BIOL 111 Final Exam Sec 3
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Why do phospholipids form bilayers?
because they are amphipathic with a polar head and nonpolar tails that interacts with and repels water to form a stable barrier
What is the “fluid” aspect of the fluid-mosaic model? What is the “mosaic”?
fluid: the ability for phospholipids and proteins within the cell membrane to move laterally along the membrane
mosaic: a mixture of many different molecules in the membrane
How fluid are saturated membranes?
less fluidity due to a straight structure that favors tight packing
How fluid are desaturated membranes?
more fluidity due to double bonds that introduce kinks and reduce the tightness of packing
What is the function of cholesterol?
to prevent membranes from becoming too rigid at low temperatures (prevents packing) and too flexible at high temperatures (prevents movement)
What happens in a hypotonic cell? Where is the solute concentration highest?
water enters and cell swells
highest inside of the cell
What happens in a hypertonic cell? Where is the solute concentration highest?
water leaves and the cell shrinks
highest outside of the cell
What happens in an isotonic cell?
water inside and outside are both equal
Which molecules can move through simple diffusion?
small, nonpolar, uncharged molecules diffuse directly through the membrane
Which molecules must move through active transport?
large, polar, charged molecules that cannot move through the cell membrane, or molecules that need to move against their concentration gradients
What is passive transport?
when molecules move down concentration gradients and do not require energy to move
What is facilitated diffusion?
when a transport protein is provided to move a molecule across a membrane
What is primary active transport?
when ATP is directly used to provide energy for a pump to move molecules against their concentration gradient
What is secondary active transport?
when stored potential energy in ion gradients is used to transport molecules against their concentration gradients
What are the major differences between the structure of prokaryotes and eukaryotes?
PRO: a nucleoid region with free floating DNA, is unicellular, and contains no organelles including a nucleus
EUK: DNA is contained within the nucleus, is usually multicellular, and contains a nucleus and organelles
What is the function of lysosomes?
to break down and recycle macromolecules like proteins, nucleic acids, lipids, and complex carbohydrates back into the cytosol
What is the function of the endoplasmic reticulum?
to synthesize specific types of proteins in the rough ER, and synthesize fatty acids, phospholipids, and cholesterol in the smooth ER
What is the function of the golgi apparatus?
the modify proteins and lipids produced in the ER, sort them to their final destinations, and synthesize many carbohydrates
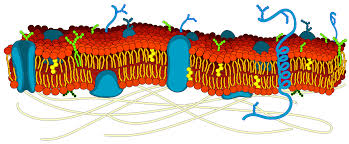
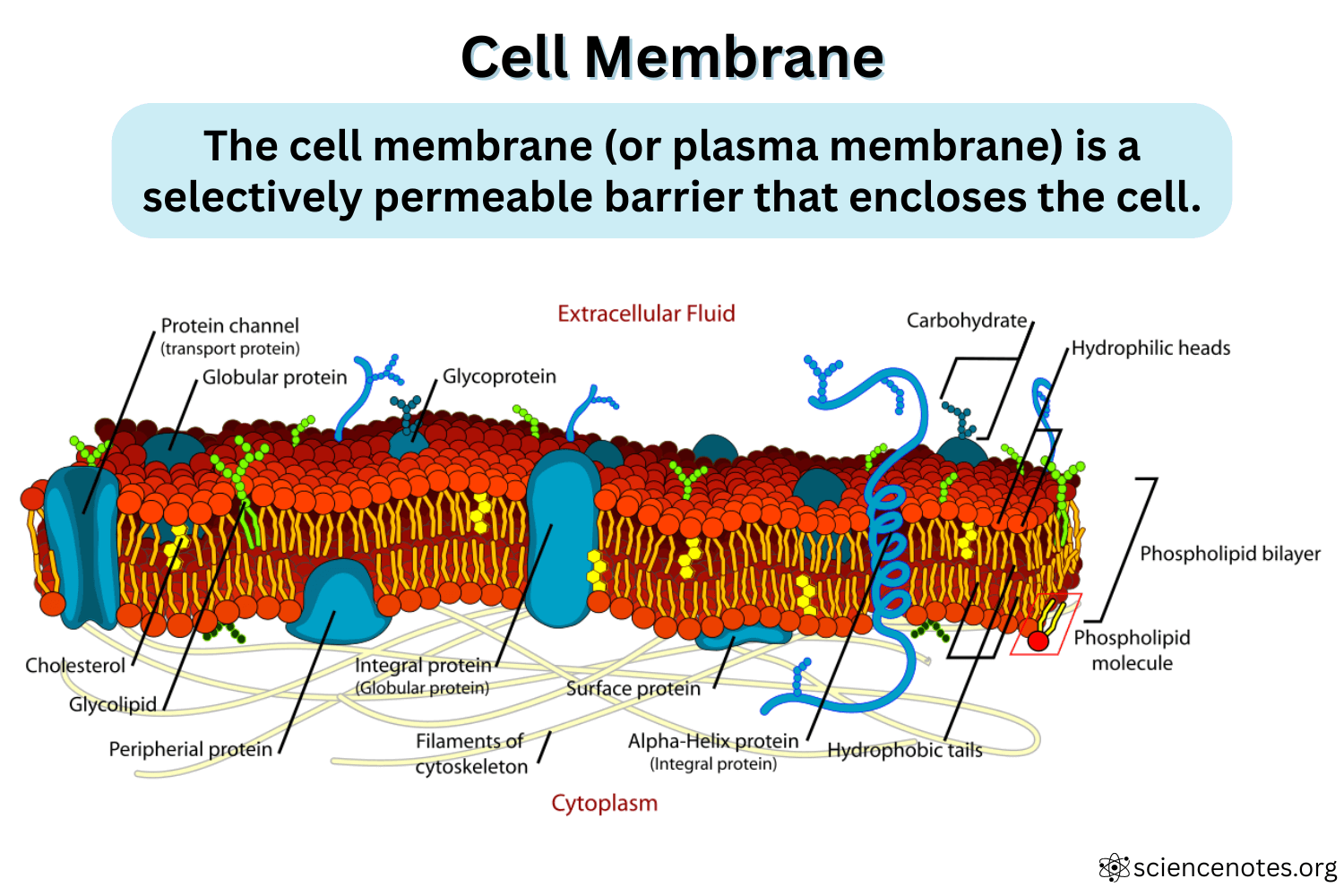
Label the components of a cell membrane:
Which diffuses more easily and why? CO2 or NA+
CO2 because it is small and nonpolar
Which membrane component is involved in cell-cell recognition?
glycolipids or glycoproteins
During osmosis, where does water move?
towards the higher solute concentration
What is selective permeability and why is it important for homeostasis?
selective permeability is the ability for membranes to allow some molecules through while blocking others, and it allows the cell to maintain a stable internal conditions
What is true of modern cell theory?
all cells come from preexisting cells, cells are the basic structural/functional units of life, and all living organisms are made up of one or more cells