Circadian Rhythms and Sleep Mechanisms
1/39
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards based on key concepts related to circadian rhythms, sleep mechanisms, and sleep disorders.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
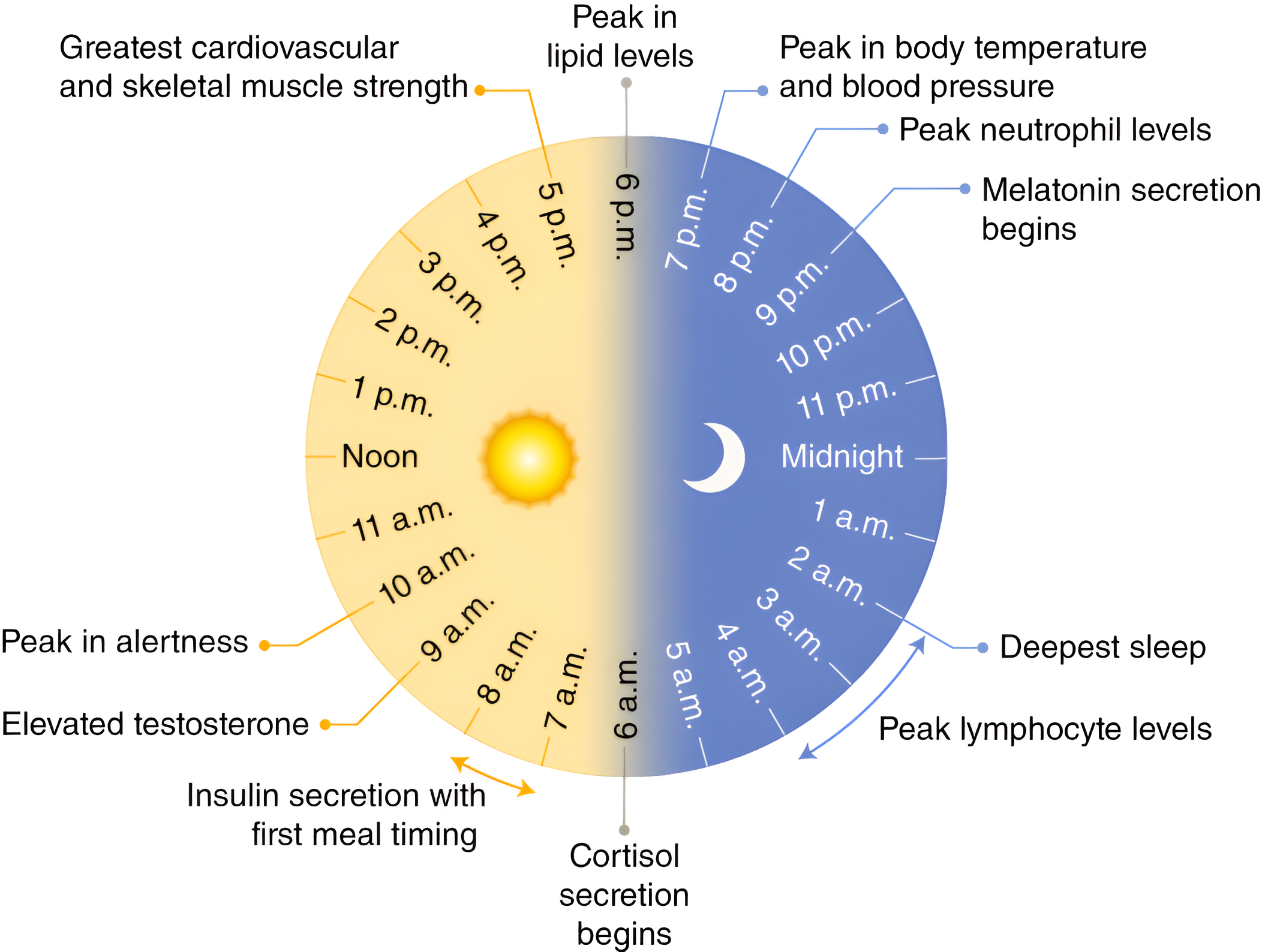
Circadian Rhythm
The body's natural 24-hour clock that regulates the sleep-wake cycle.
