Nuclear Chemistry
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
Fission is the process of creating energy by
-combining small nuclei to form a larger, more stable nucleus
-combining small nuclei to form a larger, less stable nucleus
-splitting large nuclei with bombarding protons
-splitting large nuclei with bombarding neutrons
splitting large nuclei with bombarding neutrons
Which is a common characteristic of both nuclear and conventional electric power plants?
-smoke stacks
-fuel rods
-water cooling systems
-turbines
turbines
Which feature or process is unique to nuclear power plants when compared to conventional coal-burning power plants?
-formation of steam
-smoke stacks
-generators
-control rods
control rods
Which of these is not a realistic risk associated with nuclear power plants?
-storage of spent fuel rods
-likelihood of nuclear explosion
-a meltdown from loss of coolant
-thermal pollution of the coolant source
likelihood of nuclear explosion
Which is the best critique of the following statement? "Radioactivity is so dangerous that we should do all we can to completely eliminate our exposure."
-absolutely correct. radioactivity is the ultimate danger and we should keep our exposure to zero
-not true; we should not fear radioactivity because it is a natural part of life
-somewhat true. radioactivity can be dangerous, but in some circumstances, exposure to it is unavoidable, so zero exposure is not a reasonable goal
-somewhat true. although any exposure to radioactivity is potentially deadly, there is nothing we can do to avoid it so we must be resigned to the risk
somewhat true. radioactivity can be dangerous, but in some circumstances, exposure to it is unavoidable, so zero exposure is not a reasonable goal
Which is true about radioactivity? Radioactivity
-is used to treat certain cancers
-damages white blood cells
-deforms DNA
-all of these choices are true
all of these choices are true
What is the maximum one-time dose of radiation one can receive without suffering any detectable physiological effects?
-≤ 25 rem (0.25 Sv)
-≤ 50 rem (0.5 Sv)
-≤ 100 rem (1.0 Sv)
-≤ 200 rem (2.0 Sv)
≤ 25 rem (0.25 Sv)
Which is not true of radioactive half-life? Radioactive half-life is
-the time required for the level of radioactivity in a sample to be cut in half
-independent of the amount of radioactive material present
-increased by heating of the isotope
-independent of the physical or chemical form of the isotope
increased by heating of the isotope
Which fact is not important when drawing conclusions from C-14 dating?
-living organisms exchange carbon with the atmosphere
-C-14 has a half-life of 5,730 years
-dead organisms do not exchange carbon with the atmosphere
-C-14 emits beta particles
C-14 emits beta particles
Which country gets the smallest percentage of its electrical power from nuclear reactors?
-Canada
-France
-Belgium
-Spain
Canada
Which is not a suitable option for the disposal of spent nuclear fuel?
-seal it in deep pools
-monitor it in storage near the ground surface
-bury it deep within the Earth
-seal it in a landfill
seal it in a landfill
Which is a characteristic of "surface" high-level nuclear waste storage that is not a characteristic of storing the waste in a geological repository? Waste in a geological depository is not
-as easily accessible
-feasible
-secure
-safe
as easily accessible
Most high-level nuclear waste in the United States is currently
-sealed deep within the Earth
-encased in glass and buried near the surface
-sealed in deep pools at the sites were it was produced
-stored at breeder reactors waiting for reprocessing
sealed in deep pools at the sites were it was produced
Which is not considered to be low-level radioactive waste?
-clothing for workers administering nuclear medicine
-smoke detectors
-spent fuel rods
-radioactive pharmaceuticals
spent fuel rods
The fuel for both nuclear and coal power plants must be mined. Which miners are most likely to contract black lung disease?
-coal miners
-uranium miners
-plutonium miners
-black lung is not a risk for miners of any fuel
coal miners
Smokestacks at these plants release sulfur oxides and carbon dioxide into the air:
-coal-burning plants
-nuclear plants
-both
-neither
coal-burning plants
Including fuel production and power generation, which type of power plant is responsible for more fatalities annually?
-nuclear plants
-coal-burning plants
-neither may be connected to fatalities
-fatalities are substantially the same for both
coal-burning plants
Which is not a benefit associated with nuclear power plants?
-efficient production of electricity
-reduction of CO2 in atmosphere
-inexpensive to operate
-helps reduce the levels of acid rain
inexpensive to operate
Which factor will support the growth of nuclear energy in the future?
-smaller, more efficient reactor design
-a ban on the use and development of breeder reactors
-tax incentives for the oil and gas industry
-high cost of new, safer technology
smaller, more efficient reactor design
Which factor will oppose the growth of nuclear energy in the future?
