1.3 Exchanging data
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
83 Terms
Lossy Compression
Removes non essential data from a file leading to a noticeable decrease in accuracy of the data. Data lost is non-recoverable.
Lossless Compression
Retains all the data in the file by only storing the instructions needed to reconstruct the original file. No data is lost.
Flat file
a single table and a usually written out as "Entity1(Attribute1, Attribute2, Attribute3...)"
Relational database
Separate tables are made for each entity.
Primary key
Unique identifier.
Secondary key
Allows database to be searched through quickly.
Foreign key
Attribute that links two tables together.
Entity relationship modelling
One-to-one - Each entity can only be linked to one other entity.
One-to-many - One table can be associated with many other tables.
Many-to-many - One entity can be associated with many other entities and the other way around.
Normalisation
Optimally designing data tables by reducing data redundancy and repetition.
1NF
Table with no repeating attributes.
2NF
Data that repeats across multiple records is removed and put into a new table with appropriate relationships, no partial dependencies.
3NF
All attributes that are not the primary key are fully dependent on the primary key, key dependency.
Indexing
Used to look up and access data quickly.
Capturing Data
Before data is added to a database, it has to be captured or inputted by some means or another
This can either be done by manual methods or automatic methods such as OCR, MICR or barcode readers.
SELECT
Collect fields from a given table
FROM
Specifies which table the info will come from
WHERE
Specifies the search criteria
ORDER BY
SELECT MovieTitle, DatePublished
FROM Movie
WHERE DatePublished BETWEEN #01/01/2000# AND #31/12/2005#
ORDER BY DatePublished (ASC/DESC)
JOIN
Combines rows from multiple tables based on a common field.
SELECT Movie.MovieTitle, Director.DirectorName, Movie.MovieCompany
FROM Movie
JOIN Director
ON Movie.DirectorName = Director.DirectorName
CREATE
Make new database.
CREATE TABLE TableName
(
Attribute1 INTEGER NOT NULL, PRIMARY KEY,
Attribute2 VARCHAR(20) NOT NULL
)
ALTER
Add/delete/modify columns
ALTER TABLE TableName
ADD AttributeX and their dataTypes
ALTER TABLE TableName
DROP COLUMN AttributeX
ALTER TABLE TableName
MODIFY COLUMN AttributeX NewDataType
INSERT INTO
Insert a new record
INSERT INTO (column1, column2, ...)
VALUES (value1, value2, ...)
UPDATE
Update a record
UPDATE TableName
SET column1 = value1, column2 = value2
WHERE columnX = value
DELETE
Delete a record
DELETE FROM TableName
WHERE columnX = value
