Chapter 3: Dynamics: Force and Newton's Laws of Motion - Review Terms
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
76 Terms
Force
A push or a pull that has both magnitude and direction, making it a vector quantity.
Dynamics
The study of the forces that cause objects and systems to move.
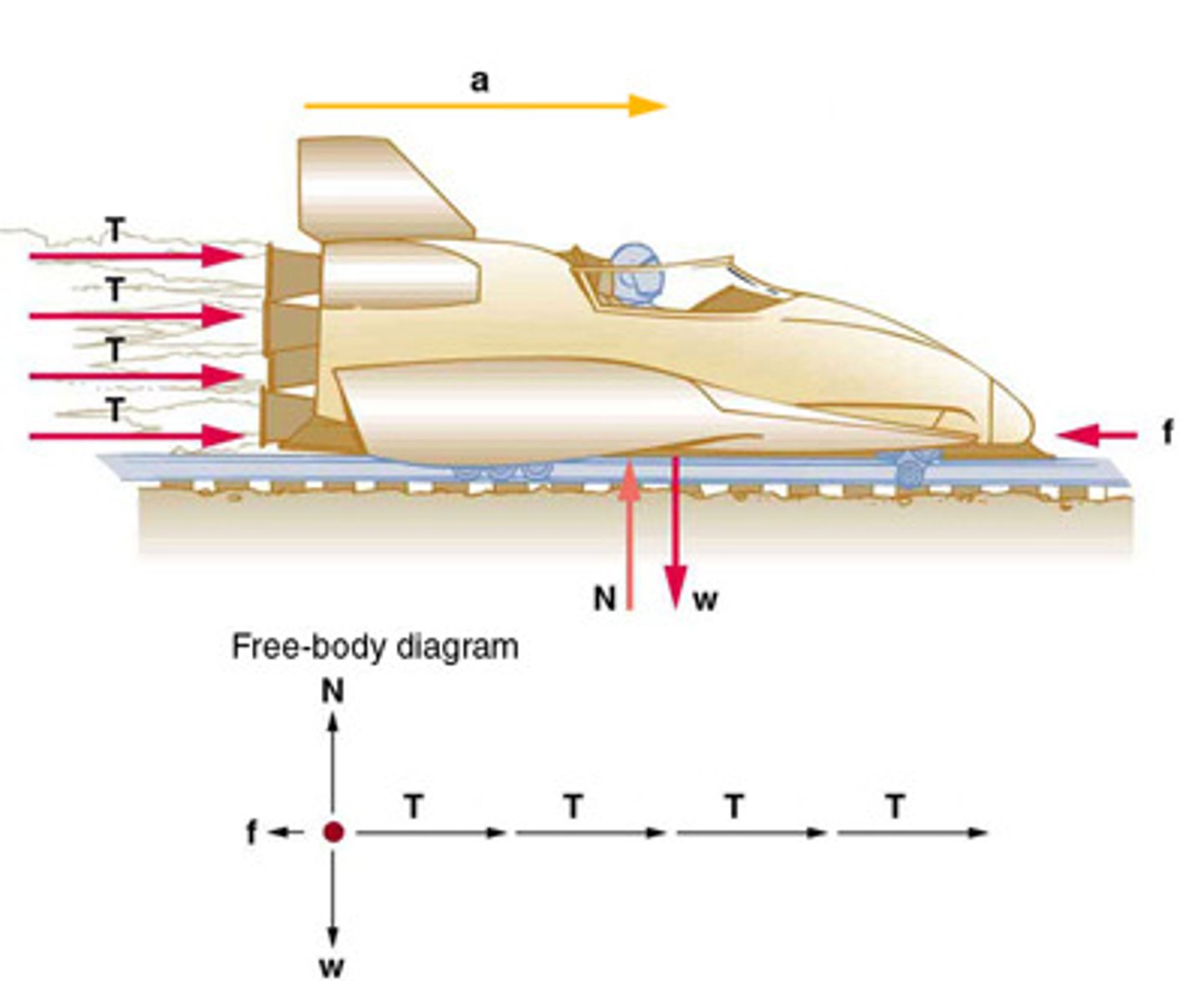
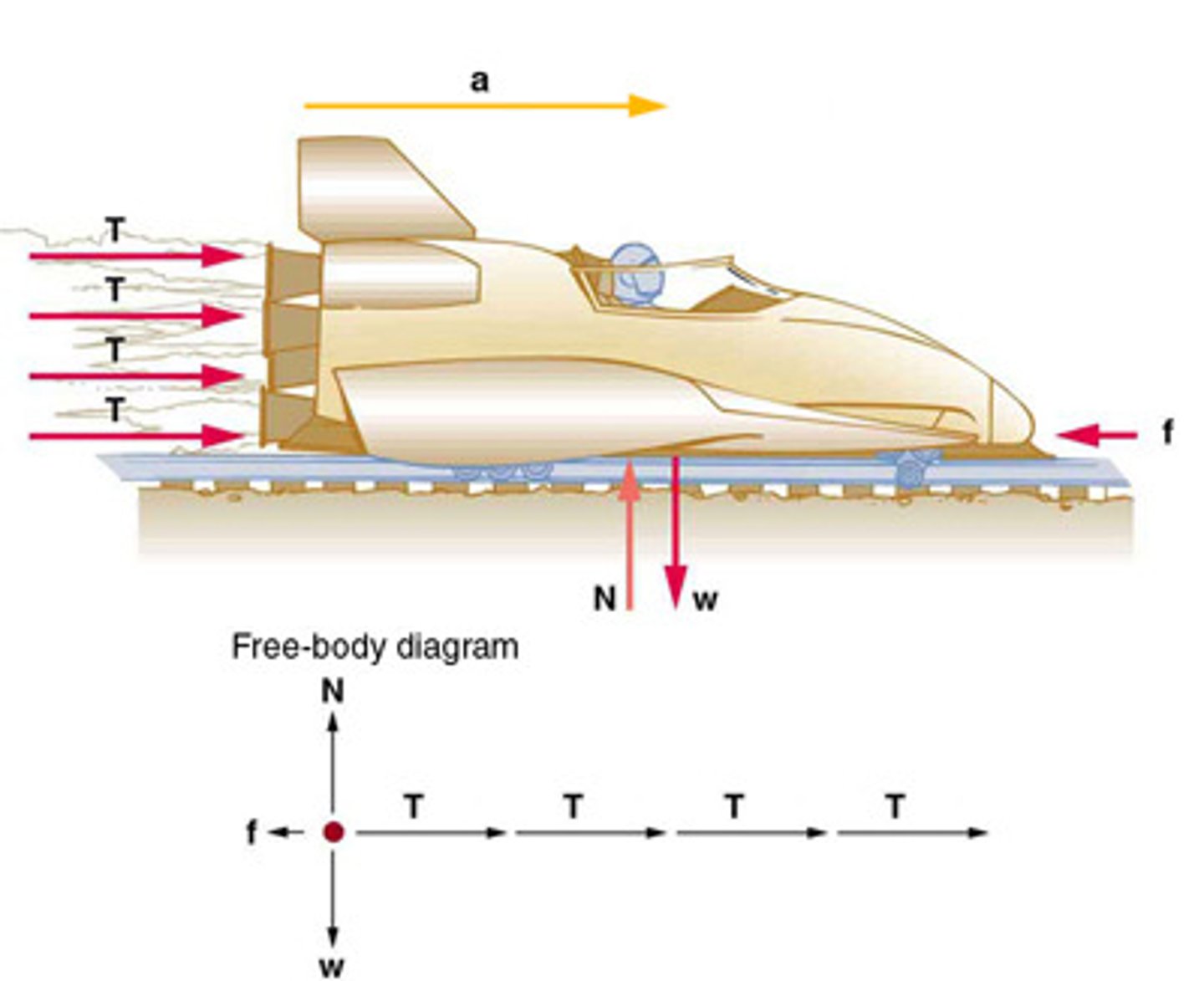
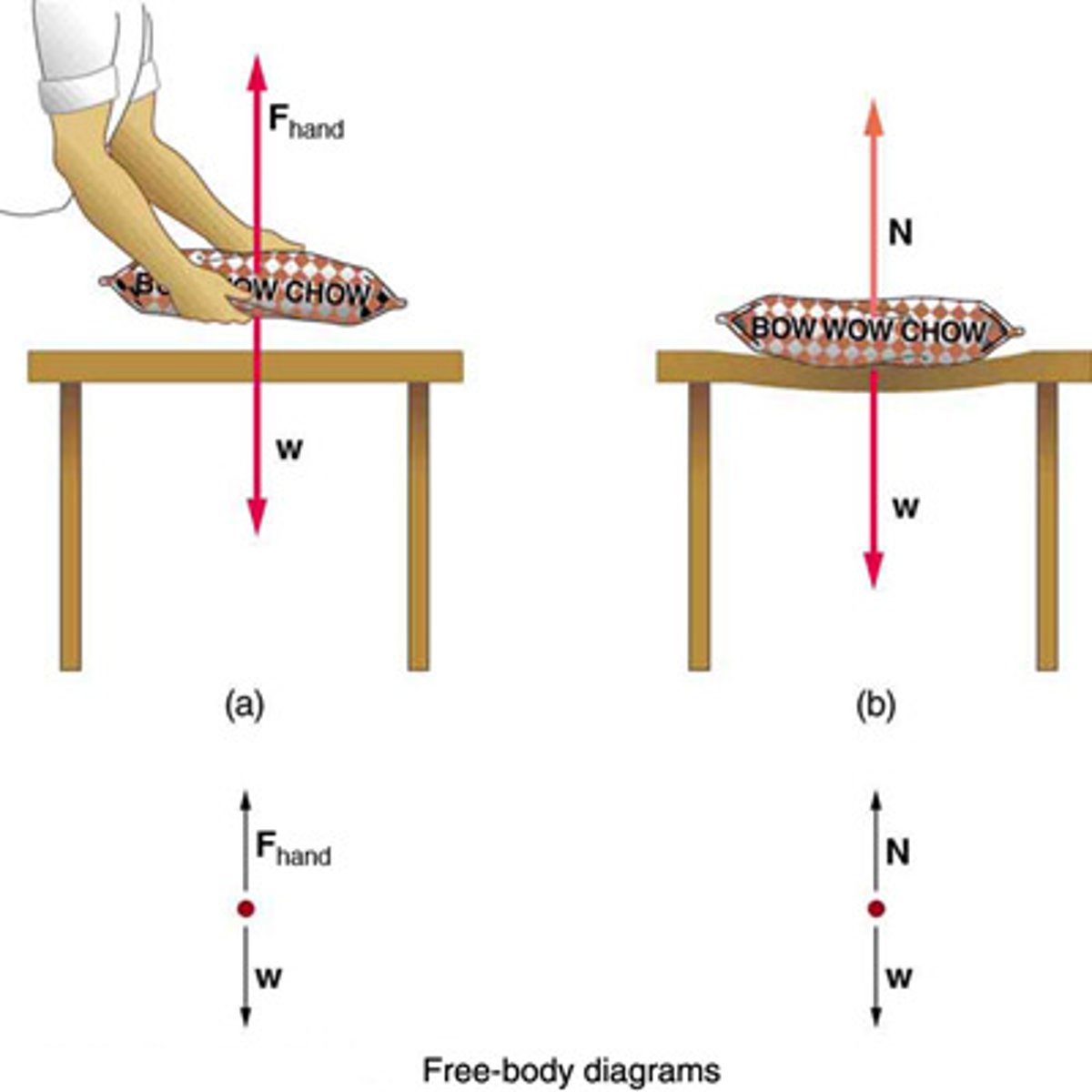
Free-Body Diagram
A technique used to illustrate all the external forces acting on a body, represented by a single isolated point.
