Chapter 6: Energy Resources and Consumption (copy)
1/77
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
78 Terms
Fossil fuels
________ are formed over time from deposits of once- living organisms and take thousands of years to form.
Natural gas
________ was formed from the remains of marine organisms and is relatively abundant and clean when compared to coal and oil.
Impurities
________ are removed from the syngas before it is combusted, which results in lower emissions of sulfur dioxide, particulates, and mercury.
Dams
________ destroy wildlife habitats and keep fish from migrating.
Energy
Defined as the fundamental entity of nature that is transferred between parts of a system in the production of physical change within the system and is usually regarded as the capacity for doing work
Sun
The source of energy for most of life on Earth
Chemical energy
It is stored in bonds between atoms in a molecule
Electrical energy
It results from the motion of electrons
Electromagnetic energy
This energy travels by waves
Mechanical energy
Consists of potential and kinetic energies
Potential Energy
Stored energy in any object
Kinetic energy
Energy in motion
Nuclear energy
It is stored in the nuclei of atoms, and it is released by splitting atoms
Thermal Energy
the energy an object has because of the movement of its molecules
British thermal unit (Btu)
It is the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 pound of water by 1°F
Btu/hr
A ton in many air conditioning applications
Horsepower (HP)
Used in automobile industries
Kilowatt hour (kWh)
A unit of power; a measure of energy used at a give moment
First Law of Thermodynamics
The law of conservation of energy; energy can't be created nor destroyed
Second Law of Thermodynamics
The total system work is always less than the heat supplied into the system
Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics
If a body A is in thermal equilibrium with another body B, and body A is also in thermal equilibrium with a body C, then this implies that the bodies B and C are also in equilibrium with each other
Renewable energy
Defined as energy that is collected from resources that are naturally replenished on a human time scale
Nonrenewable Energy Sources
Their use is not sustainable because their formation takes billions of years like fossil fuels
Fossil Fuels
Fuels formed from past geological remains of living organisms
Peat
It is an accumulation of partially decayed vegetation or organic matter, mostly wetland vegetation like mosses, sedges, and shrubs, that forms in acidic and anaerobic conditions
Coal
Formed when dead plant matter that covered much of Earths tropical land surface at one time decays into peat and is then converted into coal by the heat and pressure of deep burial over millions of years
Lignite
Often called brown coal, is the type most harmful to human health and is used almost exclusively as the primary fuel for electric power generation around the world
Bituminous
Used primarily as fuel in steam-electric power generation
Anthracite
Used primarily for residential and commercial space heating
Clean Coal
Technology that attempts to mitigate emissions of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases that arise from the burning of coal for electrical power
Carbon capture and storage (CCS)
Pumps and stores CO2 emissions underground
Natural gas
A fossil fuel formed when layers of buried plants and gases are exposed to intense heat and pressure over thousands of years
Oil
A fossil fuel produced by the decomposition of deeply buried organic material (plants) under high temperatures and pressure for millions of years
Cogeneration
Also known as combined heat and power (CHP), is an efficient technology to generate electricity and heat energy from a single source of energy
Baghouse filters
Fabric filters that can be used to reduce particulates
Burning pulverized coal at lower temperatures
Coal is crushed into a very fine powder and injected into a firebox
Coal gasification
A process that turns coal and other carbon-based fuels into gas known as "syngas."
