Major Protozoans
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
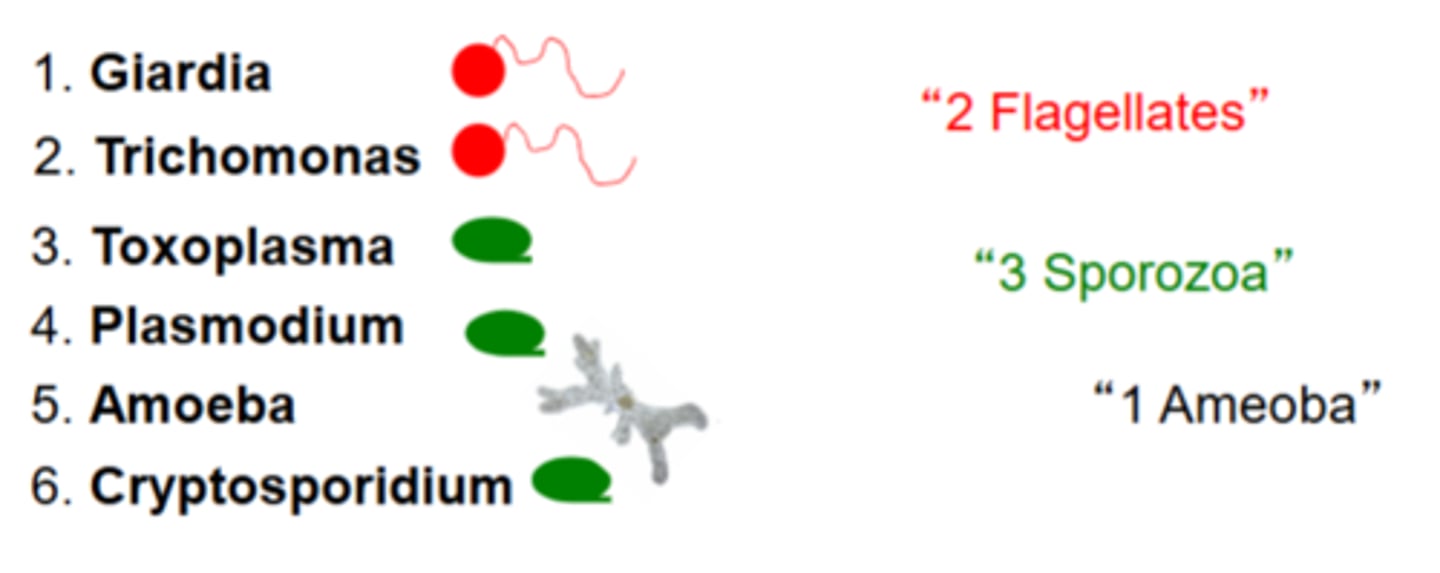
what are the 2 flagellates, 3 sporozoa, and one amoeba we need to know?
____ is the most frequent case of acute symptomatic parasite disease in the US and worldwide? This is true regardless of ____ ____
giardia; socioeconomic level
Giardia attaches and remains localized in the ___ ____. It is able to parasite a wide range of mammals. It is only sometimes _____
small intestine; zoonitic
habitat and transmission of giardia

giardia is common among ____ _____. The cysts are ____ resistant, and transmitted via the ___-___ route
outdoor enthusiasts; chlorine; fecal-oral
clinical manifestations/pathogenesis of giardia

diagnosis/treatment/prevention of giardia
diagnosis - stool O&P for systs and trophozoites, serial stool antigen test is the gold standard
treatment - metronidazole, though there is some known resistance
prevention - boiling water for at least a minute while camping and hiking
Distinctive features/virulence factors/epidemiology of T. vaginalis.
Only ____ are symptomatic
It has a large size, about equivalent to a _____, and is only seen in the trophozoite form with what important attribute?

clinical manifestations of T. vaginalis, what are some consequences of infection?

diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of T vaginals
diagnosis - serology by test strip
treatment - metronidazole, tintdazole is now approved
prevention - safe sex
What is the motility of sporozoa?
non-motile
C. parvum is the major cause of _____ in ___ patients and with _____ therapies.
diarrhea; AIDS; immunosuppressive
C. parvum shows a variety of ....... within its life cycle
cell division types and many different morphological forms
C. parvum:
what does it not need?
How is it transmitted?
What life stage is resistant in the environment?
How does contamination most commonly occur?

