Chapter 40: The Circulatory System
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
True or false: like unicellular organisms, most multicellular organisms obtain food and oxygen, and remove waste via diffusion
false
unicellular organisms obtain food and oxygen, and remove waste via diffusion—which is difficult for multicellular organisms to do
true or false: small/simple organisms, such as flatworms, dont need a circulatory system because they’re thin and small enough for diffusion to occur
true
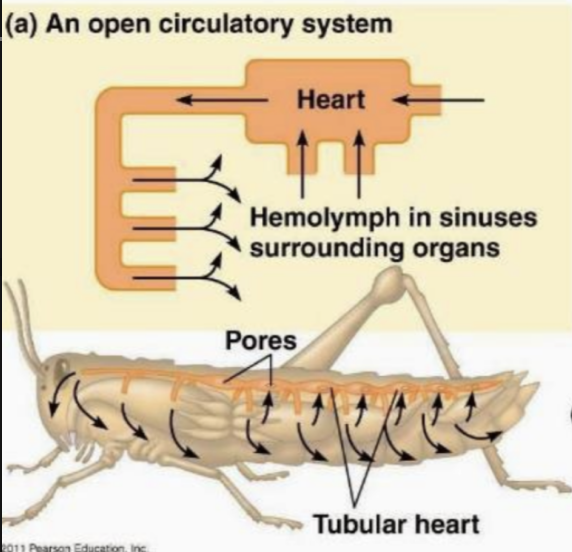
in this type of circulatory system, oxygen, nutrients, and hormones flow through cavities, which limits their transportation throughout the body
open circulatory system
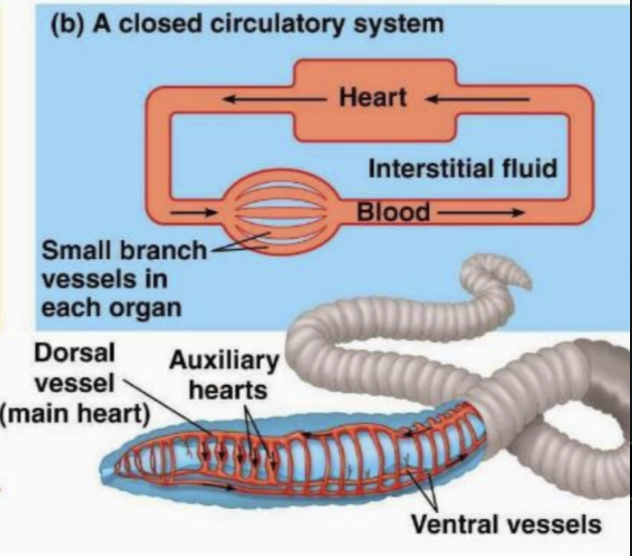
in this type of circulatory system, oxygen, nutrients, and hormones flow within blood vessels, which efficiently transports them throughout the body
closed circulatory system
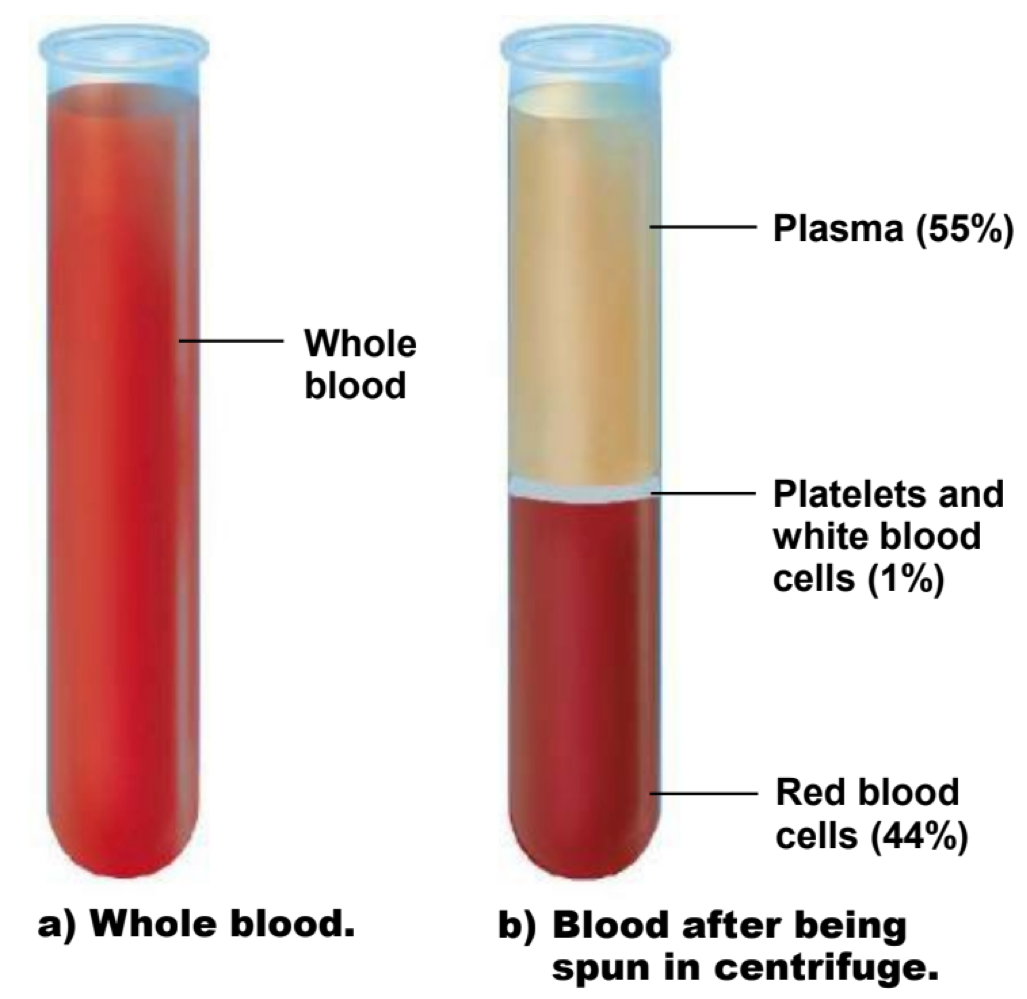
this specialized connective tissue is composed of plasma and various cellular components
blood
water, electrolytes, proteins, hormones, nutrients, gases, and wastes make up which component of blood?
plasma
you can measure the proportions of cellular components in blood via ___
hematocrit (centrifusion)
