Exam 4- lower extremity muscles
1/60
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
61 Terms
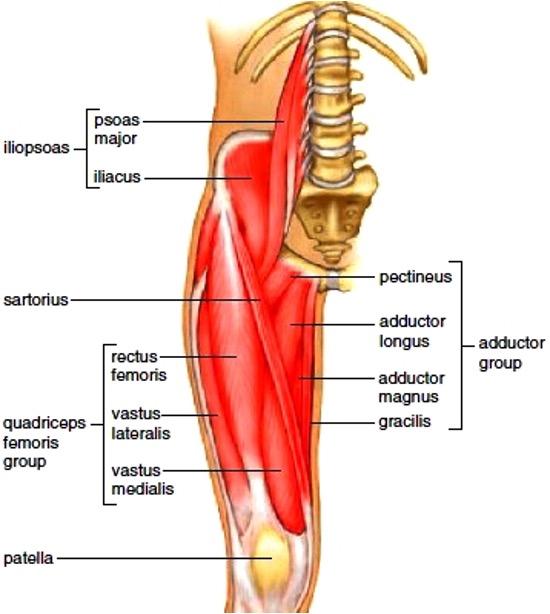
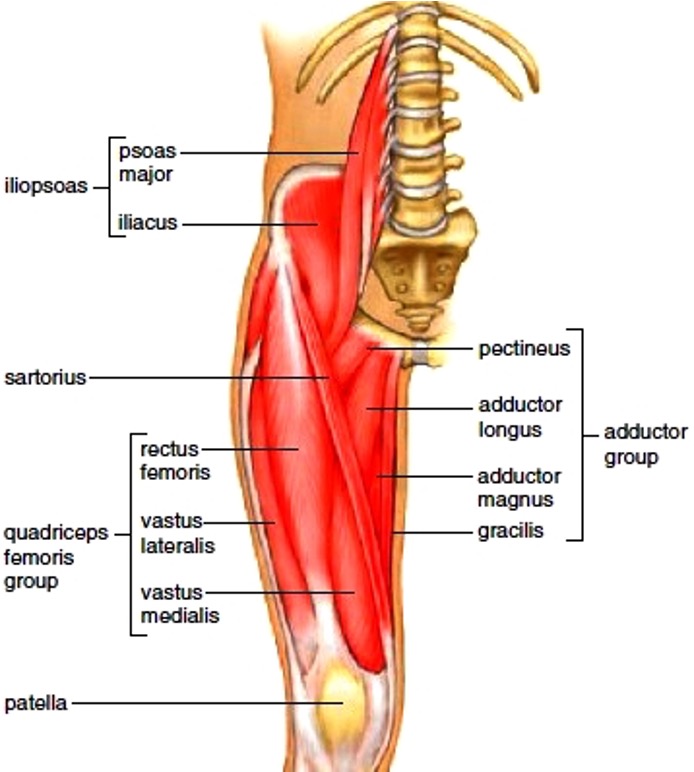
Thigh muscles anterior compartment
pectineus
sartorius
quadriceps
rectus femoris
vastus lateralis
vastus intermedius **
vastus medialis
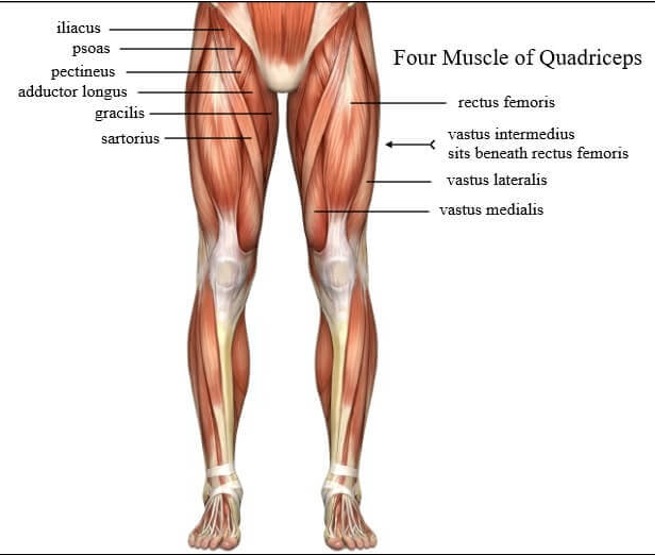
illiopsoas
psoas major
illiacus
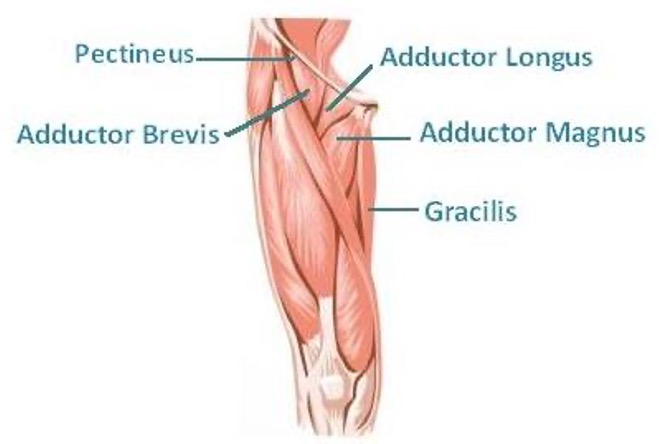
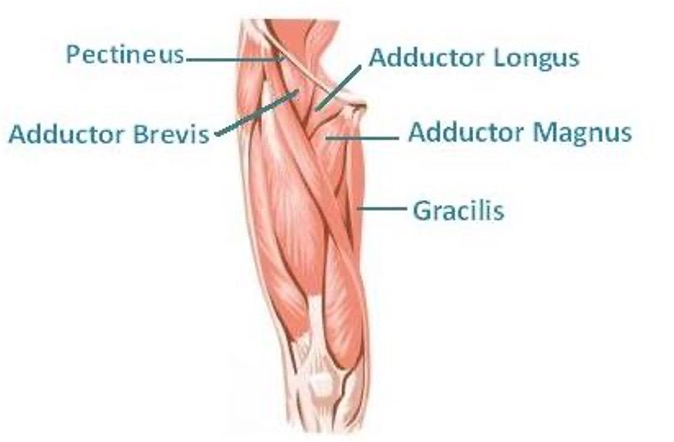
thigh muscles medial compartment
“inner thigh”
gracilis
adductor brevis
adductor longus
adductor Magnus
obturator externus
thigh muscles posterior compartment
“hamstrings”
biceps femoris
semitendinosus
semimembranosus
anterior thigh muscles, flexors of hip, and extensors of knee are innervated primarily by ____
femoral nerve
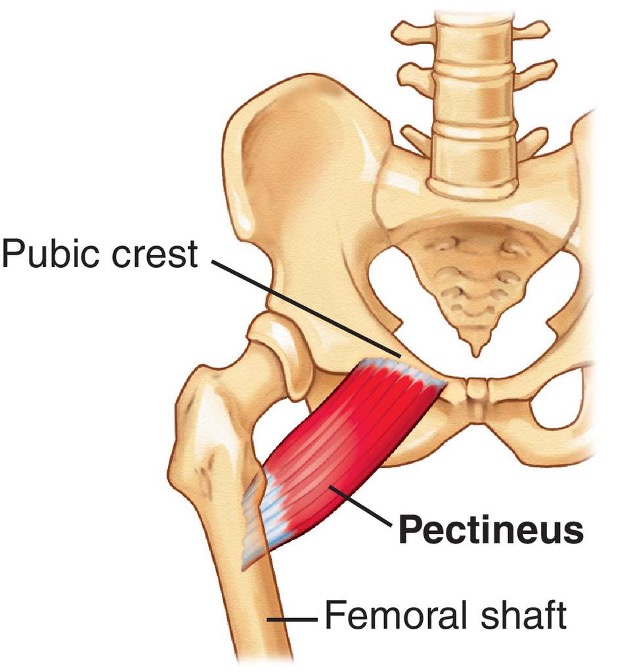
pectineus
origin: pubis
insertion: femur, just inferior to lesser trochanter
innervation: femoral n. L2-L3
action: -adduct and flex thigh
-assist with medial rotation of thigh
illiopsoas
-formed by psoas major and illiacus
-flex thigh (hip flexion)
muscles of quadriceps femoris
4 parts for extending leg at knee joint:
rectus femoris- flex thigh; extend leg at joint
vastus lateralis- extend leg at knee joint
vastus intermedius- extend leg at knee joint
