Anatomy exam 2
1/171
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
172 Terms
1. Support
2. Protection
3. Movement
4. Electrolyte balance
5. Blood formation
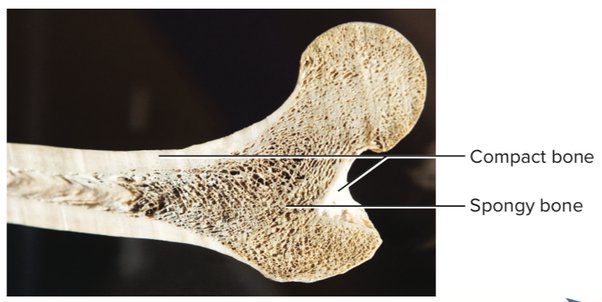
1. Compact bone
2. Spongy bone
thin and flat (ex. cranium)
- compact bone on outsides and spongy in middle (bone sandwich)
- hyaline cartilage
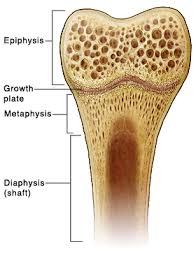
- covers ends of long bones
- shaft of long bones
- compact bone covering spongy bone
- only in long bones
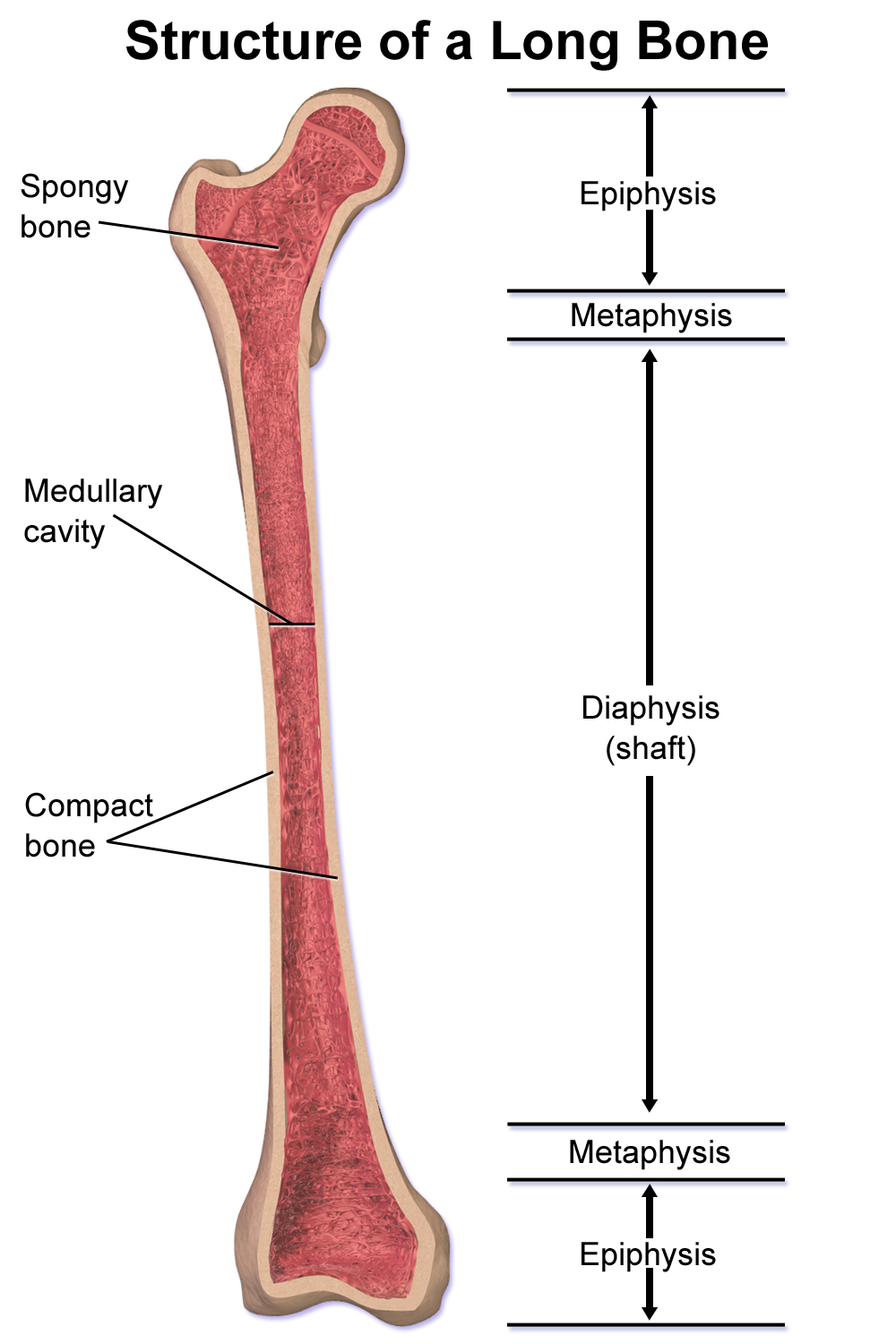
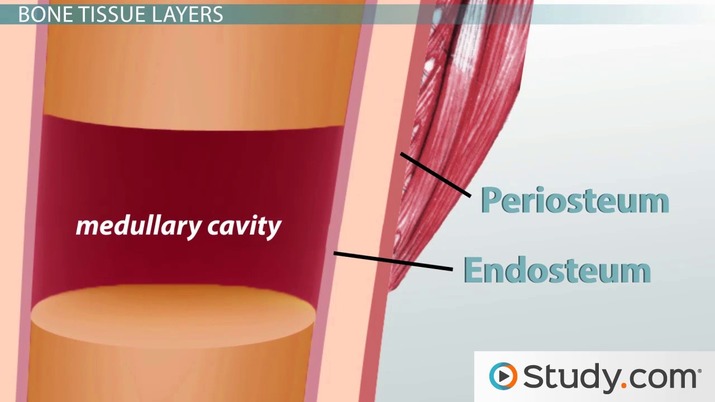
- marrow cavity
- in shaft of long bones
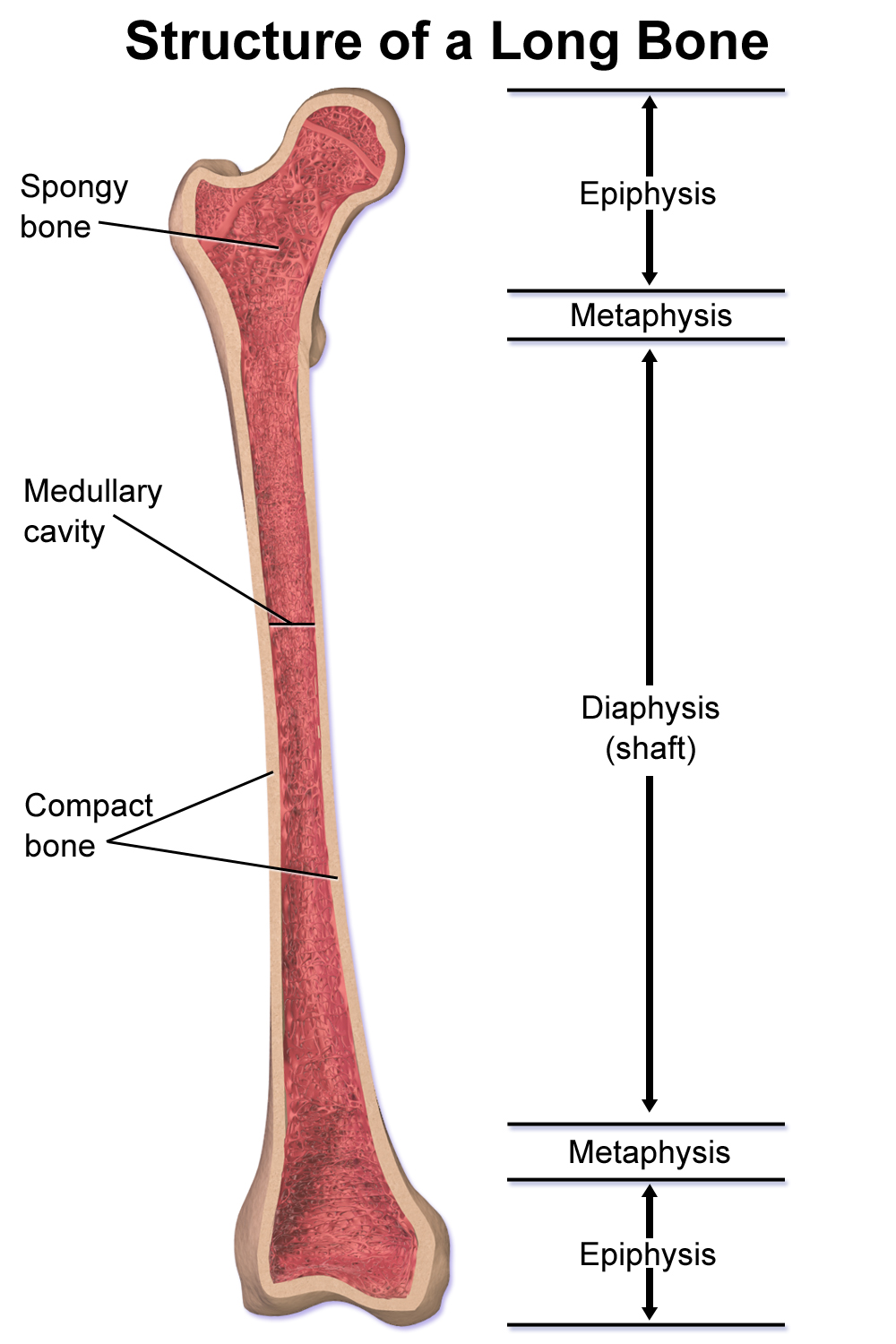
- ends of long bones
- mostly spongy bone
