Oral Pathology: Transient Lingual Papillitis, Recurrent Ulcers, and Salivary Gland Disorders
1/138
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
139 Terms
EC: whats her fav color
green
EC: where did she go to college
UF
Three patterns of transient lingual papillitis
1. localized
2. generalized
3. generalized papulokeratotic variant
what does localized transient lingual papilitis effect
one to several fungiform papillae of tongue
where is localized transient lingual papilitis frequently in
anterior portion of dorsal surface
when does localized transient lingual papilitis resolve
has spontaneous resolution within hours to some days
where is general transient lingual papilitis localized in the mouth
tip and lateral portions of dorsal surface
when does general transient lingual papilitis resolve
resolution in 7 days with occasional recurrences
which transient lingual papilitis has asymptomatic papillae
generalized papulokeratotic variant
what is the treatment for generalized transient lingual papilitis
spontaneous resolution
how do aphthous ulcerations develop
from an immunologic reaction to an oral antigen
what is the most common recurrent aphthous stomatitis
minor aphthous ulcer (mikulicz aphthae)
what do some consider an additional form of recurrent ulcers
Behcet syndrome
what is a very complex multisystem disorder of recurrent ulcers
Behcet syndrome
what are the clinical manifestations of minor variation of recurrent ulcers
1. fewest recurrence
2. shortest duration
3. lesions almost only in nonkeratinized mucosa
4. ulcers measure 3-10 mm in diameter
5. typically 1-5 ulcers
what are the clinical manifestations of major variation of recurrent ulcers
1. longest duration per episode
2. scar formation
3. ulcers are deeper and measure 1-3 cm
4. affects any oral mucosa
5. scarring may become significant but restricted to mouth opening
what are the clinical manifestations of herpetiform variation of recurrent ulcers
1. greater number of ulcers(100 in asingle episode)
2. small lesions(1-3mm in diameter)
3. may affect any oral mucosa
treatment for herpetiform ulcers
topical corticosteroids: dexamethasone solution (0.5mg/5ml)
what is the triad to recognize Behcet syndrome
1. ocular inflammation
2. oral ulcers
3. genital ulcers
what is the cause of type A (augmented) adverse drug reaction
an exaggerated (otherwise expected) pharmacological action of drug
what is stomatitis medicamentosa
a reaction of the oral mucosa to the systemic administration of a medication
where do fixed drug eruptions recur
at the same site after administration of allergen
what is the diagnosis of stomatitis medicamentosa
1. detailed medical history
2. establish temporal relationship between medication and offense
what is the diagnosis in chronic drug reactions
observe the behavior of mucosal alteration
- does it resolve when drug is discontinued?
what is the treatment for stomatitis medicamentosa
discontinue the responsible medication if possible
T/F: frequency of true oral allergic reactions is rare
True
what are the clinical manifestations of allergic contact stomatitis when localized
removal of focal trauma
- e.g.., dental metals
diagnosis of acute allergic contact stomatitis
temporal relationship between agent and clinical manifestation
- do symptoms develop after exposure to allergen?
treatment for mild cases of allergic contact stomatitis
removal of suspected agent is sufficient
treatment for perioral dermatitis
no therapy in most cases
- discontinu the causative agent (cosemetics, creams, facial products, etc)
treatment for allergic reaction to cinnamon products
discontinuation of cinnamon products
what is a lichenoid contact reaction from dental restorative materials
an allergic response that appears as a lesion on the oral mucosa in direct contact with the dental material
diagnosis of lichenoid contact reactions
1. clinical characteristics of the lesion
2. lack of lesion migration
3. correlation to adjacent dental material
what is angioedema
swelling of soft tissue
causes of angioedema
dental trauma can precipitate angioedema in both hereditary and acquired forms
what is salivary gland aplasia
developmental anomaly
what are clinical manifestations of salivary gland aplasia on physical examination?
