Pathophysiology: Fluid and Electrolytes
1/162
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
163 Terms
Intracellular fluid
Fluid inside the cells; 2/3
What is the major cation in the ICF?
Potassium
Extracellular fluid
Any fluid that remains outside the cells which includes interstitial and intravascular fluid; 1/3
What is the major cation in the ECF?
Sodium
Fluid movement
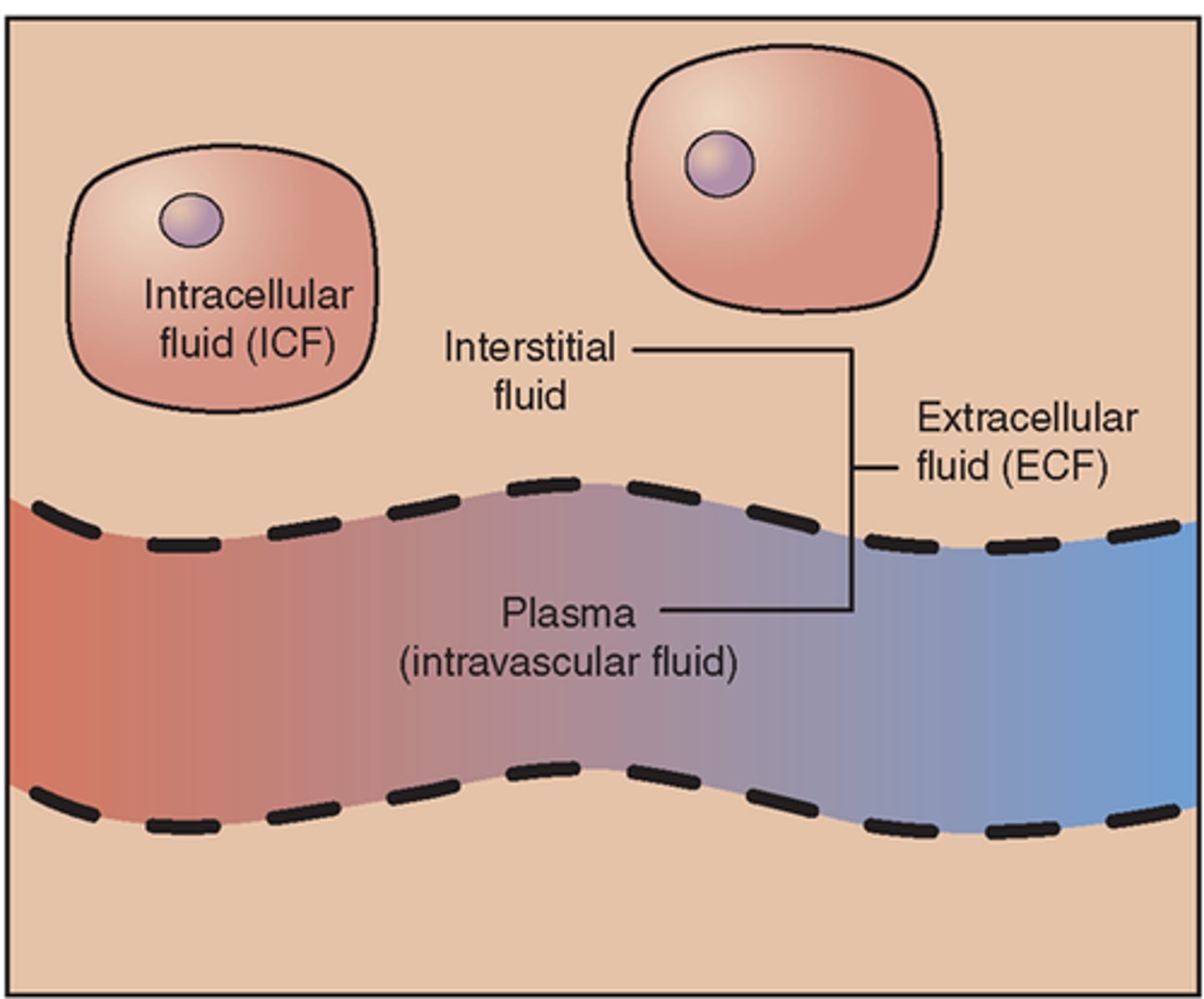
What serves as a primary barrier to movement inside/outside the cell?