Describe the presence of C. parvum in the intestine
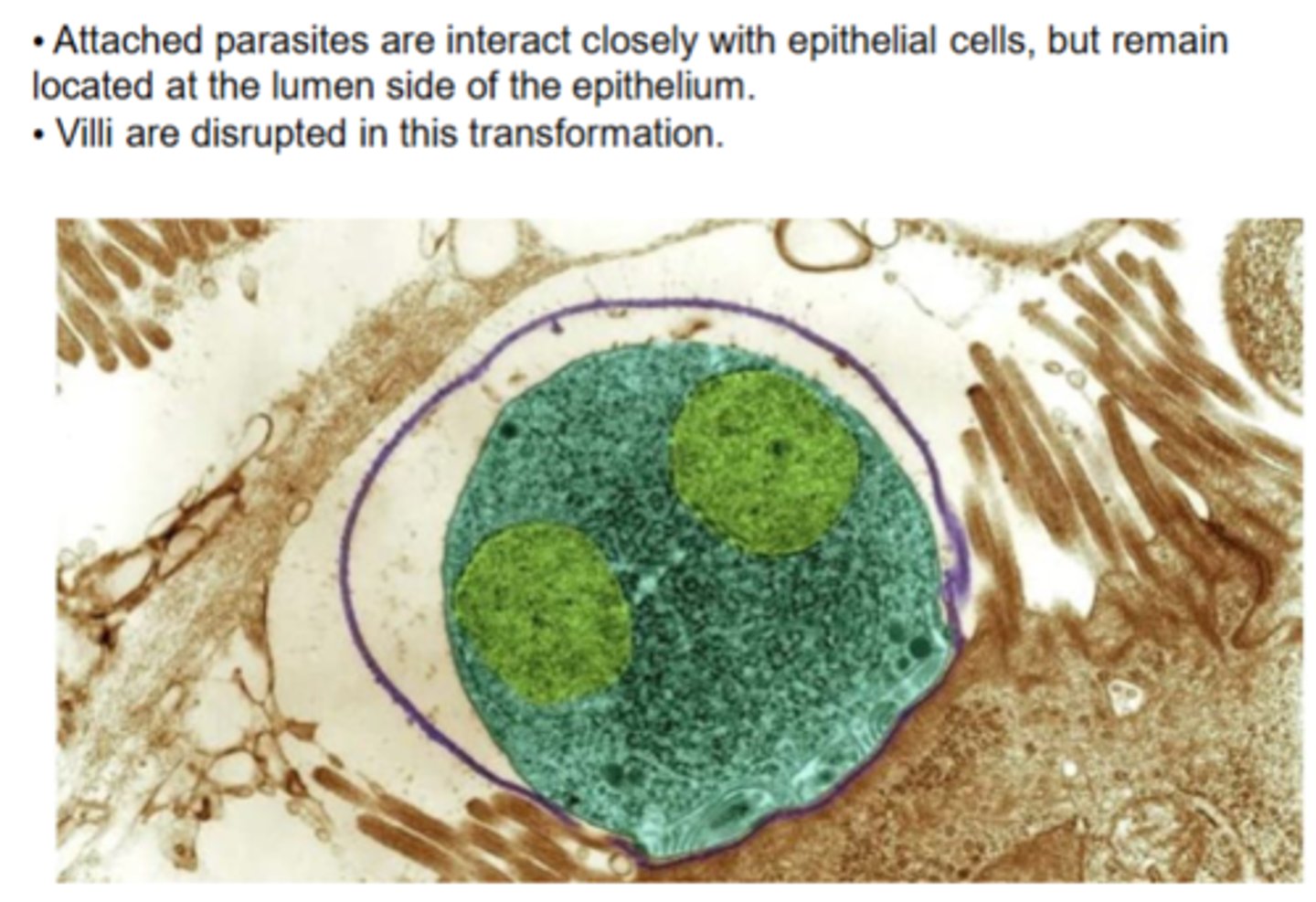
Symptoms of C. parvum