- only in long bones
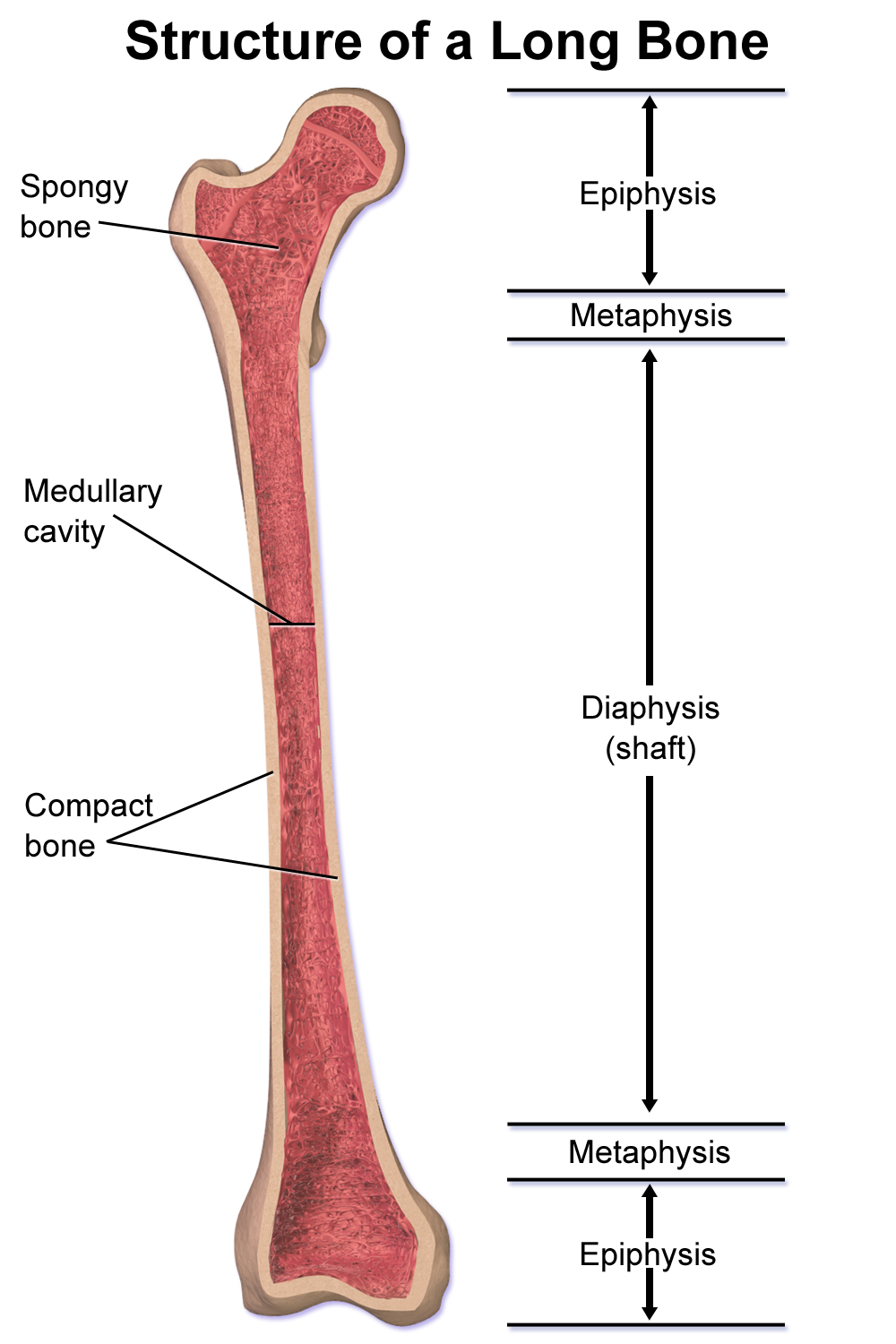
- growth plate
- turns to epiphyseal line when fully formed
- 2 layer membrane
- Provides attachment to tendons and ligaments
- rich supply of nerve fibers and blood vessels
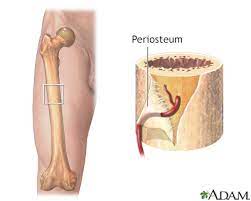
1. Fibrous layer
2. Osteogenic layer
- dense irreg. CT
- outer layer
- osteogenic cells
- turns into bone
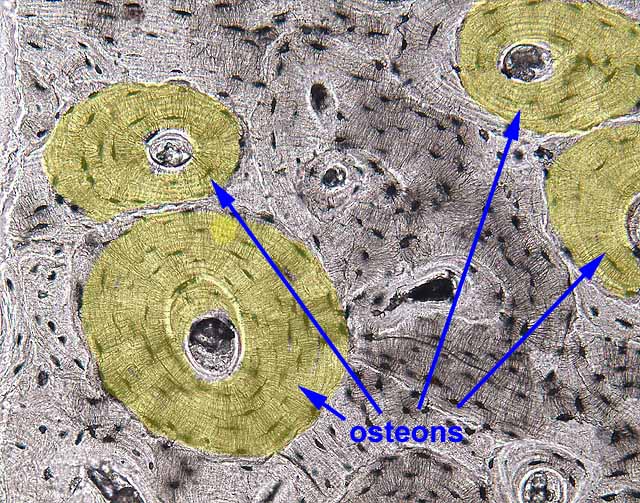
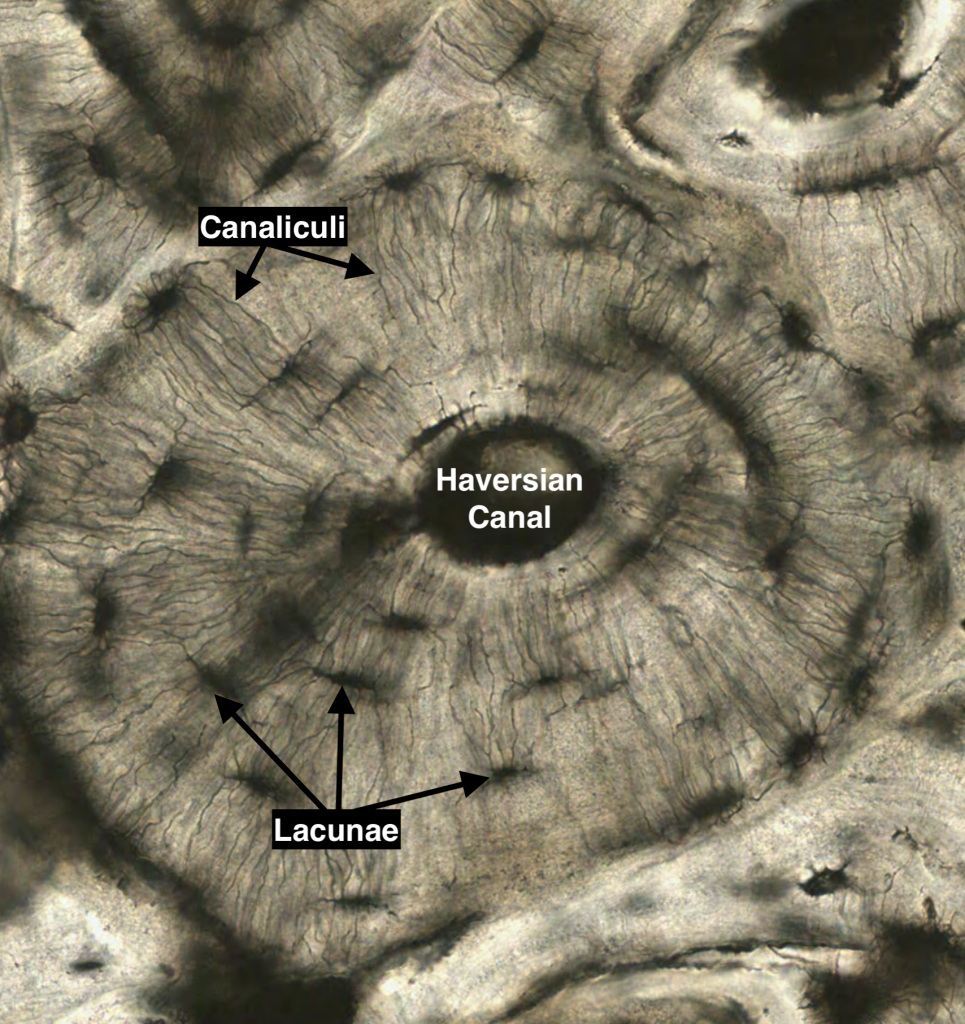
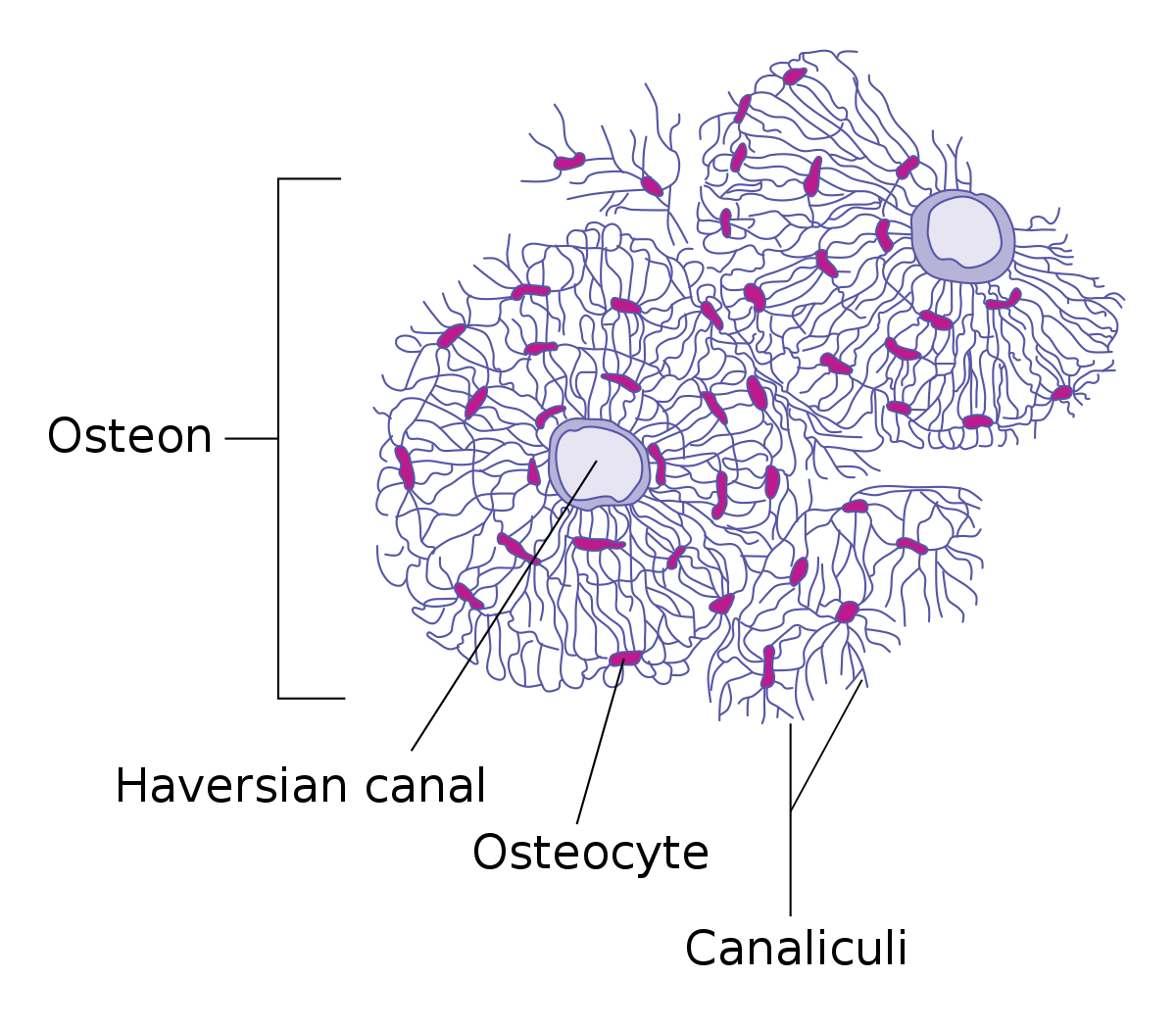
- Haversian system
- fundamental unit
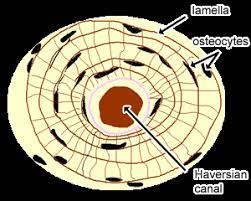
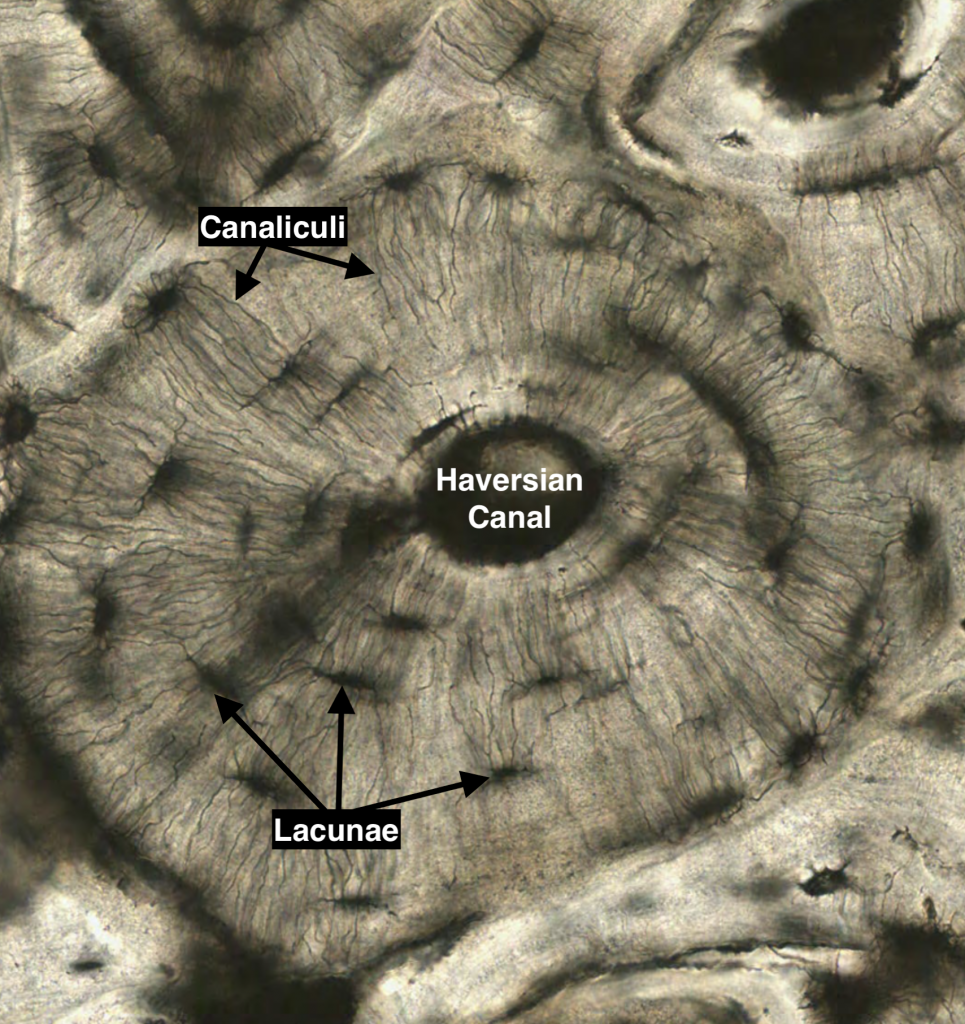
- Haversian canal
- runs through each osteon
- nerves and blood vessels
