VCE Psych Unit 3 AOS 1 - NS only
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Central Nervous System
(CNS) brain and spinal cord.
Peripheral Nervous system
Body Nerves that connect to the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord). Connects the central nervous system to the body's organs and limbs.
Autonomic Nervous System
Controls involuntary bodily functions (not consciously controlled), such as breathing, the heartbeat, and digestive processes - (PNS)
Somatic Nervous System
Controls voluntary bodily functions (consciously controlled), such as controlling skeletal muscles - (PNS)
Stimulus
Things that initiate nerve impulses (ex. hot room)
Motor Functions
Complex muscle-and-nerve acts that produce movement (walking, writing, typing running etc.)
"Electrochemical"
A nerve impulse is partially electric (change in polarity/charge) and partially chemical (neurotransmitters)
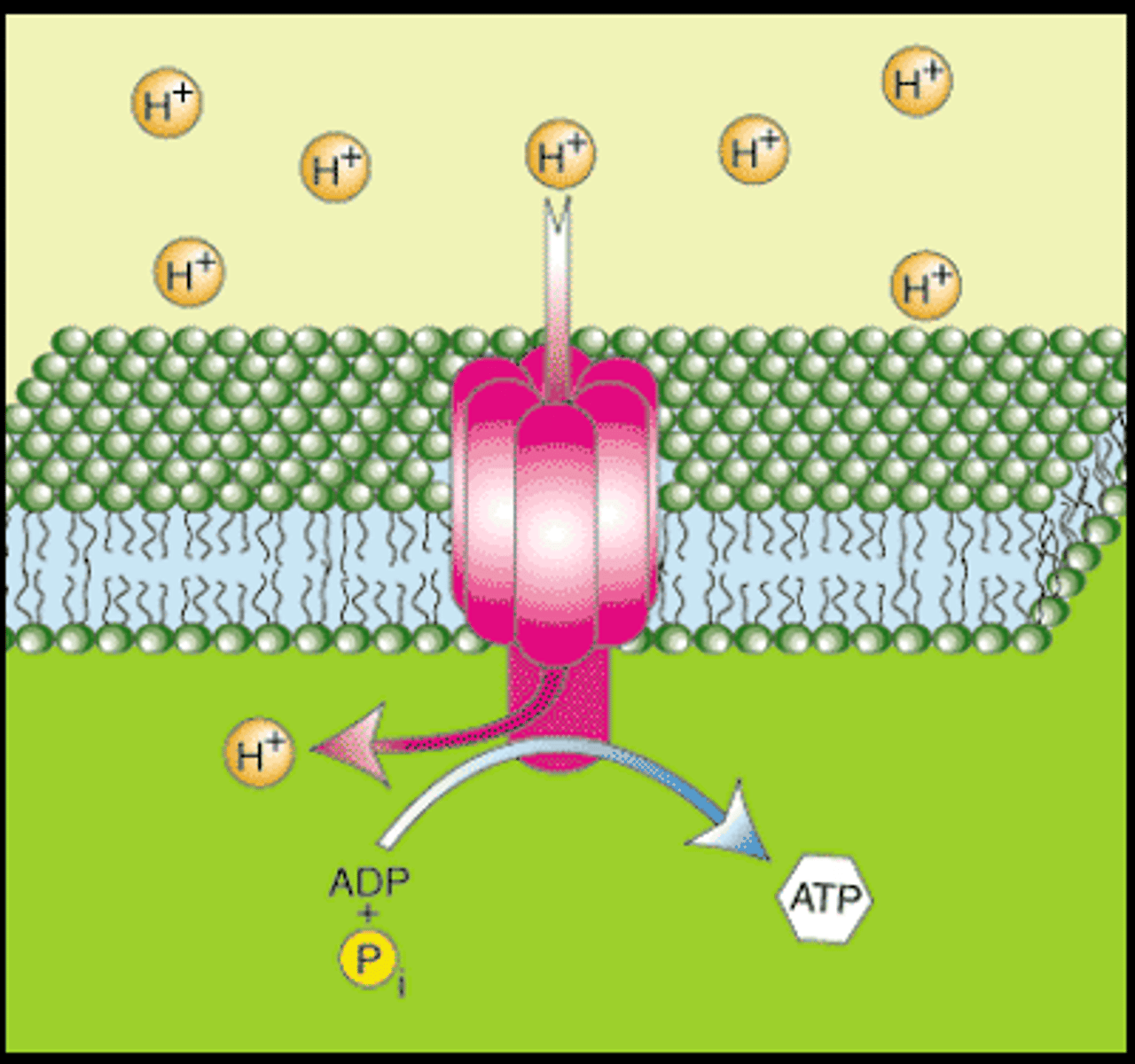
