Bio 102 Unit 5 Exam Flashcards
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
Karyotype
an image of a person’s DNA wrapped into chromosomes.
Which spot contains the chromosome determining sex?
Spot 23 contains genes related to the person’s biological sex.
What are body cells called?
Somatic Cells
What are Autosomal chromosomes?
Non-sex chromosomes (1-22)
What are Gamete Cells?
Reproductive Cells (Sperm & Eggs)
Contain half as many chromosomes as somatic cells
**Also called Haploid Cells**
What happens when two Haploid cells join during Fertilization?
The chromosome number is restored.
**AKA Diploid Cells**
Diploid (__)
Haploid (__)
*How many sets of chromosomes does each cell type have? (in terms of n)
Diploid (2n)
Haploid (n)
Find the Diploid number for each Adult:
Human: n=23 : ___
Onion: n=8 : ___
Cow: n=30 : ___
Human: 46
Onion: 16
Cow: 60
Haploid or Diploid Transitions:
Mitosis: Diploid → _____
Meiosis: Diploid → _____
Fertilization: Haploid → _____
Mitosis: Diploid → Diploid (2n → 2n)
*Number doesn’t change due to DNA replication
Meiosis: Diploid → Haploid (2n → n)
*Cuts chromosome number in half for gamete production Fertilization: Haploid → Diploid (n → 2n)
*Sperm and Egg fuse to create full set of chromosomes in offspring
What is Sexual Reproduction?
One set of DNA from the mother and one from the father join together.
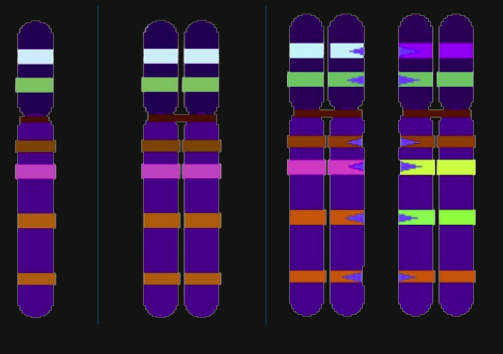
Name these 3 Chromosome types
Chromatid, Sister Chromatids, Homologous Chromosomes
What are Homologous Chromosomes?
Carriers of same variations of genes, either being from the Mother or Father (for traits)
*Ex. Eye Color
What are the 3 Stages of Meiosis?
Interphase, Meiosis 1, Meiosis 2
What happens during Interphase in Meiosis?
DNA is replicated to form sister chromatids
What happens during Meiosis 1 in Meiosis?
Homologous Chromosomes separate
What happens during Meiosis 2 in Meiosis?
Sister Chromatids separate
An _____ trait tends to spread more _____ through a sexually reproducing population than through an asexually reproducing one.
An Adaptive trait tends to spread more quickly through a sexually reproducing population than through an asexually reproducing one.
Asexual reproduction produces genetically _______ _____ of a parent
Asexual reproduction produces genetically identical copies of a parent
*Clones
What is Random Assortment?
Chromosomes go into different cells randomly
What is “Crossing Over”?
Homologous Chromosomes swap genes during Prophase 1.
What are the 3 Errors of Meiosis?
Situations where the chromosomes fail to separate during Meiosis
Gametes potentially ending up with an uneven number of chromosomes
Fertilization with these gametes leads to offspring with extra or missing chromosomes
What is Heredity?
The way genetic information is passed from parents to offspring.
What is a Gene?
A section of DNA that codes for a single trait.
What is an Allele?
A version of a gene.
Ex.
Gene: Eye Color
Allele: Blue, Green, Hazel, Brown
What makes an Allele Dominant?
If the effect masks the effect of a recessive allele paired with it, it is Dominant.
Homozygous - _____ Alleles for a Trait
Heterozygous - _____ Alleles for a Trait
Homozygous - Same Alleles for a Trait
Heterozygous - Different Alleles for a Trait
What is a Genotype?
Direct genetic Make-up (Alleles)
What is a Phenotype?
The physical trait (Appearance)
What is a Pedigree?
A chart that shows how individuals are related, and shows how traits are passed down in a family.
