Pathology FINAL
1/235
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
236 Terms
Congenital Disease
present at birth and comes from genetic/environmental factors
Hereditary Disease
genetically transmitted from either parent to child
Inflammatory Disease
results from the body's reaction to localized injurious agent
Degenerative Disease
deterioration of the body
Metabolic Disease
caused by a disturbance of the normal physiological function
Traumatic Disease
result from mechanical forces
Example of Traumatic Disease
crushing or twisting of bone
ionizing radiation
Neoplastic Disease
results in new, abnormal tissue growth
Difference between sarcoma and carcinoma
Carcinoma- derives from epithelial tissue
Sarcoma- derives from connective tissue
CHAPTER 2
The adult skeletal system has how many bones?
206
More than ...% of the body's total is calcium
98
How much % is phosphorus in the skeletal system?
75
Axial Skeleton consists of how many bones?
80
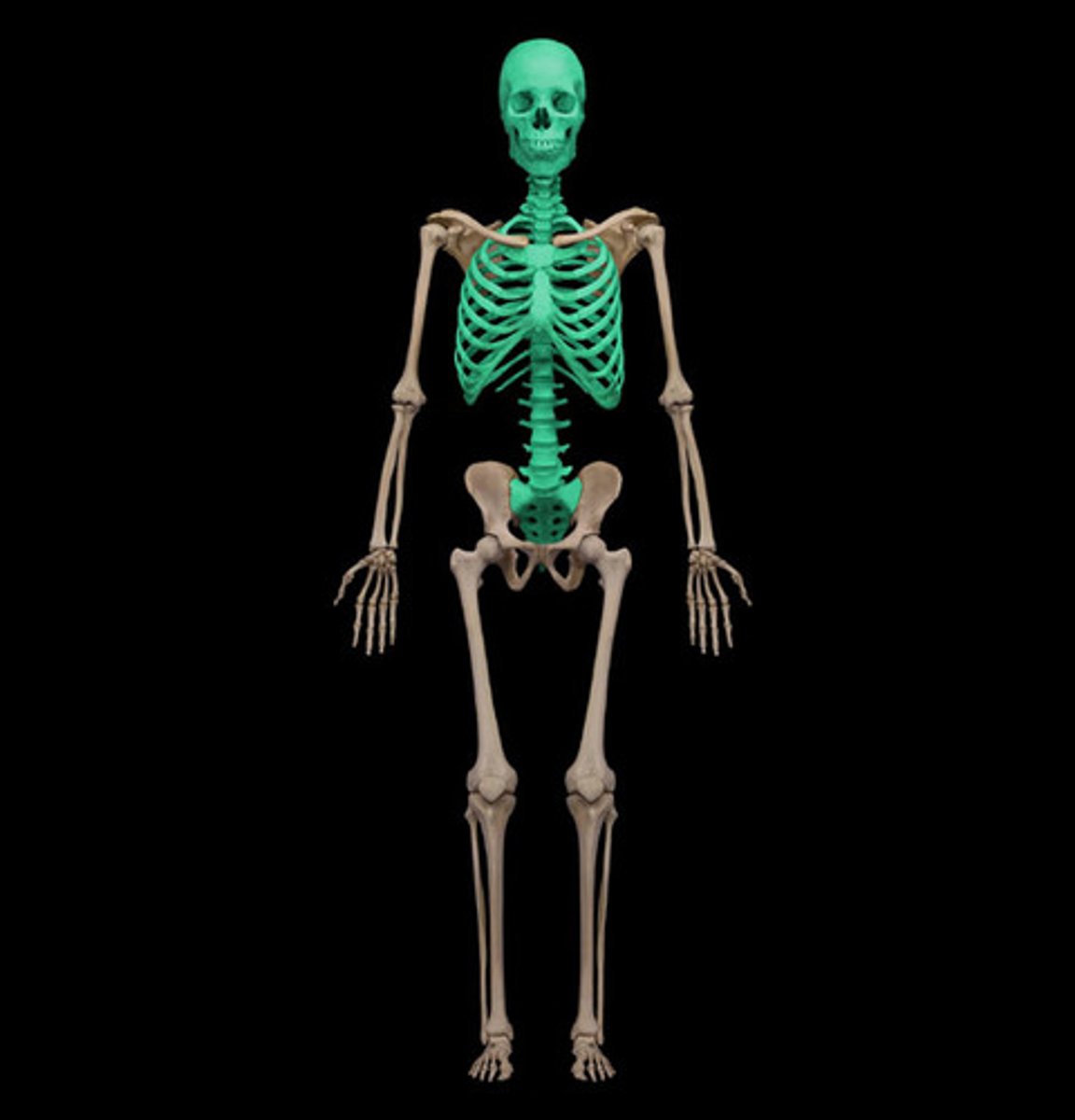
Appendicular Skeleton has how many bones?