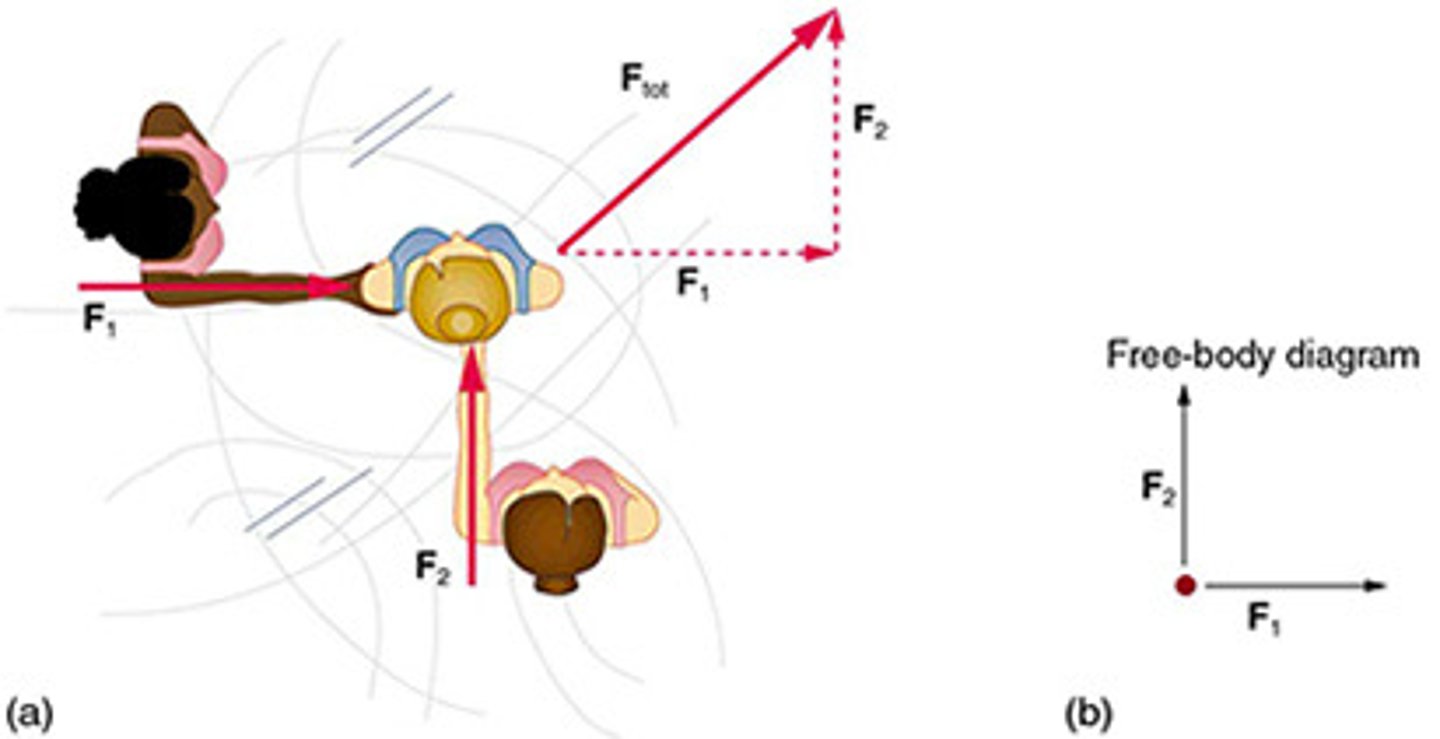
External Forces
Forces acting on a body from the outside, affecting its motion.
Newton's First Law of Motion
A body at rest remains at rest, or, if in motion, remains in motion at a constant velocity unless acted on by a net external force.
Inertia
The property of a body to remain at rest or to remain in motion with constant velocity.
Mass
A measure of the amount of matter in an object, which determines its inertia. Mass does not vary with location.
Net External Force
A force that causes a change in velocity (either a change in magnitude or direction) of an object.
Friction
An external force that opposes the motion of an object, causing it to slow down.
Cause and Effect in Physics
The principle that changes in motion are caused by external forces, as described by Newton's first law.
Universal Laws
Laws that apply generally to all physical phenomena, such as Newton's first law of motion.
Net Force
The vector sum of all external forces acting on a system.
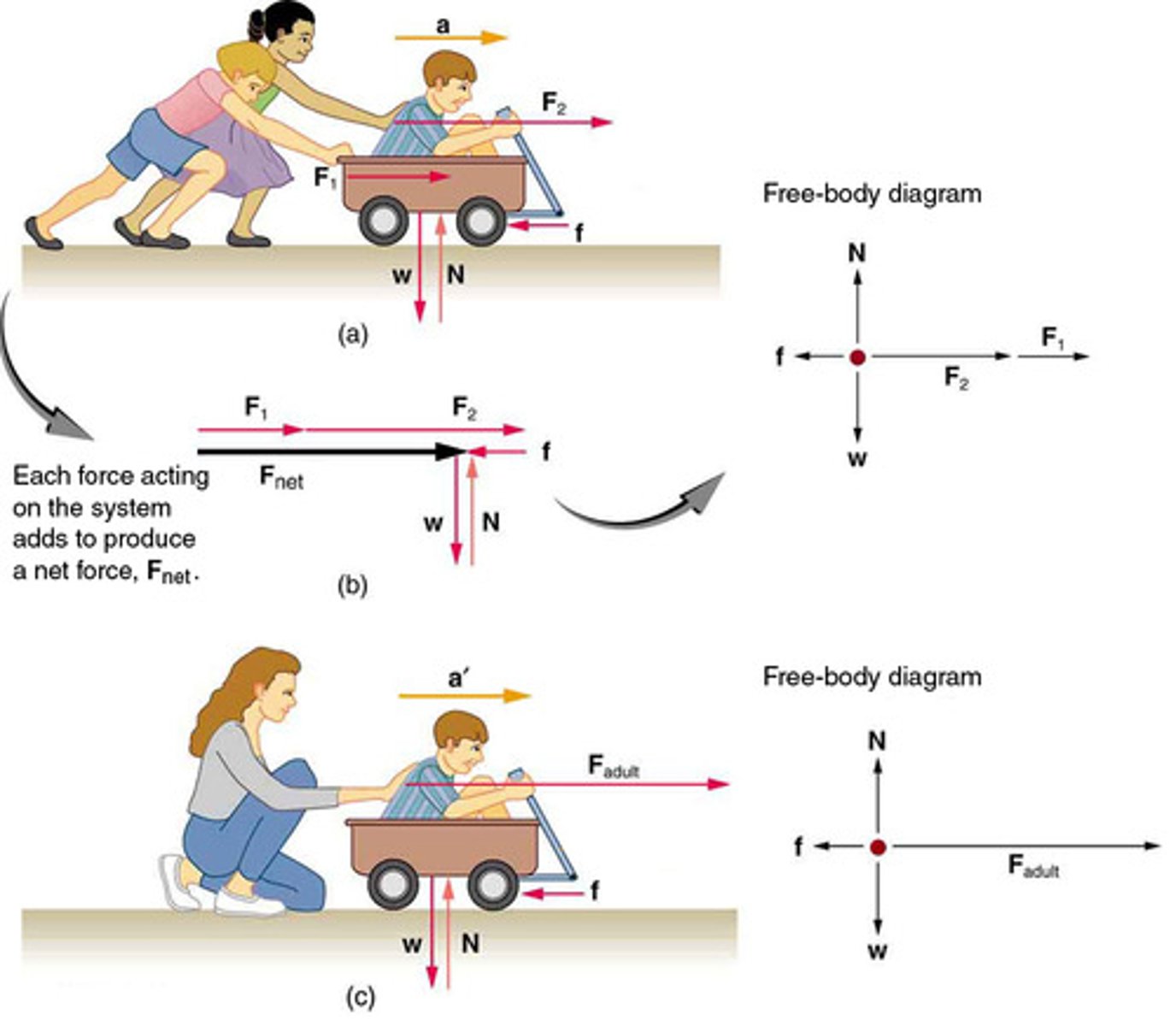
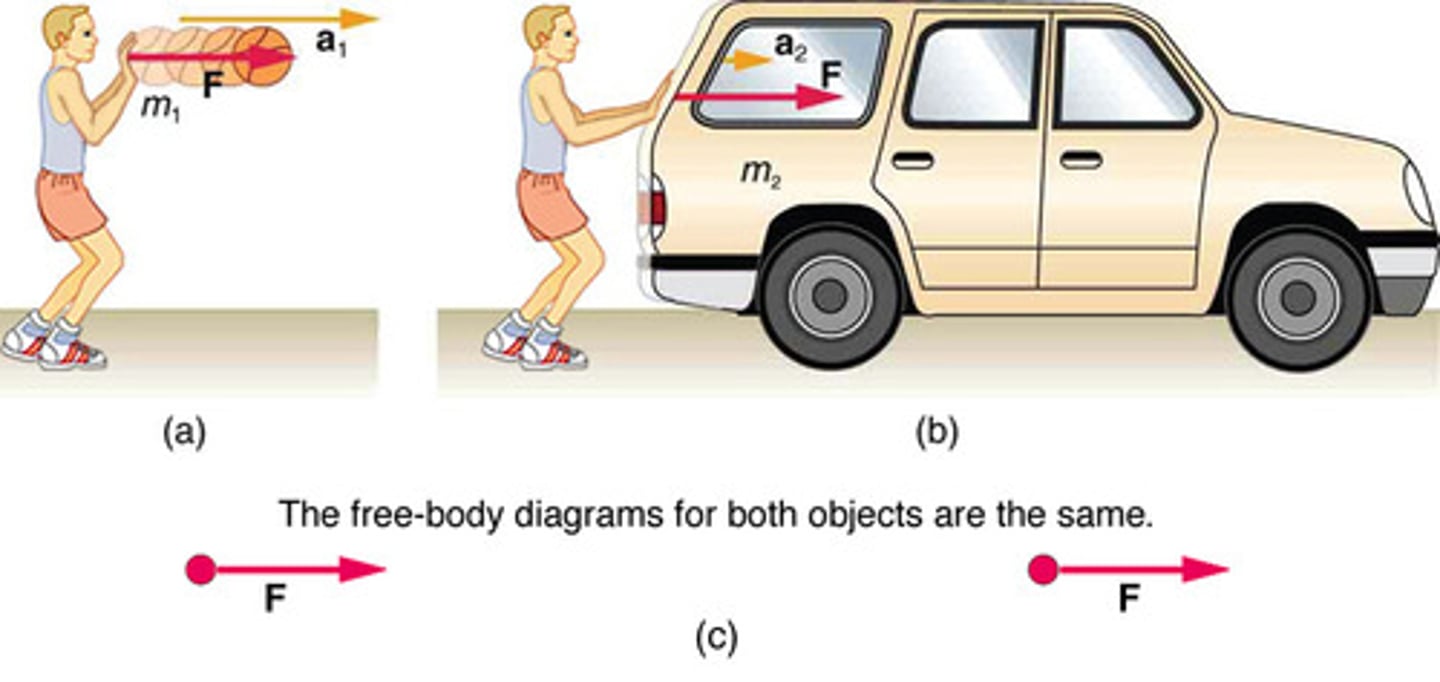
System
An object or collection of objects being analyzed, where boundaries are defined to determine external forces.
