Anthropology 161 Exam 2
1/271
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
272 Terms
Variations in ___ ____ arose over thousands of years as people migrated from the equator towards the northern latitudes.
Skin color
As humans migrated out of Africa, _____ _____ changed. An example is the outcome of colder temperatures and fewer UV rays, which resulted in less melanin being necessary.
selective pressures
Sunlight produces which vitamin?
Vitamin D
Vitamin D critical for __________: Lack of it results in rickets.
bone growth andmineralization
TRUE OR FALSE: The Equator favored more melanin while the Northern latitudes less melanin.
True
Burgman’s Rule (1847)
is an ecogeographic rule stating that individuals of a species tend to be larger in colder environments than in warmer ones.
Allen’s Rule (1877)
The principle that an animal's extremities size are heat-related; extremities are larger in hot environments and smaller in cold environments.
As humans migrated around the world, they adapted to changes in the_____ ________.
thermal environment.
Humans are ______, meaning they can maintain a generally constant internal body temperature regardless of external temperature variations.
homeothermic
Too much ___ is harmful to humans, long-time exposure stressful and can be fatal.
Heat
vasodilation
blood vessels expand, allowing more blood flow to the skin; also known as flushing (excess heat lost through skin)
______ dissipates heat (1.6 million glands).
Sweating
TRUE OR FALSE: To cope with extreme heat, humans adapted the ability of body hair reduction which as a cooling method compared to primates.
True
TRUE OR FALSE: Body size/shape variations in humans are favored by natural selection in response to extreme heat.
TRUE
Short-term adjustments to colder temperatures in humans is an example of _____.
Acclimatization
Vasoconstriction
blood vessels narrow; blood is kept away from skin surface to help retain heat
Increased Metabolic Rate
releases energy in the form of heat
Adaptation is considered a longer term adjustment. Three examples include high basal metabolic rate, vasoconstriction, and _____ (flushing: temorary
(?) - question
Most adjustment to cold are ______.
Cultural
Bergmann’s Rule
Ratio of body/mass/volume to surface area
Populations native to warm climates are _____ in body size (less mass, more surface area)
smaller
Populations native to cold climates are ____ in body size (more mass, less surface area).
larger
Allen’s Rule
appendage: torso ratio (?)
Populations native to warm climates have longer/shorter limbs to help dissipate heat.
longer
Populations native to colder climates have longer/shorter limbs to help retain heat.
shorter
Humidity
Moist humid areas with still air = inefficient sweating
Est. 25 million people live at “high” altitudes: _____ ft. above sea level and higher
10,000
Hypoxia-related stress effects = ?
TRUE OR FALSE: Thin air is considered a stress
TRUE
Hypoxia
reduction of oxygen in the atmosphere or body
Adaptation:
Larger chest size = larger lung and hearts which ensures functioning organs as more _____ comes through.
Oxygen
Adult Acclimatization:
Changes in respiration
Increased production of the ____
RRC
Developmental Acclimatization:
Increased chest size - increased _____ capact ( its not genetic change but an example of physiological plasticity)
lung
Tibetan and Quechua populations for the past 25,000 years have experienced genetic changes in response to high altitude due to the length of time of exposure to _______.
hypoxia
Skeletal Anthropology studies….?
Hominid evolution, our past, Human adaptation, Health in prehistory, Population structure and composition, and Forensic aspect
The skeleton has five major functions:
Facilitates ______
______: supports soft tissues & creates
body form, providing stability
_____ major organs of the body (brain,
spinal cord, heart and lungs)
______of blood cells
______ of minerals (calcium, phosphorus)
movement, Structure, Protects, Production, Storage
The muscles of the body are attached to the _______
bones
We move our bodies through the _____ and release of muscles
contraction
The ______ is the framework that provides the structure for the body
skeleton
Bones protect most important organs of the body:
____ protects the brain
______ protects the heart, lungs, part of liver
_____ _______ protects the spinal cord
Skull, Ribs, vertebral column
The Skeletal System produces blood cells and platelets. These are specifically produced in the _____ ________.