Diagnosis/ Treatment/Prevention
diagnosis - microscopy to identify acid-fast oocytes in the stool
treatment - electrolyte replacement
prevention - water treatment and personal hygeine
Distinctive features/virulence factors of toxoplasma gondii
- note the common household vector
- in what host does sexual reproduction take place and what kind of host does that make it?
-what other reproductive traits can toxoplasma do?

visualize the T. gondi lifecycle
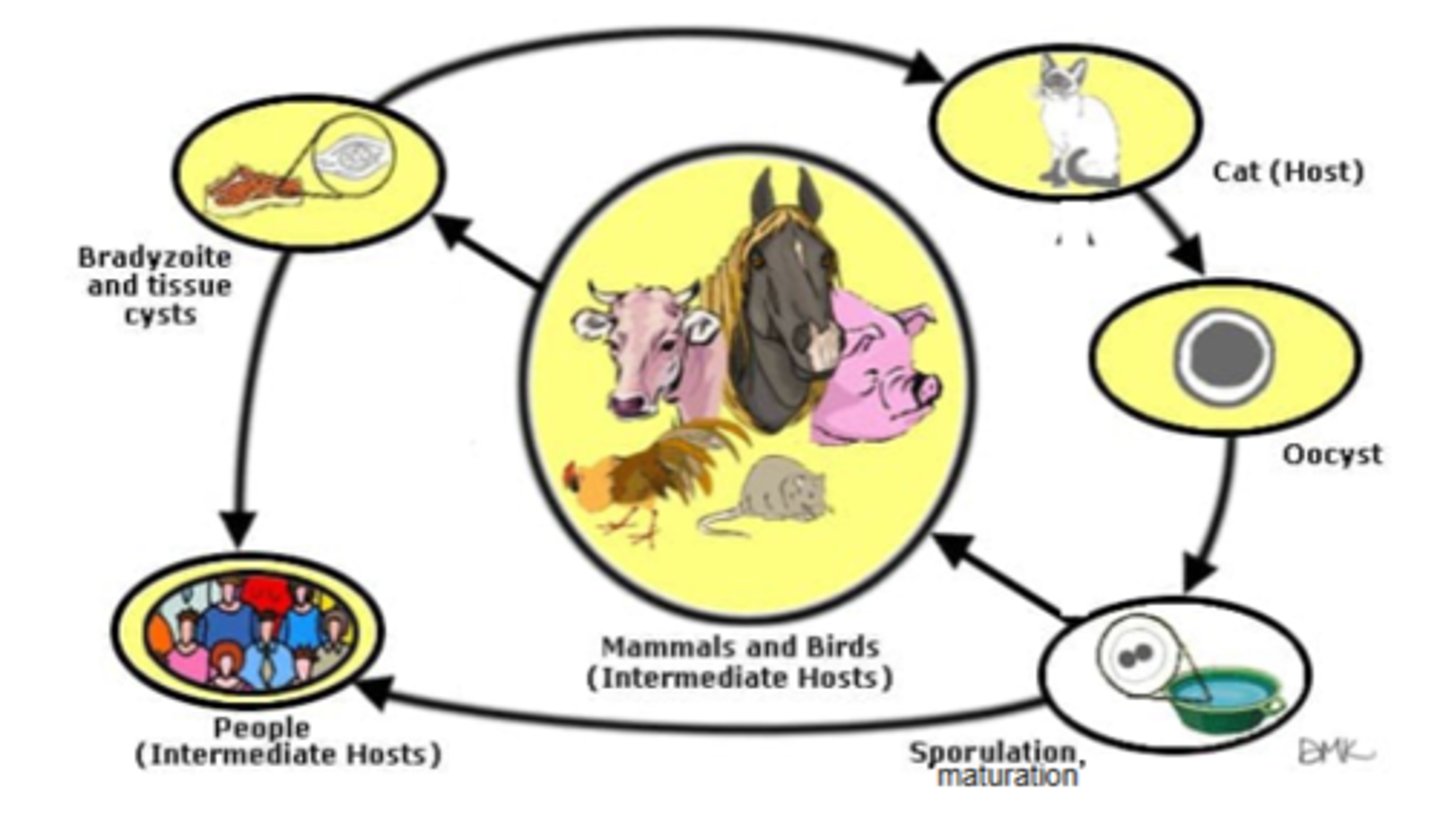
Habitat/transmission/epidemiology of T. gondi

What life stage of T. gondii do humans ingest, and then what happens?
what immune cell responds primarily to T. gondii and what does it do?