tubes that carry blood between the heart and rest of the body are known as ___
blood vessels
true or false: the heart is a contracting pump that pushes blood into muscles
false. the heart is a contracting pump that pushes blood into arteries
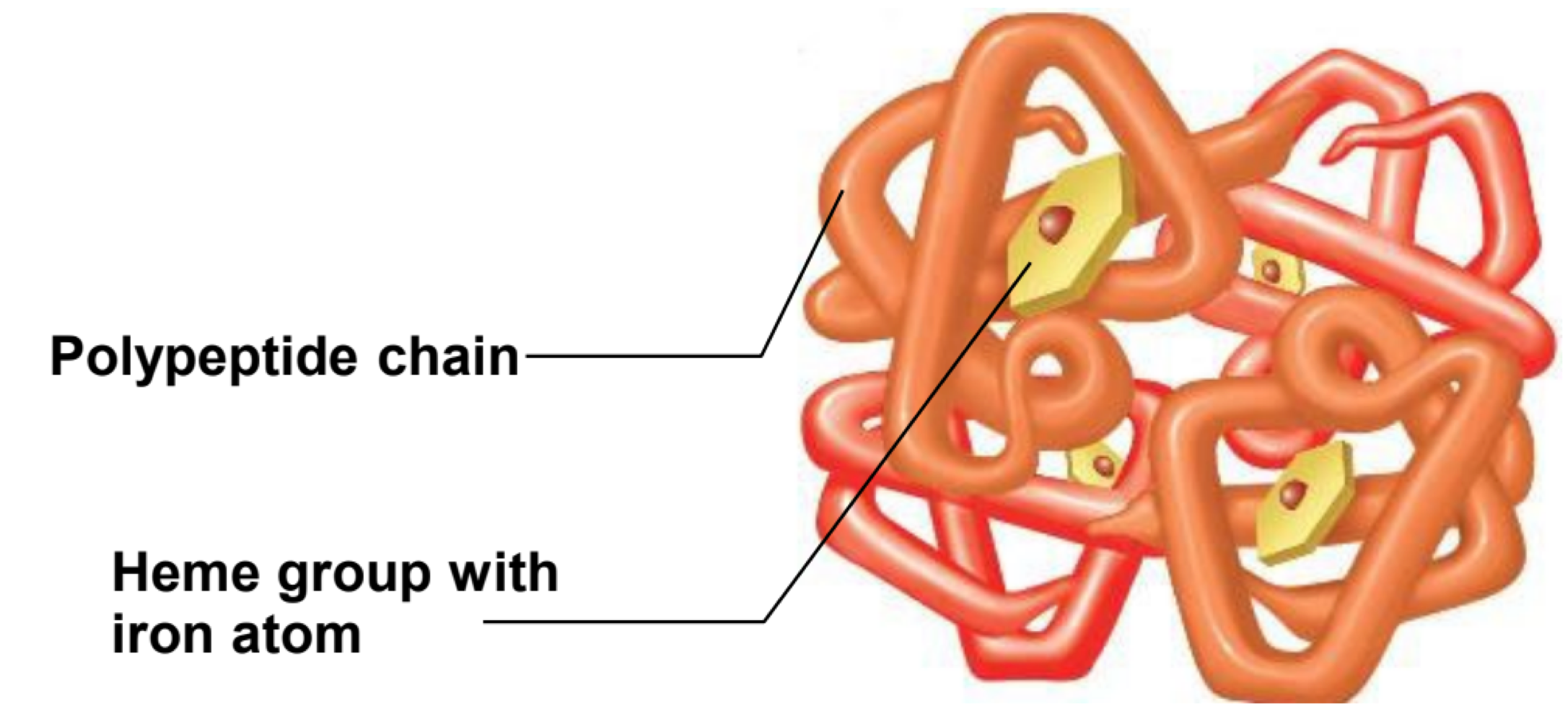
this type of blood cells transports oxygen and carbon dioxide, and lack a nucleus and most organelles
erythrocytes (RBC)
true or false: erythrocytes contain copper
false
erythrocytes contain hemoglobin
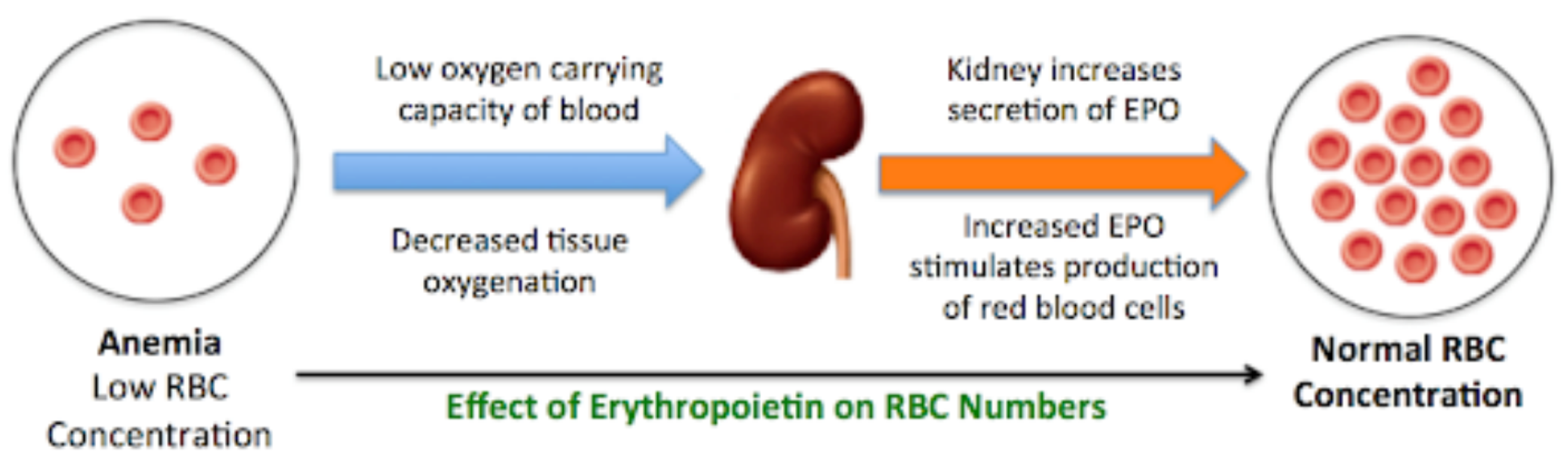
this hormone regulates the production of erythrocytes
erythropoietin (EPO)
“low oxygen levels → EPO released by kidney cells → RBC matures → oxygen levels increases → EPO production ceases” describes what kind of feedback loop?
negative feedback loop
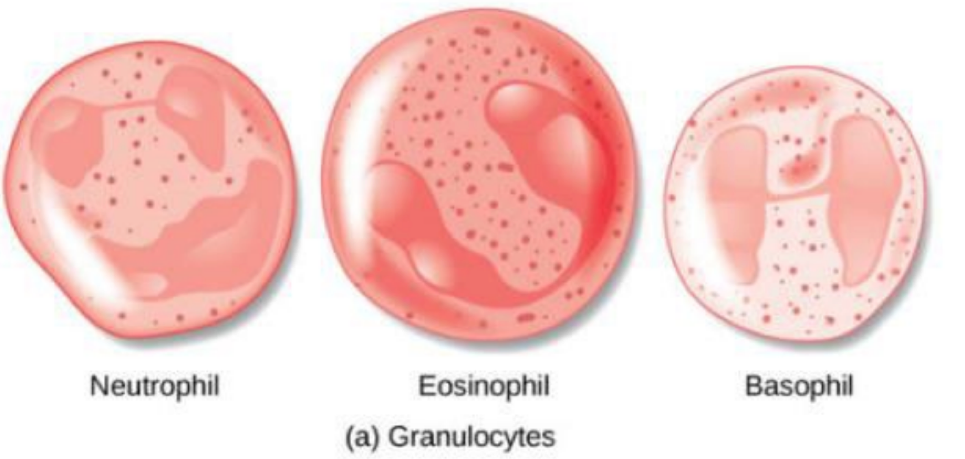
this type of blood cells protects the body from infection and regulates the inflammatory reaction
leukocytes (WBC)
neutrophils, eosinophils, and basophils have vesicles that release chemicals. thus, they’re classified as what type of leukocytes?
granular leukocytes
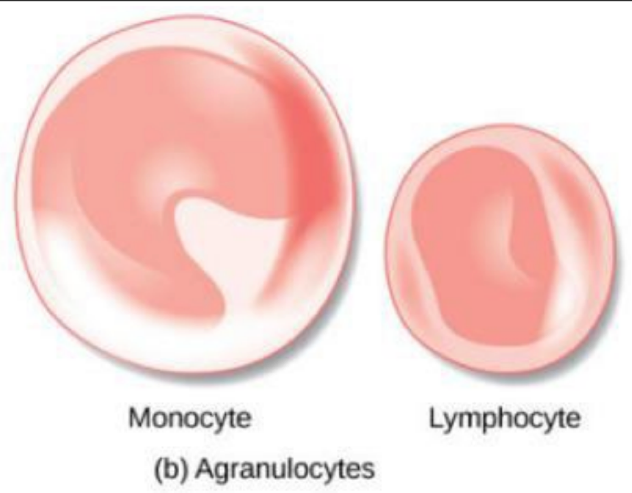
lymphocytes and monocytes lack vesicles that release chemicals. thus, they’re classified as what type of leukocytes?
agranular leukocytes
platelets are essential for blood clotting and are formed from pieces of what cells?