-standardization of reactor design
-increased operational lifetime of reactors
-shorter construction time for reactors
-transportation of high level waste to depositories
transportation of high level waste to depositories
The primary reason countries worldwide have turned to nuclear power for electricity generation is to reduce
-the greenhouse effect
-acid rain
-their reliance on fossil fuels
-the damage caused by strip mining
their reliance on fossil fuels
The annual radiation dose for most citizens of the US is between
-0 to 0.10 Sv.
-0.10 to 0.25 Sv.
-0.25 to 0.50 Sv.
-0.50 to 1.0 Sv.
0 to 0.10 Sv.
The greatest percentage of background radiation comes from
-nuclear power plants
-medical x-rays
-living things
-naturally occurring radon
naturally occurring radon
Approximately what percentage of the electrical energy generated in the United States is produced from nuclear energy?
-<2%
-10%
-20%
-50%
20%
Which form of radiation has the highest Q factor?
-UV radiation
-alpha particles
-beta particles
-X-rays
alpha particles
Which example is both a type of nuclear radiation and electromagnetic radiation?
-microwave radiation
-gamma radiation
-alpha rays
-ultraviolet radiation
gamma radiation
Rank the forms of nuclear radiation according to mass
-gamma, alpha, beta
-beta, gamma, alpha
-alpha, gamma, beta
-alpha, beta, gamma
alpha, beta, gamma
In which organ does radioactive I-131 accumulate?
-liver
-pituitary gland
-thyroid gland
-adrenal glands
thyroid gland
Which scientific law best applies to nuclear reactions?
-Conservation of Matter
-Conservation of Energy
-Conservation of Matter and Energy
-None of these choices are correct
Conservation of Matter and Energy
A breeder reactor produces which nuclear fuel?
-239Pu
-238U
-141Ba
-235U
239Pu
The radioactive decay series of U-238 terminates at which nonradioactive isotope?
-210Tl
-210Bi
-206Pb
-144Ba
206Pb
What is the most common radioactive element in our food?
-23Mg
-40K
-131I
-90Sr
40K
Which of the following is usually consumed in a breeder reactor?
-Pu-239
-U-235
-C-14
-U-238
U-235
What is vitrification?
-spent fuel elements or other mixed waste are encased in ceramic or glass
-spent fuel elements or other mixed waste are buried beneath the ocean floor
-spent fuel elements or other mixed waste are deposited in Nevada
spent fuel elements or other mixed waste are encased in ceramic or glass
Radon-222...
-is a radioactive gas produced from the decay of radium
-is naturally occurring
-is the largest contributor to background radiation
-all of the above
all of the above
Depleted uranium...
-is all U-235
-is all U-238
-is mostly, but not all U-238
-is mostly, but not all U-235
is mostly, but not all U-238
Weapons-grade uranium is...
-30% U-235
-60% U-235
-90% U-235
-90% U-239
90% U-235
alpha particle
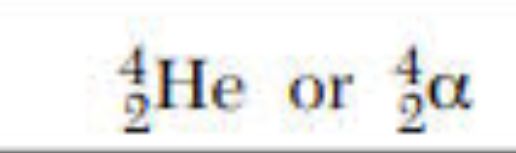
beta particle
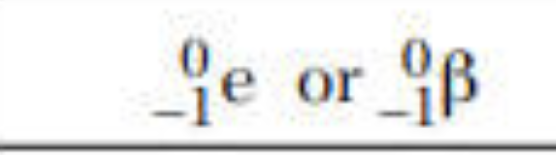
gamma radiation
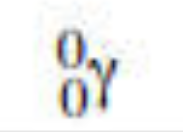
neutron
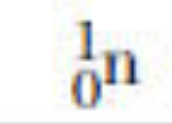
proton
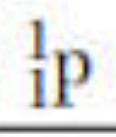
positron
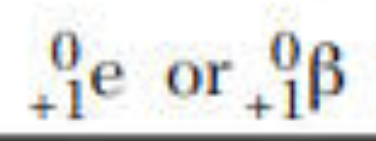
How much energy in KJ will be released by complete conversion of 4 grams of He to energy? E=mc²
4g = 4×10^-3kg
E= (4× 10^-3) x (2.99 × 10^8)²
EJ= 3.57 × 10^14
(3.57 × 10^14) x (10^-3)= 3.57 × 10^11 kj
Technitium-99 has a half-life of 6 hours. How many grams of a 10.0 gram sample would remain after exactly 18 hours?
(Tc-99)=
10g —-6hrs——>5g —6hrs—>2.5g —6hrs—>1.25g
After 18 hours, 1.25g of the 10g sample remain.