Diagnosis/ Treatment/Prevention of T. gondii

what disease do Plasmodium species cause?
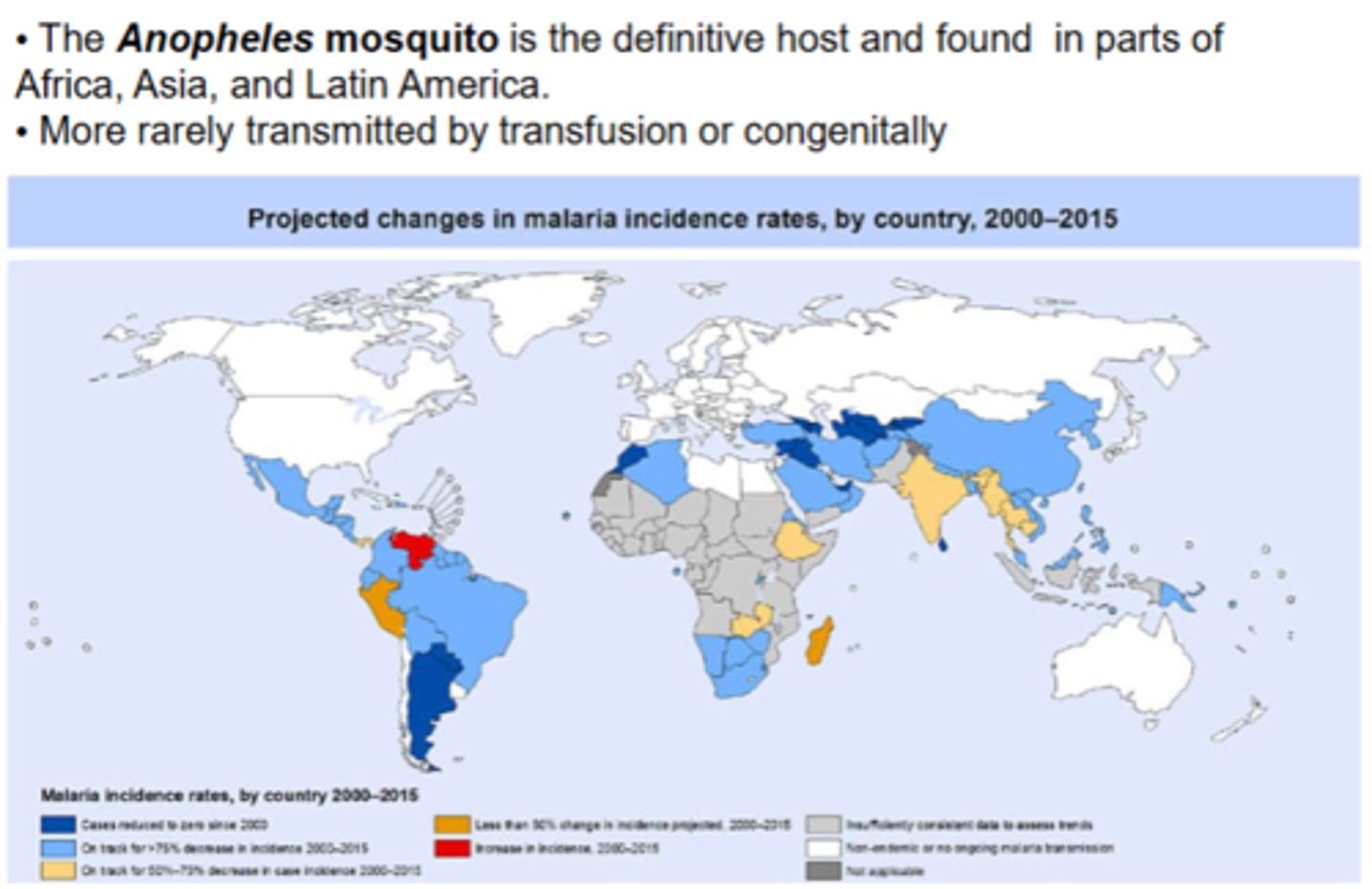
What is their distribution? what is the main species?
