15.4 Titrations
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
A solution of unknown concentration
analyte
A solution of known concentration
titrant
The point in the titration where the proportions of analyte and titrant present in the reaction mixture match those required from the stoichiometry of the chemical reaction
In acid-base: moles of H+ = moles of OH-
equivalence point
The indicator changes color to signal the completion of the reaction/titration
endpoint
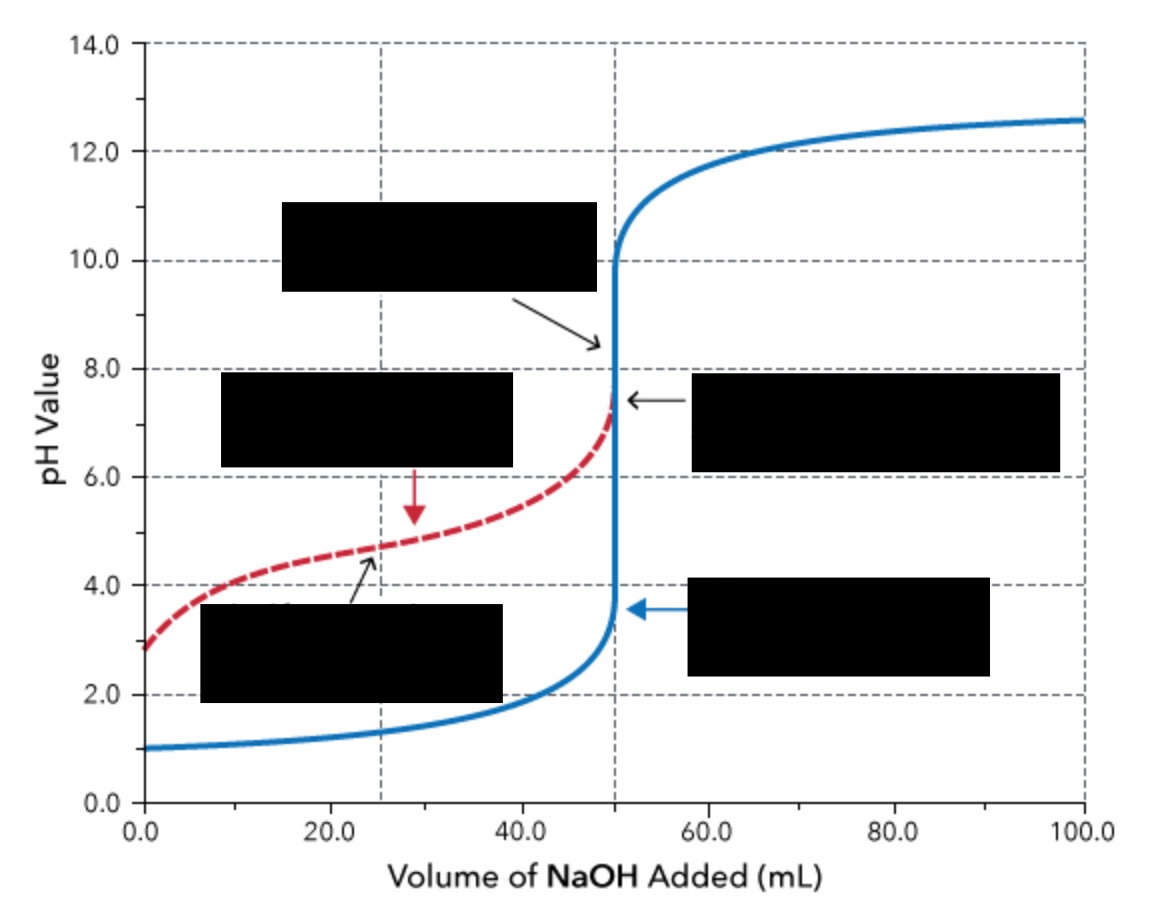
weak acid and strong base titration
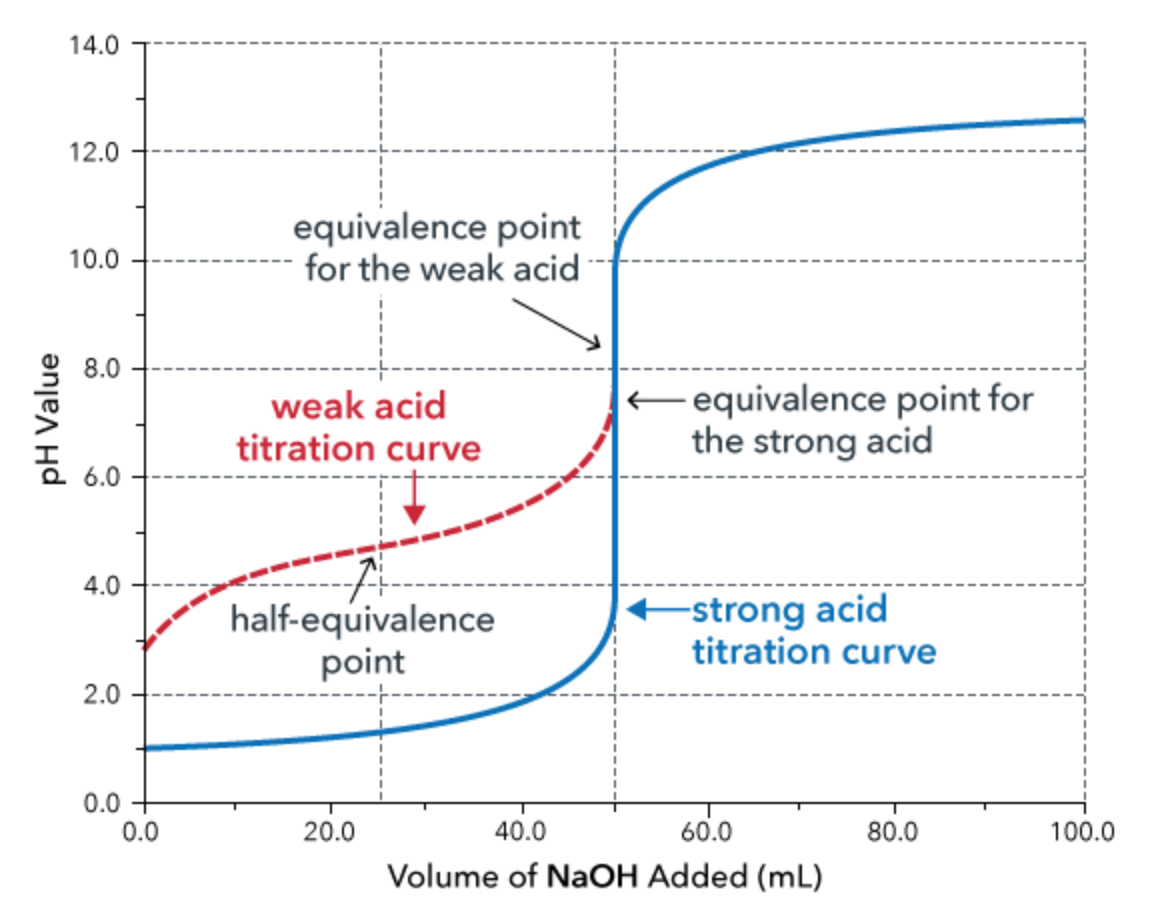
In a weak acid / strong base titration, the initial pH is that of the _________.
weak acid
What is the region before the equivalence point called?
buffer zone (note: this means that both weak acid/conjugate base or weak base/conjugate acid present)
What is significant about the half-equivalence point?