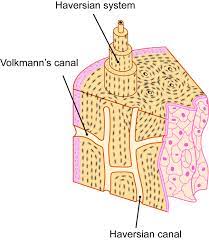
- Volkmann's canal
- perpendicular to central canal to link together
- myeloid tissue/hemopoietic tissue
- found in skull, vertebrae, ribs, sternum, and proximal heads of humerus/femur (in adults)
- fat storage
- can convert to red marrow in extreme cases of anemia
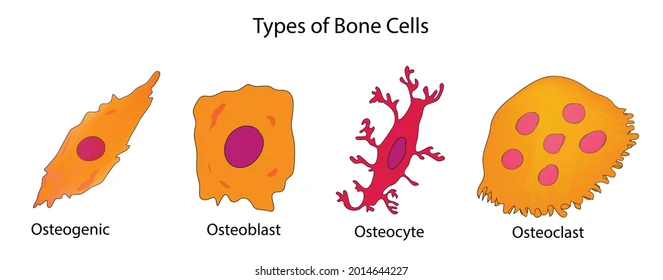
1. osteogenic cells
2. osteoblasts
3. osteocytes
4. osteoclasts
- bone stem cells
- found in periosteum and endosteum
- multiply continually
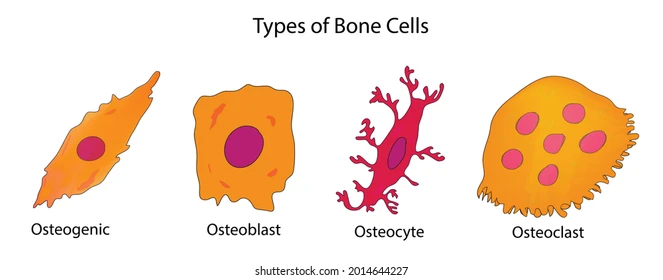
- bone forming cells
- secrete osteoid to form bony matrix
- nonmitotic
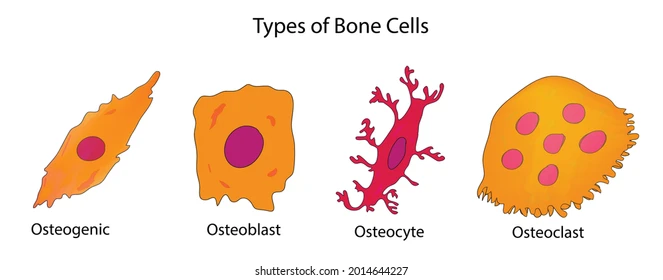
- mature bone cells found in lacunae
- maintain bony matrix