vastus medialis- extend leg at knee joint
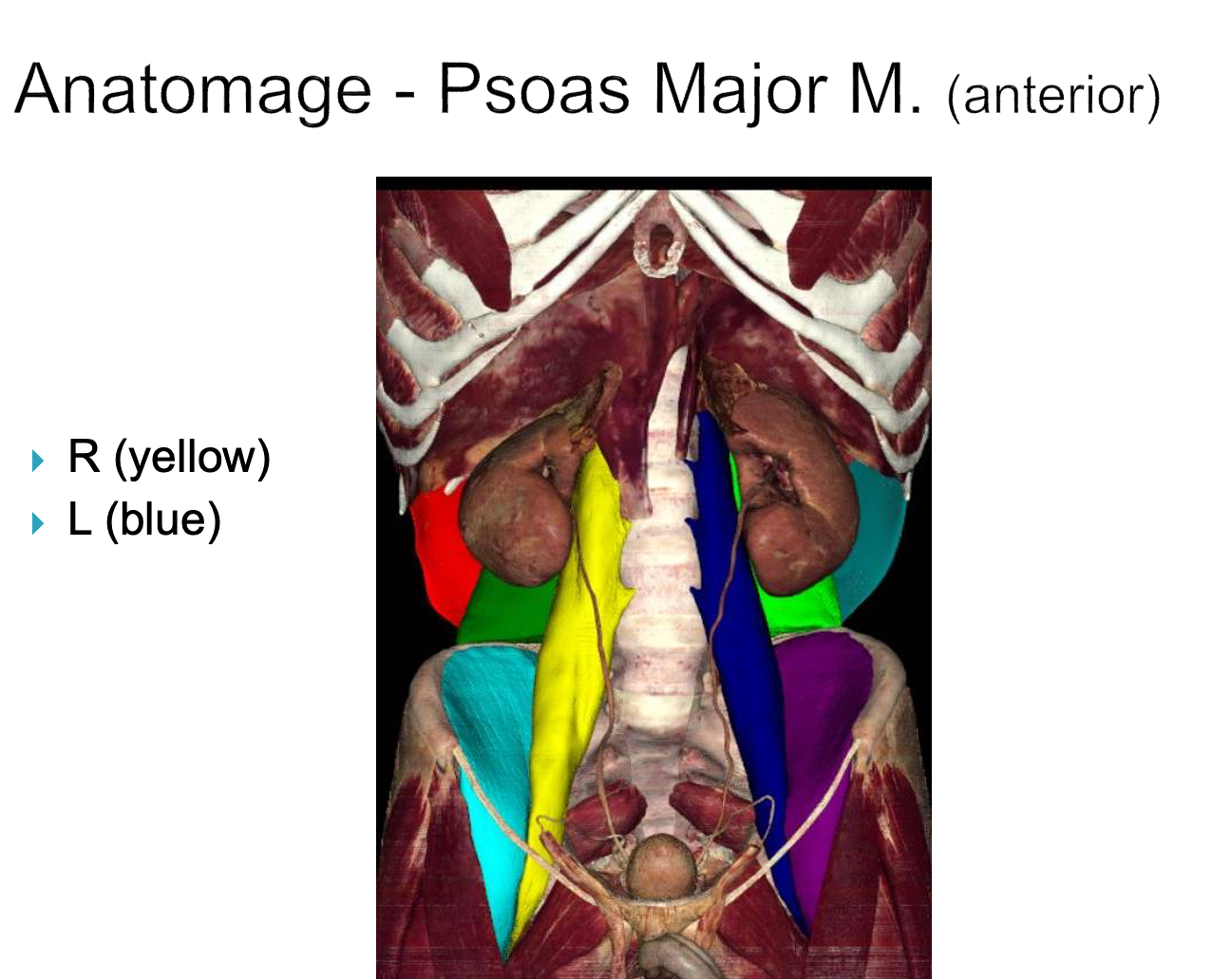
Psoas Major
origin: T12-L5
insertion: lesser trochanter of femur
innervation: anterior rami of lumbar nerves L1-L3
action: -flex thigh/hip
-lateral flexion of vertebrae column
-when sitting- flexes trunk
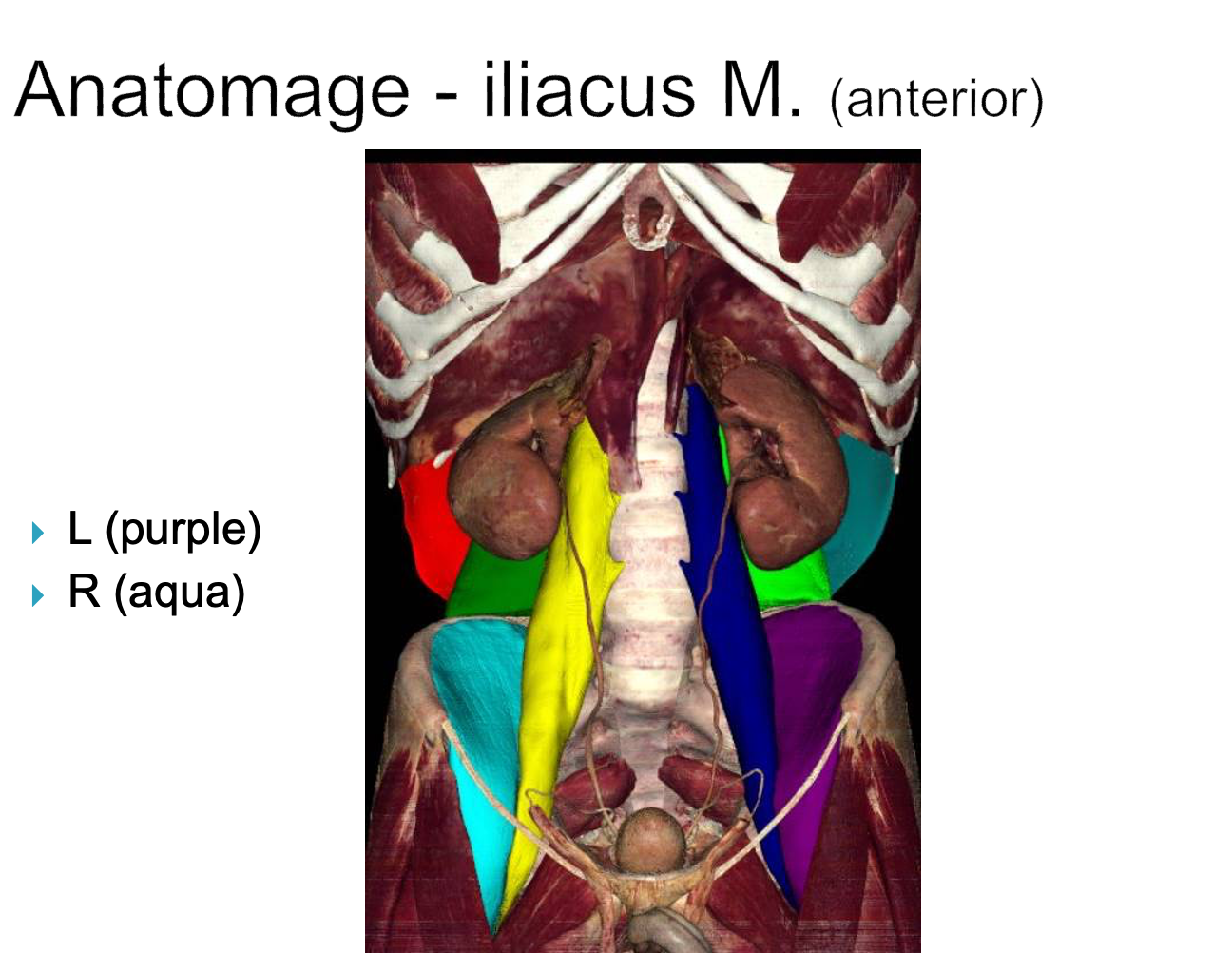
Illiacus
origin: iliac crest and sacrum
insertion: lesser trochanter of femur
innervation: femoral n. (L2-L4)
action: -flex thigh at hip joint
-stabilize hip joint
sartorius
longest muscle in the body; “tailor’s muscle”; crosses two joints (hip & knee)
origin: asis of ilium
insertion: superior part of medial surface of tibia
innervation: femoral n. L2-L3
action: -flex, abduct, and laterally rotate thigh at hip joints
-flex leg at knee joint
quadricep muscle origins
rectus femoris- anterior inferior iliac spine and ilium superior to acetabulum
vastus lateralis- greater trochanter of femur
vastus medialis- medial proximal shaft of femur
vastus intermedius- anterior and lethal surfaces of shaft of femur
quadricep muscles innervation
femoral n L2-L4
Which quad muscle steadies hip joint and helps iliopsoas flex thigh?
rectus femoris
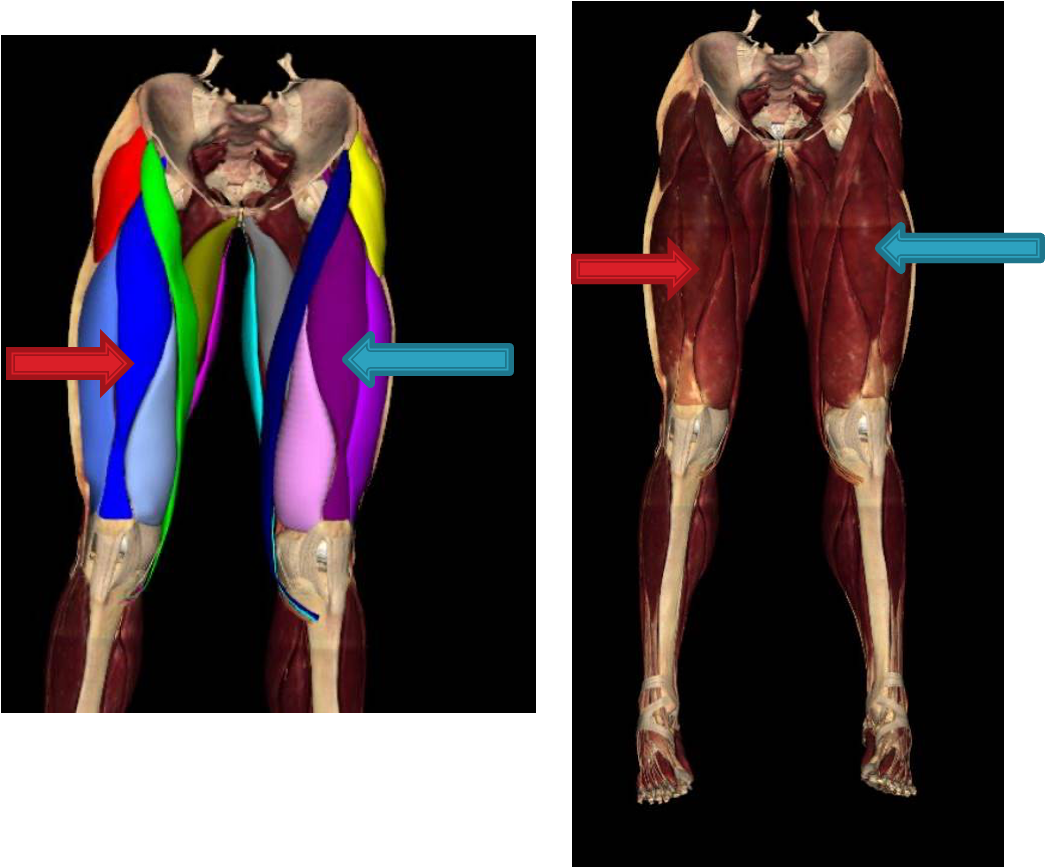
which quad muscle is crucial for walking, running, jumping, and squatting?