126
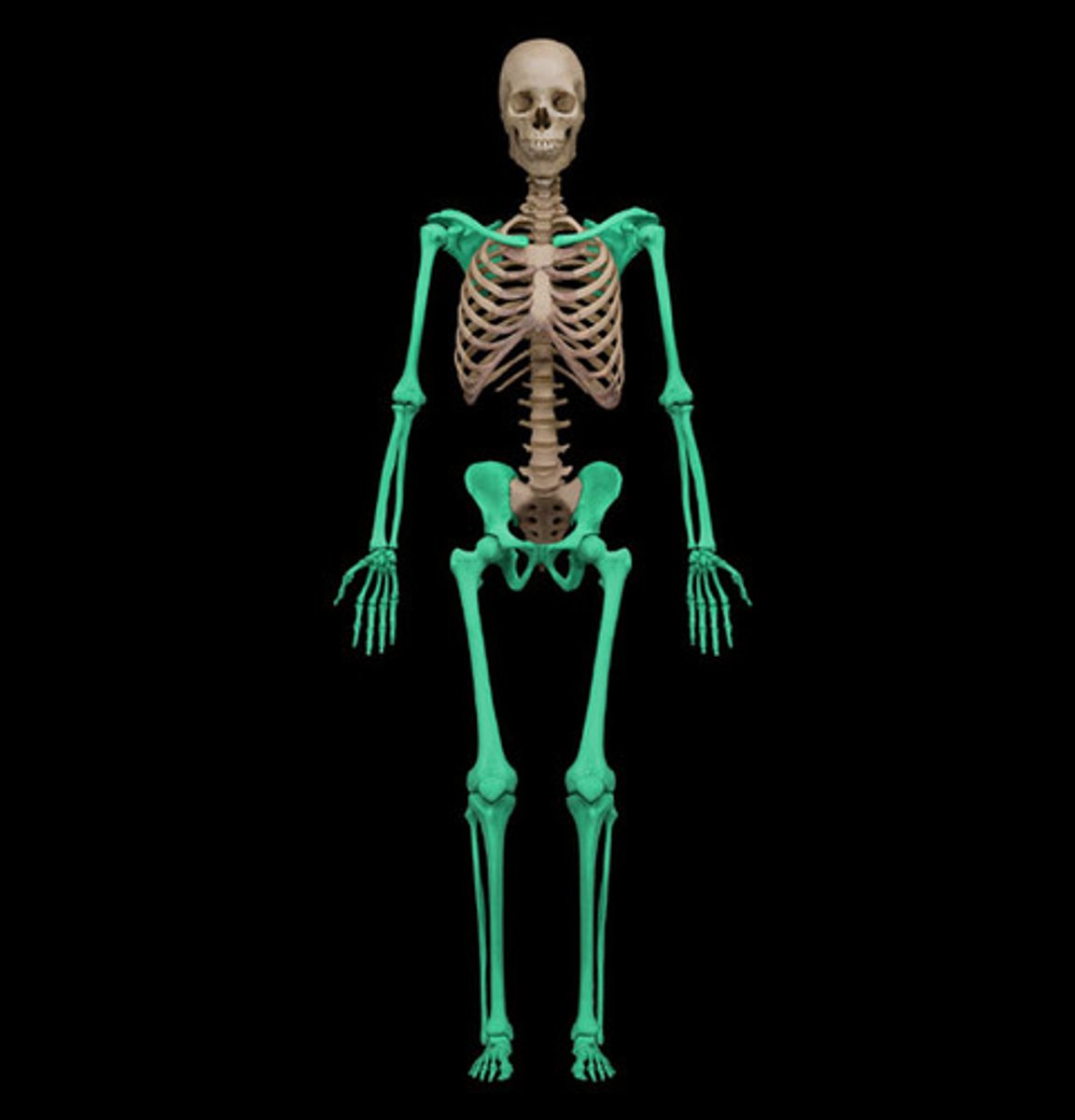
What type of tissue is the bone?
connective tissue
Outer Portion of Bone is made of?
Compact Bone
Inner Portion of Bone is made of?
Cancellous Bone (spongy)
Inner Portion of Bone is also known as the?
medullary cavity
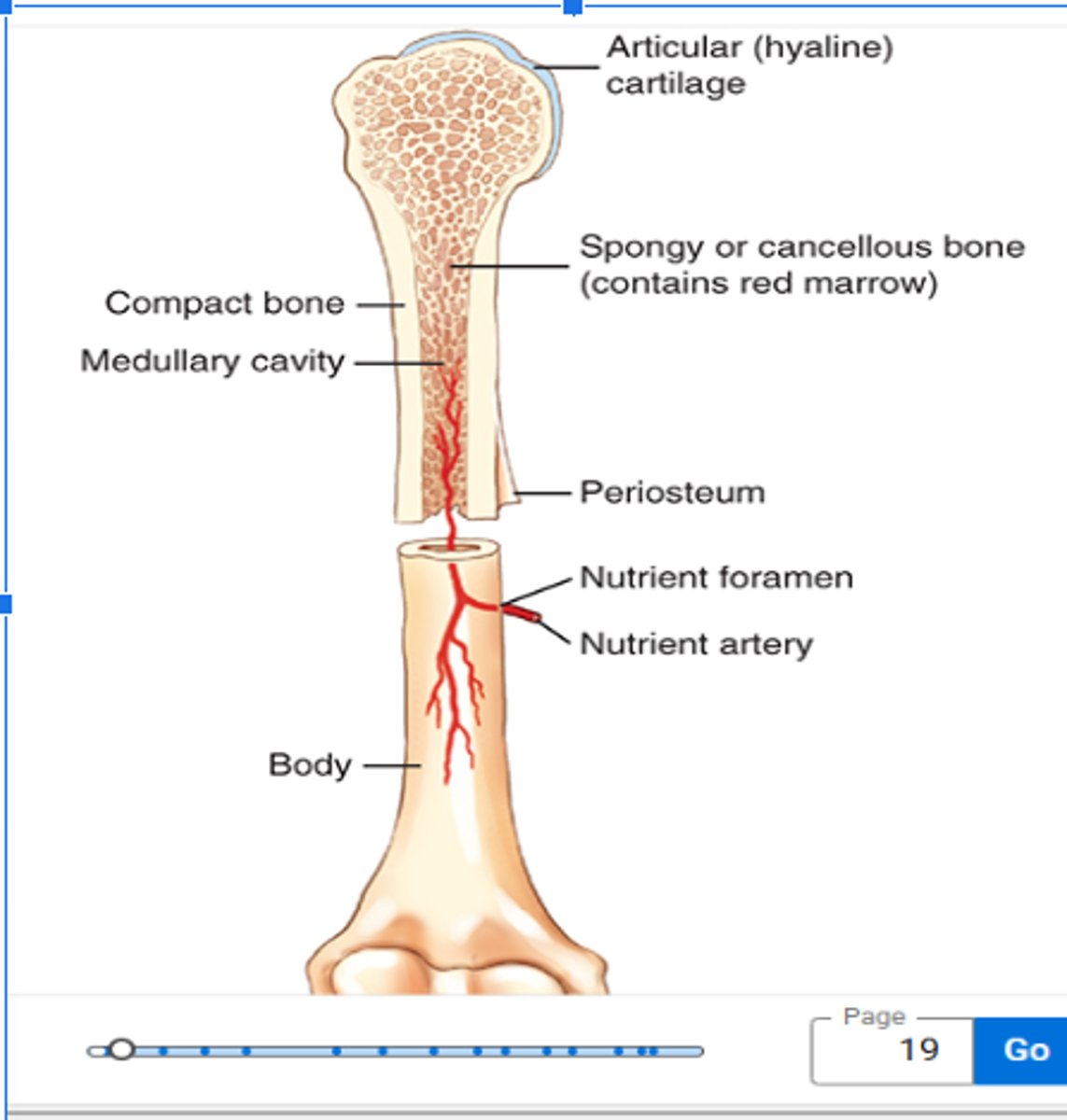
Bone Marrow is located between ?
trabeculae
Red Bone Marrow is responsible for?