megakaryocytes
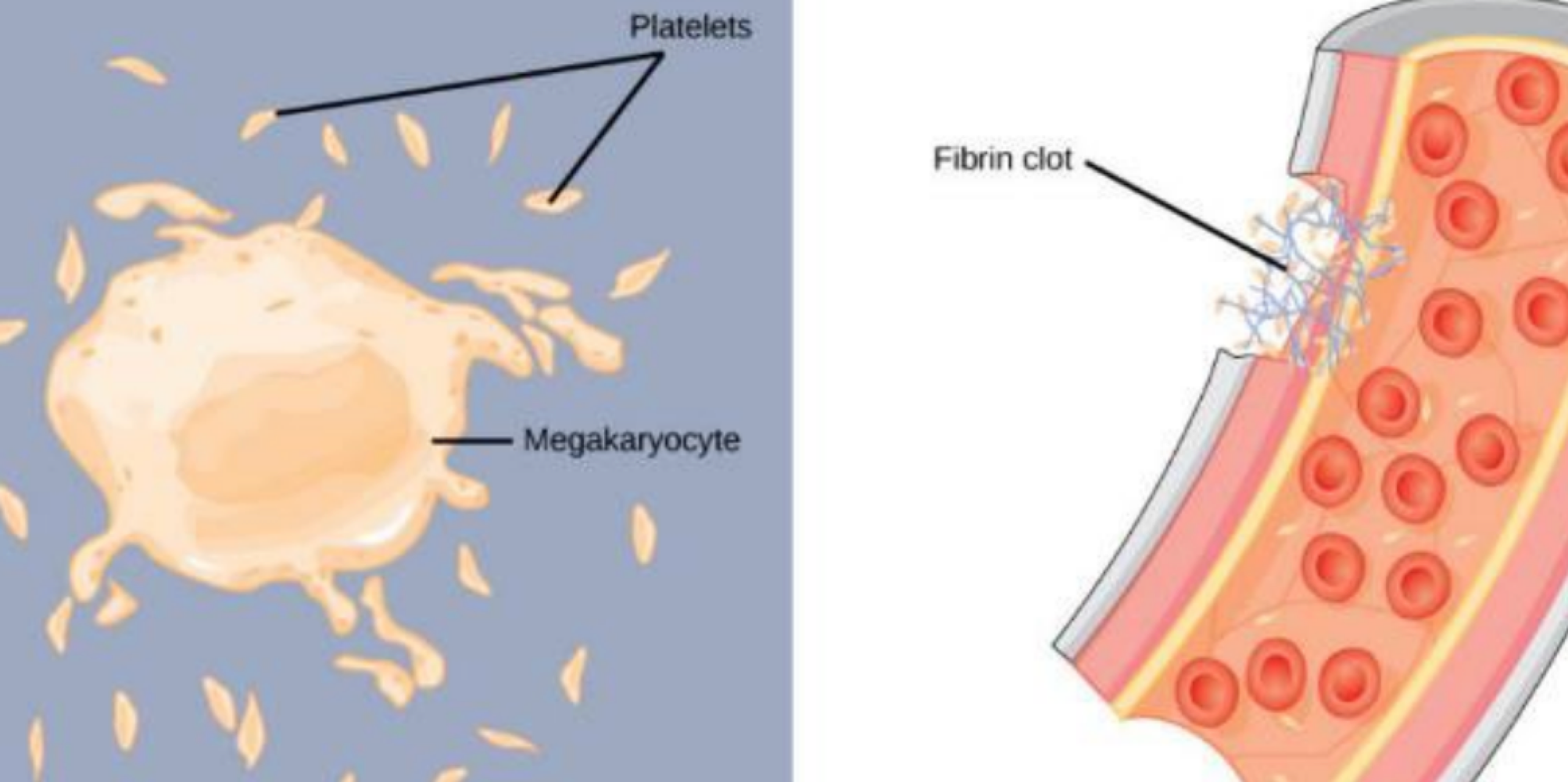
platelets help in the process of forming clots to stop bleeding, which is also referred to as ___
hemostasis
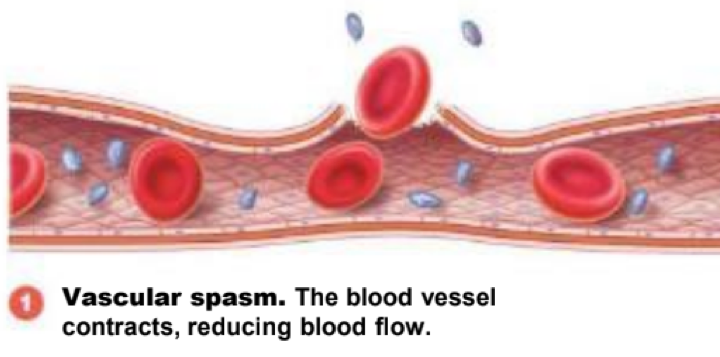
during hemostasis, blood vessels constrict to reduce blood flow. this step is also known as ___
vascular spasm (step 1)
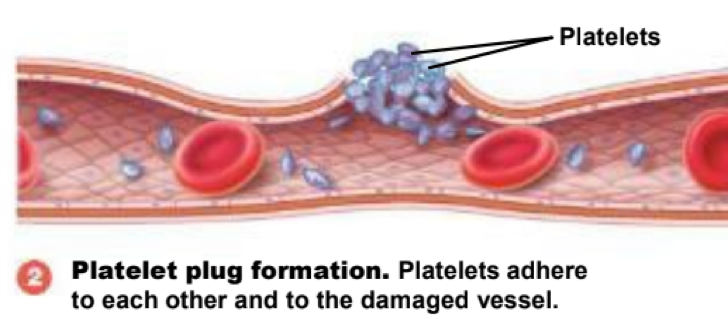
during hemostasis, platelets stick together to seal ruptured blood vessels. this step is also known as ___
platelet plug formation (step 2)
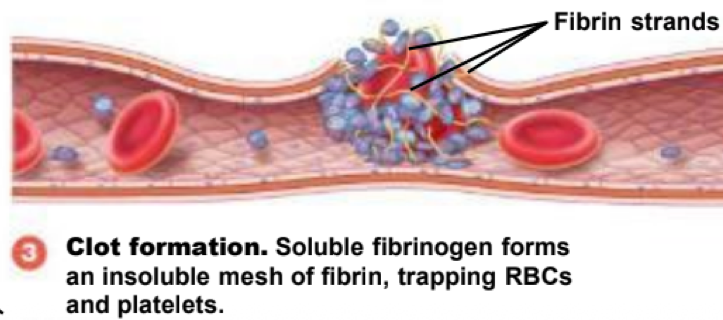
during hemostasis, blood forms into a gel to create a clot to trap erythrocytes and platelets. this step is also known as ___
coagulation (step 3)
this type of blood vessel carries blood away from the heart, and diverges into smaller vessels called arterioles
arteries
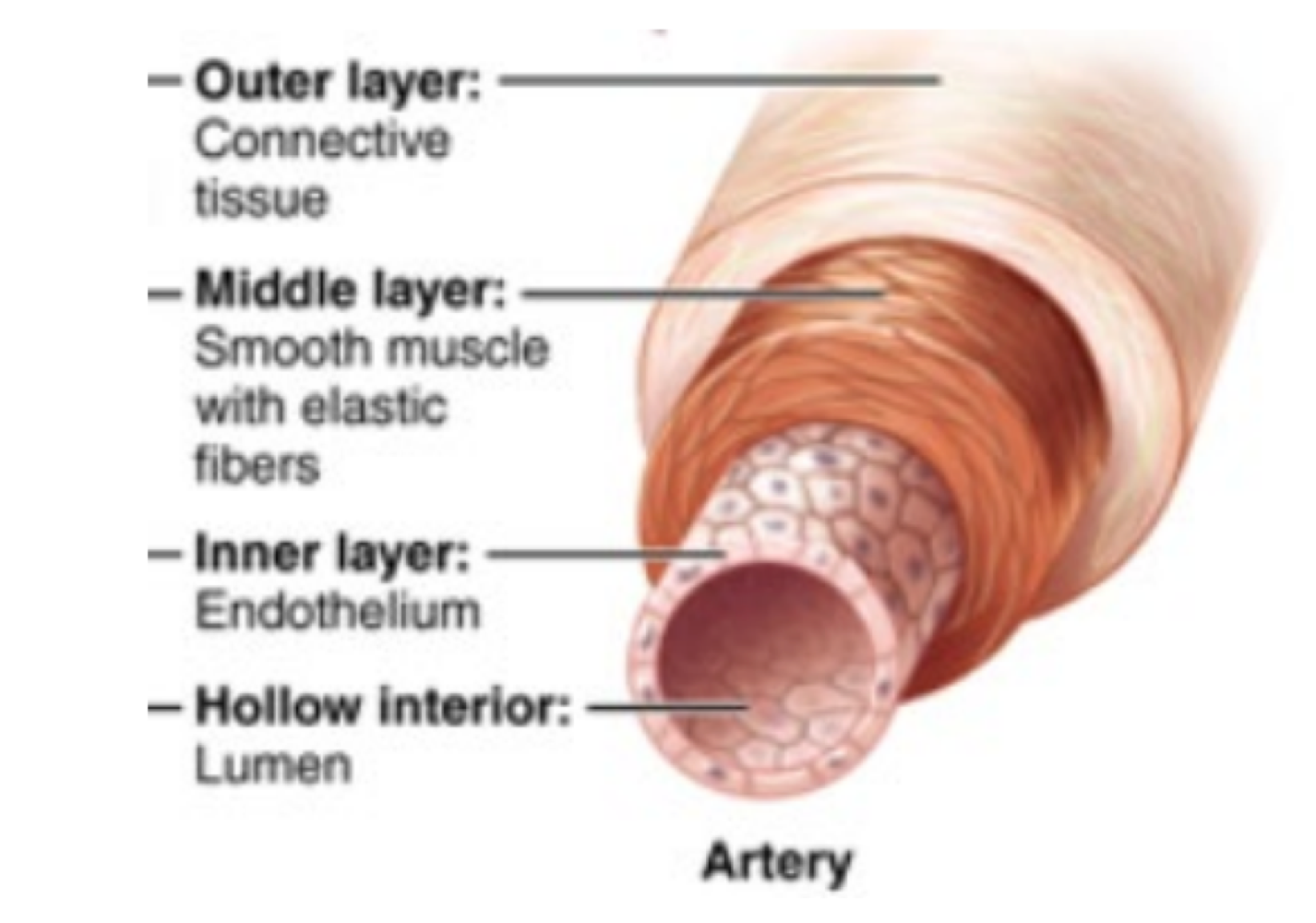
arteries are made of how many layers to carry blood away under enormous pressure?
