integumentary quiz 2
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
what does the prefix pan- mean
all
what does the prefix myc/o mean
fungus
what does the prefix path- mean
disease
what does the prefix aer/o mean
air, gas
what does the prefix tox/o mean
poison
what does the prefix py/o mean
pus
what does the suffix -cide mean
kill, destroy
what is an epidemic
people in a certain area develop the same disease at the same time
with more cases than usual
ex) smallpox, polio
what is a pandemic
a disease is common in an entire continent or the world
typically spread person-to-person in 1 other region that originally reported
ex)bubonic plague, AIDS
what is an endemic
a disease is common to a particular area
ex) malaria
what is a local infection
an infection restricted to a small area of the body
ex) a cut has become swollen & red
what is a general (systemic) infection
the infection affects the whole body (usually spread by blood)
ex) cold, flu
what is an opportunistic infection
the infection occurs after the host has become weakened by a disease
ex) AIDS develops pneumonia
what are some characteristics of pathogens
disease-causing organisms
can be bacteria, viruses, fungi, protozoa, worms, & prions
what is bacteria
they’re single-celled organisms
don’t have a nucleus
found anywhere
some produce spores (to survive dry conditions)
some produce harmful toxins
ex) botulism is caused by the toxin clostridium botulinum
what is a virus
it’s not a cellular organism
has a protein coat that surrounds genetic information
they’re responsible for:
common cold, polio, flu, mononucleosis, mumps, AIDS, plantar warts, etc
what is fungi
can be single-celled or multi-celled
ex) athlete’s foot, ringworm, yeast infection
what is a protozoa
a single-celled organism (larger than bacteria)
found in soil, water, & moist areas
examples of this type of infection are:
African sleeping sickness, beaver fever, malaria
what are prions
small protein structures that lack any DNA
found in soil, water, & moist areas
an example of a disease that can be caused by this type of infection is:
Creutzfeldt-Jacob Disease
what are parasitic worms
they’re multicellular organisms
ex) tapeworms
live in the intestines & release eggs through the digestive system
what’s are single-celled organisms
consist of only one cell, performing all necessary functions for survival independently
ex) protozoa, bacteria
what’s are multicellular organisms
composed of multiple cells organized into specialized structures, each performing specific functions
ex) parasitic worms, fungi (sometimes)
