Respiratory System Exam Study Guide
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/83
Last updated 1:10 AM on 1/30/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
84 Terms
1
New cards
lung cancer
What type of cancer do most people in the US die from?
2
New cards
the common cold
what is nasopharyngitis also known as?
3
New cards
an accumulation of carbon dioxide in the lungs
what causes emphysema?
4
New cards
a virus, bacterium, fungus, parasite (rare case)
what causes pneumonia?
5
New cards
tuberculosis
what does TB stand for?
6
New cards
mycobacterium tuberculosis
what causes tuberculosis (TB)?
7
New cards
boyle’s law
as the volume of a gas increases, the pressure of the gas decreases (inversely proportionate)
8
New cards
from a region of high concentration to a region of low concentration
which way along a concentration gradient does gas diffuse?
9
New cards
3
how many lobes does the right lung have?
10
New cards
2
how many lobes does the left lung have?
11
New cards
superior lobe, middle lobe, inferior lobe
what are the lobes of the right lung? (from top to bottom?
12
New cards
superior lobe, inferior lobe
what are the lobes of the left lung?
13
New cards
frontal sinus
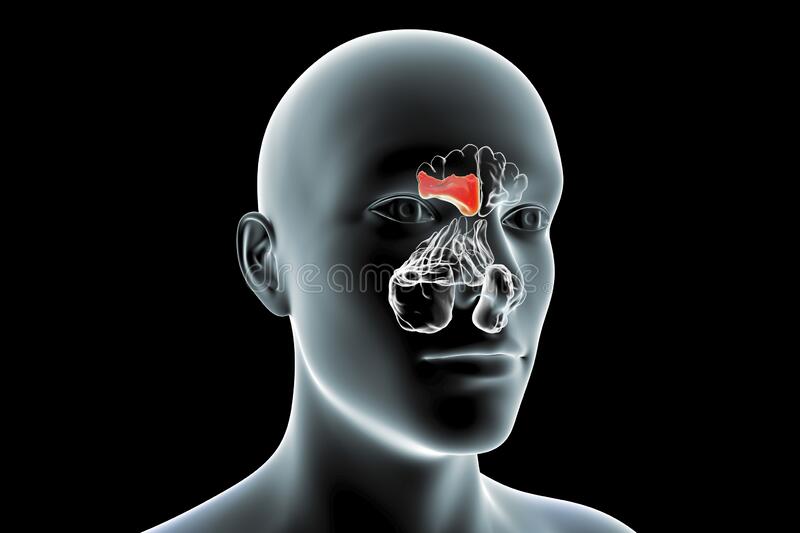
14
New cards
ethmoid sinus
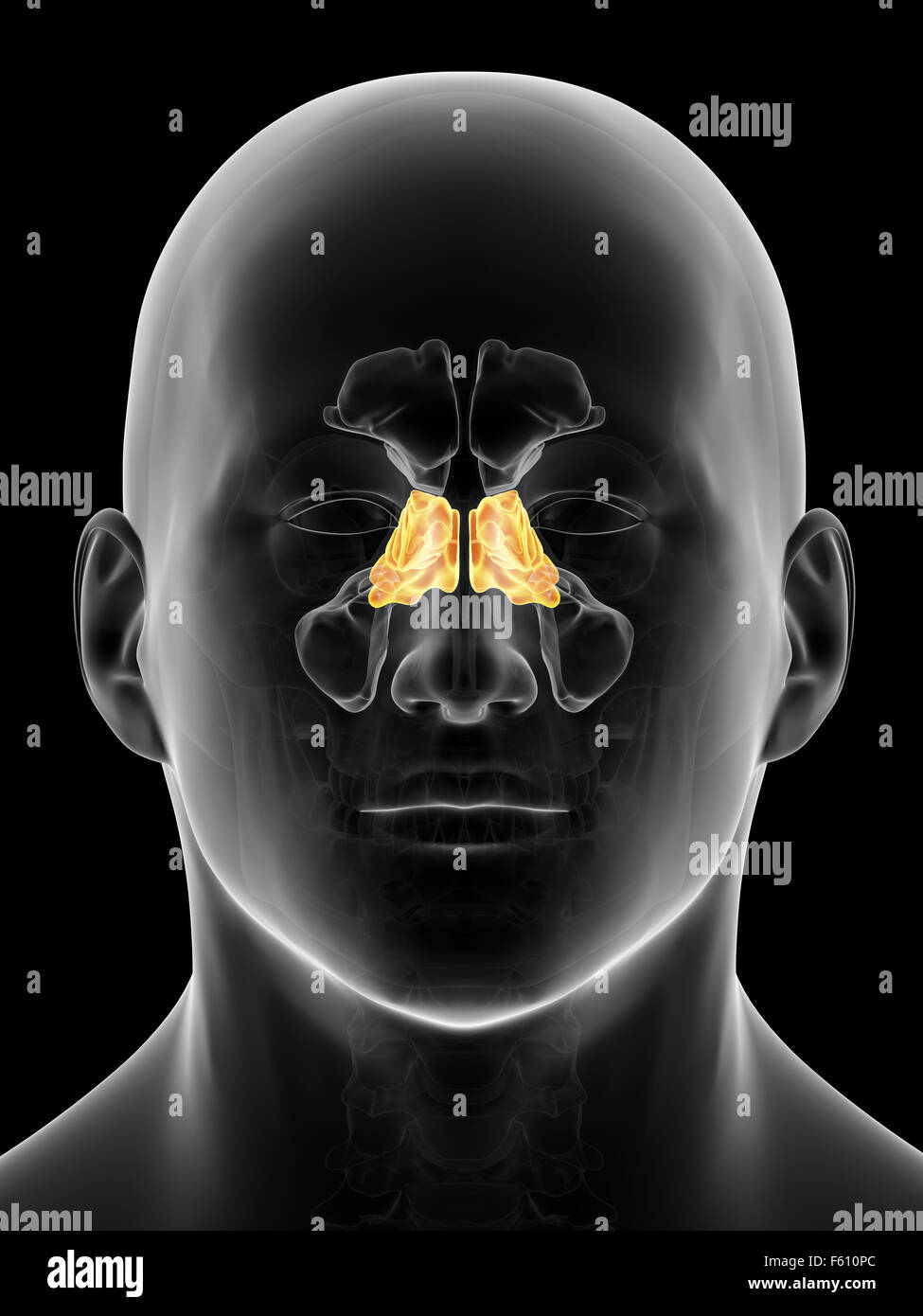
15
New cards
maxillary sinus
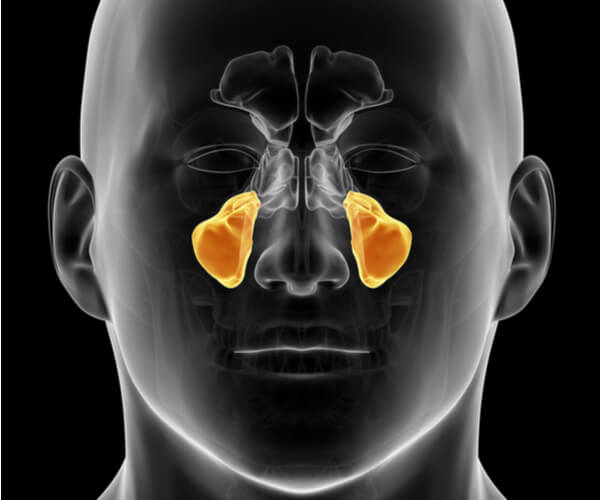
16
New cards
sphenoid sinus
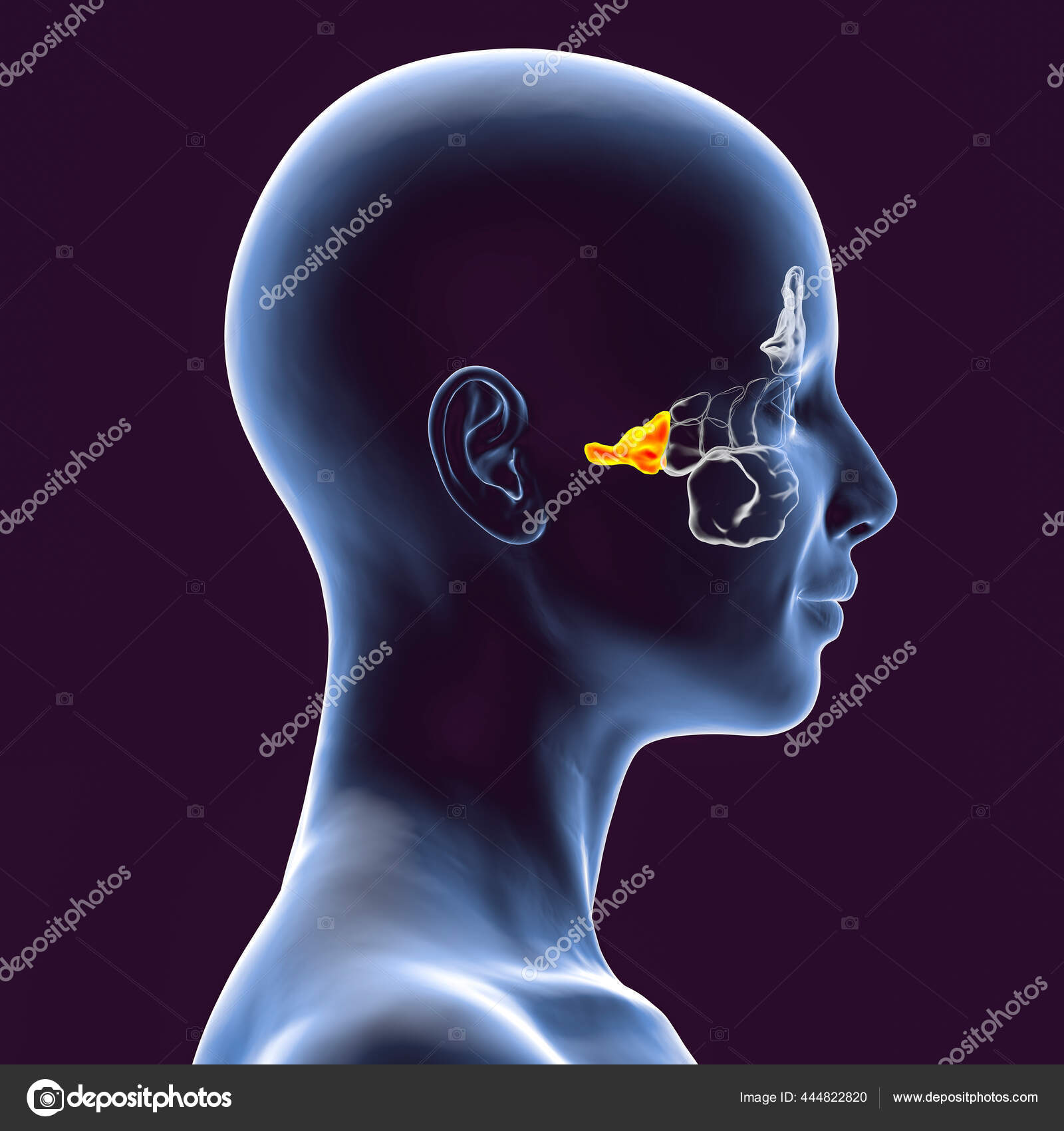
17
New cards
medulla oblongata sets breathing pace, pons coordinates transition between inspiration/expiration, stretch receptors send impulses via the vagus nerve to alert medulla to stop inspiration and begin exhalation
how is respiration controlled?
18
New cards
central chemoreceptors
monitor changes in cerebrospinal fluid pH; sensitive to carbon dioxide.
19
New cards
peripheral chemoreceptors
located in aorta and carotid arteries; are sensitive to changes in blood oxygen levels
20
New cards
peripheral chemoreceptors
stimulate respiration by sending sensory info via vagus and glossopharyngeal nerves to the brain.
21
New cards
mechanoreceptors
located in muscles and joints; detect muscle contraction and force generation during exercise
22
New cards
mechanoreceptors
stimulate quick increase in ventilation upon starting exercise
23
New cards
allergens or irritants
what causes airways to constrict during an asthma attack?
24
New cards
internal respiration
gas exchange occurs inside the body between the tissues and capillaries
25
New cards
external respiration
fresh oxygen from outside fills lungs and alveoli, allowing gas exchange between the alveoli and pulmonary blood.
26
New cards
through capillaries lining alveolar walls
where does oxygen diffuse into the blood?
27
New cards
the need to clear dust or other debris from the lower respiratory tract
what causes coughing?
28
New cards
a deep breath closing the epiglottis, then a forceful exhalation
what is the result of coughing?
29
New cards
a need to clear the upper respiratory passageways of dust or other debris
what causes sneezing?
30
New cards
the uvula closes off the oral cavity and routes air through the nose
what is the result of sneezing?
31
New cards
an irritation of the phrenic nerves that causes the diaphragm muscle to spasm
what causes hiccups?
32
New cards
sudden inspirations against the vocal cords of a closed glottis
what is the result of hiccups?
33
New cards
a need for increased oxygen in the lungs
what is the cause of yawning?
34
New cards
deep inspirations saturate the alveoli with fresh air
what is the result of yawning?