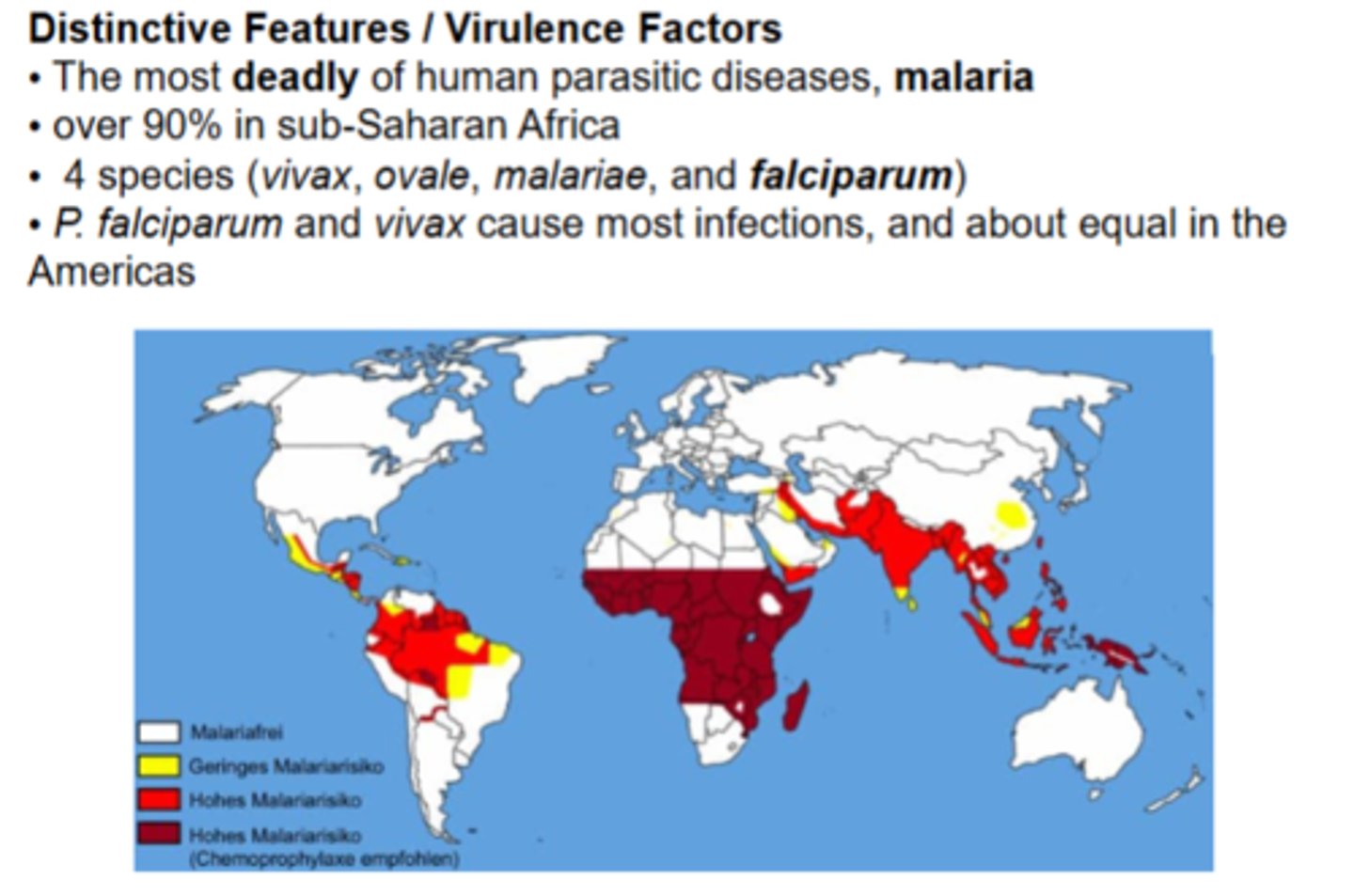
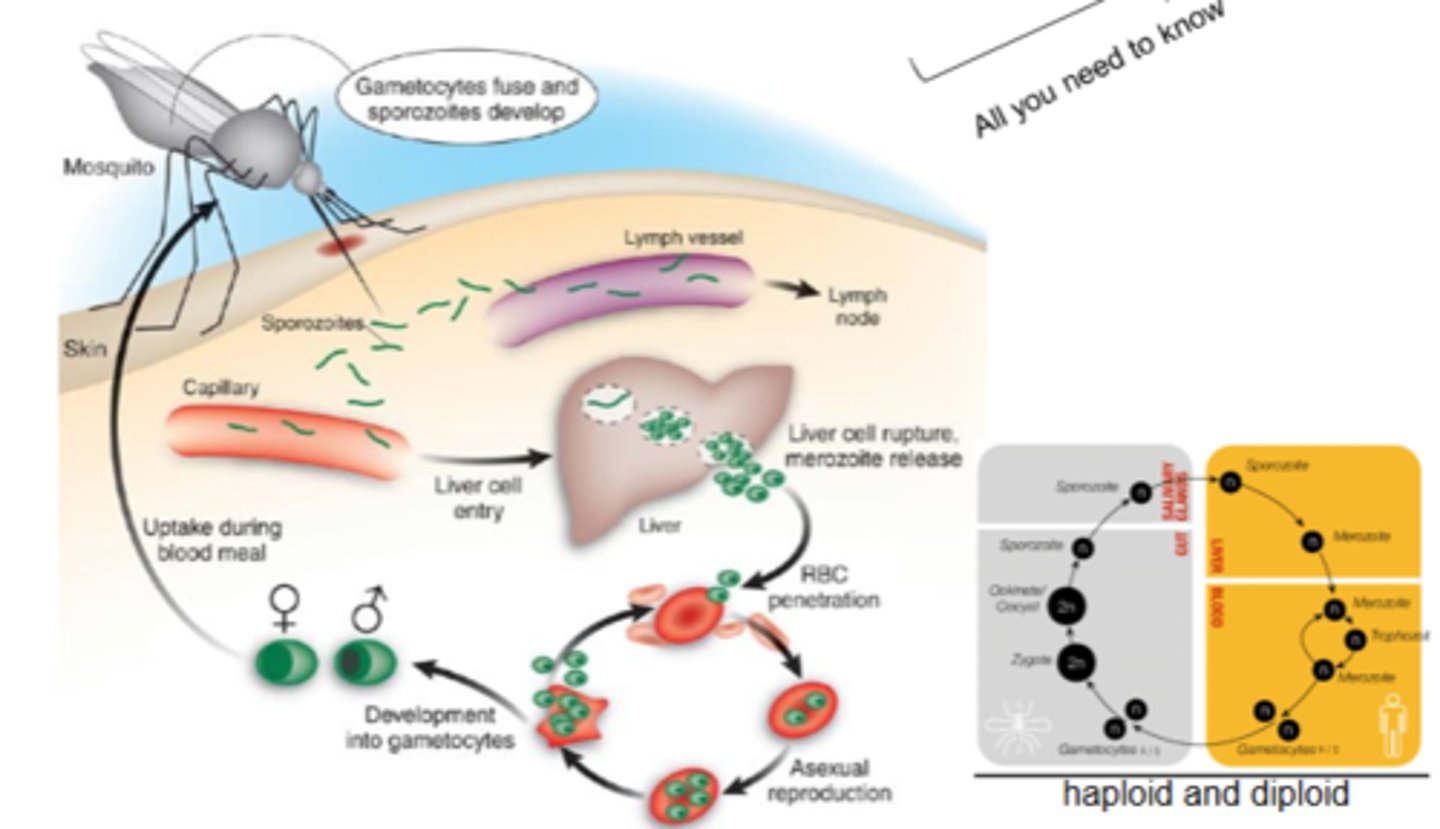
describe the lifecycle of plasmodium

