Final Questions BIO 430
1/71
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Yeyah
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
A fluorescence cube has
all of these
A 515 nm dichroic mirror
Reflects light below 515 nm, transmits above 515 nm
What is the Stoke's Shift?
The energy difference between the absorbed light and the emitted light
Which is NOT a kind of fluorescence microscopy?
Darkfield
What is super-resolution fluorescence microscopy?
microscopy able to bypass the limit of resolution imposed by point spread functions
Photobleaching should be ____ because it ____ the signal and may ____ the sample through production of _____. The best way to achieve this is by ____
avoided / quenches / harm / reactive oxygen species / keeping the fluorescence shutter closed while not actively imaging
Match the components of epifluorescence microscopy (LEFT) to the component of transmitted light microscopy (RIGHT) that has the same/similar function.
Fluorescence shutter -
Covering the light source with the black piece of metal/cardboard (blocks the source of light without turning it on or off)
Match the components of epifluorescence microscopy (LEFT) to the component of transmitted light microscopy (RIGHT) that has the same/similar function.
Field shutter -
Field iris/stop (closing this reveals a polygon)
Match the components of epifluorescence microscopy (LEFT) to the component of transmitted light microscopy (RIGHT) that has the same/similar function.
Dichroic mirror -
No equivalent in transmitted light microscopy
Match the components of epifluorescence microscopy (LEFT) to the component of transmitted light microscopy (RIGHT) that has the same/similar function.
No equivalent in epifluorescence microscopy -
Focusable/adjustable condenser
