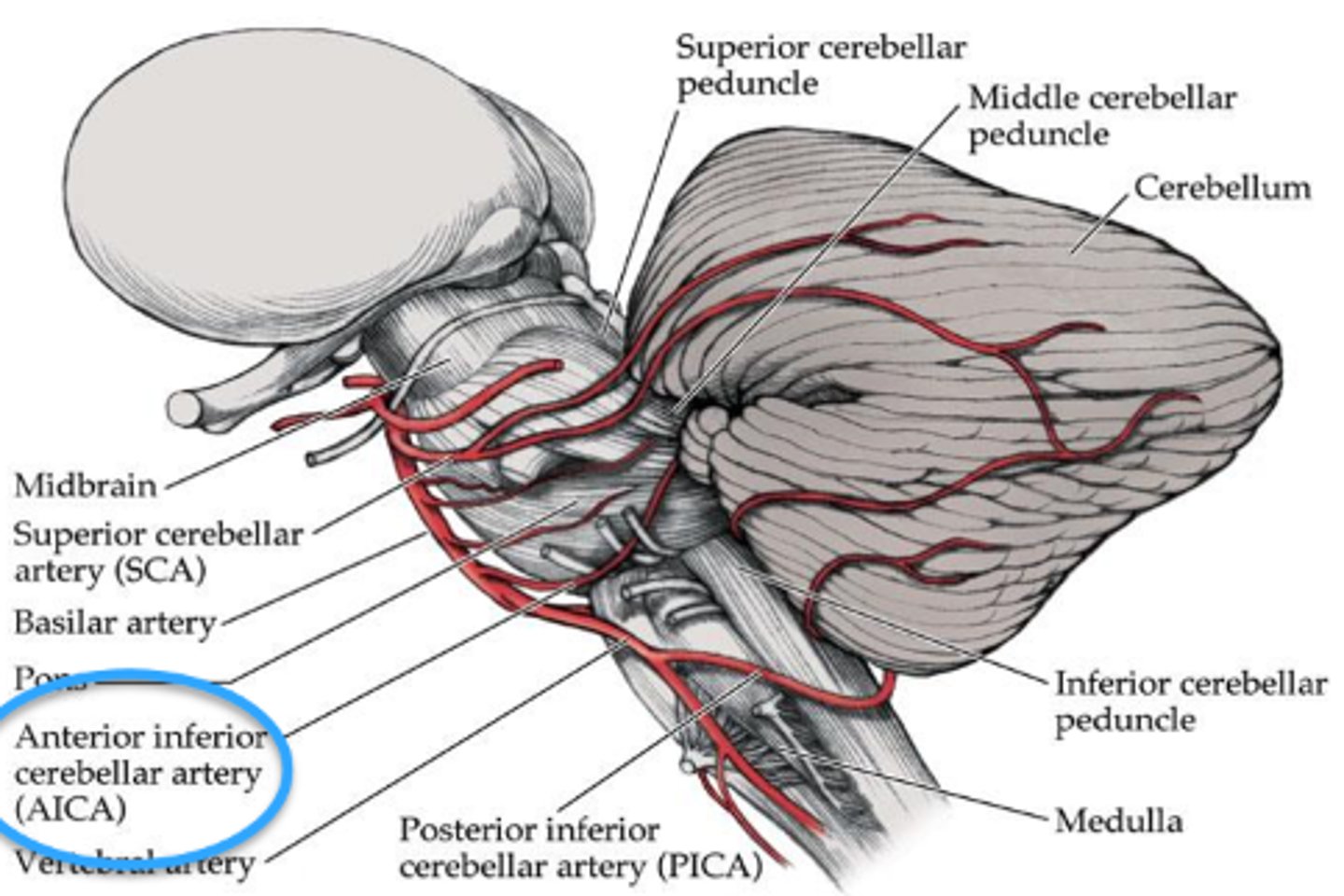
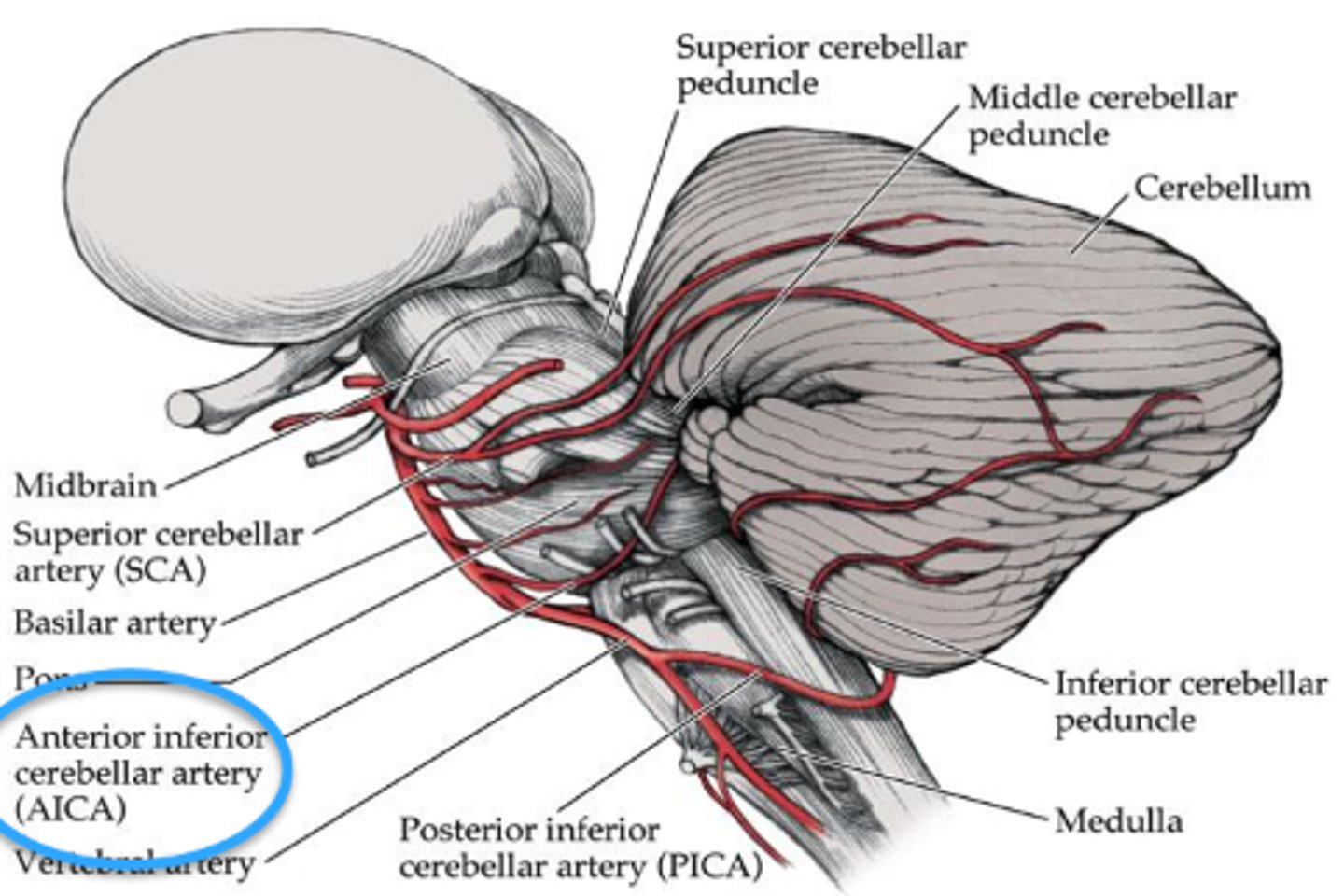
What typically causes Foville's syndrome?
lesion in the anterior inferior cerebellar artery
What is the main pupil finding in Foville's syndrome?
ipsilateral Horner's
What are some other findings in Foville's syndrome?
ipsilateral gaze palsy
ipsilateral CN VII palsy
loss of taste on ant 2/3 tongue
ipsilateral analgesia of face
ipsilateral deafness
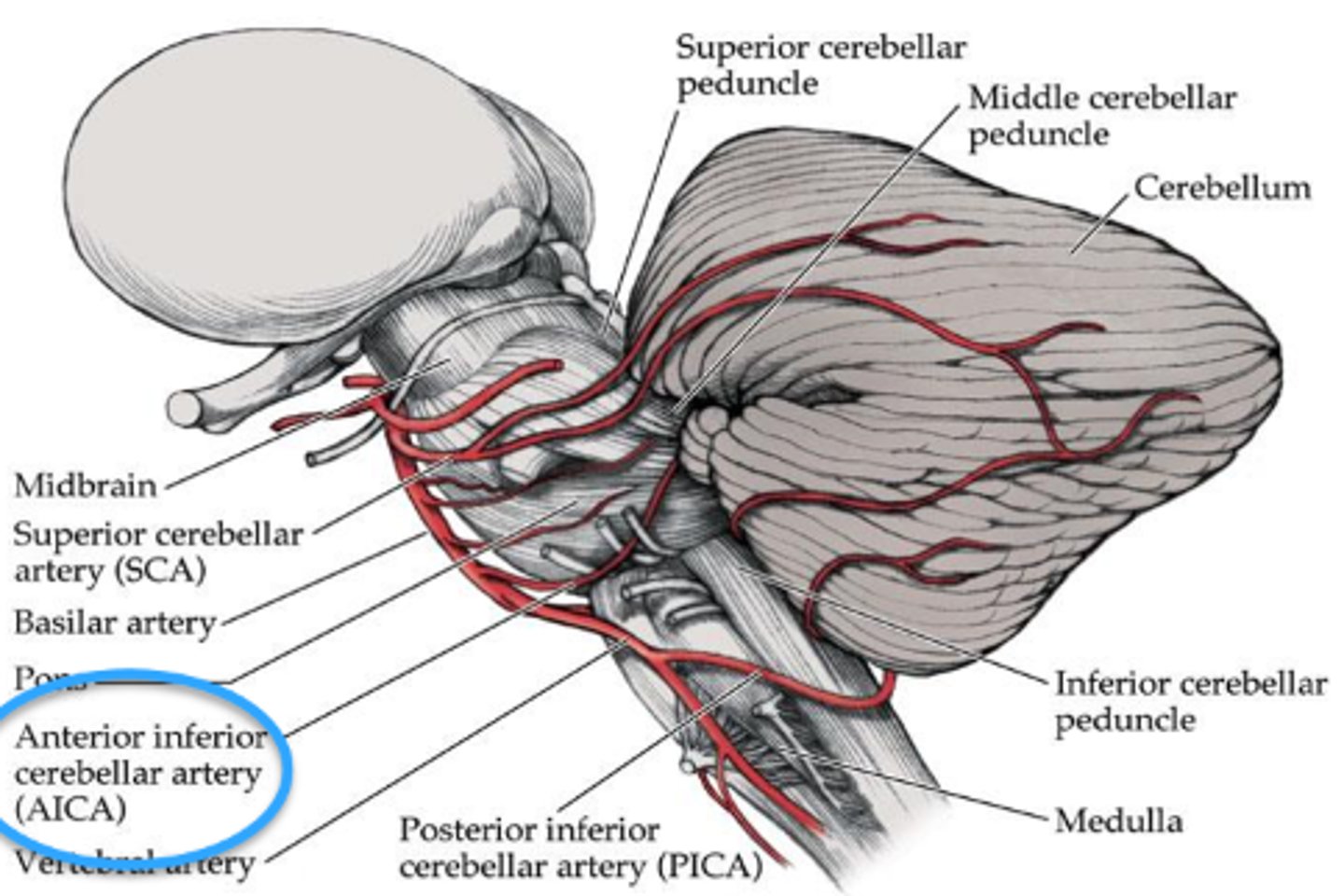
What typically causes an anterior medullary vellum lesion?
head trauma
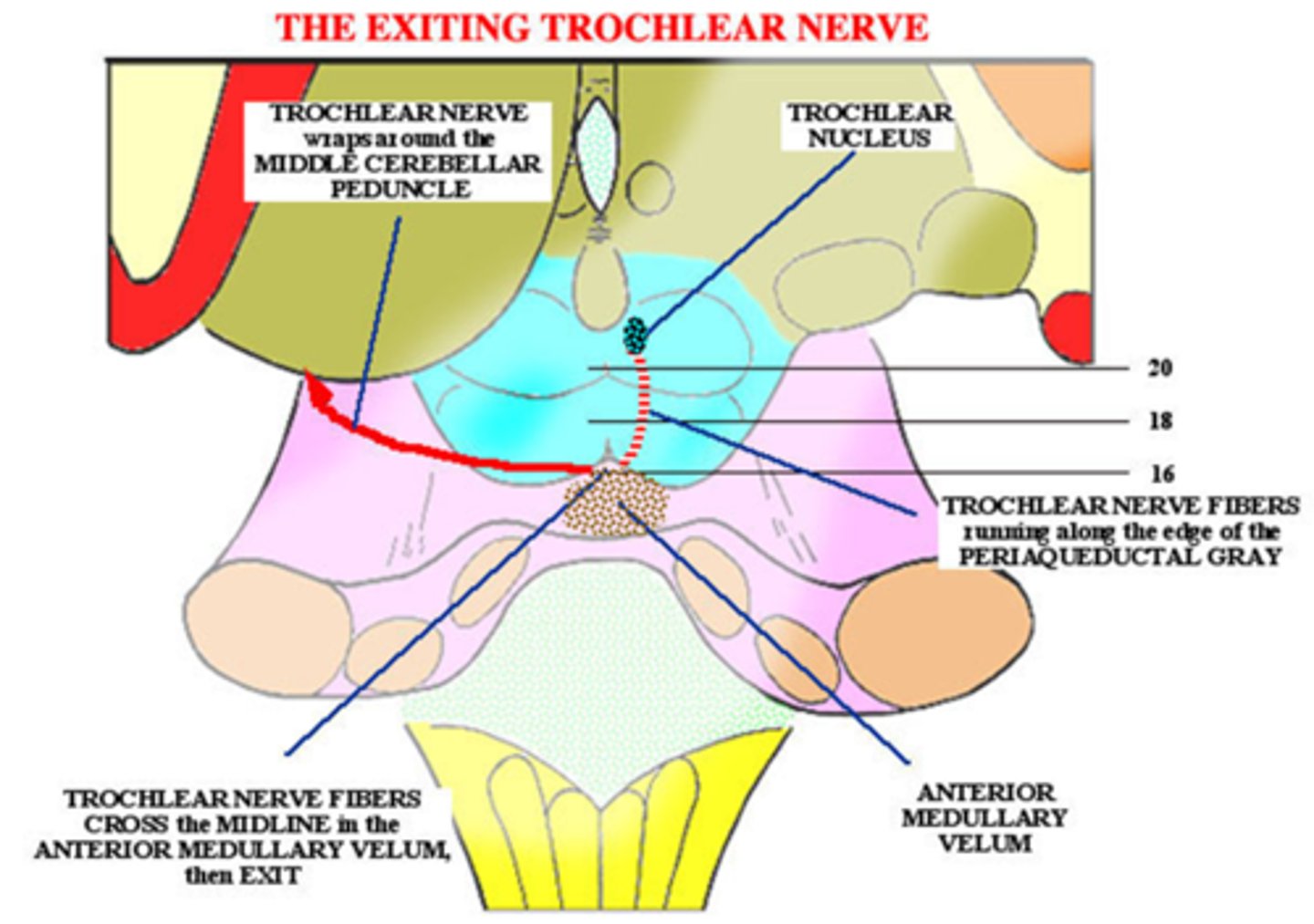
What are the 2 main ocular findings in an anterior medullary vellum lesion?
ipsilateral Horner's
contralateral CN IV palsy bc CN VI crosses over after leaving brainstem
THINK: this lesion is the area when symp fibers and CN IV come together at the inf colliculus
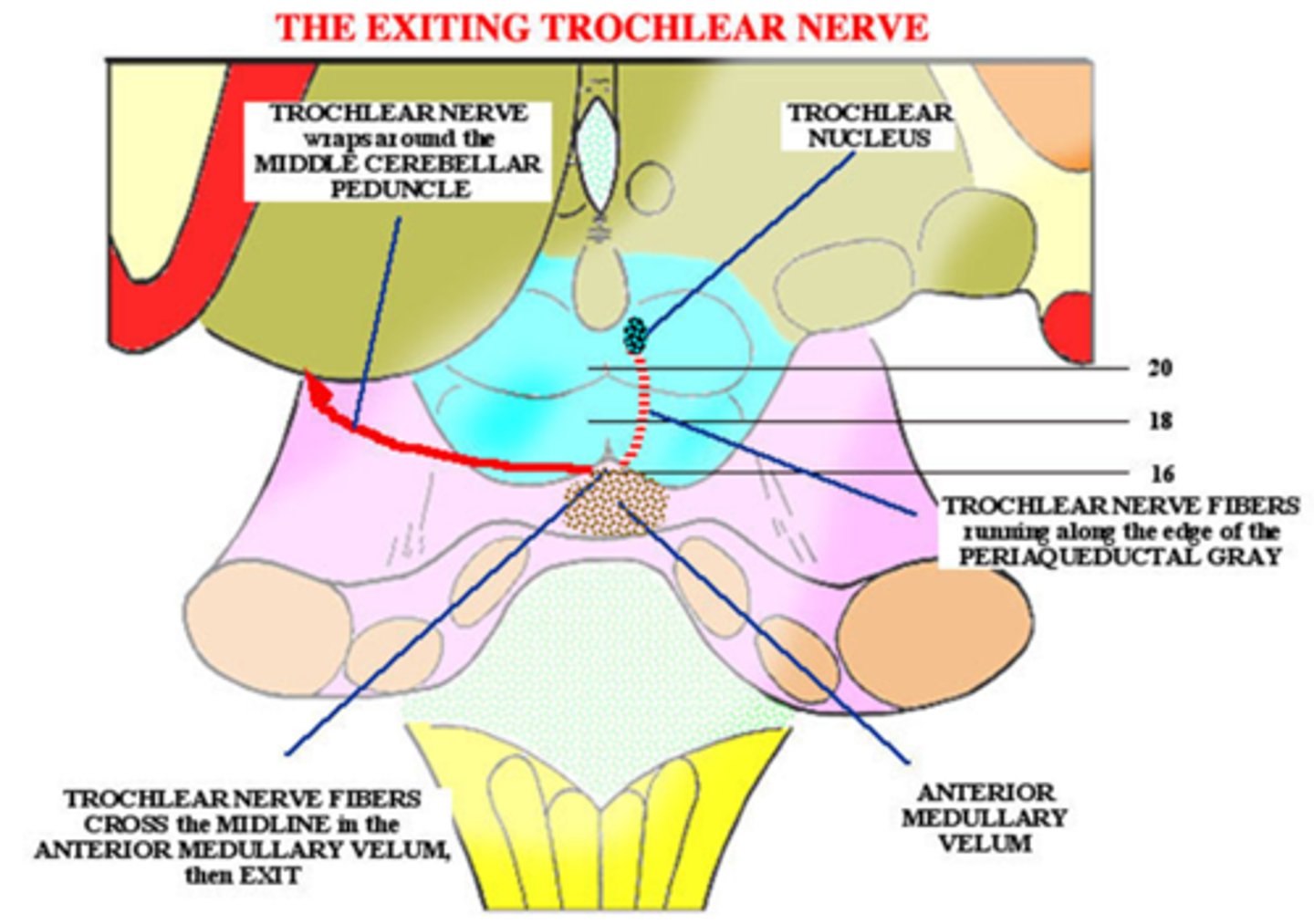
What are 2 potential spinal cord lesion causes of Horner's syndrome?
spinal birth injury
phrenic nerve syndrome
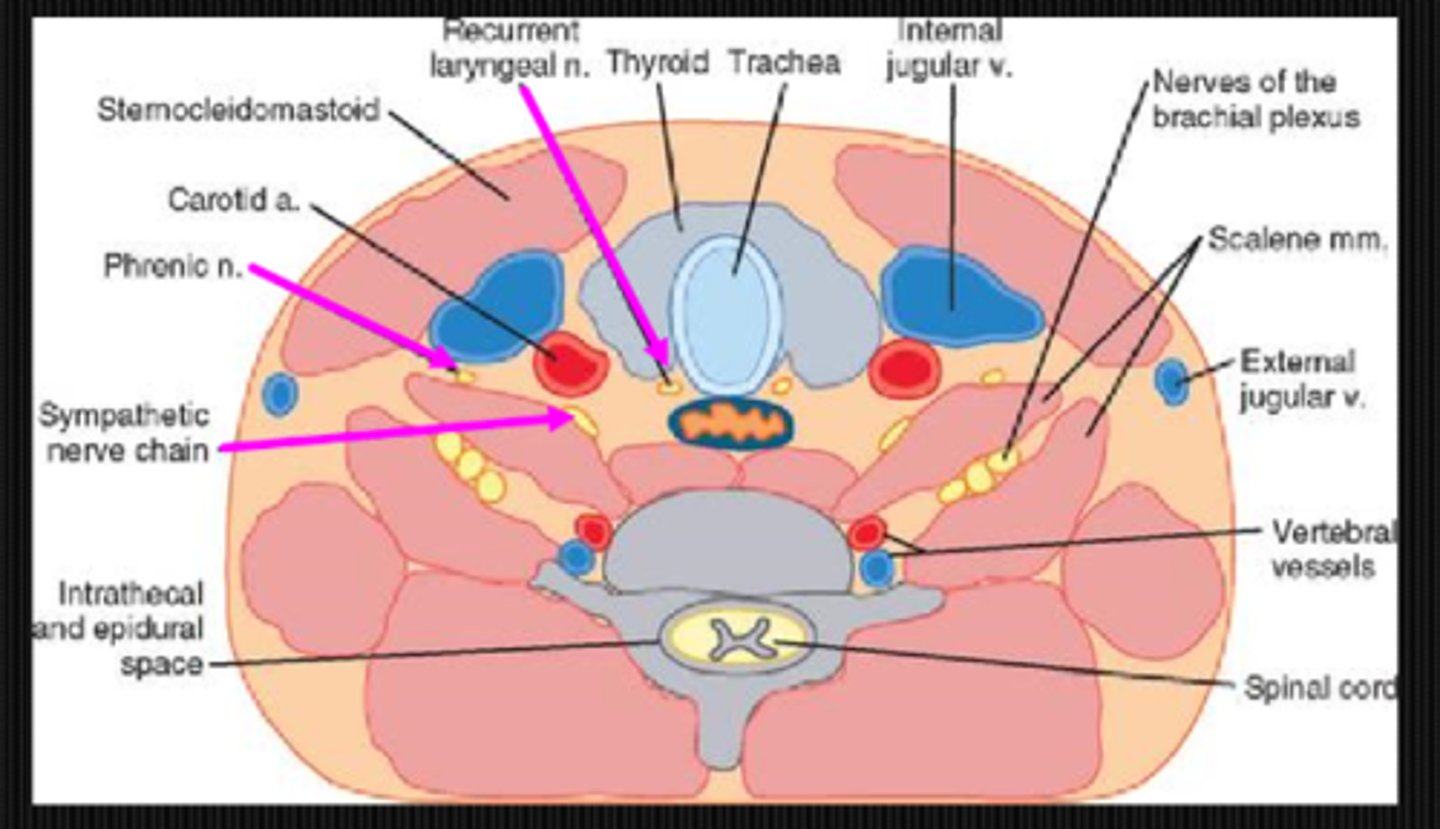
At what spinal level does phrenic nerve syndrome occur at?