At the half-equivalence point, pH = pKa
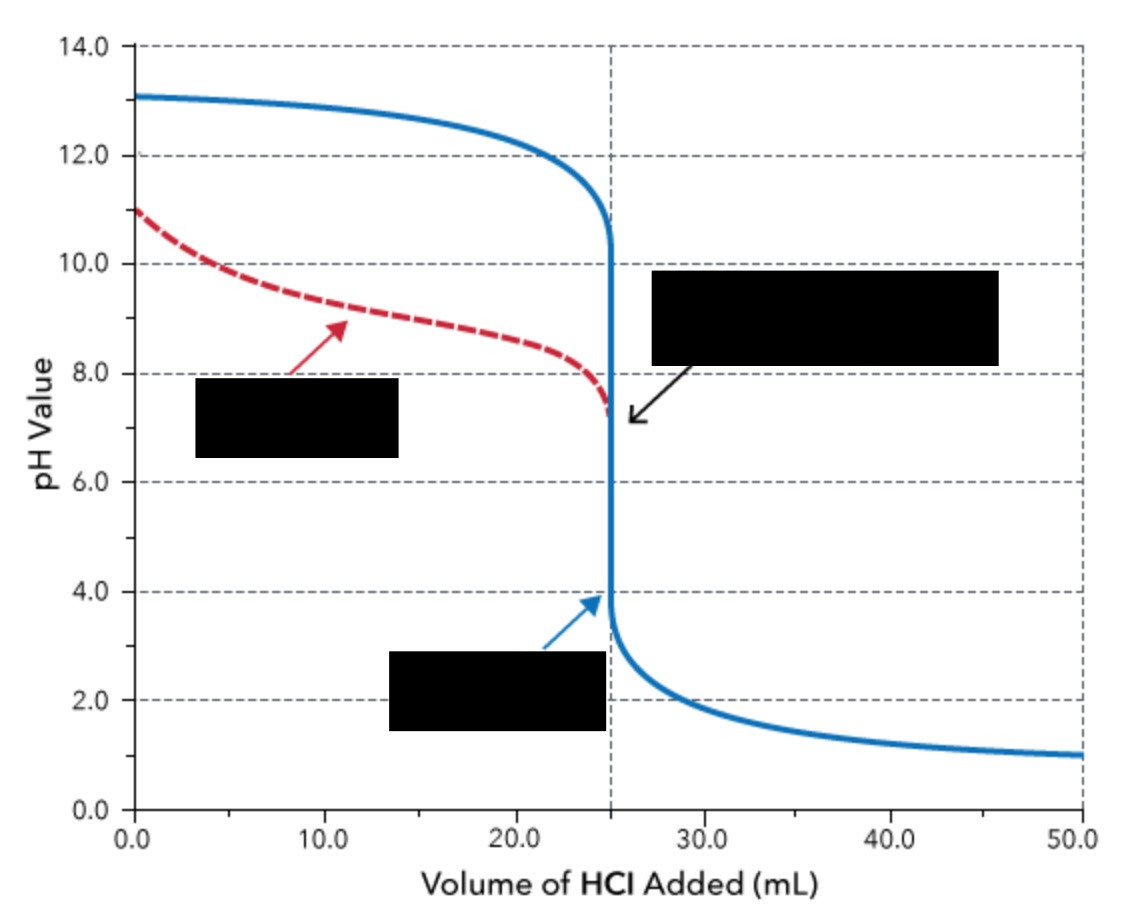
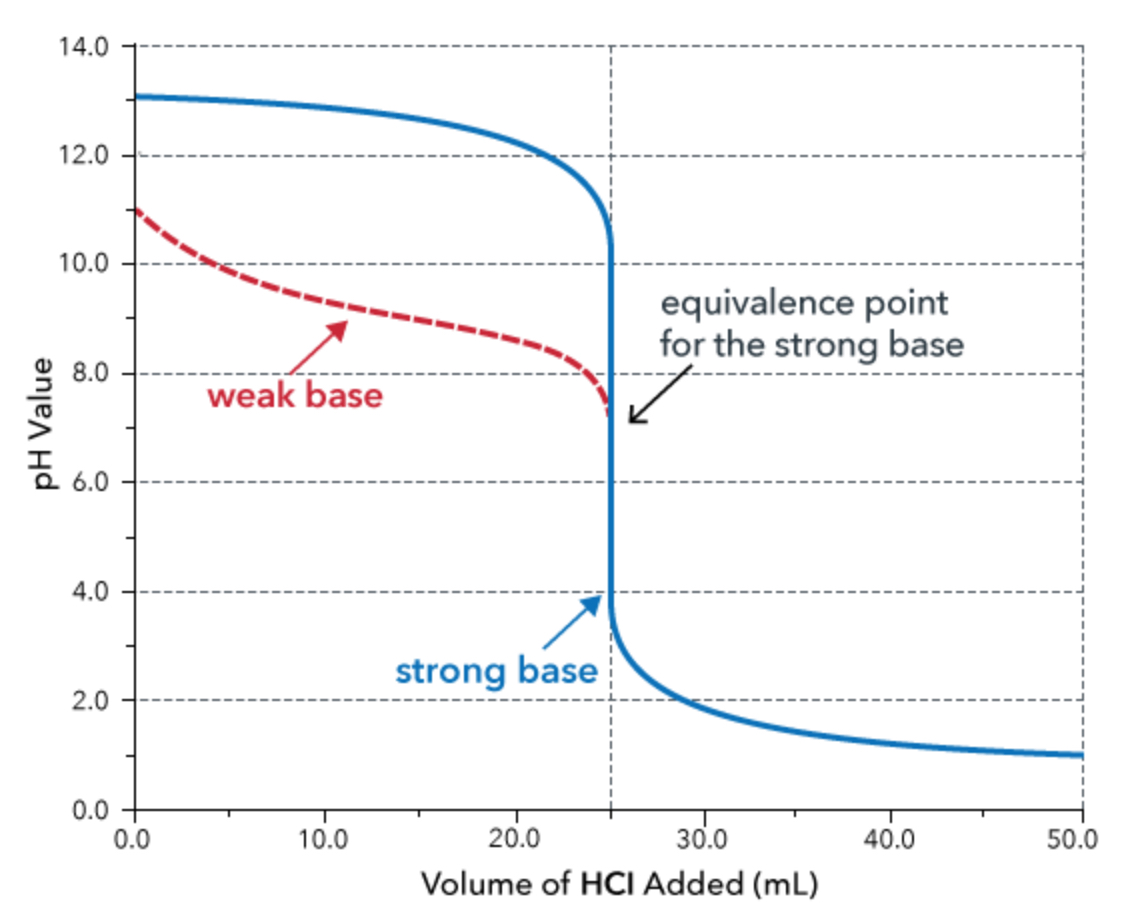
weak base and strong acid titration
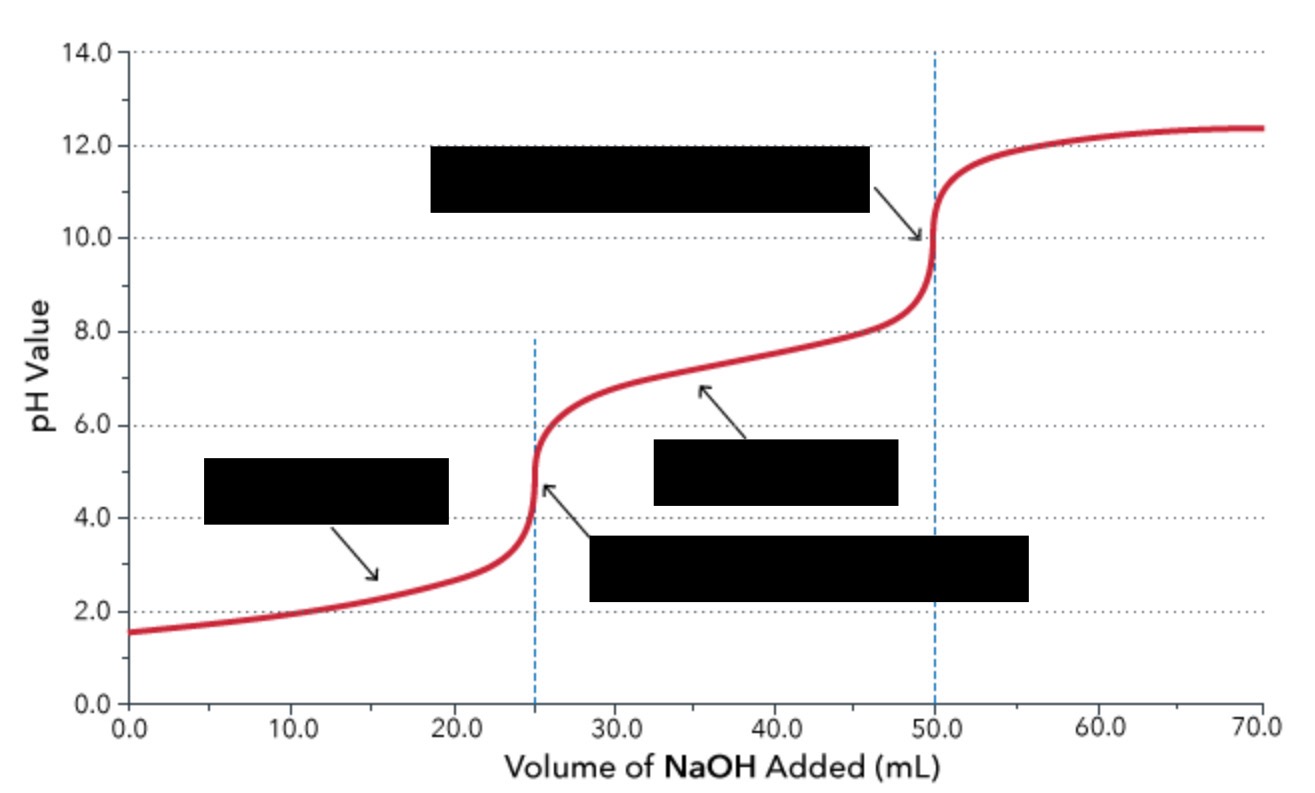