- stress sensors and influence bone remodeling
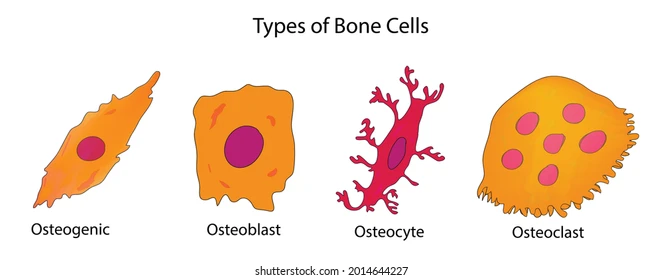
- bone dissolving cells (osteolysis)
- NOT from osteogenic cells, from stem cells
1. 85% Hydroxyapatite (crystalized calcium phosphate salt)
2. 10% calcium carbonate
3. 5% Magnesium, sodium, potassium, fluoride, sulfates, carbonates, and hydroxide ions
1. Bone formation (embryos - early childhood)
2. Bone growth (embryos - early 20's)
3. Bone remodeling (lifelong)
bone develops from fibrous membrane
- widen
- same as intramembranous ossification
- deposition and resorption
- bone mass stays the same (if healthy)
- deficient calcium in the blood
- causes excitable muscles and neurons
- can cause rickets