Match the components of epifluorescence microscopy (LEFT) to the component of transmitted light microscopy (RIGHT) that has the same/similar function.
Aperture shutter -
Condenser aperture (increasing/decreasing the amount of light let through to the sample)
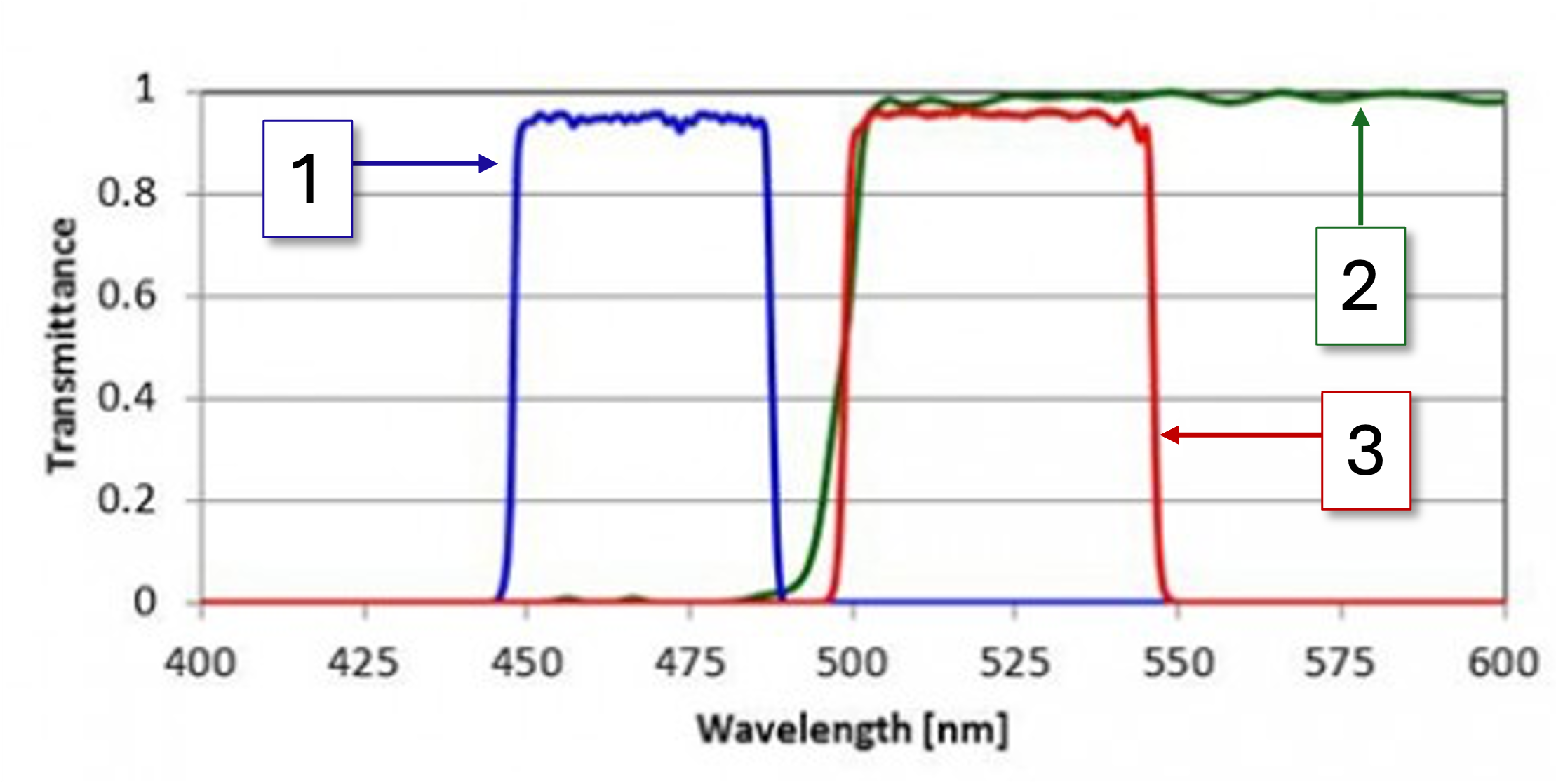
1
Bandpass excitation (light filtered by the excitation filter)
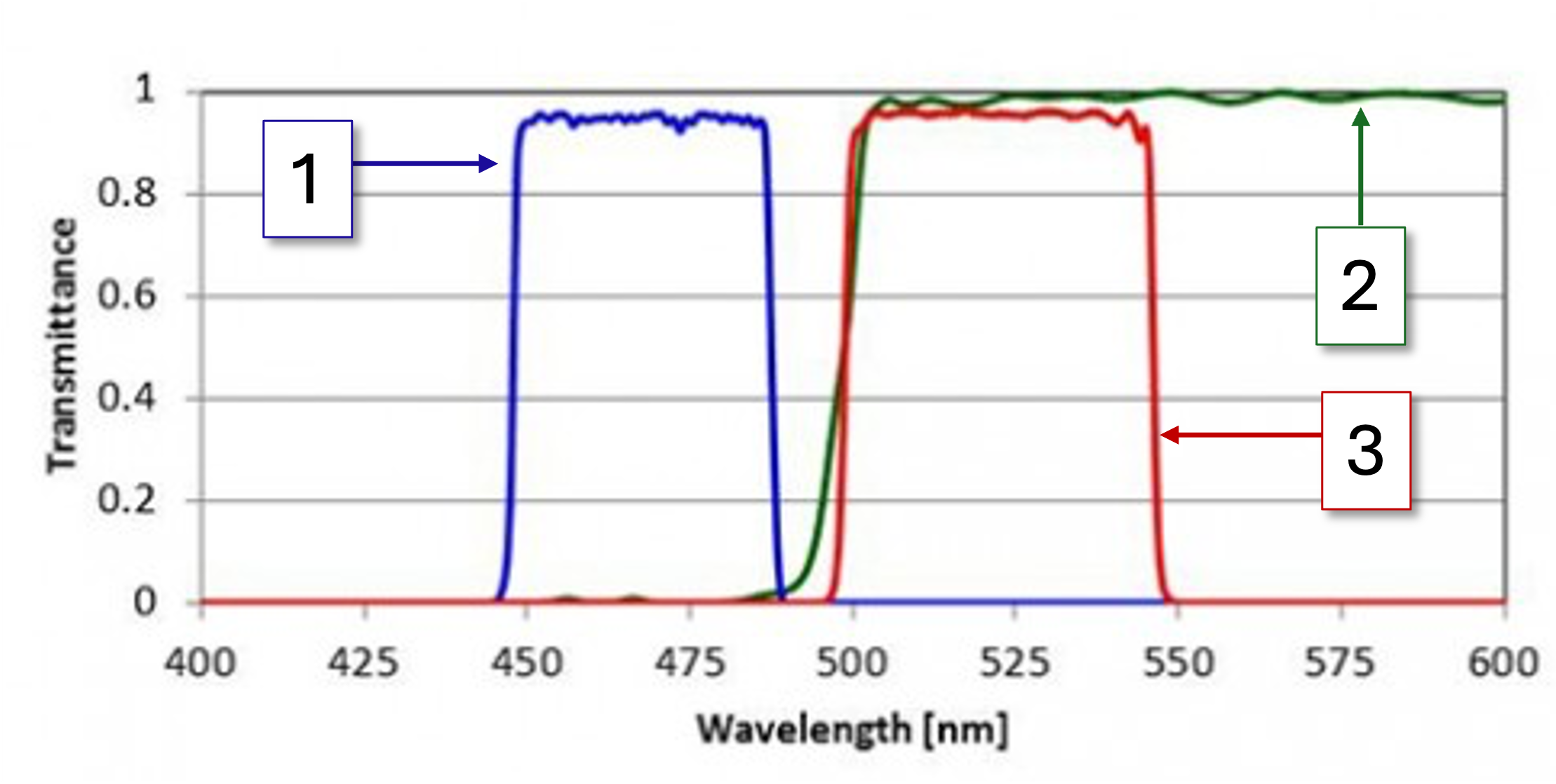
2
Light that the dichroic mirror transmits
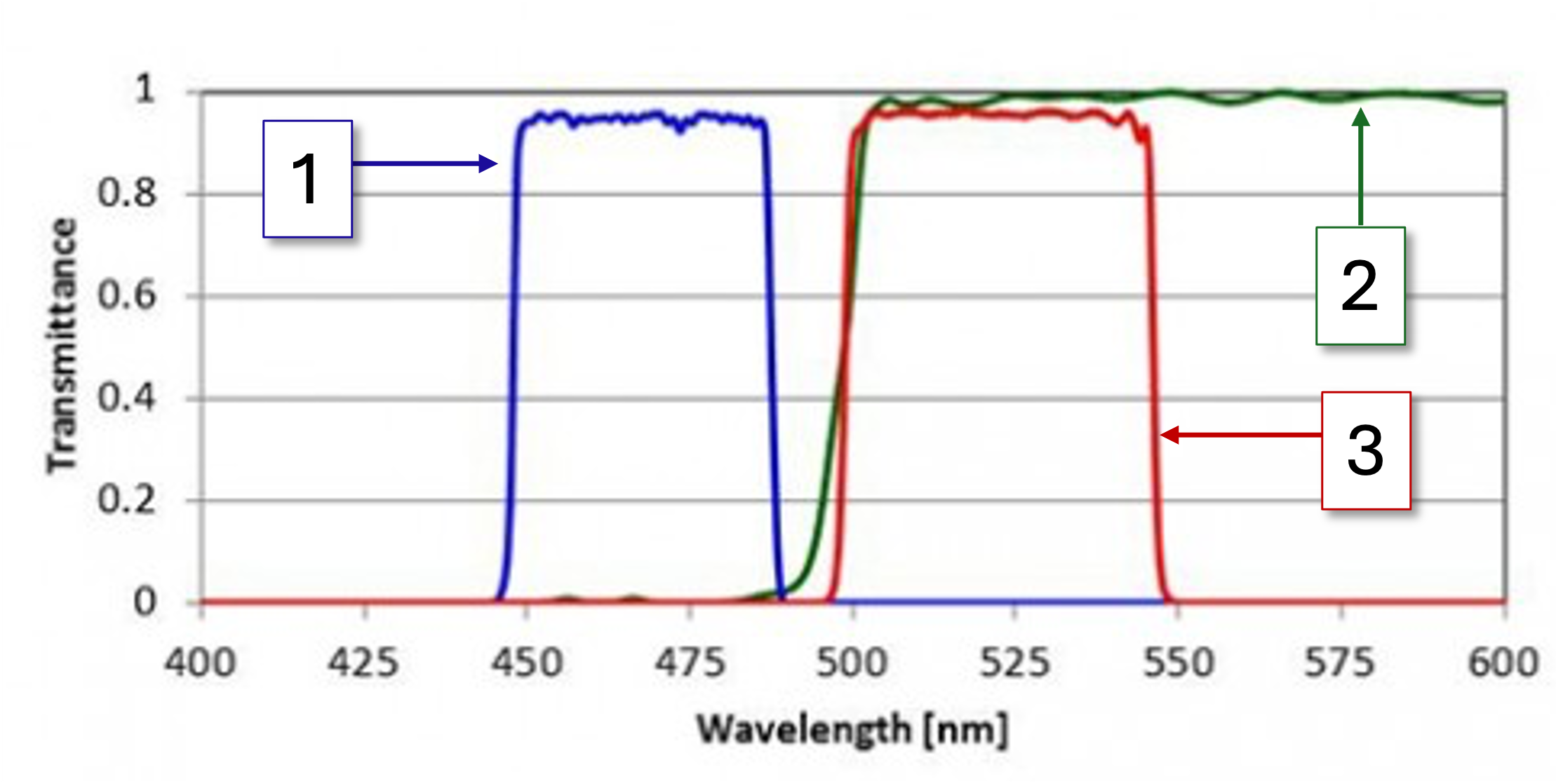
3
Bandpass emission (light filtered by the emission filter)
Which fluorescent protein would you use this cube to image?
GFP
What would we call this cube in the lab?
blue cube
The exposure on a scanner that uses a point source (laser) for illumination is its
dwell time (µs)
What does FRET stand for?
Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer
Which of the following is NOT correct?
both CCD chips and PMTs can detect multiple colors
What is the main difference between a wide field epi-fluorescent microscope and a laser scanning confocal fluorescence microscope?
confocal has a pinhole, wide field does not
Confocal microscopes are always superior to wide field microscopes.
True
For two fluorophores to be an efficient FRET pair
The emission spectrum of the donor must overlap with the excitation spectrum of the acceptor
What is a benefit of FRET and ratio imaging?
It can correct for varying fluorescent protein expression levels
What is the purpose of the pinhole?
It blocks out-of-focus light from reaching the detector
Why can you use cameras on spinning disk confocal microscopes, but not on laser scanning confocal microscopes?
There are multiple simultaneous raster scans produced by the array of holes in the spinning disks that move quickly enough to be integrated in a single exposure on a camera.
