M2(1) The Endocrine System - Intro + Hypothalamus + Pituitary Glands
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
Nervous System Comparison
Initiates responses rapidly
Short-duration responses
Acts via action potentials and neurotransmitters
Acts at specific locations determined by axon pathways
Neurotransmitters act over very short distances
Endocrine System Comparison
Initiates responses slowly
Long-durations responses
Acts via hormones released in the blood
Acts at diffuse locations (targets anywhere blood reaches)
Hormones act over long distances
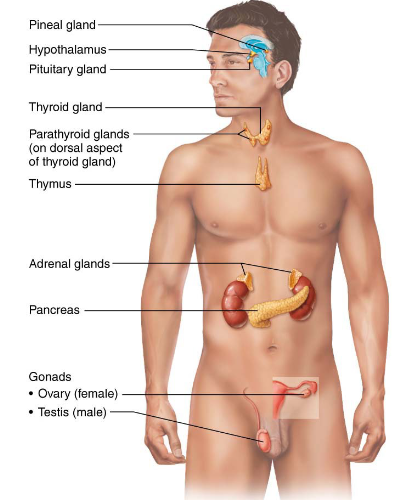
Endocrine Organs
Pineal gland
Hypothalamus
Pituitary gland
Thyroid gland
Parathyroid glands (located on dorsal aspect of thyroid gland)
Thymus
Adrenal glands
Pancreas
Gonads
Fat Soluble Hormones
Nonpolar / hydrophobic
Can cross the cell mb easily
Receptor located inside cell
Fat Soluble Hormone Steps
Fat Soluble Hormone Diffusion
Fat soluble hormone (e.g. steroid) diffuses through the plasma mb and binds to an intracellular receptorIntracellular Receptor Binding
Steroid binds to a receptor inside the cell, forming a hormone-receptor complexNuclear Translocation
If the receptor is in the cytoplasm, the hormone-receptor complex moves into the nucleusDNA Binding
The complex binds to a specific section of the DNAGene Transcription
Binding of the complex activates transcription of the target gene → mRNA is producedProtein Synthesis
mRNA directs protein synthesis
Water Soluble Hormones
Polar / hydrophilic
Cannot cross the cell mb easily
Receptor located on the cell mb
Water Soluble Hormone Steps
Water-Soluble Hormone (first messenger)
Hormone (e.g. glucagon) binds to receptor on the cell membrane, causing a conformational changeG protein activation
The activated receptor causes the G protein to exchange GDP for GTP, activating the G protein.Adenylate cyclase activation
The activated G protein stimulates adenylate cyclase in the membrane.cAMP (second messenger)
Adenylate cyclase converts ATP → cAMPProtein kinase activation
cAMP activates protein kinaseCellular response
Activated PKA phosphorylates target proteins, leading to a physiological response
→ e.g., glycogen breakdown and glucose release from liver cells.
Fat Soluble Hormone Comparison
Includes: All steroid hormones and thyroid hormone
Sources: Adrenal cortex, gonads, thyroid gland
Stored in Secretory Vesicles: No
Transport in Blood: Bound to plasma proteins
Half-Life in Blood: Long (most need to be metabolized by liver)
Location of Receptors: Typically inside cell
Mechanism of Action in Target Cell: Activate genes, causing synthesis of new proteins
Water Soluble Hormone Comparison
Includes: All AA-based hormones except thyroid hormone
Sources: All other endocrine glands
Stored in Secretory Vesicles: Yes (exit cell via exocytosis)
Transport in Blood: Typically free in plasma
Half-Life in Blood: Short (most can be removed by kidneys)
Location of Receptors: On plasma mb
Mechanism of Action in Target Cell: Typically acts through second-messenger systems
Endocrine Gland Stimuli
3 types
Humoral Stimulus
Neural Stimulus
Hormonal Stimulus
Humoral Stimulus
Hormone release is triggered by changes in blood levels of ions or nutrients.
Example:
↓Blood calcium → parathyroid gland releases PTH (parathyroid hormone) → raises blood calcium
Neural Stimulus
Hormone release is triggered by direct neural input from the nervous system.
Example:
Sympathetic nervous system stimulates adrenal medulla → releases epinephrine/norepinephrine during stress (“fight or flight”)
Hormonal Stimulus
Hormone release is triggered by another hormone.