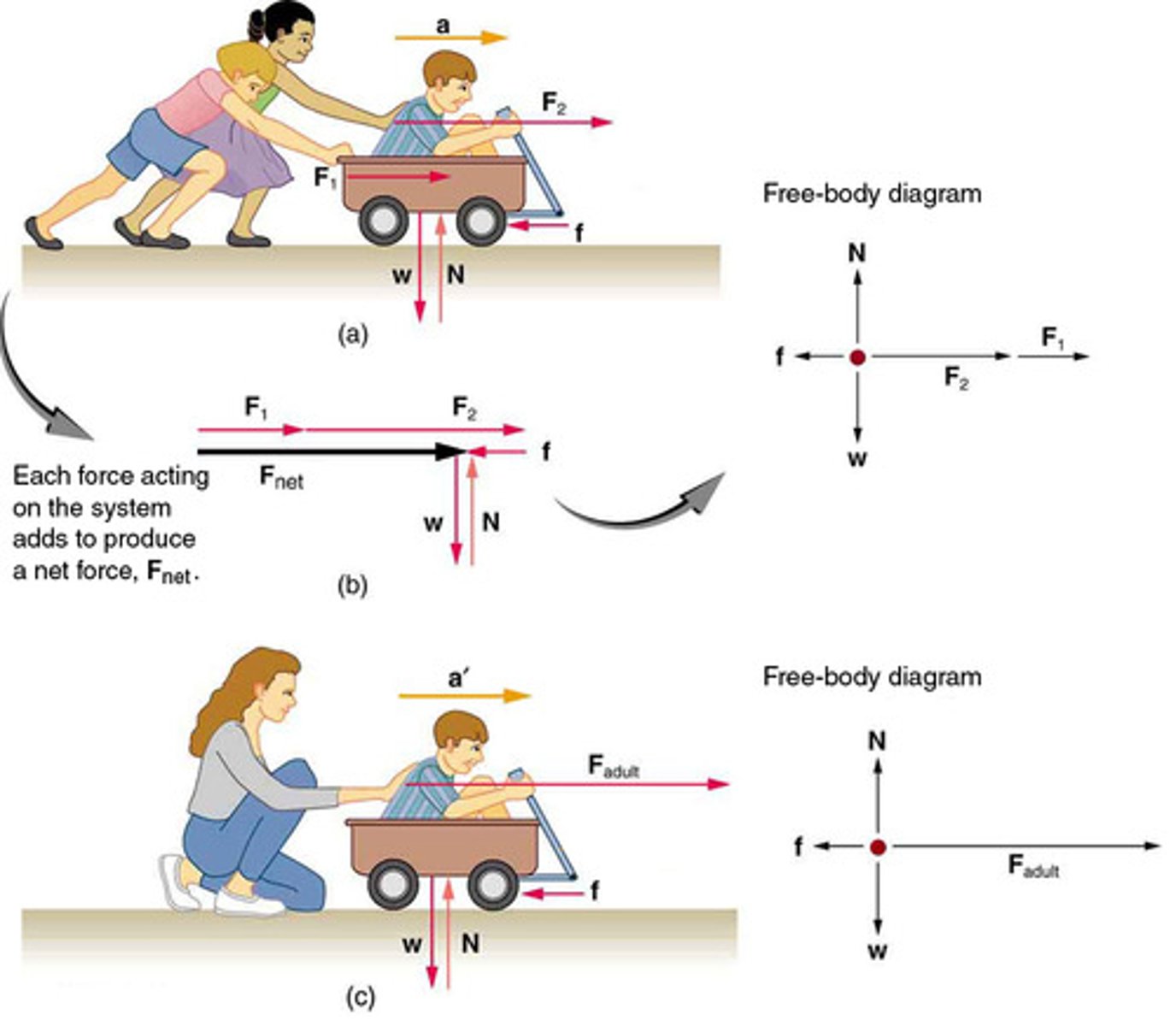
Newton's Second Law of Motion
The acceleration of a system is directly proportional to and in the same direction as the net external force acting on the system, and inversely proportional to its mass.
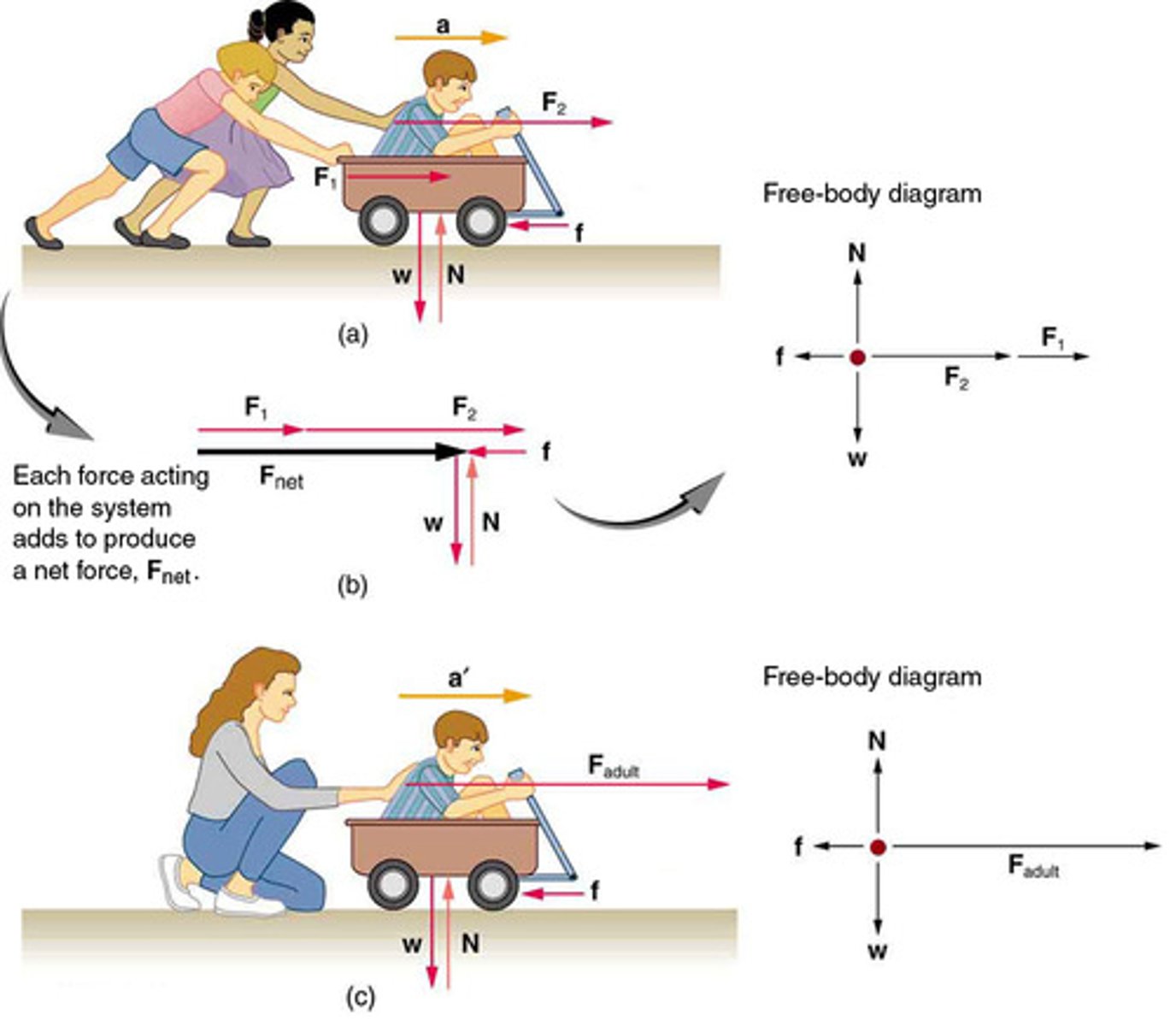
Equation for Newton's Second Law
F_net = ma, where F_net is the net external force, m is the mass, and a is the acceleration.
SI Unit of Force
The newton (N), defined as the force needed to accelerate a 1-kg mass at 1 m/s².
Weight
The gravitational force acting on an object, calculated as w = mg, where m is mass and g is the acceleration due to gravity.
Free-Fall
The condition in which the only force acting on an object is gravity.
Mass vs. Weight
Mass is the amount of matter in an object, measured in kilograms, while weight is the gravitational force on an object, measured in newtons.
Proportionality of Acceleration and Force
Acceleration is directly proportional to the net external force acting on a system.
Inversely Proportional
A relationship where one quantity increases as another decreases; in Newton's second law, acceleration is inversely proportional to mass.
Gravitational Force