Endogenous Rhythms
Rhythms generated internally, such as the circadian and circannual rhythms.
Zeitgeber
A stimulus that resets the biological clock; German for "time-giver."
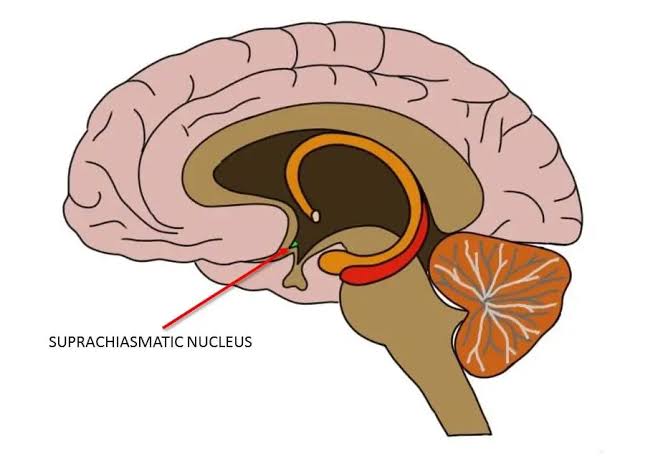
Suprachiasmatic Nucleus (SCN)
A cluster of neurons in the hypothalamus that regulates circadian rhythms.
Melatonin
A hormone released by the pineal gland that regulates sleep-wake cycles.
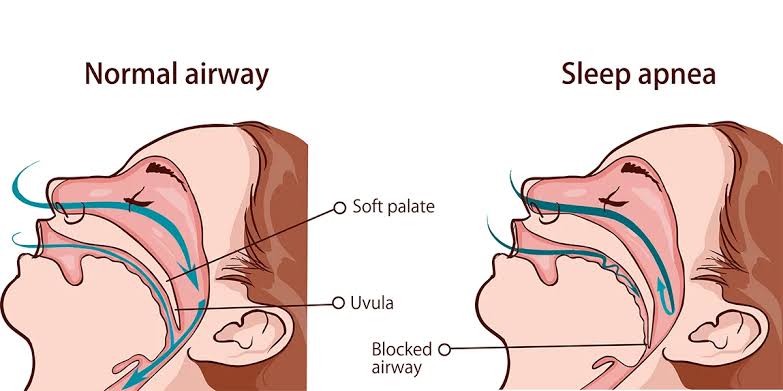
Sleep Apnea
A sleep disorder characterized by pauses in breathing or instances of shallow breathing during sleep.
Insomnia
The most common sleep disorder, characterized by difficulty falling or staying asleep.
REM Sleep
A sleep stage where most dreaming occurs, characterized by rapid eye movement and increased brain activity.
Lucid Dreaming
A state where a person is aware they are dreaming while still asleep.
Night Terrors
Intense episodes of fear during sleep, usually occurring during NREM sleep.
Pineal Gland
A gland that secretes melatonin and helps regulate sleep patterns.
Arousal
A state of being awake and alert, regulated by the reticular formation.
Coma
Extended unconsciousness due to trauma or disease, with low brain activity.
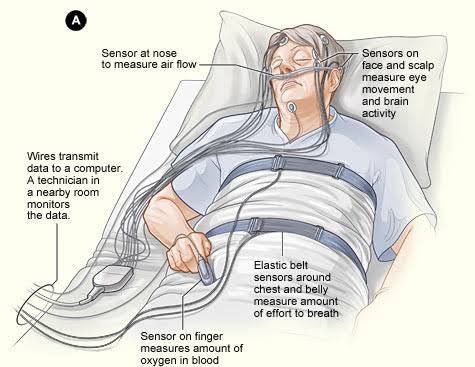
Polysomnography
A combination of EEG and eye-movement records used to track sleep stages.
GABA
A neurotransmitter that inhibits neuron activity, playing a key role in promoting sleep.
Periodic Limb Movement Disorder
A sleep disorder characterized by involuntary limb movement during sleep.
Sleep Paralysis
A temporary inability to move or speak while falling asleep or waking up.
Activation-Synthesis Hypothesis
A theory that dreams result from the brain's attempt to make sense of random neural activity.