C6
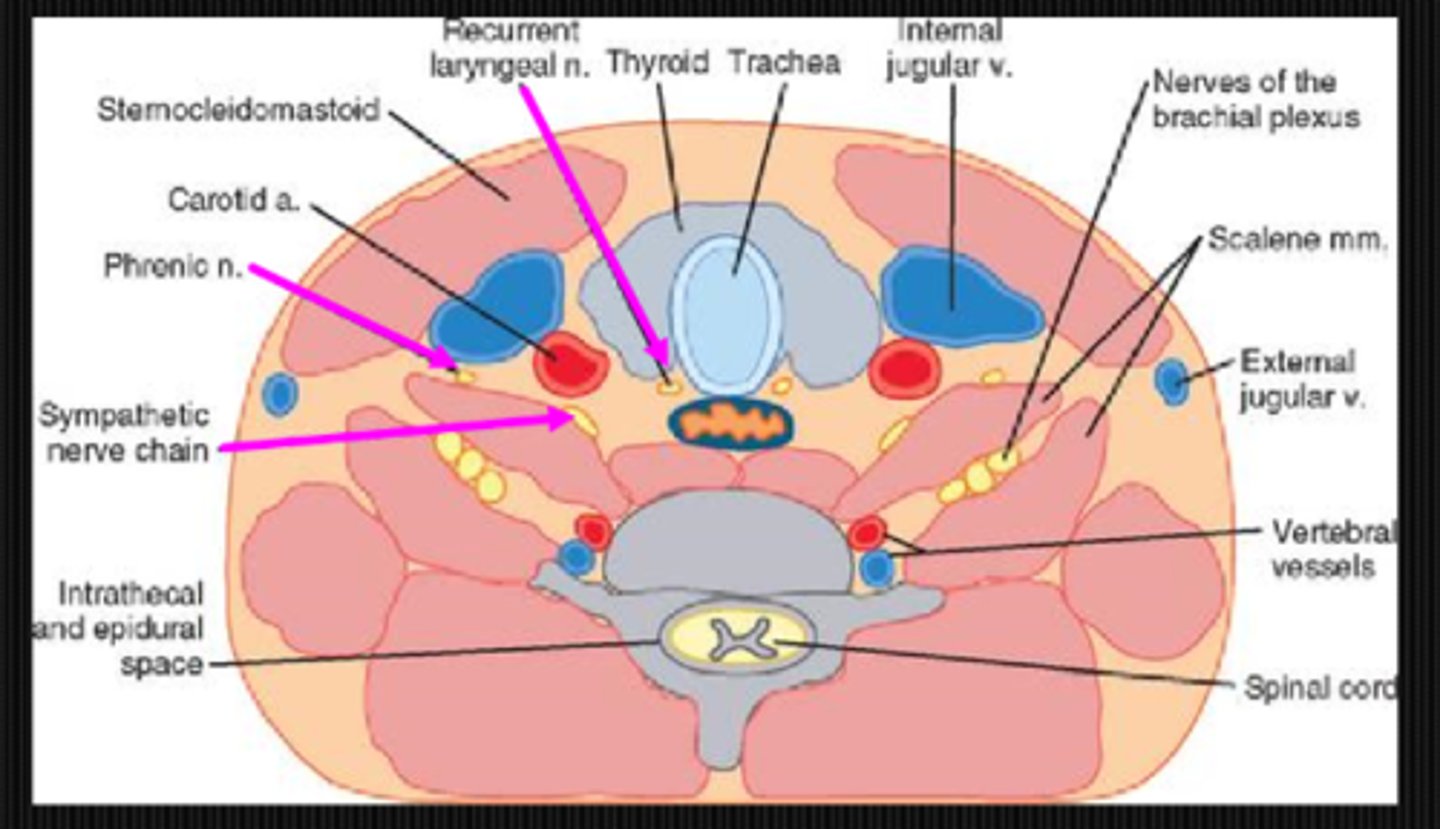
What are 3 findings of phrenic nerve syndrome?
Horner's syndrome due to symp fiber damage
breathing problems due to damage to motor input to diaphragm
hoarse voice due to recurrent laryngeal nerve damage
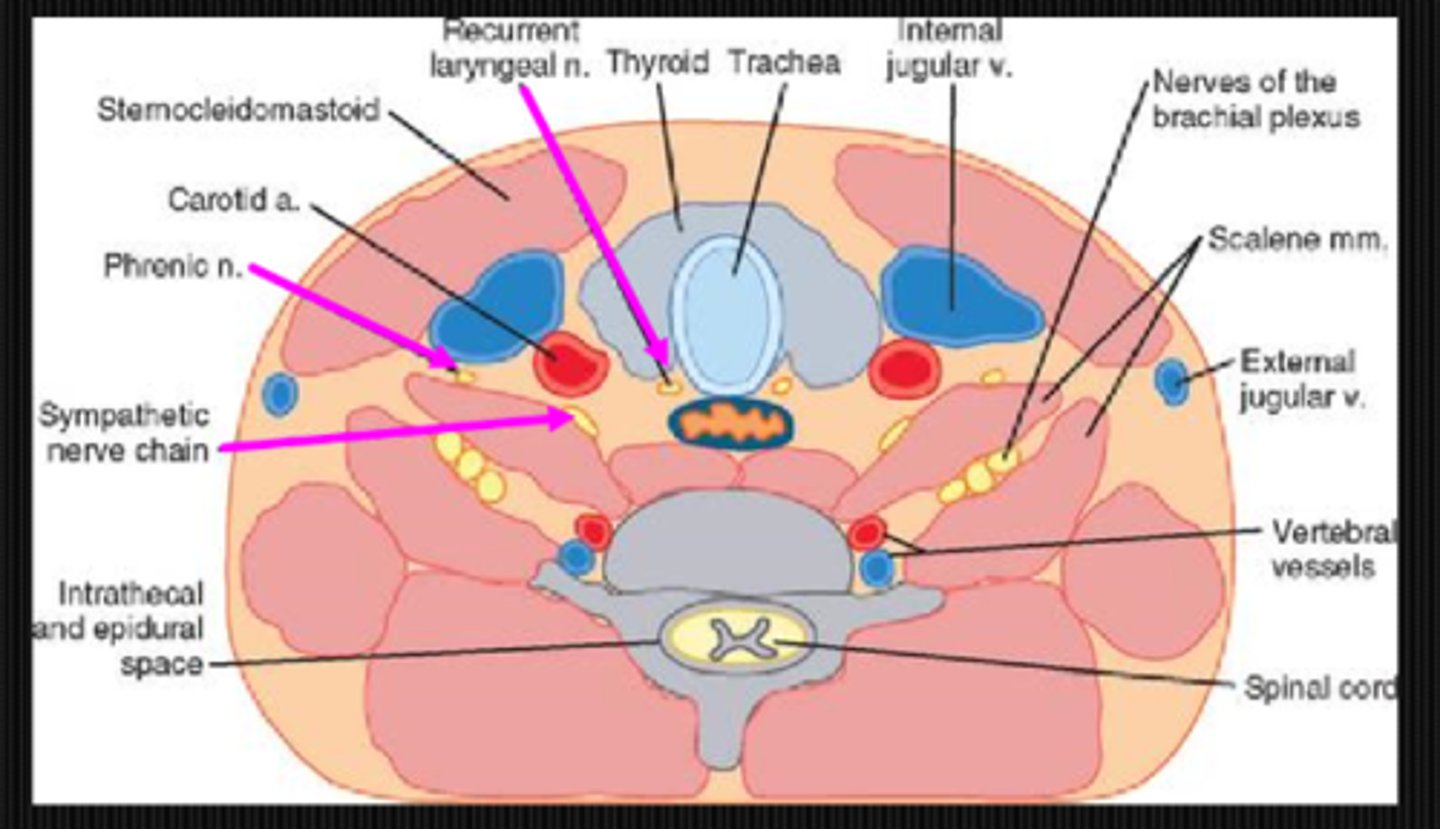
What is a potential chest lesion cause of Horner's syndrome?
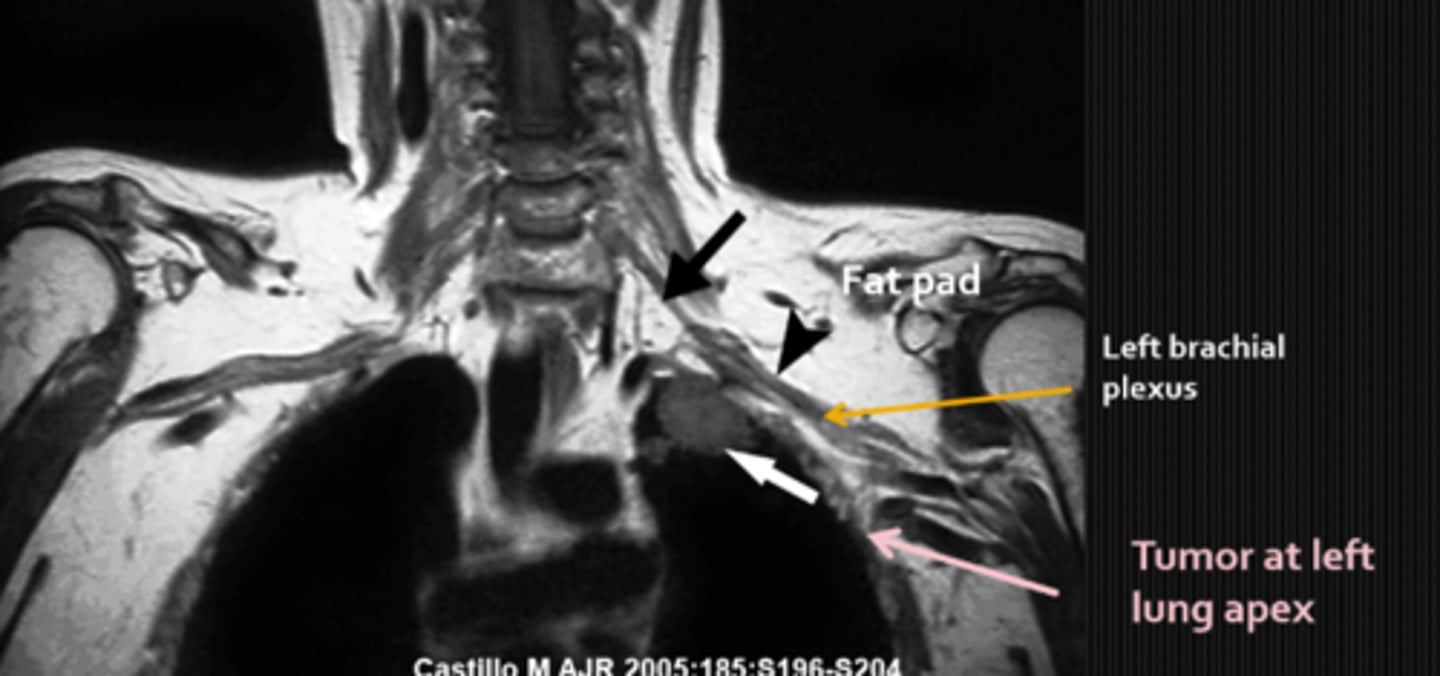
Pancoast tumor that affects the symp fibers traveling over apex of lung
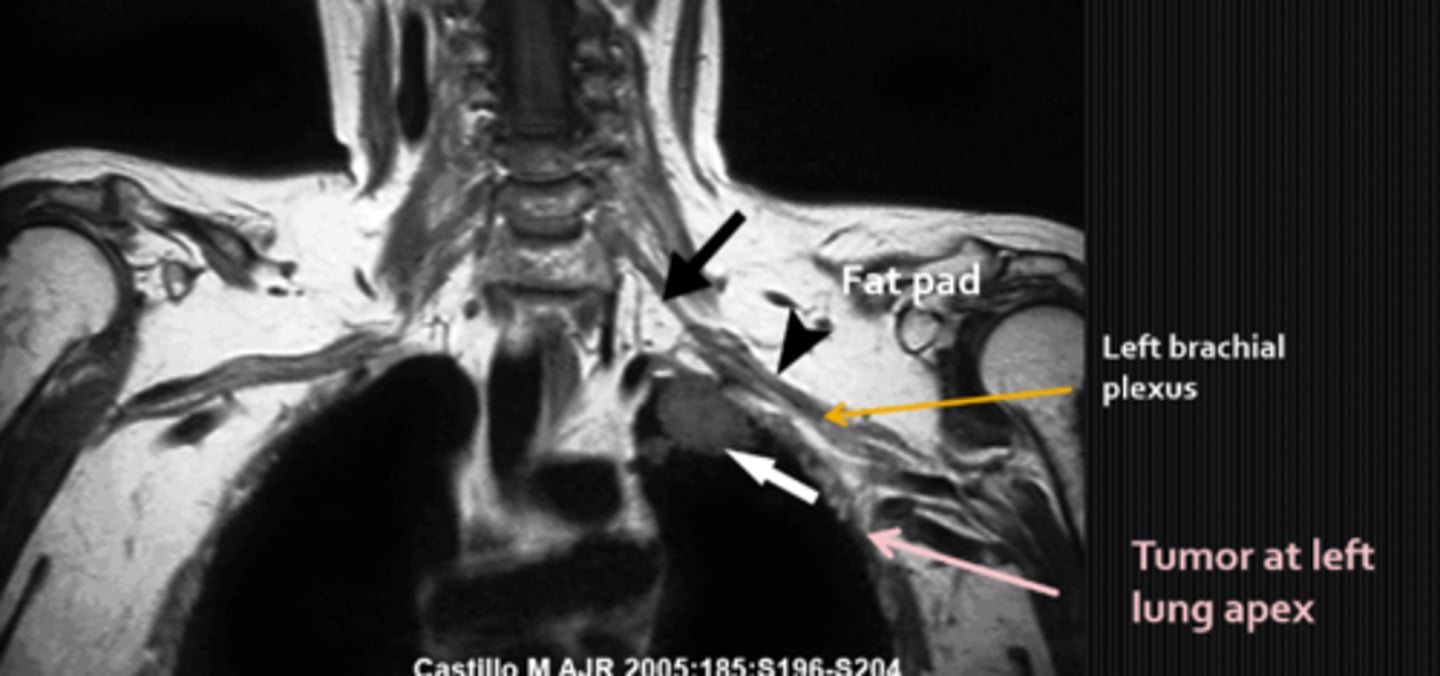
What are some findings of a Pancoast tumor?
Horner's syndrome
chest pain
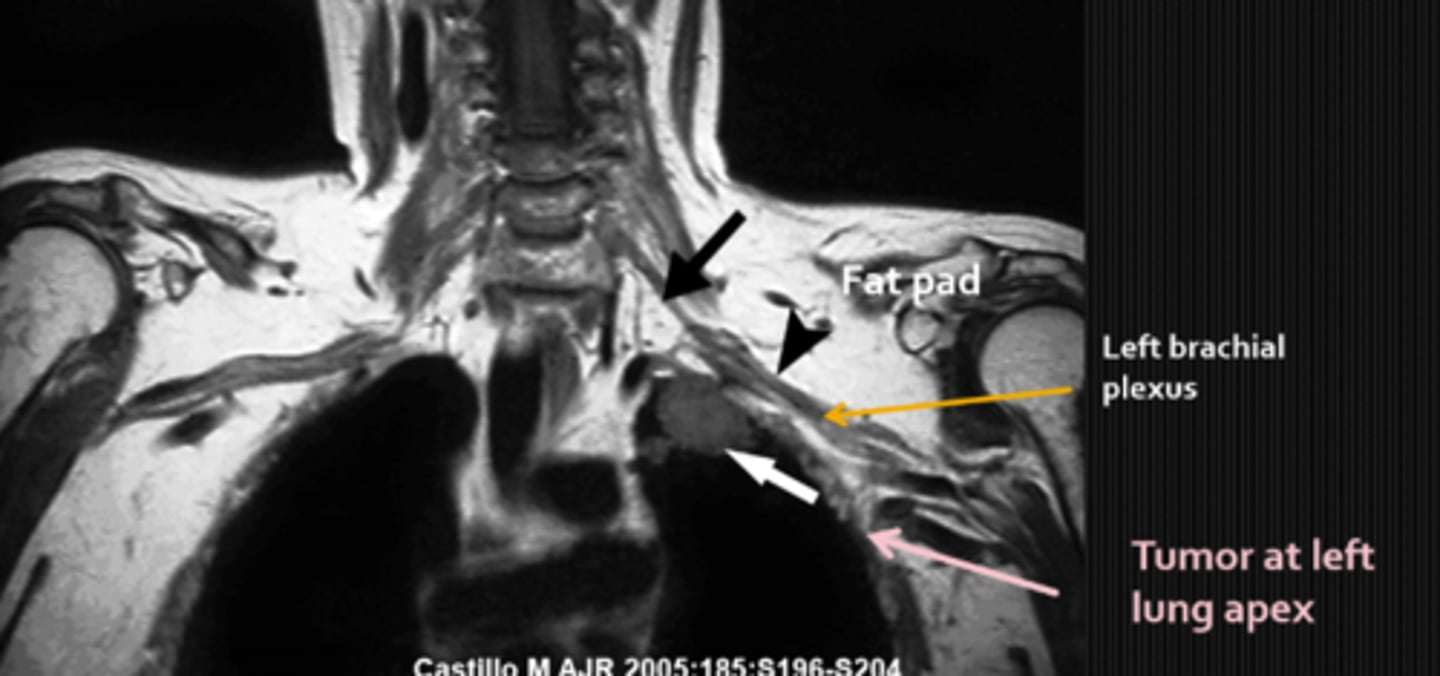
What is a potential neck lesion cause of Horner's syndrome?
symp fibers that are very close to the ICA = lesions here
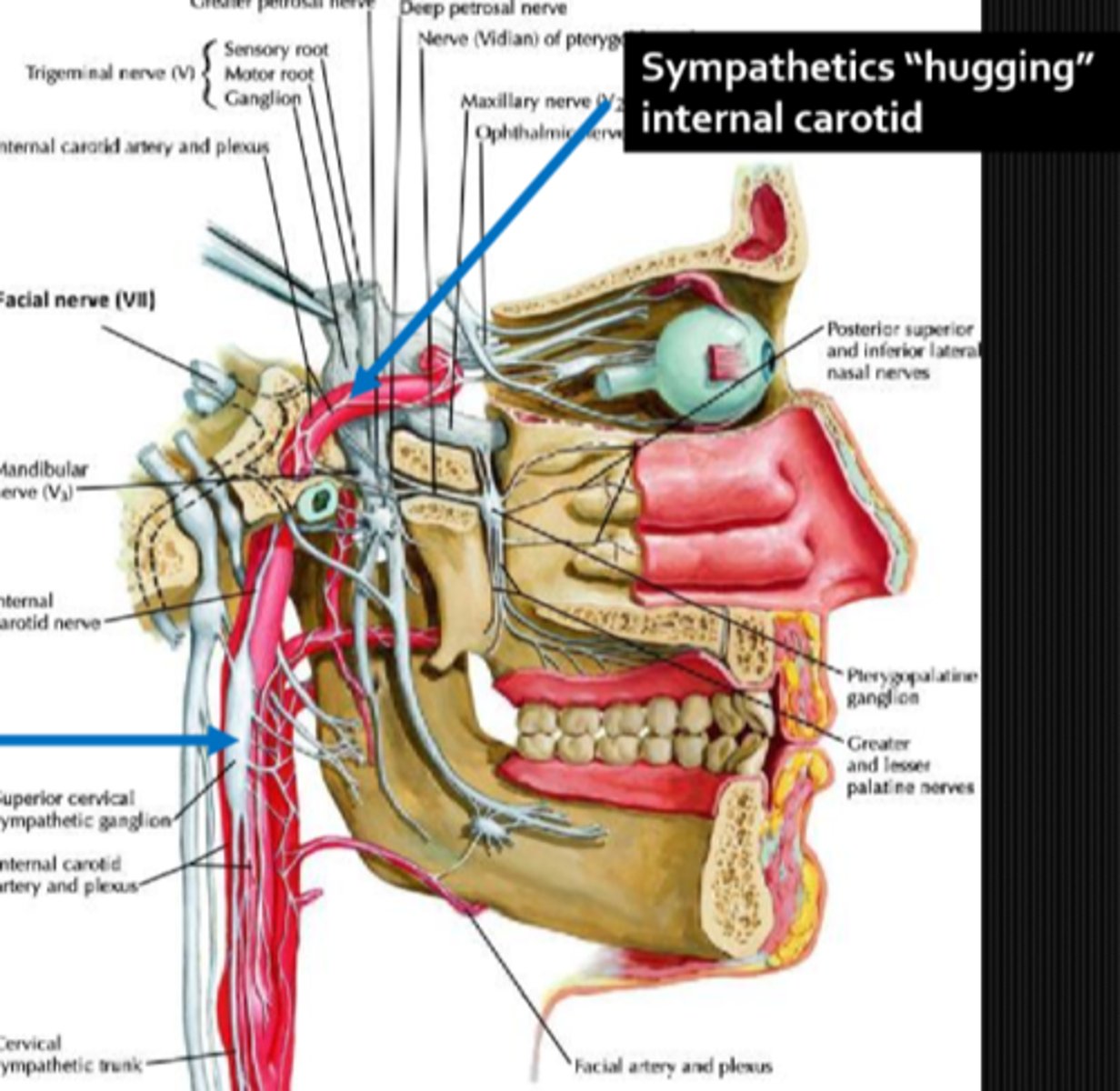
An ICA lesion like a dissection can result in Horner's syndrome. What other CN and sense(s) would be affected with this etiology?
CN 7, 9, 10 = change in taste in the ant 2/3 tongue, post 1/3 tongue, larynx
What are 4 potential head lesion causes of Horner's syndrome?