rectus femoris
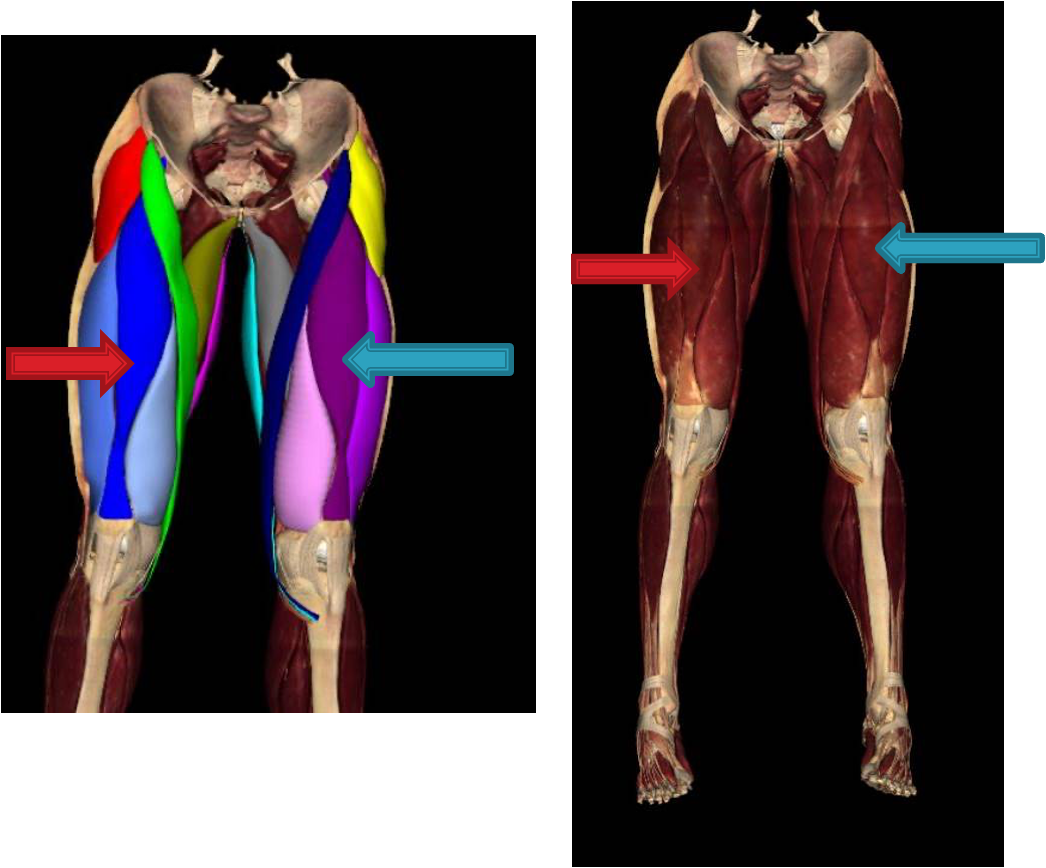
Which muscles are collectively the most powerful muscle in the body?
quadricep muscles
Quadricep muscles insertion
attaches to superior region of patella with rectus femoris tendon, which then attaches to tibial tuberosity distally as the patellar tendon
Medial compartment of thigh is primarily innervated by ______
obturator nerve
Gracilis
most superficial muscle on medial thigh
origin: body and inferior ramus of pubis
insertion: superior part of medial surface of tibia
innervation: anterior branch of obturator nerve L2-L3
action: -adduct thigh
-flex hip
-medially rotate leg
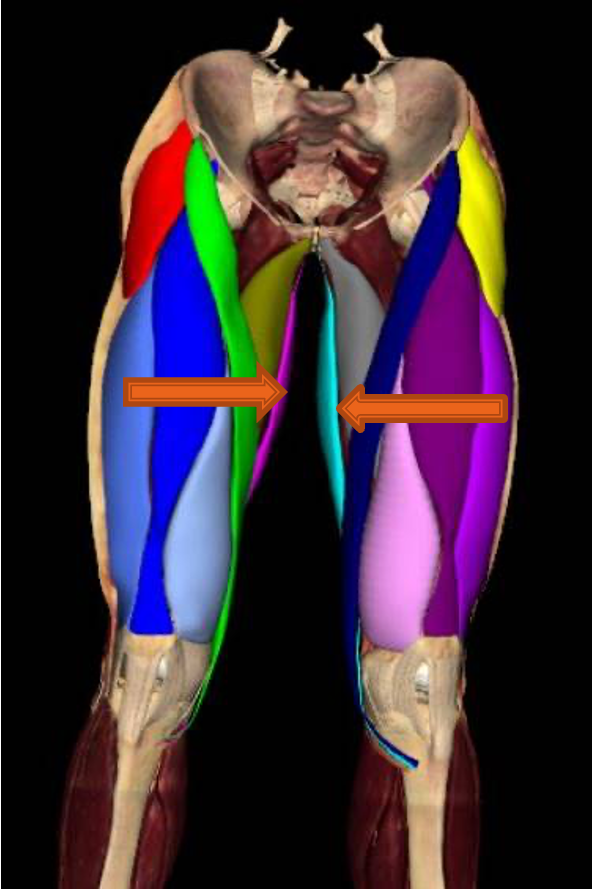
adductor longus
origin: pubis
insertion: middle femur
innervation: branch of obturator n. L2-L4
action: adduct thigh
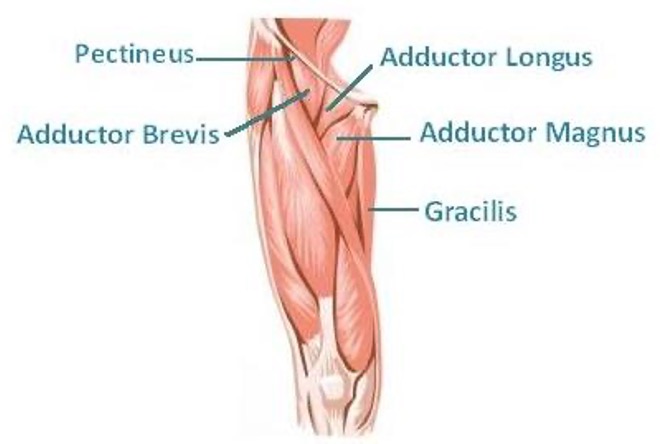
adductor brevis
origin: pubis
insertion: femur
innervation: obturator nerve, L2-L4
action: -adduct thigh
-some extend flexes thigh
adductor magnus
origin: -pubis: adductor portion
-ischial tuberosity: hamstring portion
insertion: femur
innervation: -obturator n: adductor portion
-tibial n: hamstring portion
action: -adduct thigh (adductor portion)
-extend thigh (hamstring portion)
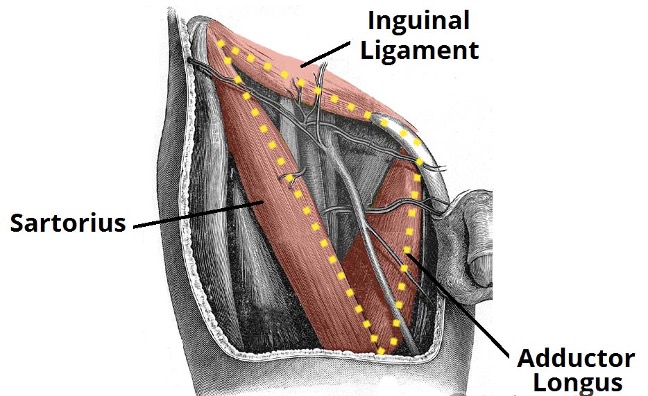
Femoral triangle boundaries
inguinal ligament superiorly forms base
sartorius m. laterally
adductor longus m. medially
superficial gluteal muscles
large muscles
-gluteus maximus: extension, lateral rotation of thigh
-gluteus medius: abduct, medially rotate thigh
-gluteus minimus: abduct, medially rotate thigh
-tensor fasciae latae: flexor of thigh, not independent
deep gluteal muscles
small muscles; lateral rotators of thigh and stabilizers of hip joints
-piriformis
-obturator internus
-superior gemelli
-inferior gemelli
-quadratus femoris
gluteus maximus
origin: ilium, sacrum and coccyx
insertion: most fibers end in iliotibial tract which inserts into lateral condyle of tibia, some fibers insert on gluteal tuberosity of femur
innervation: inferior gluteal nerve (L5-S2)
action:- major extensor of thigh
- lateral (external) rotator of thigh
- steadies thigh and assists in rising from sitting position
gluteus medius
origin: ilium
insertion: greater trochanter of femur
innervation: superior gluteal nerve (L4-S1)
action: -abduct thigh
-medial rotation of thigh
-prevent pelvis tilt when walking
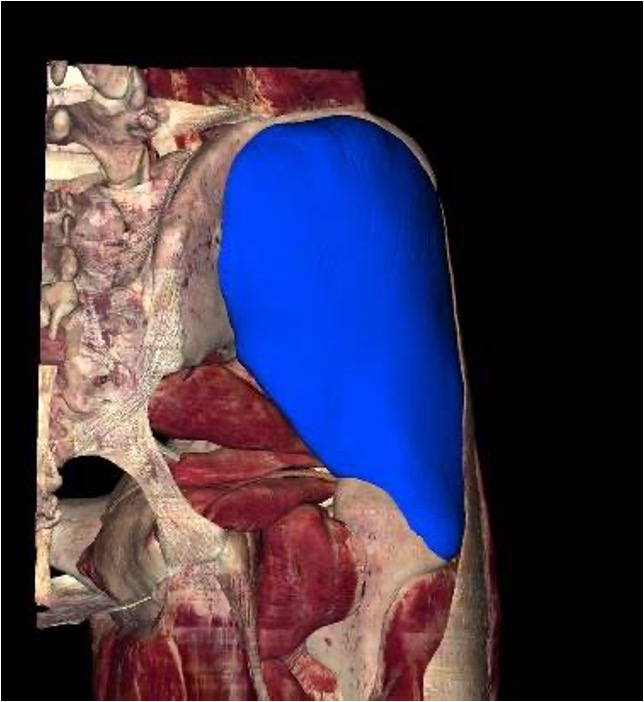
gluteus minimus
origin: ilium
insertion: greater trochanter of femur
innervation: superior gluteal nerve (L4-S1)
action: -abduct thigh
-medial rotation of thigh
-assist gluteus medius in it’s actions (prevent pelvis tilt when walking)
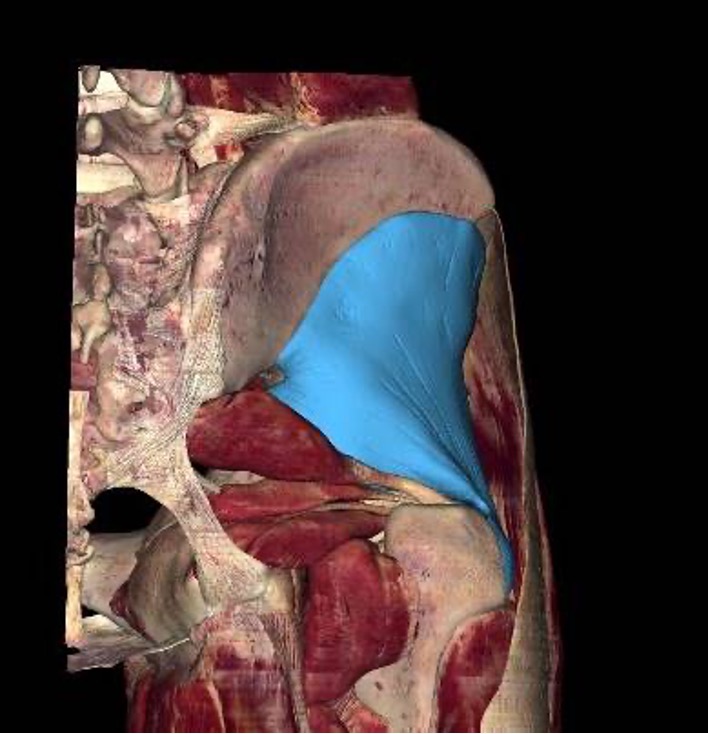
Tensor Fascia Lata m.