three thick-walled layers
true or false: arterioles lack connective tissue, and have a thin smooth muscle layer
true
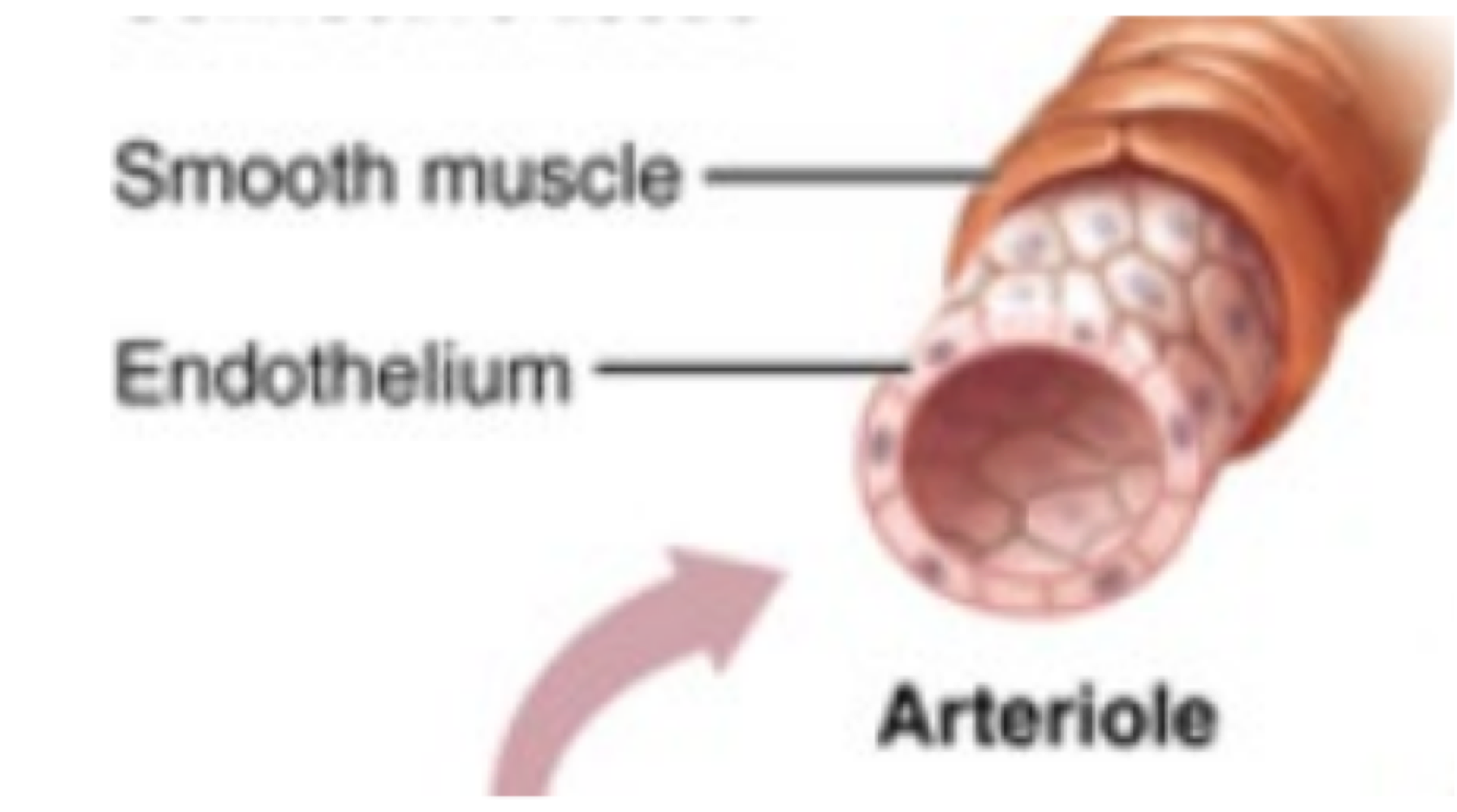
this type of blood vessel exchanges solutes and water with body cells, and converges into vessels called venules
capillaries
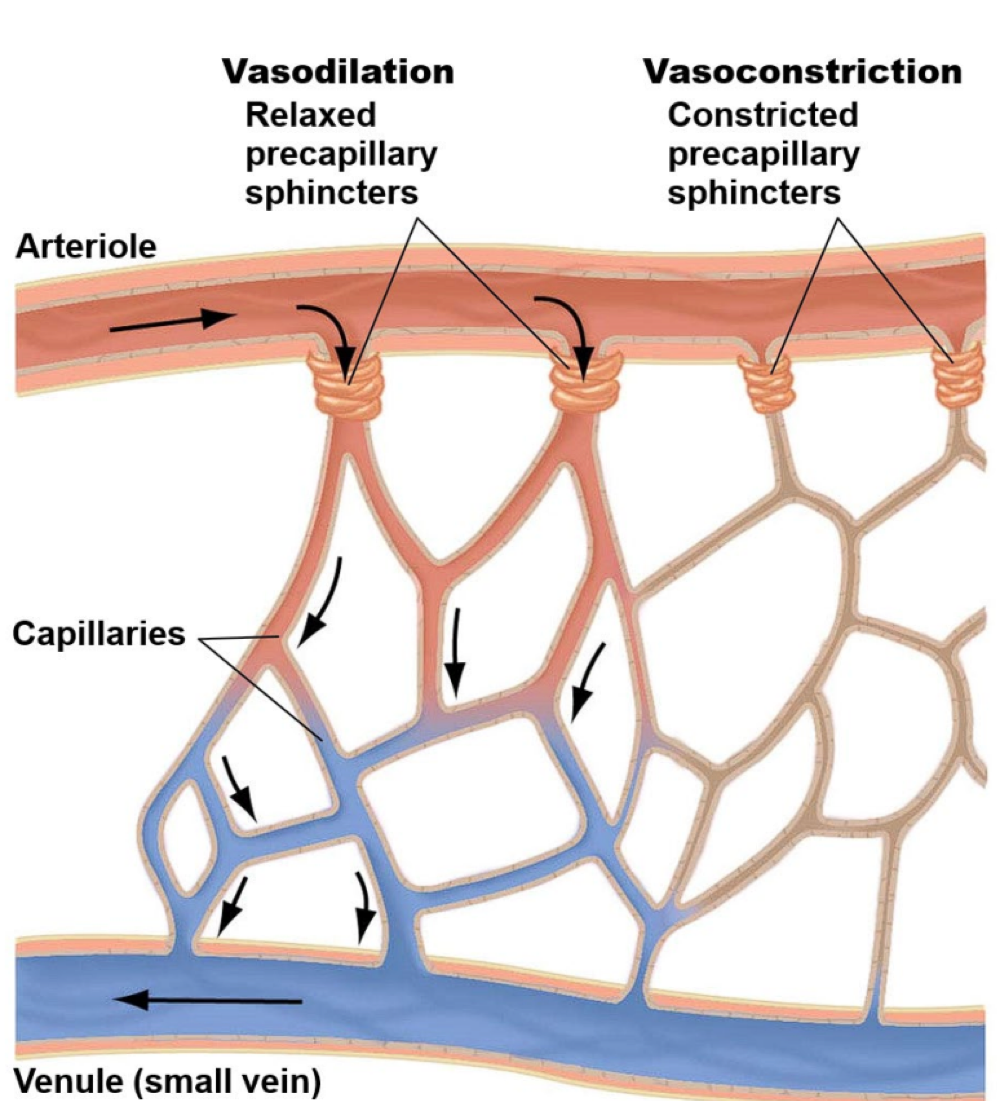
true or false: capillaries are nonporous and found everywhere in the body
false
capillaries are porous and found everywhere in the body
capillaries are made of a microscopic, thick walled layer of what type of cells to allow for material exchange via diffusion?