what is normal flora
the population of microorganisms that normally grow in our bodies
beneficial as they prevent growth of harmful organisms
what is a host
the living organism that the parasite (pathogen) lives on
what are vectors
an insect/animal that introduces an infectious organism into the body
what are carriers
individuals infected by a pathogen
may not show signs of the disease & unknowingly pass it on
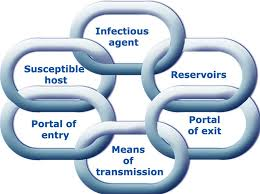
what is the chain of infection
a model used to understand the infection process
each link must be present in order for an infection to occur
the spread of infection can be prevented if the links are broken
what is virulence for a pathogen
a pathogens ability to grow & multiply
what is invasiveness for a pathogen
a pathogens ability to enter tissue
on the chain of infection, what are infectious agents
pathogenic organisms with the ability to cause disease
likelihood of an infection depends on the pathogens virulence and invasiveness
on the chain of infection, what are reservoirs
the place where pathogens can thrive and reproduce
ex) humans, animals, doorknobs
on the chain of infection, what is the portal of exit
the place of exit for pathogens to leave the reservoir
examples:
nose/mouth when coughing/sneezing
through feces or blood
on the chain of infection, what is the means of transportation
the method of transfer by which the pathogen moves or is carried from one place to another
examples:
person-to-person DIRECT contact
person-to-person INDIRECT contact
vector-borne
fecal-oral (wash ur nasty hands)
on the chain of infection, what is the portal of entry
openings that allow pathogens to enter the host
examples:
body orifices (nostrils, mouth, etc)
on the chain of infection, what is a susceptible host
someone who cannot resist a pathogen from invading the body, allowing it to multiply (resulting in infection)
they lack immunity to overcome the pathogens invasion
what is the person-to-person DIRECT contact way that infection spreads
it requires physical contact between an infected person, and someone uninfected
this type of pathogen has a limited ability to survive outside a host
examples:
coughing/sneezing on someone
sexual contact, kissing, etc
what is the person-to-person INDIRECT contact way that infection spreads
when an uninfected person touches a contaminated surface
this type of pathogen can survive outside a host for an extended time
examples:
e. coli
what is the vector-borne infection way that infection spreads