Cell membrane
Edema
general term for too much fluid
Dehydration
general term for too little fluid
Fluid homeostasis
Composition of body fluids including electrolytes, acid/base balance and regulation of fluid (both intake and output) volume
Who are the major players of fluid homeostasis?
- kidneys
- RAA system
- osmoreceptors
- thirst sensation
- baroreceptors
- antidiuretic hormone
- natriuretic peptides
Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system
signaling pathway responsible for regulating the body's blood pressure - stimulated by low pressure causing the kidneys to release an enzyme called renin (vasoconstriction)
What signals the RAAS?
- hypotension
- hypovolemia
- low cardiac output due to low circulation
- dehydration
Baroreceptors signal the secretion of....
renin from the kidneys
Renin releases....
aldosterone
Aldosterone causes sodium and water ____ and potassium ___
retention; excretion
Spironolactone
aldosterone antagonist; potassium sparing
Spirolactone releases ___ and ___ and holds onto ____
sodium and water; potassium
Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor
inhibits movement through the RAAS causing high pressure and vasodilation to lower the blood pressure
Osmoreceptors
located in the hypothalamus which respond to changes in the extracellular tonicity; monitor and respond to distribution of water between intracellular and extracellular fluid; concentration
Baroreceptors
detect pressure changes in the blood vessels to help maintain blood pressure at a constant level
Which receptors signal pressure?
Baroreceptors
Which receptors signal fluid concentration?
Osmoreceptors
Anti-diuretic hormone
another term for vasopressin, released from the posterior pituitary gland to keep up the volume in the bloodstream at all times - decrease in urine production
If pressure is low what system is kicked in?
Sympathetic nervous system - vasoconstrictor - causing pressure to increase
Anti-diuretic hormone - decreased urine output to hold onto fluid
Where are pressure sensitive receptors located?
Kidneys or afferent arterioles
What do the kidneys release?
Renin to activate RAAS to stimulate sympathetic nervous system
What do the osmoreceptors tell the body to do in time of thirst?
drink water
What is another term for antidiuretic hormone?
vasopressin
Where is vaspopressin released?
posterior pituitary
Syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone (SIADH)
too much ADH
What happens when there is too much ADH?
- fluid overload
- decreased urine output
- urine concentration increases (dark)
- blood osmolality decreases
Diabetes insipidus