Hematopoiesis- production of erythrocytes, leukocytes, thrombocytes
Osteoblasts are what type of cells?
bone-forming cells that line the medullary cavity
Osteoblasts are responsible for ?
bone growth
Osteoclasts do what?
break down the bone to enlarge the medullary cavity
Osteoclasts are responsible for?
bone remodeling and absorption of bone tissue during growth and healing
What is the shaft portion of the bone?
Diaphysis
What is the expanded end potion of the bone?
Epiphysis
What is the growth zone between the epiphysis and the diaphysis?
Metaphysis
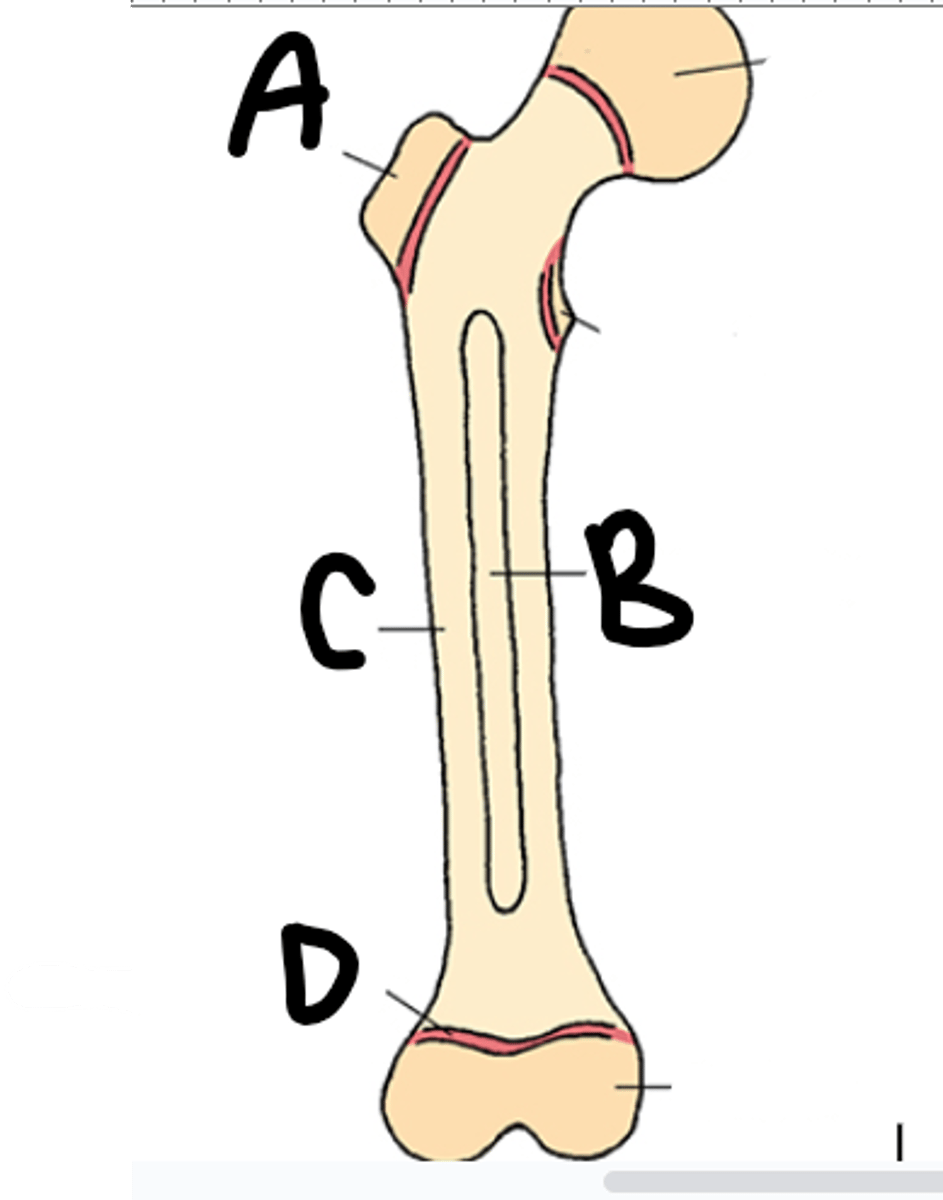
Label this picture
A- Epiphysis
B- Medullary Cavity
C- Diaphysis-body
D- Epiphyseal Plate
Osteogenesis Imperfecta is also known as
brittle bone disease
OI is what type of disease?
Rare congenital disease affecting connective tissue
OI is a result of what type of defect? autosomal or autodominant?