animals (vectors) that are capable of transmitting disease, usually through biting
they increase the transmission range of a disease due to their mobility
what is the fecal-oral transmission way that infection spreads
pathogens that infect the digestive system as they’re ingested through eating/drinking
the pathogens exit the body through feces
can be caused by inadequate hand-washing
how can the infectious agent chain-link be broken
diagnosis & treatment
how can the reservoir chain-link be broken
isolating infected individuals
disinfecting contaminated surfaces
how can the portal of exit chain-link be broken
covering cough/sneezes
how can the means of transmission chain-link be broken
proper hand-hygiene
wearing masks
how can the portal of entry chain-link be broken
proper care for open wounds
personal hygiene
how can the susceptible host chain-link be broken
immunizations/vaccines
what is the cocci bacteria
cells are round
ex) staphylococcus, streptococcus
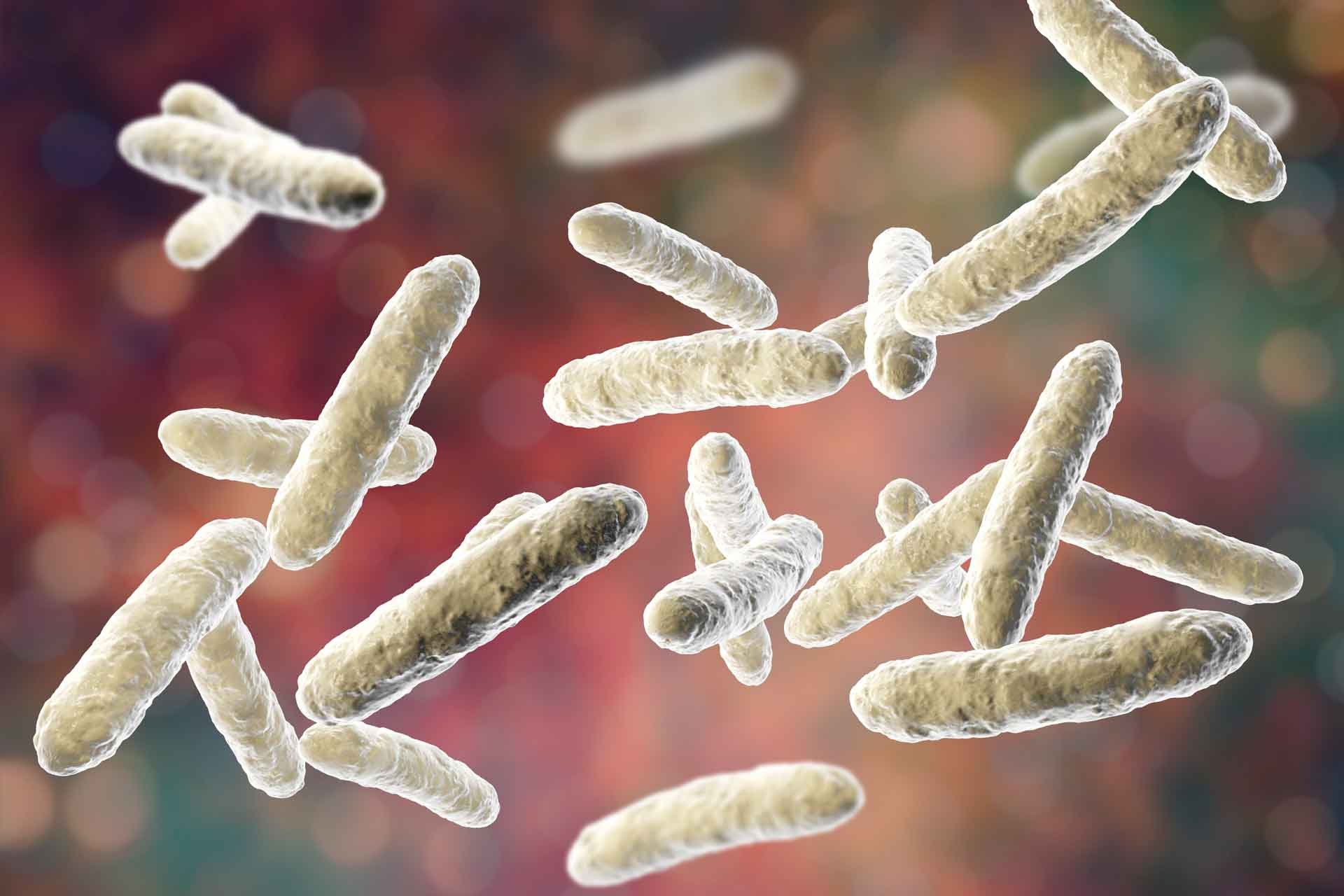
what is the bacilli bacteria
cells are rod-shaped
ex) salmonella
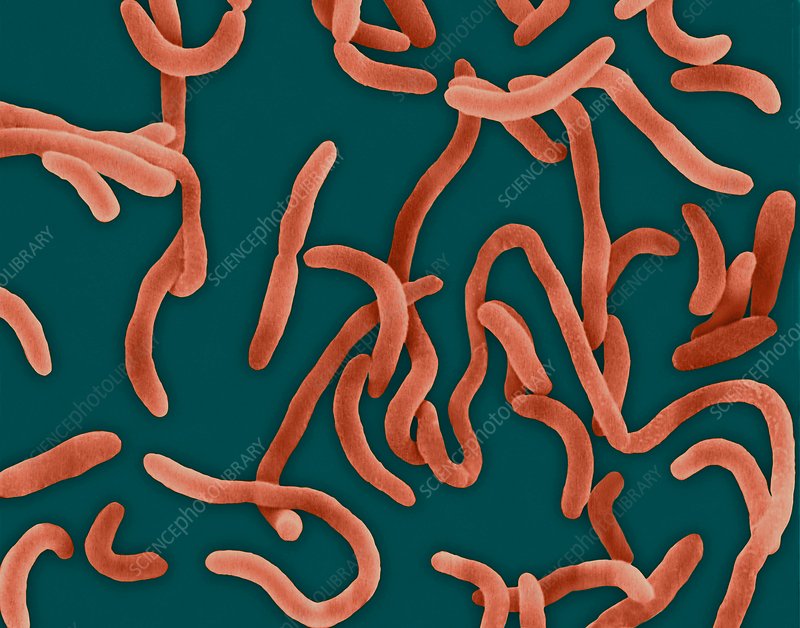
what is the curved rod bacteria
cells with curved or twisted rod-like shapes
what are the differences between bacteria & viruses
both will make you sick with similar symptoms
antibiotics will do NOTHING for viral infections
what are bacterial infections
usually lasts longer than 2 weeks
a high, persistent temperature
a thick, coloured discharge from the nose
chronic cough
what is the cause of the common cold
caused by a viral infection of the upper respiratory tract
spread through:
contaminated surfaces
air borne (coughing/sneezing)
what are some myths about the common cold
being out in the cold doesn’t cause the cold
cold medication doesn’t cure the cold, only alleviates the symptoms
what are some significant events in history of infectious diseases
The Black Death through Europe (1300s)
HIV/AIDS Epidemic worldwide (1980s)
Identify a historical pandemic and its associated pathogen
Spanish Influenza
pathogen: H1N1 influenza virus
what are disease-transmitting agents
pathogens
what does the prevalence of diseases mean
the number of existing cases of a particular disease within a defined population
ex) epidemic, pandemic, endemic, etc
what infectious agents/organism is associated with thrush
associated with fungi
what infectious agents/organism is associated with strep throat
associated with bacteria
what infectious agents/organism is associated with malaria
associated with protozoa
what infectious agents/organism is associated with the flu
associated with virus