origin: ASIS and anterior part of iliac crest
insertion: iliotibial tract/band (ITB), which attaches to lateral condyle of tibia
innervation: superior gluteal nerve (L4-S1)
action: flexion of thigh
Pririformis m.
origin: 2nd-4th sacrum
insertion: greater trochanter of femur
innervation: branches of anterior rami of sacral nerve (S1-S2)
action: -lateral rotation of extended tigh
-abduct flexed thigh
-steady femoral head in acetabulum (stabilizes hip joint)
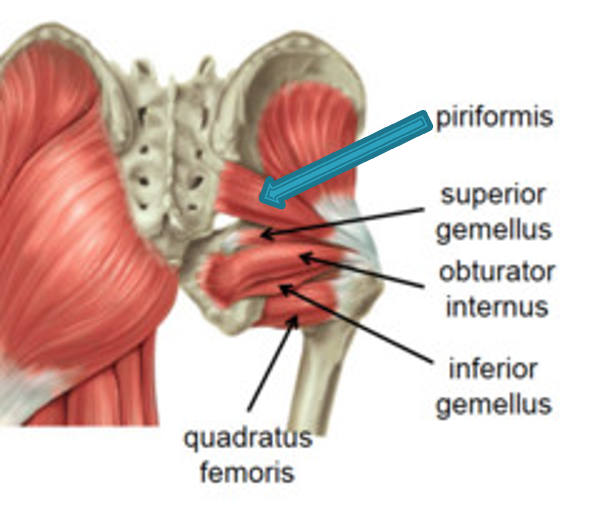
Obturator internus
origin: ilium and ischium
insertion: greater trochanter of femur
innervation: nerve to obturator internus (L5-S1)
action: -abduct thigh
-lateral rotation of thigh
-stabilize hip while walking
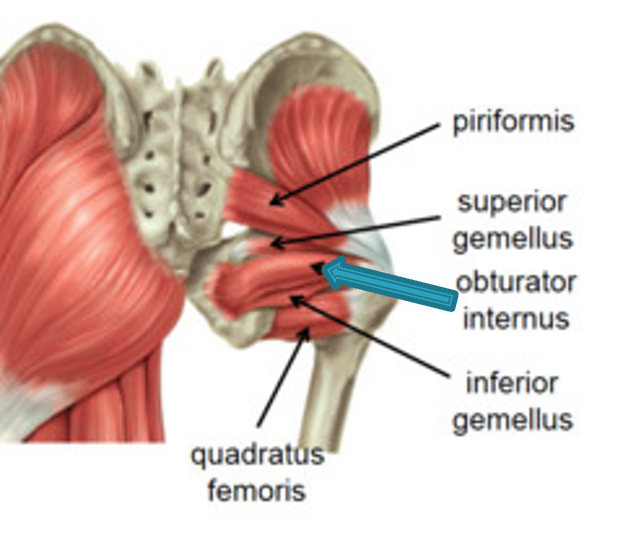
Superior Gemellus
origin: spine of ischium
insertion: medial surface of greater trochanter of femur
innervation: nerve to obturator internus (L5-S1)
action: -laterally rotates extended thigh
-abduct flexed thigh
-steady femoral head in acetabulum
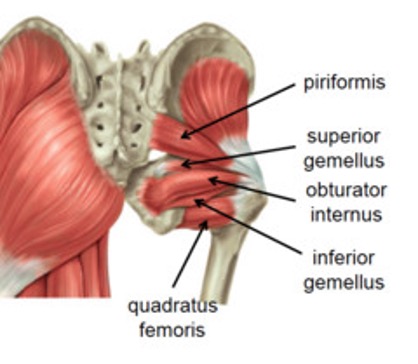
inferior gemellus
origin: ischial tuberosity
insertion: medial surface of greater trochanter of femur
innervation: nerve to quadratus femoris (L5-S1)
action: -laterally rotates extended thigh
-abduct flexed thigh
-steady femoral head in acetabulum
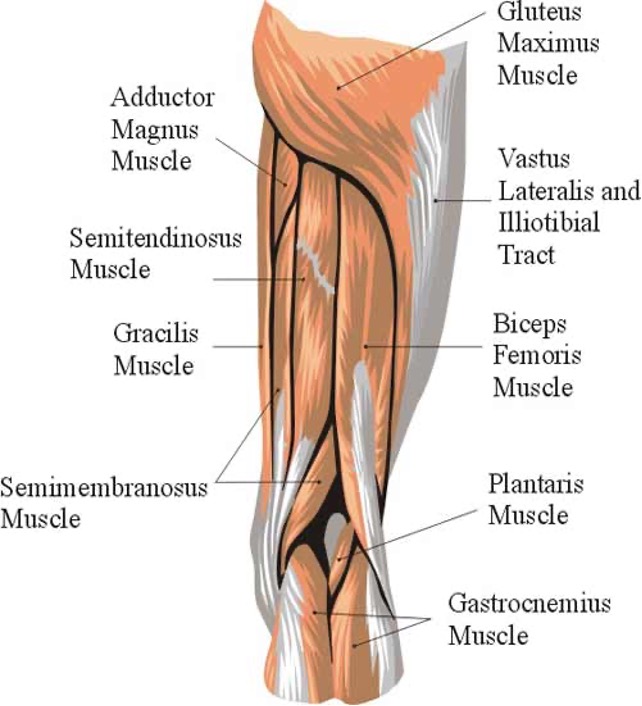
hamstring muscles
semitendinosus- extend thigh, flex/medially rotate leg