Referential Integrity
Ensuring consistency
ACID
ACID guarantees that transactions are processed.
Atomicity
Consistency
Isolation
Durability
Atomicity
All transactions will succeed or fail, never stop mid-way.
Consistency
Each transaction must obey defined validation rules of the database.
Isolation
No transaction should overwrite other transactions done by deciding the order of transactions and doing it in the correct order.
Durability
Once transaction has begun it must be completed!
Physical topology
Physical layout
Logical topology
Way in which data flows
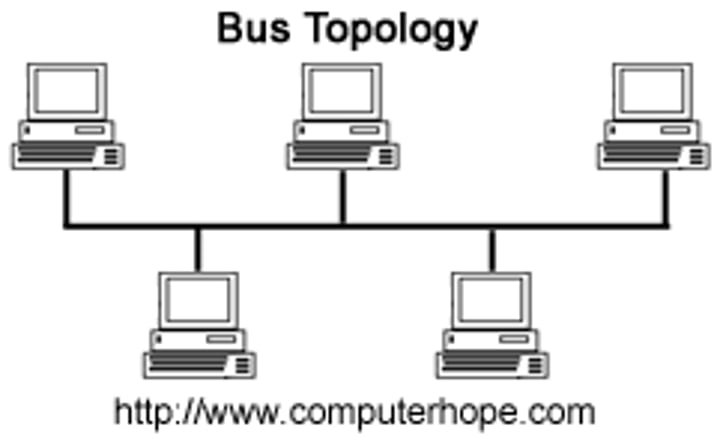
Bus topology
All terminals (devices) are connected to a backbone cable
+
Cheaper to set up, doesn't require any additional hardware
-
If backbone cable fails, the entire network gets disconnected
As traffic increases, performance decreases
All computers can see the data transmission
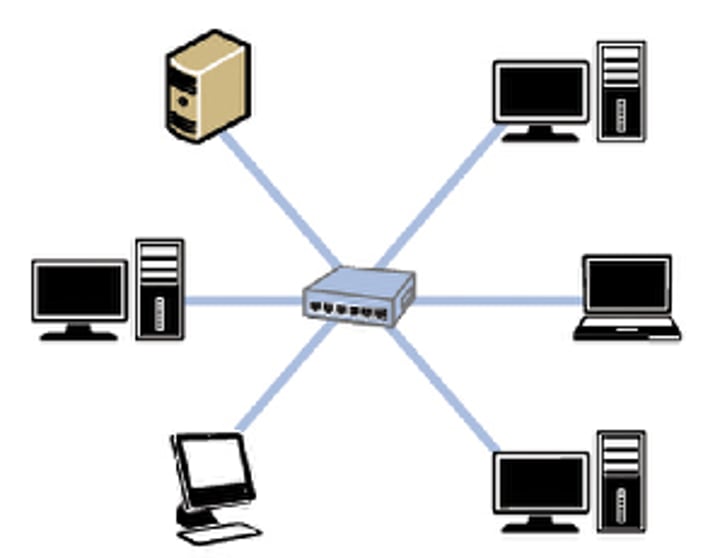
Star Topology
Uses a central node (switch/computer) to direct the flow of data
+
Performance is consistent even if network is being heavily used
If one cable fails, only that station is affected
Transmits data faster, so it gives better performance than bus topology
It's easy to add new stations
No data collisions
-
Expensive due to switch and cabling
If the central switch fails, the rest of the network fails
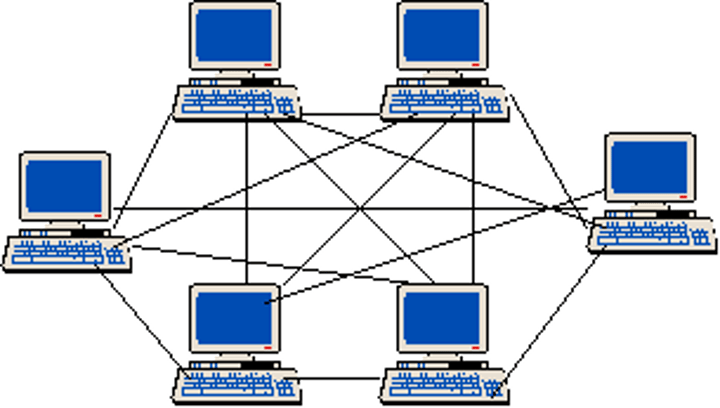
Mesh Topology
Every node is connected to every other node
+
No cabling cost
As nodes increase, the reliability and speed of network becomes better
Nodes automatically get incorporated
It's faster since nodes don't go through a central switch
-
You have to purchase devices with wireless capabilities Maintaining the network is difficult
Protocols
Rules defining how devices communicate with each other`
TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol) Stack
Stack of networking protocols that work together passing packets during communication.
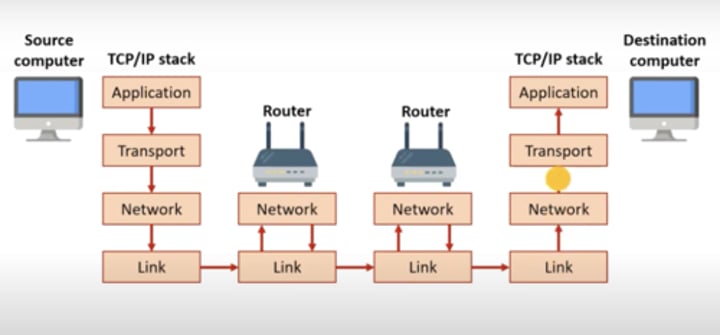
Application layer
Sending:
Specifies which protocol needs to be used in order to relate the application that's being sent.
Receiving:
Presents the data to the recipient in the form it was sent.
Transport layer
Sending:
Establishes an end to end connection between the source and recipient computer, splits the data into packets, labels them and requests retransmission of any lost packets.
Receiving:
Removes the port number and reassembles the packets.
Network layer
Sending:
Adds IP addresses
Receiving:
Removes the IP addresses
Link layer
Sending:
Connection between the network devices and adds the MAC address identifying the NIC of the source and destination computers.