Bone Marrow
An adult skeleton has ___ bones
206
An child skeleton has ___ bones
270
The function of _____ ______ is to store and release minerals.
Skeletal System
The axial skeleton consists of ___ bones.
80
What bones make up the axial skeleton?
SKULL , VERTEBRAL COLUMN, THORAX (STERNUM, and RIBS)
How many bones consist of the skull?
29 bones
Which skeleton does the skull belong to?
The avial
How many bones consist of the vertebral column?
26 bones
Which skeleton does the vetebral column belong to?
The avial
How many bones consist of the thorax (sternum and ribs)?
25 (1 and 24 respectively)
Which skeleton does the thorax belong to?
The avial
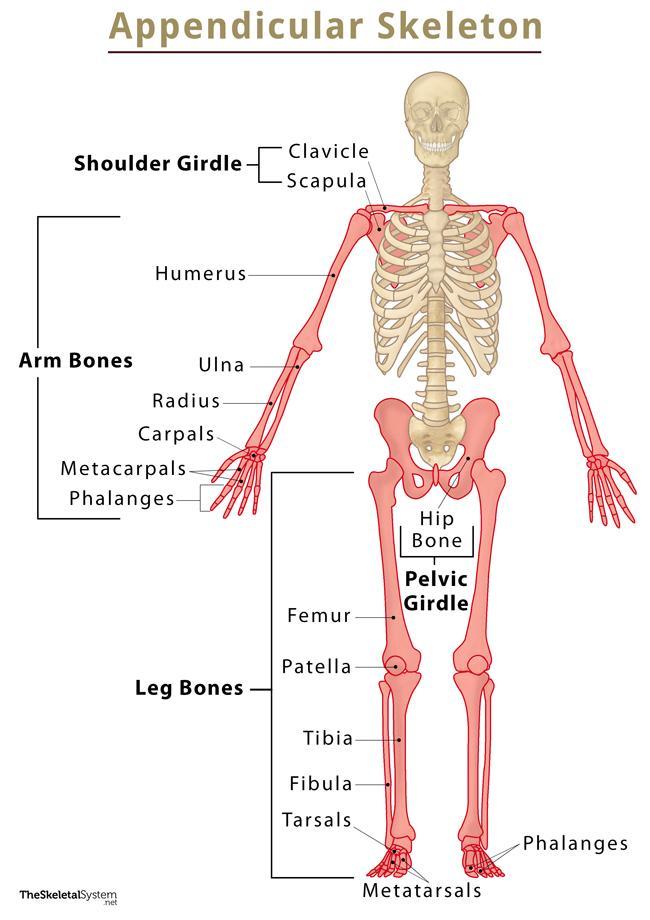
The Appendicular Skeleton consists of ____ bones.
126
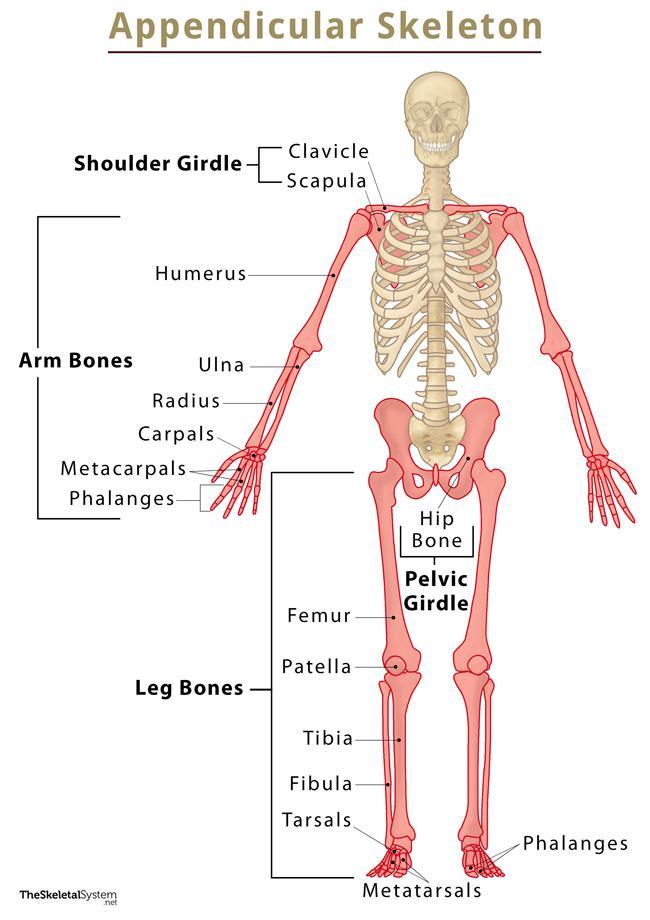
What bones make up the Appendicular Skeleton
PECTORAL GIRDLE, UPPER (forelimbs), and the PELVIC GIRDLE