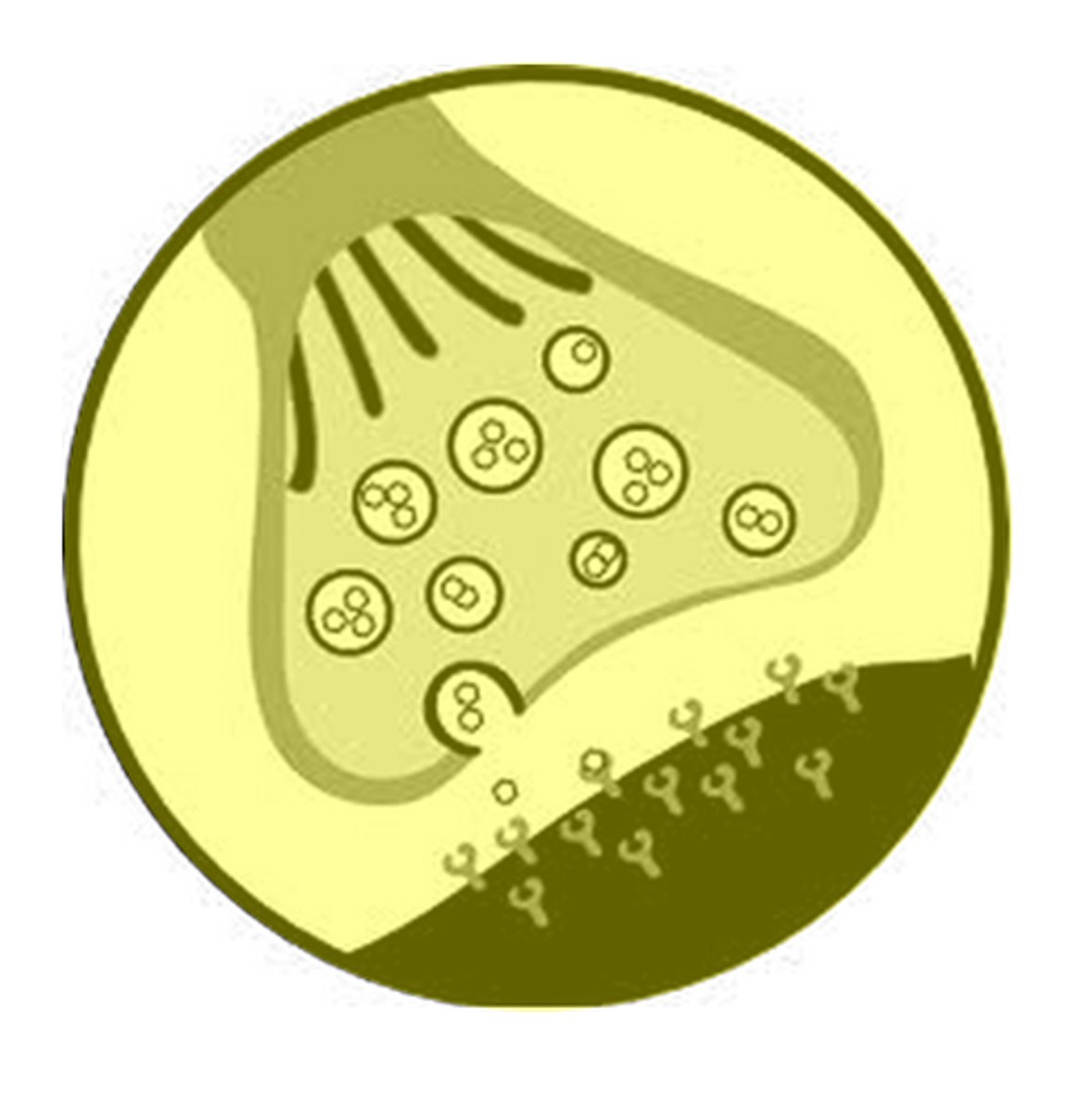
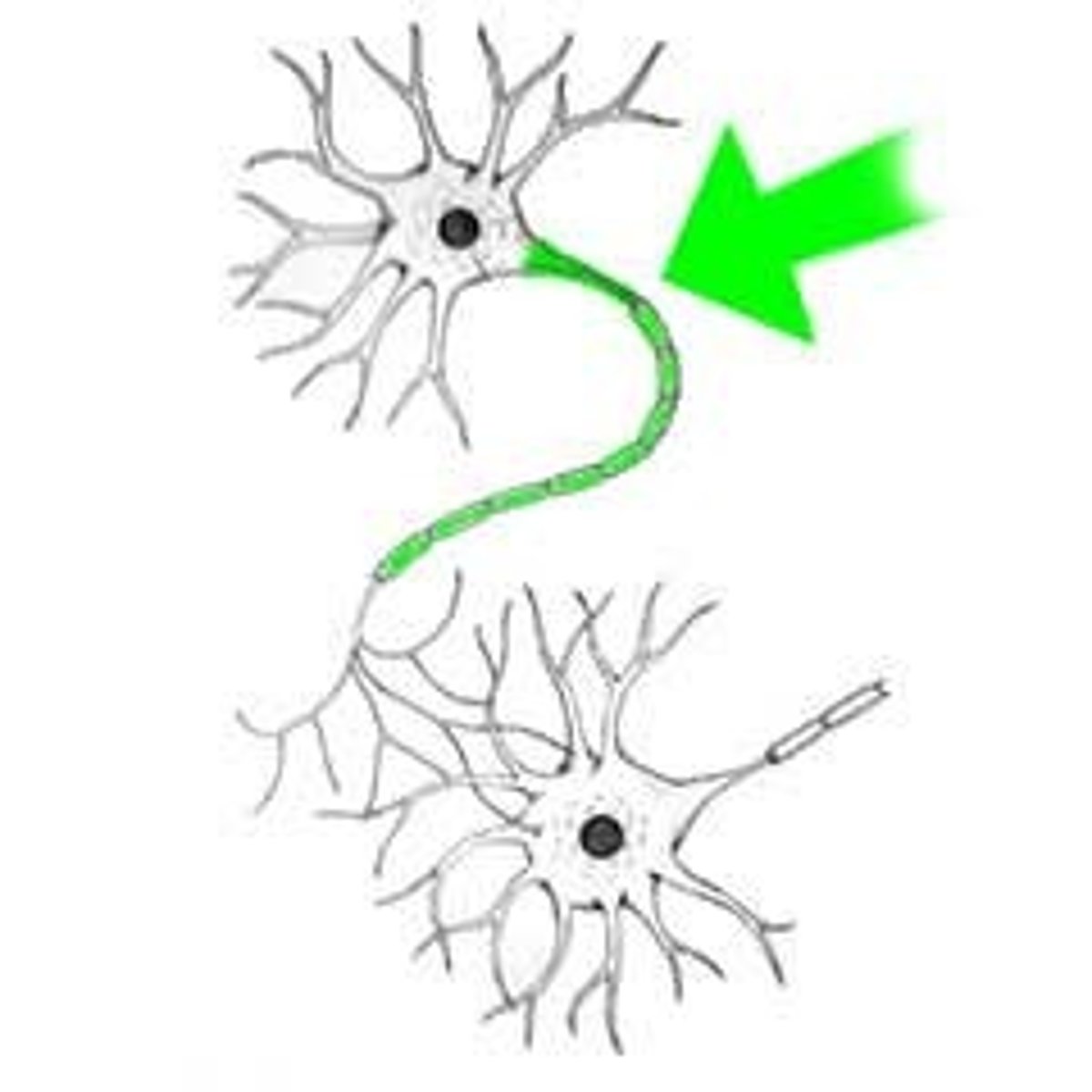
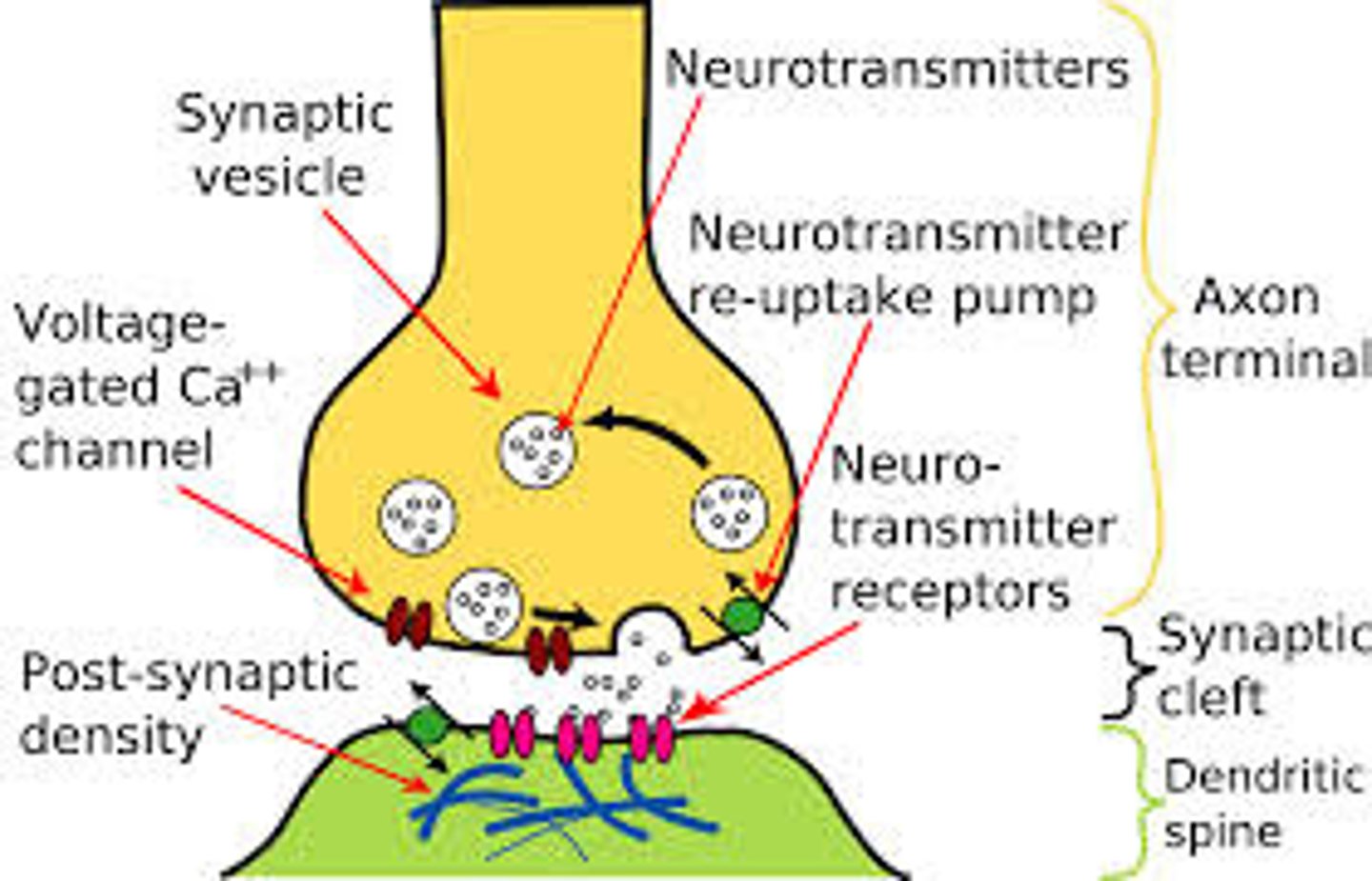
Synapse
Where the nerve impulse is sent (connection of 2 neurons) .
Action Potential changes the charge of the synapse (causes electricity) and Neurotransmitters are sent.