Example:
Hypothalamus releases hormone → anterior pituitary releases hormone → thyroid releases hormone
Tropic Hormone
A hormone that primarily stimulates another endocrine gland to release its hormone
Rather than directly causing an effect on target tissues
Hypothalamus
Hypothalamic neurons synthesize oxytocin and ADH
Controls the pituitary gland
Anterior pituitary: via releasing/inhibiting hormones (GHRH, GHIH, TRH, CRH, GnRH, PIH)
Posterior pituitary: stores and releases hormones made by the hypothalamus
Posterior Pituitary
Does not make hormones itself
Stores hormones made in the hypothalamus (oxytocin, ADH)
Hypothalamus communicates via neurons that deliver hormones
Oxytocin
Stimulus: Impulses from hypothalamic neurons in response to infant suckling, stretching of uterus during labour
Inhibited: Lack of appropriate neural stimuli
Target Organ: Uterus, Breast
Effects: Stimulates uterine contractions, Milk ejection
Hyposecretion Effects: Unknown
Hypersecretion Effects: Unknown
Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH)
Stimulus: Impulses from hypothalamic neurons in response to increased blood solute concentration or decreased blood volume
Inhibited: Adequate hydration of the body or alcohol
Target Organ: Kidneys
Effects: Stimulates kidney tubule cells to reabsorb water from forming urine back into blood
Hyposecretion Effects: Syndrome of inappropriate ADH secretion
Hypersecretion Effects: Diabetes Insipidus
Anterior Pituitary
Produces hormones
GH (growth hormone),
TSH (thyroid-stimulating hormone),
ACTH (adrenocorticotropic hormone),
FSH (follicle-stimulating hormone),
LH (luteinizing hormone)
PRL (prolactin)
Hypothalamus communicates via blood vessels (by releasing hormones)
Growth Hormone (GH)
Stimulus: GHRH release (triggered by ↓GH in blood)
Secondary Triggers: deep sleep, hypoglecemia,↑ AAs in blood, ↓ FFAs, exercise, other stressors
Inhibited: Feedback inhibition of GH and insulin-like growth factors (IGFs)
Hyperglycemia, hyperlipidemia, obesity, emotional deprivation (either increased GHIH or decreased GHRH release)
Target Organ: Liver, muscle, bone cartilage, other tissues
Effects: Stimulates somatic growth, mobilizes fats, spares glucose
Indirect growth-promoting effect (by IGFs)
Hyposecretion Effects: Pituitary dwarfism in children
Hypersecretion Effects: Gigantism in children; acromegaly in adults
Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH)
Stimulus: TRH
Indirectly in infants (by cold temperature)
Inhibited: Feedback inhibition by thyroid hormones on anterior pituitary gland and GHIH
Target Organ: Thyroid Gland
Effects: Stimulates thyroid gland to release thyroid hormones
Hyposecretion Effects: Hypothyroidism (effects similar to Graves’ disease, antibodies
Hypersecretion Effects: Hyperthyroidism (may cause myxedema)
Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH)
Stimulus: CRH
Secondary Triggers: fever, hypoglycemia, other stressors
Inhibited: Feedback inhibition by glucocorticoids
Target Organ: Adrenal Cortex
Effects: Stimulates adrenal cortex to promote release of glucocorticoids and androgens
Hyposecretion Effects: Rare
Hypersecretion Effects: Cushing’s Disease
Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH)
Stimulus: GnRH
Inhibited: Feedback inhibition by inhibin
Estrogen (females)
Testosterone (males)
Target Organ: Ovaries / Testes
Effects:
Stimulate ovarian follicle maturation and production of estrogen (females)
Stimulate sperm production (males)
Hyposecretion Effects: Failure of sexual maturation
Hypersecretion Effects: No important effects
Luteinizing Hormone (LH)
Stimulus: GnRH
Inhibited: Feedback inhibition by
Estrogen and progesterone (females)
Testosterone (males)
Target Organ: Ovaries / Testes
Effects:
Triggers ovulation, stimulates ovarian production of estrogens and progesterone (females)
Promotes testosterone production (males)
Hyposecretion Effects: Failure of sexual maturation
Hypersecretion Effects: No important effects
Prolactin (PRL)
Stimulus: ↓PIH
release enhanced by estrogens, birth control pills, breast feeding, dopamine-blocking drugs
Inhibited: Feedback inhibition by PIH (dopamine)
Target Organ: Breast Secretory Tissue
Effects: Promotes lactation
Hyposecretion Effects: Poor milk production in nursing women
Hypersecretion Effects: Galactorrhea (inappropriate milk production), cessation of menses (females), impotence (males)