The force of attraction between two masses, commonly experienced as weight on Earth.
Acceleration Due to Gravity
The acceleration experienced by an object solely under the influence of gravity, approximately 9.80 m/s² on Earth.
Newton's Third Law of Motion
Whenever one body exerts a force on a second body, the first body experiences a force that is equal in magnitude and opposite in direction to the force that it exerts.
Action-Reaction Pair
A pair of forces that are equal in magnitude and opposite in direction, as described by Newton's third law of motion.
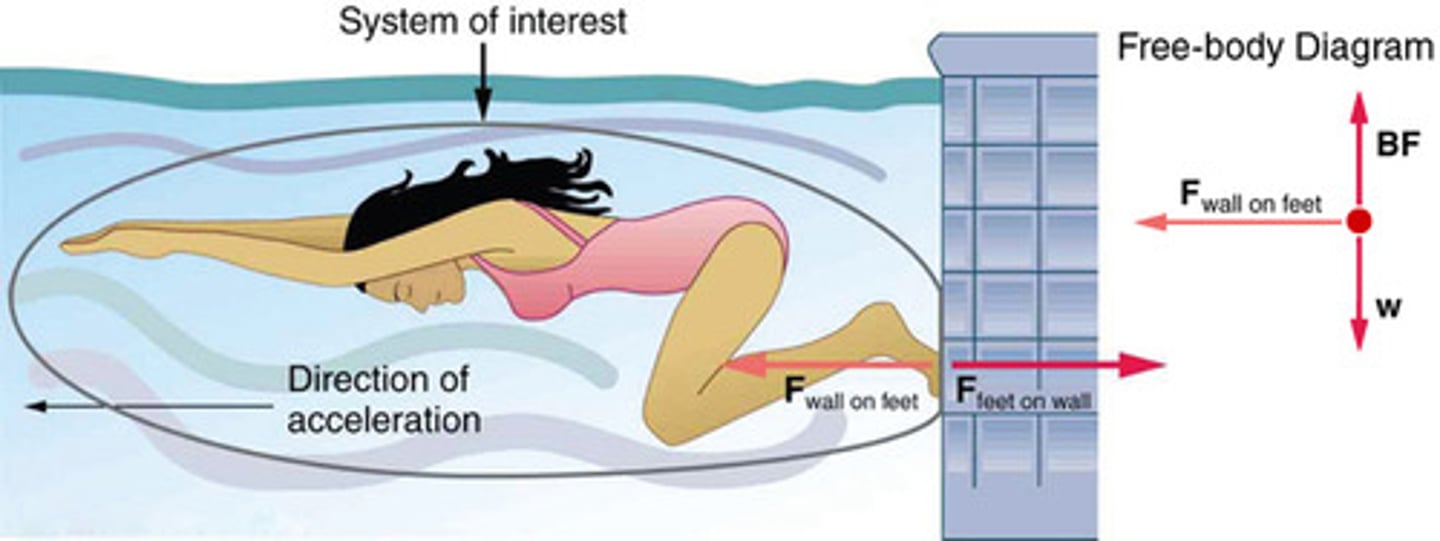
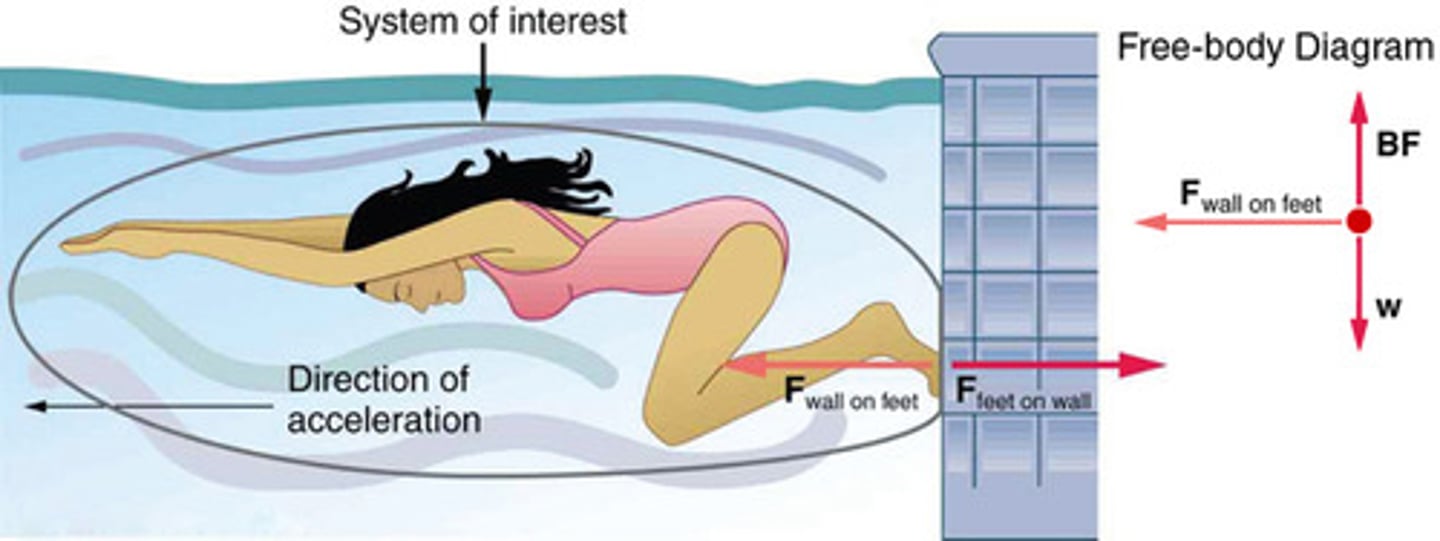
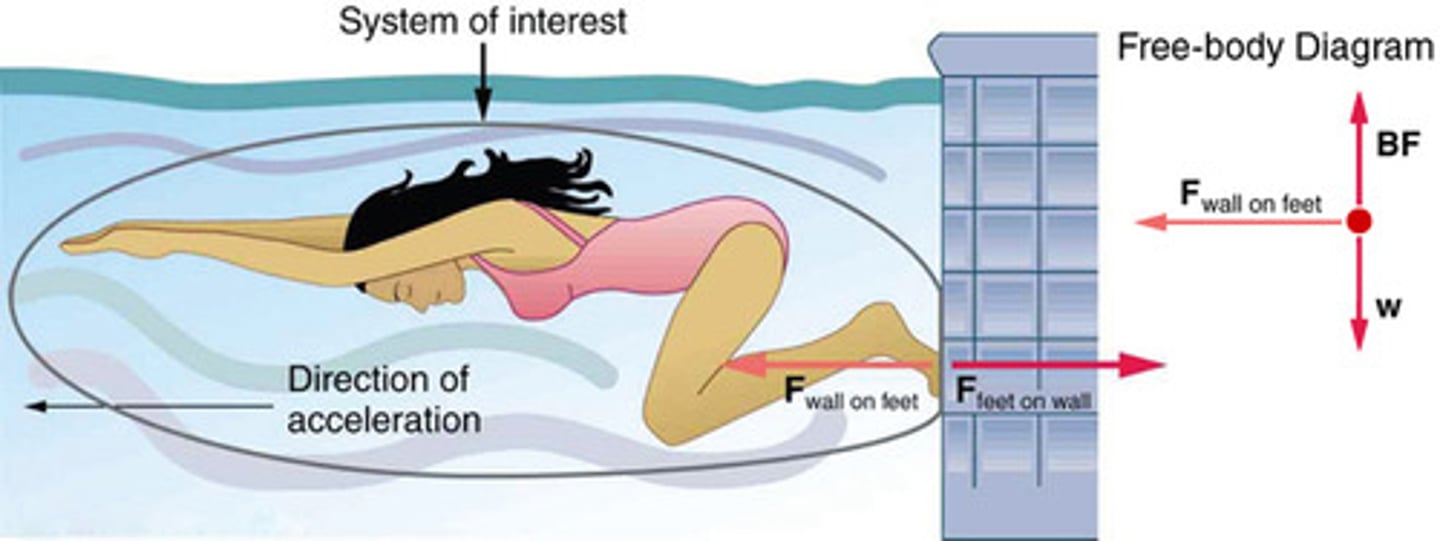
System of Interest
A defined set of objects or components that are analyzed to understand the forces acting upon them and their resulting motion.
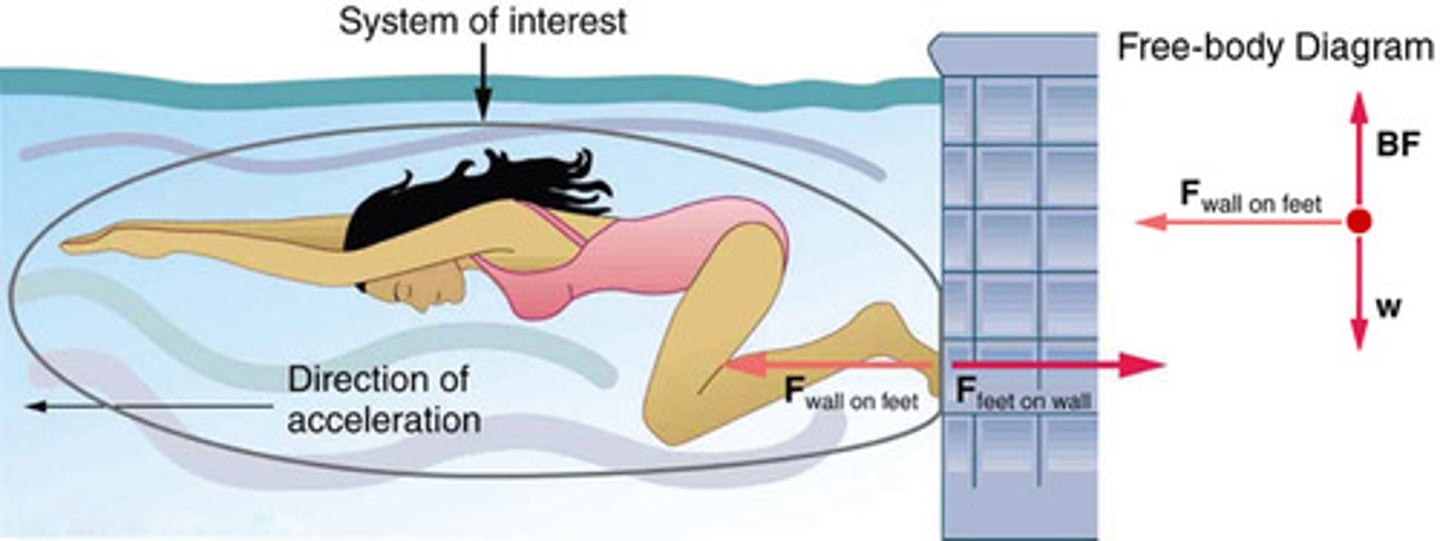
External Force
A force acting on a system from outside the system's boundary, affecting its motion.
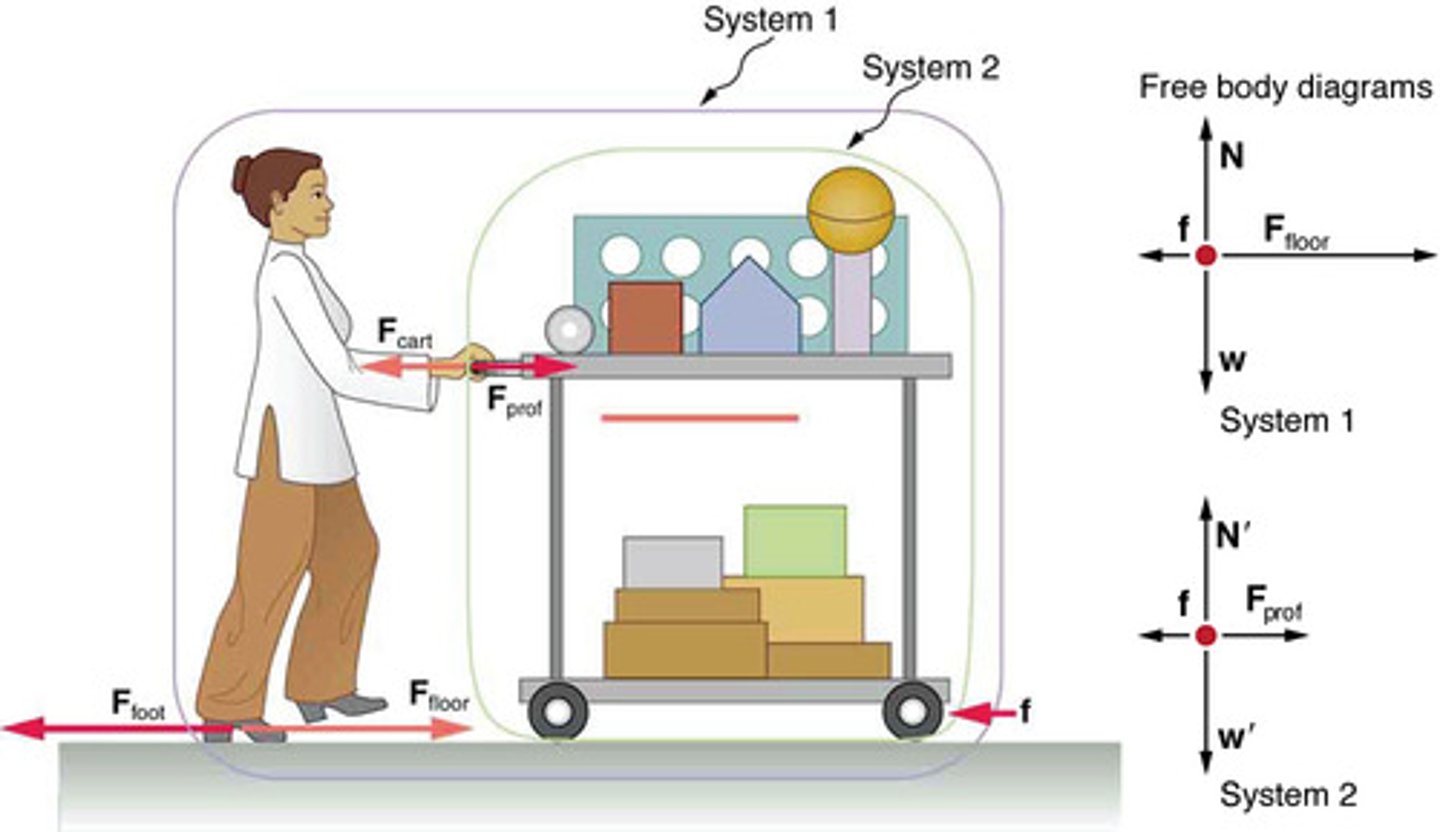
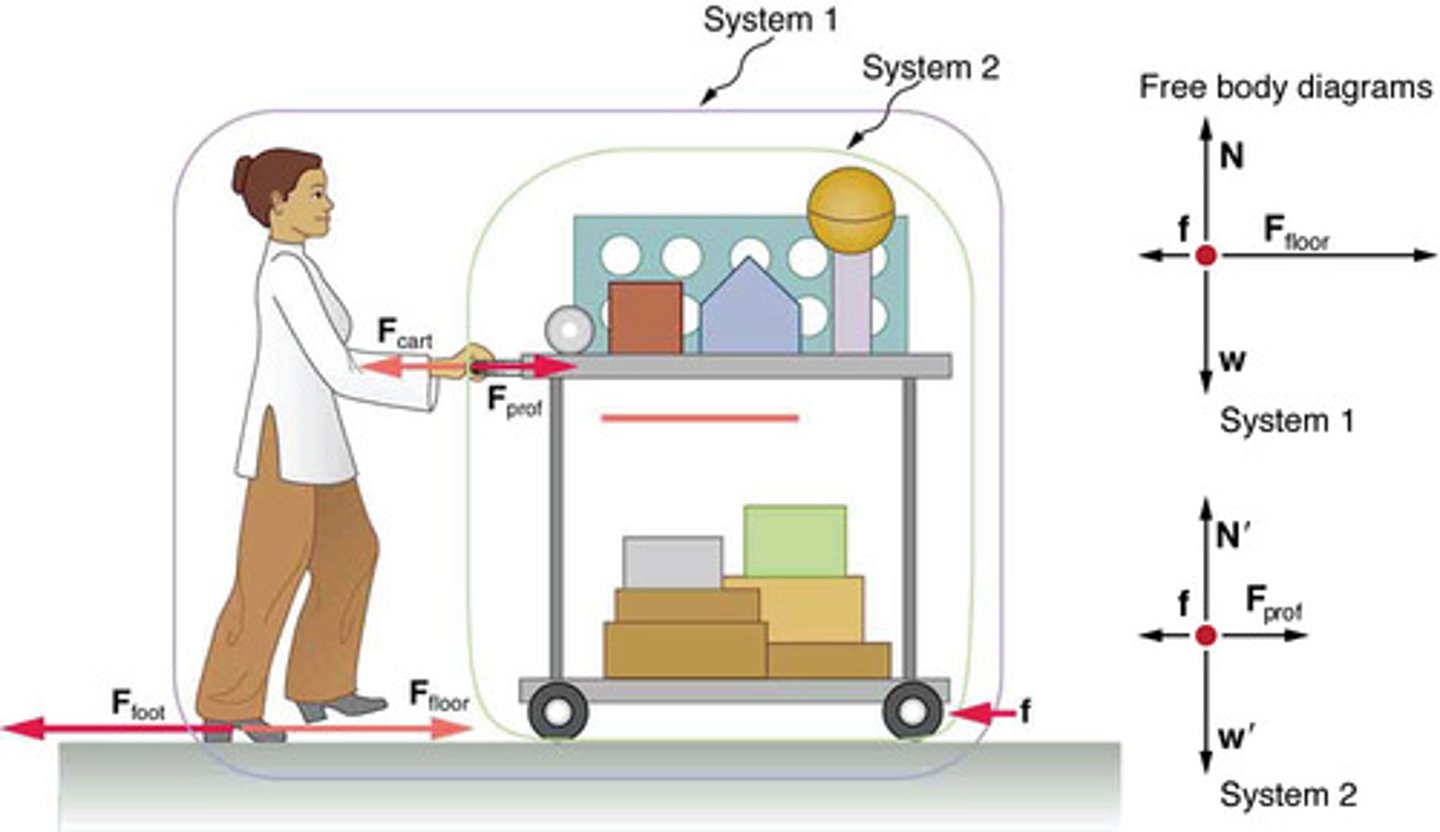
Internal Force
A force exchanged between components within a system, which does not affect the net external force on the system.