physical examination:
- face looks normal (site filled w/ connective or adipose tissue)
-absence of orifices of missing glands
- lacrimal glands or lacrimal puncta may be absent
what are the symptoms of salivary gland aplasia
- severe xerostomia
- leathery tongue
- frequent caries and erosion
what makes a mucocele not a true cyst
it lacks epithelial lining
what are the clinical manifestations of a mucocele (appearance)
dome-shaped mucosal swellings
what is the treatment for a mucocele
may rupture and heal spontaneously
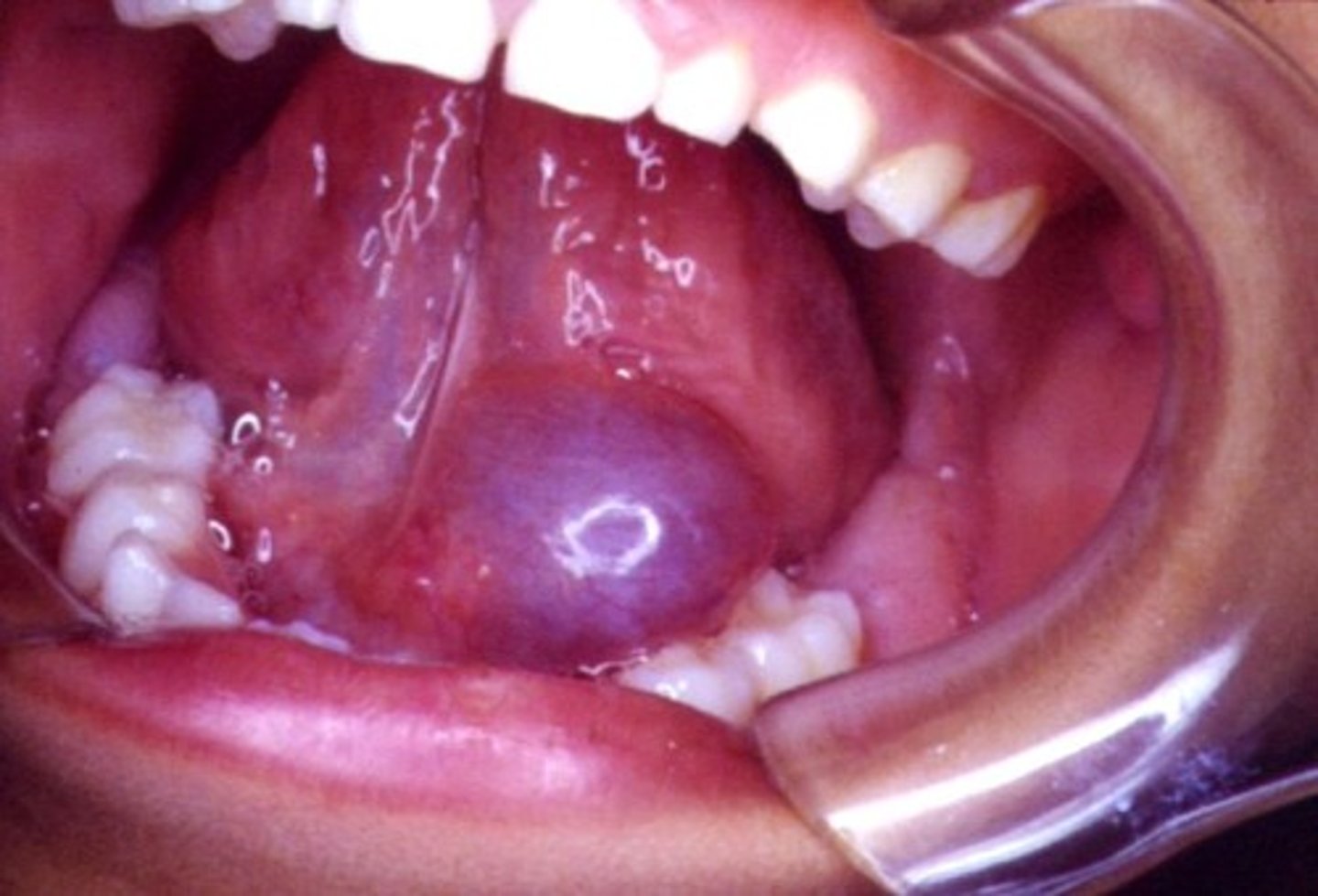
what is a ranula
a mucocele that occurs in the floor of the mouth
- arise from the sublingual gland
what are the clinical manifestations of a ranula (physical examination)
- swollen lesion in the floor of the mouth
- blue (deeper lesions are normal color)
- dome-shaped
what is the treatment for a cervical (plunging) ranula
surgical removal of feeding gland
what is the difference between a mucocele and a salivary duct cyst
a salivary duct cyst is a true developmental cyst that is lined by epithelium that is separate from the adjacent normal salivary ducts
Clinical manifestation: what are the frequent locations of salivary duct cysts
- floor of mouth
- buccal mucosa
- lips
salivary duct cyst over the Wharton duct
histopathology of mucocele
no epithelial lining, mucin accumulation in cavity
histopathology of salivary duct cyst
cavity lined by epithelial tissue
clinical manifestation of sialoithiasis: frequency?