too little ADH
What happens when there is too little ADH?
- fluid loss
- increased urine output
- urine concentration decreases (clear)
- blood osmolality increases
Osmosis
passage of liquid through a semi-permeable membrane from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration of solute
Capillary-interstitial fluid exchange
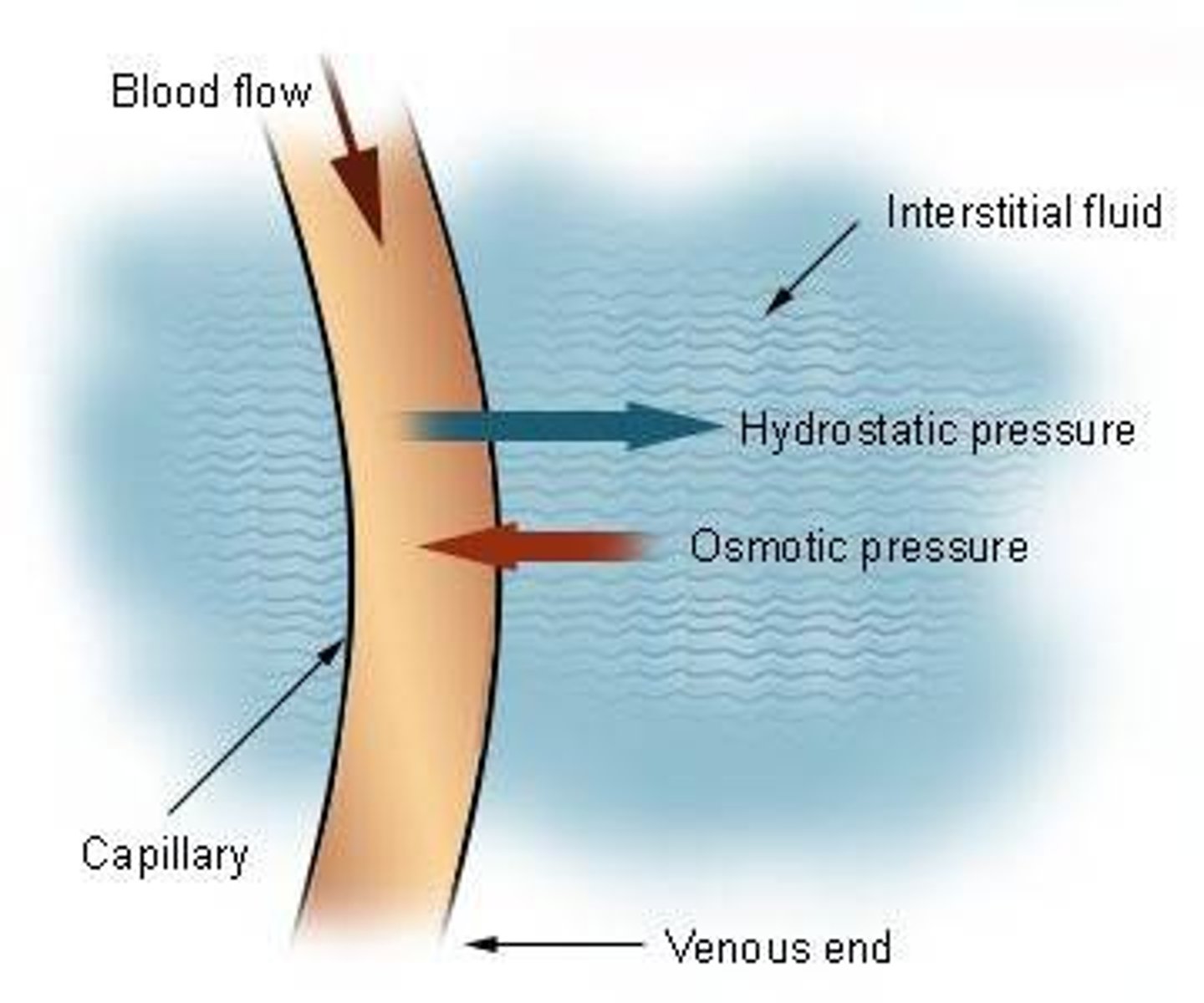
Capillary hydrostatic pressure
pressure exerted by the capillaries causing water to move out of the capillary and into the interstitial space
Capillary osmotic pressure
the pressure applied to the capillaries preventing it from passing to into a given solution by osmosis - pulls the water into the capillaries
Who is a major contributor to capillary osmotic pressure?
Albumin
Interstitial hydrostatic pressure
pressure exerted within the interstitial space opposing water from leaving the capillaries - water build up in the capillaries
Interstitial osmotic pressure
pressure applied to the interstitial space pulling water out of the capillary and into the surrounding tissue
What is the lymphatic systems importance?
accessory route for the fluid in the interstitial space
What happens to the proteins that have leaked in the interstitial space?
they get picked up from the lymphatic system
What happens when the lymphatic system doesnt work properly?
excess fluids accumulate in the interstitial space
Increased capillary filtration pressure
Edema
What disease processes cause increased vascular volume?
- heart disease
- kidney disease
- pregnancy
- venous obstruction (fluid shifting in places it shouldnt)
What disease processes cause venous obstruction?
- liver disease
- acute pulmonary edema
- venous thrombosis
What causes a decreased capillary osmotic pressure?
- increased loss of plasma proteins
- decreased production of plasma protein
What happens when capillary osmotic pressure is decreased?
pulling power is lost - lack of additional force pulling water into the blood vessel
increased loss of plasma proteins or decreased production of plasma protein
Which way does water get pulled?
water moves from areas of low osmotic pressure to high osmotic pressure
water moves from areas of high concentration to low concentration
What disease processes cause an increased loss of plasma proteins?
- protein-losing kidney diseases
- excessive burns
What disease processes cause a decreased production of plasma protein?
- liver disease
- starvation
- malnutrition
Number one player of capillary osmotic pressure
Albumin
Increased capillary permeability causes?
edema
What causes an increase in capillary permeability?