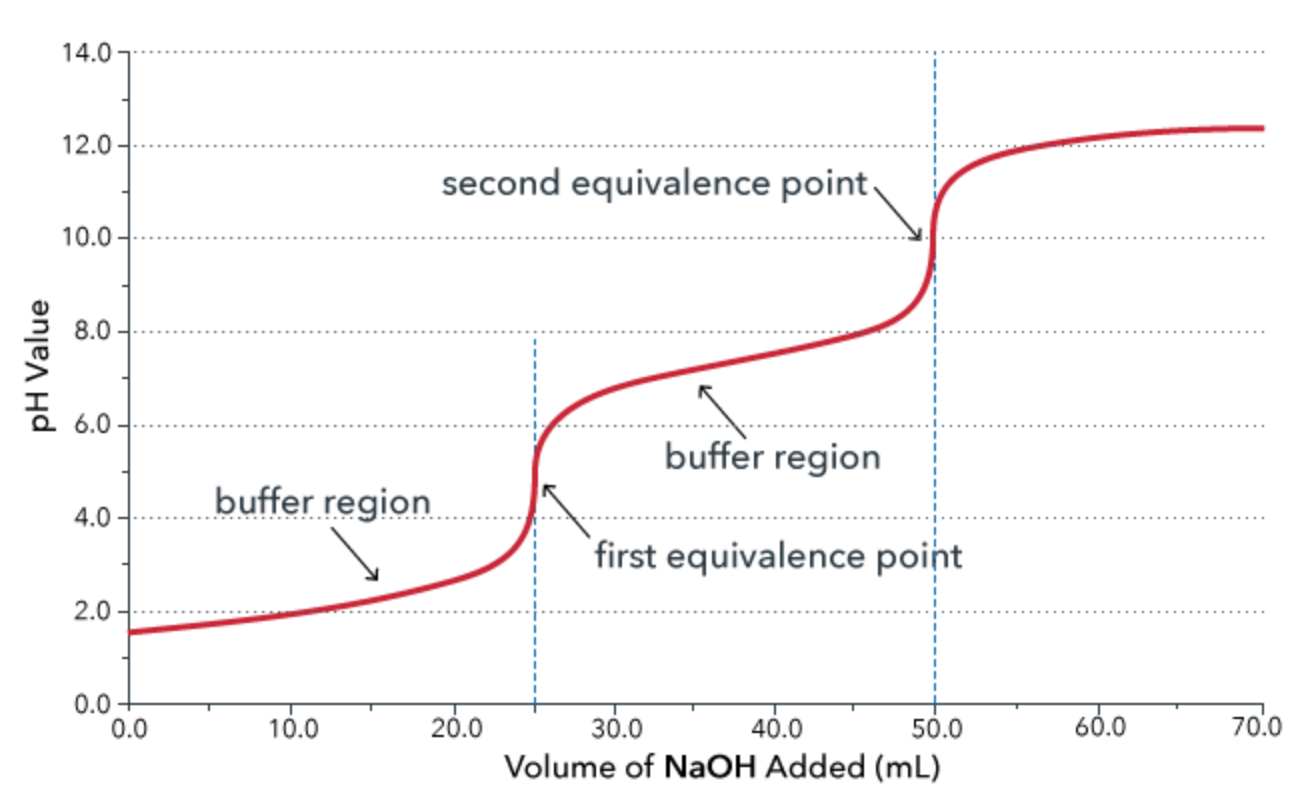
polyprotic acid titration (note: if the Ka value is too small or if the sequential Ka values are too close to each other, then the titration curve will become too flat to identify the equivalence points)
A general rule of thumb for indicators is that they change colors when the pH is ______.
pKa ± 1