epithelial cells
rings of smooth muscle that regulate blood flow through capillary beds
precapillary sphincters
what type of vessels transport fluid from the cell via capillaries containing carbon dioxide and waste
lymphatic vessels
what type of fluid is screened for bacteria by lymphatic vessels and send back into the body
lymphatic fluid
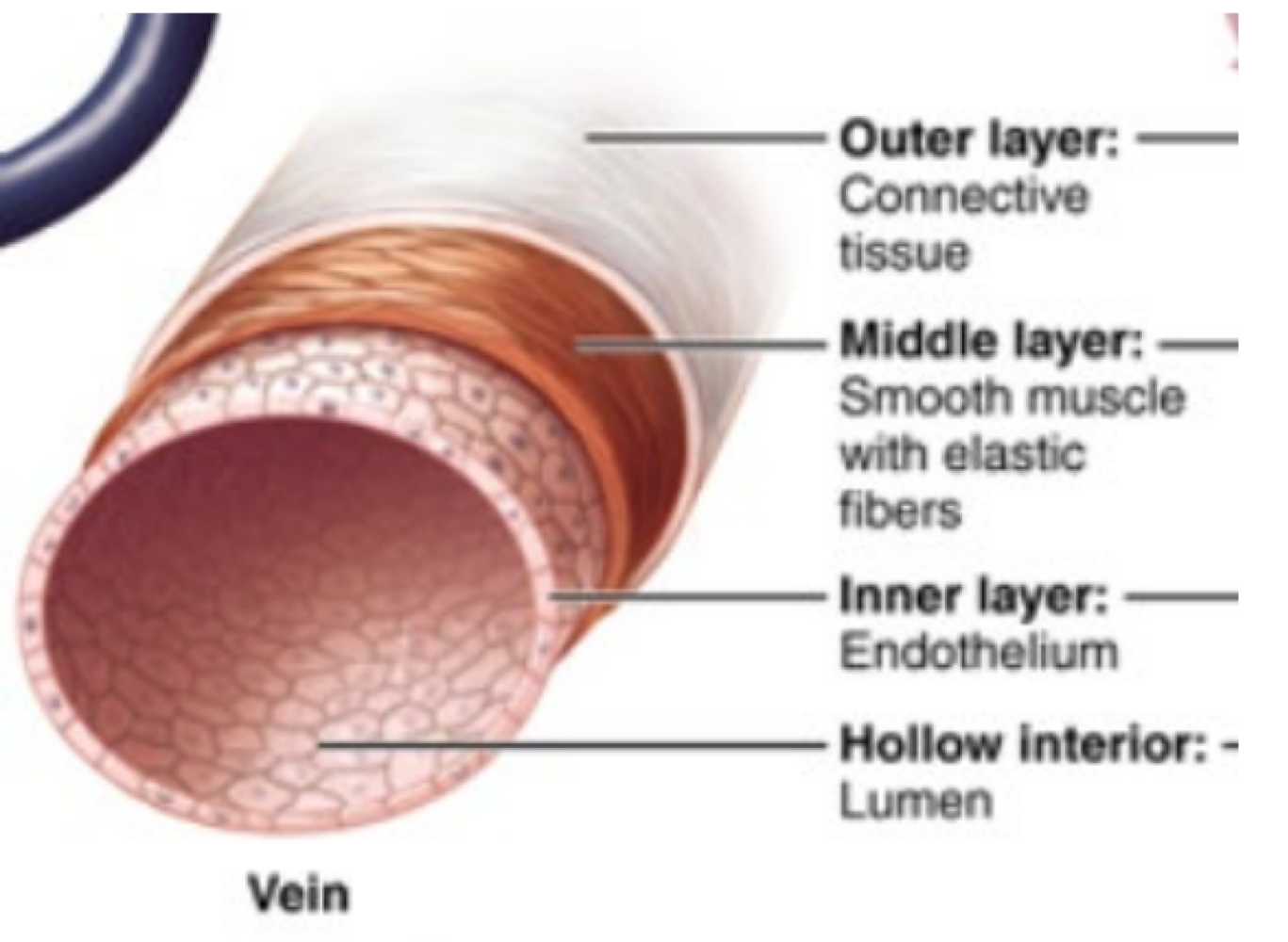
this type of blood vessel returns blood to the heart via skeletal muscle contraction and gravity and acts as a blood reservoir
veins
the heart is surrounded by a fibrous sac made of three layers. this structure is called the ___
pericardium
the thin outer layer of epithelial and connective tissue of the pericardium is called the ___
epicardium
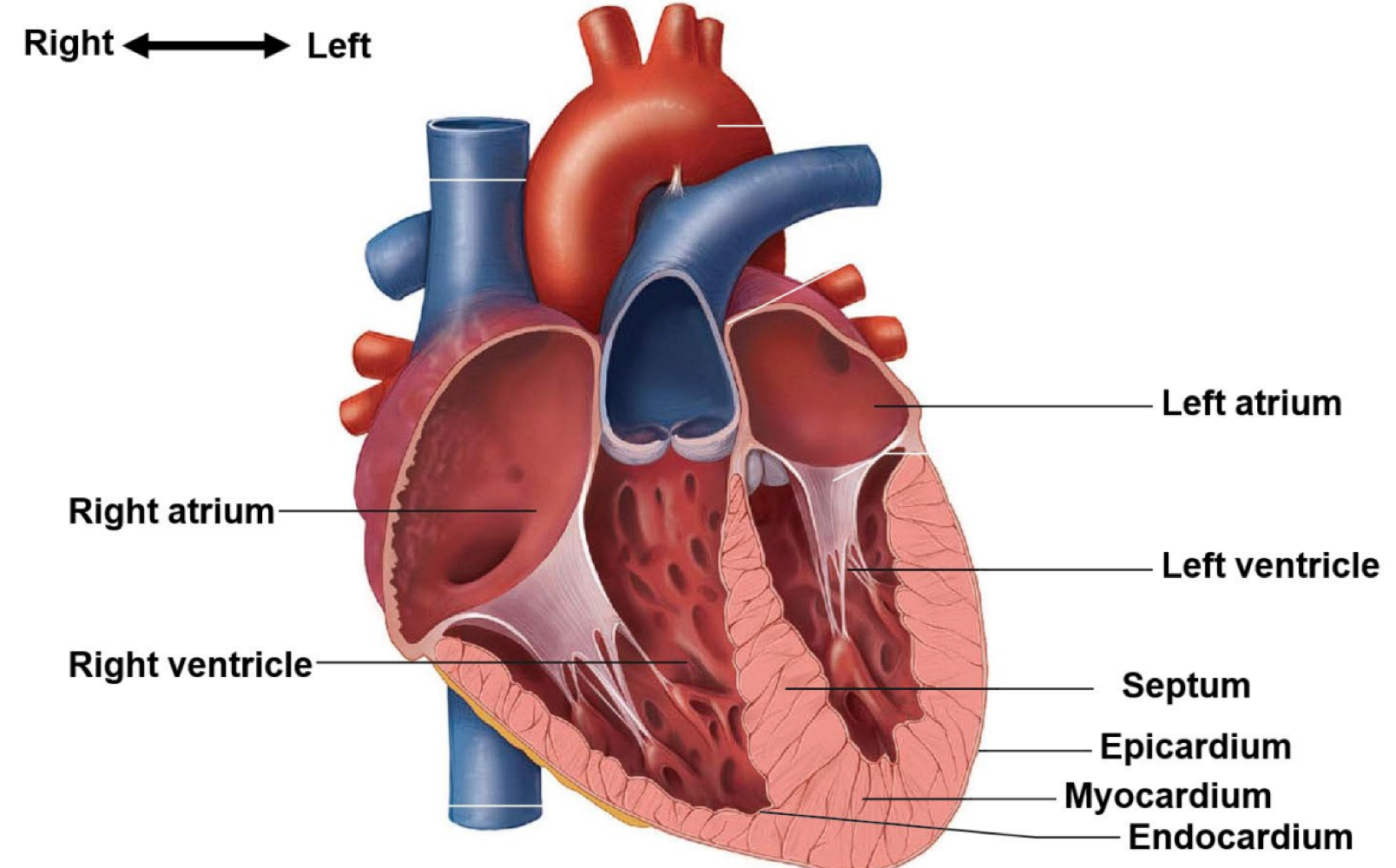
the thick middle layer of muscle of the pericardium is called the ___
myocardium
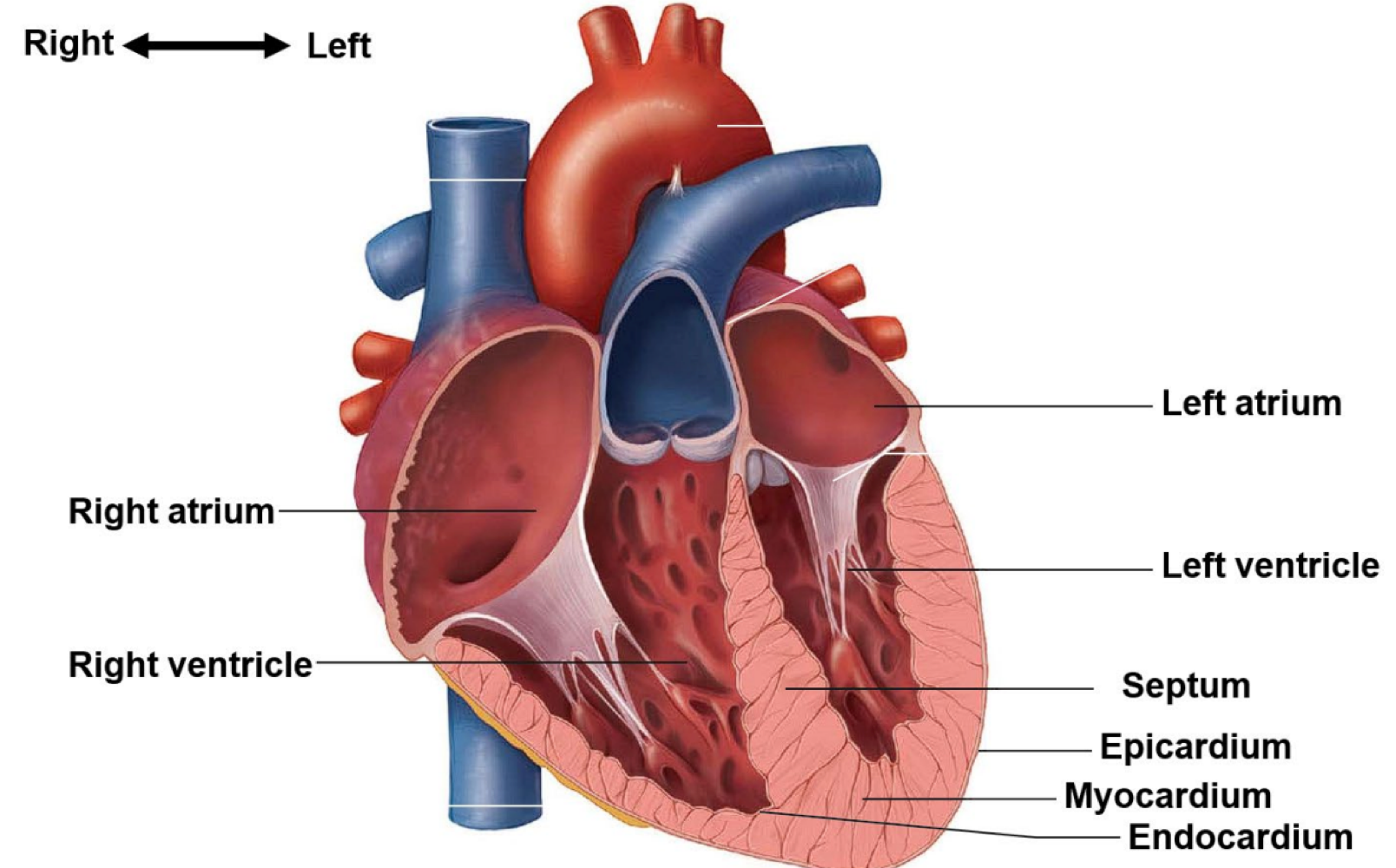
the thin inner layer of epithelial tissue of the pericardium is called the ___
endocardium
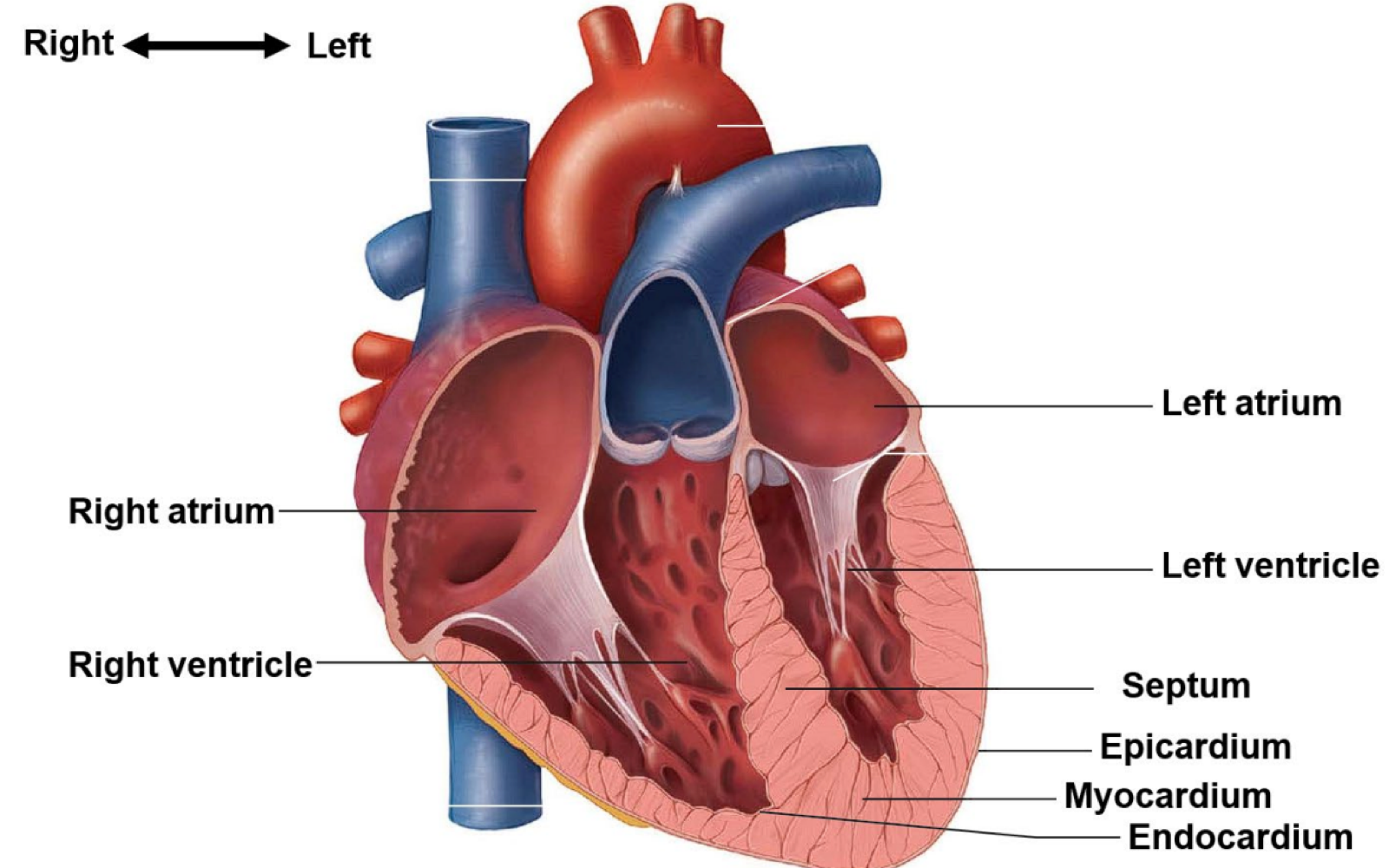
the heart is separated into 4 chambers, which are called ___
the left and right atrium, and the left and right ventricles
what muscular partition separates the right and left sides of the heart?
the septum
true or false: blood moves bidirectionally
false
blood must go in one direction, so valves prevent back flow
deoxygenated blood moves from a muscle into the right atrium via the ___
vena cava vein
the right atrium is separated from the right ventricle by the ___
right atrialventricular valve
deoxygenated blood moves from the right ventricle to the lungs via the ___
pulmonary artery
the right ventricle is separated from the pulmonary artery by the ___
pulmonary valve
in the lungs, what is added to the blood once carbon dioxide is removed?
oxygen
oxygenated blood is moved from the lungs to the left atrium via the ___
pulmonary vein
oxygenated blood moves from the left atrium to the ___
left ventricle
the left atrium is separated from the left ventricle by the ___
left atrialventricular valve
the left ventricle moves the blood toward a body system, thus organs and muscles via the ___
aorta artery
the aorta artery is separated from the left ventricle by the ___
aortic valve
how many times does blood pass through the heart?
twice
what type of blood passes through the right side of the heart?
deoxygenated blood
what type of blood passes through the left side of the heart?
oxygenated blood
true or false: the heart pumps blood through two circuits
true
the lungs, pulmonary artery, and pulmonary vein make up which circuit?
the pulmonary circuit
the rest of the body, aorta, and vena cava make up which circuit?
the systemic circuit
the complete cycle of events in the heart, for the beginning of one heartbeat to the beginning of the next heartbeat describes what cycle?