semimembranosus- extend thigh, flex/medially rotate leg
biceps femoris-
long head: flex and laterally rotate leg when knee is flexed
short head: flex and laterally rotate leg when knee is flexed
Semitendinosus
origin: ischial tuberosity (ischium)
insertion: medial superior part of tibia
innervation: tibial division of sciatic nerve (L5-S2)
action: -extend thigh
-knee flexion
-medially rotate leg when knee is flexed
-extend trunk when thigh and leg are flexed
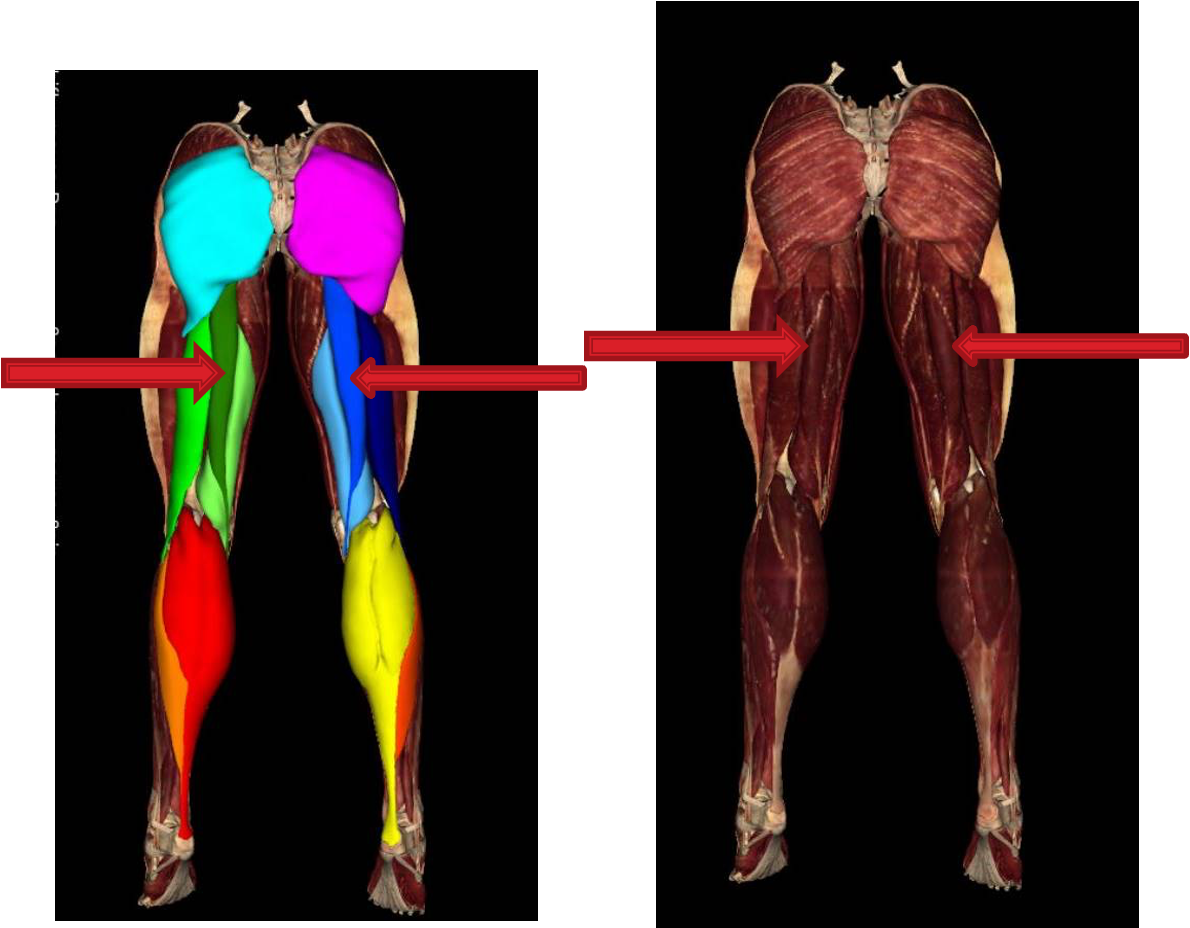
semimembranosus
origin: ischial tuberosity
insertion: posterior medial condyle of tibia
innervation: tibial division of sciatica nerve (L5-S2)
action: -extend thigh
-knee flexion
-medially rotate leg when knee is flexed
-extend trunk when thigh and leg are flexed
Biceps femoris long head
origin: ischial tuberosity
insertion: lateral side of head of fibula
innervation: tibial division of sciatic nerve (L5-S2)
action: -flex knee
-lateral rotation when knee is flexed
-extend thigh when starting to walk
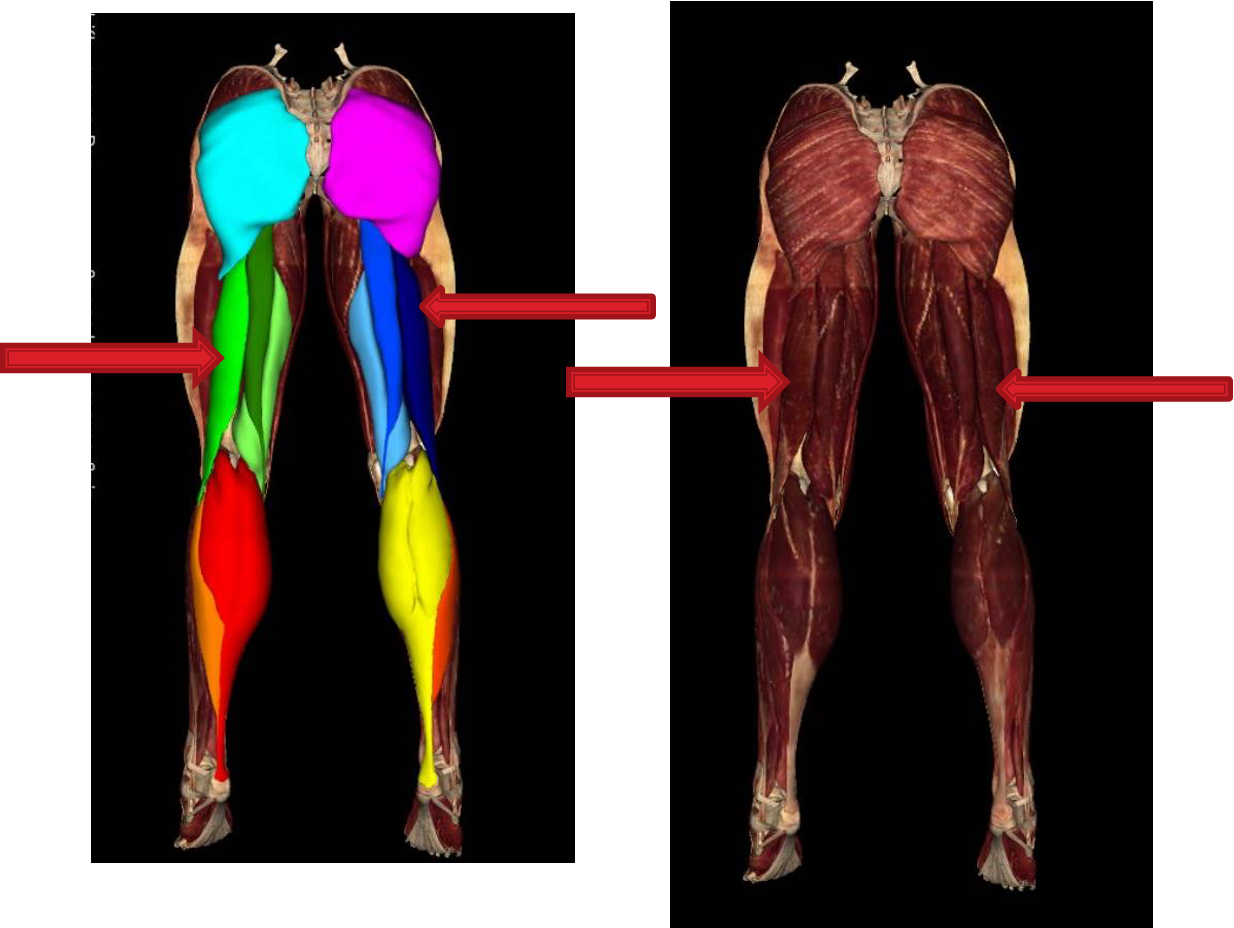
biceps femoris short head
origin: lateral femur
insertion: lateral side of head of fibula
innervation: common fibular division of sciatic nerve (L5-S2)
action: -flex knee
-laterally rotate leg when knee is flexed
-extend thigh when starting to walk
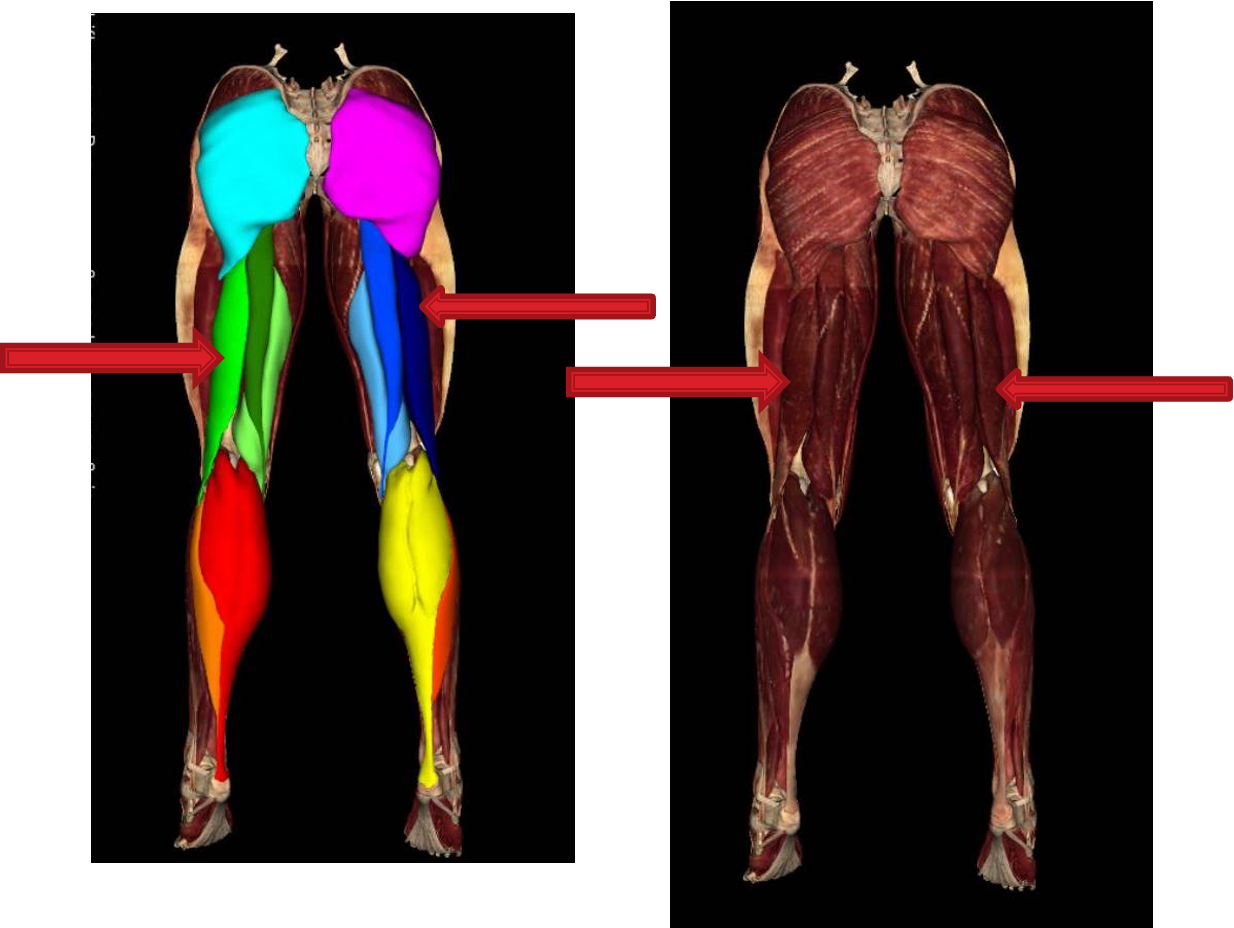
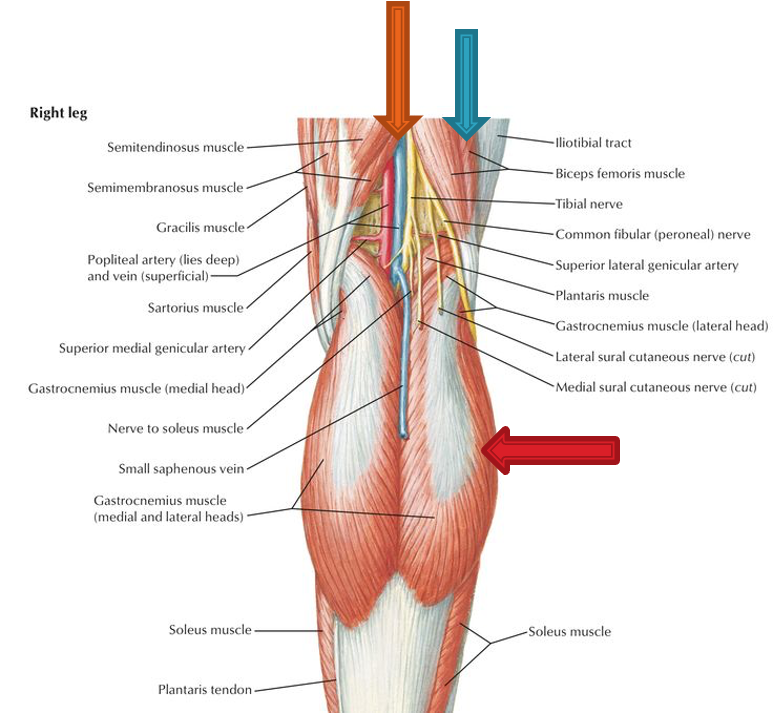
Popliteal Fossa Boundaries