35
New cards
nares
2 openings in nose which air enters
36
New cards
olfactory receptors
sensory cells that provide the sense of smell
37
New cards
conchae
3 uneven, scroll-like nasal bones extending down from the nasal cavity
38
New cards
palate
structure made of hard and soft components separating the oral and nasal cavities
39
New cards
sinuses
air-filled cavities surrounding the nose
40
New cards
pharynx (throat)
muscular passageways extending from the nasal cavity to the mouth and connects the esophagus
41
New cards
tonsils
clusters of lymphatic tissue in the pharynx that protect against infection
42
New cards
larynx (voicebox)
triangle-shaped space inferior to the pharynx; responsible for voice production
43
New cards
epiglottis
flap of cartilaginous tissue covering the opening to the trachea; diverts food and liquids to the esophagus during swallowing
44
New cards
thyroid cartilage
the largest cartilaginous plate in the larynx; also known as the adam’s apple
45
New cards
trachea (windpipe)
air tube extending from the larynx into the thorax, where it splits into left and right bronchi
46
New cards
cartilaginous rings (c-rings)
what is the trachea supported by?
47
New cards
primary bronchi
2 passageways branching off of the trachea and lead to left and right lungs
48
New cards
bronchioles
thin-walled branches and the smallest air-conducting passageways of the bronchi
49
New cards
alveoli
air sacs in the lungs from which gas is exchanged with the capillaries
50
New cards
surfactant
a phospholipid that reduces the surface tension in the alveoli and prevents them from collapsing
51
New cards
pores of kohn
small openings in the alveolar walls that allow gasses and macrophages to travel between the alveoli
52
New cards
alveolar capillary membrane
gas exchange structure that contains the alveoli and the capillaries surrounding them
53
New cards
mediastinum
area of the thoracic cavity between the lungs; houses the heart, great blood vessels, trachea, esophagus, thoracic duct, thymus gland, and other structures
54
New cards
pleural sac
thin, doubled-walled serous membrane surrounding the lungs
55
New cards
parietal pleura
outer lining of the pleural sac
56
New cards
visceral pleura
inner lining of the pleural sac
57
New cards
pulmonary ventilation
air continuously moving in and out of the lungs
58
New cards
respiratory gas transport
when oxygen and carbon dioxide gasses in the blood are transported between the lungs and different body tissues
59
New cards
static
air volume in lungs
60
New cards
dynamic
air volume in lungs **based on time**
61
New cards
tidal volume
amount of air inhale in a single breath
62
New cards
vital capacity
amount of air that can be expired after maximal inspiration
63
New cards
forced vital capacity
amount of air that can be **forcibly** expired after maximal inspiration
64
New cards
residual volume
volume of air that never leaves the lungs
65
New cards
functional residual capacity
amount of air that remains in lungs after normal expiration
66
New cards
inspiratory reserve volume
amount of air inhaled immediately after normal inspiration
67
New cards
expiratory reserve volume
amount of air exhaled or forced from lungs immediately after normal expiration
68
New cards
total lung capacity
combination of vital capacity and residual volume
69
New cards
forced expiratory volume in one second
max amount of air a person can expire in on second
70
New cards
forced expiratory volume in one second/forced vital capacity
measures overall expiratory power of the lungs
71
New cards
pharyngitis
inflammation of the phraynx
72
New cards
sinusitis
inflammation of the sinuses
73
New cards
laryngitis
inflammation of the larynx
74
New cards
tonsillitis
inflammation of the tonsils
75
New cards
nasopharyngitis
inflammation of nasal passages and pharynx
76
New cards
influenza
a viral infection that affects the respiratory system
77
New cards
acute bronchitis
temporary inflammation of mucous membranes that line the trachea and bronchial passageways, causes a cough that may produce mucous
78
New cards
pneumonia
infection of the lungs that causes inflammation; caused by virus, bacterium, fungus, or in rare cases, a parasite
79
New cards
tuberculosis
highly contagious bacterial infection caused by mycobacterium tuberculosis
80
New cards
chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
any lung disorder characterized by a long-term airway obstruction, making it difficult to breathe
81
New cards
emphysema
chronic inflammation of the lungs characterized by an abnormal increase in the air spaces near the bronchioles; causes an accumulation of carbon dioxide in the lungs
82
New cards
chronic bronchitis
long-lasting respiratory condition in which the airways of the lungs become obstructed due to inflammation of the bronchi and excessive mucous production
83
New cards
hyperventilation
excessive ventilation that leads to abnormal expulsion of carbon dioxide
84
New cards
bronchospasms
spasmodic contractions of the bronchial muscles that constrict airways in the lungs