Autosomal (only one parent needs to have the altered gene)
OI mildest type
Type One
OI most severe type
Type Eight
What is used to help diagnose types 2,3, and 4
CFS- Cultured Skin Fibroblasts
OI is caused by ?
mutations in two structural genes that affect collagen production
Two types of OI
Osteogensis Imperfecta Congenita and Osteogensis Imperfecta Tarda
Osteogensis Imperfecta Tarda vs Congenita
Congenita-present at birth
Tarda- fractures can appear for some years after birth
What is best for evaluation for OI?
radiography
OI technique
no change
3 multiple choice options
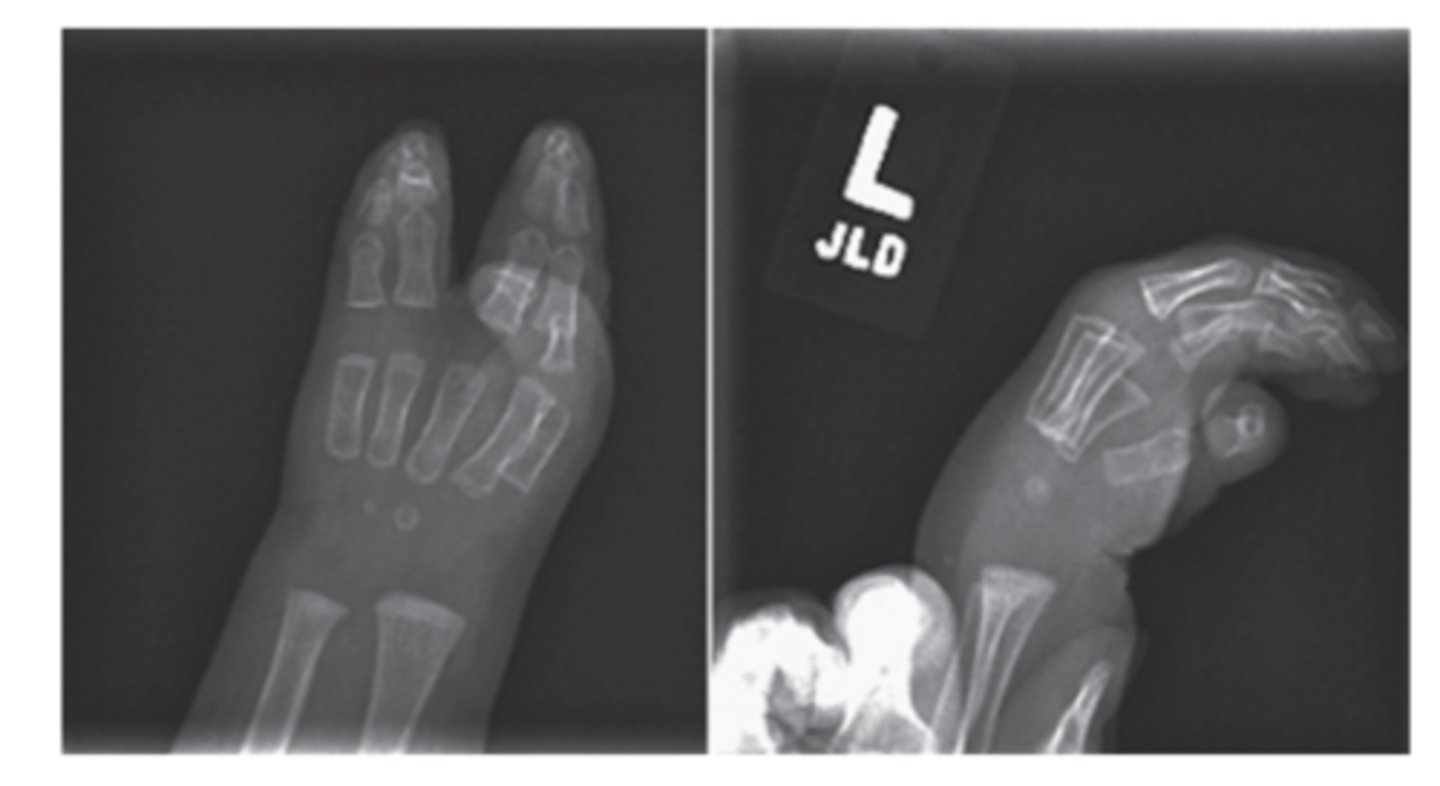
Syndactyly is failure of?
1. failure of fingers or toes to separate
Physical Appearance of Syndactyly?
webbed digits
Syndactyly
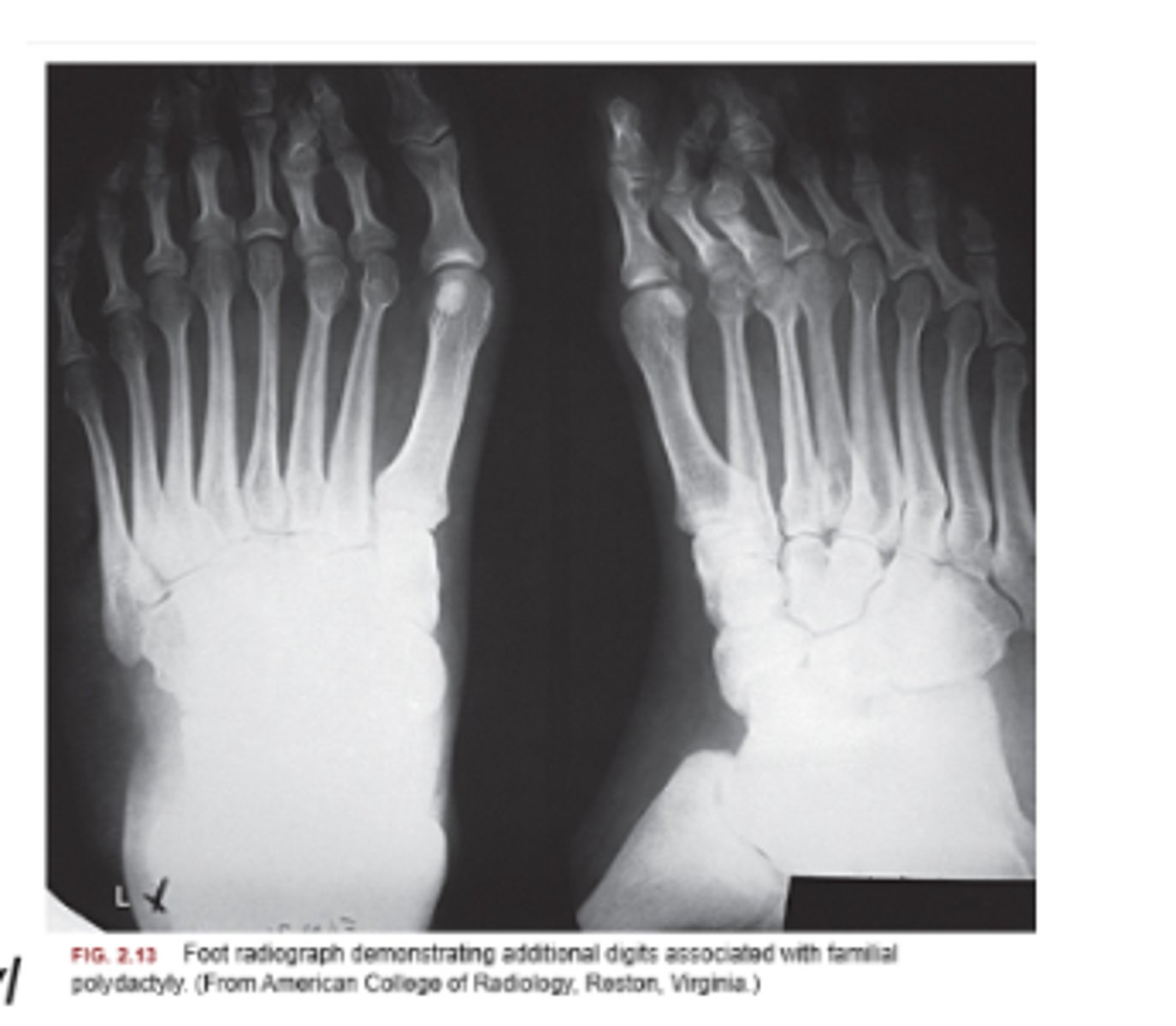
Polydactyly definition
presence of an extra digit or digits
polydactyly
Clubfoot definition
congenital malformation of the foot that prevents normal weight bearing
Clubfoot is more common in males or females?