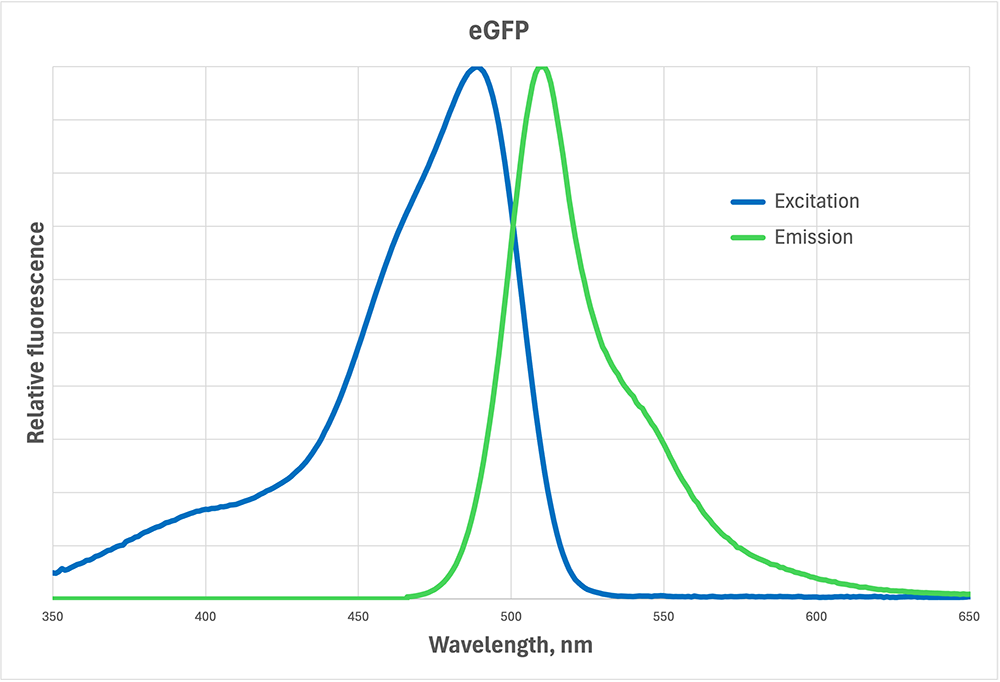
You are setting up an experiment and you need to stain peroxisomes with fluorescent dye BODIPY. Below is the excitation/emission spectrum of BODIPY (it is the same as eGFP). Of the following, which fluorescent cube should you use to image the peroxisomes?
Ex BP 450-465, DM 500, Em BP 510-530
You have a fluorescent sample that you need to image. Your sample is S. cerevisiae that expresses the membrane-bound protein Reveillie tagged with sGFP (sGFP-Rev). sGFP fluoresces blue when Rev is ubiquitinated and yellow when it is not. Rev helps protect the cell against infection, so when the cell is not fighting infection, Rev is continuously ubiquitinated for degradation. When the cell becomes infected, ubiquitination stops so that Reveillie can protect the cell from the bad guys.
You want to determine how long it takes for Rev to be at the concentration necessary to effectively protect the cell. What do you do?
Confocal - add bacteria to my cell culture, immediately take a long video, then ratio blue to yellow fluorescence over time
Which of the following is technically not superresolution but is still often picked over laser scanning confocal microscopy due to its super low out-of-focus fluorescence?
Multiphoton microscopy
Which is NOT a kind of superresolution you saw as part of the demo on Thursday? (Or at least were supposed to see...)
BBG (Blur-be-gone)
Light microscopy is limited by diffraction because:
all of these
What is FLIM good for?
All of these
You have a sample that you need to use superresolution fluorescent microscopy to image. Your sample is an Arabidopsis seedling that expresses ER-YFP (ER = endoplasmic reticulum). YFP is highly sensitive to photons. The average diameter of an ER body is 180 nm. You want to image the ER bodies in the vascular tissue (4 cell layers deep) and how they change with development of new xylem, which takes 6 to 12 hours.
Which form of microscopy would you use?
Lattice light sheet microscopy
ProteinA-GFP dimerizes when cytosolic calcium concentrations are 50 nM or above and moves slowly through the cytoplasm via cytoplasmic streaming. When calcium levels are below 50 nM, ProteinA-GFP is a monomer and moves quickly through the cytoplasm via diffusion. ProteinA-GFP fluoresces 500-520nm no matter what the concentration of calcium is, but takes longer to fluoresce as a dimer.
You want to use ProteinA-GFP to investigate how long it takes to change cytosolic calcium levels from 120 nM to 25 nM in carrot cells. Which kind of microscopy/technique would you NOT use?
Fluorescence switching
What is the smallest thing that can be imaged by electron microscopes?
atoms
What is the force that focuses electrons onto the sample?
Lorentz Law
The resolution of transmission electron microscopy is not diffraction limited, but it is limited mainly by
lens aberrations
Which does NOT limit the resolution of a scanning electron microscope?
backscattered electrons
Which kind of light microscopy is SEM most similar to?
