Cognitive Psychology Chapter 10 + Book
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
What is an emotion (or affect?)
a positive or negative experience associated with a particular pattern of physiological activity accompanied by feelings.
what is a mood?
generalized, diffused states that last longer than emotions but are less intense
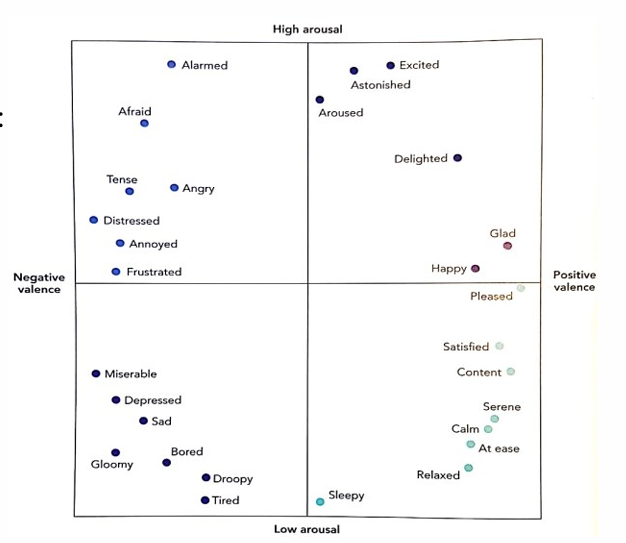
what are the two dimensions of emotional experience, what do they mean and name some examples of emotions in each quadrant
the 2 dimensions are Valence (from positive to negative on the x-axis) and Arousal (from passive to active on the Y-axis)
examples in each quadrant:
I: Delighted, Happy
II: Angry, Tense
III: Depressed, Bored, Tired
IV: Content, Relaxed
3 emotion theories
James-Lange Theory
The cannon-bard Theory
Schacter and Singer’s: two components theory of emotion
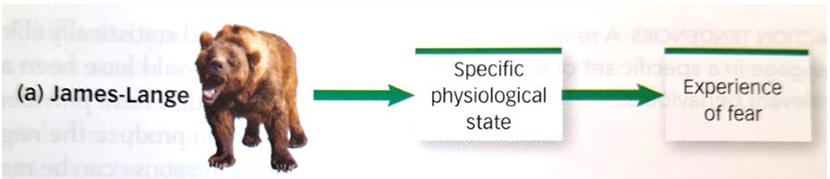
what is James-lange’s theory
An emotion arises because we feel the reaction on the body.
without a physical reaction there can’t be emotion
What is the Cannon & Bard Theory?
stimuli simultaneously trigger activity in the autonomic nervous system and the emotional experiences in the brain
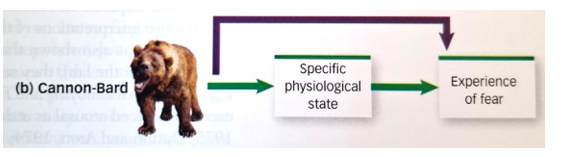
How does the Cannon & Bard theory differ from the James-Lange Theory?
Cannon and bard argue that
people cannot really detect changes in their autonomic activity (e.g. temperature) so how can these be experiences as emotion?
multiple emotions are accompanied by similar physical reaction, so which emotion should be experienced?
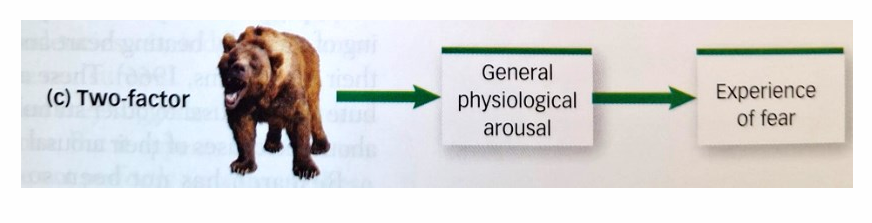
What is the Two components theory of emotion
there is a undifferentiated physiological arousal of the autonomic nervous system and a cognitive interpretation of the situation
emotions are the cognitive causal inferences about the aroused state
limbic system
role in emotions
includes the amygdala, hippocampus and gyrus cinguli
special role of the amygdala in the limbic system
involved in making an evaluation of the emotional-relevant aspects of a stimulus (appraisal)
what happens when the limbic system is damaged and how was this discovered?