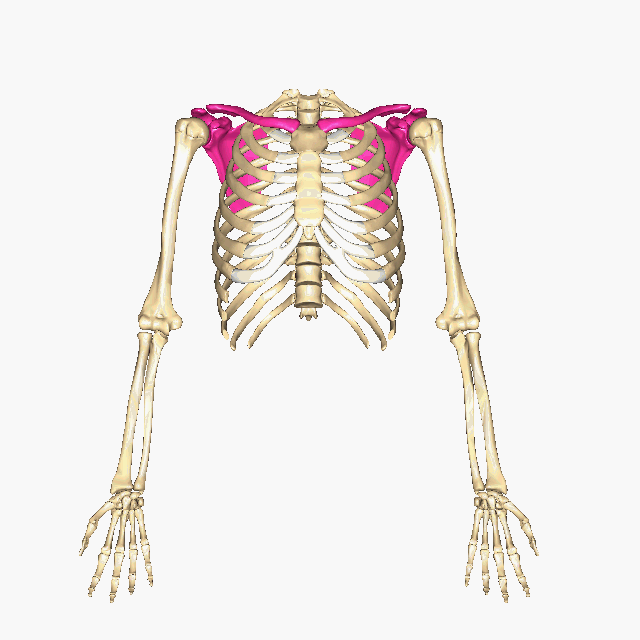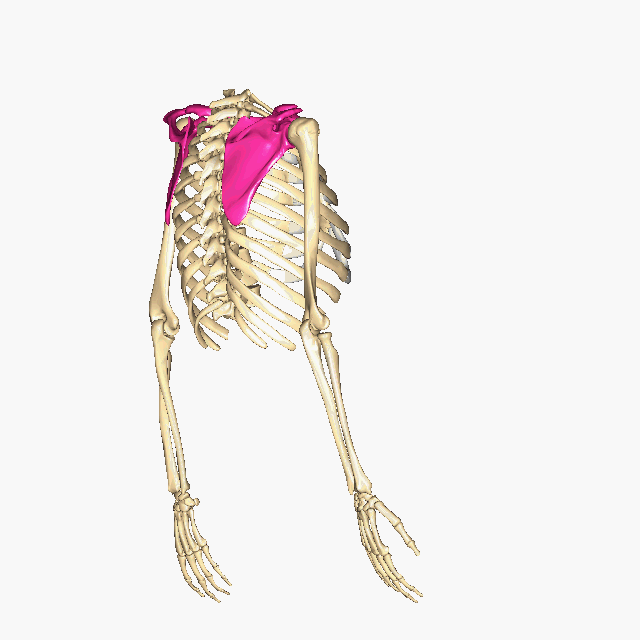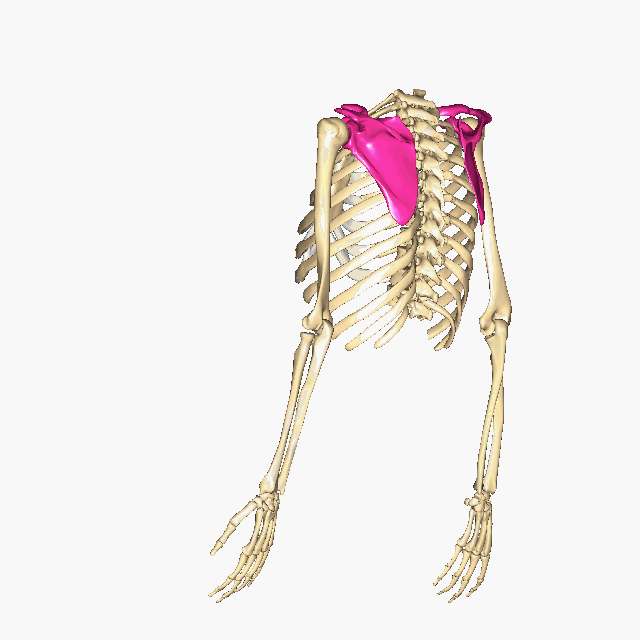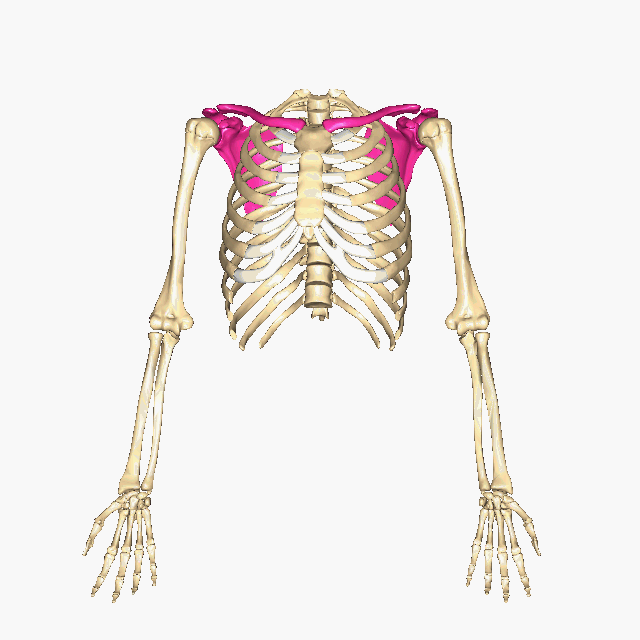
Which bones make up the PECTORAL GIRDLE? (hint: list two names)
The Clavicle and the Scapula
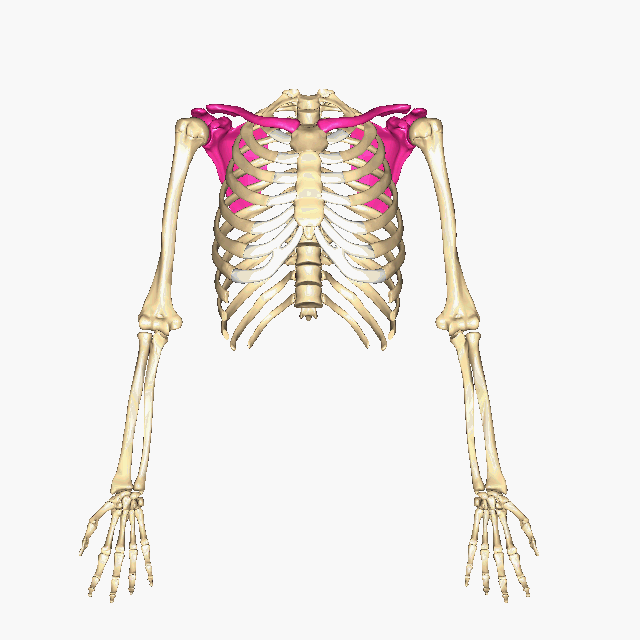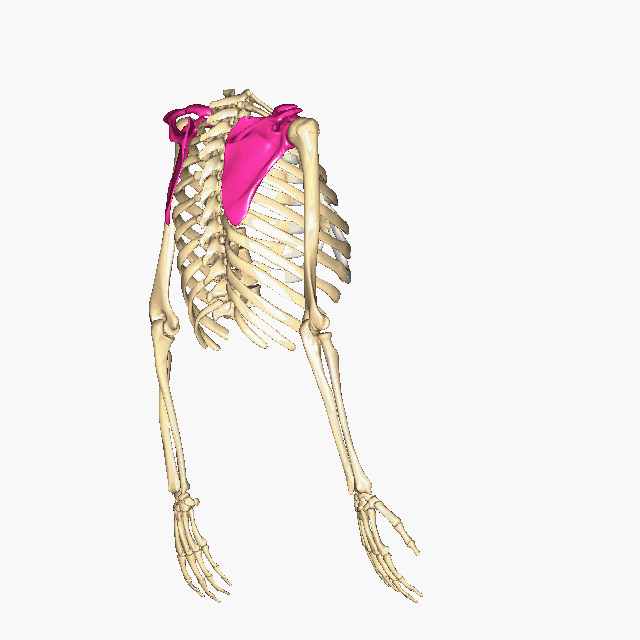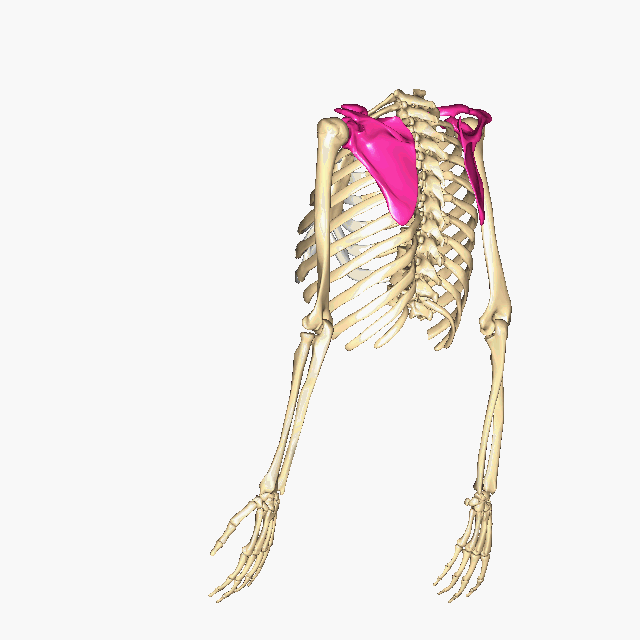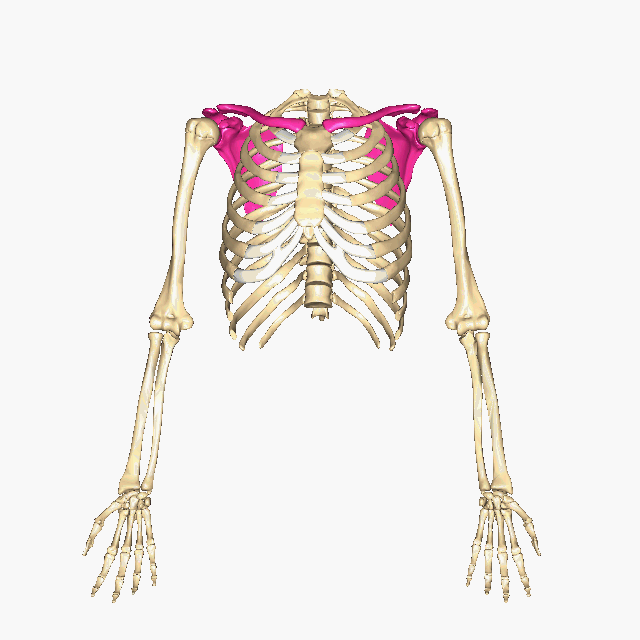
How many bones make up the PECTORAL GIRDLE? (hint: list a number)
4 bones
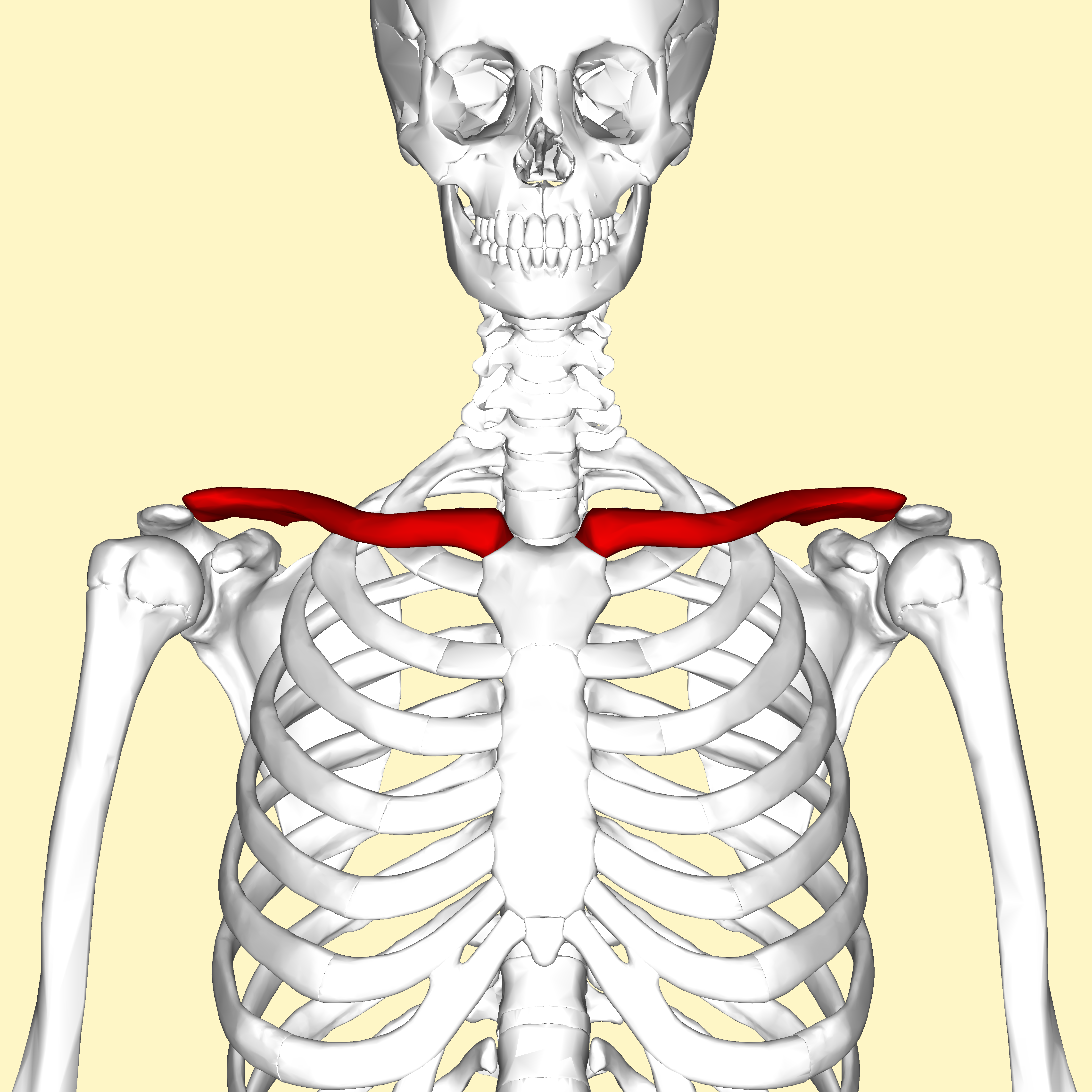
How many bones make up the clavicle? (hint: list a number)
2 bones
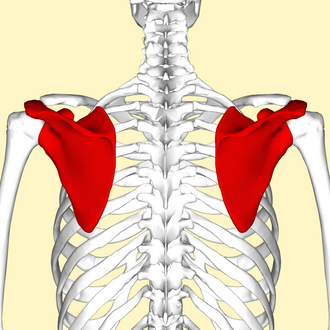
How many bones make up the scapula? (hint: list a number)
2 bones
Which bones make up the UPPER (forelimbs)? (hint: list six names)
Humerus, Ulna, Radius, Carpals, Metacarpal, and Phalanges
How many bones make up the UPPER (forelimbs)? (hint: list a number )