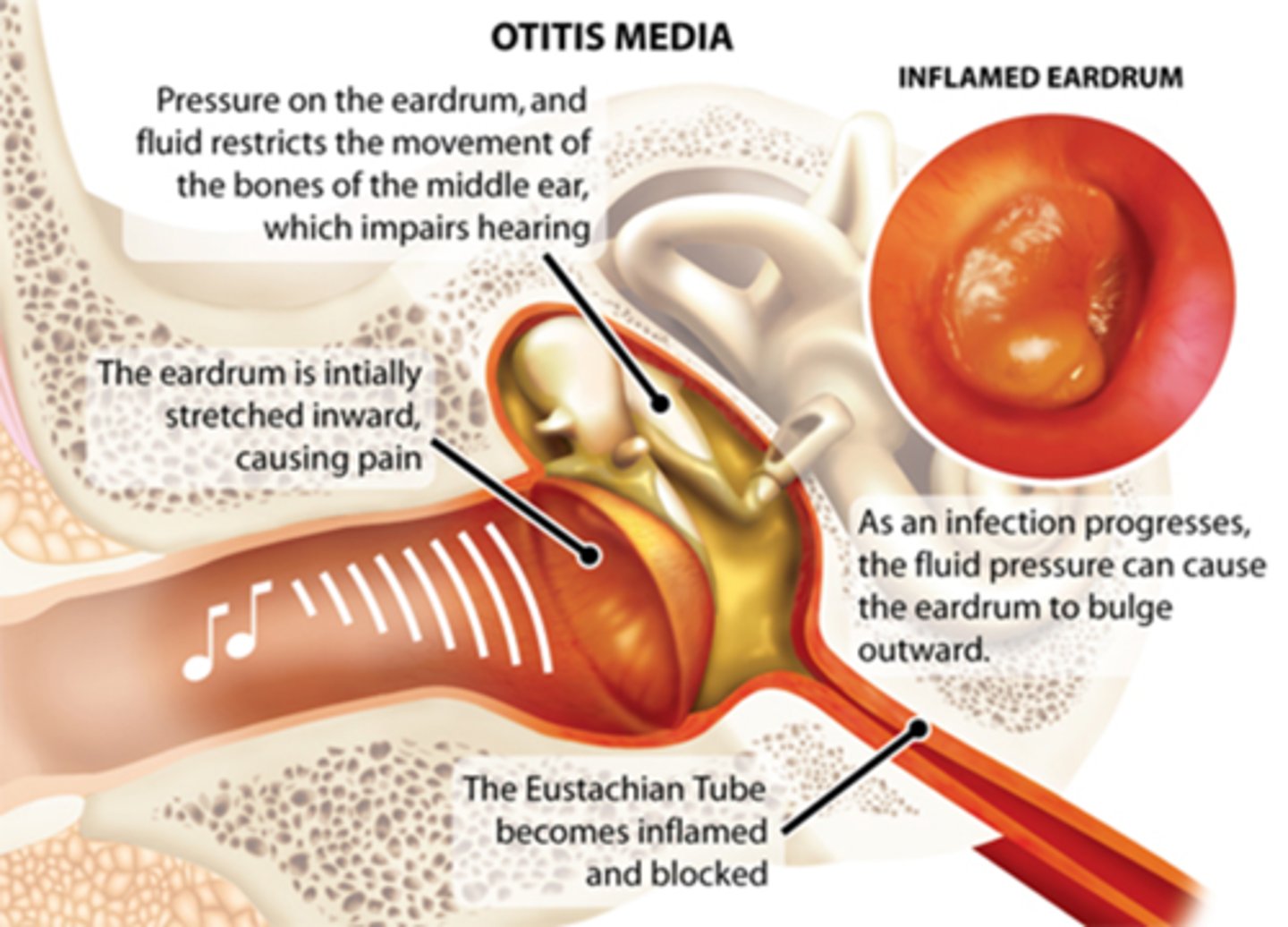
otitis media ear infection
cavernous sinus where symp fibers are close by
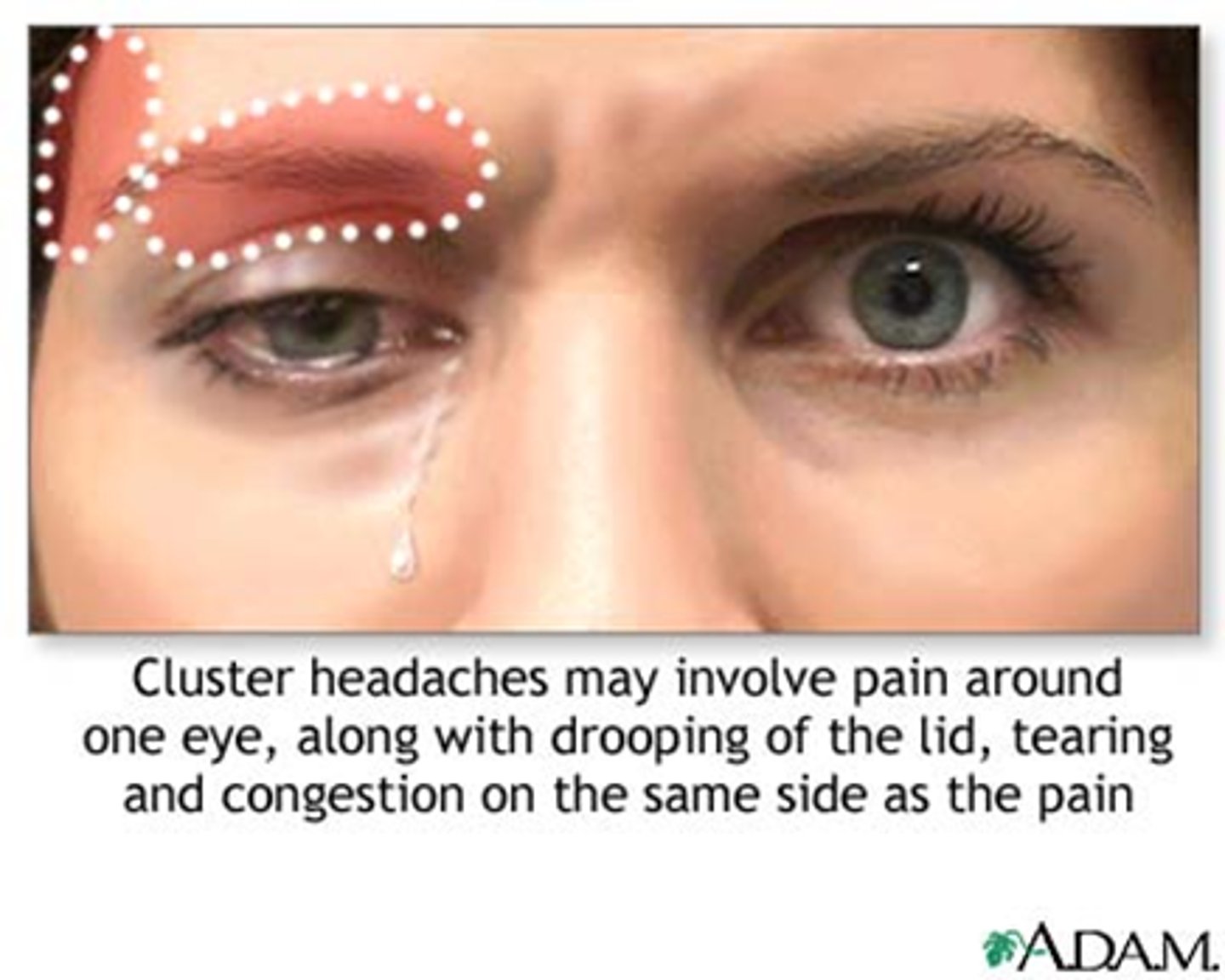
cluster HA = migraine compresses CN V1, V2, symp fibers
ICA dilation compresses CN V and symp plexus
If the pt has a Horner's with an earache, what is the likely head lesion involved?
otitis media
If the pt has a Horner's with a neck ache, what is the likely head lesion involved?
ICA dissection
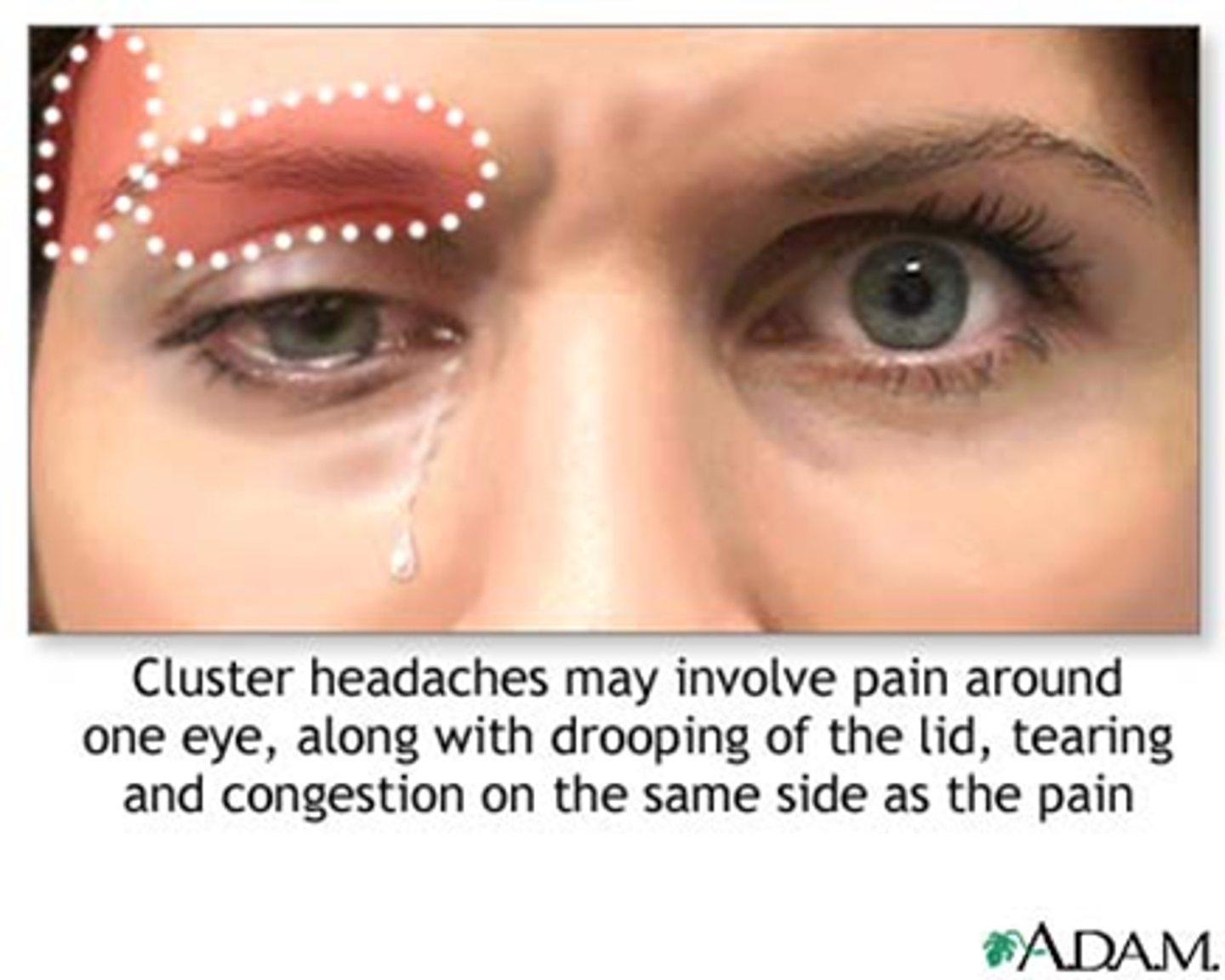
If the pt has a Horner's with a headache, red eye, or stuffy nose, what is the likely head lesion involved?
cluster HA
If the pt has a Horner's with a chest/arm ache, what is the likely lesion involved?
Pancoast tumor
If the pt has a Horner's with diplopia, what is the likely head lesion involved?
cavernous sinus lesion involving CN III, CN IV, VI
If the pt has a Horner's with a hoarseness, what is the likely head lesion involved? 2 options.
phrenic syndrome
Vernet's syndrome
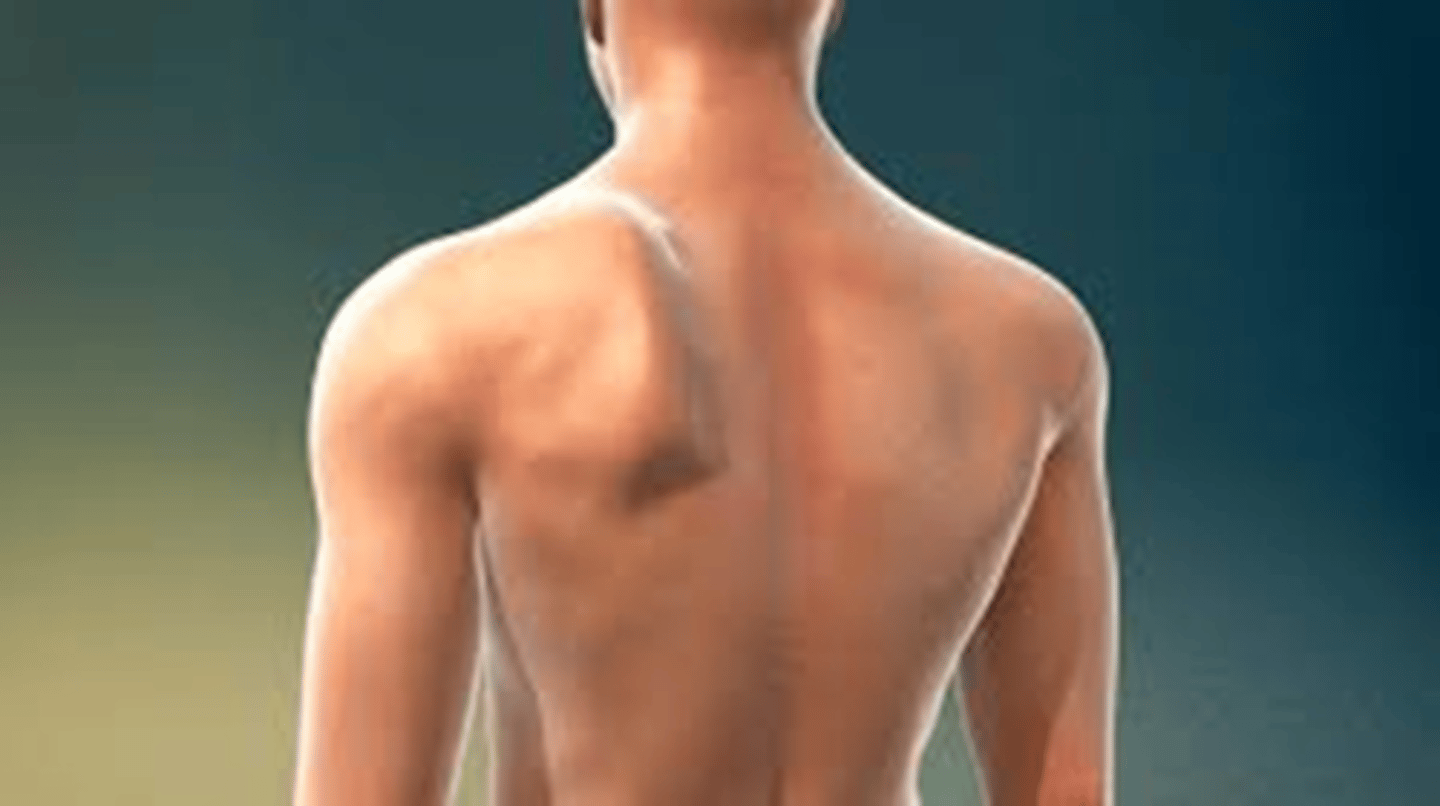
What are 5 findings seen in Vernet's syndrome (aka ECA sheath syndrome, jugular foramen syndrome)?
Horner's syndrome
hoarseness due to CN X lesion
droopy shoulder due to sternocleidomastoid issue
winged scapula due to trapezius issue
cannot say "La" due to CN XII lesion
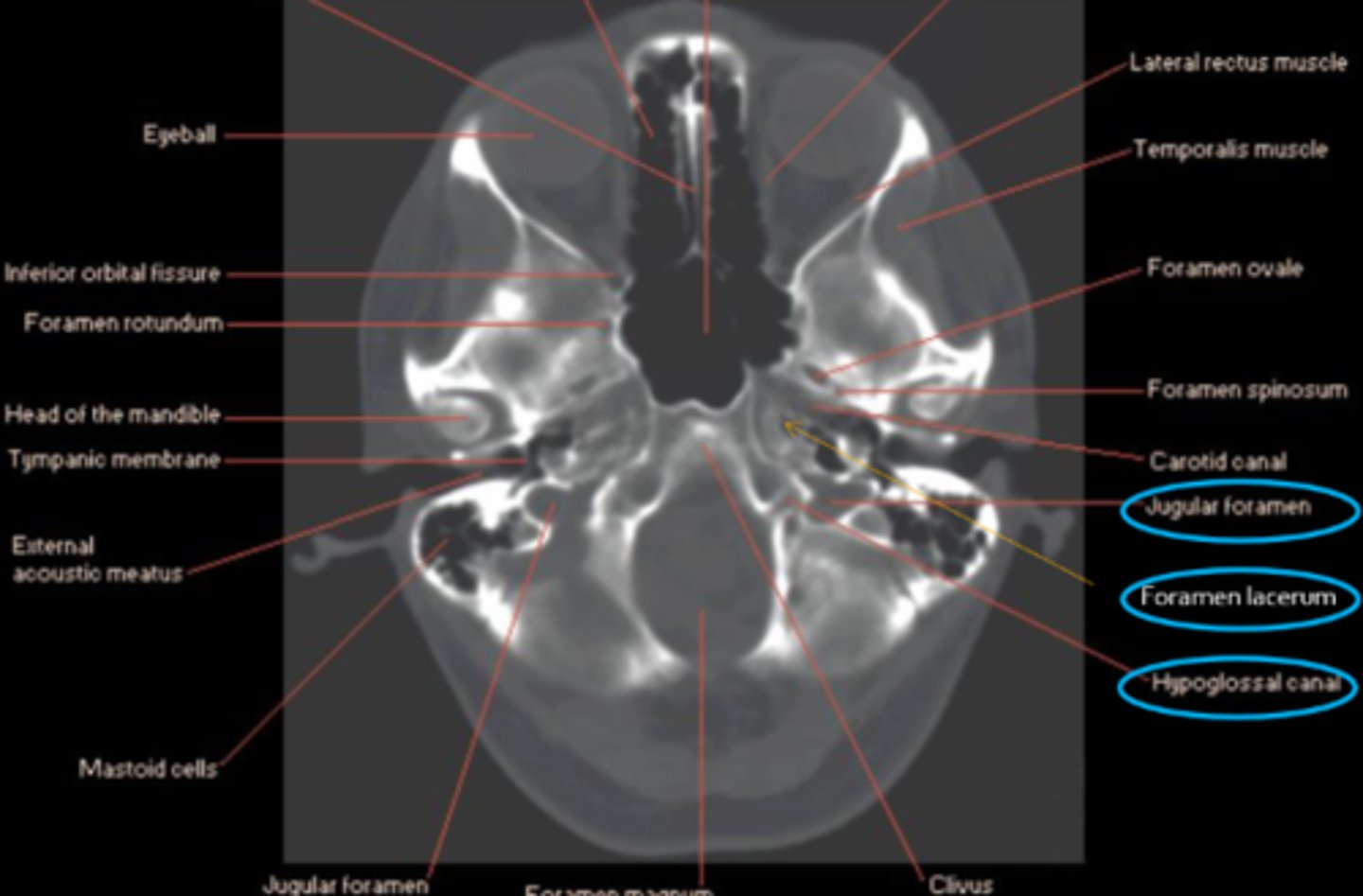
What 3 anatomical locations are targeted in Vernet's syndrome?
jugular foramen = CN IX, X, XI
foramen lacerum = ICA, symp fibers
hypoglossal canal = CN XII
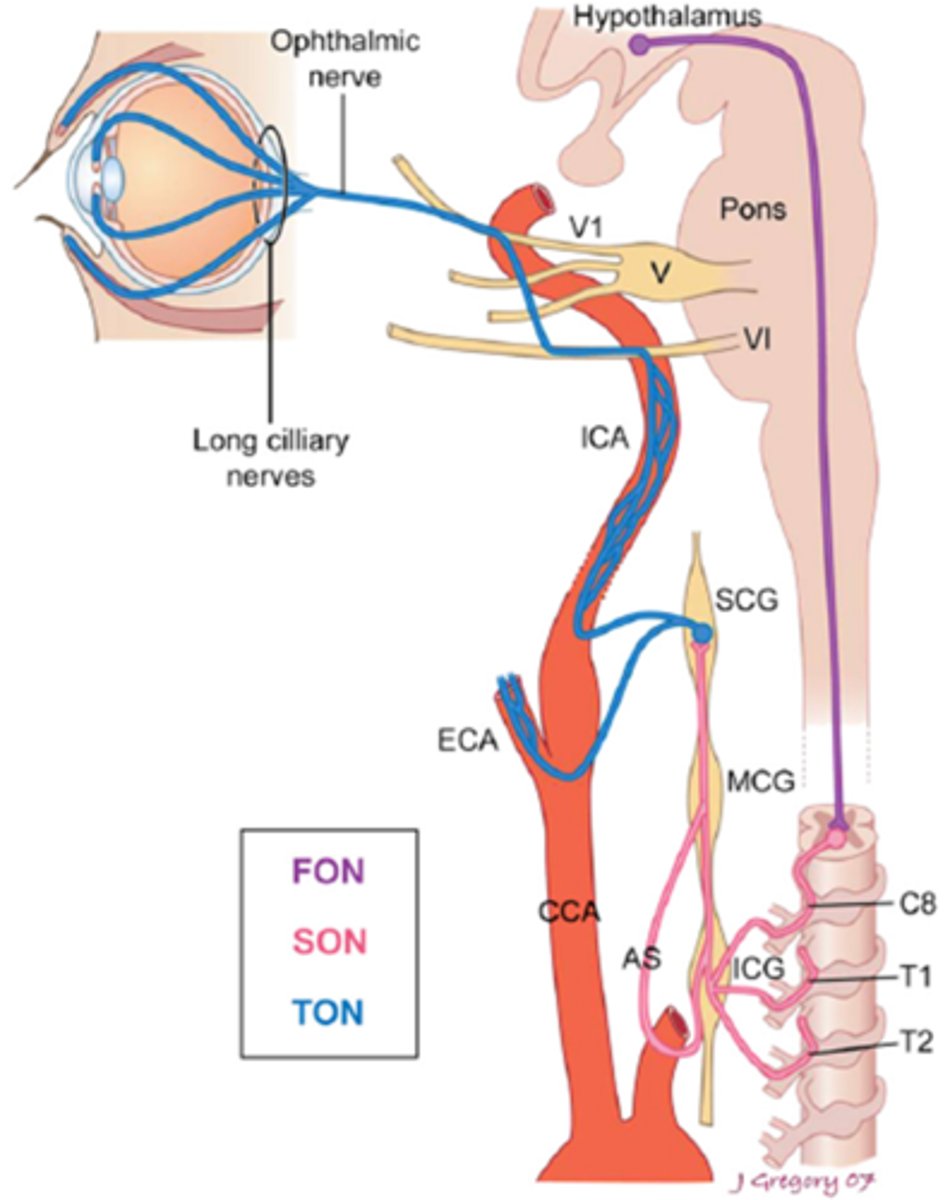
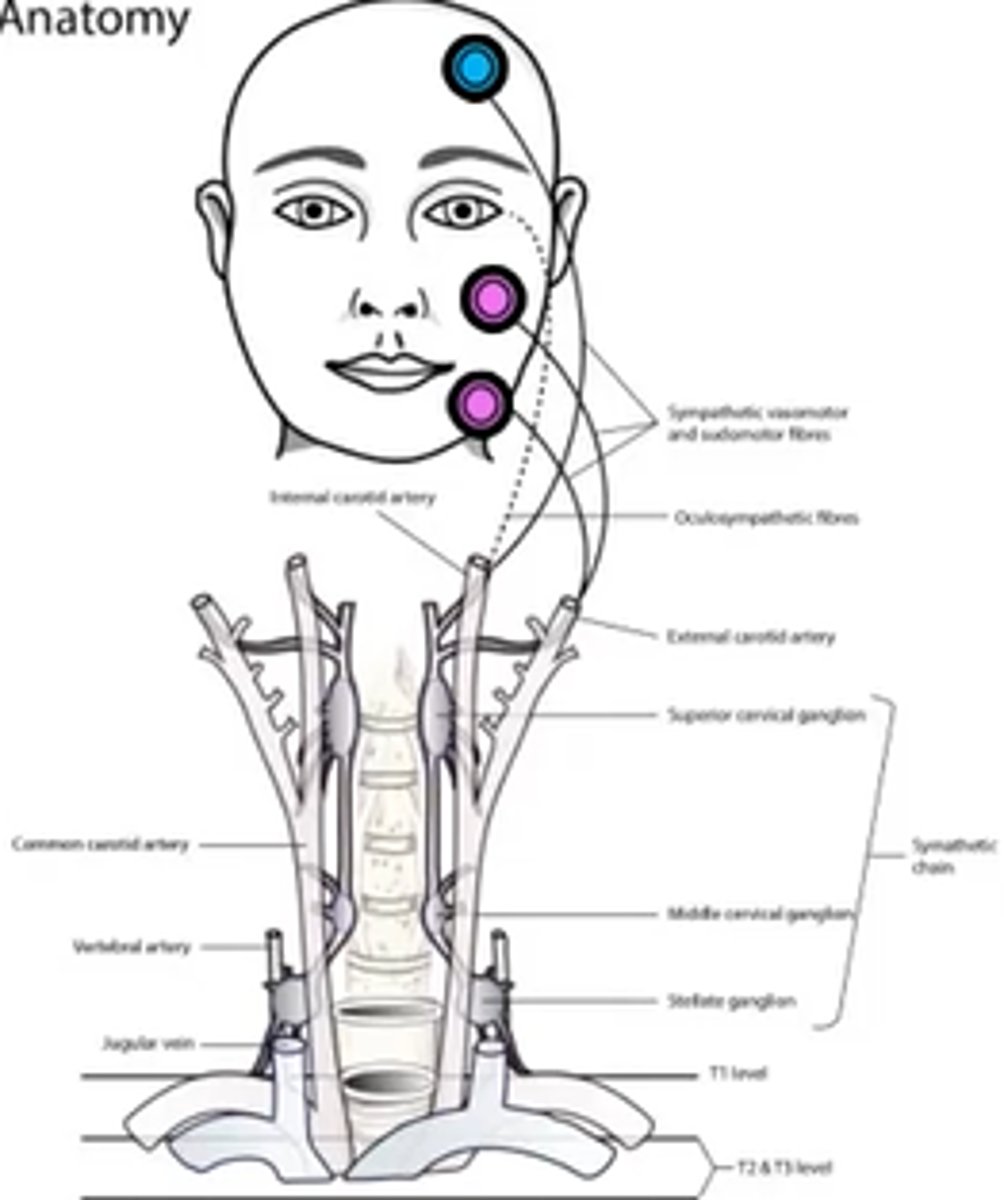
Overall, what types of conditions/lesions could cause a central / 1st neuron Horner's syndrome, as seen in purple here?