Receiving:
Removes the MAC addresses.
LAN
Local area network spread over a small geographical area
WAN
Wide area network spread over a large geographical area that requires extra hardware.
DNS
Domain name system is the system given to the method of naming internet resources, they translate domain names into IP addresses when we access a website.
Circuit switching
A method of communication where a direct link is created between two devices
Link maintained for the entire conversation
The two devices must transfer and receive data at the same rate
+
Quicker reconstruction
No delay in speech
-
Bandwidth wasted
Must transfer and receive at the same rate
Can corrupt or lose data
Packet Switching
A method of communicating packets of data across a network
A packet is just a section of the data
Packets aren't limited to a single route
+
Multiple methods to ensure data arrives
Can transfer over very large networks
Can use any path
-
Time is spent deconstructing and reconstructing data packets
Data packets
Segments of data contain information:
○ Header
■ Sender and the recipient's IP addresses
■ Protocol being used
■ Order of the packets
■ Time To Live / Hop Limit
○ Payload
■ The raw data
○ Trailer
■ Checksum, or cyclic redundancy check
Firewalls
Prevent unauthorised access to a network by comparing packets against a set of rules set by the firewall software.
Proxy servers
● Act as an intermediary, collecting and sending the data on behalf of the user
● Protect the privacy of the user who remains anonymous
● Cache frequently used website data making it faster to load
● Reduce the web traffic
● Can be used by administrators to prevent access to sensitive or irrelevant information at work or at school
Encryption
Keep data secure
Network interface card (NIC)
Required to connect to a network and assigns a unique MAC address to each device.
Switches
Used to direct flow of data across the network most commonly used in a star topology.
Wireless access point (WAP)
Allow devices to connect to a network wirelessly, used in mesh networks.
Routers
Used to connect two or more networks together.
Gateways
Used when protocols aren't the same between networks and translates the protocols so that they are the same.
Client server
The server is a powerful central computer, the server holds all the important info and has extra processing power.
+
Secure
Central backups stop the need for client backups
Sharing data and resources
-
Expensive
Need trained staff to maintain
Peer to peer network
Computers are connected to each other so they can share files, cheap to set up, allows users to share resources, and easy to maintain.
Code written within these tags is interpreted as HTML.
<html>(CODE)</html>
Link a CSS file.
<link rel="stylesheet" href="(LOCATION)">
Define the heading area.
<head>(CODE)</head>
Set the name of the tab.
<title>(TITLE)</title>
Needs to be within the head tags
Define the body of the code.
<body>(CODE)</body>
Create a header.
<h(NUM)>(TEXT)</h(NUM)>
Create an image.
<img src="(URL)" alt="(TEXT)" width="(X)" height="(Y)">
Create a hyperlink.
<a href="(LOCATION)">(TEXT)</a>
Create a division of a page that can be referred uniquely by a name.
<div id="(NAME)">(CODE)</div>
Create a form.
<form>(CODE)</form>
Create a textbox/submit button.
<input type="(text/submit)" name="(NAME)">
Has to be within form tags
Create a paragraph.
<p>(TEXT)</p>
Create an ordered/unordered list.
<(ol/ul)><li>(TEXT)</li></(ol/ul)>
The tags used to write in javascript.
<(script)>(CODE)</(script)>
How to use CSS directly into an h1 element.
<h1 style="color:blue;">
How to edit a h1 tag in a css file.
h1{ color:blue; }
How to create a class.
.infoBox{ background-color: green; }
How to create an identifier
#menu{ background-color: #A2441B; }
Keywords for background color, border color, border style, border width, font family, font size, height, and width.
background-color
border-color
border-style
border-width
font-family
font-size
height
width
How to change the contents of a HTML element.
chosenElement = document.getElementById("example");
chosenElement.innerHTML = "Hello World";
How to write directly to the document.
document.write("Hello World");
How to use an alert box.
alert("Hello World");
Search engine
Program that searches through a database of the internet addresses. They rely on index of web pages, and web crawlers.
Page rank algorithm
Determines the page rank of how many incoming links it has from other web pages and the page rank of the web pages that link to it.

Server side processing
Client sends data to a server for it to be processed. So that no info is processed on client side. Beneficial because it doesn't require plugins, can perform large calculations, not browser dependent, and its more secure.
Client side processing
Processing is done on the local device. Beneficial because webpage can immediately respond to user actions, execute quickly, gives devs more control over behaviour and look.