Thrust
The reaction force that propels a rocket forward, resulting from expelling gas backward at high velocity.
Symmetry in Forces
The concept that forces always occur in pairs, with each force having an equal and opposite counterpart.
Net External Force
The total force acting on a system from external sources, determining the system's acceleration according to Newton's second law.
Acceleration
The rate of change of velocity of an object, calculated as net external force divided by mass.
Free-Body Diagram
A graphical representation used to visualize the forces acting on a single object or system.
Normal Force
A force that acts perpendicular to the surface of contact between an object and its support, counteracting the object's weight.
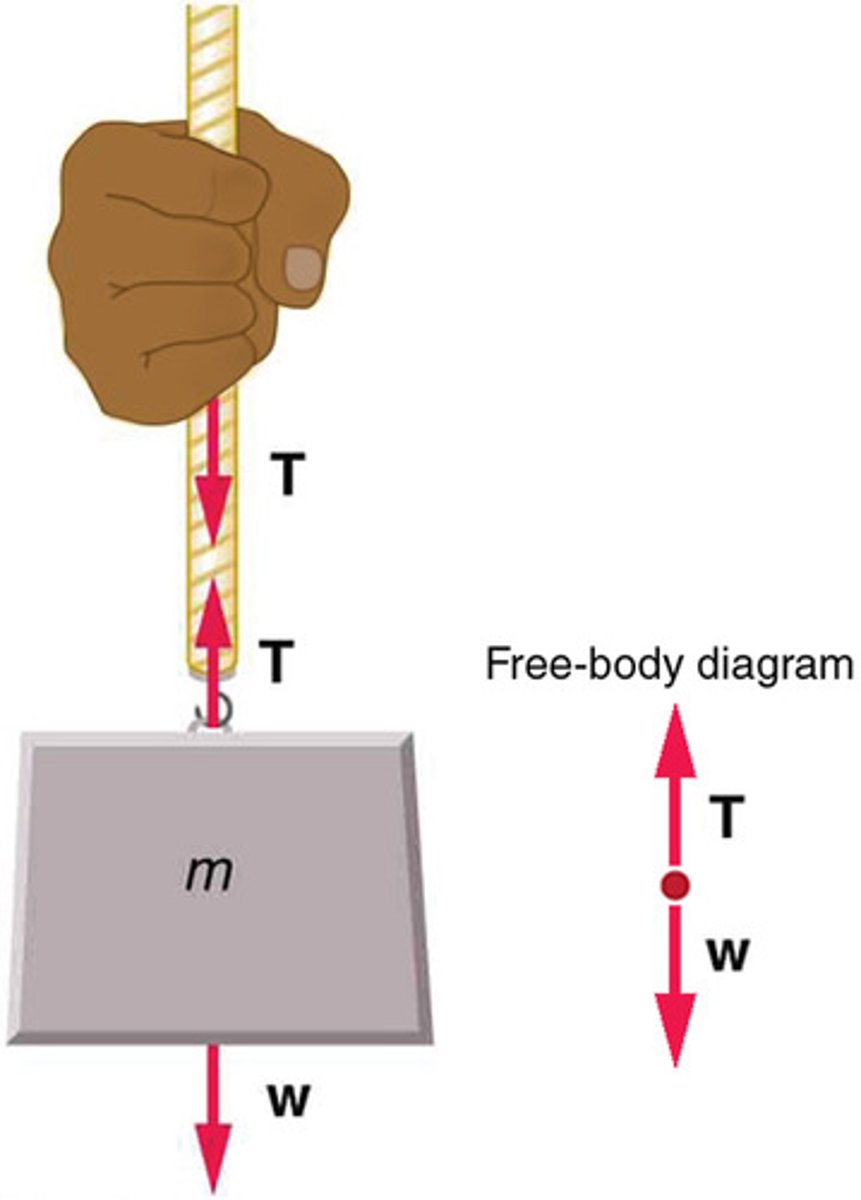
Tension Force
A force carried by a flexible medium, such as a rope or cable, acting along the length of the medium and pulling outward at its ends.
Newton's Second Law
The acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force acting on it and inversely proportional to its mass, expressed as F = ma.
Weight Components on an Incline
The force of gravity acting on an object on an incline can be resolved into two components: one perpendicular to the plane (w⊥ = mgcos(θ)) and one parallel to the plane (w∥ = mgsin(θ)).
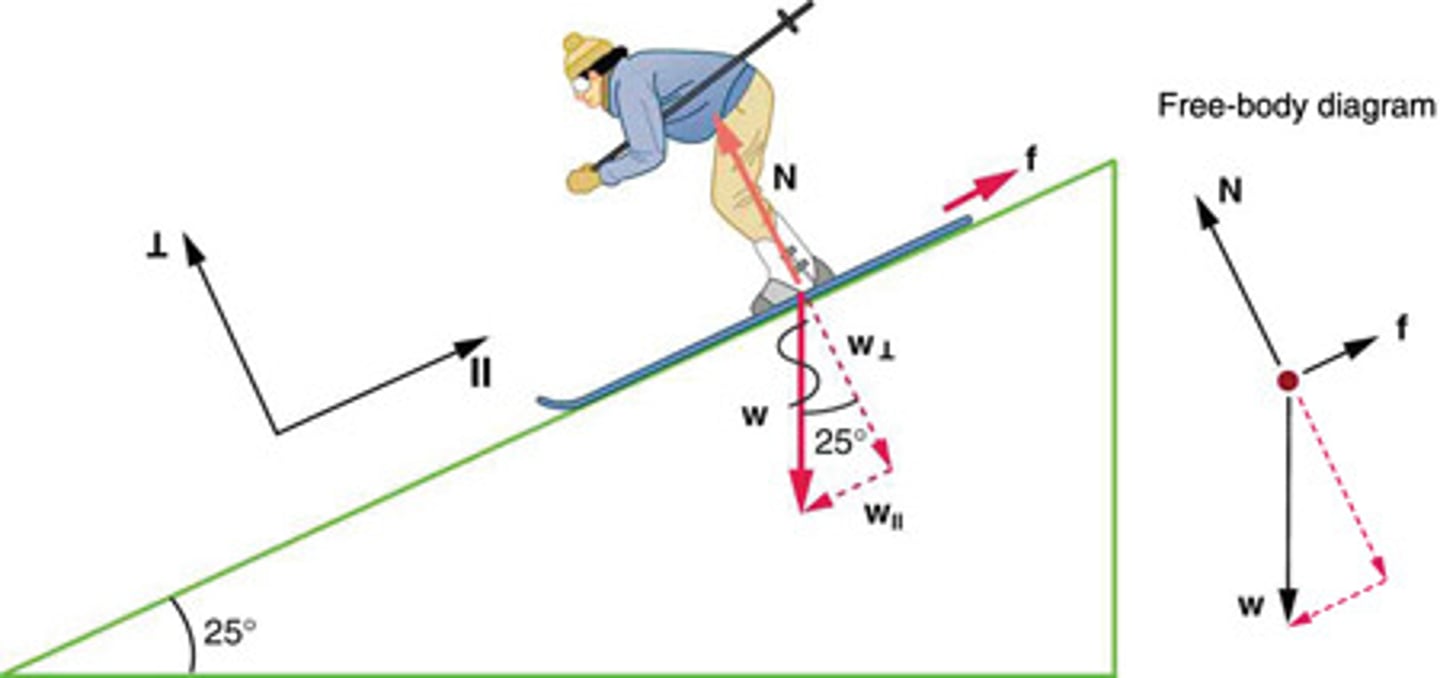
Friction Force
A force that opposes the motion of an object, acting parallel to the surface of contact.
Inertial Frame of Reference
A frame of reference in which all forces are real and Newton's laws hold in their simple forms, without fictitious forces.
Fictitious Force
A force that appears to act on a mass in a non-inertial frame of reference, such as a rotating or accelerating frame, but has no physical origin.
Real Force
A force with a physical origin, such as gravity or tension, as opposed to a fictitious force.
Newton's Laws of Motion
A set of three physical laws laid down by Isaac Newton that describe the relationship between the motion of an object and the forces acting on it.