brainstem glioma
syringoma
spinal cord tumor
Wallenberg's
THINK: brain and spinal cord
Overall, what types of conditions/lesions could cause a pre-ganlgionic / 2nd neuron Horner's syndrome, as seen in pink here?
cervical trauma/arthritis
polio
neural crest tumors
pneumothorax
lung tumor
cervical rib injuries
intrathoracic anuerysm
neck neoplasm (thyroid etc)
THINK: neck and chest
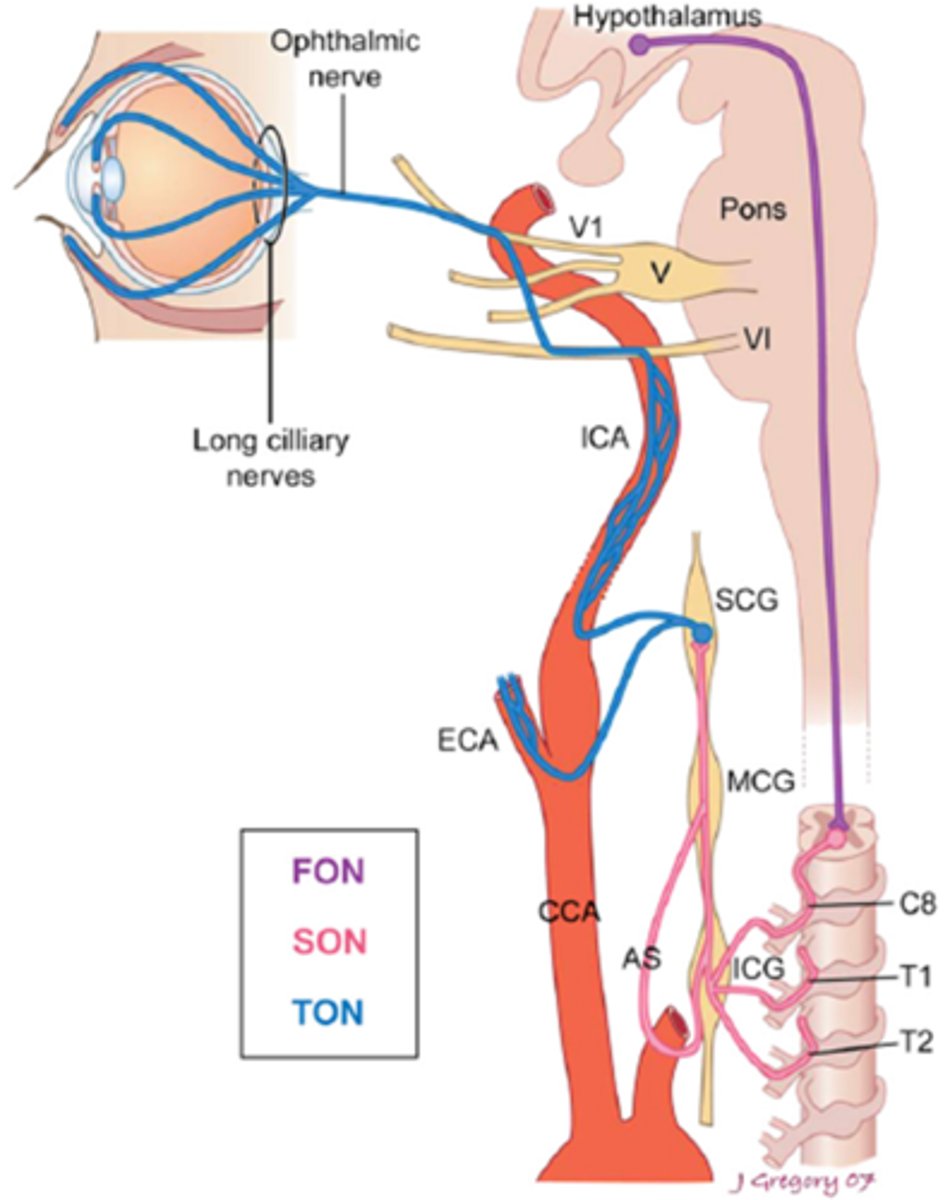
Overall, what types of conditions/lesions could cause a post-ganlgionic / 3rd neuron Horner's syndrome, as seen in blue here?
cluster HA
nasopharyngeal tumors
otitis media
ICA
cavernous sinus
THINK: head and neck
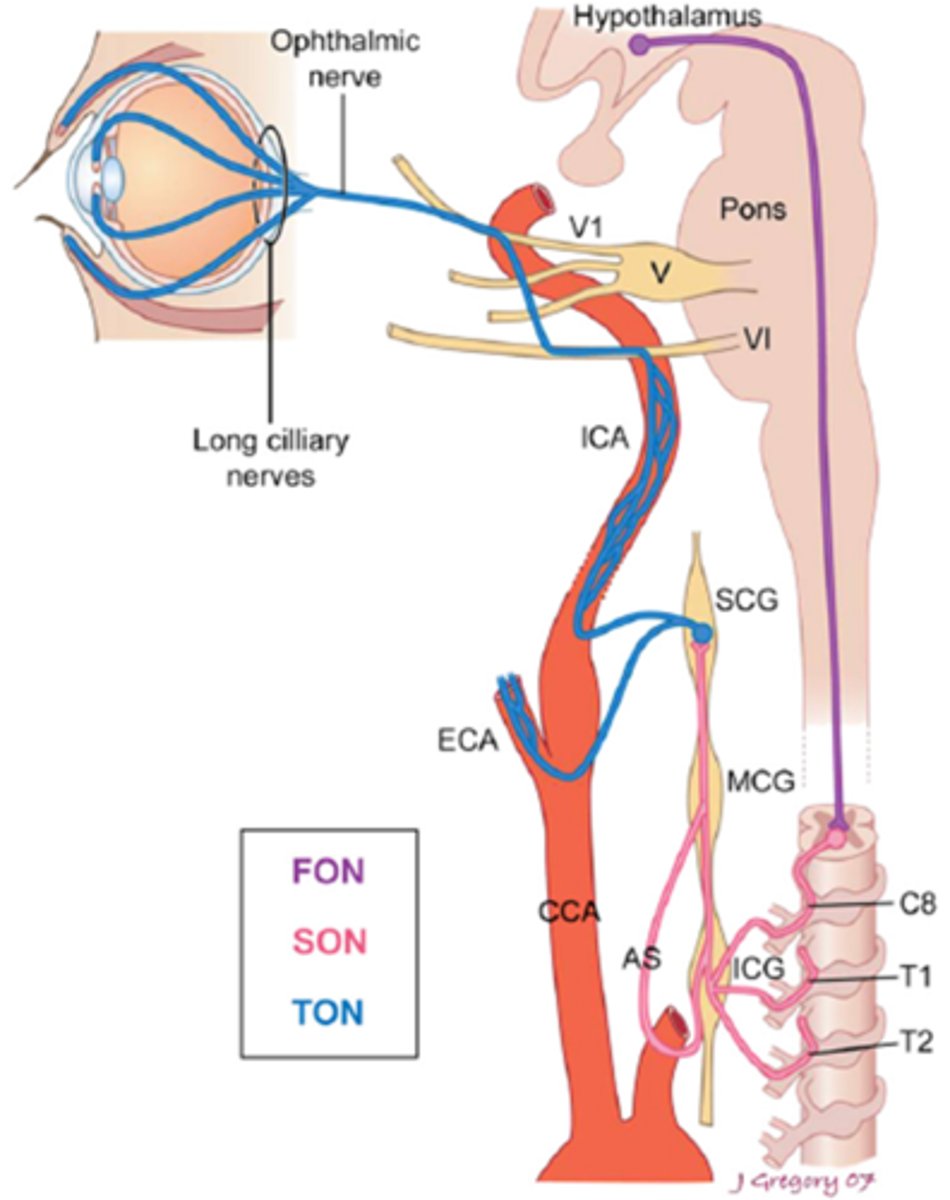
What is the most common cause of a Horner's syndrome in pt's ages birth to 20 years old?
trauma
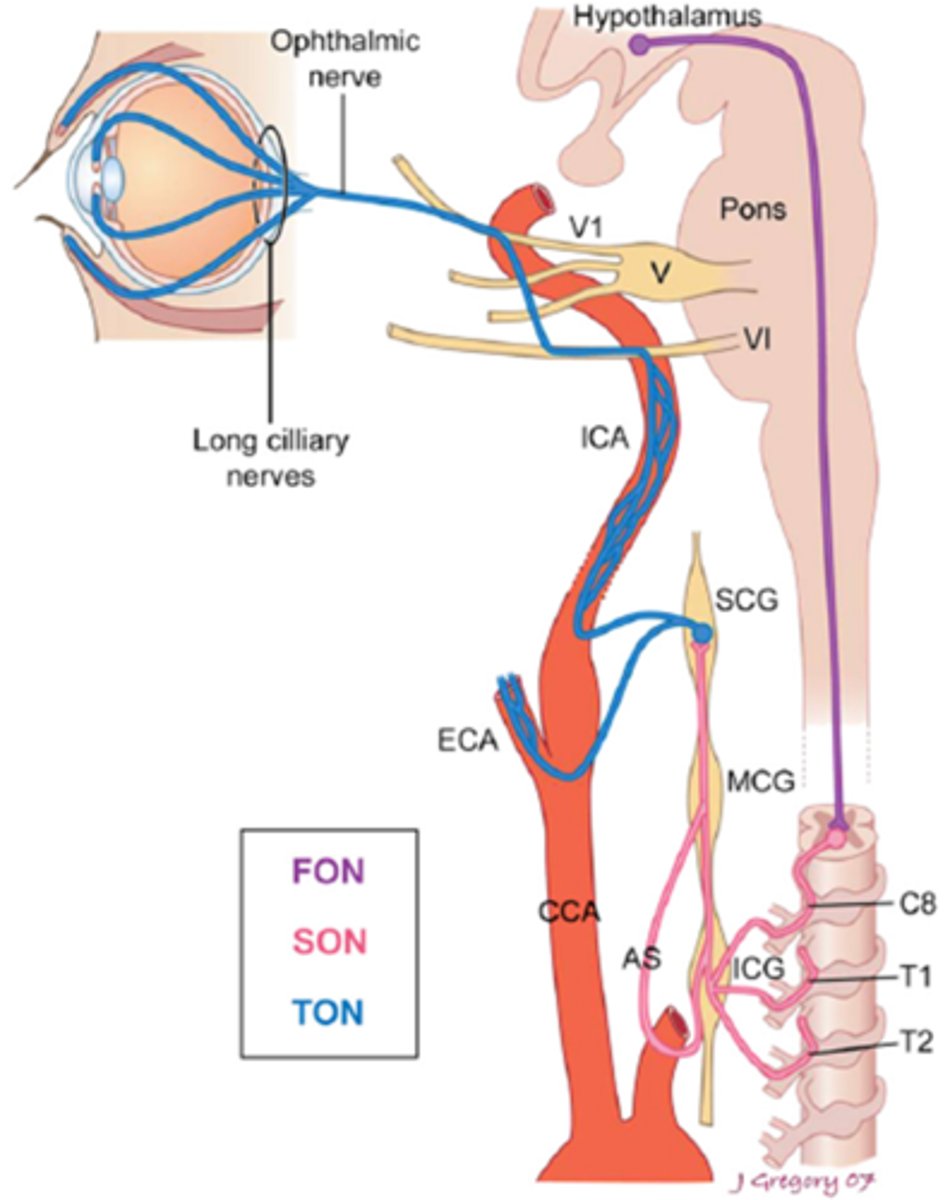
What is the most common cause of a Horner's syndrome in pt's ages 30 to 50 years old?
neoplasm
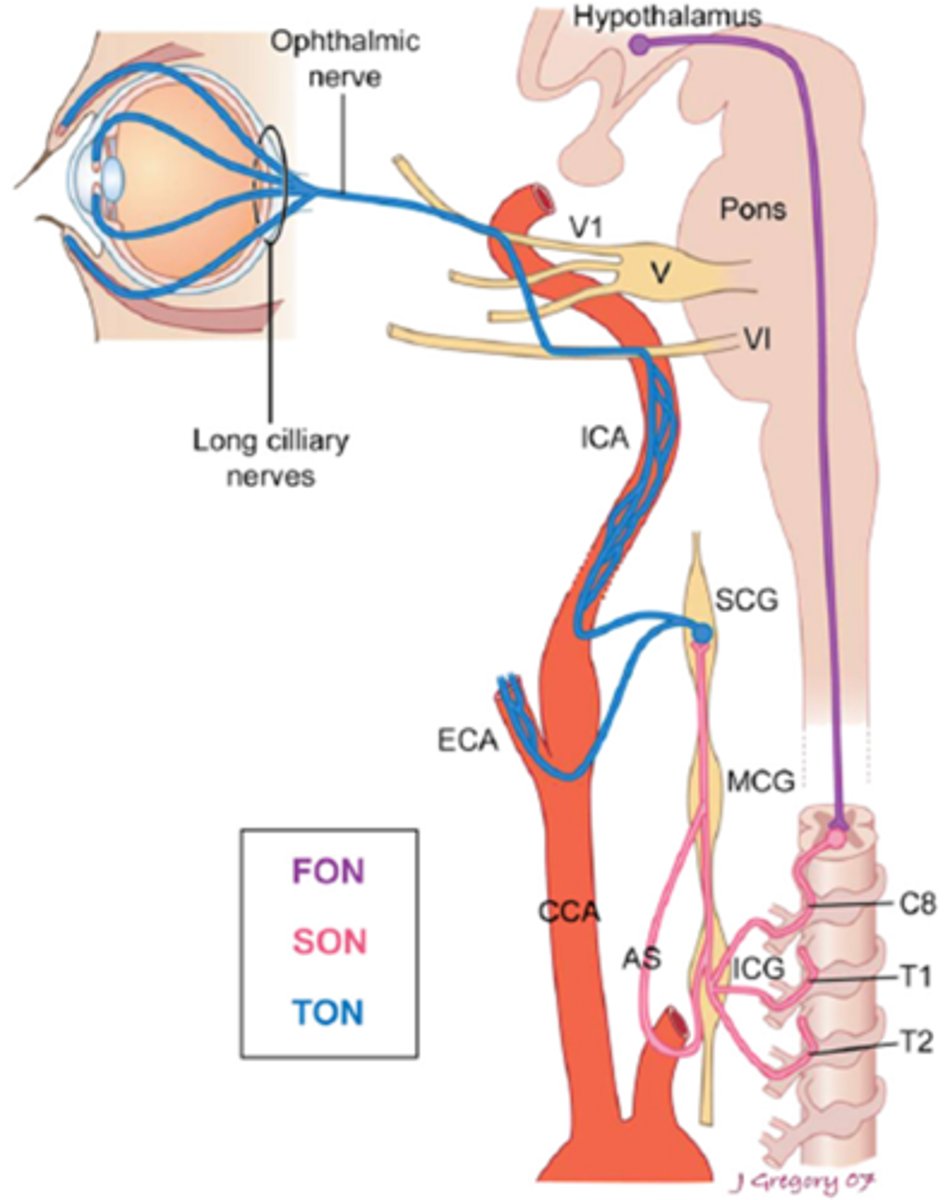
What is the most common cause of a Horner's syndrome in pt's ages 50+ years old?
malignant neoplasm
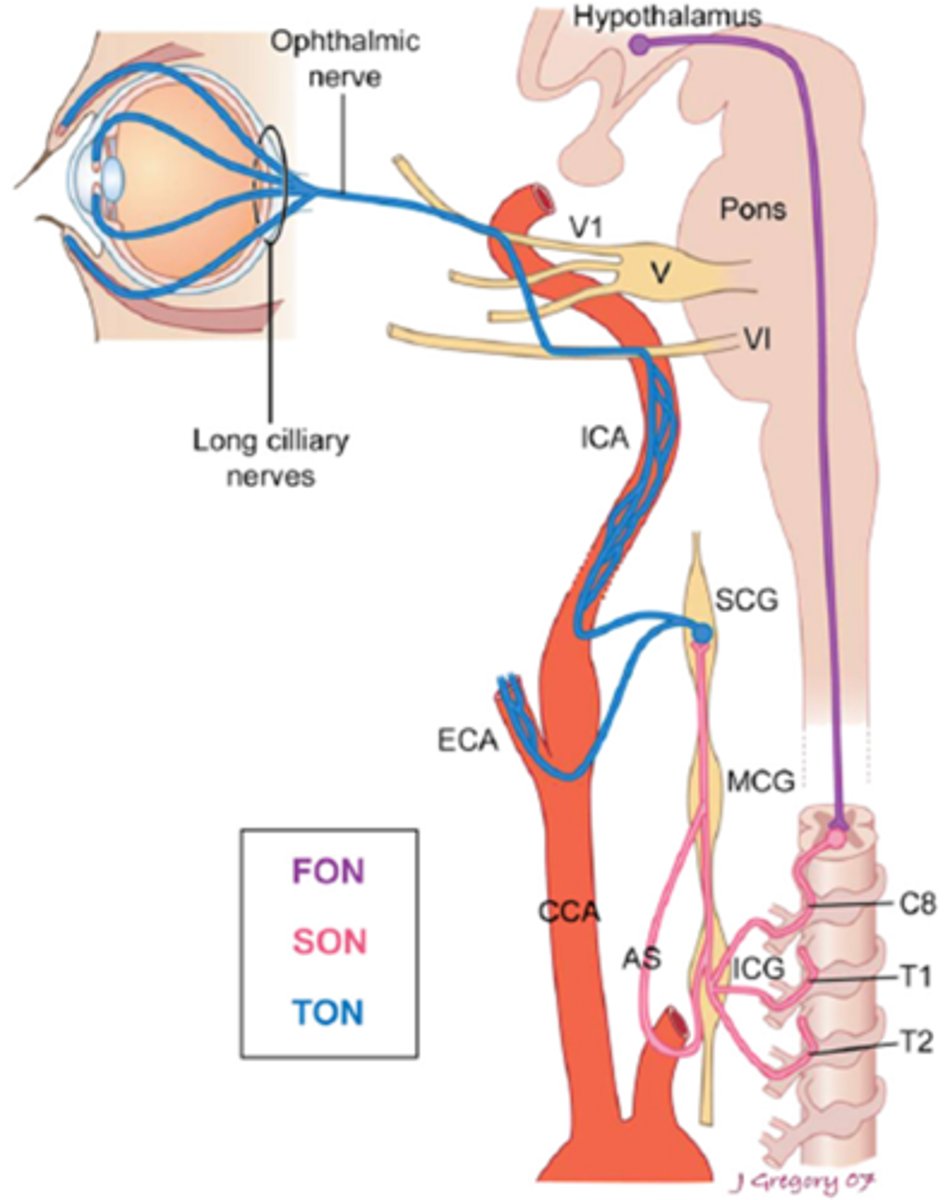
What is the most common cause of a Horner's syndrome in the chest or neck (esp if quiet/painless)?
neoplasm
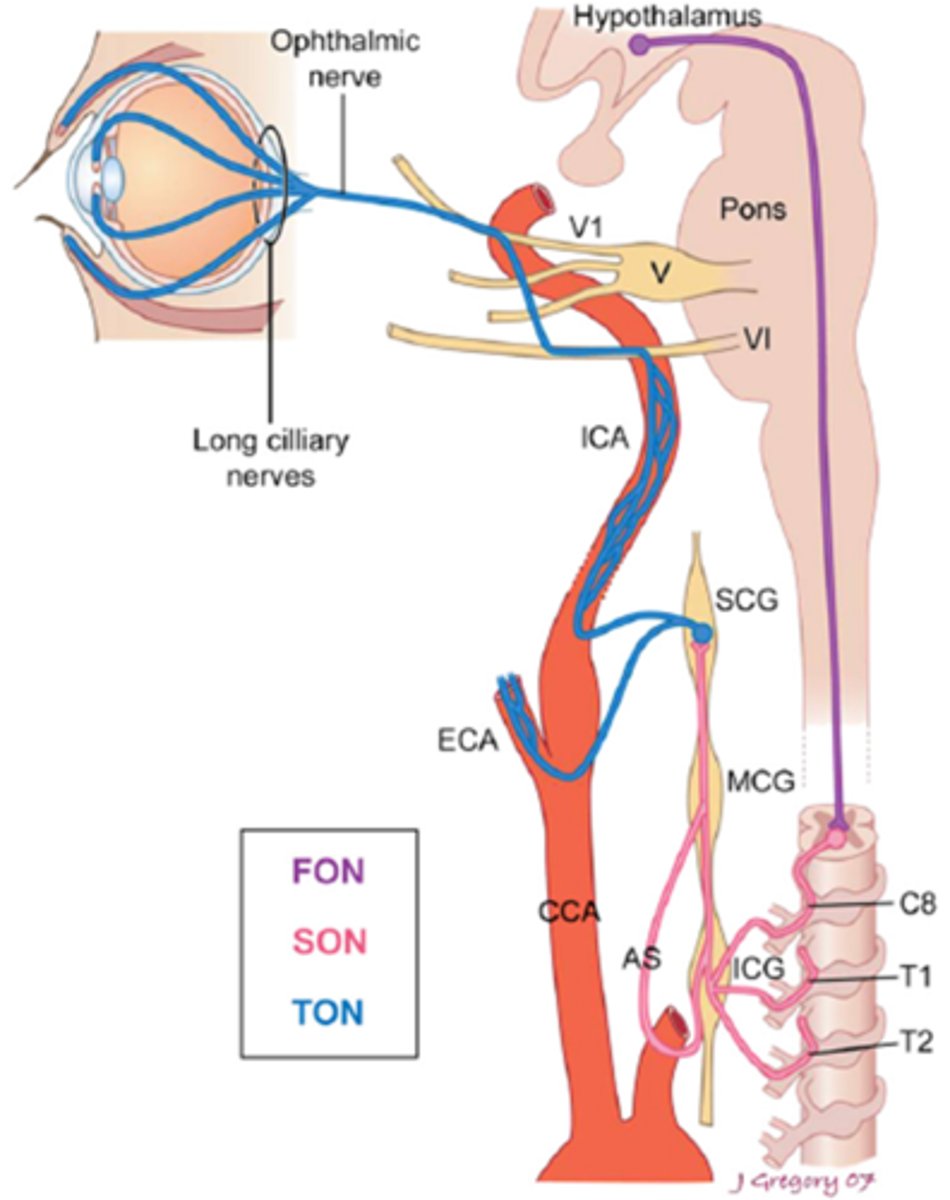
What is the most common cause of a Horner's syndrome in the anterior spinal root?