Epi-illuminated stereomicroscopy
What is the function of the metal rings of increasing voltage in the field emission source? What is the function of the condenser magnetic lenses?
The field emission source rings positively accelerate the electrons; the condenser lens focuses the electrons onto the sample
Select all imaging modalities that use raster-based imaging.
Laser scanning confocal microscopy
STED
STEM
SEM
Why are there two cameras on transmission electron microscopes?
One is for viewing the sample while setting it up, one is to take a final images. This is to protect the CMOS chip from a misaligned electron beam.
Setting up an electron microscopy for proper imaging has a lot of steps. Of the following, which step would result in the most resolution loss ("worst image") if it were skipped?
vacuuming the sample chamber
What does SEM stand for?
Scanning electron microscopy
Information about the elemental composition of a sample can be obtained using backscattered electrons and X-rays in SEM, but only under which conditions?
The sample is uncoated
Proper dehydration, particularly through critical point drying, is crucial for SEM sample preparation. If a sample were not critically point dried and instead just air-dried for the same amount of time, what issue could arise during imaging?
Evaporation from the surface of the sample would occur, interfering with image acquisition.
Which method does NOT allow for 3D imaging in SEM?
Freeze substitute dehydration
Which organism is often imaged with scanning electron microscopes due to its tolerance to low pressure?
Tardigrades
What is the primary reason for properly fixing samples for electron microscopy?
To maintain the structural integrity of the sample
Which of the following is NOT a necessary step in preparing a sample for high res imaging in vacuum with SEM?
Sectioning
In TEM, if atoms from element A scatter electrons at a larger angle than atoms from element B, what would an area of element A look like relative to areas of element B?
darker
How can contrast be improved in TEM samples?
by staining them with heavy metals
You have use electron microscopy when you want to image something less than 200nm since that is the diffraction-limited resolution of light microscopes.
False
Gel is spread over the skin before an ultrasound to ensure good imaging and resolution. Which quality of the gel and the skin have to match in order for this to happen?
Acoustic impedance
What is Anna Ludwig credited with saying when she saw the first ever x-ray of her hand taken in 1895?
Now I have seen my death
Regarding the ability to penetrate different tissue types, which statement is most accurate when comparing CT and ultrasound?
CT excels at penetrating bone and dense tissues, while ultrasound is limited by bone and air.
In computed tomography, what is the pixel?
the readout from the scintillator-photodiode sensor
Which quality of the sound wave does doppler scanning measure?
frequency
What is an x-ray?
all of these
CT scanning in a medical unit is done from multiple angles, rotating around the patient. Plotting the 1D transmitted intensities as a function of angle of acquisition produces a
sinogram
Which of the following physical principles is most fundamental to the creation of a CT image?
Differential attenuation of X-ray photons by various tissues
You want to capture one CT scan of a zebrafish embryo every day for 7 days to see the surface of different organs developing. Which kind of CT scanning would you use?
Industrial micro-CT scanning with soft x-rays
What is an ultrasound wave?
can be created by a piezoelectric transducer (PZT)
What does fMRI do?
measures brain activity based on blood oxygen levels and blood flow
T2 relaxation is
all of these
The time between RF pulses is the
the TR, or repetition time
Referring to the MRI demo at the TIPS center: What did the scan of the pineapple look like?
The T1 and T2 scans looked similar with both showings details of the pineapple, but had relatively low contrast, and only the center of the pineapple being bright in the T2 scan due to its high water content.
Why is the hydrogen nucleus, the protein, used for most MRI?
All of these
Which kind of ultrasound was NOT demonstrated at the TIPS center?
concave mid-frequency, shallow tissue penetration, large area
Why is carbon 12 not used for MRI?
the spins of the protons and neutrons cancel each other out
T1 relaxation is
the change in energy based on spin up to spin down orientation ratio
About how much does a 3 Tesla MRI machine cost?
3 million dollars
Gradient coils are used to
provide the x-, y-, and z- readout of the spatial frequencies of the voxels