males
Plantar Flexion deformity is associated with?
Clubfoot
Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip definition (pg. 27)
malformation of the acetabulum
Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip occurs more in what gender?
Females
Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip ratio of births
1/1000 births
What modality might be used to diagnose Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip early in life?
Sonography
Scoliosis definition
abnormal lateral deviation of the spine
In Scoliosis, the spine usually curves which way in the T-spine. Which way in the L-spine?
T-Spine- convex to the right
L-Spine- convex to the left (think L and L)
Up to what percentage is scoliosis idiopathic? (unknown cause)
80
Scoliosis generally does not become visually apparent until what stage?
adolescence
Scoliosis tends to affect which gender more?
females
What is it called when the primary issue is outside the spine?
Functional or Nonstructural Scoliosis
Best modality for Scoliosis
Radiography
How is scoliosis corrected?
brace/body cast or spinal fusion
Osteomyelitis definition
inflammation of bone marrow (itis) and surrounding bone(osteo)
Osteomyelitis is caused by?
pathogenic microorganism spread via the bloodstream from an infection
Signs and Symptoms of Osteomyelitis (4)
1. pain
2. heat
3. swelling
4. Redness
Imaging Modalities for Osteomyelitis (3)
1. MRI
2. NM
3. Radiography
Technique for Osteomyelitis
subtractive
Hematogenous Osteomyelitis develops where?
at the ends of long bones
Osteosarcoma definition
most common primary malignancy of skeleton in children and young adults which arise from osteoblasts
Osteosarcoma is caused by?
deletion of genetic material on chromosome 13 and the oncogene src
what is essential for the development of osteosarcoma?
genetic instability
Osteosarcoma is frequently found where in long bones?
metaphysis of long bones - mostly in distal femur and proximal tibia
Modalities for Osteosarcoma
1. Radiography
2. MRI
3. NM
Technique for Osteosarcoma
additive
CHAPTER 3- Respiratory System
--
Ventilation
air in and out the lungs
Diffusion
gas exchange between the lungs and the circulatory system
Upper Respiratory Tract consists of? (4)
1. nose
2. mouth
3. pharynx
4. larynx
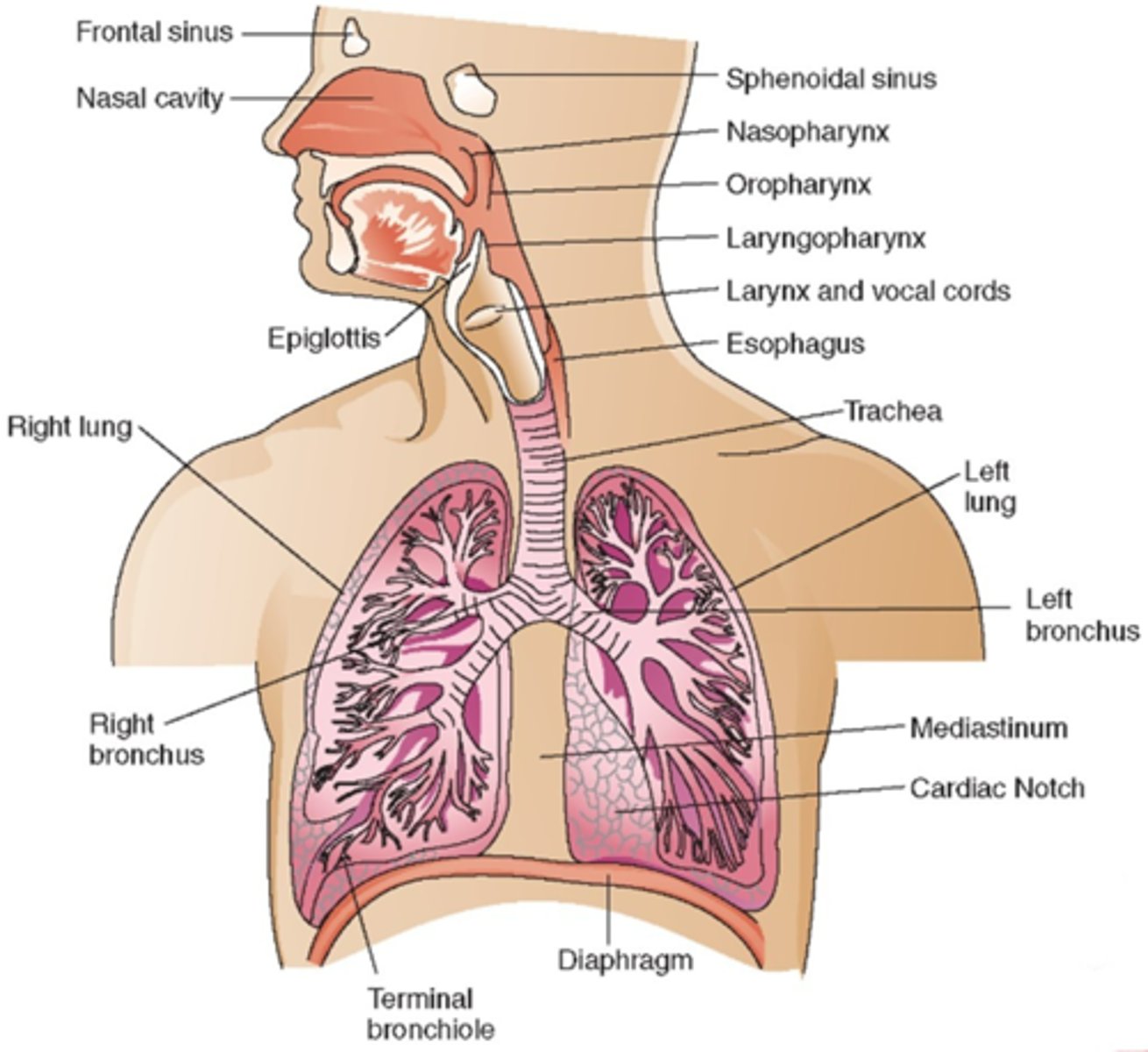
Lower Respiratory Tract consists of? (4)
1. Trachea
2. Bronchi
3. Alveoli
4. Lungs
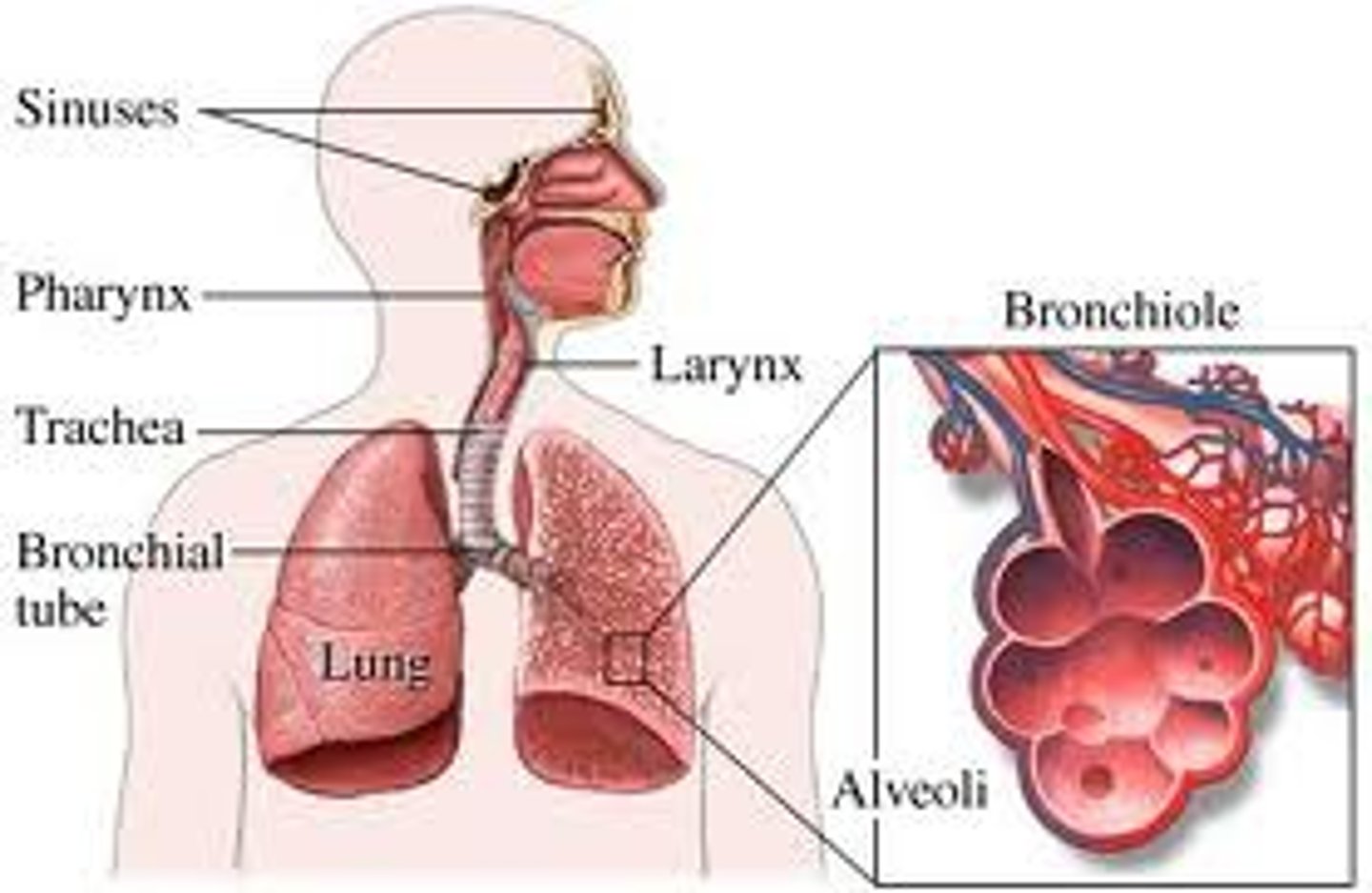
Visceral vs Parietal Pleura
Visceral = vital organs- covers the organs (inner layer)
Parietal- pertains to cavity wall lining (outer layer)
What X-ray is most frequently used?