trauma
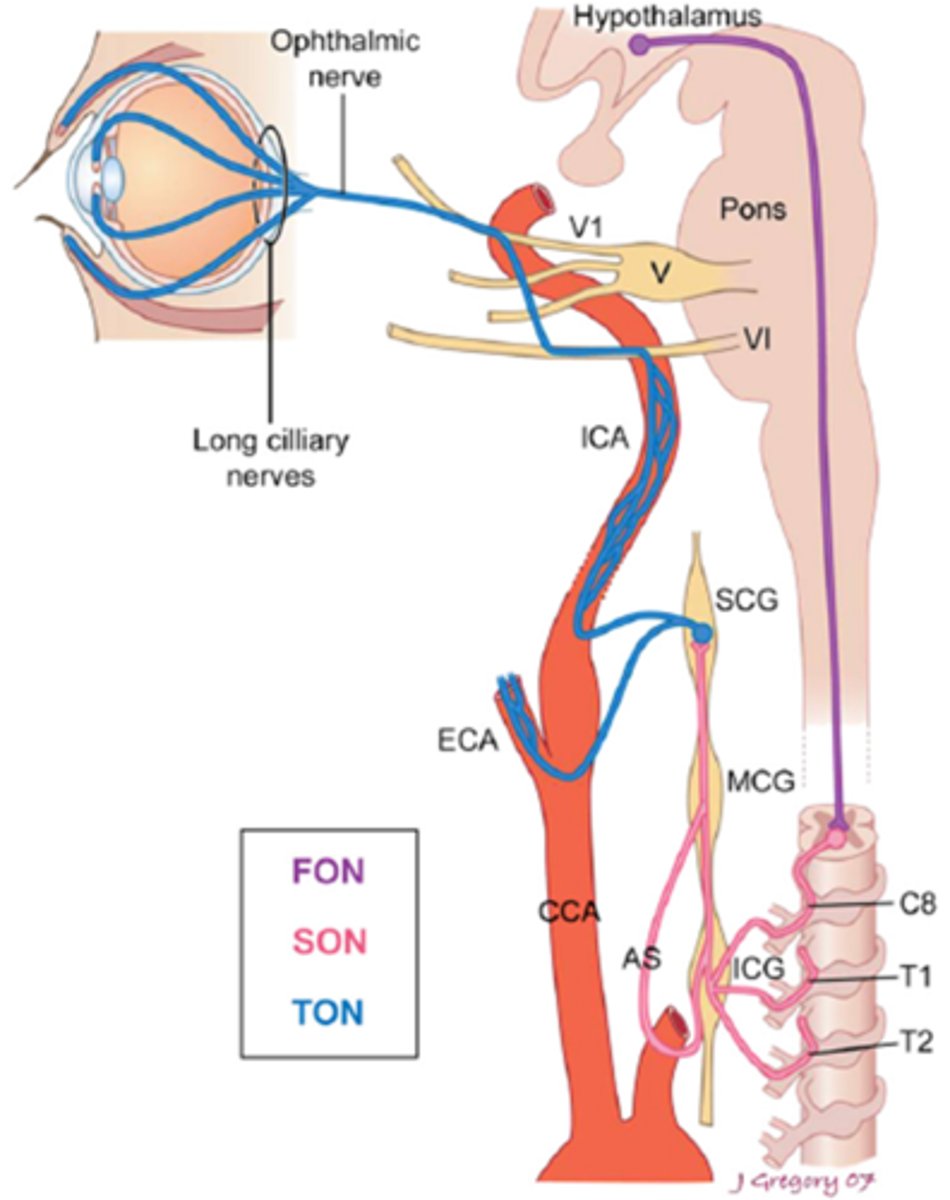
What is the most common cause of a Horner's syndrome in the brainstem?
vascular disease
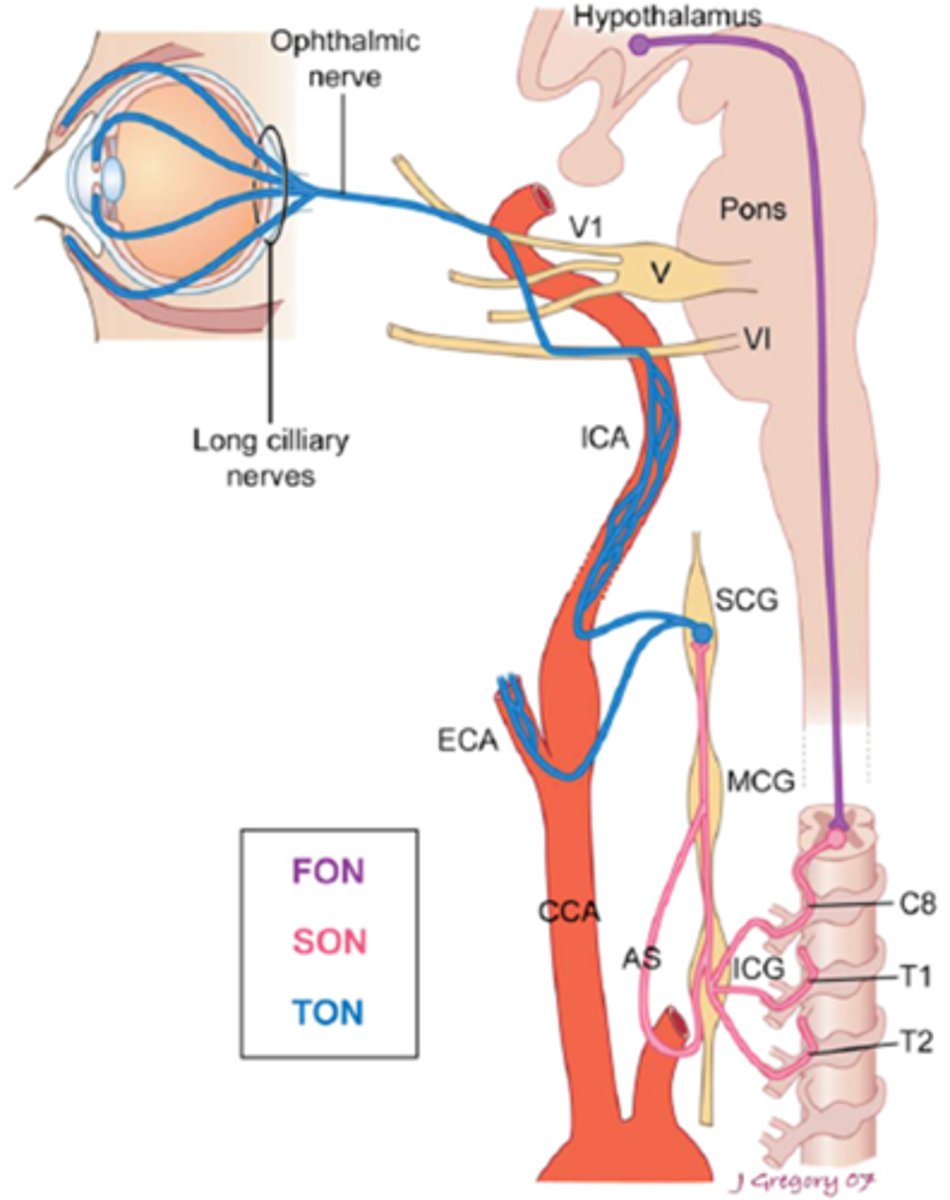
What is the most common cause of a Horner's syndrome in the head or upper neck (esp if painful)?
benign vascular HA
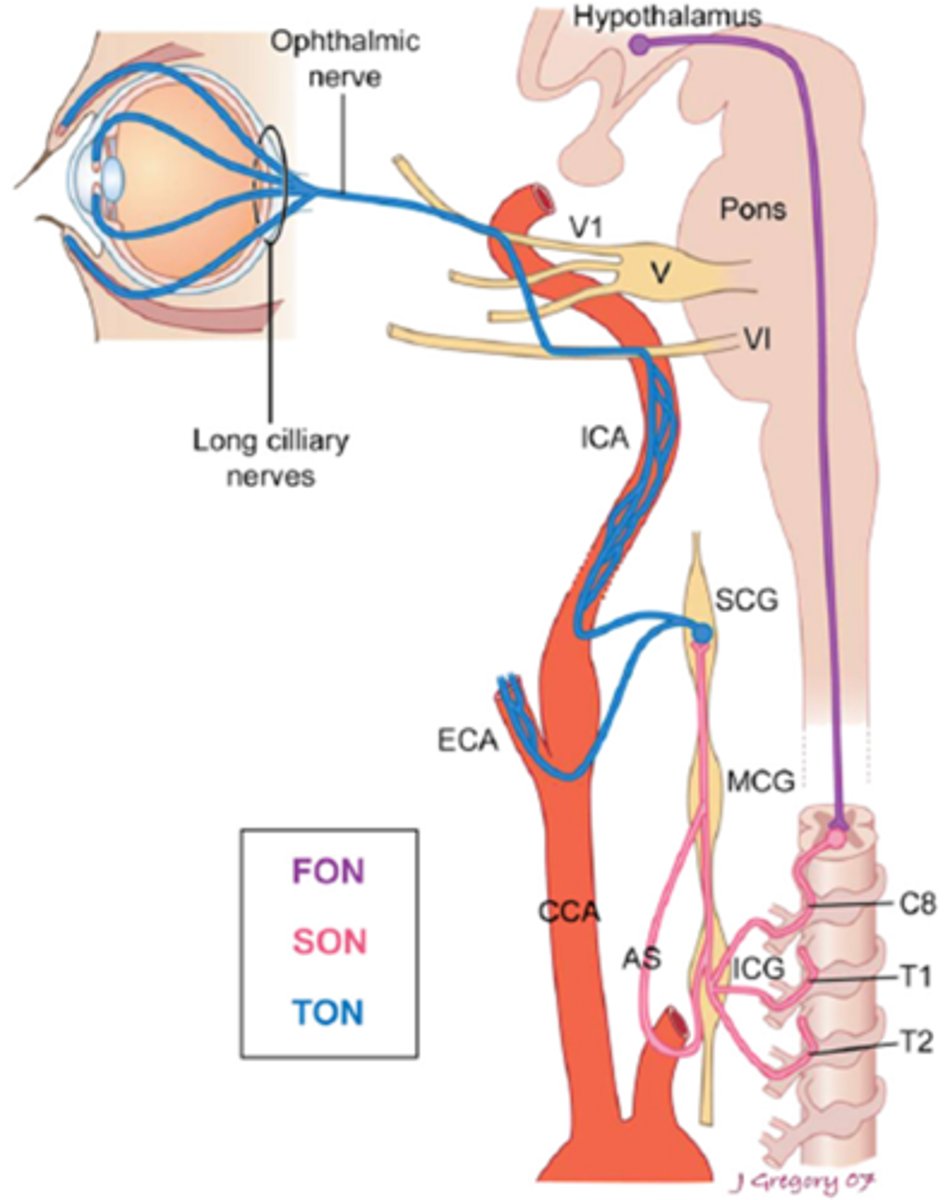
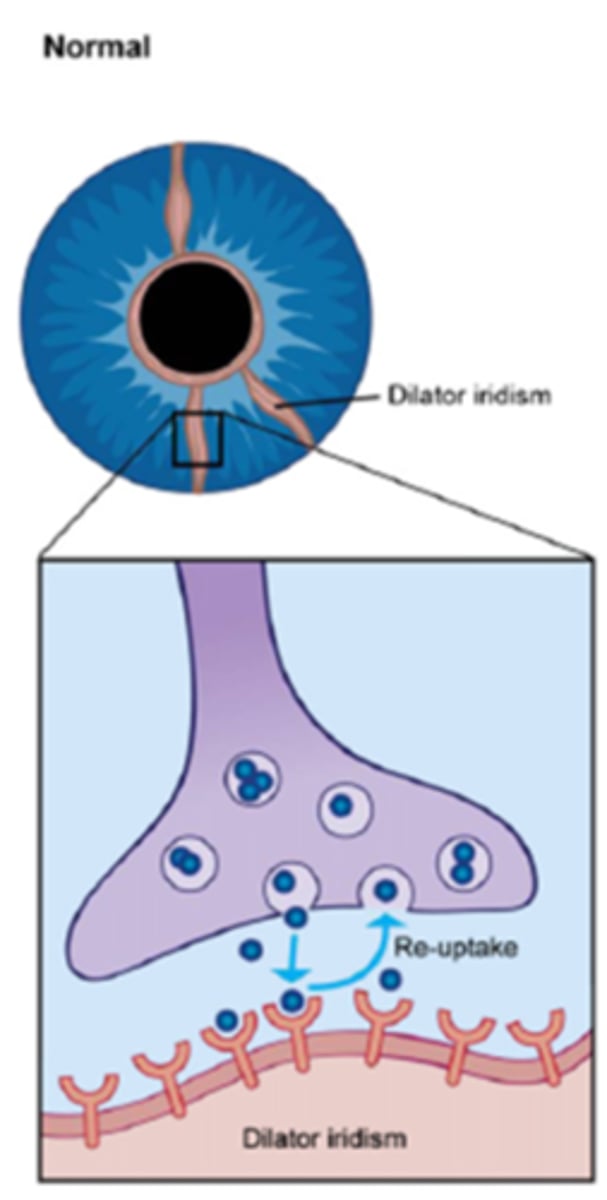
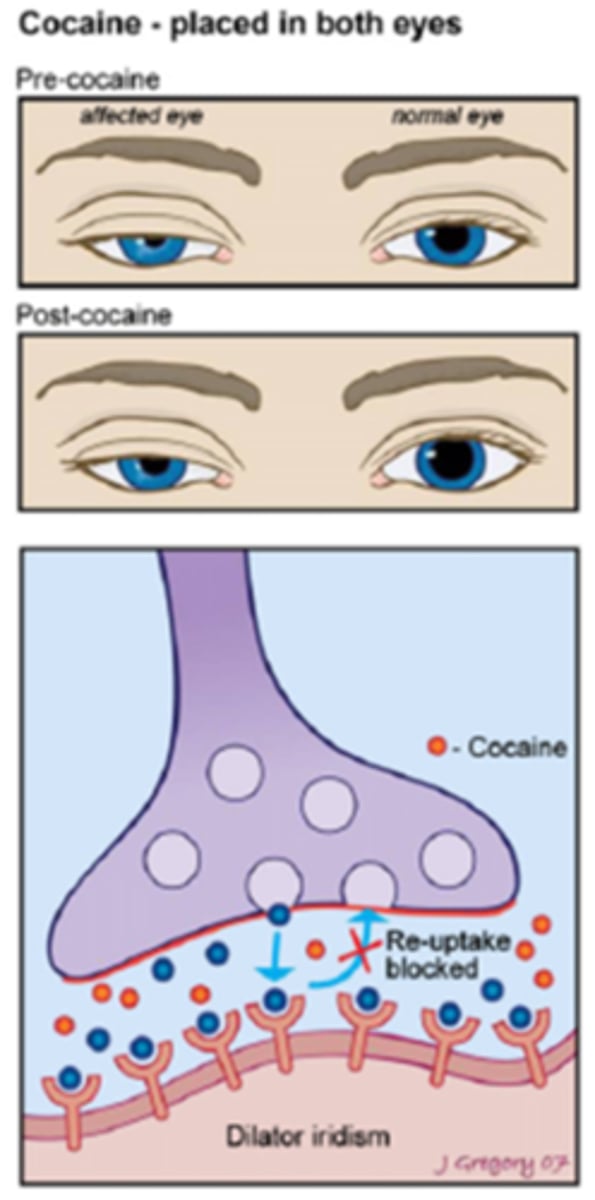
Explain the normal action potential in the nerve terminal at the iris dilator mm.
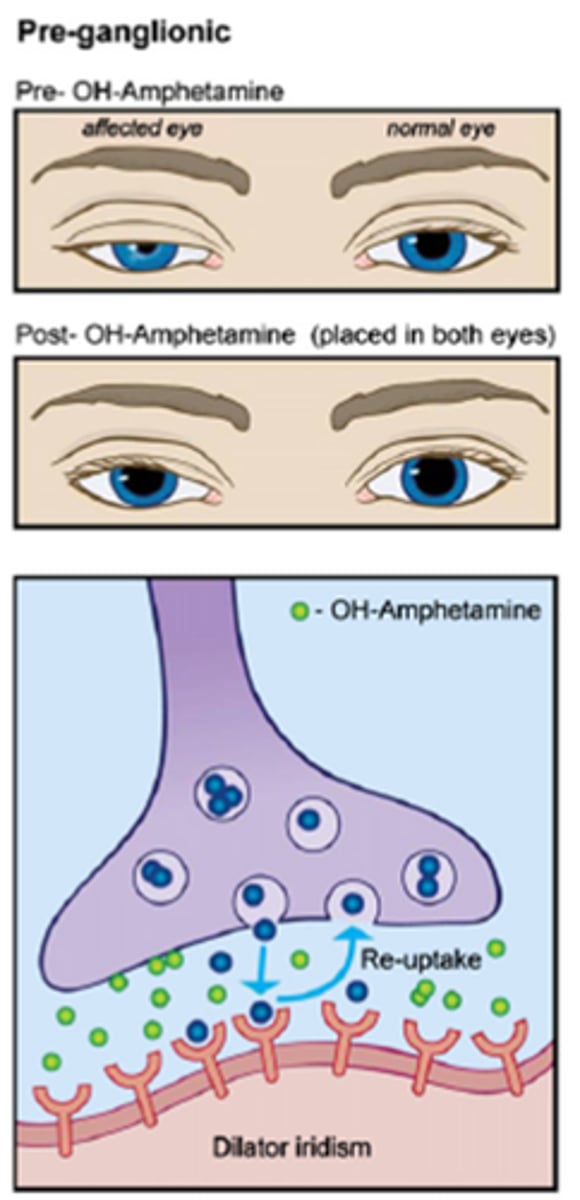
NE released into NMJ = NE binds to receptors sites = NE then moved away by bloodstream, enzymatically broken down, re-uptake into pre-synaptic terminal
What drop can we use to more definitively diagnose a Horner's syndrome?
cocaine 10% is used in the supersensitivity test
Recall: what is the general MOA/drug class of cocaine?
indirect symp agonist
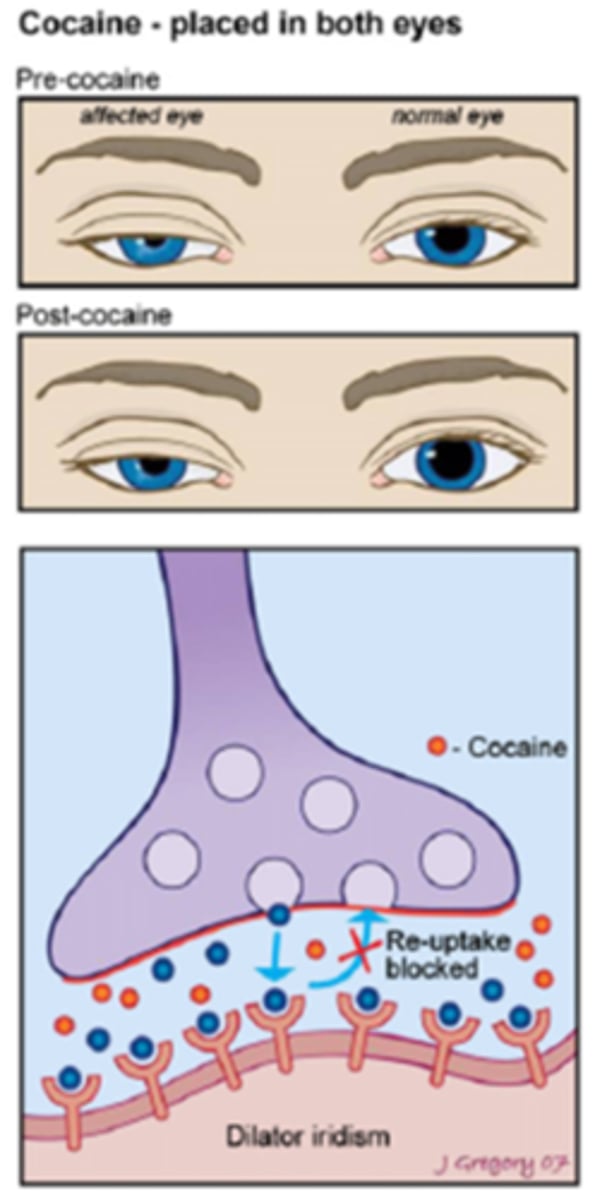
How does cocaine alter the response in a normal eye?
indirect symp agonist = NE remains pooled at the NMJ = increased symp stimulation = pupil dilates
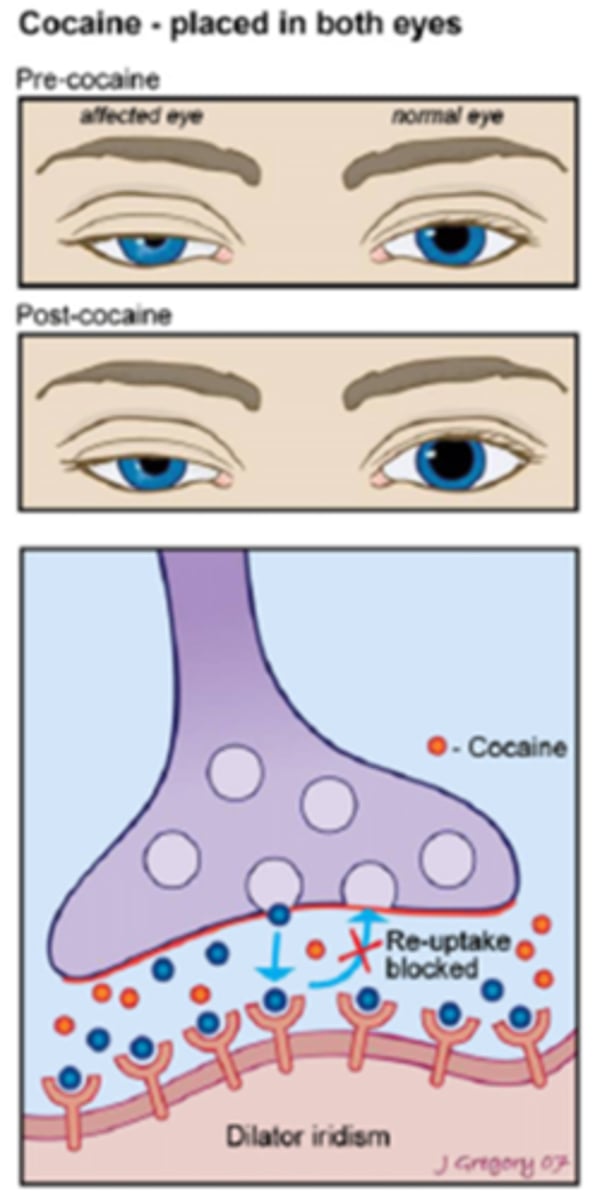
How does cocaine alter the response in a Horner's syndrome eye?