- inflammation
- allergic reactions
- malignancy
- tissue injury
- burns
Obstruction of lymphatic flow causes?
edema
What causes an obstruction of lymphatic flow?
- malignant obstruction of lymph structures
- surgical removal of lymph nodes
Third spacing
trapping of extracellular fluid in the transcellular spaces - spaces that have the capacity to hold fluid but shouldnt
Areas with continual movement are closely related to the....
lymphatic system
Which organs are closely related to the lymphatic system?
heart, abdomen and lungs
Examples of third spacing
pleural effusion, abdominal ascites, pericardial effusion
Dehydration
state of diminished water volume in the body either occurring vascularly or cellular
Vascular dehydration
diminished water volume within the vascular space
Cellular dehydration
diminished water volume within the cells
What do the osmoreceptors signal during dehydration?
thirst
What do the baroreceptors signal during dehydration?
stimulate the sympathetic nervous system causing vasoconstriction of the arterial vessel and increased HR
What happens when dehydration occurs and there isnt enough blood volume getting to the kidneys?
the RAAS is initiated causing water and sodium to be retained
RAAS signals ____ as a vasoconstrictor
Angiotensin II
Natriuretic peptide
released when baroreceptors sense too much volume - signaling the body to pee
If you have diarrhea what is your bodies response?
anti-diuretic hormone will increase to hold onto fluid
If a heart failure patient has edema what will increase?
capillary pressure to get rid of fluid
What ions influence neurotransmission and muscular contraction?
sodium, potassium and calcium
Sodium influx
depolarizes skeletal muscles
Calcium influx
cardiac muscle contractions through voltage gate channels
Normal sodium range
135 - 145 mEq/L
Sodium is the primary _____ cation
extracellular fluid
How does sodium effect hormone regulation?
- aldosterone
- natriuretic peptides
Aldosterone
hormone that signals the kidney for sodium to follow water back into the blood
Atrial natriuretic peptide and brain natriuretic peptide
natriuretic peptides released by the heart (atrial) and brain in response to high pressure and volumes
Urodilatin
natriuretic peptide released by the kidney
Normal chloride level
96 - 106 mEq/L
Hypovolemia
decreased volume of circulating blood in the body
Causes of hypovolemia
- inadequate fluid intake
- excess GI losses
- excess renal losses
- excessive skin losses
- third spacing
What effect does hypovolemia have on the cells?
none, cells do not change shape
What would a patient present with if they have hypovolemia?
- increased HR
- decreased BP
- weak, thready pulse
- thirst
- sunken eyes
- poor skin turgor
Hypervolemia
increased volume of circulating blood in the body
Causes of hypervolemia
- decreased sodium
- decreased water elimination
- heart failure
- renal function
- corticosteroid excess
What affect does hypervolemia have on the cells?
none; cells do not change shape
What would a patient present with hypervolemia?
- edema
- full bounding pulse
- weight gain
- decreased BUN
- decreased creatinine
- dilutional effects
What is the most common electrolyte disorder?
hyponatremia
Hyponatremia
too little sodium circulating in the blood causing cells to swell altering de/repolarization
<135 mEq/L
Causes of hyponatremia
- diuretics
- extrarenal losses
- vomiting
- diarrhea
- GI suctioning
- burns
- use of excess hypotonic saline
What is an example of a hypotonic solution?
0.45% NaCl
Hypervolemia in combination with hyponatremia
water excess and decreased sodium as a response to water intoxication (psychogenic disorder)
decreased urine formation
What are symptoms of hyponatremia?
- cramping
- weakness
- fatigue
- GI cramps
- lethargy
What are the serious effects of hyponatremia?
- seizures
- cerebral edema
- loss of deep tendon reflexes
Serious effects of hyponatremia is correlated with....
a release of ADH
Hypernatremia
excess sodium circulating in the blood usually due to free water loss causing cells to become dehydrated altering membrane potentials
> 147 mEq/L
What causes the body to retain sodium?
- inappropriate administration of hypertonic saline solution
- over-secretion of aldosterone
What would cause the body to over-secrete aldosterone?
excess secretion of adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)
What is an example of a hypertonic solution?
D5 1/2 NS, Lactated Ringers (LR),