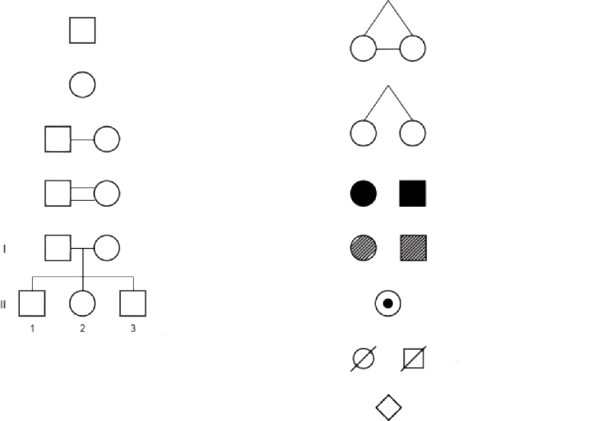
Name as many Symbols as possible on this Pedigree
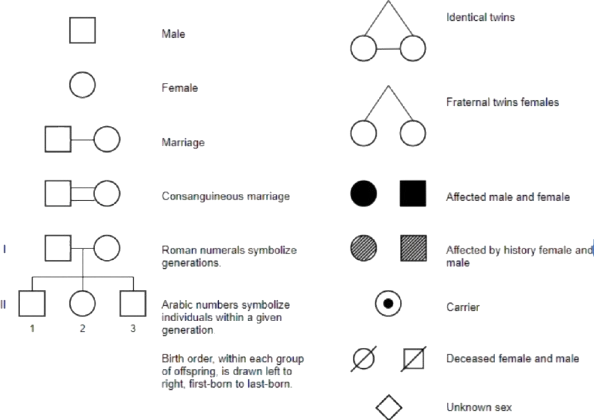
Male
Female
Marriage
Consanguineous marriage
Identical Twins
Fraternal Twins (females)
Affected male and female
Affected by history female and male
Carrier, Deceased female and male
Unknown sex
Roman numerals symbolize generations.
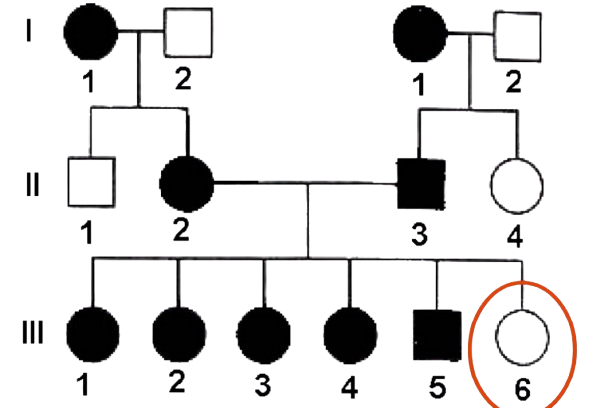
Write as much as possible about the Circled Individual
Tracked Trait is Freckles (Dominant)
Female, Homozygous Recessive, Youngest Sibling
What is the Law of Segregation?
Alleles for the same gene that separate during Meiosis
What is Mendel’s Parent (P) Generation?
When Mendel crossed two homozygous plants.
(One Dominant, One Recessive)
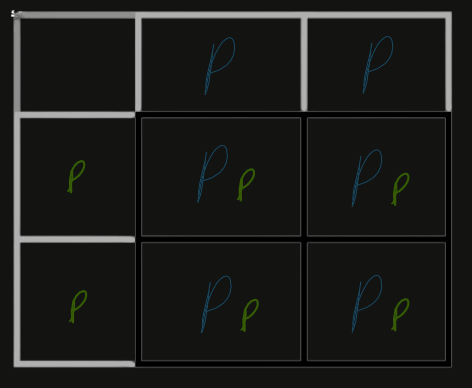
What was Mendel’s F1 Generation?
The product of the Parent generation, where all plants were Heterozygous.
What was Mendel’s F2 Generation?
When Mendel crossed two plants from the (heterozygous) F1 Generation, producing a single single Recessive Phenotype (White).
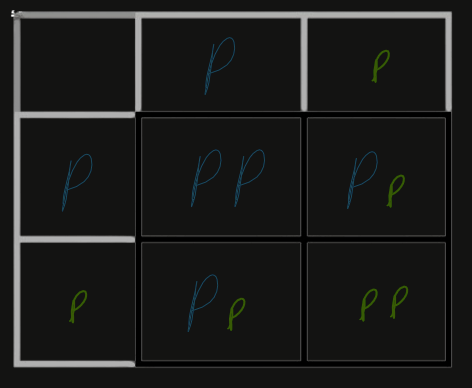
What does a Monohybrid Trait mean?
1 Gene with 2 Alleles.
Ex. Mendel’s Generation Testing
What is the Loci?
The location on a chromosome where one gene exists.
What is the Y Chromosome? What does it have?
A small chromosome with 70-100 Genes.
Contains the SRY gene with codes for Male development.
If mutation present on SRY gene, embryo develops Female genitalia, despite having the Male chromosome.
What is the X Chromosome? What does it have?
A large chromosome with 900-2000 genes.
Involved in various biological processes.
All humans need at least 1 X chromosome to survive.
How is Sex-linked inheritance different from normal Monohybrid problems?
In Sex-linked inheritance, the letter is placed on the Chromosomes to distinguish how X-linked traits are passed down in Males vs. Females.
Normal Monohybrid problems use single letters to symbolize one gene.
Gene B is an X-linked gene that is involved with normal color vision. The recessive allele (b) causes red/green colorblindness. What possible offspring genotypes could result from a mother who is Heterozygous and a father who is Hemizygous Dominant?