fear responses decrease
discovered through removal of temporal lobe and amygdala in monkeys
what is the Klüver-Bucy syndrome
damage to temporal lobe and amygdala (as observed in the monkey experiment by Kluver and Bucy) which result in:
lack of fear
no distinction possible between good or bad food (everything was consumed)
no distinction between good or bad mates
What is the Nucleus Accumbens
part of limbic system
important role in reinforcing and rewarding stimuli
activated when viewing pleasant, emotionally arousing pictures or pleasant emotional scenes.
what was the first indication that the frontal lobes were evolved in emotional regulation?
Phineas Gage became very unsocial after accident
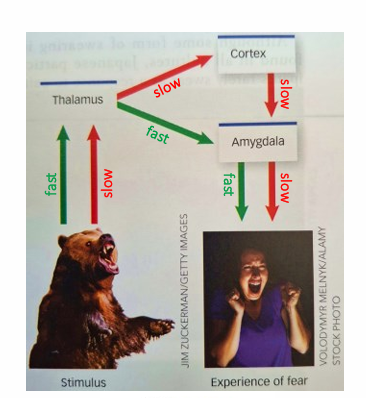
what did LeDoux invent on the emotions in the brain?
The Fast and Slow pathway system
What is the difference between the Fast and Slow pathways?
Fast pathway goes from the thalamus to the amygdala and only says ‘is this good or bad’
Slow pathway goes from the thalamus to the cortex and then to the amygdala and questions what is going on which takes a longer time
emotional expression
any observable sign of an emotional state
universality hypothesis (6 basics)
emotional expressions have the same meaning for everyone
Happiness, sadness, fear, anger, surprise and disgust/contempt
facial feedback hypothesis
emotional expressions (in the face) can cause the emotional experiences they signify
people who hold a pen in their mouth feel happier as it contracts the zygomatic major muscles of the face in the same way a smile does
display rules
norms for controlling emotional expressions
there is a difference in how you act when either your sister or your boss tells you that they hate your haircut
what are the techniques involved for following display rules
intensification
deintensification
masking
neutralizing
what is intensification in display norms
exaggerating the expressions (like when opening a gift and saying you love it)
what is deintensification in display norms
muting the expression (trying to look less happy when you e.g. pass an exam but your friend did not)
what is masking in display norms
expressing a different emotion than what you are feeling (displaying pleasant emotions when you are experiencing disgust)
what is neutralizing in display norms
feeling an emotion but not expressing anything (judge has an ‘aha’ moment when listening to a lawyer but cannot show that)
what happens to muscles in a real smile vs a fake smile
genuine smile involves the zygomatic major (mouth) and the orbicularis oculi (eye wrinkles), but a fake smile does not involve the eye wrinkles
real emotions tend to be more symmetrical in the face
on what principle is the lie detector based?
on the principle that emotions are related to responses to the autonomous nervous system (increased heart rate, larger pupils, sweating etc.) that are not always under control of the brain
it measures changes of resistance in perspiration, hear rate or muscle tension.
two types of question in a lie detector test
key question vs control questions
did you kill the dog? / is your name X?
Guilty knowledge method
do you recognize any of these knives?
In what ways does emotions motivate behaviour
they inform us about the world
can become objectives we strife towards
How do emotions inform us about the world?
object recognition is accompanied by emotional component (safe/unsafe, mine/not mine etc.)
What is the imposter/copy (Capgras syndrome/delusion)
a person holds the delusion that a friend or parent, spouse etc has been replaced by an imposter.
how can emotions become the objective we strive towards?