The _____ _____ is the definitive host of P. falciparum. what are two rare ways it can be transmitted?
Describe what happens with a mosquito infected with P. falciparum bites a human
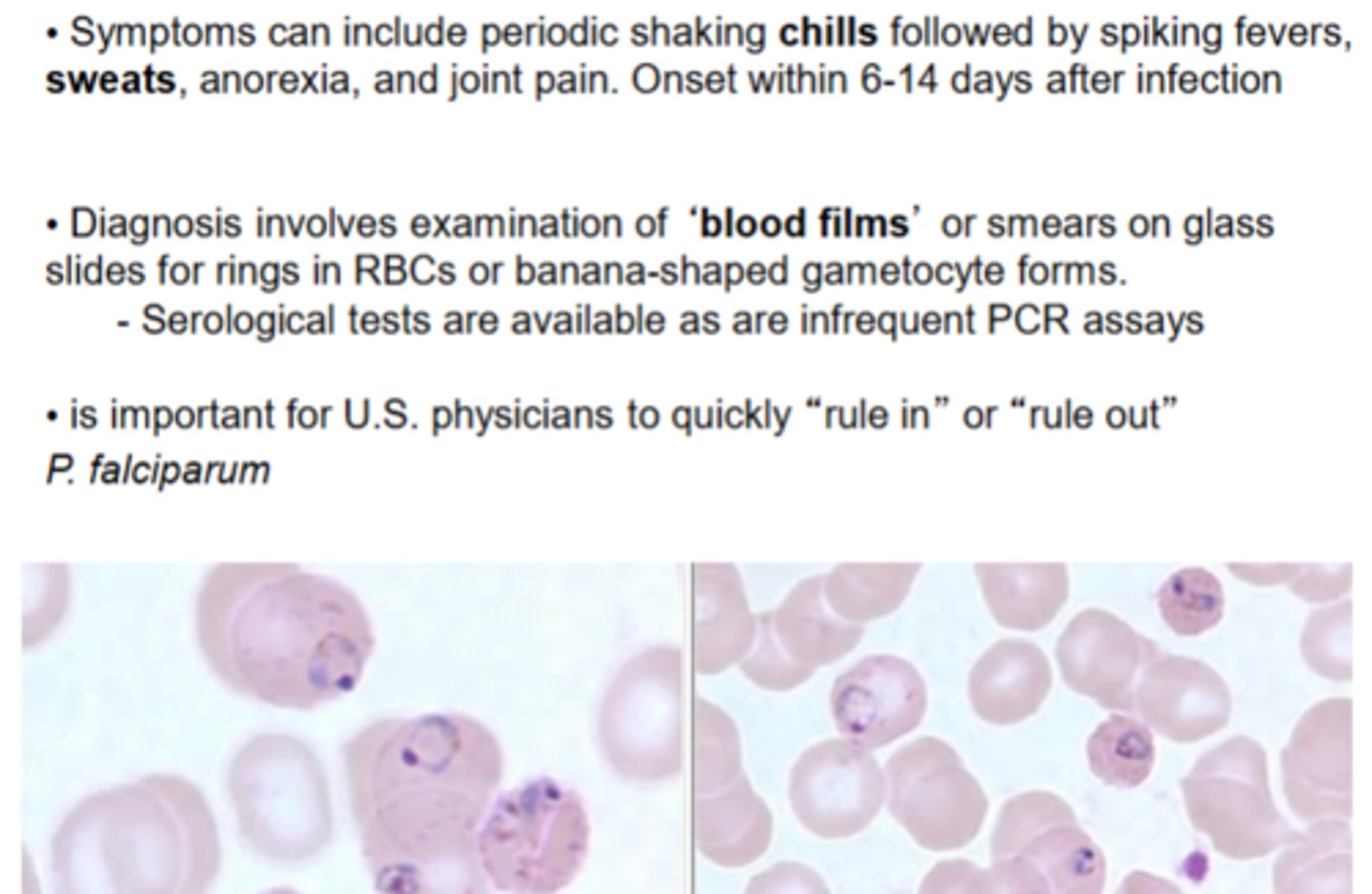
describe clinical manifestations/ pathogenesis of Plasmodium infection

Diagnosis of plasmodium infection
treatment and prevention of P. falciparum
species identification
chloroquine, CDC reporting, travelers can use prophylactic treatment, insect control
most distinctive feature of amoebas. what are the two forms in the lifecycle?

in what organisms is E. histolytica found in?
how does transmission occur?
Describe the cyst

Where is Amoebiasis caused by E. histolytica common? where has transmission been noted?

How is E. histolytica diagnosed?

treatment and prevention of E. histolytica

what organism causes amebic meningoencephalitis?
N. fowleri
Naegleria carries out its entire lifecycle in ____ ____ and humans are an ____ or ______ host when infections occur in the _____ _____
warm waters; accidnetal; dead-end; nasal epithelium
How is N. fowleri diagnosed?