superior: biceps femoris (superior lateral), semimembranosus and semitendinosus (superior medial)
inferior: gastrocnemius (inferolateral and inferomedial)
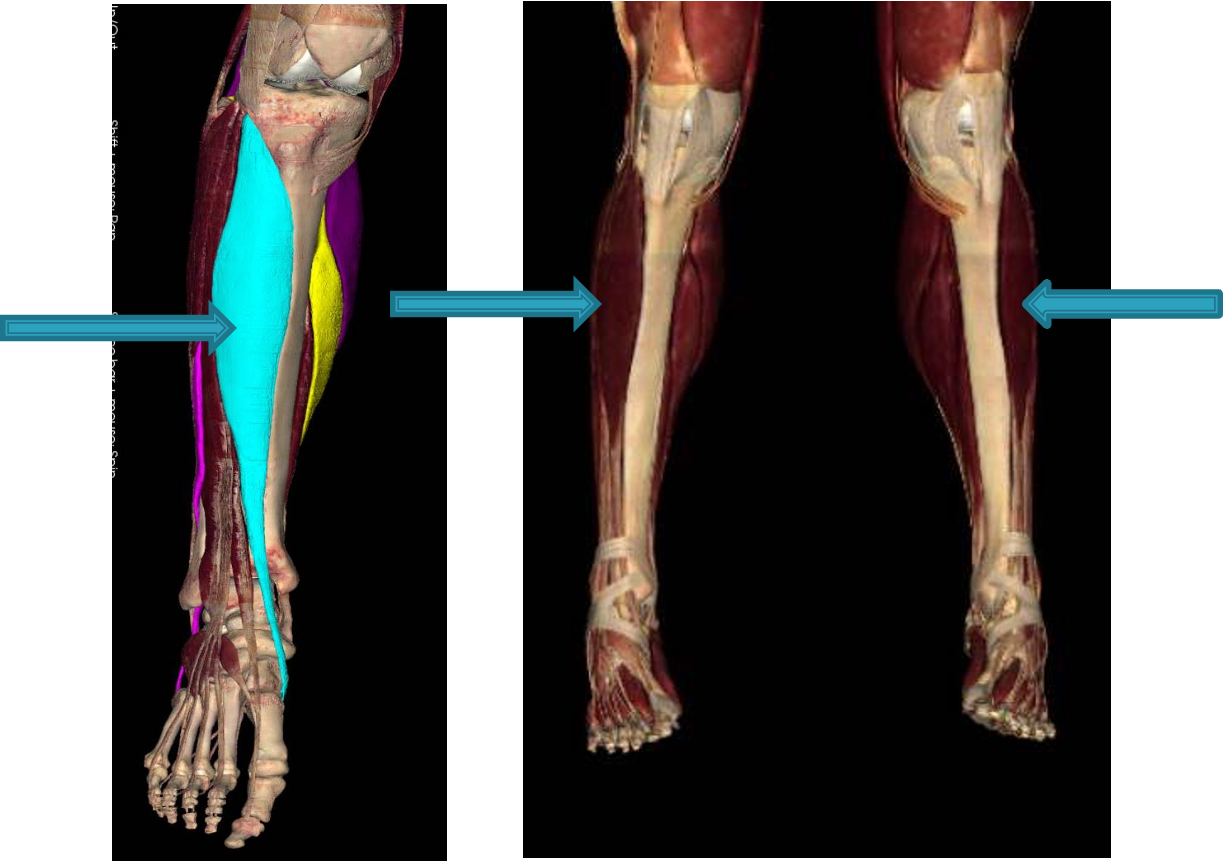
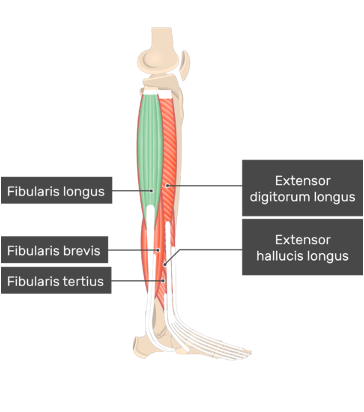
muscles of anterior compartment of leg (dorsiflexor/extensor)
tibialis anterior: dorsiflex ankle, invert foot, support arch of foot longitudinally
extensor digitorum longus: extend lateral 4 digits, dorsiflex ankle
extensor hallucis longus: extend great toe, dorsiflex ankle
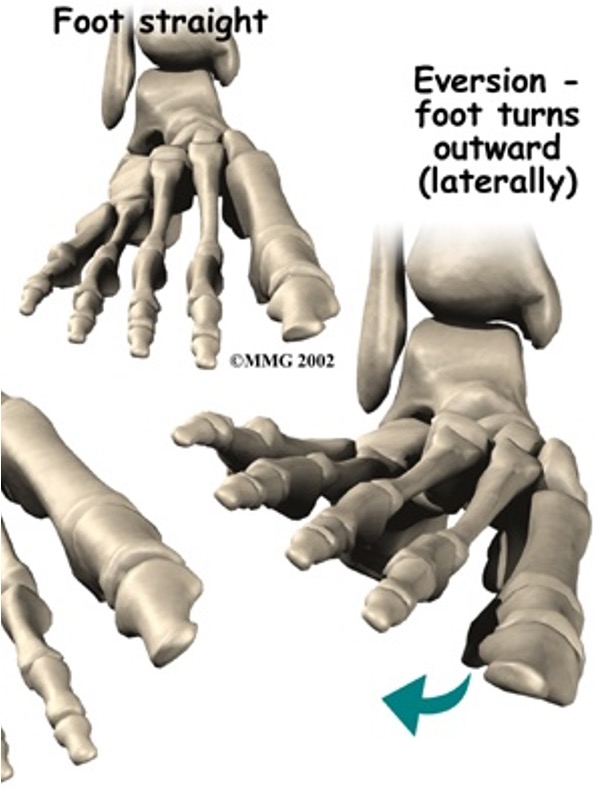
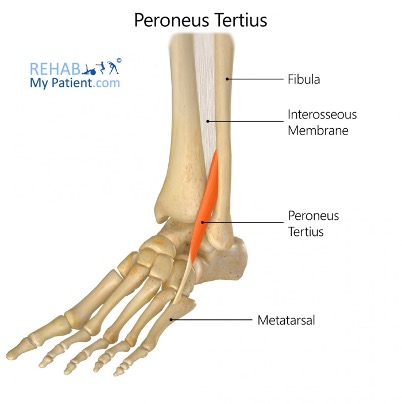
peroneus (fibularis) Tertius: dorsiflex ankle, everts foot
Tibialis anterior
origin: lateral condyle and superior ½ of lateral surface of tibia
insertion: medial and inferior surfaces of medial cuneiform and base of first metatarsal
innervation: deep fibular nerve (L4-L5)
action: dorsiflex and invert the foot
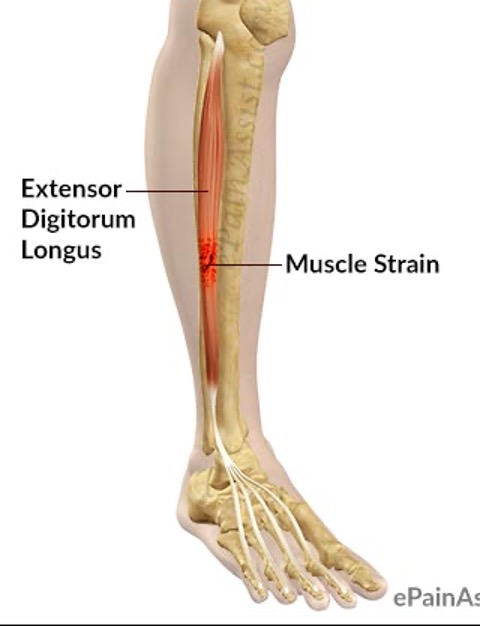
extensor digitorum longus
origin: lateral condyle of tibia
insertion: middle and distal phalanges of lateral 4 digits
innervation: deep fibular nerve (L4-L5)
action: extension of toes and ankle
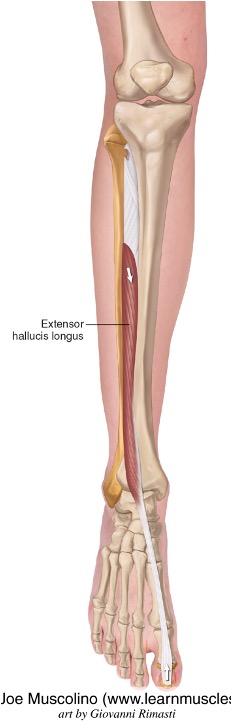
extensor hallucis longus
origin: middle part of anterior surface of fibula
insertion:dorsal aspect of base of distal phalanx of first digit (great toe)
innervation: deep fibular nerve (L4-L5)
action: extend great toe and dorsiflexion of foot at ankle
peroneus (fibularis) Tertius m.