Aristotle’s hedonistic principle: we seek to maximize pleasure and minimize pain.
motivation
purpose for, or cause of an, action. this can be driven by many things, but some behaviour seems to be hardwired
instrinct
inherited and innate tendency to fulfil a goal
drive
a behaviourist term referring to an internal state that is generated by a suboptimal physiological state
homeostatis
tendency of a system to take action in order to keep itself in a certain state
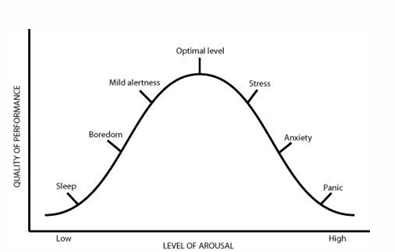
what is Yerkes-Dodson’s law
there is an optimal state of arousal corresponding to a particular task.
When arousal is too low or too high, it leads to poorer performance
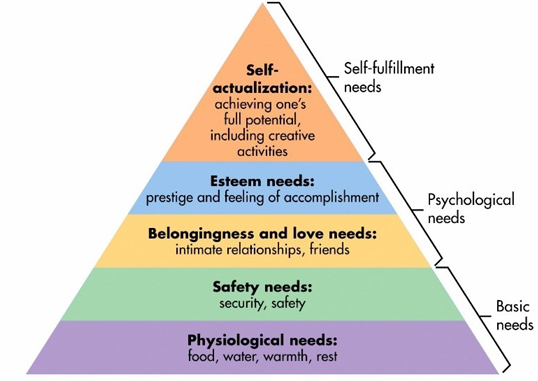
need
a psychological concept in which it is generally assumed that ‘lower’ needs need to be satisfied first
what are the two most powerful needs?
need to eat and to mate
How do we experience hunger?
a signal of hunger can be turned on and off
Ghrelin (a chemical in the stomach) signals the hypothalamus to increase the feeling of hunger, and leptin (secreted by fat cells) can send a signal to the hypothalamus to reduce hunger
What is the signal sending by Ghrelin called?
an orexigenic signal
What is the signal by the Leptin called?
an anorexigenic signal
what in the brain turns the hunger signal on?
the Lateral Hypothalamus turns the hunger signal on.
if destroyed, rats even with a lot of food will starve themselves
what in the brain turns the hunger signal off?
the Ventromedial hypothalamus turns the hunger signal off
if destroyed, animals will gorge themselves up to the point of illness/obesity
Obesity (in an environmental perspective)
we are designed for an environment where food is scarce.
we are attracted to food that provide a large amount of calories per bite
we store excess energy as fat
fat cells do not die (only size decreases when dieting)
metabolism decreases during dieting
oestrogen and testosterone
many female animals have no interest in sec except when ovulating. this is regulated by oestrogen
sex drive determined by testosterone in both males and females
motivation (needs perspective)
to engage in other behaviour then eating and sex are more psychological in nature
why is extrinsic motivation by definition not bad?
the Marshmallow/ice-cream test: eat one marshmallow/scoop of ice cream now, or wait and receive a second one → a measure of self-discipline) can be a better predictor of academic achievement than IQ.
through what three reasoning can motives change over time
over justification effect/motivational crowding out
punishment can also create intrinsic motivation
threats can backfire
Over justification effect/motivational crowding out
intrinsic motivation replaced by extrinsic motivation when behaviour is rewarded
e.g. students volunteered to help for free, but now that assistants get paid you do it for the money instead of the fact that you want to volunteer
punishment can also create intrinsic motivation
children who are not interested in a toy become interested when told they would be punished when touching it
students with no intrinsic motivation to cheat became interested in cheating when explicitly warned against it
threats can backfire
if late pick-up children in childcare centres get fined, unwanted behaviour increases. the intrinsic motivation to be on-time was gone when the fine gave parents an excuse to come late
affective forecasting
the process by which people predict their emotional reactions to future events