the cardiac cycle
the period of relaxation in the cardiac cycle is known as ___
diastole
the period of contraction in the cardiac cycle is known as ___
systole
during the cardiac cycle, both atria contract, forcing blood into the ventricles. this is also known as ___
atrial systole (step 1)
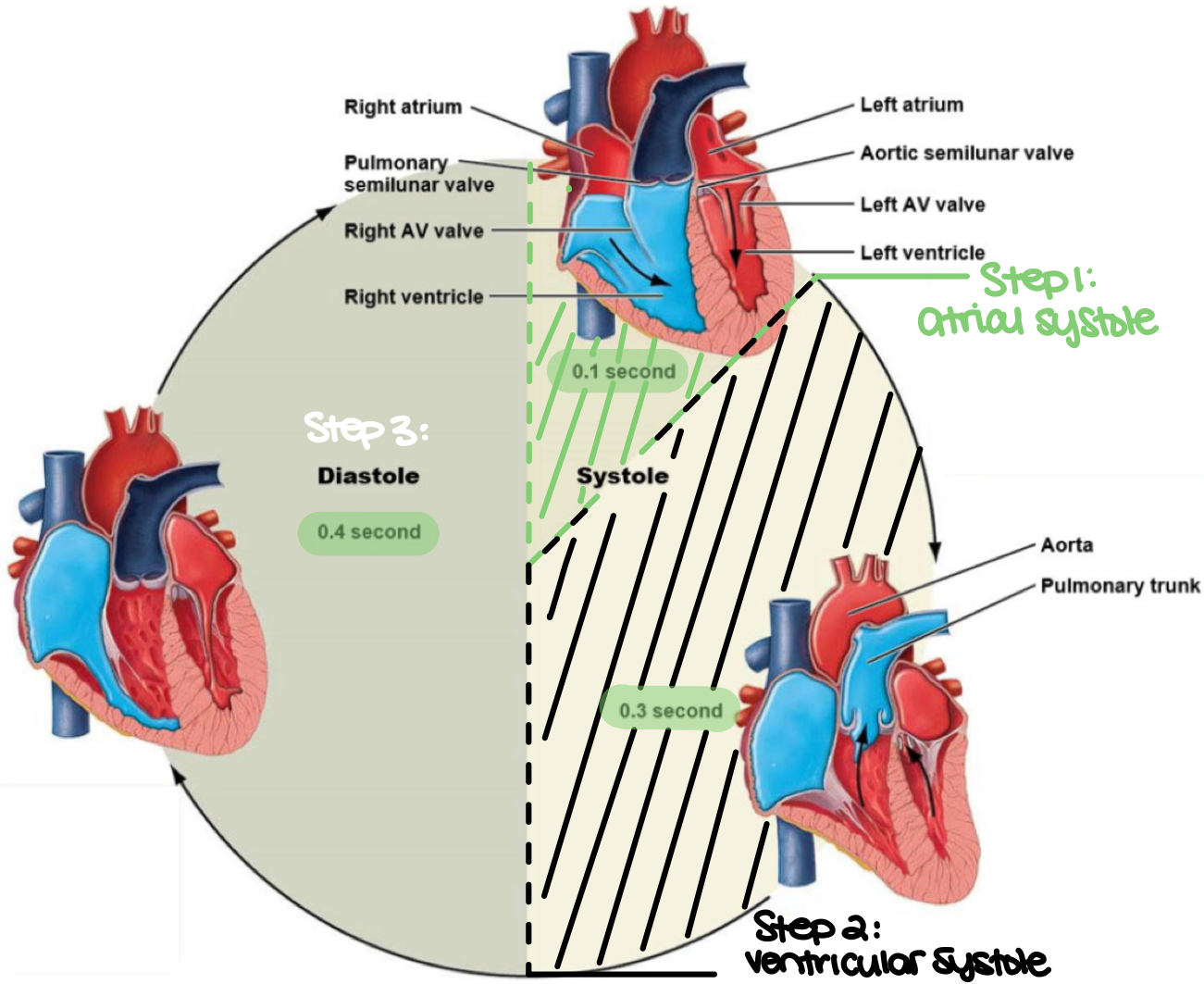
true or false: during atrial systole, both atrialventricular valves are open while the pulmonary and aortic valves are closed
true
during the cardiac cycle, both ventricles contract, causing the atrialventricular valves to close while the pulmonary and aortic valves open to allow blood in. this is also known as ___
ventricular systole (step 2)
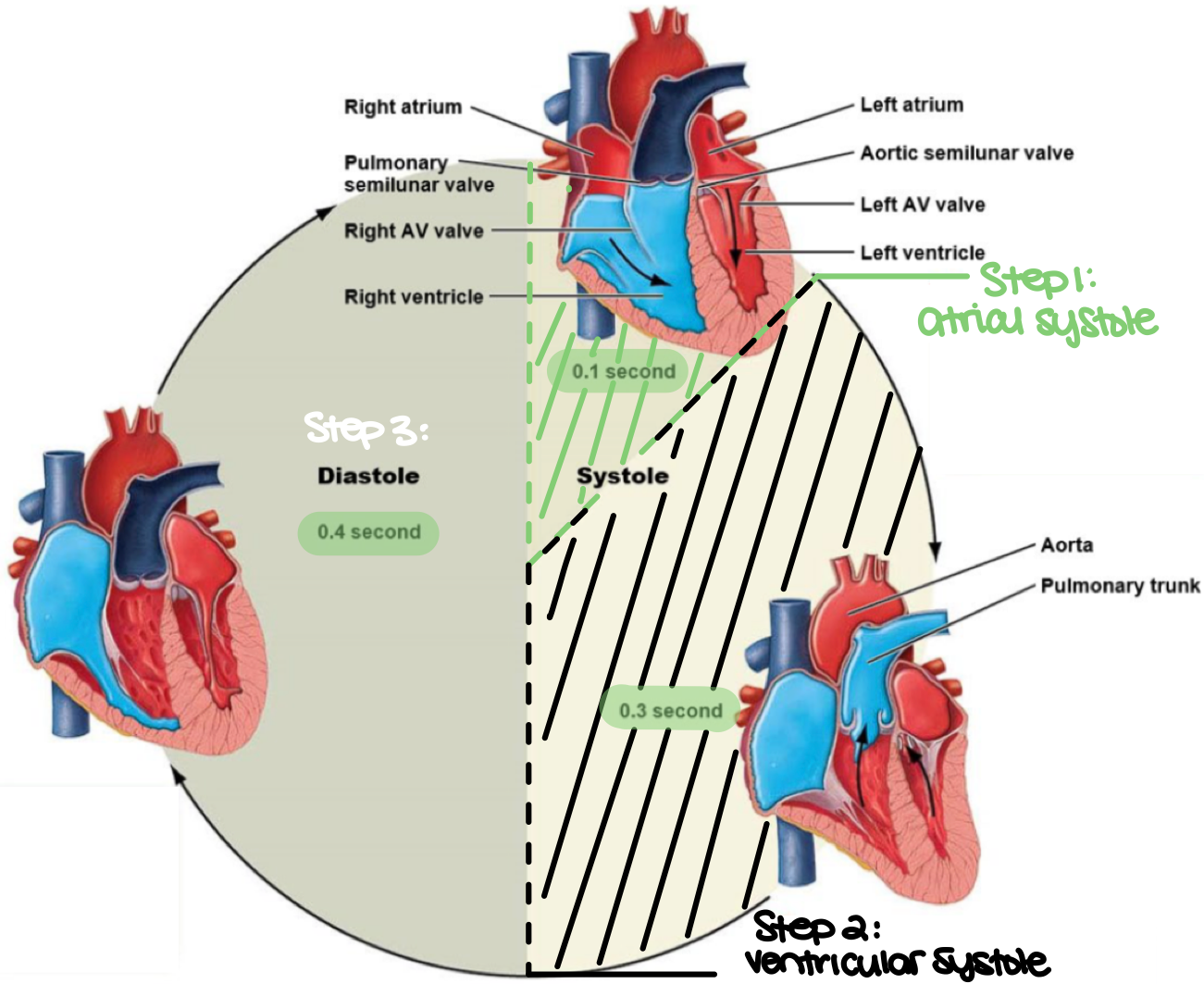
during the cardiac cycle, both ventricles relax and passively fill with blood through the atrialventricular valves. this is also known as ___