no nerve impulse = no NE is present in the NMJ = so cocaine has very little effect = pupil does NOT dilate
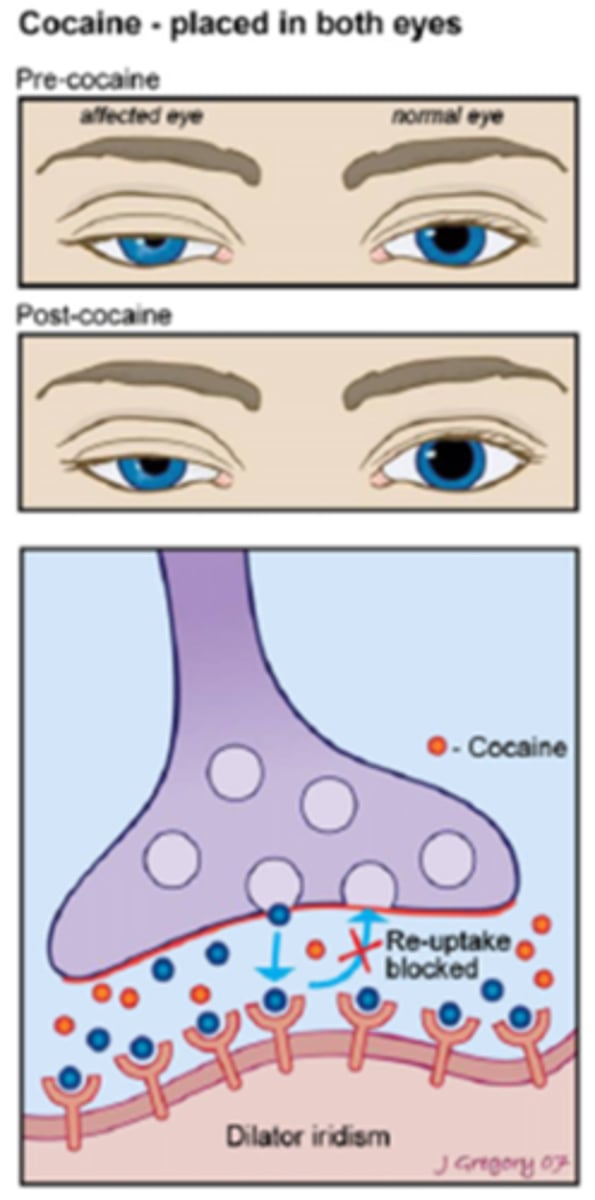
Explain how the cocaine test works in this pt who presented for OD Horner's syndrome.
before cocaine OU = anisocoria greater in dim illumination, OD reverse ptosis
after cocaine OU = normal OS dilates, abnormal OD remains the same size = anisocoria change >1mm present = positive test
What are some drawbacks of the cocaine test?
hard to obtain cocaine bc of scheduling status
inhibits hydroxyamphetamine reuptake so cannot conduct this test later
may remain in urine up to 2 days after in drug tests
if symp nerve pathway damaged fron trauma then the test is less sensitive
dark irises may have a slower response and up to 3 hours before interpreting
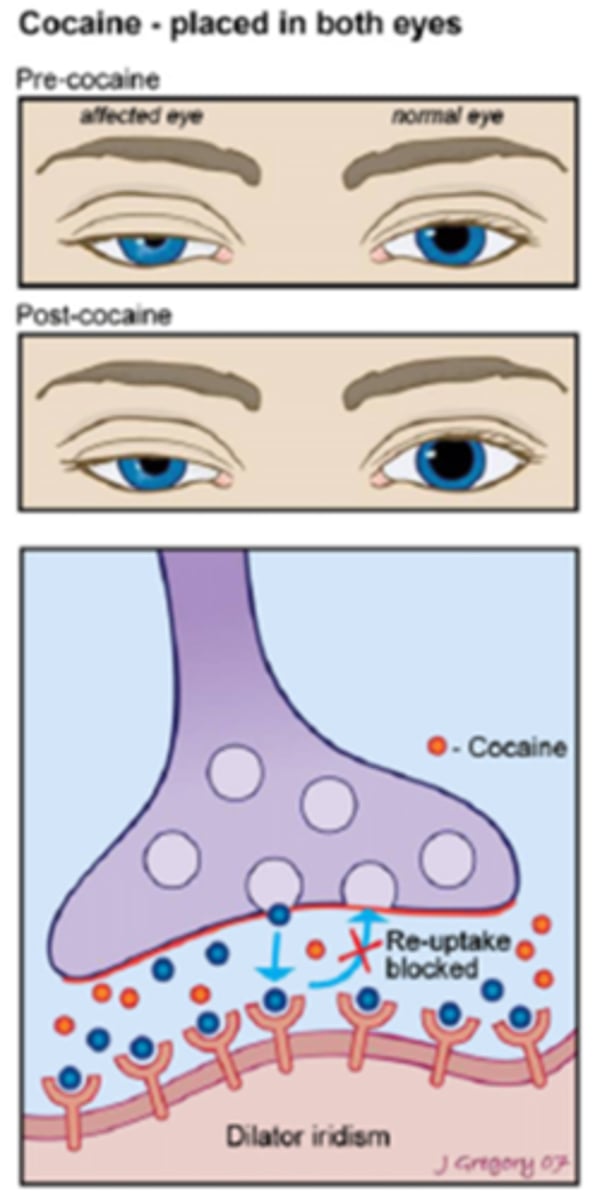
Overall, a normal pupil will ___________ in response to cocaine.
dilate
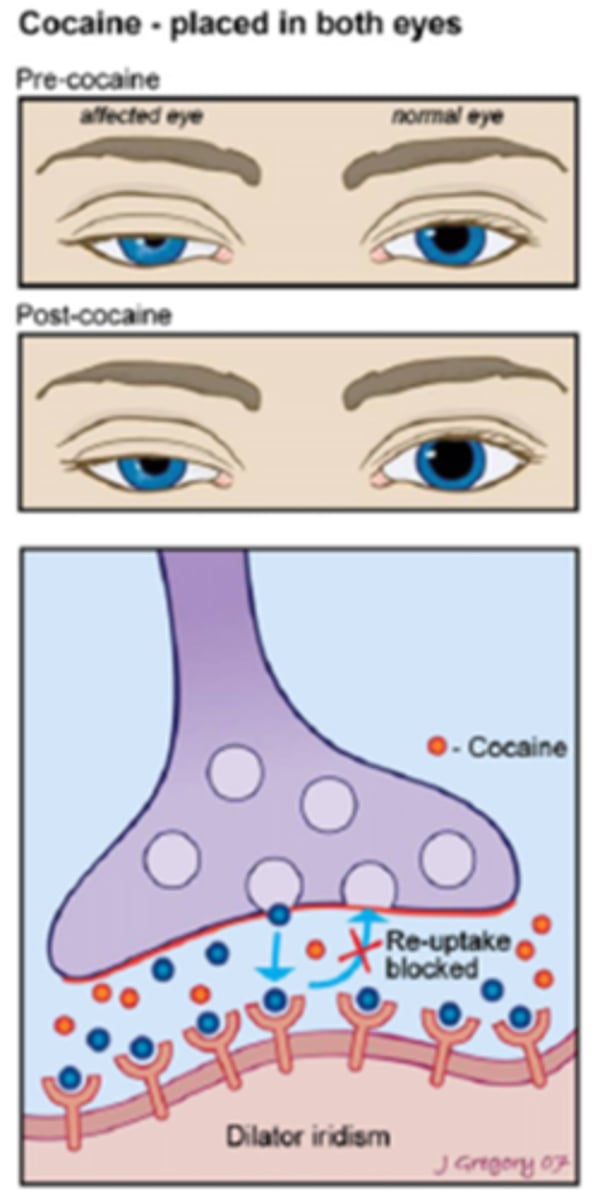
Overall, a Horner's pupil will ___________ in response to cocaine.
NOT dilate
What drop can be used as an alternative to cocaine to more definitively diagnose a Horner's syndrome?
apraclonidine 1%
Recall: what is the general MOA/drug class of apraclonidine?
direct alpha agonist
THINK: will have the opposite effect of cocaine
How does apraclonidine alter the response in a normal eye?
no symp denervation = normal amount of alpha receptors = apraclonidine has it's normal weaker effect on iris dilator mm = minimal dilation if any
How does apraclonidine alter the response in a Horner's syndrome eye?
symp denervation = upregulation of alpha receptors = apraclonidine has a stronger effect on iris dilator mm = pupil dilates
Overall, a normal eye will ___________ in response to apraclonidine.
NOT dilate or minimally dilate
Overall, a Horner's eye will ___________ in response to apraclonidine.
dilate
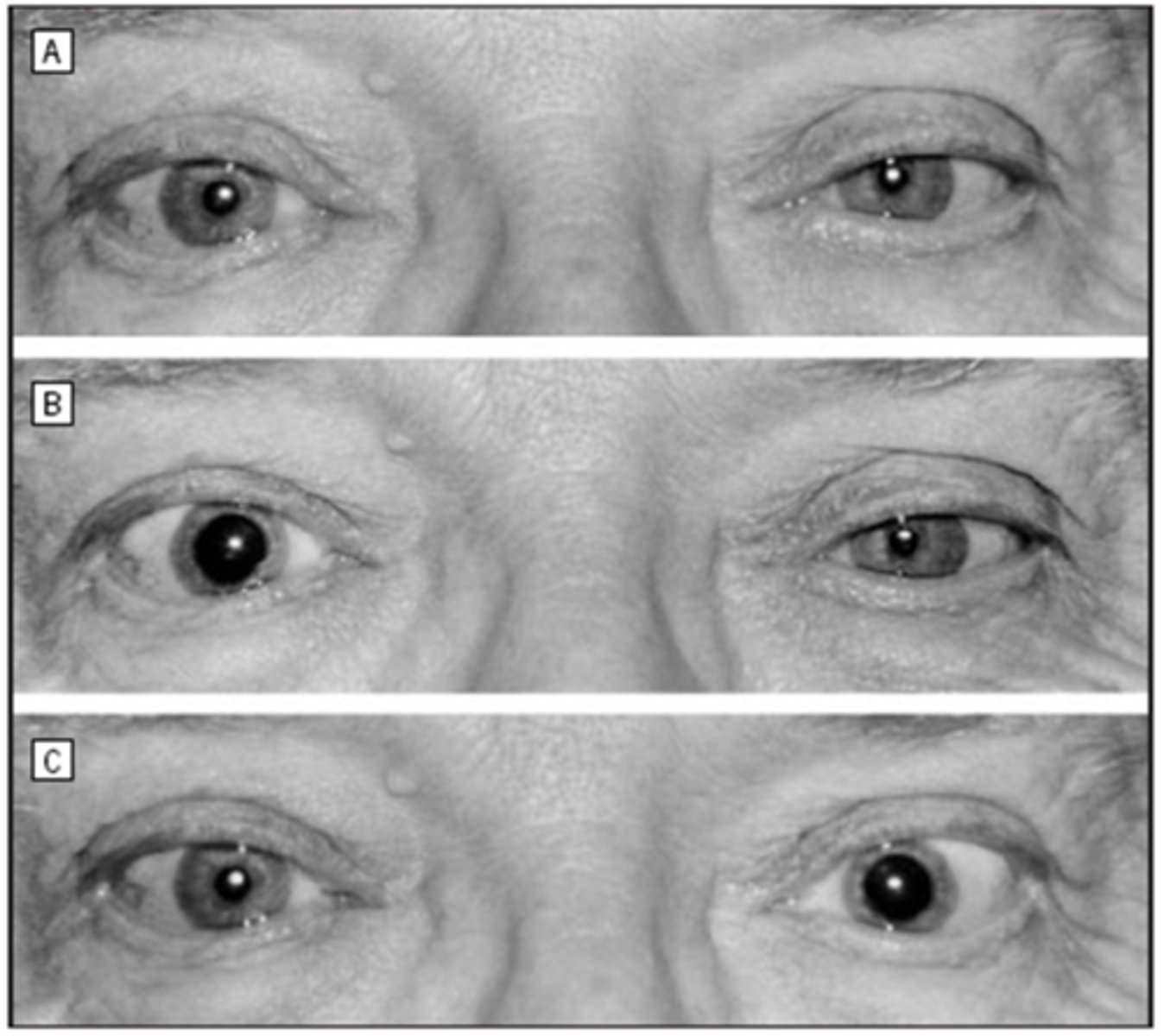
Explain how the cocaine test and apraclonidine test works in this pt who presented for OS Horner's syndrome.
before drops OU = anisocoria greater in dim illumination, OS ptosis
after cocaine OU = normal OD dilates, abnormal OS remains the same size
after apraclonidine OU = normal OD does not dilate, abnormal OS dilates = reversal of anisocoria = positive test
What drop can be used to localize a Horner's syndrome?
hydroxyamphetamine 1%

Recall: what is the general MOA/drug class of hydroxyamphetamine?
indirect symp agonist

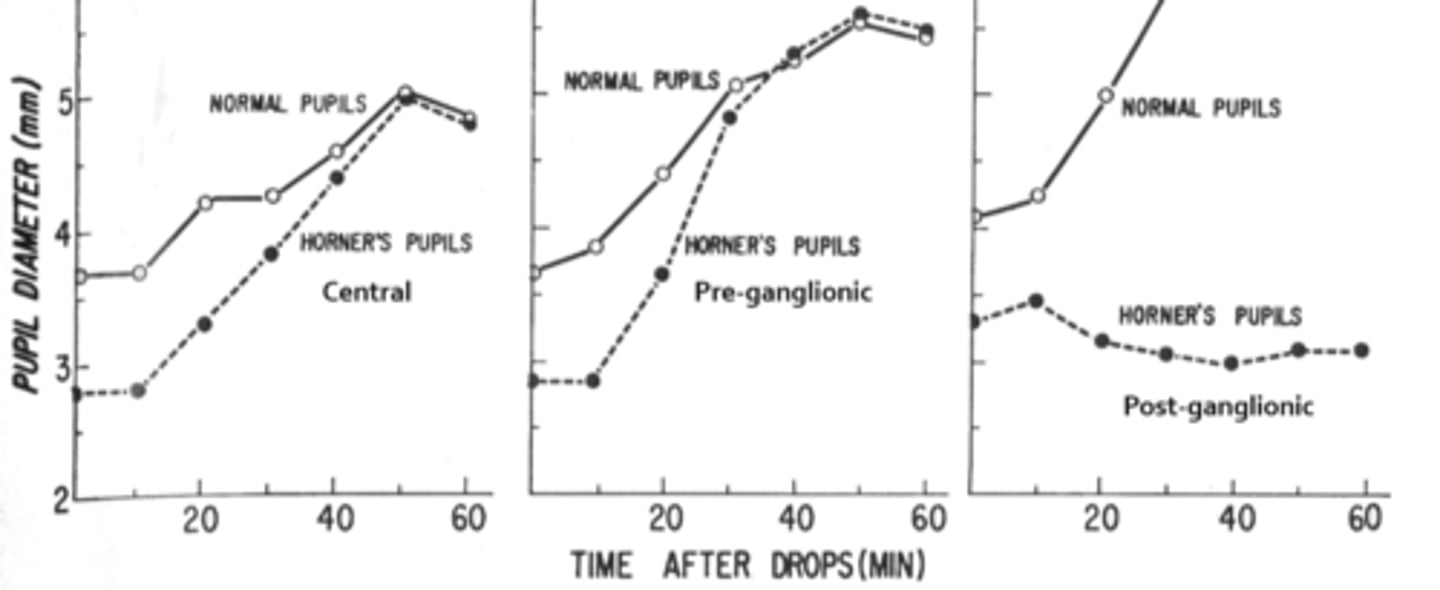
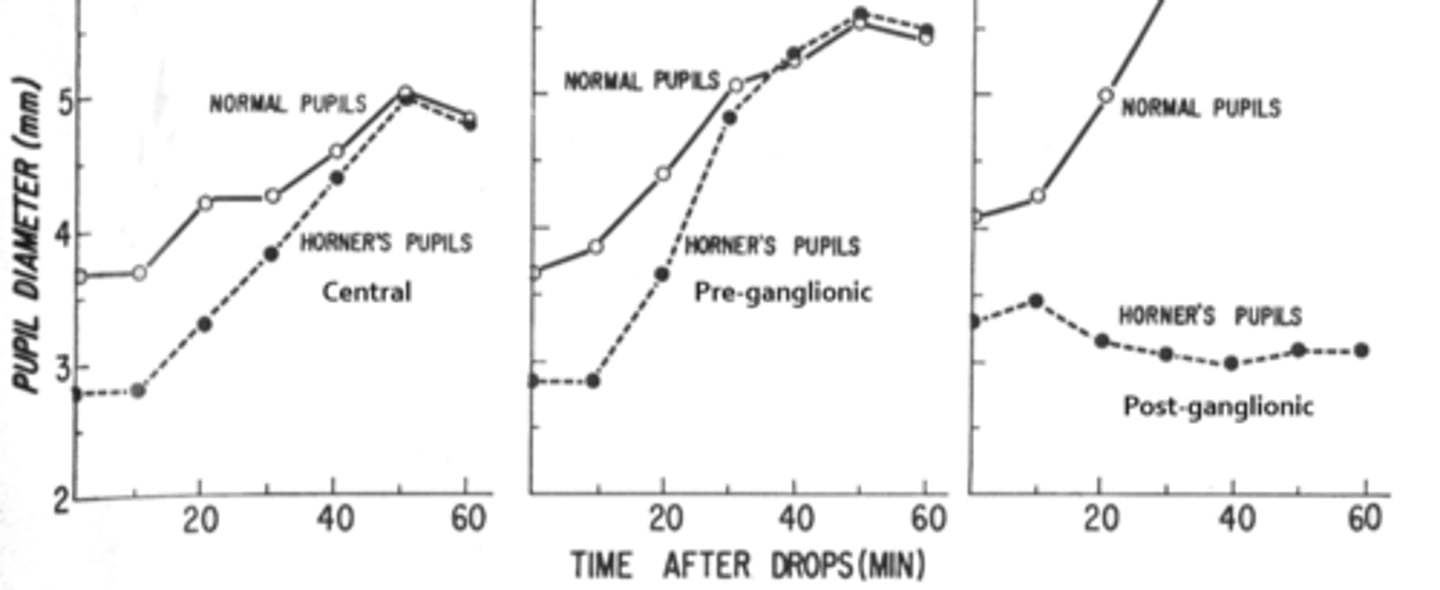
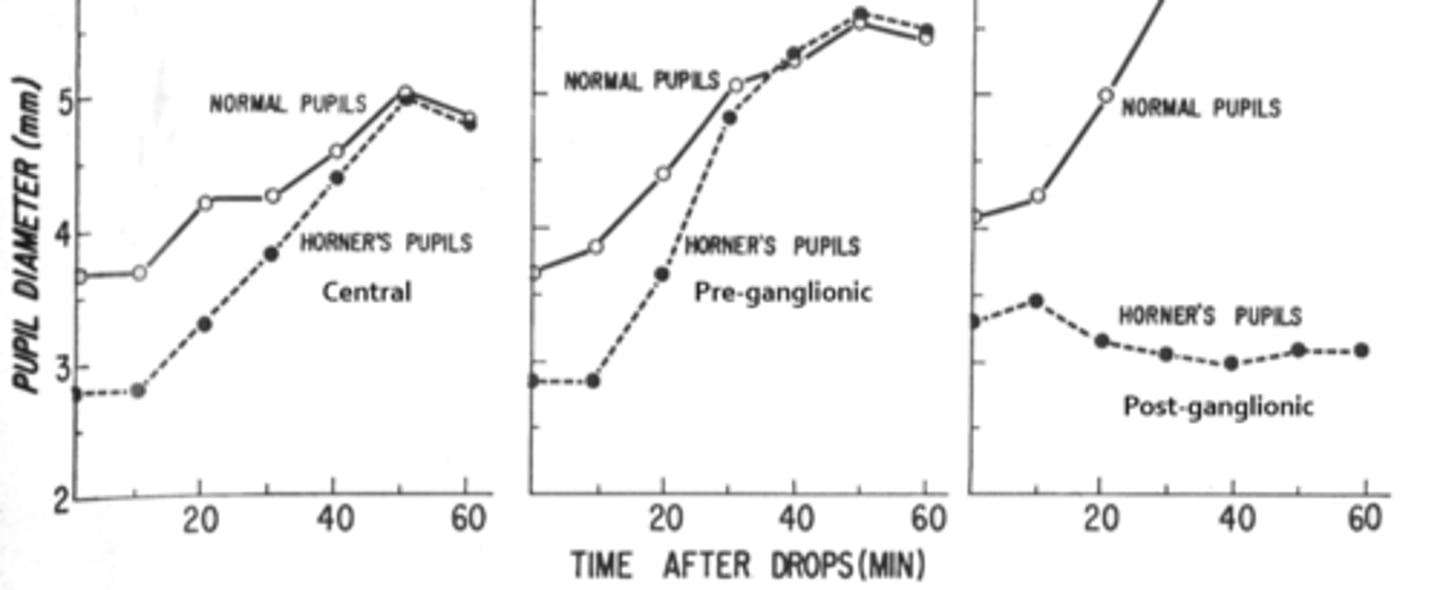
Overall, how does hydroxyamphetamine differentiate between a pre and post sup cervical ganglion Horner's?
post-superior cervical ganglion Horner's (3rd order neuron) = does NOT dilate
pre-superior cervical ganglion Horner's (2nd order neuron) = DOES dilate

How does a normal eye respond to hydroxyamphetamine?
healthy, normal eye = lots of NE = hydroxyamphetamine forces lots of NE into the NMJ = pupil dilates
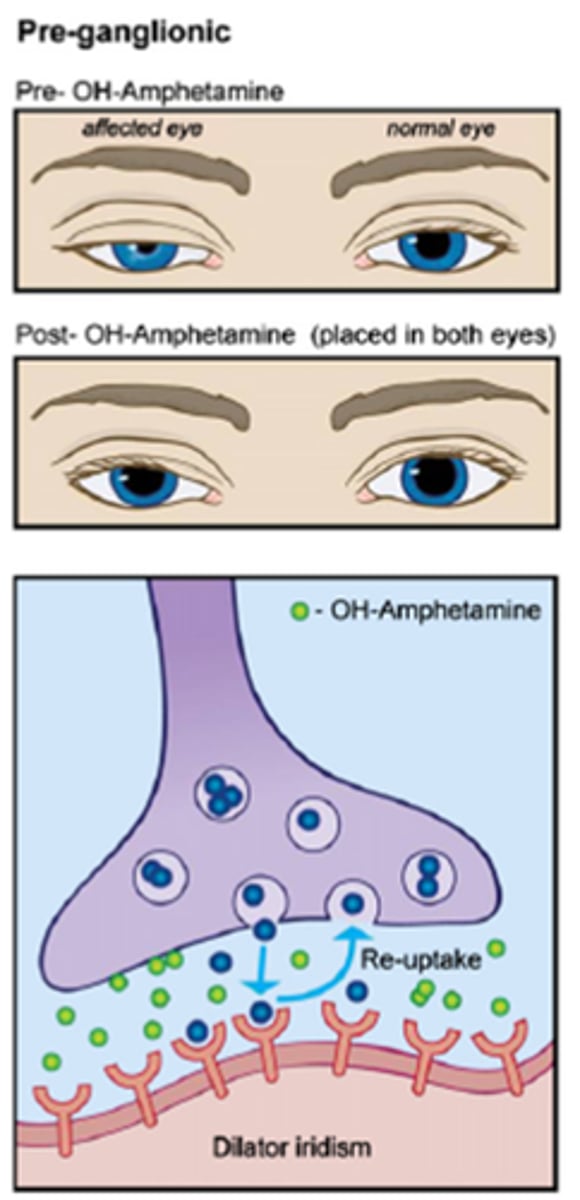
How does a pre-ganglionic (2nd neuron) Horner's eye respond to hydroxyamphetamine?