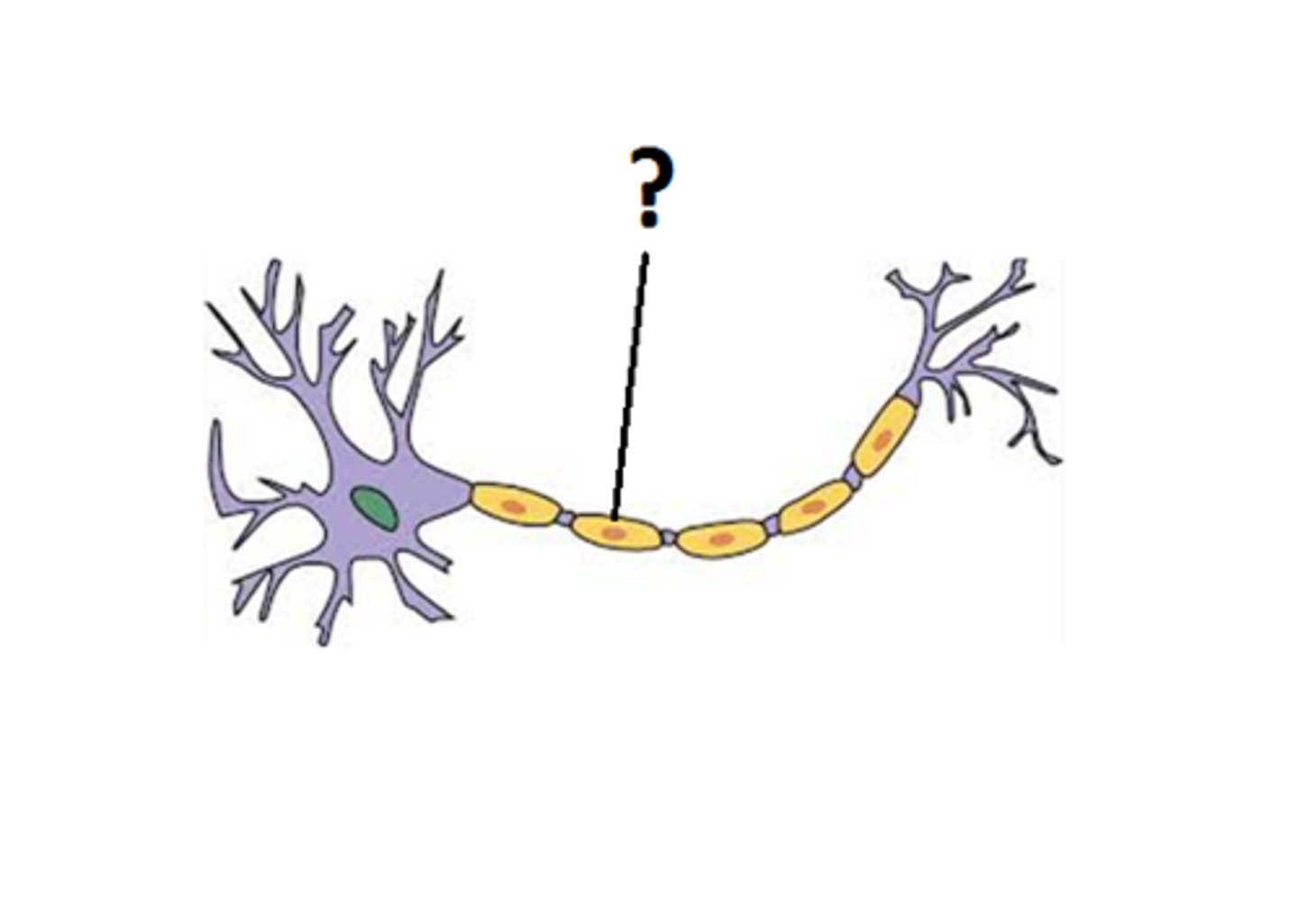
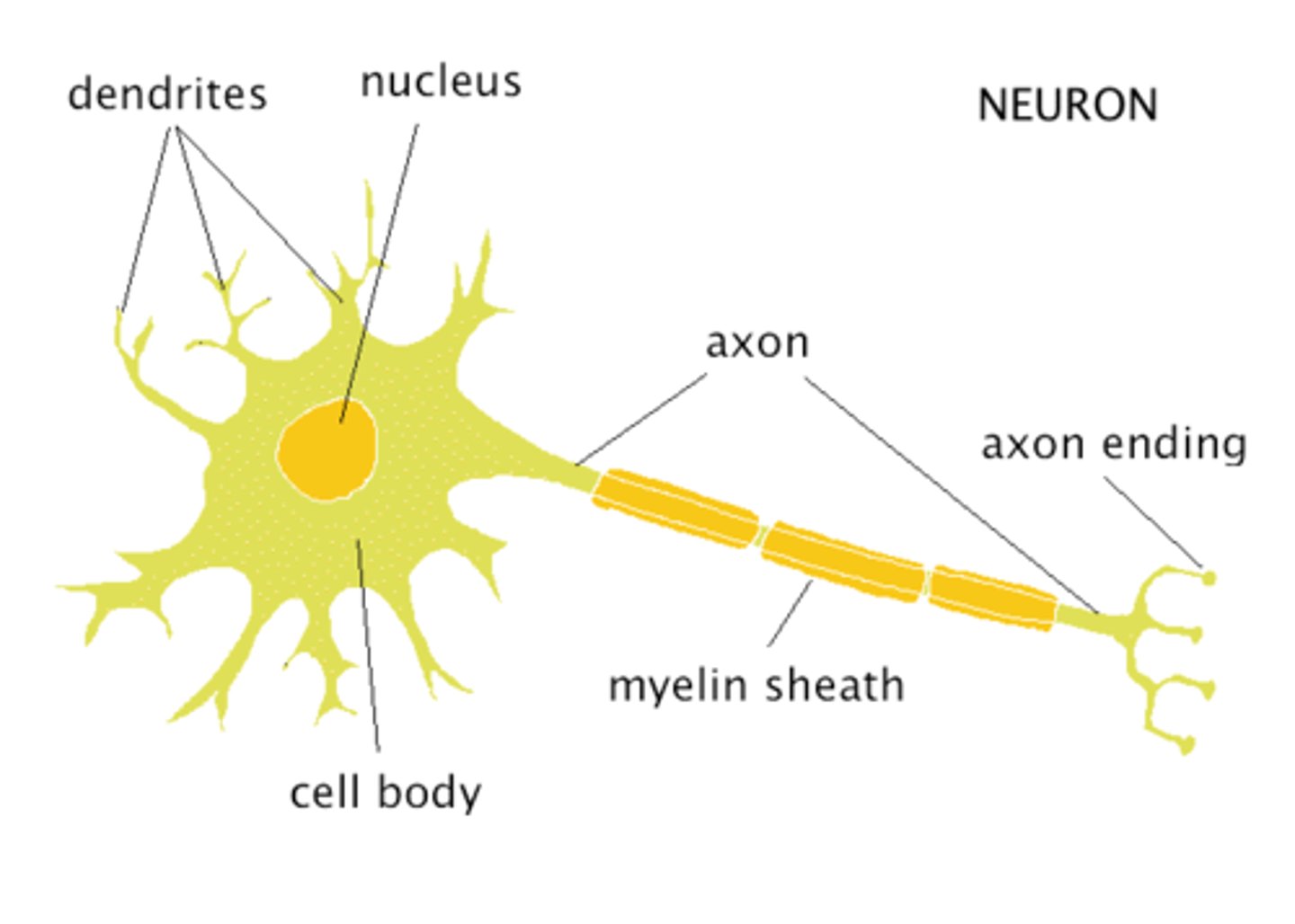
Myelin Sheath
Offers protection to the neuron, Speeds up nerve impulses.
Axon
The long threadlike part of a nerve cell that carry the nerve impulse
Dendrites
Branch like extensions on a neuron that GET signals and connect to the synapse
Neurotransmitters
Chemicals that transmit signals across a synapse from one neuron to another 'target' neuron
Sensory Neuron
Nerve cells that transmit sensory information (sight, smell, sound etc.)