- constant muscle contraction
- caused when calcium blood levels reach below 6mg/dL

- excessive calcium in the blood
- slow reflexes, depression of NS, cardiac arrest
1. Calcirol
2. Calcitonin
3. Parathyroid hormone
1. UV causes keratinocytes to turn cholesterol to vit. D
2. Liver converts vit. D to calcidiol
3. Kidneys converts calcidiol to calcitriol
- lowers blood calcium levels
- secreted by thyroid gland
- raises blood calcium levels
- increases osteoclast production to free calcium ions and send to blood stream
- increases kidney's ability to absorb calcium
- inhibits osteoclast activity
- can cause osteoporosis if too much is secreted
- stimulates osteoblasts
- prevents osteoporosis
- after menopause, it's created less causing higher chances of osteoporosis
- modulates activity of growth hormone, ensuring proper proportions
- in excess can cause hypercalcemia
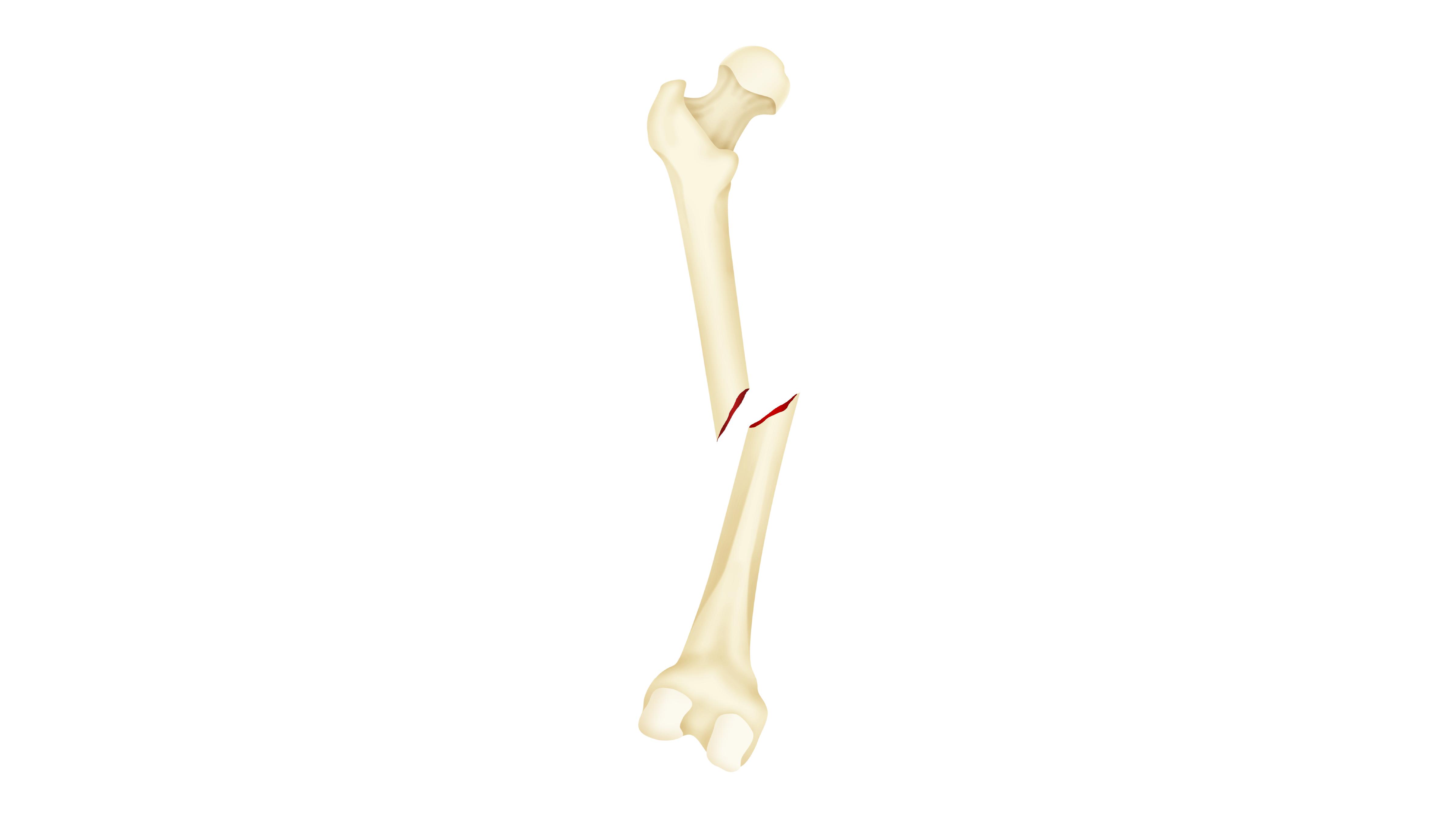
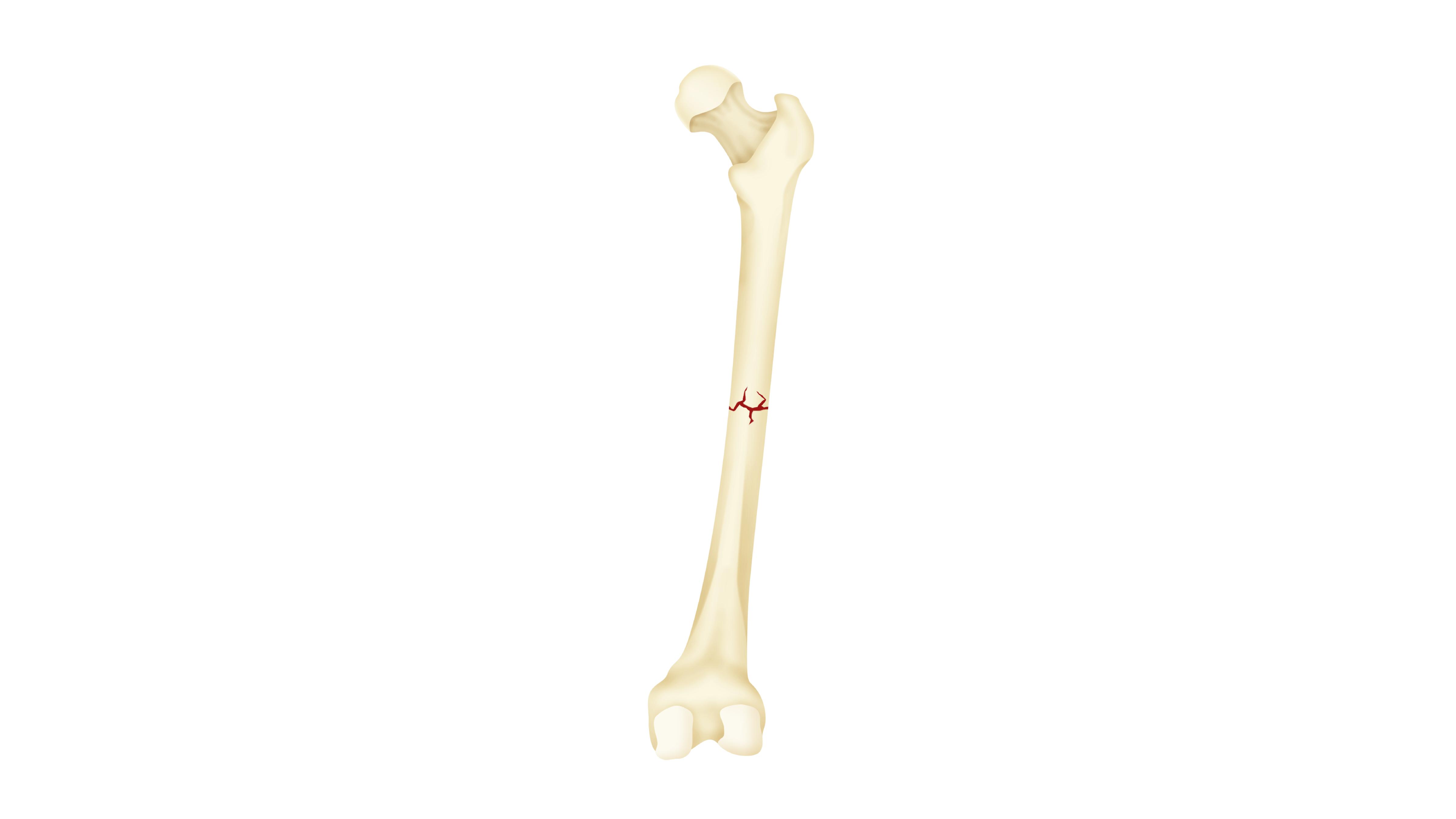
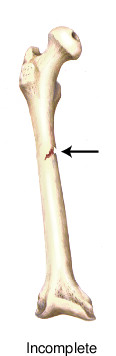
- greenstick
- Bone is still connected in someplace
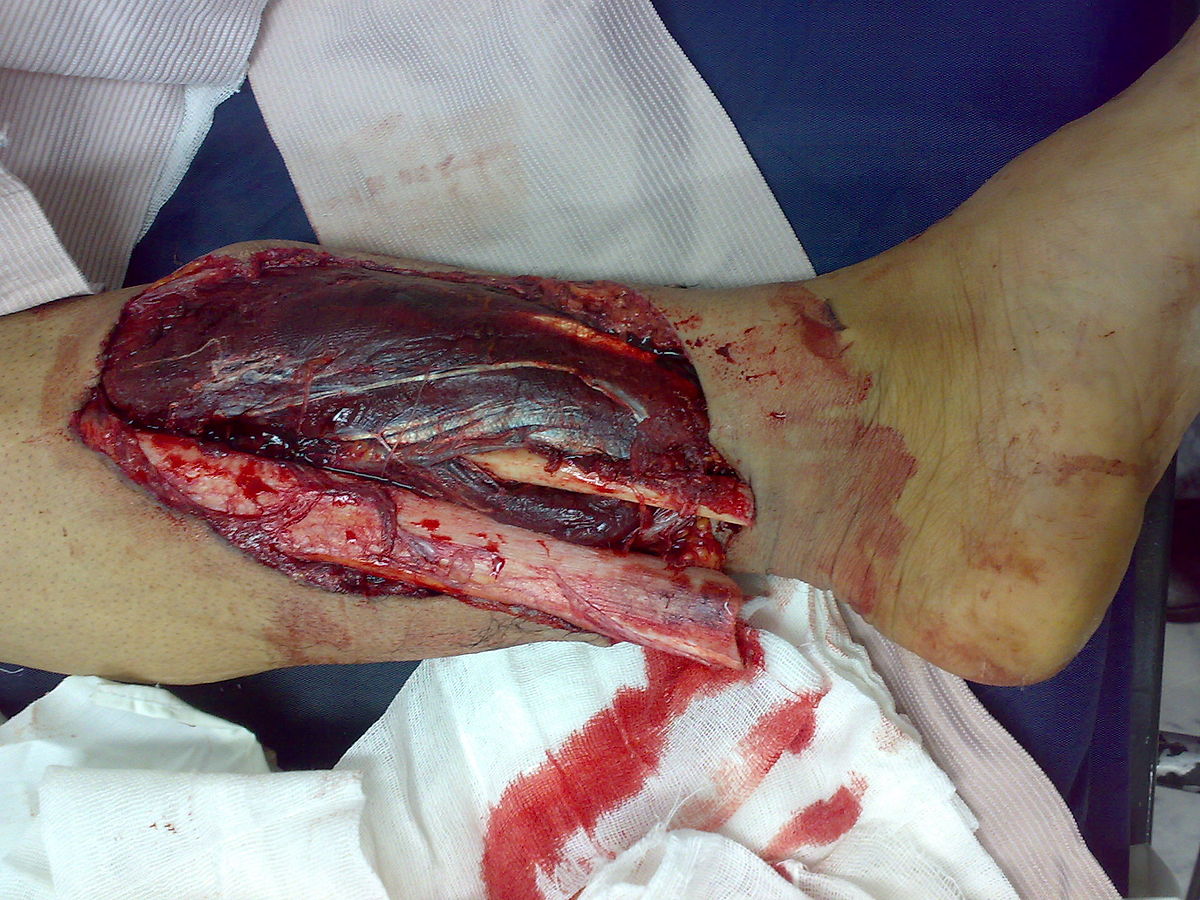
- external reduction
- bones are in a cast
- no surgery
- internal fixation
- bones are secured with surgical pins and wires
1. hematoma formation
2. fibrocartilage callus formation
3. bony callus formation
4. bone remodeling
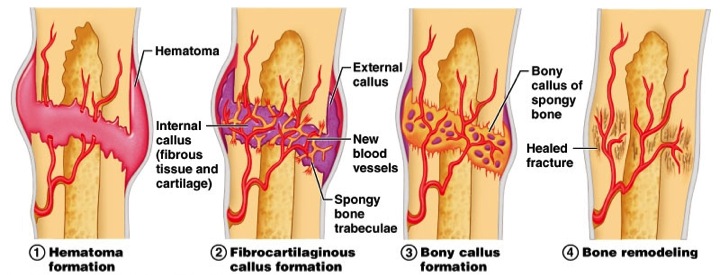