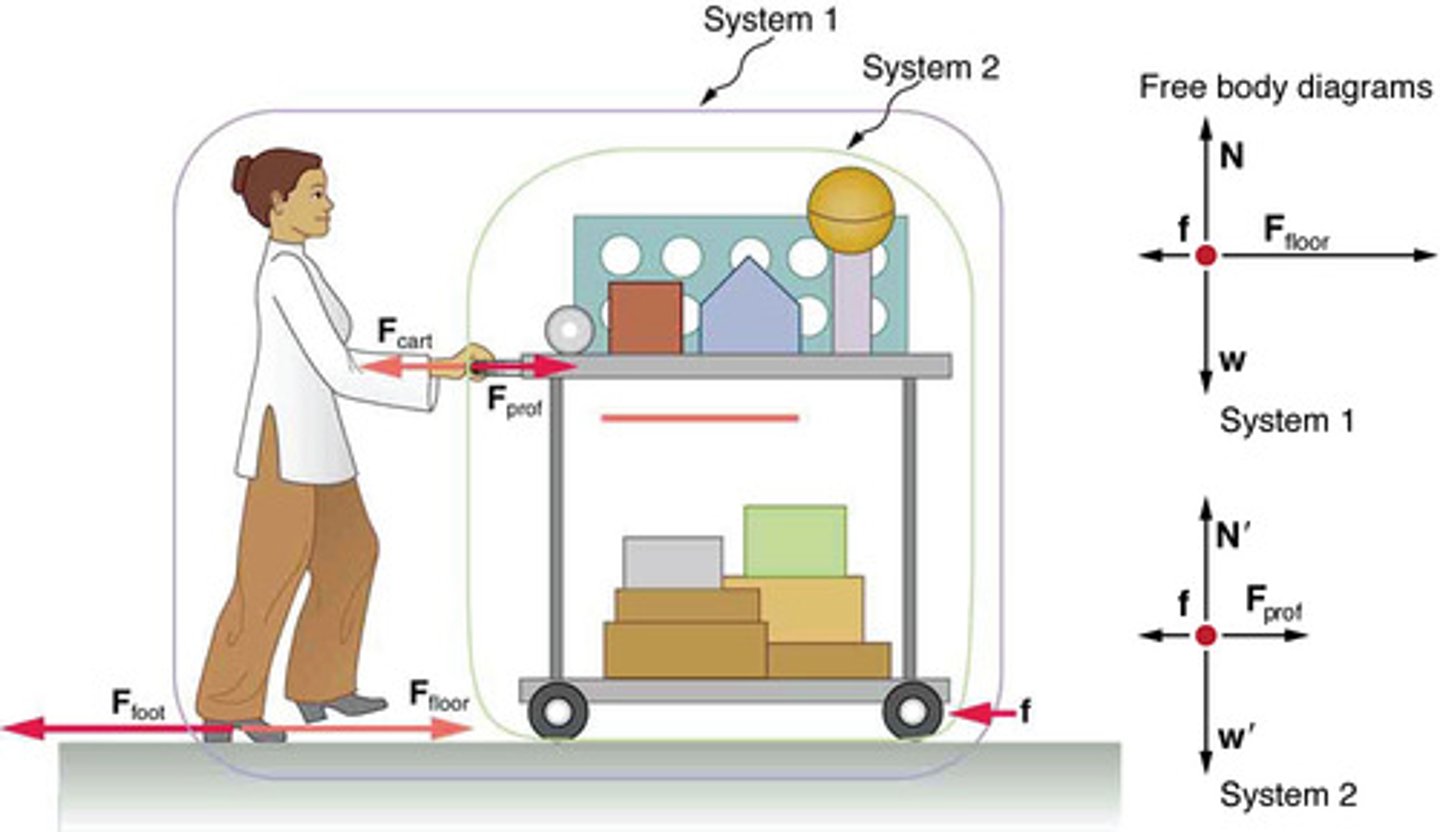
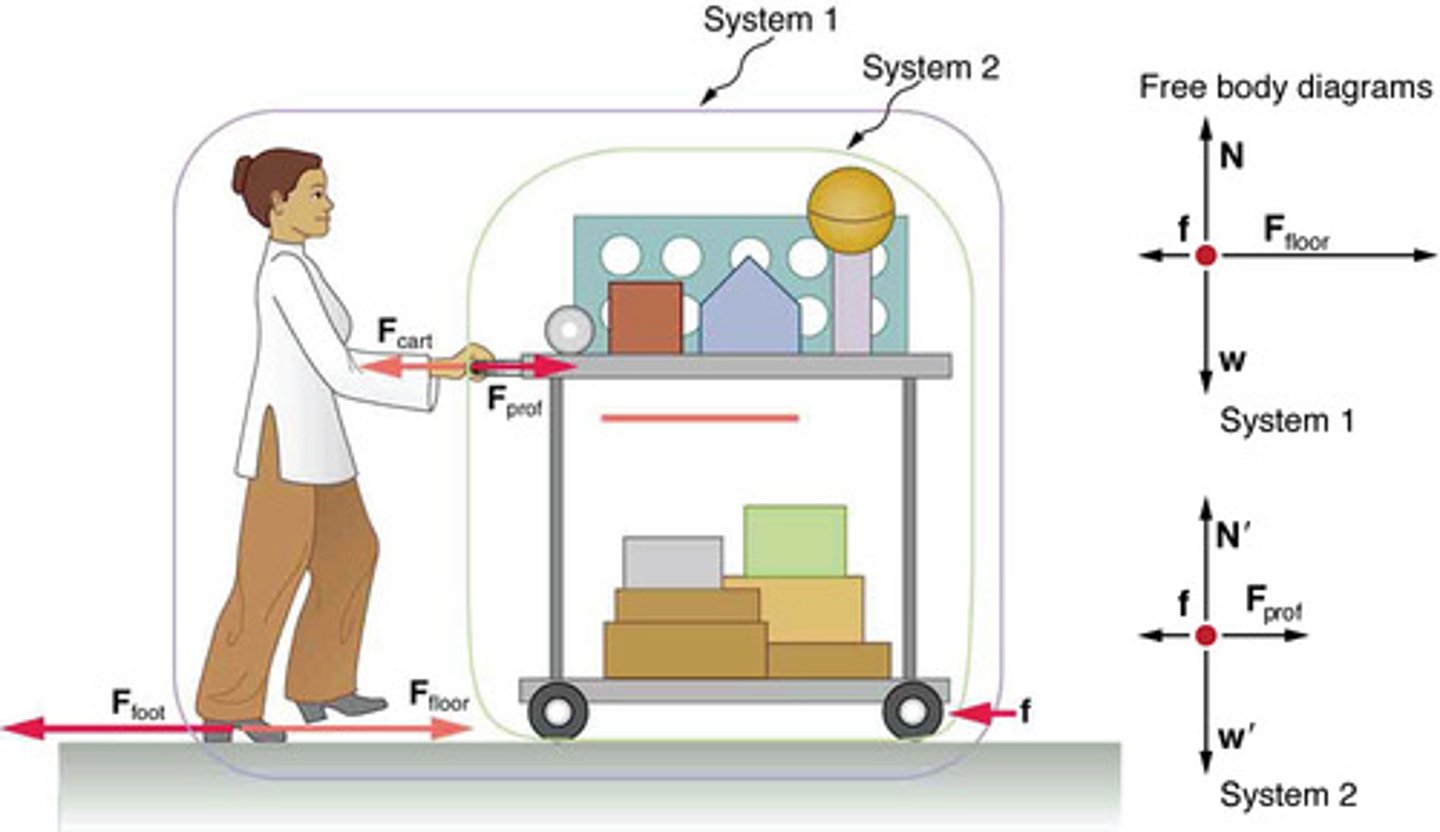
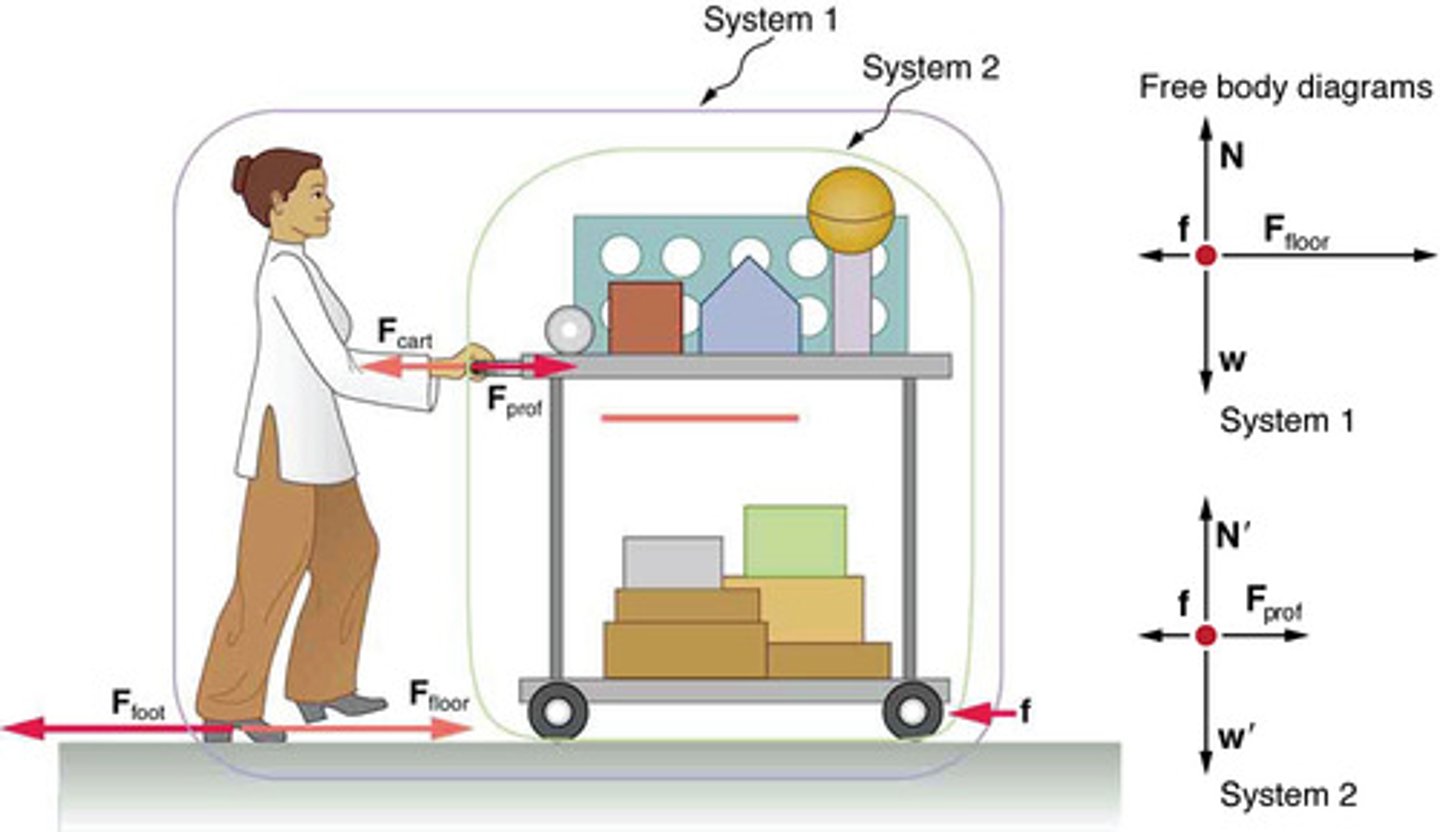
External Forces
Forces that act on a system from outside its boundary, relevant for applying Newton's second law.
Internal Forces
Forces exchanged between components within a system, not included in free-body diagrams when applying Newton's second law.
System of Interest
The specific part of a physical scenario chosen for analysis, crucial for identifying external forces in Newton's second law applications.
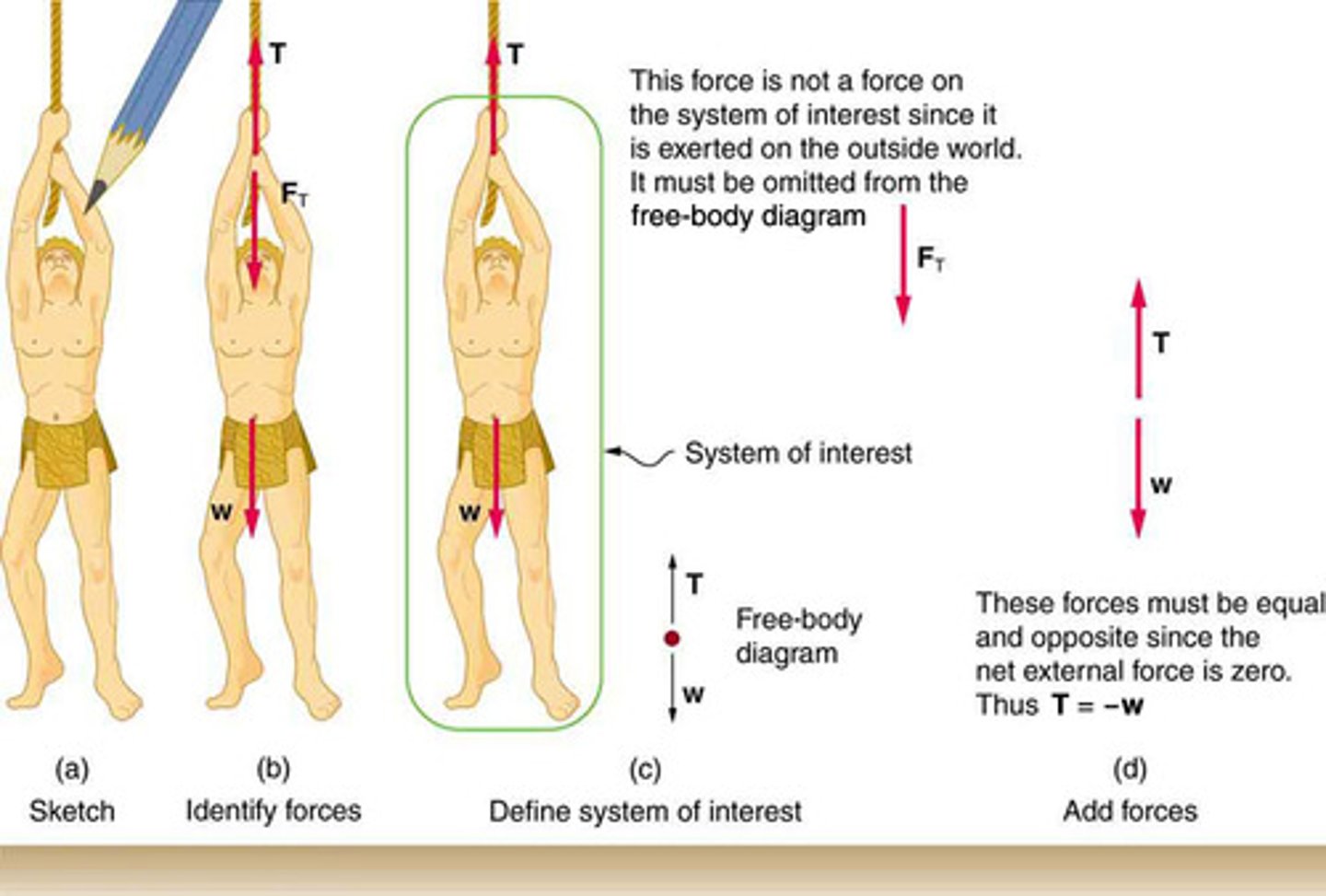
Net Force
The vector sum of all external forces acting on a system, determining the system's acceleration according to Newton's second law.