still lots of NE = hydroxyamphetamine forces lots of NE into the NMJ = pupil dilates
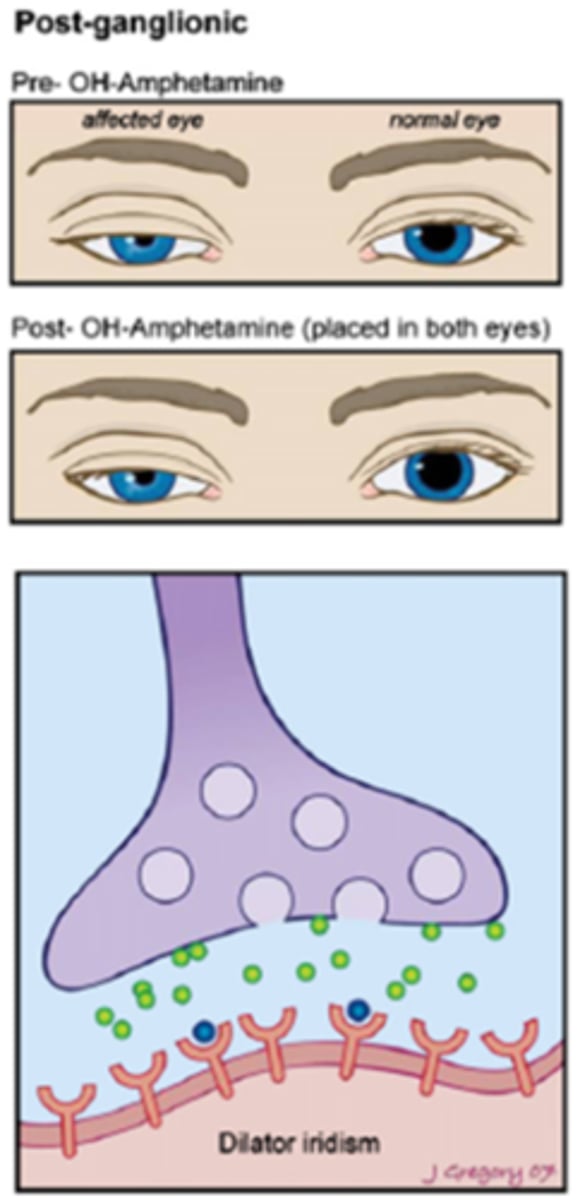
How does a post-ganglionic (3rd neuron) Horner's eye respond to hydroxyamphetamine?
very little NE = hydroxyamphetamine cannot force NE into the NMJ = pupil does NOT dilate
A normal pupil will _____________ to hydroxyamphetamine.
dilate
A central or pre-ganglionic Horner's pupil will _____________ to hydroxyamphetamine.
dilate
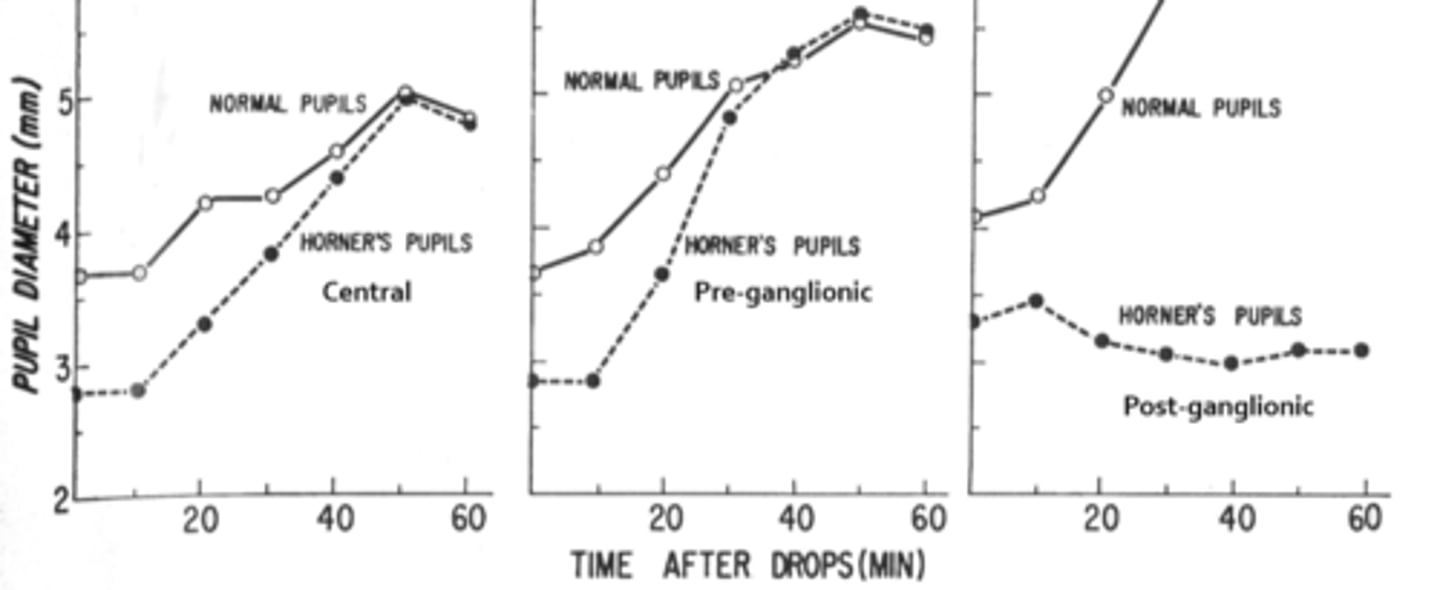
A post-ganglionic pupil will _____________ to hydroxyamphetamine.
NOT dilate
Recall that you cannot use the hydroxyamphetamine test within 2 days after which other drop? Why?
cocaine drop bc cocaine blocks re-uptake of NE at the nerve terminal, and hydroxyamphetamine works by being absorbed into nerve and forcing NE out
Ex) You suspect your Horner's pt has a left Pancoast tumor. What would the results of the hydroxyamphetamine test show in this case?
affects the left 2nd order neuron = OS pupil will dilate (as will the normal one)
Ex) Your OD Horner's pt presents with a right ear ache. What would the results of the hydroxyamphetamine test show in this case?
affects the right 3rd order neuron = OD pupil will NOT dilate, OS pupil will
What drop can you use as an alternative to hydroxyamphetamine?
phenylephrine 1% (diluted compared to regular 2.5%)
Recall: what is the MOA/drug class of phenylephrine 1%?
direct symp agonist
How does a normal eye respond to phenylephrine 1%?
receptors are not super-sensitive to dilute Phenyl bc you still get occasional spont release of NE into synapse = NO dilation or minimal dilation
How does a central (1st) or pre-ganglionic (2nd) Horner's eye respond to phenylephrine 1%?
receptors are not super-sensitive to dilute Phenyl bc you still get occasional spont release of NE into synapse = NO dilation or minimal dilation
How does a post-ganglionic (3rd) Horner's eye respond to phenylephrine 1%?
nearly no NE lest if vesicles to get spont release = neurons are starved for NE = very sensitive = dilation
Ex) You suspect your Horner's pt has a stroke. What would the results of the phenylephrine test show in this case?
central cause of Horner's = no dilation in either eye in response to dilute phenyl
Ex) Your OD Horner's pt presents with a right ear ache. What would the results of the phenylephrine test show in this case?
3rd order neuron affected = OD pupil dilates, OS pupil does not dilate
The symp fibers that supply the sweat glands of the face travel with which artery?
internal maxillary branch of the ECA
The symp fibers that supply the sweat glands of the forehead travel with which artery?
ICA
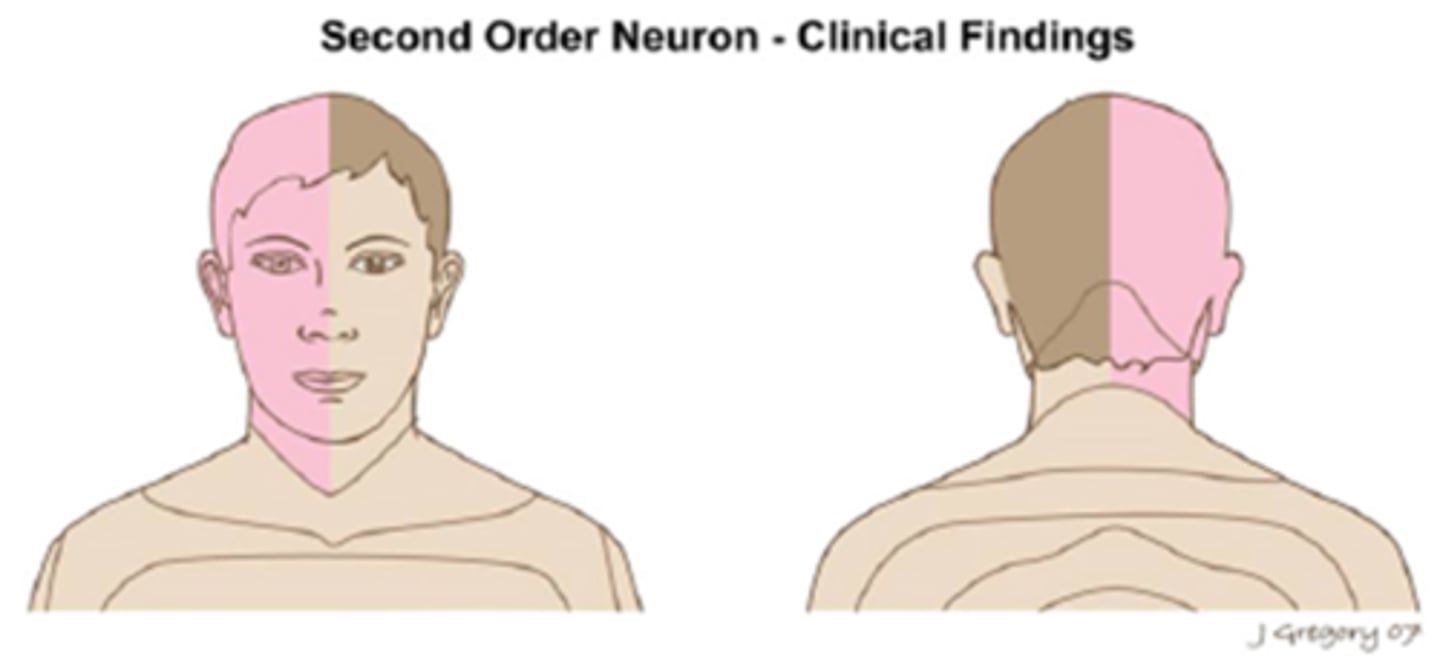
Pre-ganglion Horner's (lesions below the sup cervical ganglion) will cause anyhydrosis on which side and what areas?
ipsilateral anyhydrosis of the entire face
if high enough to be in spinal cord = upper body anydrosis
if high enough to be in brainstem = entire body anyhydrosis
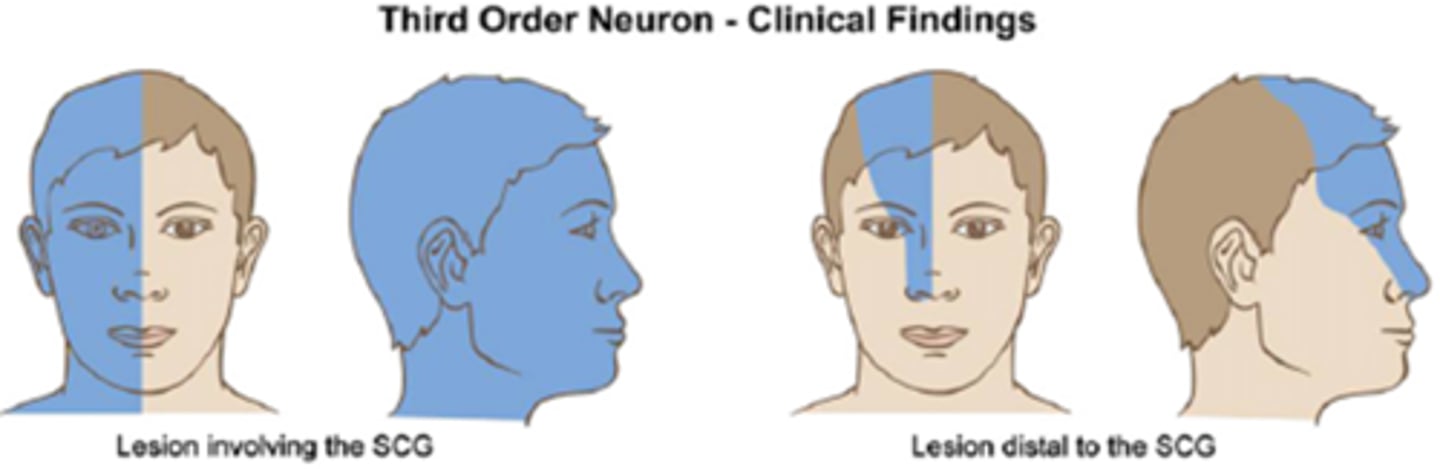
Post-ganglion Horner's (lesions at or above the ICA) will cause anyhydrosis on which side and what areas?
ipsilateral anyhydrosis of the forehead only
Ex) Your OD Horner's pt presents with a right ear ache. What would the results of the sweat test show in this case?
right forehead doesn't sweat
left forehead does sweat
right face does sweat
left face does sweat
What is the dilation lag test used to assess Horner's?
use photos/video to compare pupil sizes in the dark at 5sec and 10sec
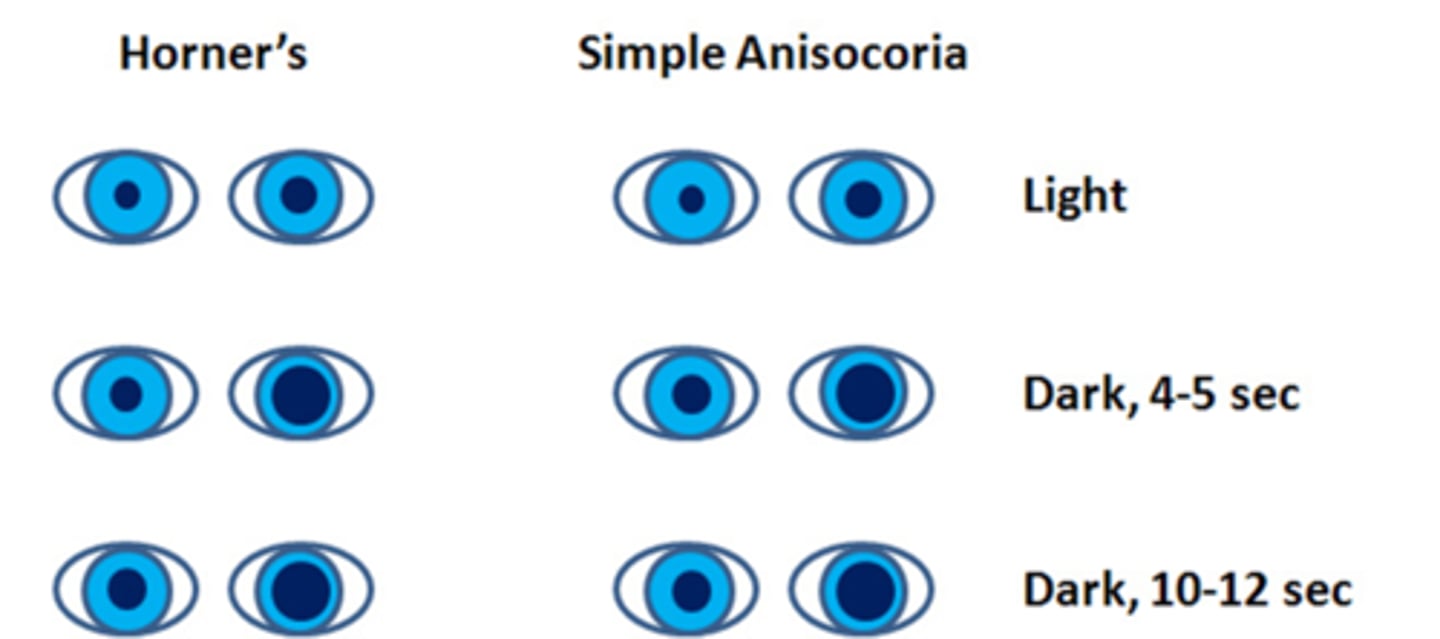
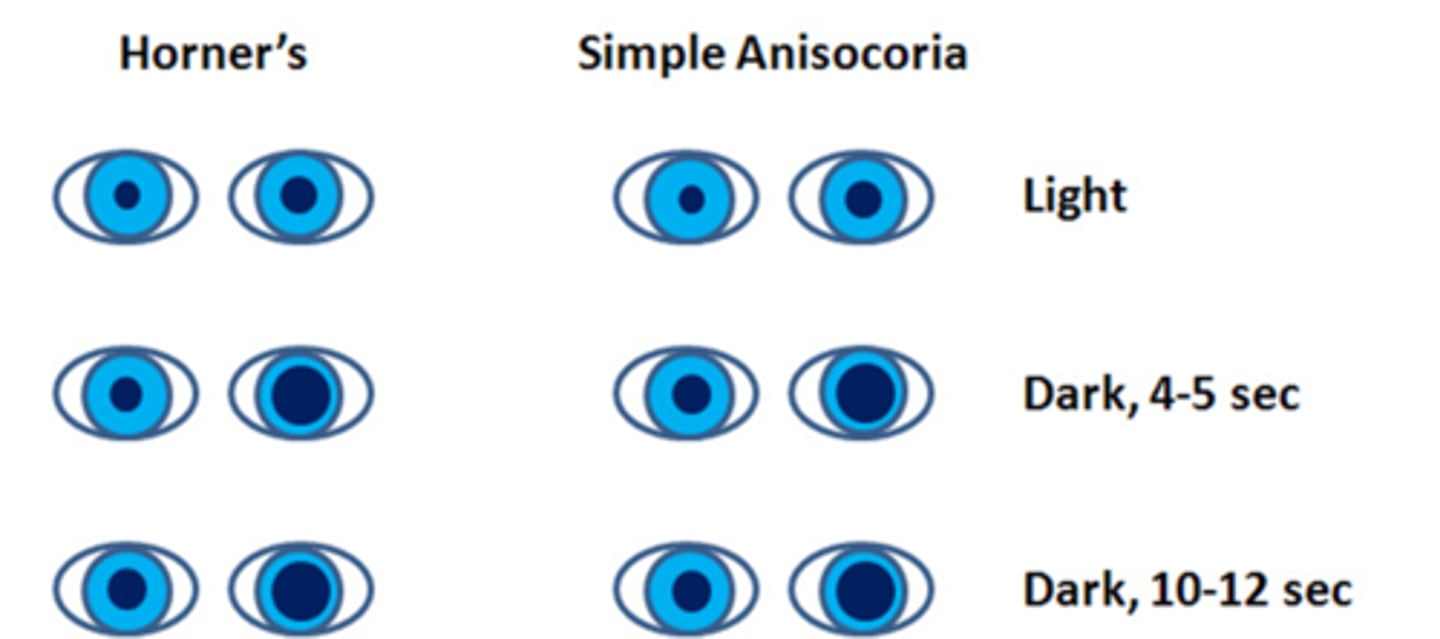
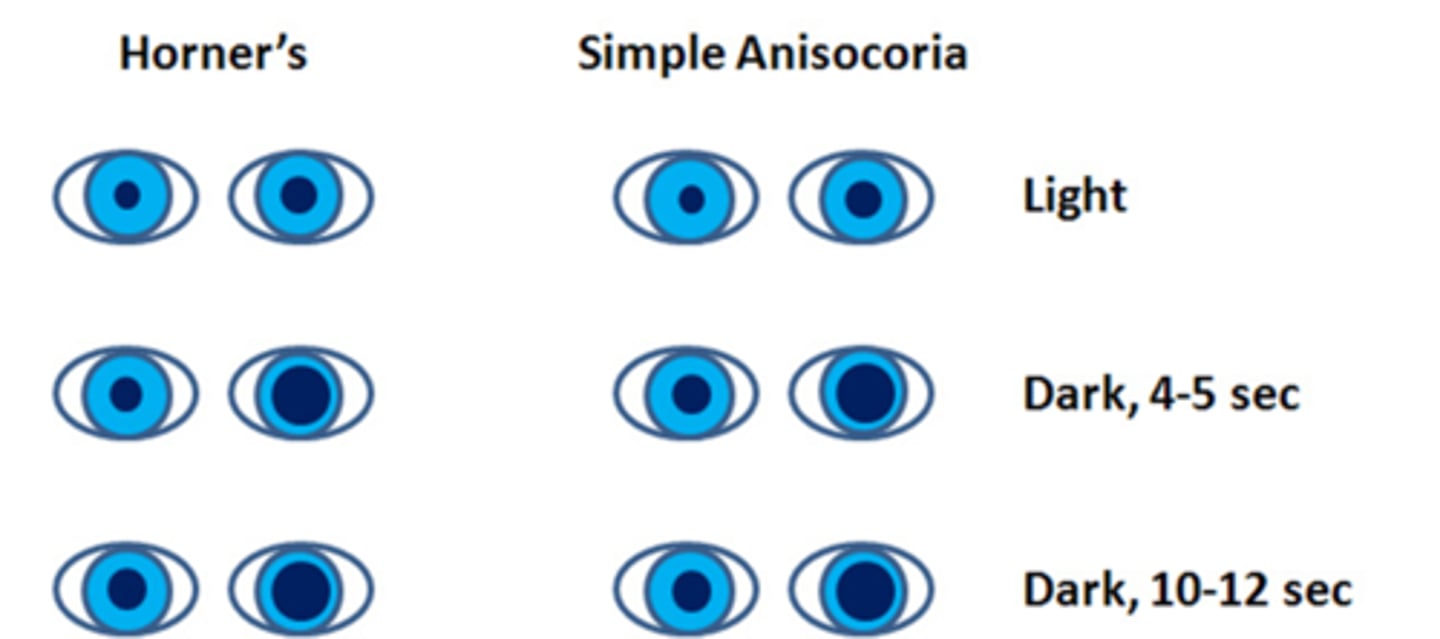
How does a Horner's syndrome appear on the dilation lag test?
symp issue = pupil dilates very slowly = pupil will de a different size at 5sec vs 10sec (whereas normal pupil dilates fast/by 5sec)
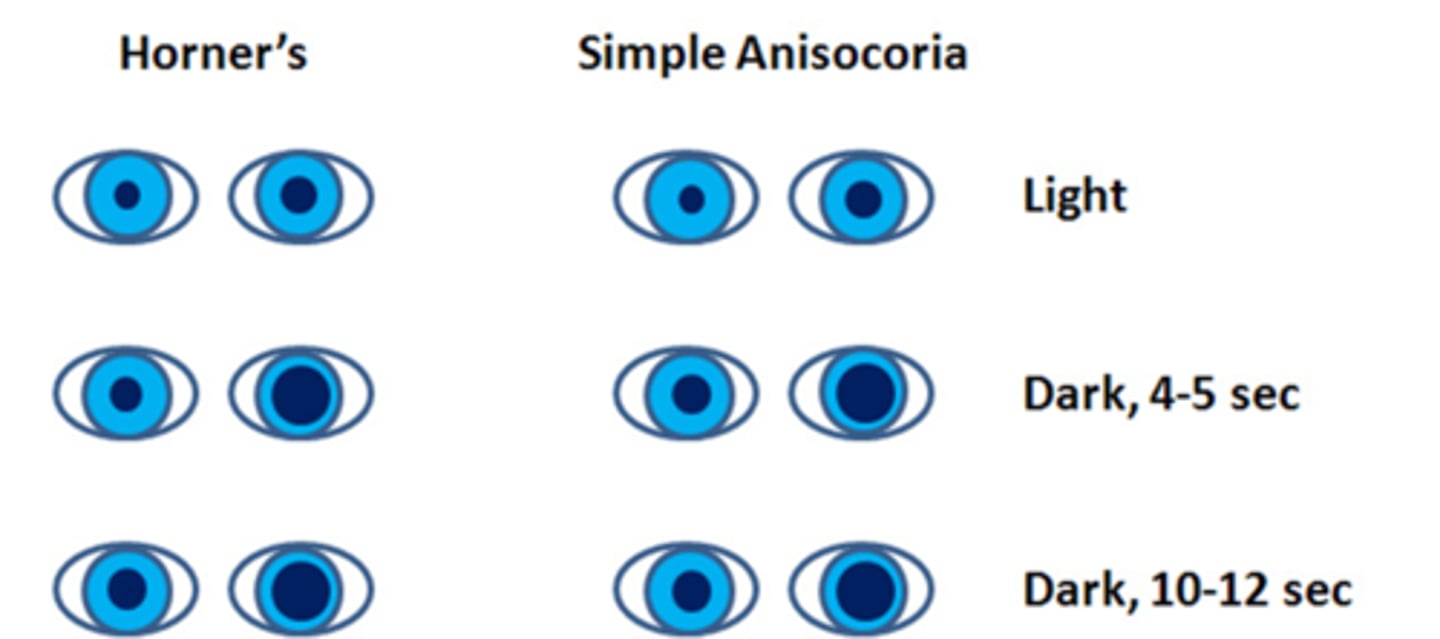
How does simple congenital anisocoria appear on the dilation lag test?
similar to normal pupil, size will be the same at 5sec vs 10sec bc the pupil is normal/healthy
Is the dilation lag test typically more or less reliable than the cocaine test?
more reliable!