diastole (step 3)
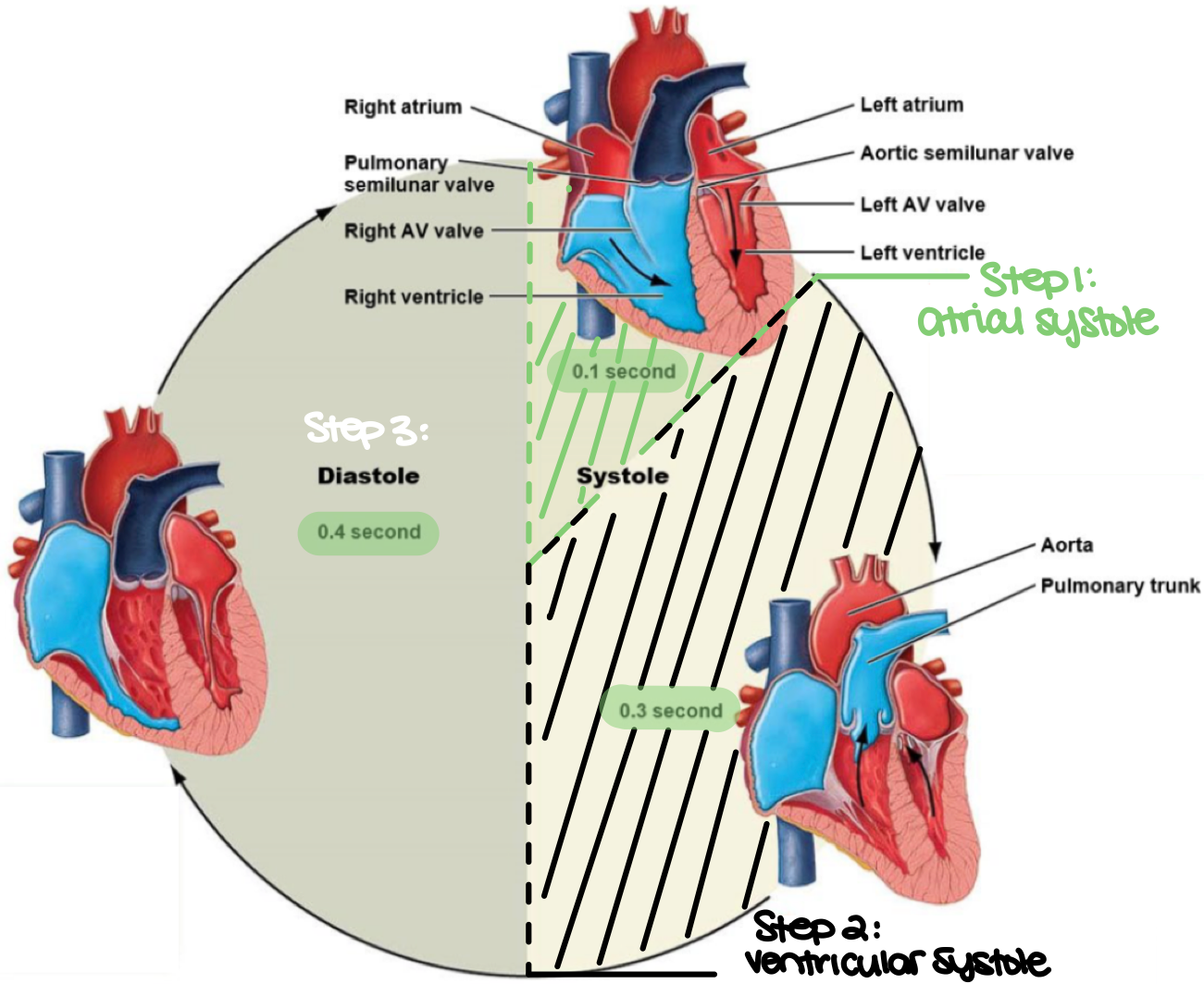
true or false: during diastole, the pulmonary and aortic valves are open, and both atria remain contracted
false. during diastole, the pulmonary and aortic valves are closed, and both atria remain relaxed
true or false: the cardiac muscle is unique because it creates its own action potentials
true
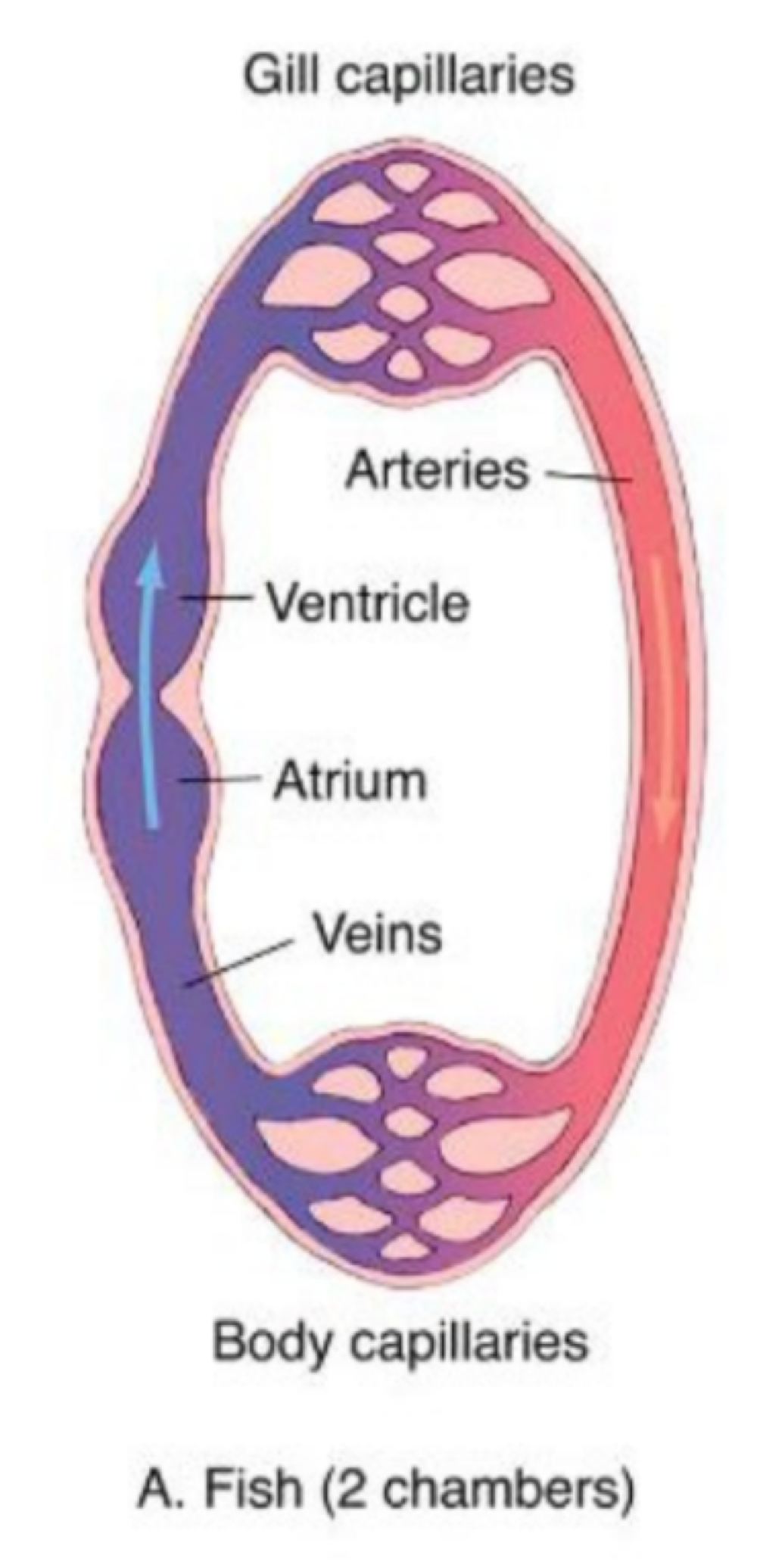
how are hearts classified among vertebrates?
how heartbeats are initiated, and the number of chambers
true or false: vertebrates have multi-chambered hearts
true
fish use gills for gas exchange, and have how many chambers in their heart?
2 chambers
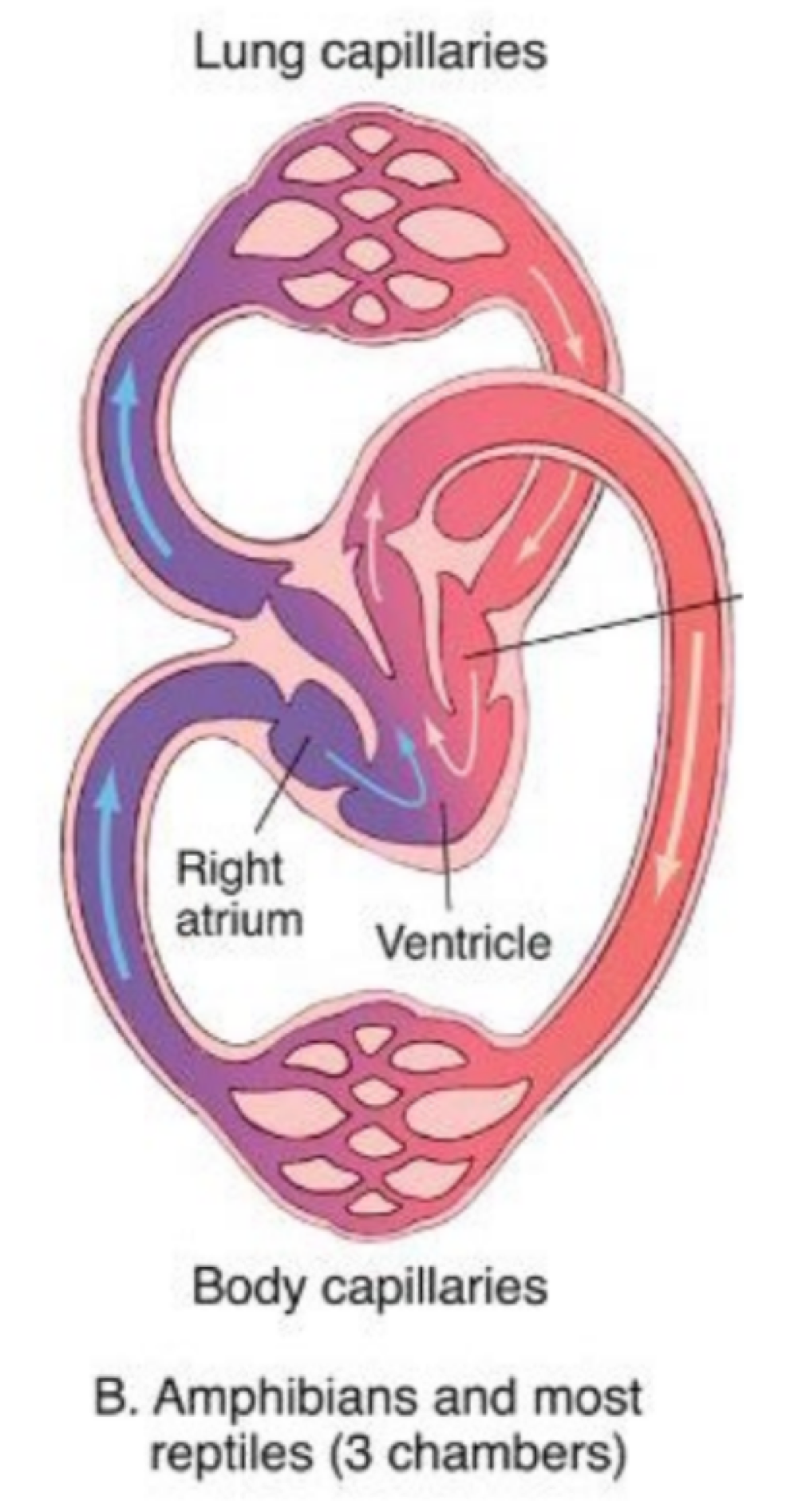
amphibians and reptiles have 1 ventricle and 2 atria in what type of chambered heart?
3 chambered heart