Newton's Second Law
The net force acting on an object is equal to the mass of the object multiplied by its acceleration (F = ma).
Drag Force
A frictional force exerted by fluids, such as air or water, that opposes the motion of an object.
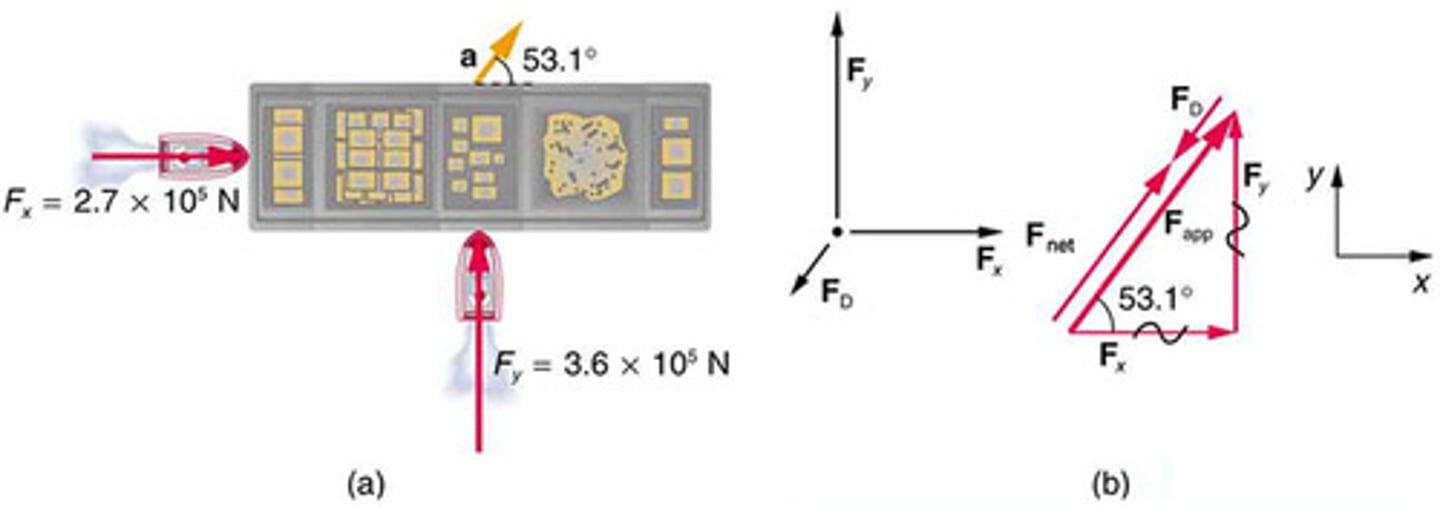
Tension
The force exerted by a rope or wire when it is used to transmit force.
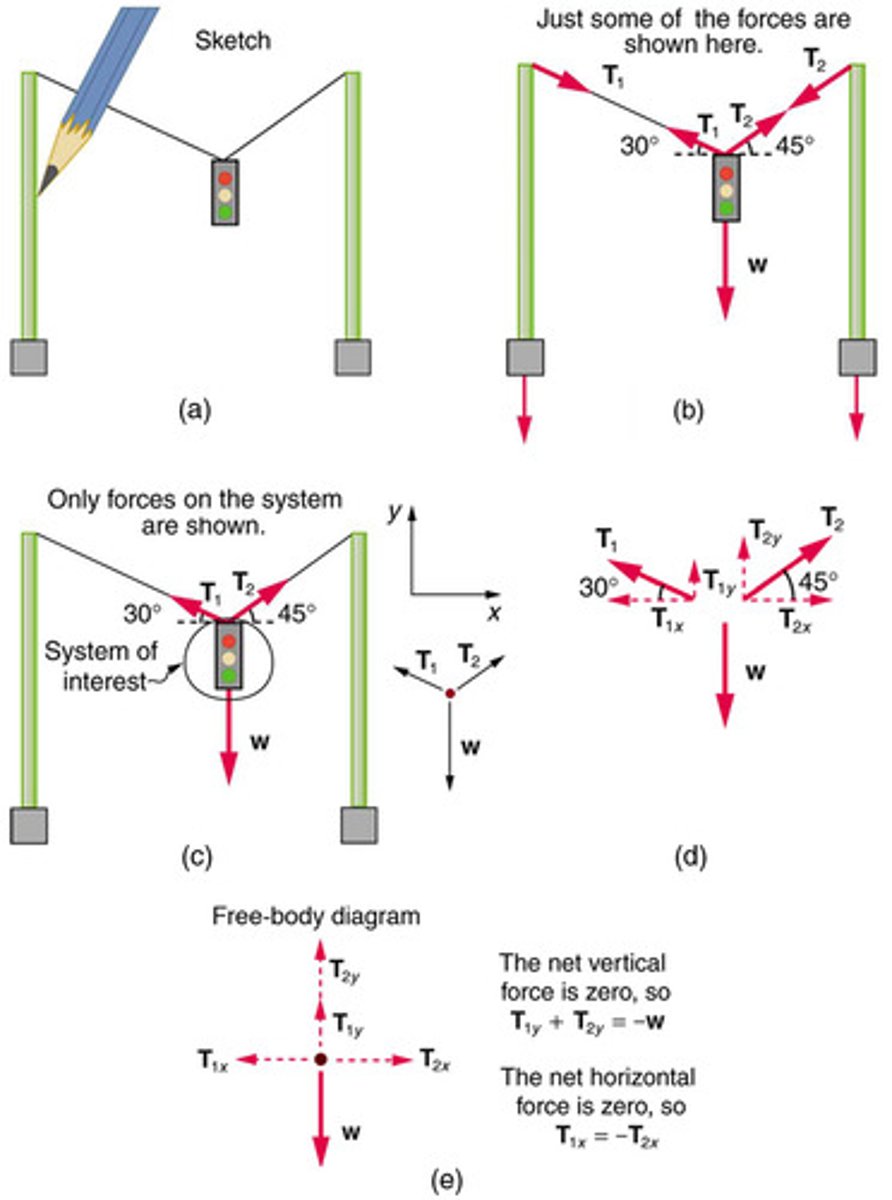
Free-Body Diagram
A graphical representation used to visualize the forces acting on an object.
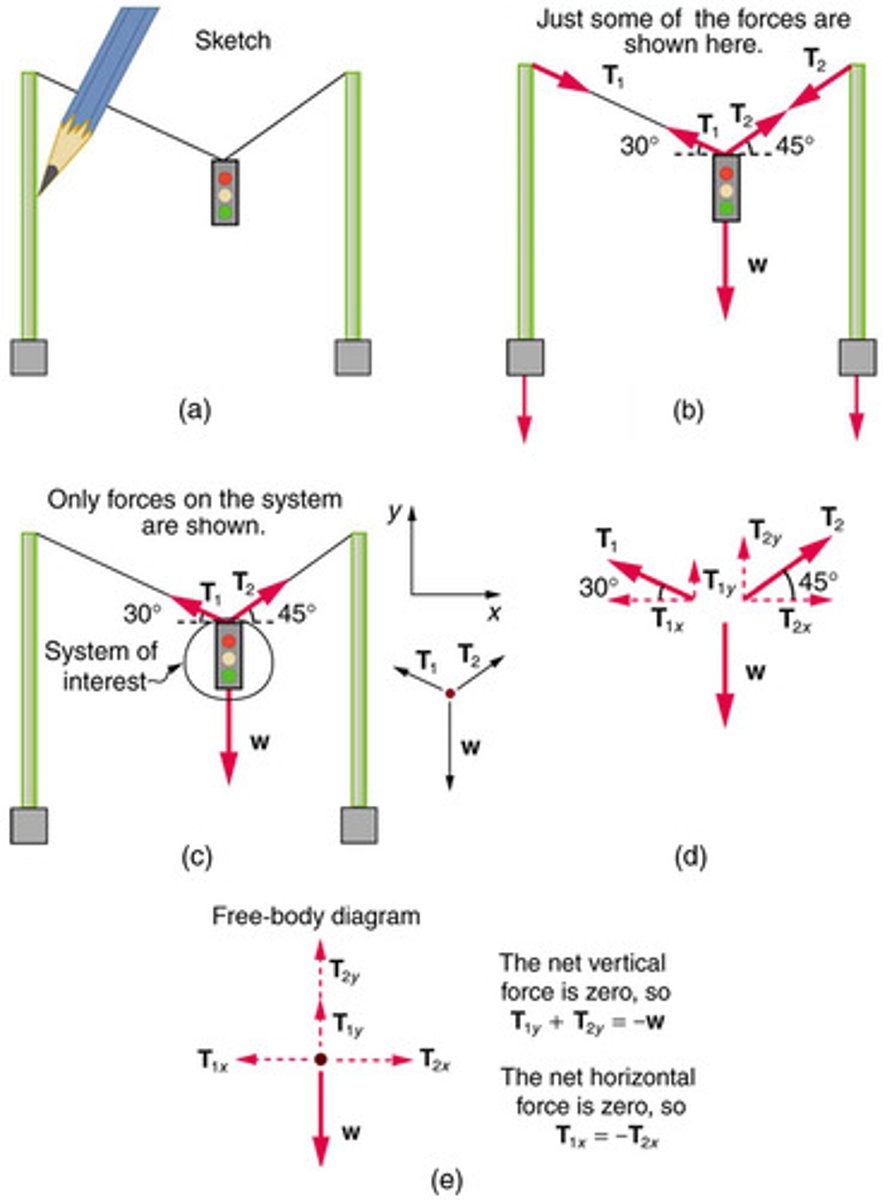
Net Force
The vector sum of all forces acting on an object.
Acceleration
The rate of change of velocity of an object with respect to time.
Normal Force
The force exerted by a surface perpendicular to the object resting on it.
Newton's Third Law
For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction.
Force
An interaction that, when unopposed, will change the motion of an object.
Weight
The force exerted on a body by gravity, calculated as the mass of the body times the acceleration due to gravity (w = mg).
Resultant Force
The single force which represents the vector sum of two or more forces acting on a point.
Friction
The resistance that one surface or object encounters when moving over another.
Vector Components
The parts of a vector that lie along the axes of a coordinate system.
Equilibrium
A state in which opposing forces or influences are balanced, resulting in no net force and no change in motion.