Cyclone separator
A method of removing particulates through rotational (spinning) effects and gravity
Electrostatic precipitator
A filtration device that removes fine particles, like dust and smoke, from a flowing gas using an electrostatic charge
Fluidized-bed combustion
A method of burning coal in which the amount of air required for combustion far exceeds that found in conventional burners
Scrubbers
Systems that inject chemical(s) into a dirty exhaust stream to "wash out" acidic gases
Sorbents
Activated charcoal, calcium compounds, or silicates can convert gaseous pollutants in smokestacks into compounds that baghouse filters, electrostatic precipitation, or scrubbers can collect
Law of Supply
All other factors being equal, as the price of a good or service increases, the quantity of goods or services that suppliers offer will increase, and vice versa
Law of Demand
All other factors being equal, the quantity of the item purchased is inversely related to the price of the item
Methane Hydrates (Clathrates)
These are recently discovered source of methane that form at low temperature and high pressure
Oil shale
An organic-rich, fine-grained sedimentary rock containing a solid mixture of organic chemical compounds (kerogen) from which liquid hydrocarbons (shale oil) can be produced
Synfuels
Any fuel produced from coal, natural gas, or biomass through chemical conversion
Tar sands
Contain bitumen-a semi-solid form of oil that does not flow
Hydraulic fracturing
oil and gas well development process that typically involves injecting water, sand, and chemicals under high pressure into a bedrock formation via a well
Nuclear Meltdown
A severe nuclear reactor accident that results in core damage from overheating
U-235; mused to harness nuclear energy
Less than 1% of all-natural uranium on Earth
Critical Mass
The minimum amount of U-235 required for a chain reaction
U-238
The most common isotope of uranium and has a half-life of 4.5 billion years
Pu-239
It has a half-life of 24,000 years and is produced in breeder reactors from U-238
Core
Contains up to 50,000 fuel rods
Fuel
Enriched (concentrated) U-235 is usually the fuel
Control rods
Move in and out of the core to absorb neutrons and slow down the reaction