origin: inferior 1/3 of anterior surface of fibula
insertion: dorsum of base of 5th metatarsal
innervation: deep fibular nerve (L5-S1)
action: dorsiflex and evert foot
muscles of lateral compartment of leg (everter)
peroneus (fibularis) longus: evert foot, plantar flex ankle, support arch of foot transversely
peroneus (fibularis) brevis: evert foot
peroneus (fibularis) longus m.
origin: head and superior 2/3 of lateral surface of fibula
insertion: base of first metatarsal & medial cuneiform
innervation: superficial fibular nerve (L5-S2)
action: evert foot, weakly plantar flex ankle, supports transverse arch of foot
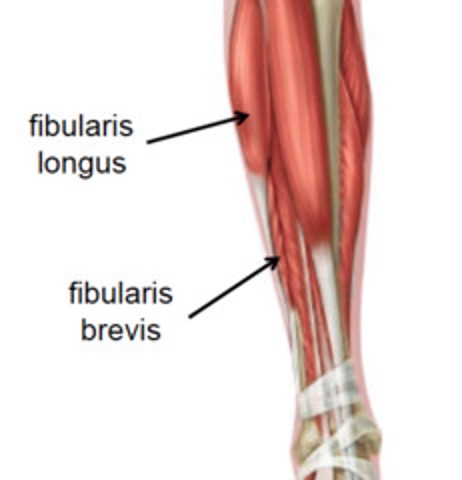
peroneus (fibularis) brevis
origin: inferior 2/3 of lateral surface of fibula
insertion: dorsal surface of tuberosity of base of fifth metatarsal
innervation: superficial fibular nerve (L5-S2)
action: evert foot, weakly plantar flex ankle
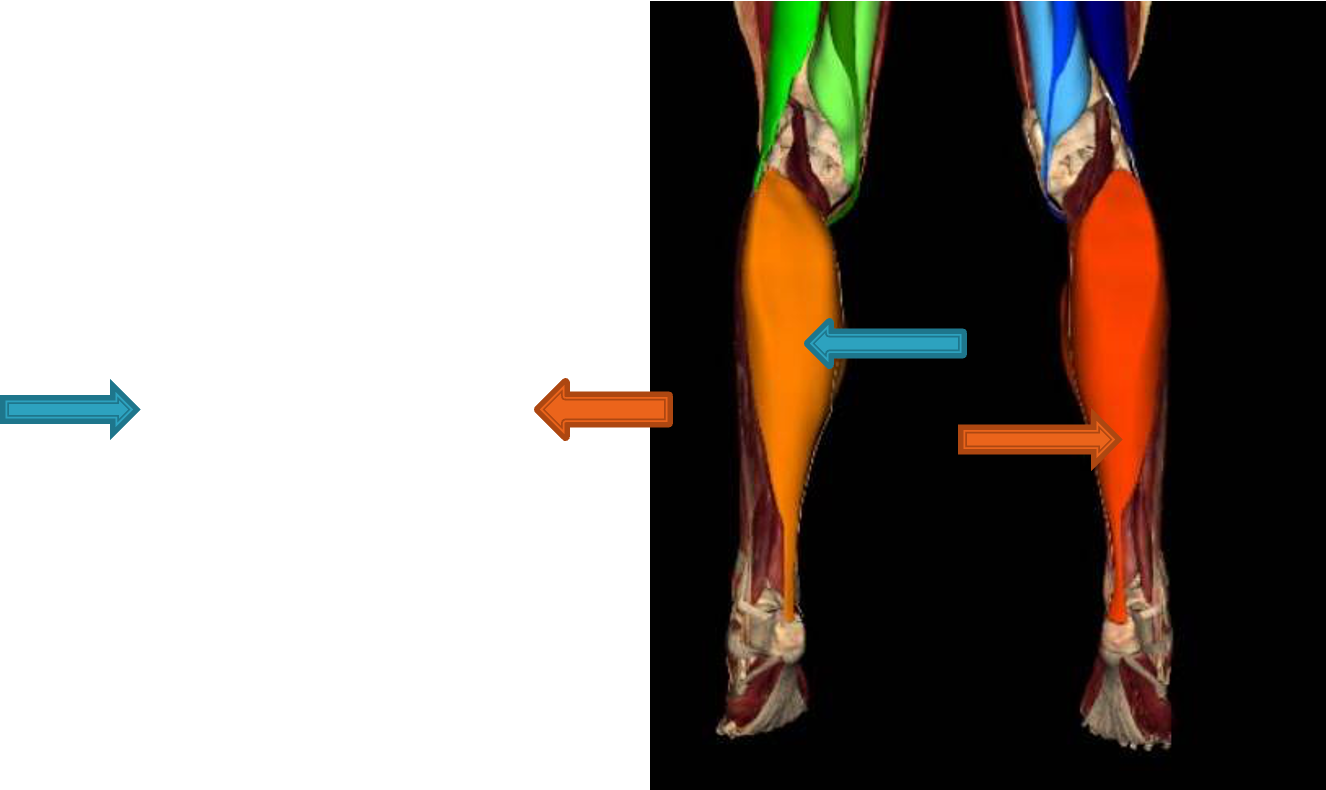
muscles of posterior compartment of leg - superficial
(supplied by tibial nerve and posterior tibial and fibular vessels)
gastrocnemius: plantar flex ankle/foot when knee extended, raise heel while walking, flex leg at knee joint
soleus: plantar flex foot, steadies leg on foot
plantaris: plantar flex foot
muscles of posterior compartment of leg - deep
popliteus: flex knee
flexor hallucis longus: flex great toe, plantar flex foot, longitudinal arch support
flexor digitorum longus: flexes lateral 4 digits, plantar flex foot, longitudinal arch support
tibialis posterior: plantar flex foot, invert foot, medial longitudinal arch support
Gastrocnemius
origin: lateral condyle and medial condyle of femur
insertion: posterior surface of calcaneus via achilles tendon
innervation: tibial nerve (S1-S2)
action: plantar flex ankle when knee is extended, raises heel during walking and flex leg at knee joint
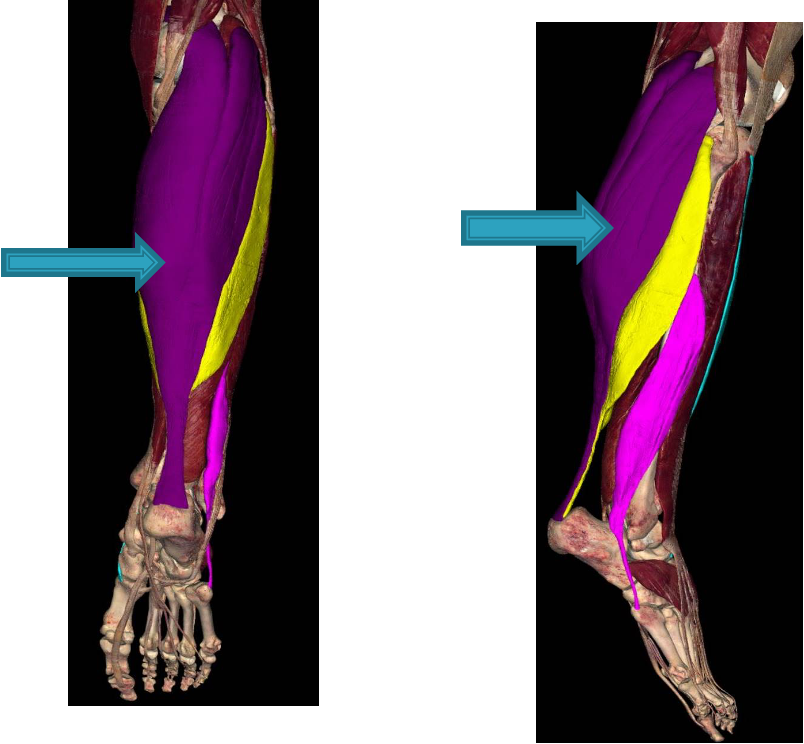
Soleus
deep to gastrocnemius; is “workhouse” of plantarflexion
origin: head of fibula and medial border of tibia
insertion: posterior surface of calcaneus via Achilles tendon
innervation: tibial nerve (S1-S2)