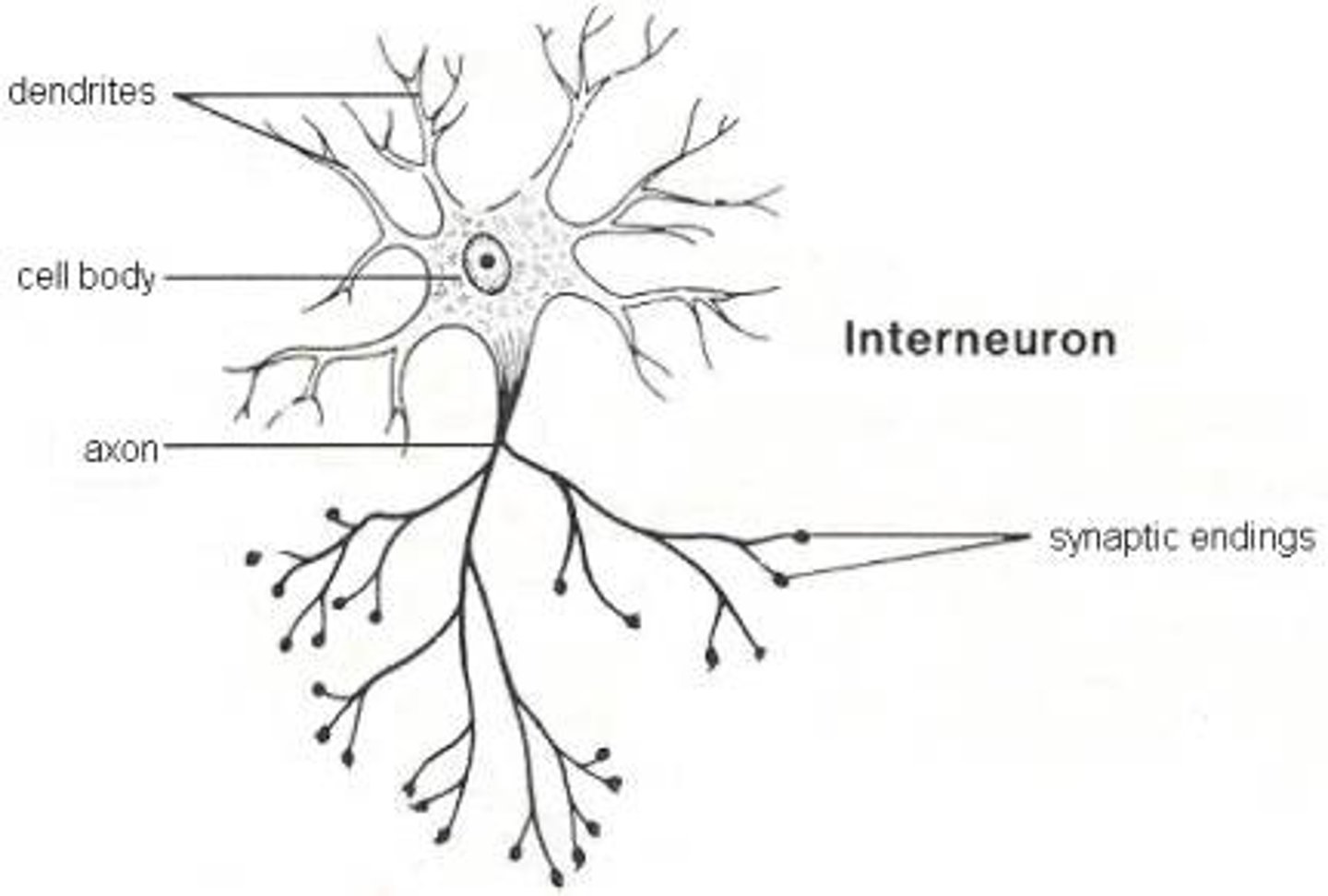
Interneuron
Nerve cells that connect motor neurons and sensory neurons. Only found in the CNS.
Motor Neuron
Nerve cells responsible for making an action or movement happen.
Efferent Tracts
A nerve pathway that goes downwards from the brain toward the PNS carrying motor information
Afferent Tracts
A nerve pathway that goes upward from the spinal cord toward the brain carrying sensory information
Excitatory Neurtransmitters
Stimulates a post synaptic neuron to fire. Activates the brain.
Inhibitory Neurotransmitters
Stops a post synaptic neuron from firing. Calms the brain and helps create balance.
Adrenaline
a hormone that may affect memory consolidation of emotionally arousing experiences; also called epinephrine
Glutamate
an EXCITATORY neurotransmitter that plays crucial roles in the growth and strengthening of synaptic connections during learning and memory formation
GABA
An INHIBITORY neurotransmitter in the brain, which decreases the likelihood of the post-synaptic neuron firing
Long-term depression (LTD)
long-lasting and experience-dependent WEAKENING of synaptic connections between neurons that are NOT regularly co-activated
- enables forgetting/pruning of unused pathways
Long-term potentiation (LTP)
long-lasting and experience-dependent STRENGTHENING of synaptic connections that are regularly co-activated
- enables faster memory retrieval and/or performance of skills
Sprouting
the ability of dendrites or axons to develop new extensions or branches
Rerouting
the ability of a neuron that is connected to a damaged neuron to create an alternative synaptic connection with an undamaged neuron
Pruning
the elimination of synaptic connections that are not adequately activated