- bone resorption is much greater than deposition
- hollow and weakened bones
- mesenchyme develops into hyaline cartilage covered with perichondrium
- chondrocytes produce cartilage to increase thickness
- primary ossification center forms
- perichondrium starts to produce osteoblasts
- osteoblasts secrete bony layer around diaphysis
- blood vessels infiltrate the center of diaphysis
- osteoblasts deposit bone at the primary ossification center
- secondary ossification center is formed
- cartilage is only articular or in growth plate
- epiphysis fill with spongy bone
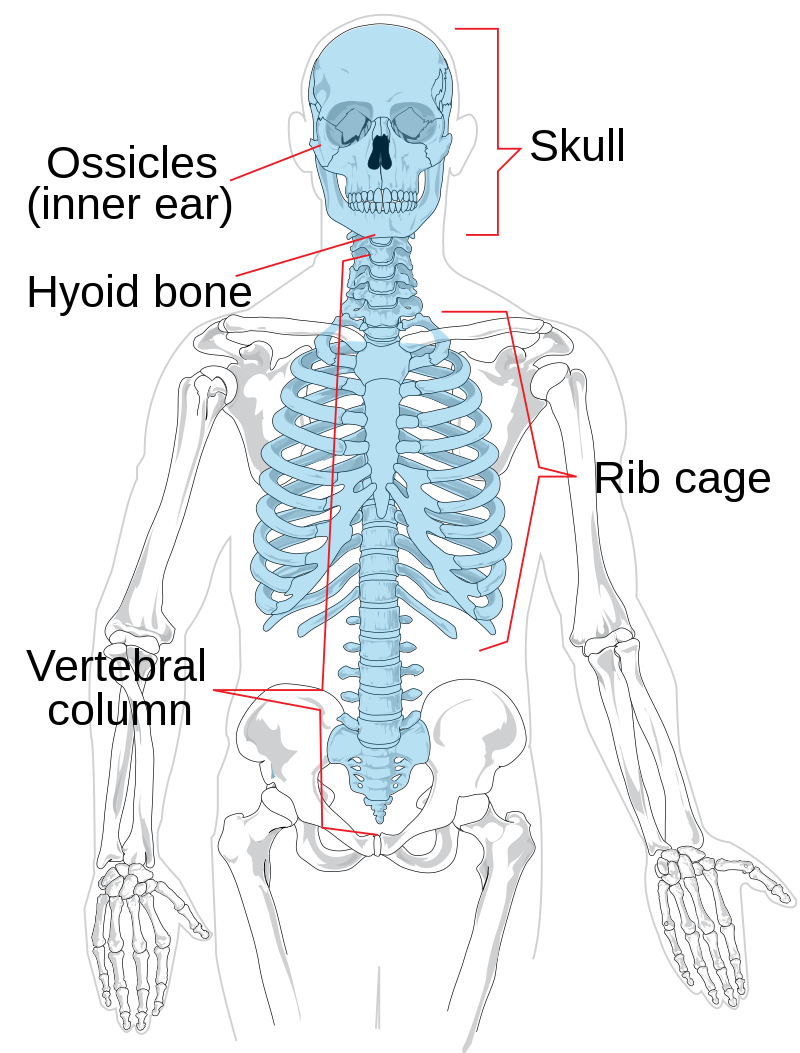
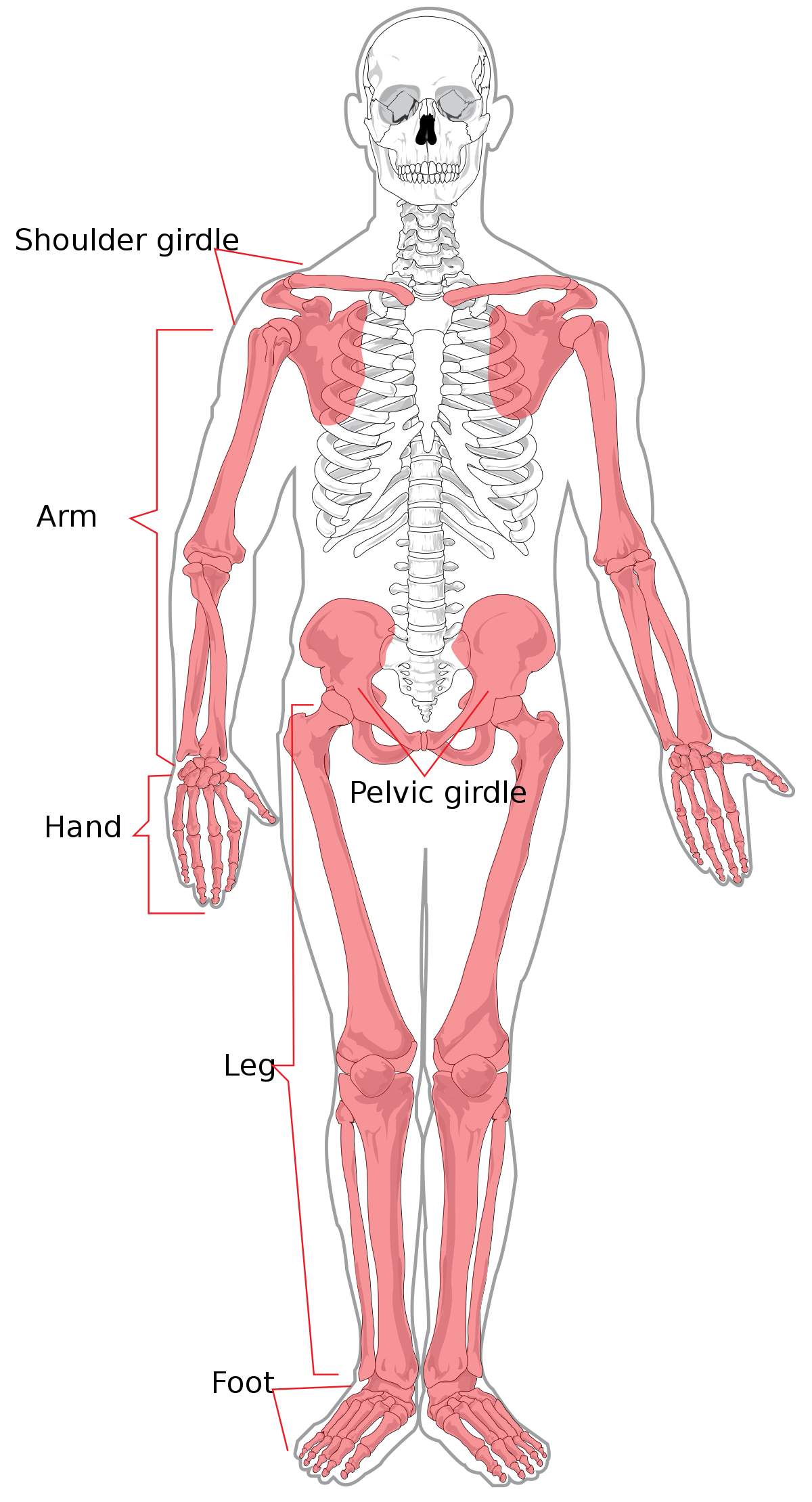
-supports and protects organs in body cavities