action: plantarflexes ankle
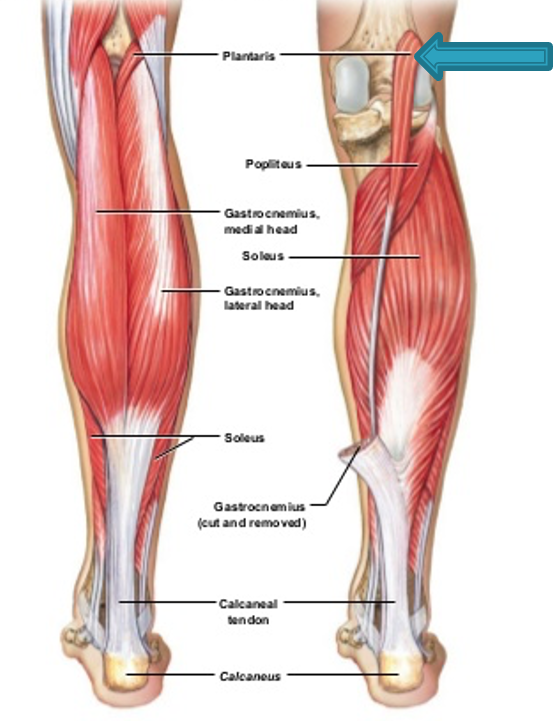
Plantaris
origin: lateral supracondylar of femur
insertion: calcaneus via calcaneal tendon
innervation: tibial nerve (S1-S2)
action: weakly assists gastrocnemius in plantarflexing ankle
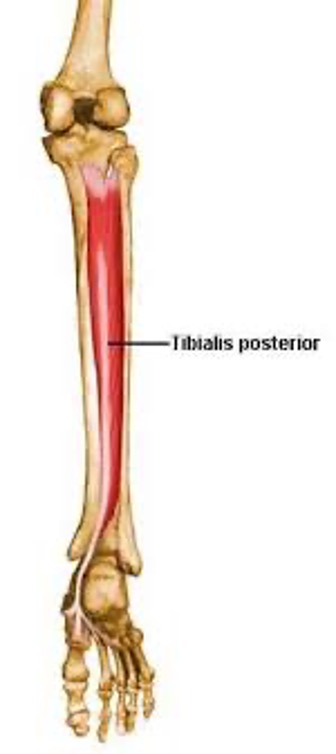
tibialis posterior
deepest, most medial
origin: posterior tibia and posterior fibula
insertion: navicular, cuneiforms, cuboid and bases of 2nd-4th metatarsals
innervation: tibial nerve (L4-L5)
action: plantar flexes ankle, inverts foot, supports medial longitudinal arch of foot
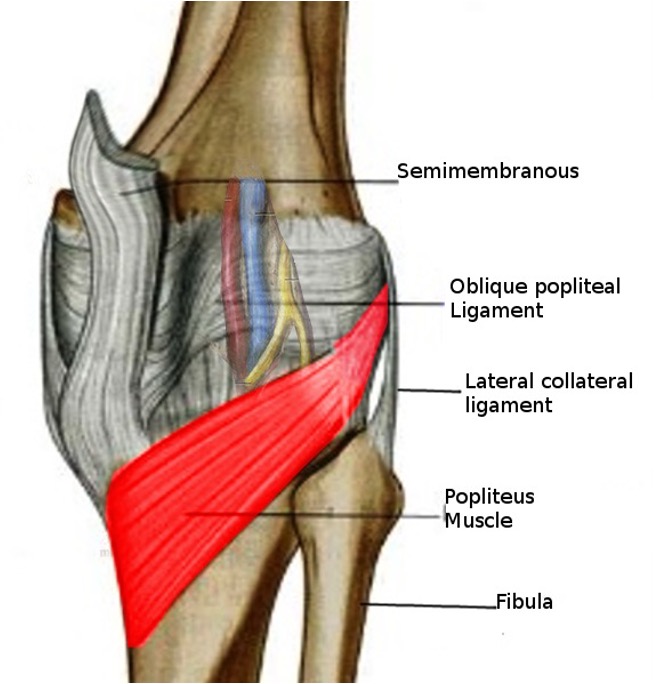
popliteus
origin: lateral femoral condyle and lateral meniscus
insertion: posterior surface of tibia
innervation: tibial nerve (L4-S1)
action: -flex knee
-laterally rotating femur on fixed tibia
-medially rotating tibia of unplanted limb
flexor hallucis longus
“push off muscle”
origin: posterior fibula
insertion: base of distal phalanx of great toe
innervation: tibial nerve (S2-S3)
action: -flex great toe at all joints
-plantarflex ankle
-support medial longitudinal arch of foot
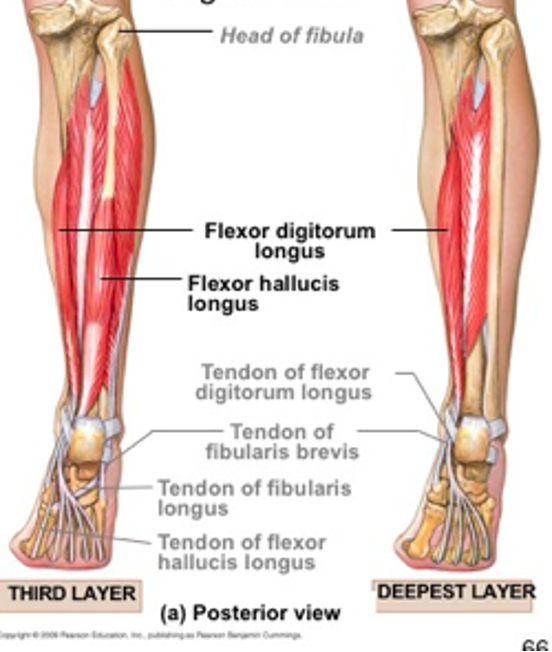
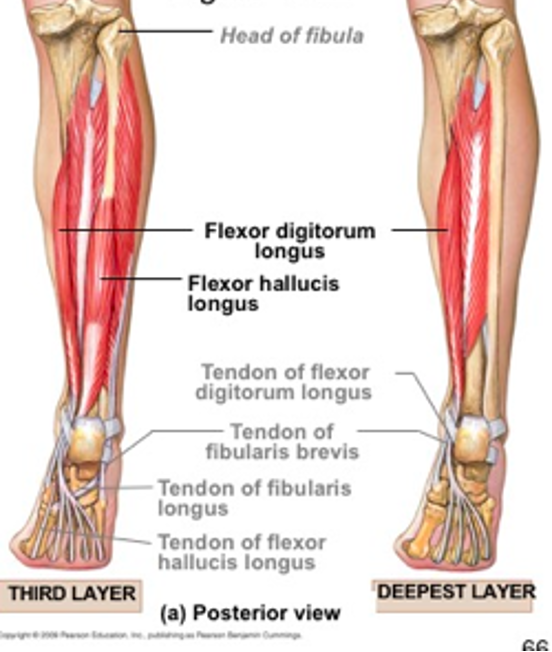
flexor digitorum longus
origin: medial posterior tibia
insertion: bases of distal phalanges of lateral 4 digits
innervation: tibial nerve (S2-S3)
action: -flex lateral 4 digits
-plantarflex ankle
-support longitudinal arch of foot
foot muscles: plantar interossei (3 muscles)
adducts digits 3-5, flex MTPs
foot muscles: dorsal interossei (4 muscles)
abduct digits 2-4, flex MTPs
extensor digitorum brevis (foot)
origin: calcaneus
insertion:toes
innervation: peroneal nerve
action: extends digits 2-4
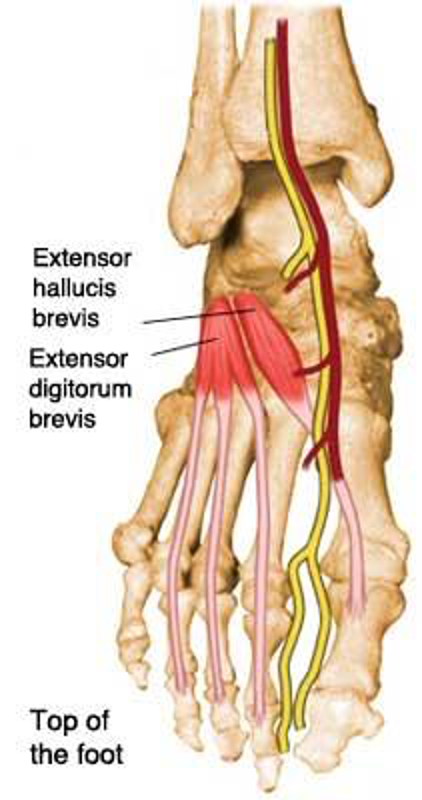
extensor hallucis brevis (foot)
origin: calcaneus
insertion: phalanx of 1st digit
innervation: peroneal nerve
action: extend 1st digit
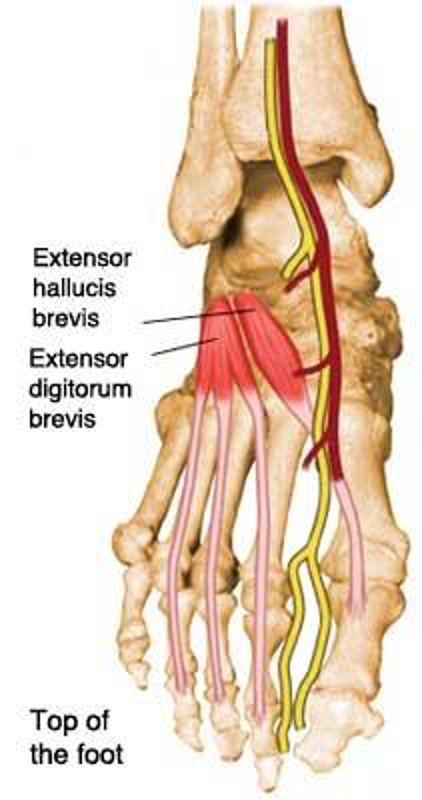
musles of ankle inversion
tibialis anterior
tibialis posterior
(occurs at subtalar joint)
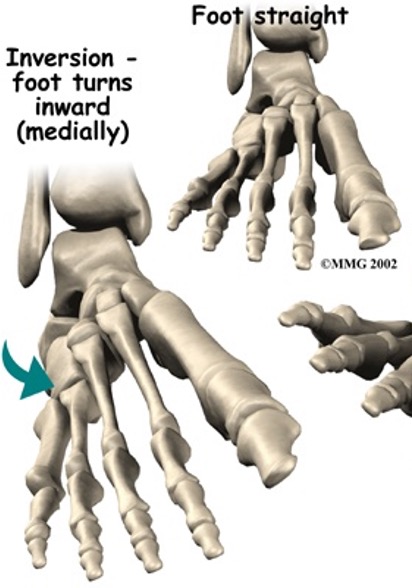
muscles of ankle eversion
peroneus longus
peroneus brevis