Which eye here has the Horner's syndrome?
slower redilation velocity (slope) in the OD = OD Horner's
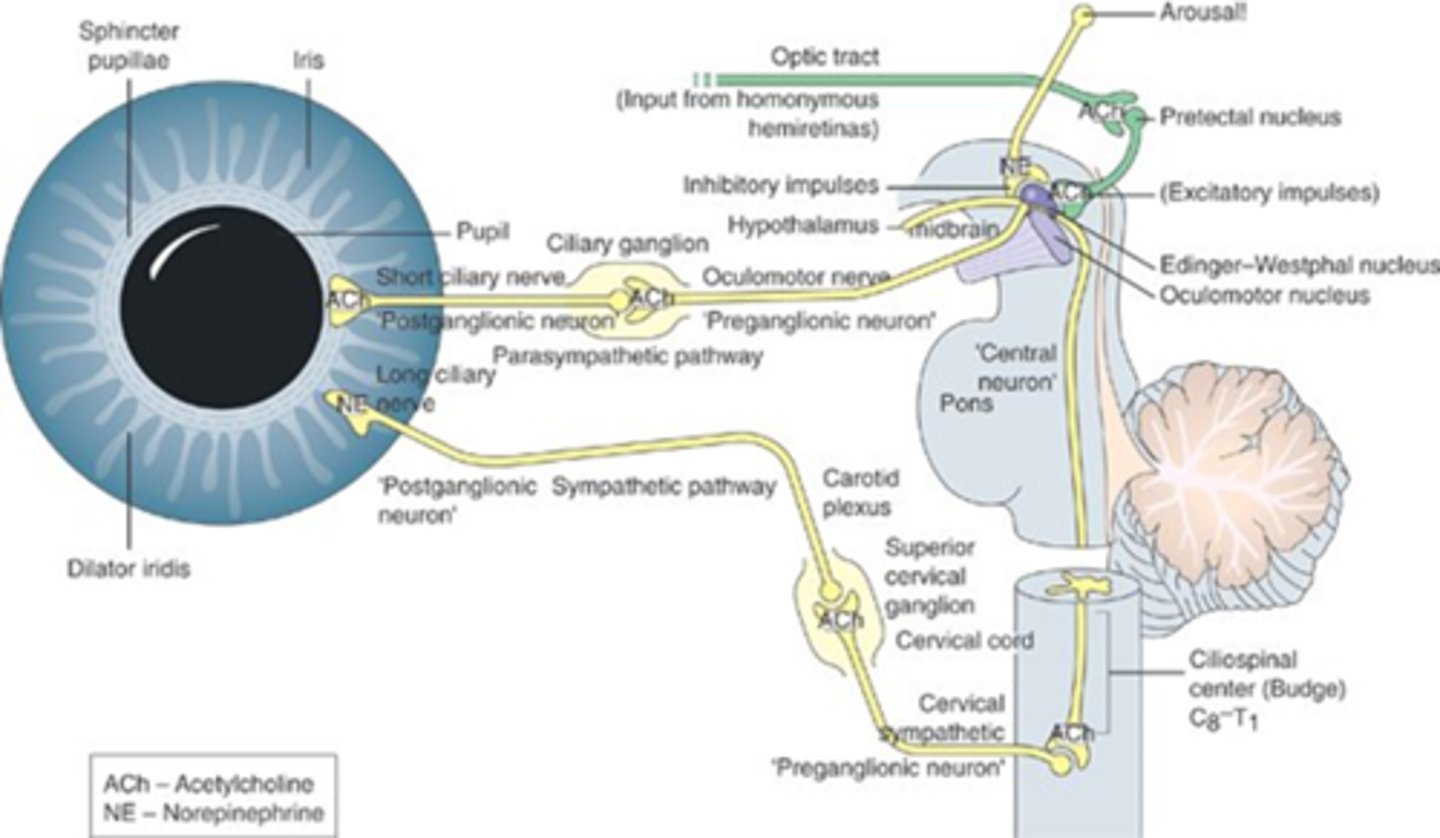
Explain the pathway resulting in iris constriction.
E-W nucleus parasymp fibers = oculomotor nerve = ciliary ganglion = short ciliary nerve = iris sphincter
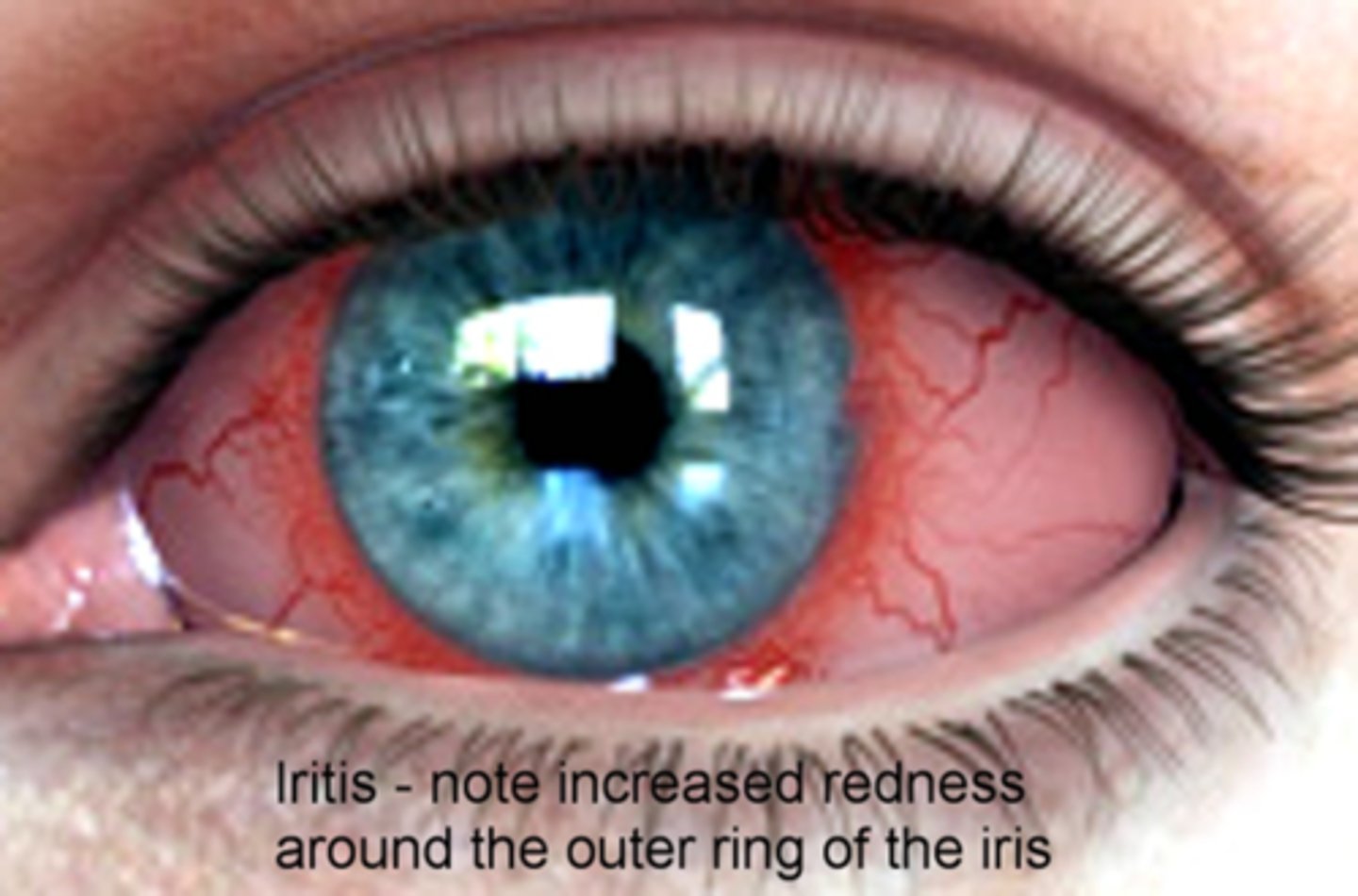
What are some etiologies with the muscle causing a small pupil?
uveitis due to CB spasm
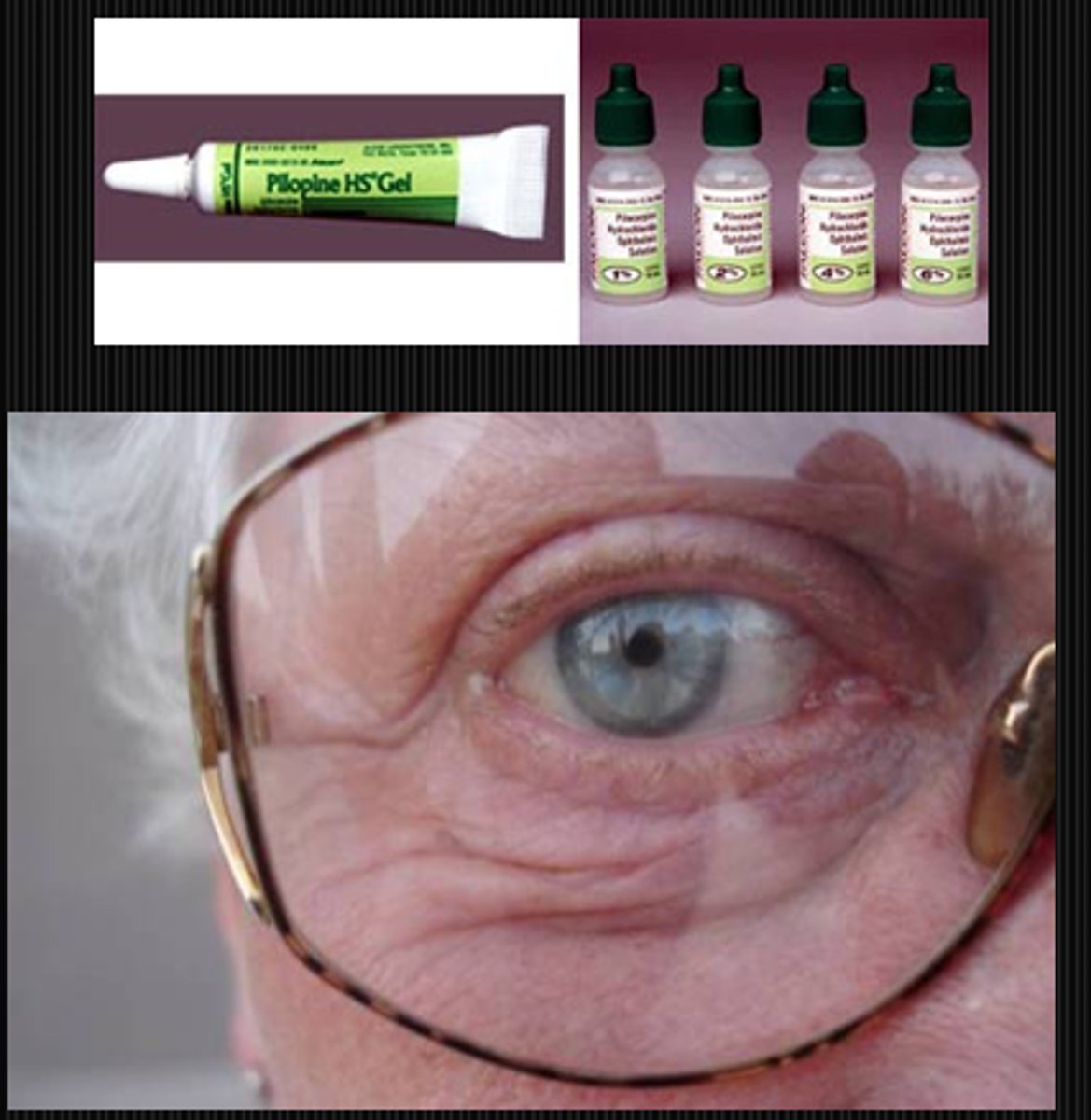
What are some etiologies with the NMJ causing a small pupil?
miotic drugs like pilocarpine
senile miosis due to reduced symp activity with age = increased parasymp dominance
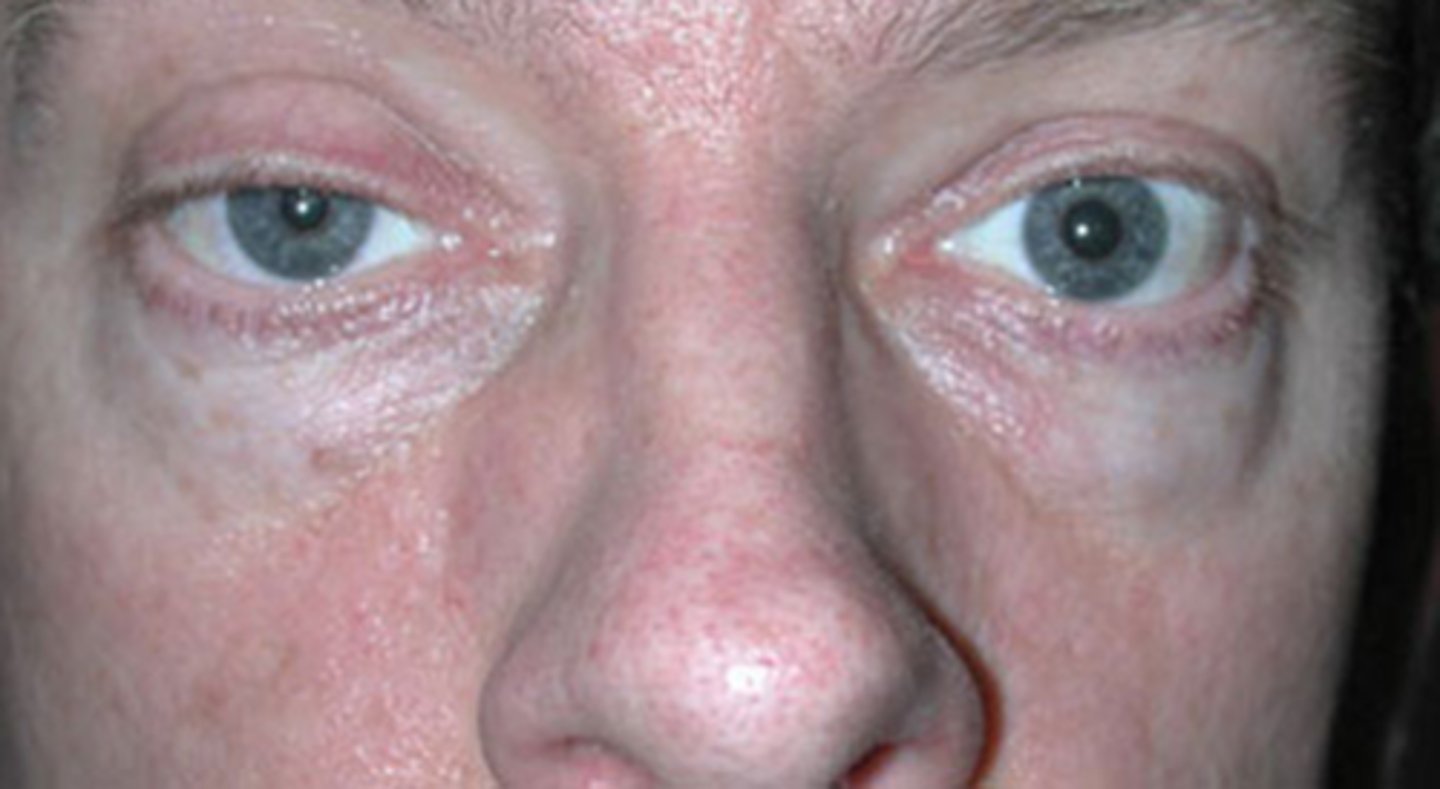
What are some etiologies with the nerve causing a small pupil?
Horner's syndrome (see Horner's Quizlet set)
What do we typically call miosis due to a brain problem?
Argyll-Robertson Pupil
What is syphilis?
infectious veneral disease caused by the Treponema pallidum spirochete
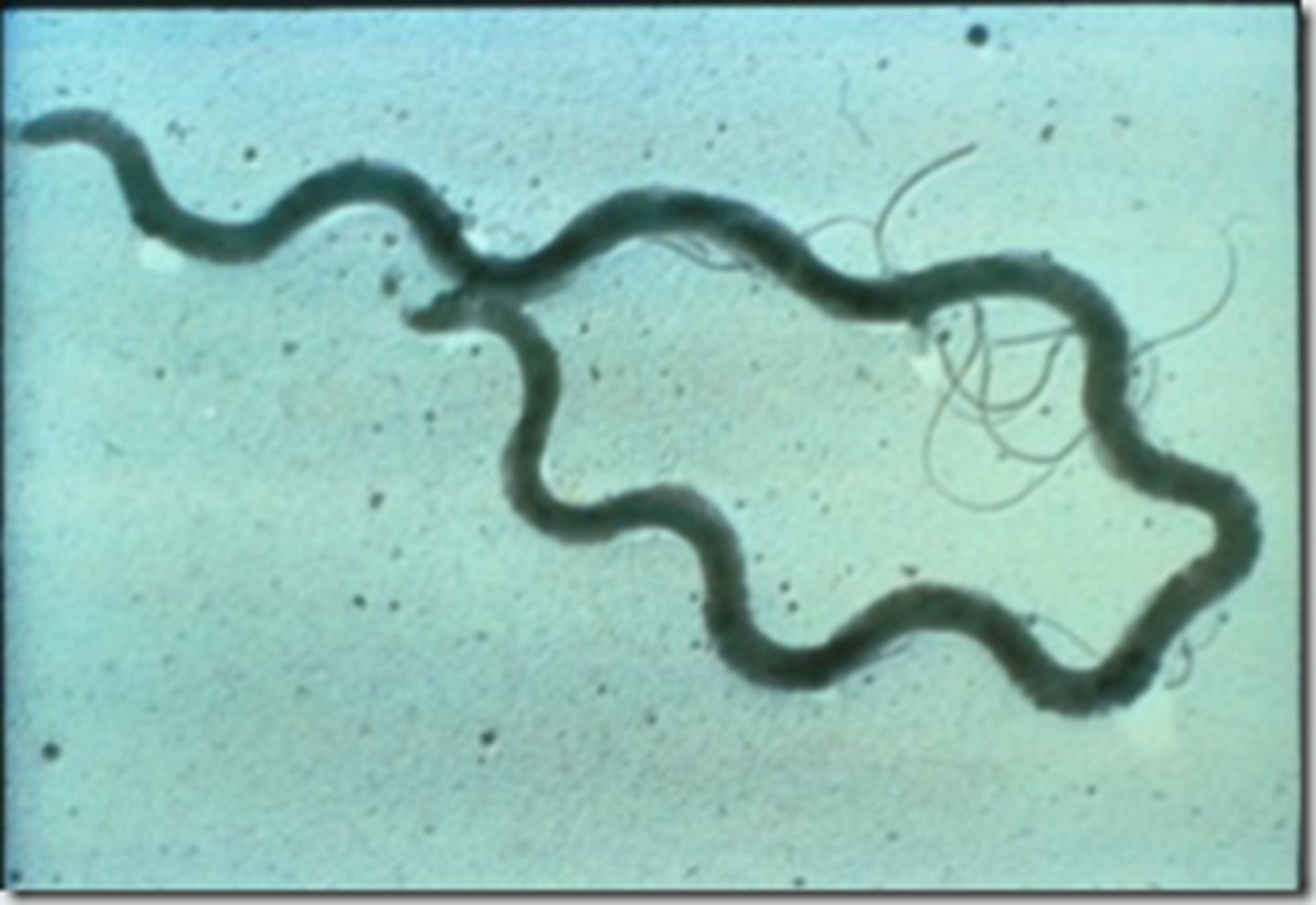
What occurs in the primary stage of syphilis?
pt is inoculated or infected with the spirochete = chancres
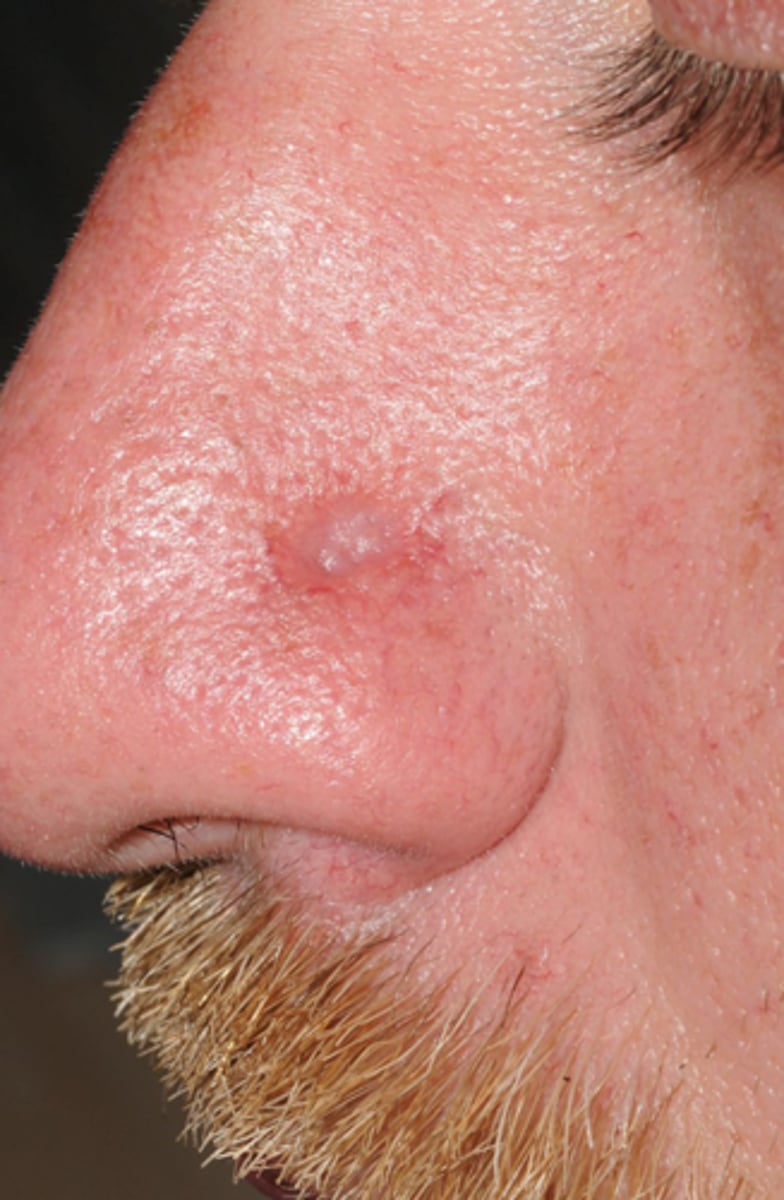
What occurs in the secondary stage of syphilis?
skin rash
lymphadenopathy
fevere
malaise
inflam of mucous memb (mouth, nose)