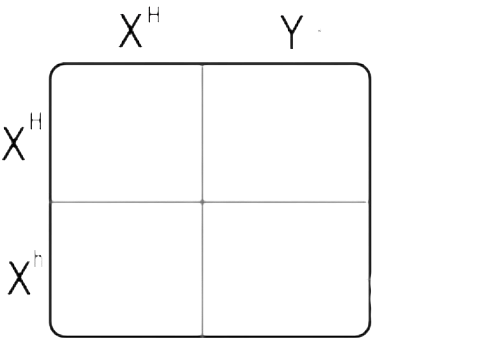
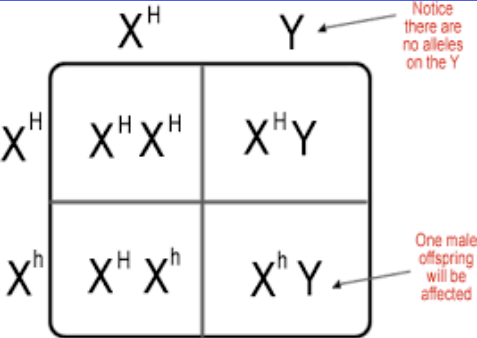
What is the Law of Independent Assortment?
Genes are sorted into gametes independently of other genes.
What are Dihybrid Experiments?
Testcrosses that check for a dominant relationship between multiple alleles for two traits.

In peas, a round shape is dominant (R), and wrinkly is recessive (r). Yellow color is dominant (Y) and green is recessive (y).
Cross two pea plants that are heterozygous for BOTH traits.
*Equation for basic understanding of calculating percentage in Dihybrid Models
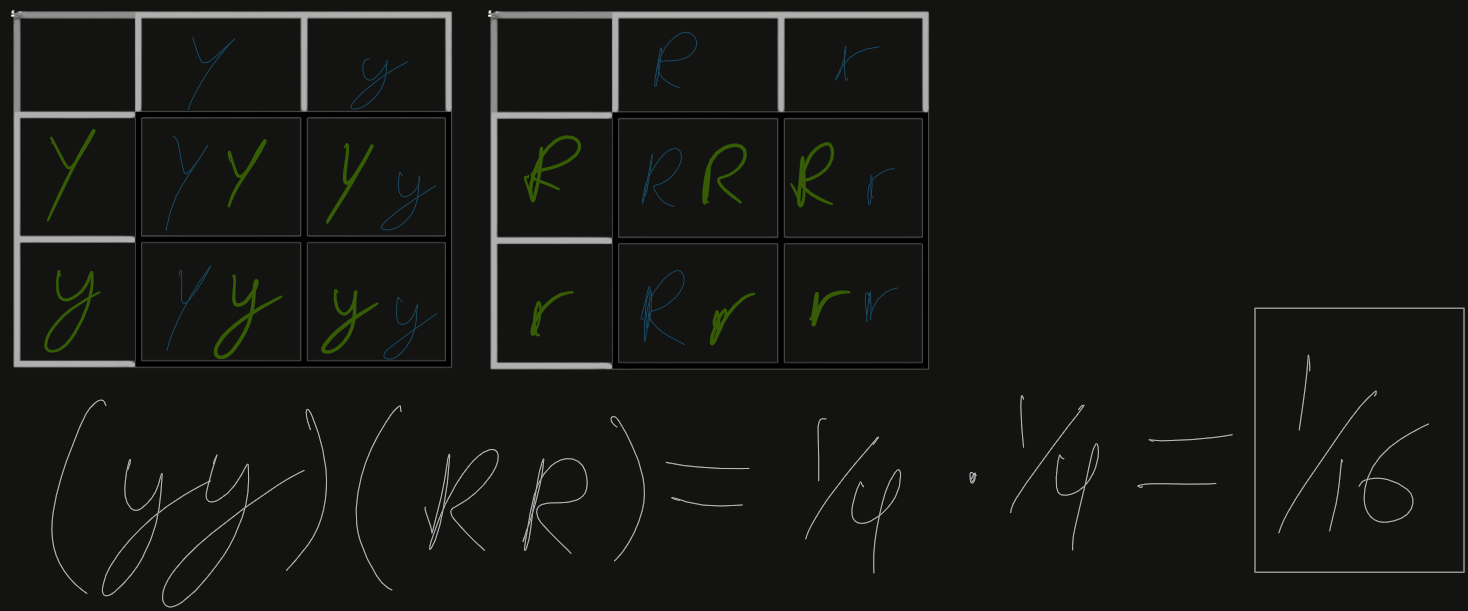
What is Codominance?
When Two nonidentical alleles of a gene are both fully expressed in heterozygotes, so neither is dominant or recessive.
*May occur in multiple allele systems
What is Incomplete Dominance?
When one allele is not fully dominant over its partner.
A blending of alleles can occur in heterozygotes.
What is Pleiotropy?
One gene product influences two or more traits.
Ex. Agouti gene in mice. causes BOTH yellow color and obesity.
What are Polygenic Traits?
When a gene involves more than one controlling gene for a single trait.
Ex. Eye color, Skin Color