60 bones
How many bones make up the Humerus? (hint: list a number)
2 bones
How many bones make up the Ulna? (hint: list a number)
2 bones
How many bones make up the Radius? (hint: list a number)
2 bones
How many bones make up the Carpals? (hint: list a number)
16 bones
How many bones make up the Metacarpals? (hint: list a number)
10 bones
How many bones make up the Phalanges? (hint: list a number)
28 Bones
Which bone makes up the PELVIC GIRDLE? (hint: list one name)
Os coxae
How many bones make up the PELVIC GIRDLE? (hint: list a number)
2 bones
How many bones make up the Os coxae? (hint: list a number)
2 bones
The lower extrimities, also known as the Hindlimb Bones, of the Appendicular Skeleton consists of how many bones?
60 bones
The lower extrimities, also known as the Hindlimb Bones, of the Appendicular Skeleton consists of which bones? (Hint: List nine names)
Femur (2)
Patella (2)
Tibia (2)
Fibula (2)
Talus (2)
Calcaneus (2)
Tarsals (10)
Metatarsals (10)
Phalanges
How many bones make up the Femur? (hint: list a number)
2 bones
How many bones make up the Patella? (hint: list a number)
2 bones
How many bones make up the Tibia? (hint: list a number)
2 bones
How many bones make up the Fibula? (hint: list a number)
2 bones
How many bones make up the Talus? (hint: list a number)
2 bones
How many bones make up the Calcaneus? (hint: list a number)
2 bones
How many bones make up the Tarsals? (hint: list a number)
10 bones
How many bones make up the Metatarsals? (hint: list a number)
10 bones
How many bones make up the Phalanges? (hint: list a number)
28 bones
Living tissue or ____ changes and can be studied over time.
morphology
Bones articulate at the ______, _____, and _____. (Hint: List three names)
Joints, cartilage, and ligaments