-attaches to muscles of: head, neck, trunk, respiration, and appendicular skeleton
- 8
- protect brain and attachment for facial muscles
- 14
- secure teeth
- contain cavities for sense organs
- cavities in the skull that surround the nasal area
- warm and humidify air
- reduces weight of skull
- enhances resonance of the voice
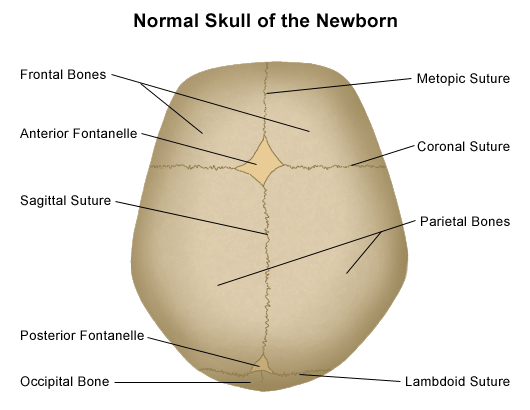
- takes 2 years to fully ossify
- large soft spot on infant's head
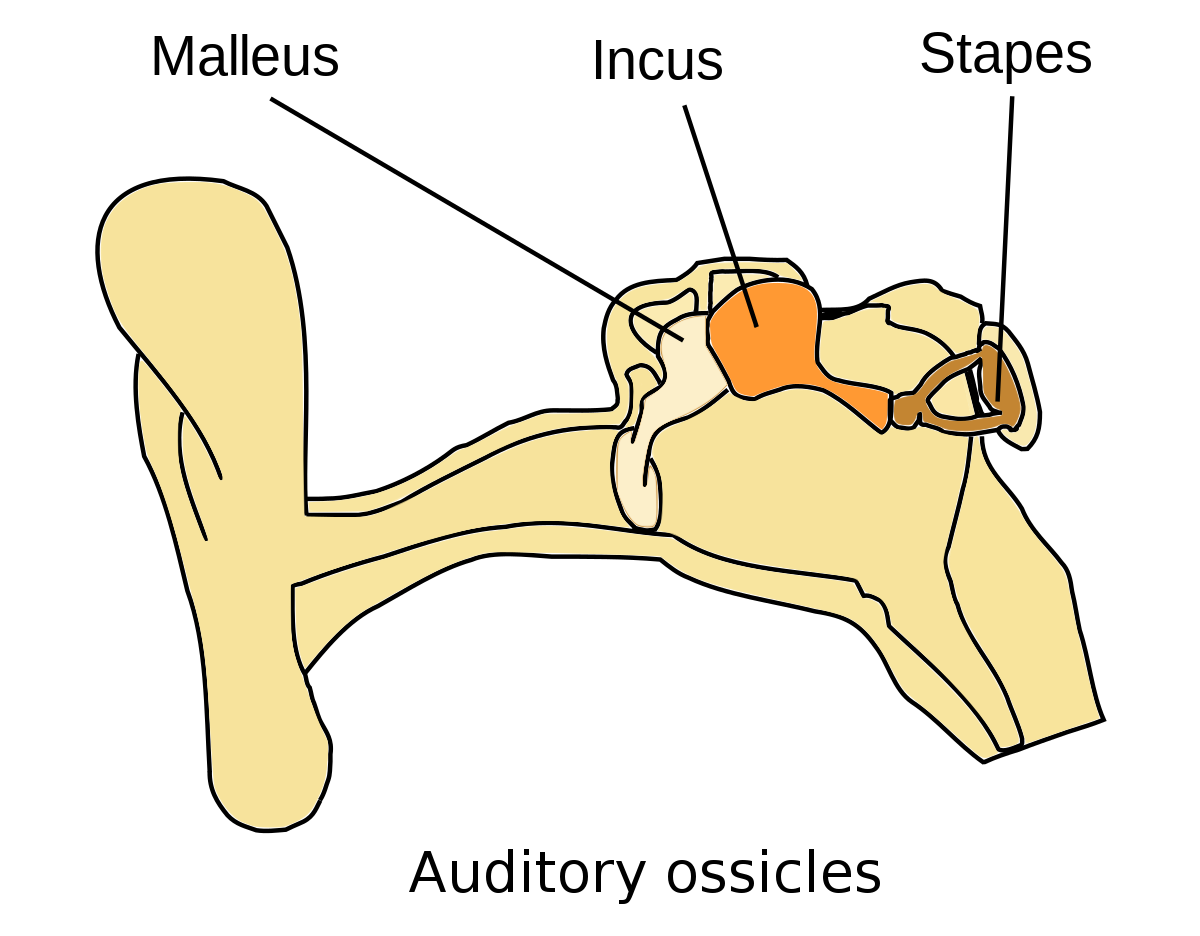
- hammer
- first of the three auditory ossicles of the middle ear
- anvil
- middle of the three auditory ossicles of the middle ear
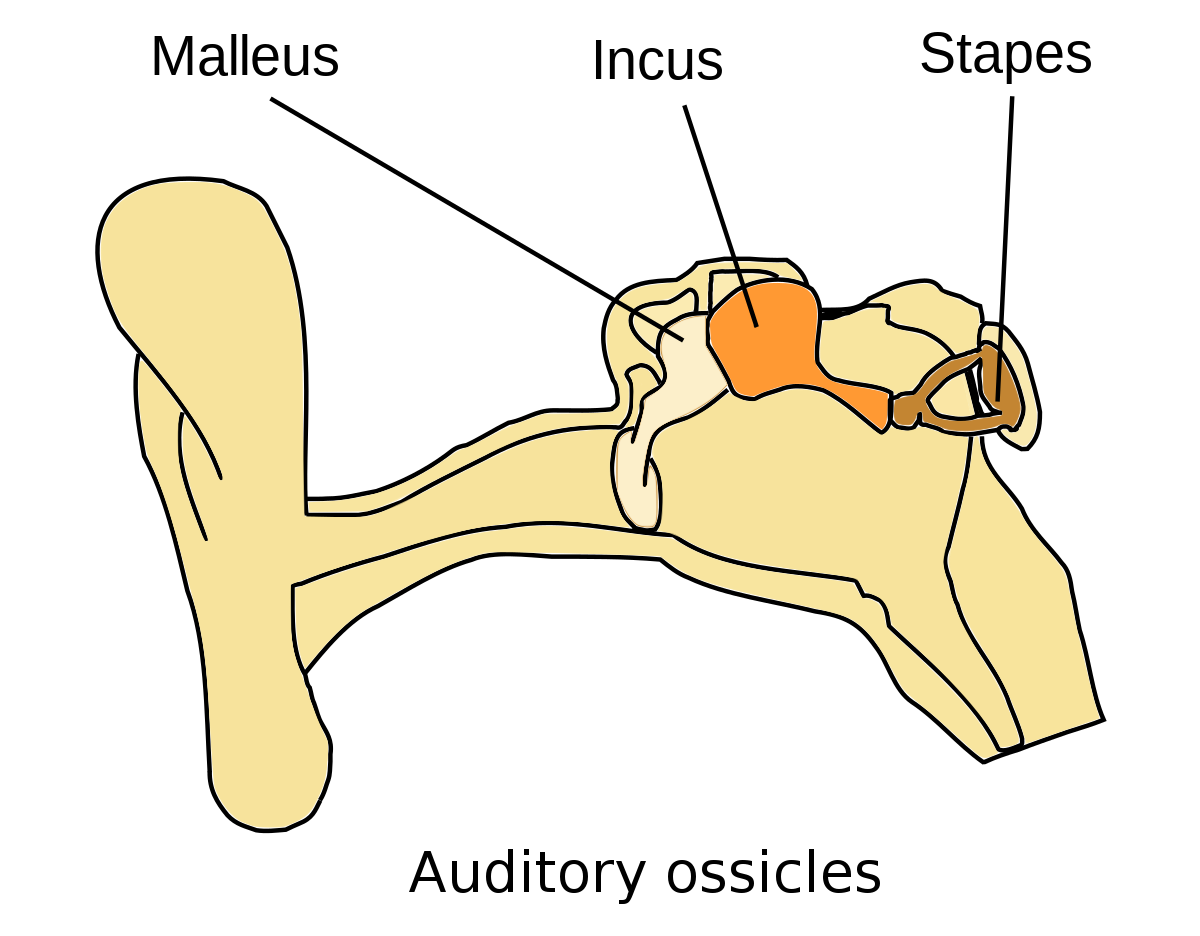
- stirrup
- last of the three auditory ossicles of the middle ear