Chest X-Ray
Subtractive Disease
easier than normal for x-ray to penetrate
Additive Disease
harder for x-ray to penetrate
Example of additive disease
Pneumonia
Example of subtractive disease
Emphysema
Position defintion
arrangement of the individual's body (erect, supine, recumbent)
Projection definition
path of x-ray beam (AP/PA)
What is used when individual is too ill for an erect chest x-ray?
AP projection
An individual should sit in what position to demonstrate air-fluid levels ?
erect
which projection is useful in separating superimposed structures such as sternum, esophagus, and thoracic spine?
Oblique Projections
which projection is useful in demonstrating apices of the lungs?
Lordotic Projection
Which muscles are normally demonstrated overlying the lung fields?
pectoral muscles
Cystic Fibrosis definition
A disorder resulting from a genetic defect transmitted as an autosomal recessive gene that affects the function of exocrine glands
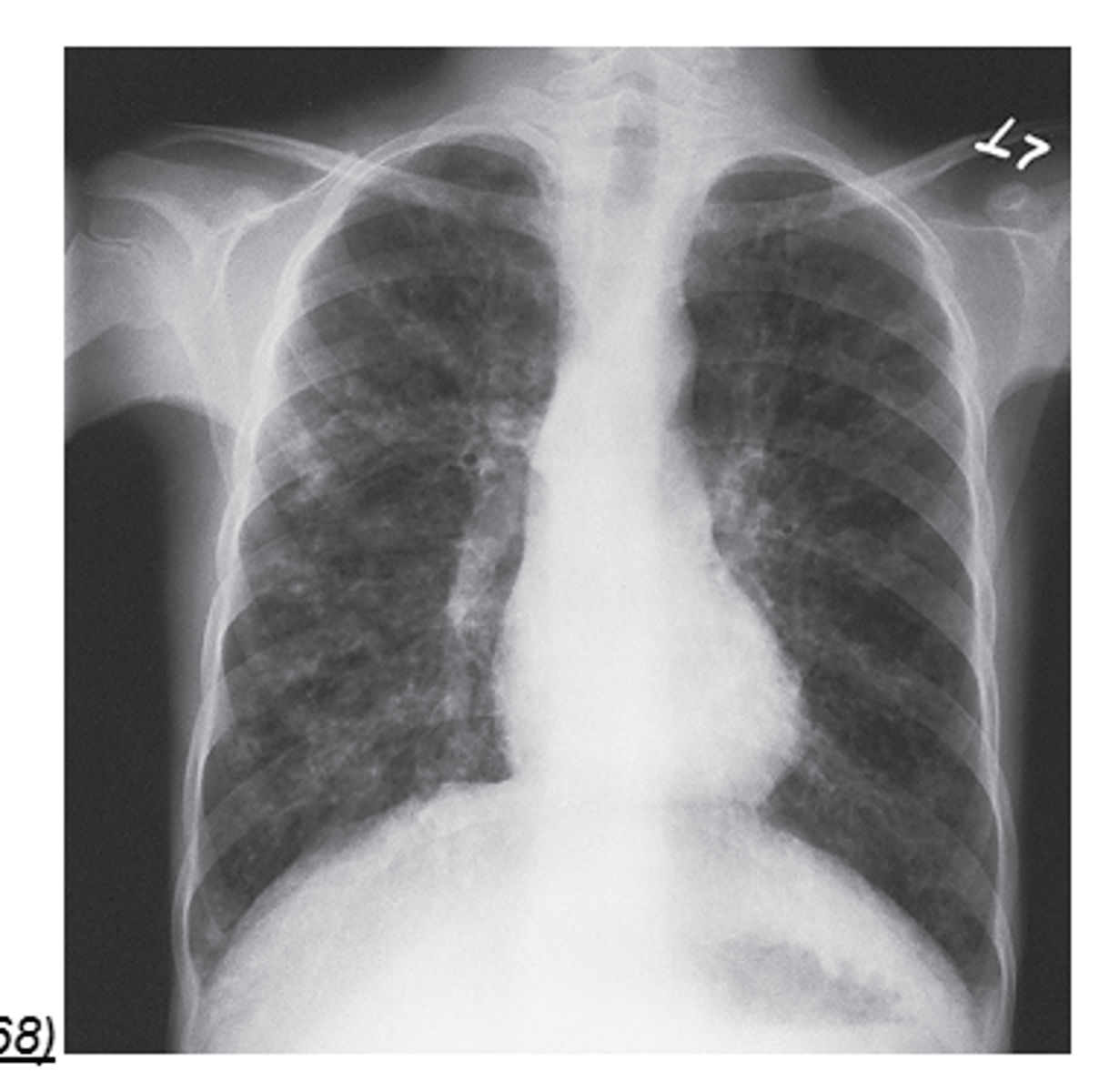
Modality for Cystic Fibrosis
Radiography
most common lethal genetic disease in white children
Cystic Fibrosis
CHAPTER 3- CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
--
Embolus Definition
any foreign material within the blood such as an air bubble, fat, bacteria, fat, and amniotic fluid
Embolism definition
occurs when a mass of matter in the bloodstream collects and creates an embolus
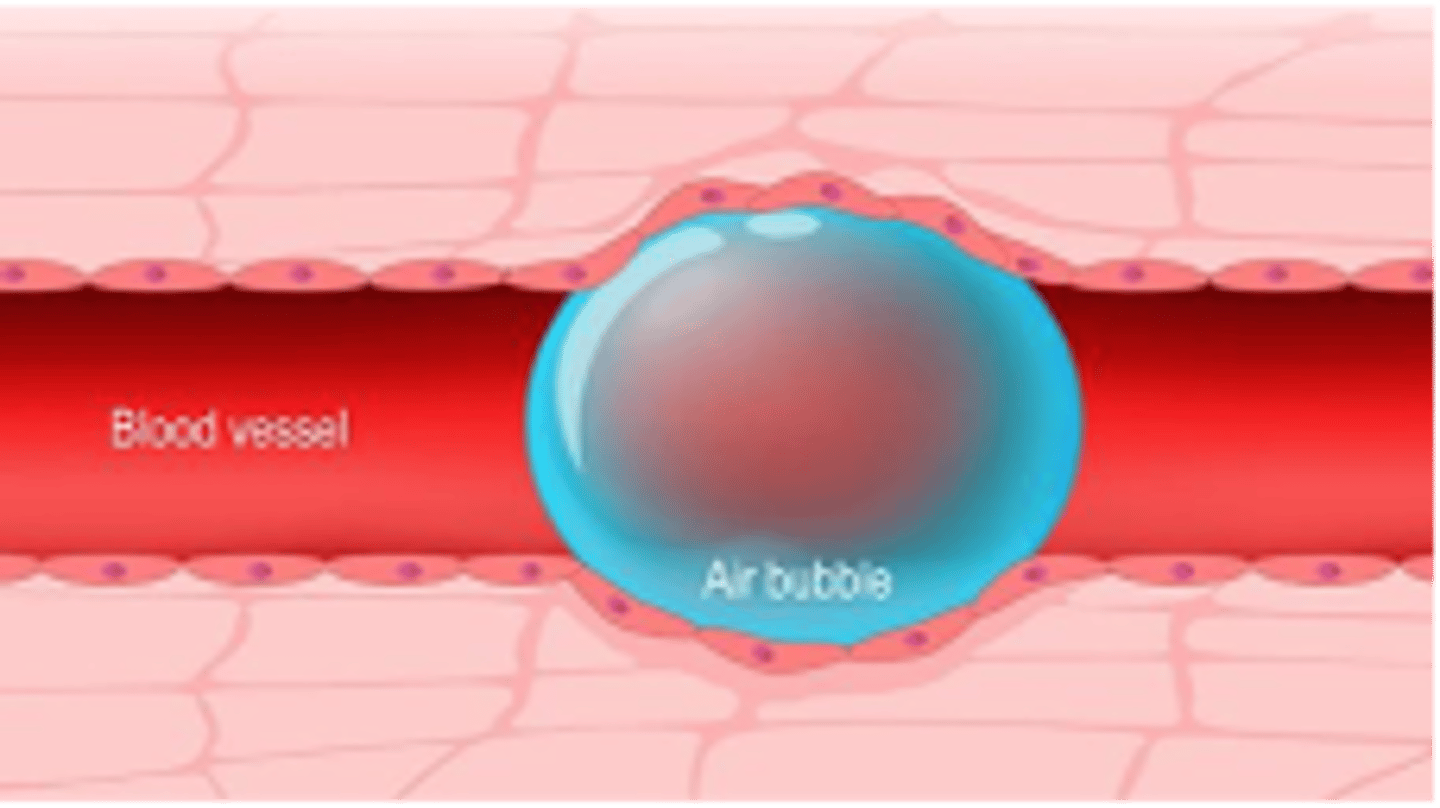
Embolus can lead to what?
ischemia- lack of oxygen
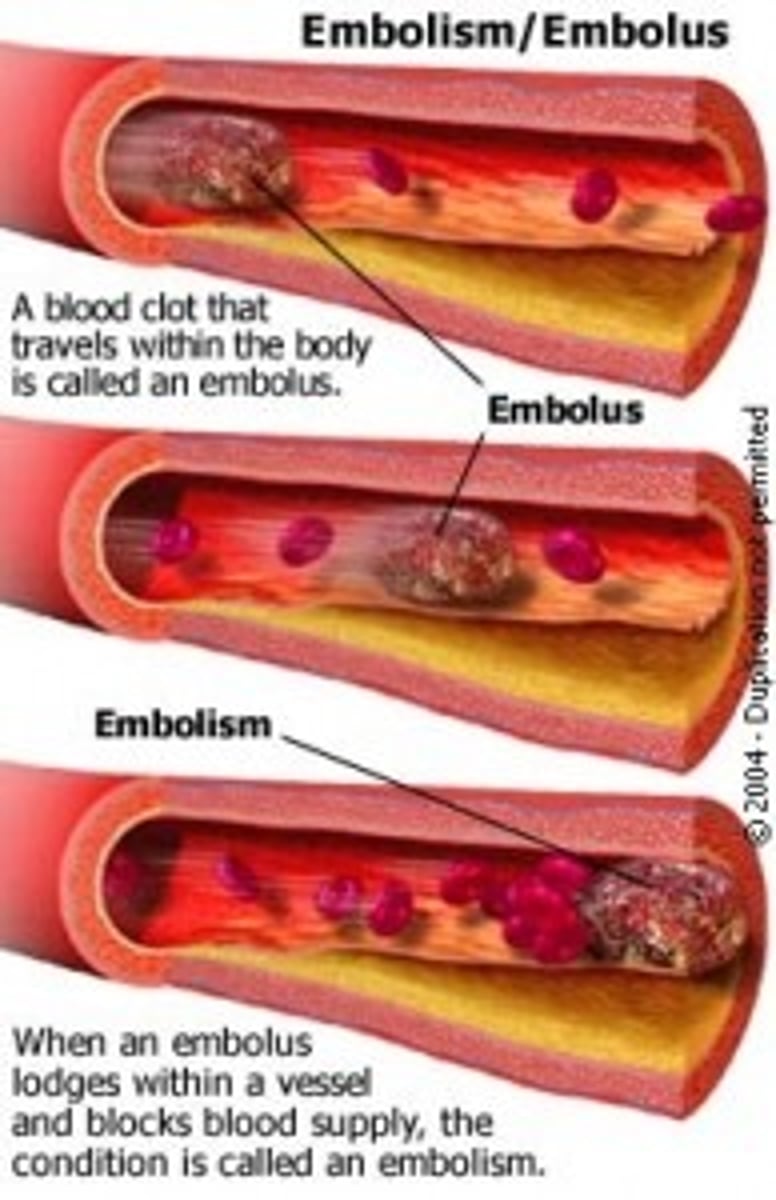
Pulmonary Embolism
when an embolus forms in a pulmonary artery
CHAPTER 5 -GI SYSTEM/ HEPAT/ABDOMEN
--
Nine regions of abdomen
right hypochondriac
epigastric
left hypochondriac
right lateral
umbilical
left lateral
right inguinal
hypogastric
left inguinal