_____ are connections between different skeletal
elements.
Joints
Joint's are connected by _____, which are tough, dense, elastic and compressible connective tissue
cartilage
______ are closely packed parallel bundles of collagen fibers, bind joint together to prevent dislocation
ligaments
Bones are _____ (less than 20% of the weight of the entire body)
light weight
Bones are comprised of three things: 25% water, 25% _____ (protein), and 50% crystallized mineral salts
collagen
The crystallized mineral salts in bones are calcium phosphate and _______.
Hydroxyapatite
Hydroxyapatite
dense inorganic form of calcium phosphate that fills the collagen matrix, making bone hard and rigid
TRUE OR FALSE: Bones can repair and reshape itself in response to external stressors (i.e. muscle hypertrophy)
True
Living bone consists of three layers: 1) the ______, or outside skin of the bone; 2) the hard ______ _____, supporting the weight of the body; and 3) ______ ____ (bone marrow). (Hint: list three names)
periosteum, compact bone, spongy bone
Compact bones (or cortical)
solid dense bone located in the bone shafts and on the external bone
At joints compact bone covered by_________.
cartilage
_____ or the cancellous, trabecular bone is lightweight, and honeycombed in structure.
Spongy
TRUE OR FALSE: Bone marrow is located within the space of the trabeculae.
TRUE
Trabecular bone
sites of red marrow production in the growing skeleton (hematopoietic)
hematopoietic consists of Red and white blood cells and _______.
platelets
The ______ cavity is surrounded by compact bons, additionally producing yellow marrow (fat cells).
Medullary
As you grow, red marrow is gradually replaced
with _____ marrow
yellow
What are the three types of bone marrow?
red, yellow, gelatinous