Newton's First Law
An object at rest stays at rest and an object in motion stays in motion with the same speed and in the same direction unless acted upon by an unbalanced force.
System of Interest
The specific object or group of objects that are being analyzed in a problem.
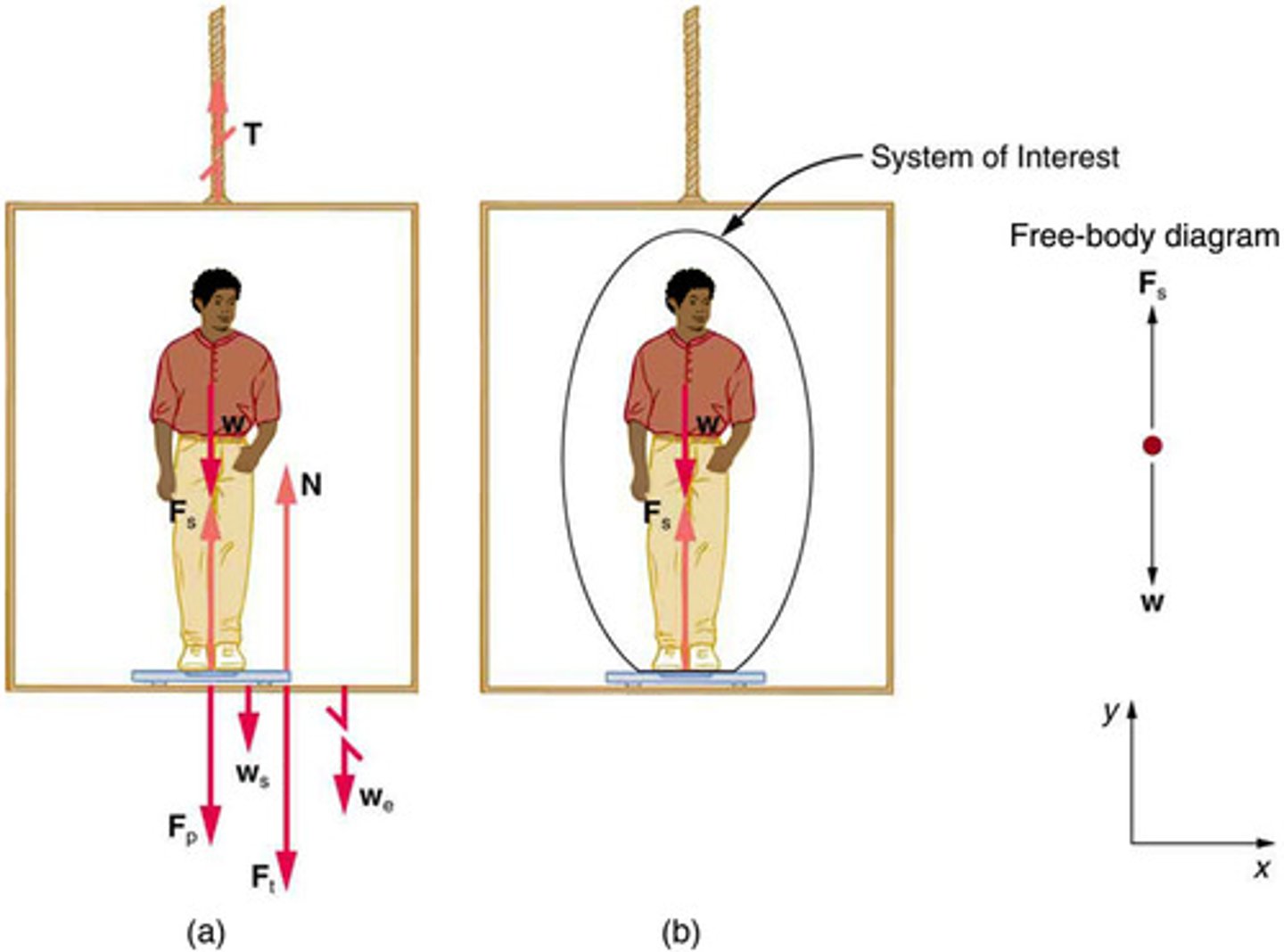
Problem-Solving Strategy
A systematic approach to solving physics problems, often involving identifying knowns and unknowns, and applying relevant principles.
Four Basic Forces
The four fundamental forces in nature are the gravitational force, electromagnetic force, weak nuclear force, and strong nuclear force.
Gravitational Force
A fundamental force that is always attractive and acts over infinite range, affecting the motion of astronomical bodies and the nature of space and time.
Electromagnetic Force
A fundamental force that can be attractive or repulsive, acts over infinite range, and is responsible for electric and magnetic interactions.
Weak Nuclear Force
A fundamental force responsible for processes like beta decay, acting over a very short range and involving W+W+, W−W−, and Z0Z0 bosons.
Strong Nuclear Force
A fundamental force that holds atomic nuclei together, acting over a short range and involving gluons as carrier particles.
Carrier Particles
Particles that mediate the fundamental forces, such as photons for electromagnetic force and gluons for strong nuclear force.
Electroweak Force
A unified force that combines electromagnetic and weak nuclear forces under conditions of extremely high density and temperature.
Force Field
A region of space around an object where a force is exerted on other objects, used to describe forces acting at a distance.
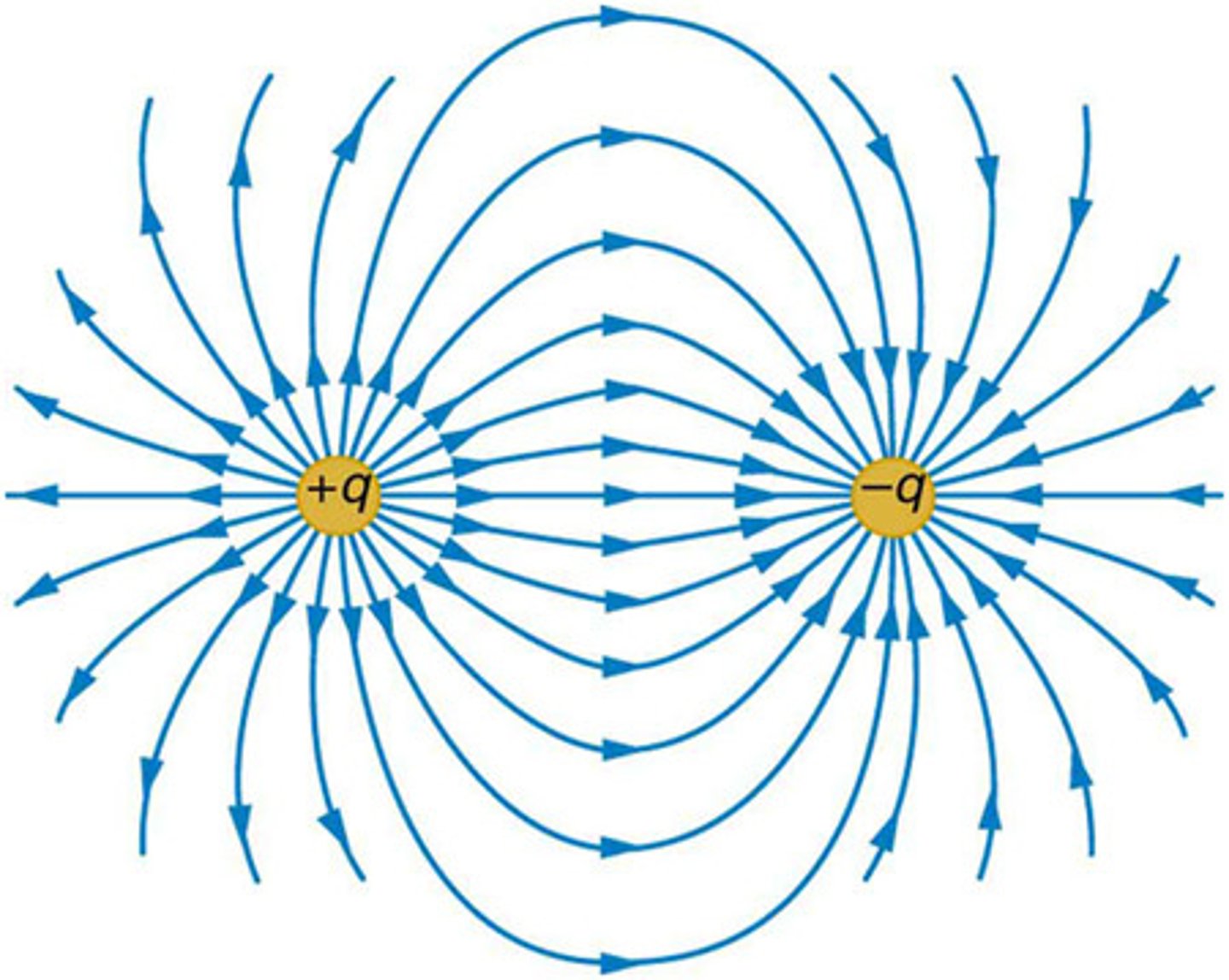
Photon
The carrier particle for the electromagnetic force.
Gluon
The carrier particle for the strong nuclear force.
Vector Bosons
Particles such as W+W+, W−W−, and Z0Z0 that mediate the weak nuclear force.
Particle Exchange
The process by which forces are transmitted between objects through the exchange of carrier particles.
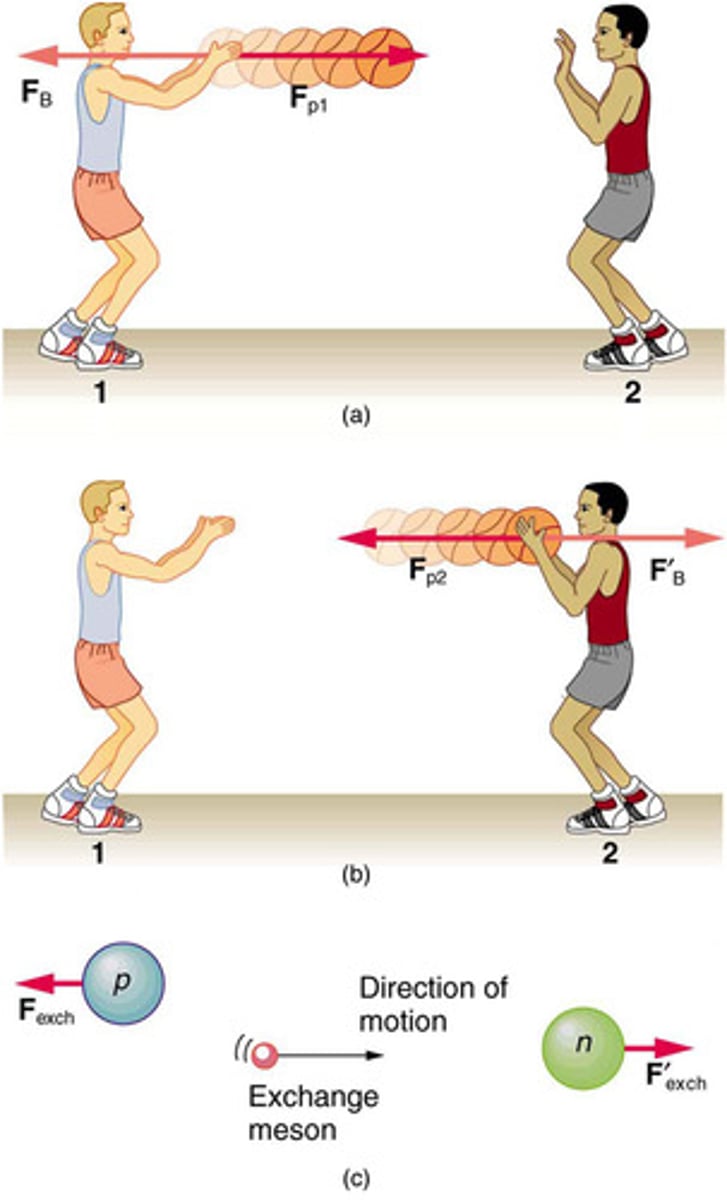
Electromagnetism
The unification of electric and magnetic forces into a single force.