Moderator
It reduces the speed of fast neutrons, thereby allowing a sustainable chain reaction
Coolant
Removes heat and produces steam to generate electricity
Biomass
It ****is biological material derived from living, or recently living, organisms that can be burned in large incinerators to create steam that is used for generating electricity
Anaerobic digestion
A collection of processes by which microorganisms break down biodegradable material, in the absence of oxygen, to produce methane gas, which is then burned to produce energy
Biofuel
A liquid fuel produced from living organisms
Solar energy
It consists of collecting and harnessing radiant energy from the sun to provide heat and/or electricity
Passive solar heating
It does not include any type of mechanical heating device and functions by incorporating building features that absorb heat and then release it slowly to maintain the temperature throughout the building
Residential photovoltaic system
It consists of solar panels to absorb and convert sunlight into electricity, a solar inverter to change the electric current from DC to AC, and a battery storage and backup system
Dams
These are built to trap water, which is then released and channeled through turbines that generate electricity
Wind turbines work very simply
instead of using electricity to make wind-like a fan-wind turbines use wind to make electricity
Wind Farms
Wind turbines clustered together
Phantom Load
Refers to the energy that an appliance or an electronic device consumes when it is not actually turned on
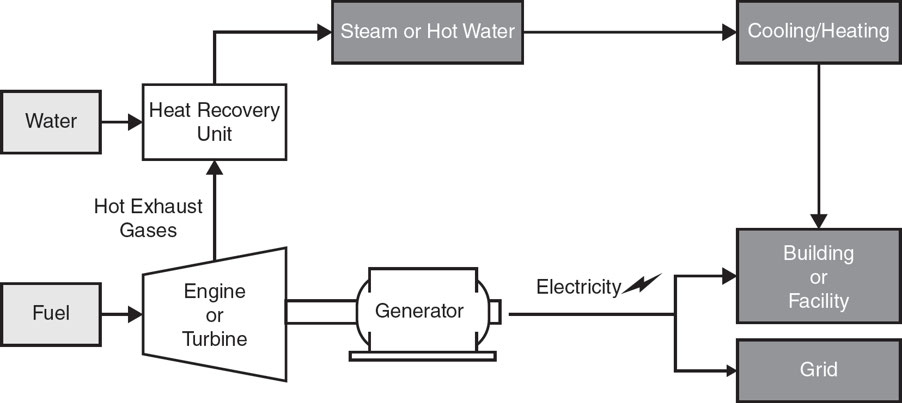
Cogeneration system
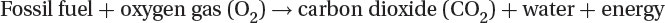
combustion of any fossil fuel reaction
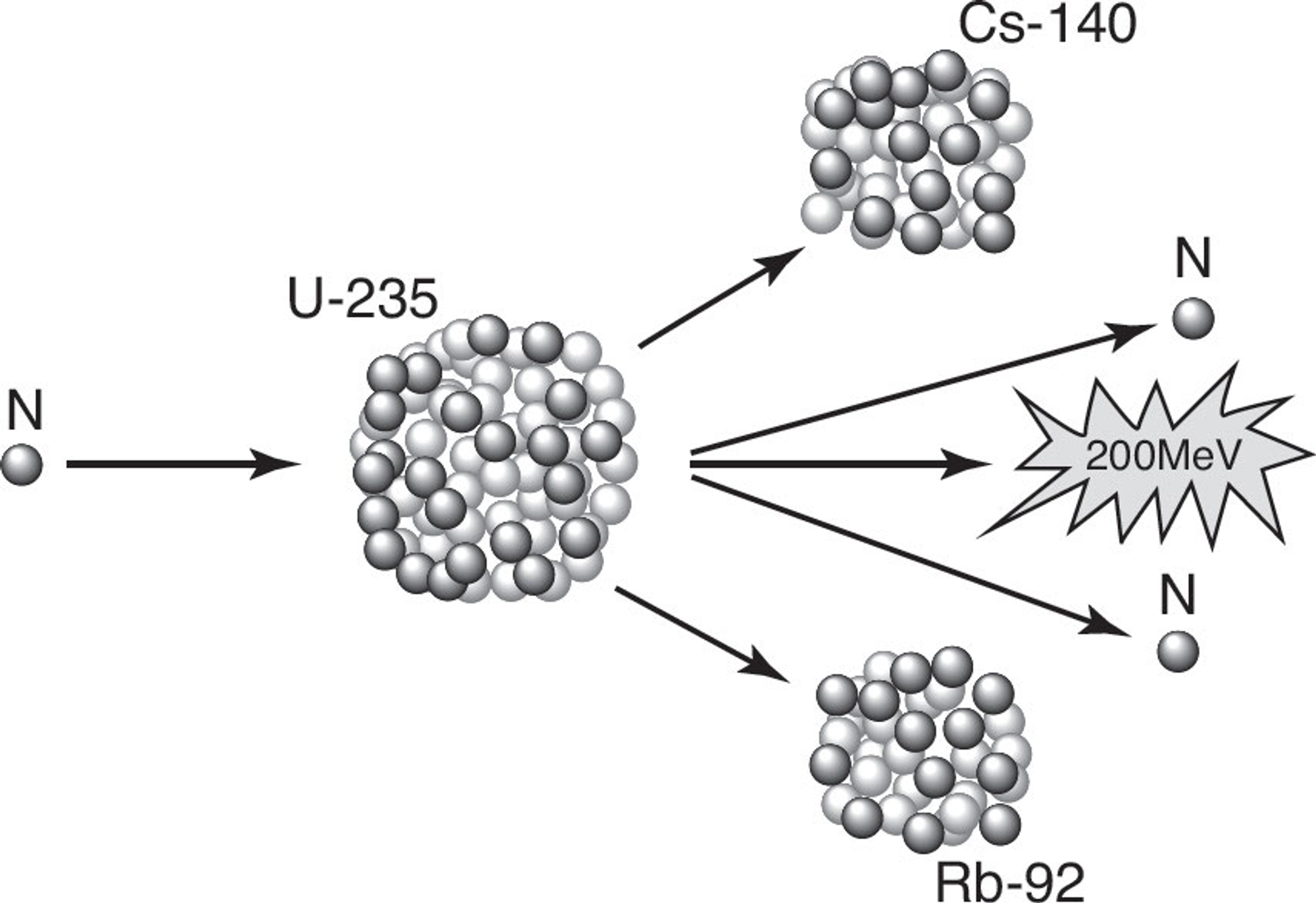
Nuclear Fission
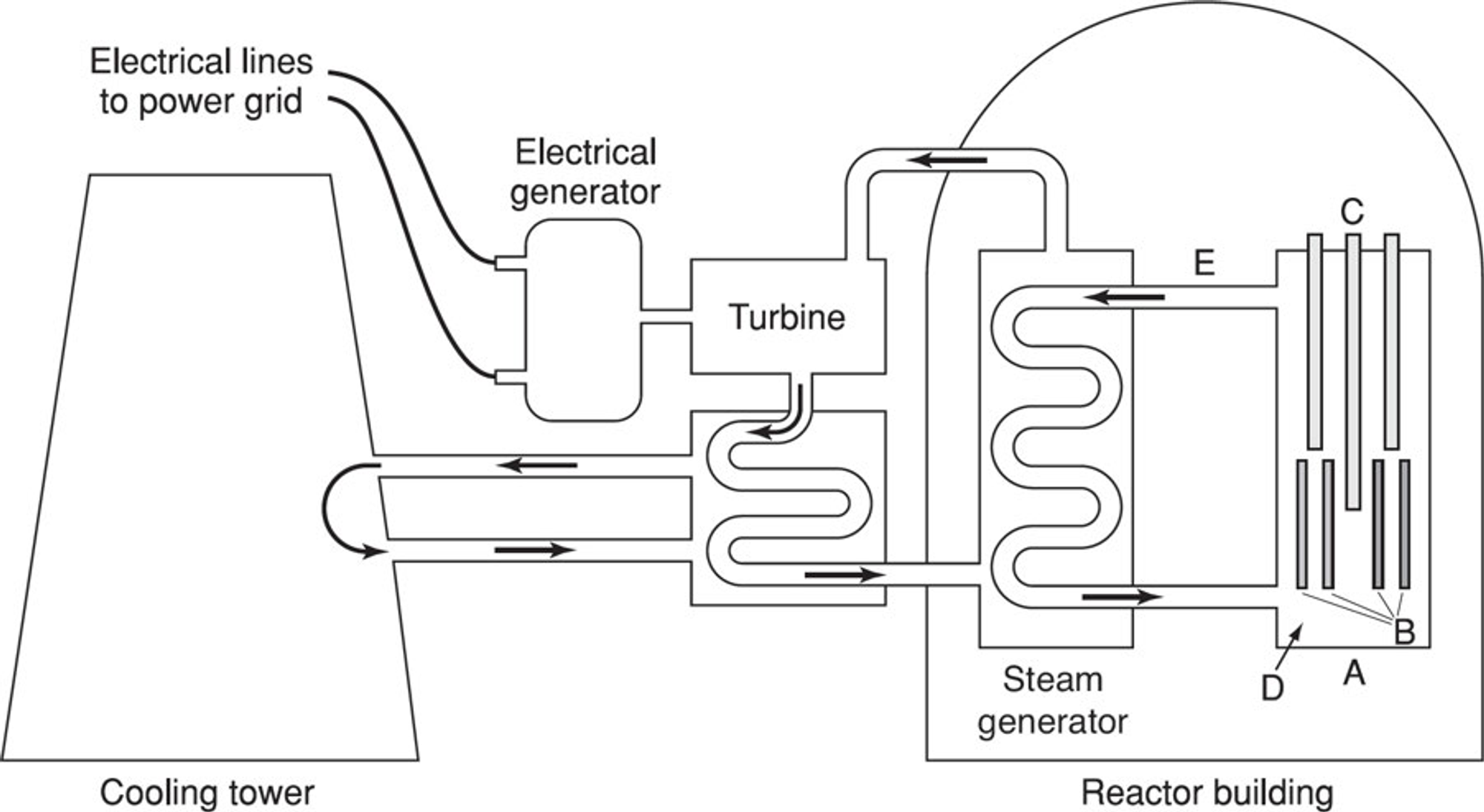
Nuclear Plant
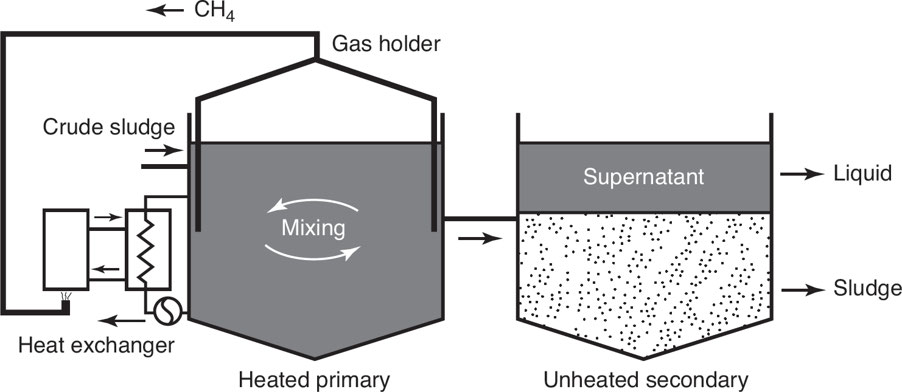
Anaerobic Digester
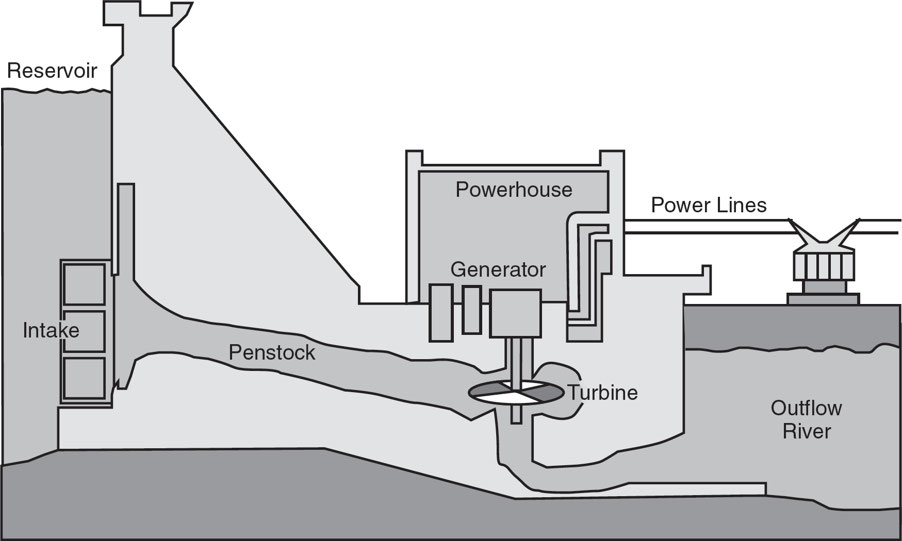
Hydroelectric Dam
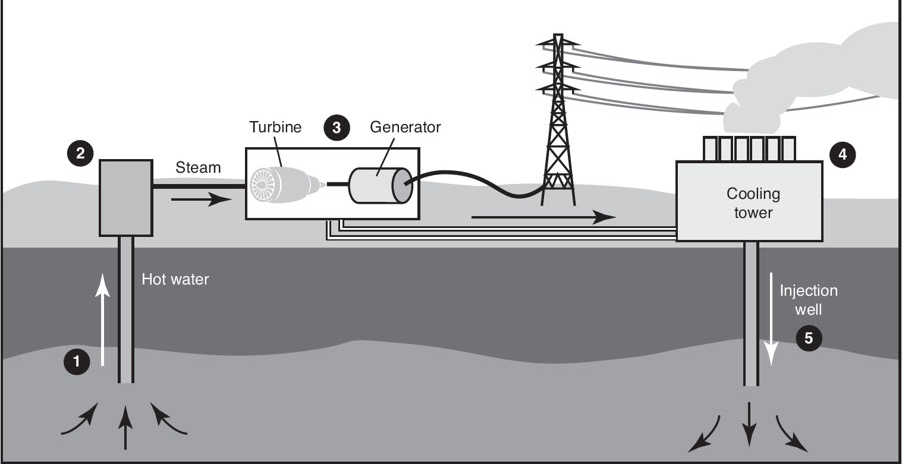
Geothermal Plant
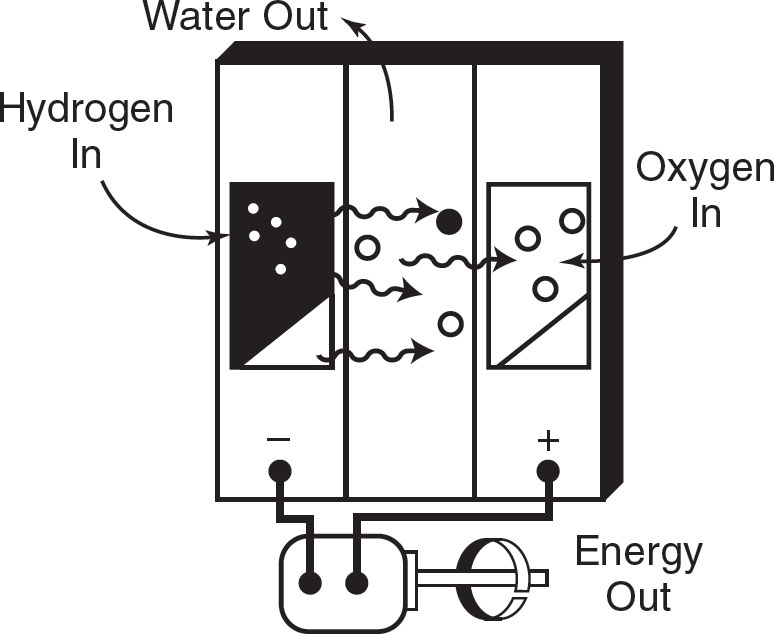
Hydrogen Fuel Cell
Whenever one form of energy is transformed into another, some of that energy is converted into a less usable form of energy, such as heat.
Second Law of Thermodynamics