most common in the ductal system of submandibular gland
symptoms of sialolithiasis
- episodes of pain
- swelling of affected gland
- mealtimes: symptoms become more intense
what determines the severity of symptoms of sialolithiasis
1. degree of obstruction
2. amount of backpressure within the gland
Treatment for sialolithiasis (small)
conservative treatment aimed to facilitate passage of stone:
- gentle massage of the gland
- sialogogues
- moist heat
- increased fluid intake
Treatment for sialolithiasis (large)
surgical removal depending on glandular damage
what is sialadentis
inflammation of a salivary gland
what causes sialadenitis
viral infections:
- mumps (most frequent)
- HIV
- Flu
what are the non-infectious causes of Sialadenitis
- Sjogren syndrome
- Sarcoidosis
- Radiation therapy
- Various allergens
what glands are affected in acute bacterial sialidenitis
most common in parotid glands
clinical manifestations of chronic sialadenitis
periodic swelling and pain associated with mealtime (stimulation of salivary flow)
Clinical manifestations (sialadenitis): Juvenile recurrent parotitis
most common inflammatory condition in children in US
what is xerostomia
dry mouth: usually associated w/ hypofunction of salivary glands
What are the complications of xerostomia?
reduced salivary flow
leads to:
- oral candidiasis
- increased risk of dental decay, most cervical and root caries ( xerostomia-related caries)
What is Sjogren's syndrome?
chronic, systemic autoimmune disorder that principally involves the salivary and lacrimal glands
Sjogren's Syndrome causes (2 things)
Xerostomia (dry mouth)
Xeropthalmia (dry eye)
- keratoconjunctivitis sicca
what is it called when you have both xerostomia (dry mouth) and xerophthalmia (dry eye) in sjogren syndrome
sicca syndrome
what are the clinical forms of sjogren syndrome
1. primary sjogren syndrome
2. secondary sjogren syndrome
what is primary sjogren syndrome
sicca syndrome alone (no other autoimmune disorder present)
what is secondary sjogren syndrome
sicca syndrome with another autoimmune disease present
what is benign epithelial lesions associated with
human papillomavirus (HIV)
what are examples of HPV related lesions
- squamous papilloma
- verruca vulgaris
- condyloma acuminatum
- multifold epithelial hyperplasia
- fungiform papilloma
- inverted papilloma
How do you get HPV (modes of transmission)
- sexual and nonsexual person-to-person contact
- salivary transfer
- contaminated objects (fomites)
- autoinoculation
- breast feeding
- perinatal transmission
- possible prenatal transmission
which HPV types have a high risk of malignant transformation (2)
16 and 18
what is squamous papilloma
benign condition induced by HPV
what HPV type are commonly associated with squamous papilloma (2)
6 and 11
clinical manifestations: where do you find squamous papilloma
found anywhere in the oral mucosa
clinical manifestation: appearance on inspection of squamous papilloma?
exophytic nodule
treatment for squamous papilloma
conservative surgical incision, including base of lesion
what is verruca vulgaris
focal, benign, HPV-induced hyperplasia of stratified squamous epithelium
what is verruca vulgaris mostly caused by
HPV 2
where can you find verruca vulgaria
-common in the skin
-infrequent in oral mucosa
What is condyloma acuminatum?
venereal wart
- HPV-induced proliferation of stratified squamous epithelium of the anogenital region, mouth, and larynx
what common STD is an indicator of sexual abuse in children
condyloma acuminatum
what are the risk factors of multifocal epithelial hyperplasia
- lower socioeconomic status
- crowded living conditions
- poor hygiene
- malnutrition
- HIV infection
What types of HPV are common in fungiform papilloma (2)
6 and 11
clinical presentation of fungiform papilloma
- unilateral nasal obstruction
- epistaxis
treatment for fungiform papilloma
complete surgical excision
what is inverted papilloma
most common sinonasal papilloma variant
what papilloma variant have the greatest potential for local destruction and malignant transformation
inverted papilloma
what HPV types are most prevalent in inverted papilloma (4)
6, 11, 16, and 18
clinical manifestation: inverted papilloma peaks at what age
50s and 60s
clinical manifestation: signs and symptoms of inverted papilloma
- unilateral nasal obstruction
- epistaxis
- purulent discharge
- hyposmia
- headache
- local deformity
epithelial lesions NOT associated with HPV
- verruciform xanthoma
- oral melanotic macule
- leukoplakia
- erythroplakia
what is oral melanotic macule
flat, brown, mucosal discoloration produced by a focal increase in melanin deposition and, possibly, a concomitant increase in the number of melanocytes
treatment for oral melanotic macule
excisional biopsy is recommended to differentiate from malignant melanoma
what is leukoplakia
a white patch or plaque that cannont be characterized clinically or pathologically as any other disease
- precancerous lesion (white when wet)
what is the most common oral precancer
Leukoplakia
where are most leukoplakias located that show dysplasias or carcinomas
- tongue
- lip vermilion
- oral floor
clinical manifestation: proliferative verrucous leukoplakia (PVL)
- special high-risk form of leukoplakia
- multiple, slowly spreading, keratotic plaques w/ rough surface projections
clinical manifestation: erythroleukoplakia (speckled leukoplakia)
usually advanced dysplasia is shown in biopsies
clinical manifestation: mixed lesions (mixture of subtypes of leukoplakias)
biopsies should be taken from areas w/ higher risk of malignant or dysplastic changes