Neurocognitive Hypothesis
A theory that dreams are spontaneous thoughts occurring during reduced sensory input.
Hibernation
A prolonged state of dormancy that reduces metabolism and conserves energy.
PGO (Post-Geniculate-Occipital waves)
burst of electrical activity that occurs during REM sleep and is linked to dream imagery.
Narcolepsy
a condition characterized by frequent periods of sleepiness during the day.
Melatonin
Regulates sleep/wake cycle, Controls puberty onset, Affects seasonal changes
Vegetative State
Alternates between sleep and moderate arousal, No awareness or purposeful behavior, Autonomic responses
Brain Death
No brain activity or response to any stimulus, Confirmed after 24 hours of no brain activity, Ethical to remove life support after brain death is confirmed
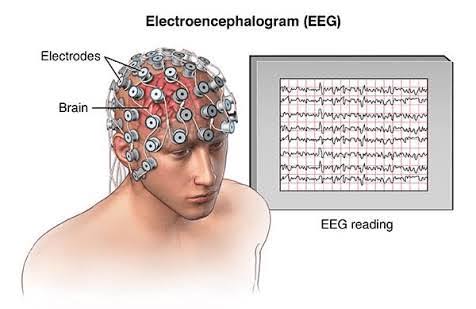
Electroencephalograph (EEG)
Measures brain electrical activity by recording potentials from cells and fibers near the scalp.
Pontomesencephalon
located between the pons and midbrain a part of the reticular formation that plays the central role of controlling alertness and arousal.
Neurotransmitter Orexin
What cause is related to Narcolepsy?
NREM Sleep
Does Periodic Limb Movement Disorder happen during REM or NREM sleep?
REM Behaviour Disorder
It’s when people apparently act on their dreams during their REM periods.
Night Terrors
It’s a case of sleep disorder more severe than a nightmare.
Sleep sex or sexsomnia
an analogous condition of sleepwalking
Hippocampus
part of the brain does learning experiences replay during sleep
Neurocognitive hypothesis
a theory that sees dreams as thought-like activity influenced by memory, emotions, and visual imagery during sleep
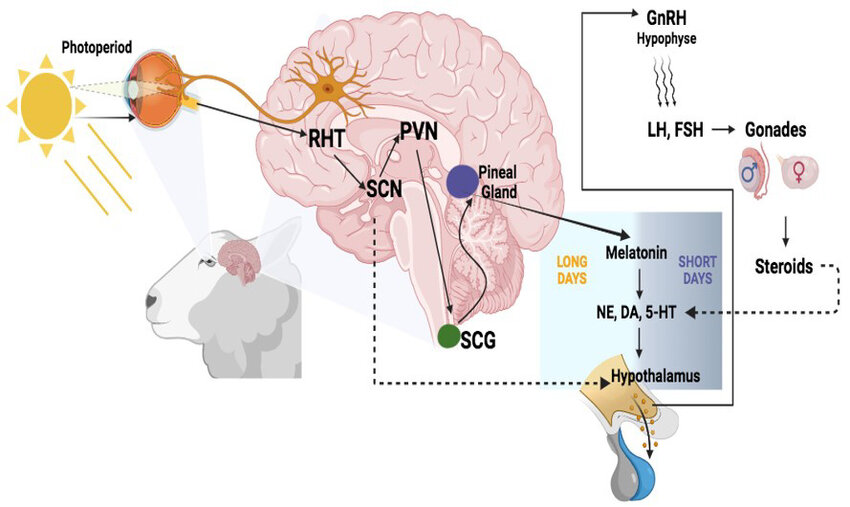
Retinohypothalamic path
A special pathway to give information about light to SCN from the retina.
Period (PER) and Timeless (TIM)
The two specific genes that control sleep-wake cycle
Morning Person or Lark
A type of person who reaches their peak early and becomes less alert later in the day.
As people age, REM and the total sleep decrease, and one theory suggests that REM helps oxygenate the corneas by moving the eyes during sleep.
How do REM and NREM sleep change with age, and what is one theory about REM sleep’s function?
Random brainstem signals interpreted by the cortex.
What explains why we dream of flying or being paralyzed during sleep based on brain activity patterns?
Sleep
Actively produced by the brain, Characterized by decreased activity and response to stimuli